Diet-Related Changes of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Blood and Feces in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids
1.2. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
2. Methodology
2.1. Search Strategy
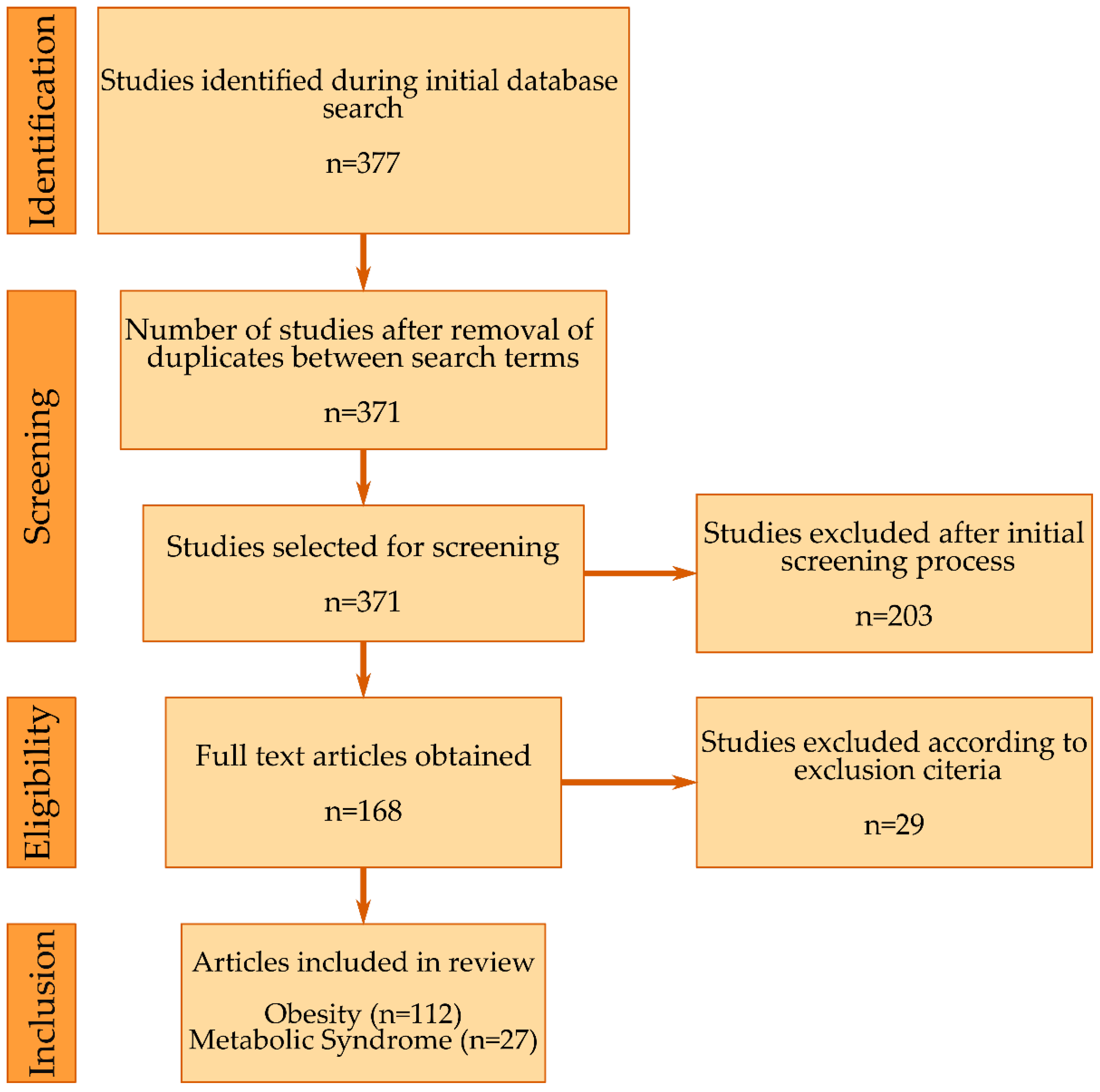
2.2. Selection, Screening and Inclusion
3. Short-Chain Fatty Acids between Diet and Metabolism
3.1. Animal Studies
3.1.1. Diet
3.1.2. SCFA Supplementation
| Acetate | Propionate | Butyrate |
|---|---|---|
| Ameliorated obesity [88] | Reduced body weight and fasting insulin levels [96] | Had no significant effect [82] |
| Normalized weight gain, insulin, TNF-α and leptin levels [48] | Increased adiponectin expression [135] | Altered gut microbiota to be similar to LFD [117] |
| Increased adiponectin expression [135] | Prevented weight gain [145] | Ameliorated obesity, steatohepatitis [38] |
| Prevented weight gain [145] | Reduced body weight gain, improved insulin response [92] | |
| Decreased leptin and insulin levels [146] | ||
| Reversed HFD induced dysmetabolism [150] | ||
| Increased adiponectin expression [135] |
3.1.3. Probiotics and Gut Microbiota
3.2. In-Vitro Studies
3.3. Human Studies
Dietary Supplementation
3.4. Diet and SCFAs
3.5. Gut Microbiota and SCFAs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cait, A.; Hughes, M.R.; Antignano, F.; Cait, J.; Dimitriu, P.A.; Maas, K.R.; Reynolds, L.A.; Hacker, L.; Mohr, J.; Finlay, B.B.; et al. Microbiome-Driven Allergic Lung Inflammation Is Ameliorated by Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, J.M.W.; de Souza, R.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Emam, A.; Jenkins, D.J.A. Colonic Health: Fermentation and Short Chain Fatty Acids. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; de Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rekha, K.; Venkidasamy, B.; Samynathan, R.; Nagella, P.; Rebezov, M.; Khayrullin, M.; Ponomarev, E.; Bouyahya, A.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acid: An Updated Review on Signaling, Metabolism, and Therapeutic Effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Control of Body Weight and Insulin Sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, D.L.; Clifton, P.M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Human Colonic Function: Roles of Resistant Starch and Nonstarch Polysaccharides. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1031–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortensen, P.B.; Holtug, K.; Bonnén, H.; Clausen, M.R. The Degradation of Amino Acids, Proteins, and Blood to Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Colon Is Prevented by Lactulose. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H.; Pomare, E.W.; Branch, W.J.; Naylor, C.P.; Macfarlane, G.T. Short Chain Fatty Acids in Human Large Intestine, Portal, Hepatic and Venous Blood. Gut 1987, 28, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Gulanski, B.I.; de Feyter, H.M.; Weinzimer, S.A.; Pittman, B.; Guidone, E.; Koretski, J.; Harman, S.; Petrakis, I.L.; Krystal, J.H.; et al. Increased Brain Uptake and Oxidation of Acetate in Heavy Drinkers. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost, G.; Sleeth, M.L.; Sahuri-Arisoylu, M.; Lizarbe, B.; Cerdan, S.; Brody, L.; Anastasovska, J.; Ghourab, S.; Hankir, M.; Zhang, S.; et al. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate Reduces Appetite via a Central Homeostatic Mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaki, S.-I.; Tazoe, H.; Hayashi, H.; Kashiwabara, H.; Tooyama, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kuwahara, A. Expression of the Short-Chain Fatty Acid Receptor, GPR43, in the Human Colon. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazoe, H.; Otomo, Y.; Karaki, S.-I.; Kato, I.; Fukami, Y.; Terasaki, M.; Kuwahara, A. Expression of Short-Chain Fatty Acid Receptor GPR41 in the Human Colon. Biomed. Res. 2009, 30, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, E.; Grootaert, C.; Verstraete, W.; van de Wiele, T. Propionate as a Health-Promoting Microbial Metabolite in the Human Gut. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Miyamoto, N.; Shibata, K.; Valasek, M.A.; Motoike, T.; Kedzierski, R.M.; Yanagisawa, M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Stimulate Leptin Production in Adipocytes through the G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milovic, V.; Teller, I.C.; Turchanowa, L.; Caspary, W.F.; Stein, J. Effect of Structural Analogues of Propionate and Butyrate on Colon Cancer Cell Growth. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2000, 15, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, G.; Belzacq, A.-S.; Haouzi, D.; Rouault, A.; Métivier, D.; Kroemer, G.; Brenner, C. Propionibacteria Induce Apoptosis of Colorectal Carcinoma Cells via Short-Chain Fatty Acids Acting on Mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheppach, W. Effects of Short Chain Fatty Acids on Gut Morphology and Function. Gut 1994, 35, S35–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Subramanian, U.; Venkidasamy, B.; Thirupathi, P.; Samynathan, R.; Shariati, M.A.; Rebezov, M.; Chung, I.-M.; Rengasamy, K.R.R. Emerging Role of Nutritional Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) against Cancer via Modulation of Hematopoiesis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Hernández, M.A.; Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Blaak, E.E. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate in Body Weight Control and Insulin Sensitivity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.J.; Goldsworthy, S.M.; Barnes, A.A.; Eilert, M.M.; Tcheang, L.; Daniels, D.; Muir, A.I.; Wigglesworth, M.J.; Kinghorn, I.; Fraser, N.J.; et al. The Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptors GPR41 and GPR43 Are Activated by Propionate and Other Short Chain Carboxylic Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11312–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, G.L. Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. Minerva Endocrinol. 2004, 29, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clavijo, L.C.; Pinto, T.L.; Kuchulakanti, P.K.; Torguson, R.; Chu, W.W.; Satler, L.F.; Kent, K.M.; Suddath, W.O.; Pichard, A.D.; Waksman, R. Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction Is Associated with Increased Infarct Size and In-Hospital Complications. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2006, 7, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.V. Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Stroke. Clin. Cornerstone 2004, 6 (Suppl. 3), S30–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, P.; Morgante, M.; Pansini, A.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Rizzo, M.; Lombardi, A.; Frullone, S.; Santulli, G. Effects of Insulin Resistance on Mitochondrial (Dys)Function. Atherosclerosis 2022, 341, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansini, A.; Lombardi, A.; Morgante, M.; Frullone, S.; Marro, A.; Rizzo, M.; Martinelli, G.; Boccalone, E.; de Luca, A.; Santulli, G.; et al. Hyperglycemia and Physical Impairment in Frail Hypertensive Older Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 831556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, T.L.; Seidell, J.C. The Public Health Impact of Obesity. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2001, 22, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peeters, A.; Barendregt, J.J.; Willekens, F.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Al Mamun, A.; Bonneux, L. NEDCOM, The Netherlands Epidemiology and Demography Compression of Morbidity Research Group Obesity in Adulthood and Its Consequences for Life Expectancy: A Life-Table Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaidi, J.A.; Wright, R.S.; Grill, J.P.; Hensrud, D.D.; Murphy, J.G.; Squires, R.W.; Kopecky, S.L. Obesity Is Associated with Premature Occurrence of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Cardiol. 2001, 24, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity as a Major Risk Factor for Cancer. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 291546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alpsoy, Ş. Exercise and Hypertension. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1228, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, S.; Kim, S.; Bersamin, A.; King, A.C.; Gardner, C.D. Dietary Adherence and Weight Loss Success among Overweight Women: Results from the A TO Z Weight Loss Study. Int J. Obes. 2008, 32, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bliesner, A.; Eccles-Smith, J.; Bates, C.; Hayes, O.; Ho, J.Y.; Martins, C.; Truby, H.; Nitert, M.D. Impact of Food-Based Weight Loss Interventions on Gut Microbiome in Individuals with Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, A.; Glastras, S.J.; Wong, M.Y.W.; Pollock, C.A.; Saad, S. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Diabetes and Obesity-Related Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Interplay between Gut Microbiota and Diet in Cardio-Metabolic Health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliocca, G.; Mone, P.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, K.N.; Dicksved, J.; Zoki, C.; Fristedt, R.; Pelve, E.A.; Langton, M.; Landberg, R. The Effects of High Fiber Rye, Compared to Refined Wheat, on Gut Microbiota Composition, Plasma Short Chain Fatty Acids, and Implications for Weight Loss and Metabolic Risk Factors (the RyeWeight Study). Nutrients 2022, 14, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Shi, L.; He, C.; Wang, C.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; An, Y.; Dai, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Rutin-Activated Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis Is Correlated with Increased Intestinal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 2495–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Weng, D.; Ju, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Cui, L.; Sun, S.; et al. Clostridium Butyricum Inhibits Fat Deposition via Increasing the Frequency of Adipose Tissue-Resident Regulatory T Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthyala, S.D.V.; Shankar, S.; Klemashevich, C.; Blazier, J.C.; Hillhouse, A.; Wu, C.-S. Differential Effects of the Soluble Fiber Inulin in Reducing Adiposity and Altering Gut Microbiome in Aging Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 105, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhu, W.; Edirisuriya, P.; Ai, Q.; Nie, K.; Ji, X.; Zhou, K. Characterization of Metabolites and Biomarkers for the Probiotic Effects of Clostridium Cochlearium on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese C57BL/6 Mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Tung, C.-L.; Yang, Y.-C.S.H.; Lin, I.-H.; Ng, X.E.; Tung, Y.-T. Endurance Exercise Ameliorates Western Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis through Modulation of Microbiota and Its Metabolites. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzarella, E.U.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Ullah, H.; Esposito, C.; Santarcangelo, C.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pastoriza, S.; Zaccaria, V.; Xiao, J.; et al. Evaluating the Effects of a Standardized Polyphenol Mixture Extracted from Poplar-Type Propolis on Healthy and Diseased Human Gut Microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łagowska, K.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. A Low Glycemic Index, Energy-Restricted Diet but Not Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Supplementation Changes Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid and Serum Lipid Concentrations in Women with Overweight or Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.; Hui, S.; Xu, H. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids Partially Mediate the Beneficial Effects of Inulin on Metabolic Disorders in Obese Ob/Ob Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfora, E.E.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Müller, M.; Bastings, J.; Vaughan, E.E.; van Den Berg, M.A.; Holst, J.J.; Venema, K.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Blaak, E.E. Fiber Mixture-Specific Effect on Distal Colonic Fermentation and Metabolic Health in Lean but Not in Prediabetic Men. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2009297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukorako, P.; Lemoine, N.; Biertho, L.; Lebel, S.; Roy, M.-C.; Plamondon, J.; Tchernof, A.; Varin, T.V.; Anhê, F.F.; St-Pierre, D.H.; et al. Consistent Gut Bacterial and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Signatures in Hypoabsorptive Bariatric Surgeries Correlate with Metabolic Benefits in Rats. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskova, N.; Heczkova, M.; Modos, I.; Videnska, P.; Splichalova, P.; Pelantova, H.; Kuzma, M.; Gojda, J.; Cahova, M. Determination of Butyrate Synthesis Capacity in Gut Microbiota: Quantification of but Gene Abundance by QPCR in Fecal Samples. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyi, K.S.; Owolabi, M.N.; Atuma, C.L.; Agunbiade, T.B.; Alabi, B.Y. Acetate Rescues Defective Brain-Adipose Metabolic Network in Obese Wistar Rats by Modulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-W.; Ou, Y.-C.; Tang, K.-S.; Yu, H.-R.; Huang, L.-T.; Tain, Y.-L.; Lin, I.-C.; Sheen, J.-M.; Hou, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; et al. Metformin Ameliorates Maternal High-Fat Diet-Induced Maternal Dysbiosis and Fetal Liver Apoptosis. Lipids Health Dis 2021, 20, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Román-Sagüillo, S.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Linares, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Urioste-Fondo, A.; Álvarez-Cuenllas, B.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; et al. Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Gut Microbiota Composition and Faecal Metabolome Related to Obesity Remission. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, D.; Craig, S.J.C.; Cai, J.; Tian, Y.; Paul, I.M.; Savage, J.S.; Marini, M.E.; Hohman, E.E.; Reimherr, M.L.; Patterson, A.D.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Stool of Two-Year Old Children from the INSIGHT Study Reveals Links between Butyrate and Child Weight Outcomes. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gual-Grau, A.; Guirro, M.; Crescenti, A.; Boqué, N.; Arola, L. In Vitro Fermentability of a Broad Range of Natural Ingredients by Fecal Microbiota from Lean and Obese Individuals: Potential Health Benefits. Int. J. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Man Hoi, M.P.; Ding, W.; et al. Gut Commensal-Derived Butyrate Reverses Obesity-Induced Social Deficits and Anxiety-like Behaviors via Regulation of Microglial Homeostasis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 908, 174338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroover, L.; Vázquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Vandermeulen, G.; Luypaerts, A.; Raes, J.; Courtin, C.M.; Verbeke, K. Wheat Bran with Reduced Particle Size Increases Serum SCFAs in Obese Subjects without Improving Health Parameters Compared with a Maltodextrin Placebo. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cuesta, M.C.; Del Campo, R.; Garriga-García, M.; Peláez, C.; Requena, T. Taxonomic Characterization and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production of the Obese Microbiota. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 598093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Cui, C.; Wei, H.; Peng, J.; Zheng, R. The Effect of Functional Fiber on Microbiota Composition in Different Intestinal Segments of Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, I.; Lam, W.S.; Marasini, D.; Brownmiller, C.; Savary, B.J.; Lee, J.A.; Carbonero, F.; Lee, S.-O. In Vitro Fecal Fermentation Patterns of Arabinoxylan from Rice Bran on Fecal Microbiota from Normal-Weight and Overweight/Obese Subjects. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisner, J.; Filipe Rosa, L.; Kaden-Volynets, V.; Stolzer, I.; Günther, C.; Bischoff, S.C. Prebiotic Inulin and Sodium Butyrate Attenuate Obesity-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction by Induction of Antimicrobial Peptides. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, R.; Nakamura, K.; Ukawa, S.; Okada, E.; Nakagawa, T.; Imae, A.; Kunihiro, T.; Kimura, T.; Hirata, T.; Tamakoshi, A. Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Obesity in a Community-Based Japanese Population: The DOSANCO Health Study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, R.; Okamura, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Majima, S.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Takakuwa, H.; Sasano, R.; et al. Erythritol Ameliorates Small Intestinal Inflammation Induced by High-Fat Diets and Improves Glucose Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota Structure with Probiotics and Isoflavone Alleviates Metabolic Disorder in Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziętek, M.; Celewicz, Z.; Kikut, J.; Szczuko, M. Implications of SCFAs on the Parameters of the Lipid and Hepatic Profile in Pregnant Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.M.; da Silva, N.B.M.; de Freitas, R.M.P.; de Freitas, M.B.D.; Chaves, J.B.P.; Oliveira, L.L.; Martino, H.S.D.; de Cássia Gonçalves Alfenas, R. Effects of Yacon Flour Associated with an Energy Restricted Diet on Intestinal Permeability, Fecal Short Chain Fatty Acids, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Markers Levels in Adults with Obesity or Overweight: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 64, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mueller, N.T.; Differding, M.K.; Zhang, M.; Maruthur, N.M.; Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J.; Yeh, H.-C. Metformin Affects Gut Microbiome Composition and Function and Circulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids: A Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.-Z.; Zhou, F.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Wu, J.-L.; Huang, J.-A.; Liu, Z.-H. Combined Use of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) and Caffeine in Low Doses Exhibits Marked Anti-Obesity Synergy through Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4105–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.-G.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Li, D.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q. Bidirectional Interaction of Nobiletin and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3516–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-T.; Huang, W.-J.; Chiang, B.-L.; Tseng, P.-H. Butyrate Modulates Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Isolated from Polygenic Obese and Diabetic Mice to Drive Enhanced Immunosuppression. Cytotherapy 2021, 23, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, L.; Dou, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, H. Effect of Trilobatin from Lithocarpus Polystachyus Rehd on Gut Microbiota of Obese Rats Induced by a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, Q.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Bifidobacterium Adolescentis Isolated from Different Hosts Modifies the Intestinal Microbiota and Displays Differential Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Properties in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mio, K.; Otake, N.; Nakashima, S.; Matsuoka, T.; Aoe, S. Ingestion of High β-Glucan Barley Flour Enhances the Intestinal Immune System of Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Prebiotic Effects. Nutrients 2021, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Kessoku, T.; Ozaki, A.; Kasai, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Nogami, A.; Honda, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Imajo, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Associated with Hepatic Fibrosis in Non-Obese Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Aoe, S. High β-Glucan Barley Supplementation Improves Glucose Tolerance by Increasing GLP-1 Secretion in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, P.; Luo, J.; Shen, L.; Zhang, S.; Gu, H.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gan, M.; et al. Dietary Betaine Prevents Obesity through Gut Microbiota-Drived MicroRNA-378a Family. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1862612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, F.; Phetcharaburanin, J.; Glymenaki, M.; Nordbeck, A.; Hankir, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Marchesi, J.R.; Li, J.V. Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery in Zucker Rats Induces Bacterial and Systemic Metabolic Changes Independent of Caloric Restriction-Induced Weight Loss. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemani, F.; Barrett, H.L.; Gomez-Arango, L.; Josh, P.; David McIntyre, H.; Callaway, L.K.; Morrison, M.; Tyson, G.W.; Dekker Nitert, M. Pregnant Women Who Develop Preeclampsia Have Lower Abundance of the Butyrate-Producer Coprococcus in Their Gut Microbiota. Pregnancy Hypertens 2021, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.M.; Tran, C.D.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Stonehouse, W.; Bowen, J.; Johnson, N.; Thompson, C.H.; Watson, E.-J.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Rogers, G.B. Almond Consumption Affects Fecal Microbiota Composition, Stool PH, and Stool Moisture in Overweight and Obese Adults with Elevated Fasting Blood Glucose: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Res. 2021, 85, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Tao, T.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q. Dietary Intake of Mixture Coarse Cereals Prevents Obesity by Altering the Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Amakye, W.K.; Pan, J.; Chu, X.; Ma, B.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The Associations of the Gut Microbiome Composition and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Concentrations with Body Fat Distribution in Children. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3379–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.-M.; Chen, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, K.E.; Park, K.W.; Yoon, J.-H. Lactobacillus Sakei ADM14 Induces Anti-Obesity Effects and Changes in Gut Microbiome in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Curtasu, M.V.; Bendiks, Z.; Marco, M.L.; Nørskov, N.P.; Knudsen, K.E.B.; Hedemann, M.S.; Lærke, H.N. Effects of Dietary Fibre and Protein Content on Intestinal Fibre Degradation, Short-Chain Fatty Acid and Microbiota Composition in a High-Fat Fructose-Rich Diet Induced Obese Göttingen Minipig Model. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10758–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Chen, J.; Yi, K.; Peng, L.; Xie, J.; Gou, X.; Peng, T.; Tang, L. Phlorizin Ameliorates Obesity-Associated Endotoxemia and Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Targeting the Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Integrity. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1842990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Knotts, T.A.; Goodson, M.L.; Barboza, M.; Wudeck, E.; England, G.; Raybould, H.E. Metabolic Responses to Butyrate Supplementation in LF- and HF-Fed Mice Are Cohort-Dependent and Associated with Changes in Composition and Function of the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Romero, S.; Léniz, A.; Martínez-Maqueda, D.; Amézqueta, S.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Hereu, M.; Torres, J.L.; Portillo, M.P.; Pérez-Jiménez, J. Inter-Individual Variability in Insulin Response after Grape Pomace Supplementation in Subjects at High Cardiometabolic Risk: Role of Microbiota and MiRNA. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyarmati, P.; Song, Y.; Dotimas, J.; Yoshiba, G.; Christison, A. Cross-Sectional Comparisons of Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels among Children with Varied Weight Classifications. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Ma, S.; Ye, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Sair, A.T.; Pan, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; et al. High-Dietary Fiber Intake Alleviates Antenatal Obesity-Induced Postpartum Depression: Roles of Gut Microbiota and Microbial Metabolite Short-Chain Fatty Acid Involved. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13697–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, B.A.; Lu, P.; Alake, S.E.; Keirns, B.; Anderson, K.; Gallucci, G.; Hart, M.D.; El-Rassi, G.D.; Ritchey, J.W.; Chowanadisai, W.; et al. Pinto Beans Modulate the Gut Microbiome, Augment MHC II Protein, and Antimicrobial Peptide Gene Expression in Mice Fed a Normal or Western-Style Diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 88, 108543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijova, E.; Strojný, L.; Bertková, I.; Bomba, A.; Štofilová, J. Dietary Lactobacillus Plantarum LS/07 and Inulin in the Management of Chronic Disease Risk Factors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2020, 67, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelek, C.; Mignion, L.; Joudiou, N.; Terrasi, R.; Gourgue, F.; van Hul, M.; Delzenne, N.; Gallez, B.; Corbet, C.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. Acetate: Friend or Foe against Breast Tumour Growth in the Context of Obesity? J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14195–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. A High-Fat Diet Increases Gut Microbiota Biodiversity and Energy Expenditure Due to Nutrient Difference. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; You, H.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Joo, S.K.; Yu, J.; Park, S.; Kang, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Distinct Signatures of Gut Microbiome and Metabolites Associated with Significant Fibrosis in Non-Obese NAFLD. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, R.R.; Cook, T.M.; Gavini, C.K.; White, C.R.; Jones, J.R.; Bovo, E.; Zima, A.V.; Brown, I.A.; Dugas, L.R.; Zakharian, E.; et al. Fecal Transplantation and Butyrate Improve Neuropathic Pain, Modify Immune Cell Profile, and Gene Expression in the PNS of Obese Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26482–26493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, F.T.; Yap, Y.A.; Crisma, A.R.; Portovedo, M.; Murata, G.M.; Hirabara, S.M.; Ribeiro, W.R.; Marcantonio Ferreira, C.; Cruz, M.M.; Pereira, J.N.B.; et al. Tributyrin Attenuates Metabolic and Inflammatory Changes Associated with Obesity through a GPR109A-Dependent Mechanism. Cells 2020, 9, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.K.; Deehan, E.C.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, M.; Baskota, N.; Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Cole, J.; Tuncil, Y.E.; Seethaler, B.; Wang, T.; et al. Gut Microbiota Modulation with Long-Chain Corn Bran Arabinoxylan in Adults with Overweight and Obesity Is Linked to an Individualized Temporal Increase in Fecal Propionate. Microbiome 2020, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, Z.C.; Silverman, J.D.; Dressman, H.K.; Wei, Z.; Dallow, E.P.; Armstrong, S.C.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production by Gut Microbiota from Children with Obesity Differs According to Prebiotic Choice and Bacterial Community Composition. mBio 2020, 11, e00914-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Giacco, R.; Laiola, M.; Della Pepa, G.; Luongo, D.; Mangione, A.; Salamone, D.; Vitaglione, P.; Ercolini, D.; Rivellese, A.A. Acute and Chronic Improvement in Postprandial Glucose Metabolism by a Diet Resembling the Traditional Mediterranean Dietary Pattern: Can SCFAs Play a Role? Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengeler, A.C.; Gart, E.; Wiesmann, M.; Arnoldussen, I.A.C.; van Duyvenvoorde, W.; Hoogstad, M.; Dederen, P.J.; Verweij, V.; Geenen, B.; Kozicz, T.; et al. Propionic Acid and Not Caproic Acid, Attenuates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Improves (Cerebro) Vascular Functions in Obese Ldlr−/−.Leiden Mice. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9575–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farup, P.G.; Valeur, J. Changes in Faecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids after Weight-Loss Interventions in Subjects with Morbid Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamar, G.; Santamarina, A.B.; Casagrande, B.P.; Estadella, D.; de Rosso, V.V.; Wagner, R.; Fagundes, M.B.; Pisani, L.P. Prebiotic Potencial of Juçara Berry on Changes in Gut Bacteria and Acetate of Individuals with Obesity. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3767–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, A.; Kikuchi, K.; Ichimura, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; Moritoki, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Tsunashima, H.; Onda, T.; Kuniyoshi, N.; Nariyama, T.; et al. Fructo-Oligosaccharides Ameliorate Steatohepatitis, Visceral Adiposity, and Associated Chronic Inflammation via Increased Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in a Mouse Model of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowah, S.A.; Hirche, F.; Milanese, A.; Johnson, T.S.; Grafetstätter, M.; Schübel, R.; Kirsten, R.; Ulrich, C.M.; Kaaks, R.; Zeller, G.; et al. Changes in Plasma Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels after Dietary Weight Loss Among Overweight and Obese Adults over 50 Weeks. Nutrients 2020, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.P.N.; Dos Santos Amorim, P.R.; Bastos, R.R.; de Faria, E.R.; de Castro Moreira, M.E.; do Carmo Castro Franceschini, S.; do Carmo Gouveia Peluzio, M.; de Luces Fortes Ferreira, C.L.; Priore, S.E. Abundance of Gut Microbiota, Concentration of Short-Chain Fatty Acids, and Inflammatory Markers Associated with Elevated Body Fat, Overweight, and Obesity in Female Adolescents. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 7346863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, T.J.; Sul, W.J.; Oh, H.N.; Lee, Y.-K.; Lim, H.L.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C. Butyrate Attenuated Fat Gain through Gut Microbiota Modulation in Db/Db Mice Following Dapagliflozin Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.-S.; Song, E.-J.; Nam, Y.-D.; Nam, T.G.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Seo, M.-J.; Seo, D.-H. Effects of Enzymatically Modified Chestnut Starch on the Gut Microbiome, Microbial Metabolome, and Transcriptome of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.G.; Bellissimo, C.J.; Yeo, E.; Fei Xia, Y.; Petrik, J.J.; Surette, M.G.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Sloboda, D.M. Obesity during Pregnancy Results in Maternal Intestinal Inflammation, Placental Hypoxia, and Alters Fetal Glucose Metabolism at Mid-Gestation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, C.P.; Rosa, V.H.C.; Martins, B.C.; Soares, A.C.; Santos, I.B.; Monteiro, E.B.; Moura-Nunes, N.; da Costa, C.A.; da Rocha Pinheiro Mulder, A.; Daleprane, J.B. Resistant Starch from Green Banana (Musa Sp.) Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fat Liver Accumulation and Increases Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, T.; Yano, H. Effect of Dietary Cellulose Nanofiber and Exercise on Obesity and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat-Diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farup, P.G.; Lydersen, S.; Valeur, J. Are Nonnutritive Sweeteners Obesogenic? Associations between Diet, Faecal Microbiota, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Morbidly Obese Subjects. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 4608315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battson, M.L.; Lee, D.M.; Li Puma, L.C.; Ecton, K.E.; Thomas, K.N.; Febvre, H.P.; Chicco, A.J.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. Gut Microbiota Regulates Cardiac Ischemic Tolerance and Aortic Stiffness in Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 317, H1210–H1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Su, M.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Y. Eurotium Cristatum, a Potential Probiotic Fungus from Fuzhuan Brick Tea, Alleviated Obesity in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5032–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zou, J.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Xiexin Tang Ameliorates Dyslipidemia in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats via Elevating Gut Microbiota-Derived Short Chain Fatty Acids Production and Adjusting Energy Metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 112032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Walden, T.B.; Cai, D.; Ahl, D.; Bertilsson, S.; Phillipson, M.; Nyman, M.; Holm, L. Dietary Fiber in Bilberry Ameliorates Pre-Obesity Events in Rats by Regulating Lipid Depot, Cecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Formation and Microbiota Composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, G.; Kang, X.; Liu, H. Baicalin Improves Intestinal Microecology and Abnormal Metabolism Induced by High-Fat Diet. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 857, 172457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, C.; Song, B.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Gao, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota Mediates the Protective Effects of Dietary β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) against Obesity Induced by High-Fat Diets. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10019–10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hao, W.; He, Z.; Kwek, E.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liang, N.; Ma, K.Y.; Lei, L.; He, W.-S.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Tea Water Extracts on the Body Weight and Gut Microbiota in C57BL/6J Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2847–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, P.M.; Schoemaker, M.H.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K.; Lambers, T.T.; van Tol, E.A.F.; Acerini, C.L.; Olga, L.; Petry, C.J.; Hughes, I.A.; et al. Human Milk Short-Chain Fatty Acid Composition Is Associated with Adiposity Outcomes in Infants. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Park, S.; Chung, Y.; Kim, B.; Park, H.; Huang, E.; Jeong, D.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, B.; Hyun, C.-K.; et al. Amelioration of Obesity-Related Biomarkers by Lactobacillus Sakei CJLS03 in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Murine Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, W.; Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Ling, W. Supplementation with Sodium Butyrate Modulates the Composition of the Gut Microbiota and Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Yan, X.; Su, L. Anti-Inflammation Effects of Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulphate from Acaudina Molpadioides by Altering Gut Microbiota in Obese Mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Nagpal, R.; Wang, S.; Gagliano, J.; Kitzman, D.W.; Soleimanian-Zad, S.; Sheikh-Zeinoddin, M.; Read, R.; Yadav, H. Prebiotics from Acorn and Sago Prevent High-Fat-Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance via Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis Modulation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 67, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ding, Z.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P.; Mu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, L. Jamun (Eugenia Jambolana Lam.) Fruit Extract Prevents Obesity by Modulating the Gut Microbiome in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1801307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleophas, M.C.P.; Ratter, J.M.; Bekkering, S.; Quintin, J.; Schraa, K.; Stroes, E.S.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B. Effects of Oral Butyrate Supplementation on Inflammatory Potential of Circulating Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Healthy and Obese Males. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okouchi, R.; Shuang, E.; Yamamoto, K.; Ota, T.; Seki, K.; Imai, M.; Ota, R.; Asayama, Y.; Nakashima, A.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Simultaneous Intake of Euglena Gracilis and Vegetables Exerts Synergistic Anti-Obesity and Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Álvarez-Quintero, R.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Sierra, J.A.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Higher Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels Are Associated with Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis, Obesity, Hypertension and Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors. Nutrients 2018, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gart, E.; Souto Lima, E.; Schuren, F.; de Ruiter, C.G.F.; Attema, J.; Verschuren, L.; Keijer, J.; Salic, K.; Morrison, M.C.; Kleemann, R. Diet-Independent Correlations between Bacteria and Dysfunction of Gut, Adipose Tissue, and Liver: A Comprehensive Microbiota Analysis in Feces and Mucosa of the Ileum and Colon in Obese Mice with NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayengbam, S.; Lambert, J.E.; Parnell, J.A.; Tunnicliffe, J.M.; Nicolucci, A.C.; Han, J.; Sturzenegger, T.; Shearer, J.; Mickiewicz, B.; Vogel, H.J.; et al. Impact of Dietary Fiber Supplementation on Modulating Microbiota-Host-Metabolic Axes in Obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 64, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Rudenko, O.; Egerod, K.L.; Husted, A.S.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Akrami, R.; Kristensen, M.; Schwartz, T.W.; Bäckhed, F. Microbial Fermentation of Flaxseed Fibers Modulates the Transcriptome of GPR41-Expressing Enteroendocrine Cells and Protects Mice against Diet-Induced Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E453–E463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugas, L.R.; Bernabé, B.P.; Priyadarshini, M.; Fei, N.; Park, S.J.; Brown, L.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Nelson, D.; Toh, E.C.; Gao, X.; et al. Decreased Microbial Co-Occurrence Network Stability and SCFA Receptor Level Correlates with Obesity in African-Origin Women. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyńska, R.; Litwin, M.; Sliżewska, K.; Szalecki, M.; Berdowska, A.; Bandurska, K.; Libudzisz, Z.; Kapuśniak, J. Bacterial Microbiota and Fatty Acids in the Faeces of Overweight and Obese Children. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, R.C.; Kim, H.; Fang, C.; Bennett, W.; Nemec, M.; Sirven, M.A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Deutz, N.; Britton, R.A.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U.; et al. Body Mass Index as a Determinant of Systemic Exposure to Gallotannin Metabolites during 6-Week Consumption of Mango (Mangifera Indica L.) and Modulation of Intestinal Microbiota in Lean and Obese Individuals. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Lin, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, X. Effects of Dietary Fiber Supplementation on Fatty Acid Metabolism and Intestinal Microbiota Diversity in C57BL/6J Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12706–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Larsen, N.; de Mello Tieghi, T.; Adorno, M.A.T.; Kot, W.; Saad, S.M.I.; Jespersen, L.; Sivieri, K. Modulation of Gut Microbiota from Obese Individuals by in Vitro Fermentation of Citrus Pectin in Combination with Bifidobacterium Longum BB-46. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8827–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, C.; Cross, T.-W.L.; Devendran, S.; Neumer, F.; Theis, S.; Ridlon, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; de Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of Prebiotic Inulin-Type Fructans on Blood Metabolite and Hormone Concentrations and Faecal Microbiota and Metabolites in Overweight Dogs. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zarrinpar, A.; Chaix, A.; Xu, Z.Z.; Chang, M.W.; Marotz, C.A.; Saghatelian, A.; Knight, R.; Panda, S. Antibiotic-Induced Microbiome Depletion Alters Metabolic Homeostasis by Affecting Gut Signaling and Colonic Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Beek, C.M.; Canfora, E.E.; Kip, A.M.; Gorissen, S.H.M.; Olde Damink, S.W.M.; van Eijk, H.M.; Holst, J.J.; Blaak, E.E.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Lenaerts, K. The Prebiotic Inulin Improves Substrate Metabolism and Promotes Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production in Overweight to Obese Men. Metabolism 2018, 87, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, C.; Liang, A.; Fan, X.; Wang, R.; Li, P.; Qi, K. Effects of SCFA on the DNA Methylation Pattern of Adiponectin and Resistin in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Male Mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yue, S.; Yang, Z.; Feng, W.; Meng, X.; Wang, A.; Peng, C.; Wang, C.; Yan, D. Oral Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Reduces Obesity in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolism. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, J.; Watanabe, K.; Taira, S.; Kasubuchi, M.; Li, X.; Irie, J.; Itoh, H.; Kimura, I. Barley β-Glucan Improves Metabolic Condition via Short-Chain Fatty Acids Produced by Gut Microbial Fermentation in High Fat Diet Fed Mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hartigh, L.J.; Gao, Z.; Goodspeed, L.; Wang, S.; Das, A.K.; Burant, C.F.; Chait, A.; Blaser, M.J. Obese Mice Losing Weight Due to Trans-10,Cis-12 Conjugated Linoleic Acid Supplementation or Food Restriction Harbor Distinct Gut Microbiota. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, R.; Sui, W. Raspberry Anthocyanin Consumption Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Modulating Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, E.C.; da Silva, J.F.; Navia-Pelaez, J.M.; Leonel, A.J.; Lopes, L.G.; Menezes-Garcia, Z.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Capettini, L.D.S.A.; Teixeira, L.G.; Lemos, V.S.; et al. Sodium Butyrate Modulates Adipocyte Expansion, Adipogenesis, and Insulin Receptor Signaling by Upregulation of PPAR-γ in Obese Apo E Knockout Mice. Nutrition 2018, 47, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Ishaq, S.L.; Liu, Z.; Bukowski, M.R. Colonic Aberrant Crypt Formation Accompanies an Increase of Opportunistic Pathogenic Bacteria in C57BL/6 Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 54, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, J.M.; Mailing, L.J.; Niemiro, G.M.; Moore, R.; Cook, M.D.; White, B.A.; Holscher, H.D.; Woods, J.A. Exercise Alters Gut Microbiota Composition and Function in Lean and Obese Humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Serino, M.; Blasco-Baque, V.; Azalbert, V.; Barton, R.H.; Cardellini, M.; Latorre, J.; Ortega, F.; Sabater-Masdeu, M.; Burcelin, R.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interacts with Markers of Adipose Tissue Browning, Insulin Action and Plasma Acetate in Morbid Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Yin, J. Anthocyanins in Black Rice, Soybean and Purple Corn Increase Fecal Butyric Acid and Prevent Liver Inflammation in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3178–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitkunat, K.; Stuhlmann, C.; Postel, A.; Rumberger, S.; Fankhänel, M.; Woting, A.; Petzke, K.J.; Gohlke, S.; Schulz, T.J.; Blaut, M.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Inulin, but Not Guar Gum, Prevent Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance through Differential Mechanisms in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelgrim, C.E.; Franx, B.A.A.; Snabel, J.; Kleemann, R.; Arnoldussen, I.A.C.; Kiliaan, A.J. Butyrate Reduces HFD-Induced Adipocyte Hypertrophy and Metabolic Risk Factors in Obese LDLr−/−.Leiden Mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canfora, E.E.; van der Beek, C.M.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Goossens, G.H.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Holst, J.J.; van Eijk, H.M.; Venema, K.; Smidt, H.; Zoetendal, E.G.; et al. Supplementation of Diet With Galacto-Oligosaccharides Increases Bifidobacteria, but Not Insulin Sensitivity, in Obese Prediabetic Individuals. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 87–97.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, G.H.; Rios-Morales, M.; Gerding, A.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Olinga, P.; Bakker, B.M. The Effects of Butyrate on Induced Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Precision-Cut Liver Slices. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, W.; Mizerski, A.; Rył, A.; Słojewski, M.; Sipak, O.; Piasecka, M.; Laszczyńska, M. Alterations in Fecal Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) and Branched Short-Chain Fatty Acids (BCFAs) in Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Metabolic Syndrome (MetS). Aging 2021, 13, 10934–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyanju, O.A.; Badejogbin, O.C.; Areola, D.E.; Olaniyi, K.S.; Dibia, C.; Soetan, O.A.; Oniyide, A.A.; Michael, O.S.; Olatunji, L.A.; Soladoye, A.O. Sodium Butyrate Arrests Pancreato-Hepatic Synchronous Uric Acid and Lipid Dysmetabolism in High Fat Diet Fed Wistar Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartstra, A.V.; Schüppel, V.; Imangaliyev, S.; Schrantee, A.; Prodan, A.; Collard, D.; Levin, E.; Dallinga-Thie, G.; Ackermans, M.T.; Winkelmeijer, M.; et al. Infusion of Donor Feces Affects the Gut-Brain Axis in Humans with Metabolic Syndrome. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ye, C.; Leung, E.L.-H.; Zhu, L.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. Bletilla Striata Oligosaccharides Improve Metabolic Syndrome through Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Metabolites in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, R.; Costabile, G.; Nigro, E.; Giacco, R.; Vetrani, C.; Anniballi, G.; Luongo, D.; Riccardi, G.; Daniele, A.; Annuzzi, G. Nutritional Factors Influencing Plasma Adiponectin Levels: Results from a Randomised Controlled Study with Whole-Grain Cereals. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, P.; Scheithauer, T.; Bakker, G.J.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Khan, M.T.; Herrema, H.; Ackermans, M.; Serlie, M.J.M.; de Brauw, M.; et al. Donor Metabolic Characteristics Drive Effects of Faecal Microbiota Transplantation on Recipient Insulin Sensitivity, Energy Expenditure and Intestinal Transit Time. Gut 2020, 69, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velikonja, A.; Lipoglavšek, L.; Zorec, M.; Orel, R.; Avguštin, G. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolic Parameters after Dietary Intervention with Barley Beta Glucans in Patients with High Risk for Metabolic Syndrome Development. Anaerobe 2019, 55, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, K.; Watanabe, S.; Xiao, J.; Nagatomo, R.; Ogawa, H.; Tsunematsu, T.; Umemoto, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Akatsu, H.; Inoue, K.; et al. Effect of Coffee or Coffee Components on Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouter, K.; Bakker, G.J.; Levin, E.; Hartstra, A.V.; Kootte, R.S.; Udayappan, S.D.; Katiraei, S.; Bahler, L.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Tremaroli, V.; et al. Differential Metabolic Effects of Oral Butyrate Treatment in Lean versus Metabolic Syndrome Subjects. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Shang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shui, G.; Lam, S.M.; Blanchard, C.; Strappe, P. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Enriched Rice Bran Diet Attenuates Insulin Resistance and Balances Energy Expenditure via Modification of Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, K.; Xiao, J.; Nagatomo, R.; Umemoto, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Akatsu, H.; Inoue, K.; Tsuneyama, K. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome and Plasma Short-Chain Fatty Acid Profiles in a Spontaneous Mouse Model of Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.P.; Singh, S.; Bijalwan, V.; Kumar, V.; Khare, P.; Baboota, R.K.; Singh, P.; Boparai, R.K.; Singh, J.; Kondepudi, K.K.; et al. Co-Supplementation of Isomalto-Oligosaccharides Potentiates Metabolic Health Benefits of Polyphenol-Rich Cranberry Extract in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice via Enhanced Gut Butyrate Production. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2897–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Gutiérrez, B.; Gámez-Belmonte, R.; Suárez, M.D.; Lavín, J.L.; Aransay, A.M.; Olivares, M.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Zarzuelo, A. A Synbiotic Composed of Lactobacillus Fermentum CECT5716 and FOS Prevents the Development of Fatty Acid Liver and Glycemic Alterations in Rats Fed a High Fructose Diet Associated with Changes in the Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Lyu, W.; Xie, M.; Yuan, Q.; Ye, H.; Hu, B.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, X. Effects of α-Galactooligosaccharides from Chickpeas on High-Fat-Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3160–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, S.; Schioldan, A.G.; Moore, M.E.; Dige, A.; Lærke, H.N.; Agnholt, J.; Bach Knudsen, K.E.; Hermansen, K.; Marco, M.L.; Gregersen, S.; et al. Effects of Arabinoxylan and Resistant Starch on Intestinal Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomised Crossover Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upadhyaya, B.; McCormack, L.; Fardin-Kia, A.R.; Juenemann, R.; Nichenametla, S.; Clapper, J.; Specker, B.; Dey, M. Impact of Dietary Resistant Starch Type 4 on Human Gut Microbiota and Immunometabolic Functions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrani, C.; Costabile, G.; Luongo, D.; Naviglio, D.; Rivellese, A.A.; Riccardi, G.; Giacco, R. Effects of Whole-Grain Cereal Foods on Plasma Short Chain Fatty Acid Concentrations in Individuals with the Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrition 2016, 32, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chassaing, B.; Zhang, L.; San Yeoh, B.; Xiao, X.; Kumar, M.; Baker, M.T.; Cai, J.; Walker, R.; Borkowski, K.; et al. Microbiota-Dependent Hepatic Lipogenesis Mediated by Stearoyl CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) Promotes Metabolic Syndrome in TLR5-Deficient Mice. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Den Besten, G.; Gerding, A.; van Dijk, T.H.; Ciapaite, J.; Bleeker, A.; van Eunen, K.; Havinga, R.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. Protection against the Metabolic Syndrome by Guar Gum-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Depends on Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, A.; Walton, G.E.; Tzortzis, G.; Vulevic, J.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Gibson, G.R. Development of a Bread Delivery Vehicle for Dietary Prebiotics to Enhance Food Functionality Targeted at Those with Metabolic Syndrome. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Den Besten, G.; Havinga, R.; Bleeker, A.; Rao, S.; Gerding, A.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake Fluxes by Mice on a Guar Gum Supplemented Diet Associate with Amelioration of Major Biomarkers of the Metabolic Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojärvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E.; et al. Impact of Diet and Individual Variation on Intestinal Microbiota Composition and Fermentation Products in Obese Men. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartvigsen, M.L.; Lærke, H.N.; Overgaard, A.; Holst, J.J.; Bach Knudsen, K.E.; Hermansen, K. Postprandial Effects of Test Meals Including Concentrated Arabinoxylan and Whole Grain Rye in Subjects with the Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomised Study. Eur J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; Gøbel, R.J.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Forssten, S.D.; Lahtinen, S.J.; Jakobsen, M. Effect of Lactobacillus Salivarius Ls-33 on Fecal Microbiota in Obese Adolescents. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.F.S.; Grześkowiak, Ł.; Franceschini, S.C.C.; Bressan, J.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F.; Peluzio, M.C.G. Higher Level of Faecal SCFA in Women Correlates with Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fava, F.; Gitau, R.; Griffin, B.A.; Gibson, G.R.; Tuohy, K.M.; Lovegrove, J.A. The Type and Quantity of Dietary Fat and Carbohydrate Alter Faecal Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Excretion in a Metabolic Syndrome “at-Risk” Population. Int J. Obes. 2013, 37, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutkins, R.W.; Krumbeck, J.A.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D.; Fahey, G.; Goh, Y.J.; Hamaker, B.; Martens, E.C.; Mills, D.A.; Rastal, R.A.; et al. Prebiotics: Why Definitions Matter. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome: Major Fermentation by-Products and Their Impact on Host Health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
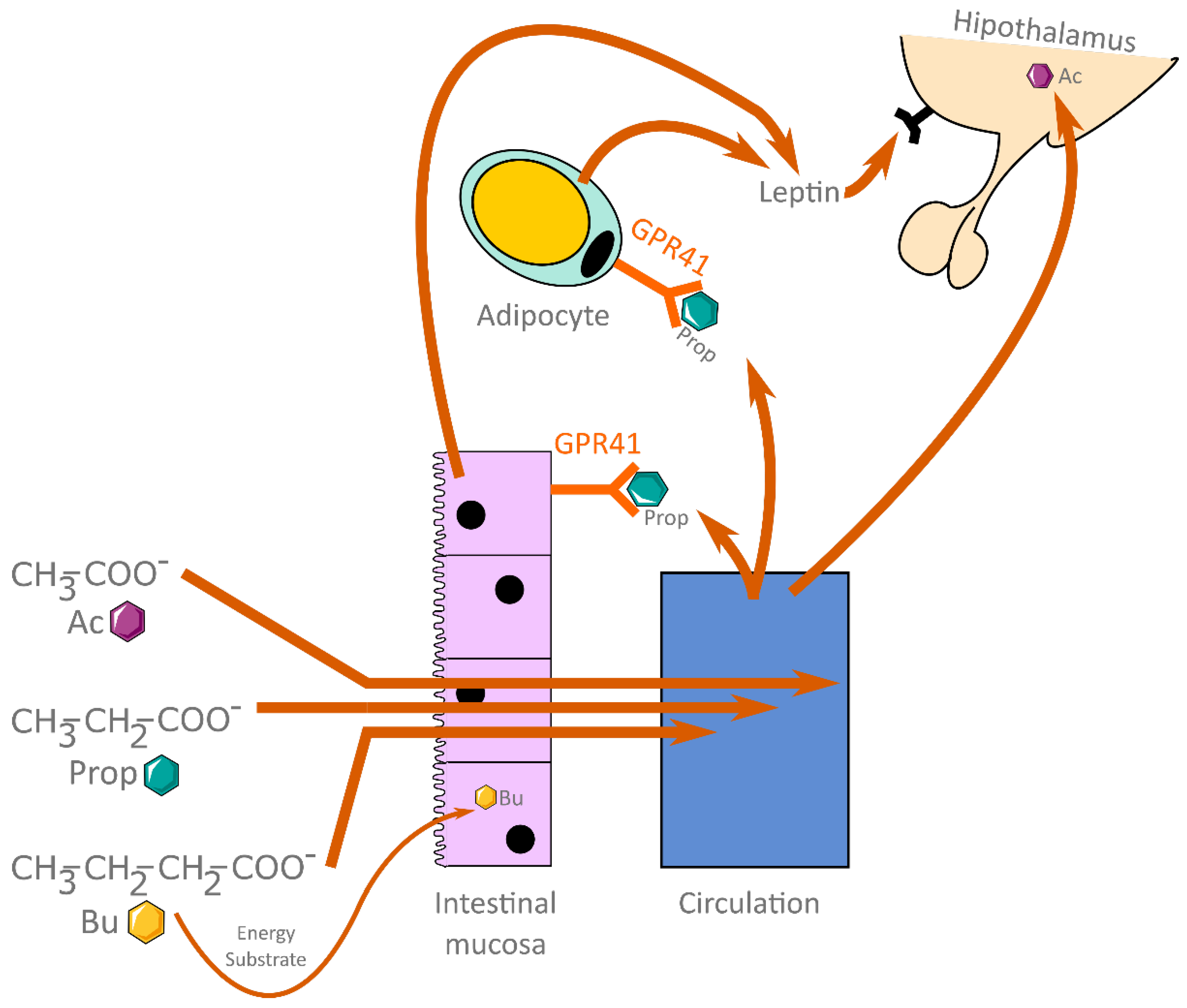

| Dietary Supplement | SCFA Variations | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Bilberry | ↑fSCFA, bSCFA | [111] |
| Guar gum | ↑fAc, fBu | [56] |
| ↑fSCFA | [167,169] | |
| Erythritol | ↑fSCFA, bSCFA | [60] |
| Nobiletin | ↑fSCFA | [66] |
| Baicalin | ↑fSCFA | [112] |
| Barley β-glucan | ↑fSCFA | [70] |
| ↑fAc, fProp | [72] | |
| ↑fBu | [137] | |
| Betaine | ↑fAc, fBu | [73] |
| Coarse cereal mixture | ↑fSCFA | [77] |
| Phlorizin | ↑fSCFA | [81] |
| Inulin | ↑fSCFA | [85] |
| Pinto beans | ↑fBu | [86] |
| Deinococcus geotermalis modified chestnut starch | ↑fAc | [103] |
| Green banana | ↑fSCFA | [105] |
| β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate | ↑fProp | [113] |
| Tea extract | ↑fSCFA | [114] |
| Chondroitin sulfate | ↑bSCFA | [118] |
| Jamun fruit extract | ↑fSCFA | [120] |
| Euglena + vegetables | ↑fSCFA | [122] |
| Flaxseed fiber | ↑fSCFA | [126] |
| Bacterial cellulose + konjac glucomannan | ↑fAc, fProp, fBu | [130] |
| Hydroxysafflor yellow A | ↑fSCFA | [136] |
| Anthocyanins | ↑fBu | [139,144] |
| Bletilla striata | ↑fAc ↓fProp | [152] |
| Cranberry extract + isomalto-oligosaccharides | ↑fSCFA, fBu | [160] |
| Chickpea α-galacto-oligosaccharides | ↑fProp, fBu | [162] |
| Caffeine + epigallocatechin-3-gallate | ↑fAc, fProp | [65] |
| Trilobatin | ↑fProp, fBu | [68] |
| Xiexin Tang | ↑fSCFA | [110] |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid enriched rice bran | ↑fProp, fBu | [158] |
| Trans-10,cis-12 Conjugated linoleic acid | ↑bAc, fBu | [138] |
| Lard fat + sucrose | ↑bProp | [124] |
| Lard fat + sucrose + fructose | ↓bAc, bBu | [124] |
| Probiotic | SCFA Variations | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis | ↓fSCFA | [69] |
| Clostridium cochlearum | ↓fSCFA | [40] |
| Eurotium cristatum | ↑fBu | [109] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | ↑fSCFA | [87] |
| Lactobacillus reuteri | ↑fBu, bBu | [53] |
| Lactobacillus sakei | ↑fSCFA, bSCFA | [116] |
| ↑fBu | [79] |
| Dietary Supplement | SCFA Variations | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Arabinoxylan | ↑bAc, bBu | [171] |
| ↑fAc, fBu | [163] | |
| ↑fProp | [93] | |
| Inulin | ↑bAc | [134] |
| Grape pomace | ↓fBu | [83] |
| Rye | ↑bBu | [36] |
| Yacon flour | ↓fSCFA | [63] |
| Energy-restricted diet | No effect on bSCFA | [100] |
| ↓fAc, fBu | [43] | |
| Intermittent-fasting diet | No effect on bSCFA | [100] |
| Mediterranean diet | ↑bBu | [95] |
| Vegan diet | ↑fBu | [47] |
| Barley β-glucan | ↑fProp | [155] |
| Galacto-oligosaccharides | No effect on bSCFA or fSCFA | [147] |
| Almond | No effect on fSCFA | [76] |
| Pea fiber | ↑fAc | [125] |
| Whole-grain cereal | ↑bAc, bSCFA | [153] |
| ↑bProp | [165] | |
| Wheat bran | ↑bAc, bProp, bSCFA 1 | [54] |
| Refined cereal | ↑bAc, bSCFA | [153] |
| Mango | ↑fBu 2 | [129] |
| Resistant starch type 4 | ↑fProp, fBu | [164] |
| Juçara berry | ↑fAc | [98] |
| Saturated fat | ↑fSCFA | [174] |
| Monounsaturated fat | ↑fSCFA | [174] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilyés, T.; Silaghi, C.N.; Crăciun, A.M. Diet-Related Changes of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Blood and Feces in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Biology 2022, 11, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111556
Ilyés T, Silaghi CN, Crăciun AM. Diet-Related Changes of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Blood and Feces in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111556
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlyés, Tamás, Ciprian N. Silaghi, and Alexandra M. Crăciun. 2022. "Diet-Related Changes of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Blood and Feces in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome" Biology 11, no. 11: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111556
APA StyleIlyés, T., Silaghi, C. N., & Crăciun, A. M. (2022). Diet-Related Changes of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Blood and Feces in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Biology, 11(11), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111556








