Psychological Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: Insights into Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Long COVID-19
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
3. Cause, Prevalence, and Risk Factors of COVID-19-Associated Psychological Effects
4. Psychiatric Sequelae of COVID-19
5. Pathophysiology of COVID-19’s Psychological Effects
5.1. SARS-CoV-2 Entry into the Brain/CNS
5.2. Implications of Immune Inflammatory Signaling on Neuropsychiatric Disorder
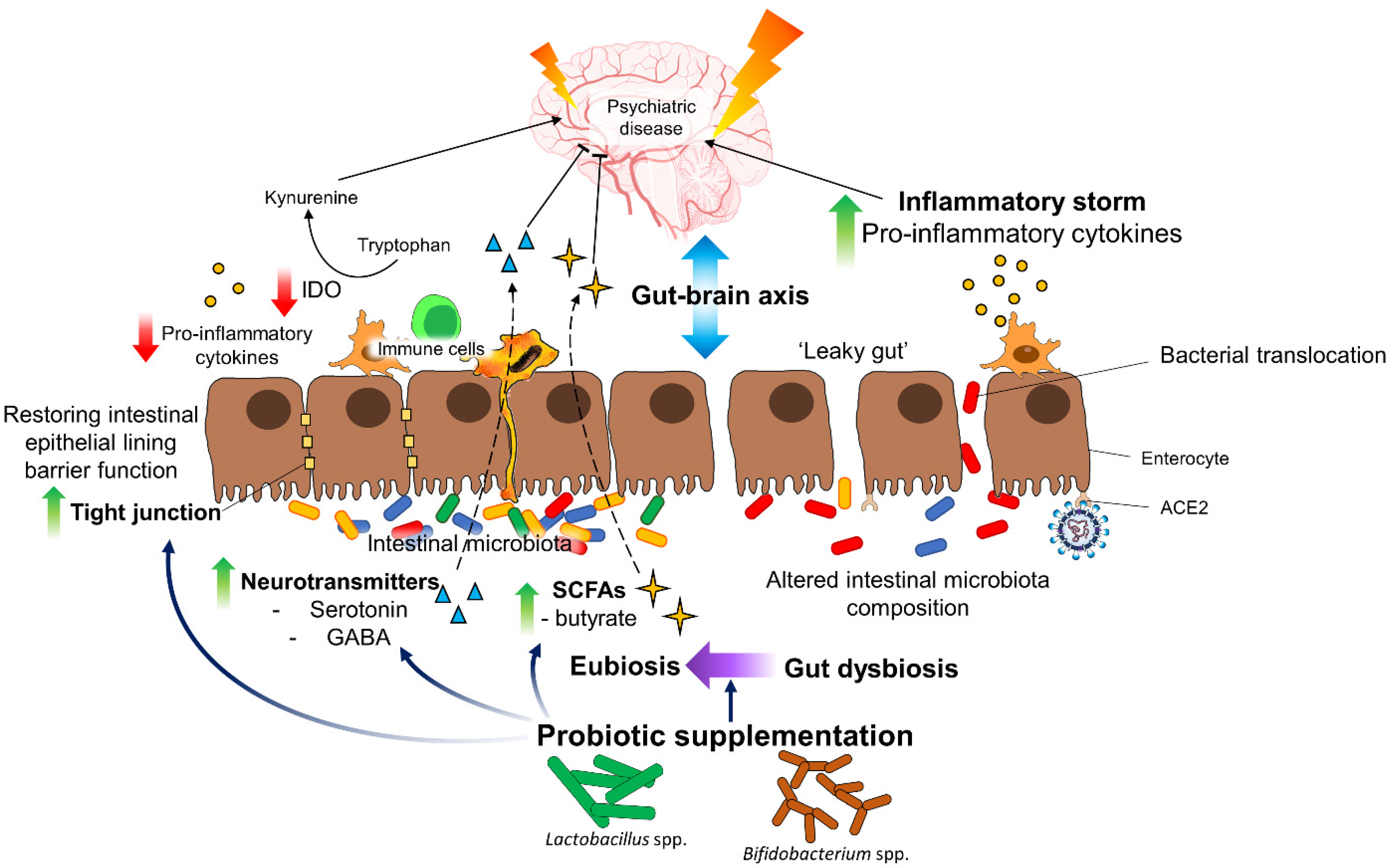
6. Possible Therapeutic Options
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Veldhuis, A.; Malhotra, T. Neuropsychiatric and Cognitive Sequelae of COVID-19. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.G.; Palladini, M.; De Lorenzo, R.; Magnaghi, C.; Poletti, S.; Furlan, R.; Ciceri, F.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Benedetti, F.; COVID-19 BioB Outpatient Clinic Study group. Persistent psychopathology and neurocognitive impairment in COVID-19 survivors: Effect of inflammatory biomarkers at three-month follow-up. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 dashboard. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Thye, A.Y.-K.; Law, J.W.-F.; Pusparajah, P.; Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs): An impending global crisis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Update on Omicron. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2021-update-on-omicron (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-sars-cov-2-variant-of-concern (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevik, M.; Kuppalli, K.; Kindrachuk, J.; Peiris, M. Virology, transmission, and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2. BMJ 2020, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Gu, X.; Kang, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X. 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: A cohort study. Lancet 2021, 397, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkur, A.K.; Akdis, M.; Azkur, D.; Sokolowska, M.; van de Veen, W.; Brüggen, M.C.; O’Mahony, L.; Gao, Y.; Nadeau, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID-19. Allergy 2020, 75, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanen, C.; Vermes, I. Apoptosis and inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 1995, 4, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, P.; Fan, J. Programmed cell death and its role in inflammation. Mil. Med. Res. 2015, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nailwal, H.; Chan, F.K.-M. Necroptosis in anti-viral inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, I.; Miao, E.A. Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ye, Q. Cellular Immune Response to COVID-19 and Potential Immune Modulators. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, B.R.; Baquero, F.; Ankomah, P.P.; McCall, I.C. Phagocytes, antibiotics, and self-limiting bacterial infections. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levin, B.R.; Antia, R. Why we don’t get sick: The within-host population dynamics of bacterial infections. Science 2001, 292, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, G.P.; Biros, E.; Letson, H.L.; Morris, J.L. Living in a Hostile World: Inflammation, New Drug Development, and Coronavirus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icenogle, T. COVID-19: Infection or autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpert, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. SARS-CoV-2, the autoimmune virus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, C. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuki, K.; Fujiogi, M.; Koutsogiannaki, S. COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.-T.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheung, T.; Ng, C.H. Timely mental health care for the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak is urgently needed. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psychiatry, L. Send in the therapists? Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsalem, D.; Dixon, L.B.; Neria, Y. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak and mental health: Current risks and recommended actions. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.P.; Chesney, E.; Oliver, D.; Pollak, T.A.; McGuire, P.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Zandi, M.S.; Lewis, G.; David, A.S. Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric presentations associated with severe coronavirus infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis with comparison to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kępińska, A.P.; Iyegbe, C.O.; Vernon, A.C.; Yolken, R.; Murray, R.M.; Pollak, T.A. Schizophrenia and influenza at the centenary of the 1918-1919 Spanish influenza pandemic: Mechanisms of psychosis risk. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, H.; Patel, K.; Greenwood, D.C.; Halpin, S.; Lewthwaite, P.; Salawu, A.; Eyre, L.; Breen, A.; O’Connor, R.; Jones, A. Long-term clinical outcomes in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreaks after hospitalisation or ICU admission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.H.-B.; Wing, Y.-K.; Yu, M.W.-M.; Leung, C.-M.; Ma, R.C.; Kong, A.P.; So, W.; Fong, S.Y.-Y.; Lam, S.-P. Mental morbidities and chronic fatigue in severe acute respiratory syndrome survivors: Long-term follow-up. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 2142–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.; Currier, G.W.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wei, J. Posttraumatic stress disorder in convalescent severe acute respiratory syndrome patients: A 4-year follow-up study. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2009, 31, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.K.; Wong, C.; Tsang, J.; Wong, K. Psychological distress and negative appraisals in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Psychol. Med. 2004, 34, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, M.G.; De Lorenzo, R.; Conte, C.; Poletti, S.; Vai, B.; Bollettini, I.; Melloni, E.M.T.; Furlan, R.; Ciceri, F.; Rovere-Querini, P. Anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors: Role of inflammatory and clinical predictors. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-F.; Li, W.; Deng, H.-B.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.-H.; Bo, H.-X.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.-Y. Prevalence of depression and its association with quality of life in clinically stable patients with COVID-19. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzo, R.; Conte, C.; Lanzani, C.; Benedetti, F.; Roveri, L.; Mazza, M.G.; Brioni, E.; Giacalone, G.; Canti, V.; Sofia, V. Residual clinical damage after COVID-19: A retrospective and prospective observational cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharaj, A.; Thomas, N.; Ellul, M.A.; Davies, N.W.; Pollak, T.A.; Tenorio, E.L.; Sultan, M.; Easton, A.; Breen, G.; Zandi, M. Neurological and neuropsychiatric complications of COVID-19 in 153 patients: A UK-wide surveillance study. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, J.Y.-M. The SARS-associated stigma of SARS victims in the post-SARS era of Hong Kong. Qual. Health Res. 2008, 18, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Humphris, G.; Griffiths, R. Psychological morbidity following critical illness-the rationale for care after intensive care. Clin. Intensive Care 1998, 9, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.K.; Webster, R.K.; Smith, L.E.; Woodland, L.; Wessely, S.; Greenberg, N.; Rubin, G.J. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: Rapid review of the evidence. Lancet 2020, 395, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asmundson, G.J.; Taylor, S. Coronaphobia: Fear and the 2019-nCoV outbreak. J. Anxiety Disord. 2020, 70, 102196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, C.; Castellanos, T.; Abrams, M.; Vazquez, C. The impact of economic recessions on depression and individual and social well-being: The case of Spain (2006–2013). Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2018, 53, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, N.; Docherty, M.; Gnanapragasam, S.; Wessely, S. Managing mental health challenges faced by healthcare workers during covid-19 pandemic. BMJ 2020, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderlind, W.M.; Rabinovitz, B.B.; Miao, I.Y.; Oberlin, L.E.; Bueno-Castellano, C.; Fridman, C.; Jaywant, A.; Kanellopoulos, D. A systematic review of neuropsychological and psychiatric sequalae of COVID-19: Implications for treatment. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, G.M.; Júnior, V.D.d.O.T.; de Meiroz Grilo, M.L.P.; Coelho, M.L.G.; de Lima-Araújo, G.L.; Schuch, F.B.; Galvão-Coelho, N.L. Mental Health in COVID-19 Pandemic: A Meta-Review of Prevalence Meta-Analyses. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.-D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.-N.; Zhao, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Chen, H. Anxiety and depression and its correlates in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2021, 25, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbehzadeh, S.; Tavahomi, M.; Zanjari, N.; Ebrahimi-Takamjani, I.; Amiri-Arimi, S. Physical and mental health complications post-COVID-19: Scoping review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2021, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, D.L.; Holdsworth, L.; Jawad, N.; Gunasekera, P.; Morice, A.H.; Crooks, M.G. Post-COVID-19 symptom burden: What is long-COVID and how should we manage it? Lung 2021, 199, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, B.; Cassar, M.P.; Tunnicliffe, E.M.; Filippini, N.; Griffanti, L.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Okell, T.; Sheerin, F.; Xie, C.; Mahmod, M. Medium-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on multiple vital organs, exercise capacity, cognition, quality of life and mental health, post-hospital discharge. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 31, 100683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasoni, D.; Bai, F.; Castoldi, R.; Barbanotti, D.; Falcinella, C.; Mulè, G.; Mondatore, D.; Tavelli, A.; Vegni, E.; Marchetti, G. Anxiety and depression symptoms after virological clearance of COVID-19: A cross-sectional study in Milan, Italy. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Islam, U.S.; Mosaddek, A.S.M.; Potenza, M.N.; Pardhan, S. Treatment, persistent symptoms, and depression in people infected with COVID-19 in Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Borst, B.; Peters, J.B.; Brink, M.; Schoon, Y.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Schers, H.; van Hees, H.W.; van Helvoort, H.; van den Boogaard, M.; van der Hoeven, H. Comprehensive health assessment three months after recovery from acute COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf, M.; Antoni, M.; Ter Kuile, M.; Arbous, M.; Duinisveld, A.; Feltkamp, M.; Groeneveld, G.; Hinnen, S.; Janssen, V.; Lijfering, W. Short-term outpatient follow-up of COVID-19 patients: A multidisciplinary approach. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 32, 100731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonazza, F.; Borghi, L.; di San Marco, E.C.; Piscopo, K.; Bai, F.; Monforte, A.d.A.; Vegni, E. Psychological outcomes after hospitalization for COVID-19: Data from a multidisciplinary follow-up screening program for recovered patients. Res. Psychother. Psychopathol. Process Outcome 2020, 23, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Soddu, D.; Balbo, P.E.; Baricich, A.; Zeppegno, P.; Avanzi, G.C.; Baldon, G.; Bartolomei, G.; Battaglia, M.; Battistini, S. Respiratory and psychophysical sequelae among patients with COVID-19 four months after hospital discharge. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2036142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Acharya, S.P.; Singh, S.; Patra, S.; Mishra, B.R.; Kar, N. Post traumatic stress symptoms, anxiety, and depression in patients after intensive care unit discharge–a longitudinal cohort study from a LMIC tertiary care centre. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chudzicka-Czupała, A.; Tee, M.L.; Núñez, M.I.L.; Tripp, C.; Fardin, M.A.; Habib, H.A.; Tran, B.X.; Adamus, K.; Anlacan, J. A chain mediation model on COVID-19 symptoms and mental health outcomes in Americans, Asians and Europeans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lipsitz, O.; Nasri, F.; Lui, L.M.; Gill, H.; Phan, L.; Chen-Li, D.; Iacobucci, M.; Ho, R.; Majeed, A. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Baumeister, R.F.; Veilleux, J.C.; Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, S. Risk factors associated with mental illness in hospital discharged patients infected with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 292, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannan, A.; Mehedi, H.; Chy, N.; Qayum, M.O.; Akter, F.; Rob, M.; Biswas, P.; Hossain, S.; Ayub, M.I. A multi-centre, cross-sectional study on coronavirus disease 2019 in Bangladesh: Clinical epidemiology and short-term outcomes in recovered individuals. New Microbes New Infect. 2021, 40, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, X.; Ekumi, I.O.; Wang, J.; An, Y.; Li, Z.; Yuan, B. Psychological distress and its correlates among COVID-19 survivors during early convalescence across age groups. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020, 28, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speth, M.M.; Singer-Cornelius, T.; Oberle, M.; Gengler, I.; Brockmeier, S.J.; Sedaghat, A.R. Mood, anxiety and olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19: Evidence of central nervous system involvement? Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.R.; Oyem, P.C.; Viguera, A.C. Prevalence of psychiatric morbidity following discharge after COVID-19 hospitalization. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2020, 69, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.-N.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Cho, B.; Sohn, J.H. The psychological burden of COVID-19 stigma: Evaluation of the mental health of isolated mild condition COVID-19 patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajure, M.; Tariku, M.; Mohammedhussein, M.; Dule, A. Depression, Anxiety and Associated Factors Among Chronic Medical Patients Amid COVID-19 Pandemic in Mettu Karl Referral Hospital, Mettu, Ethiopia, 2020. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeria, M.; Cejudo, J.C.; Sotoca, J.; Deus, J.; Krupinski, J. Cognitive profile following COVID-19 infection: Clinical predictors leading to neuropsychological impairment. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 9, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroiu, L.; Dumea, E.; Nastase, F.; Niculet, E.; Fotea, S.; Ciubara, A.B.; Stefanopol, I.A.; Nechita, A.; Anghel, L.T.; Ciubara, A. Assessment of Depression in Patients with COVID-19. Brain-Broad Res. Artif. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Cai, X.; Song, S.; Zhao, J.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K. Correlation between immune response and self-reported depression during convalescence from COVID-19. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Barnett, J.; Brill, S.E.; Brown, J.S.; Denneny, E.K.; Hare, S.S.; Heightman, M.; Hillman, T.E.; Jacob, J.; Jarvis, H.C. ‘Long-COVID’: A cross-sectional study of persisting symptoms, biomarker and imaging abnormalities following hospitalisation for COVID-19. Thorax 2021, 76, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Jung, J.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.B.; Song, K.-H. Psychological consequences of survivors of COVID-19 pneumonia 1 month after discharge. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalon, N.; Dorman-Ilan, S.; Hasson-Ohayon, I.; Hertz-Palmor, N.; Shani, S.; Basel, D.; Gross, R.; Chen, W.; Abramovich, A.; Afek, A.; et al. Trajectories of post-traumatic stress symptoms, anxiety, and depression in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A one-month follow-up. J. Psychosom. Res. 2021, 143, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, C.; An, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z. Prevalence and predictors of posttraumatic stress disorder, depression and anxiety among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in China. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindegaard, N.; Benros, M.E. COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: Systematic review of the current evidence. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozamiz-Etxebarria, N.; Dosil-Santamaria, M.; Picaza-Gorrochategui, M.; Idoiaga-Mondragon, N. Stress, anxiety, and depression levels in the initial stage of the COVID-19 outbreak in a population sample in the northern Spain. Cad. Saude Publica 2020, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Pappa, S.; Ntella, V.; Giannakas, T.; Giannakoulis, V.G.; Papoutsi, E.; Katsaounou, P. Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and insomnia among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpin, S.J.; McIvor, C.; Whyatt, G.; Adams, A.; Harvey, O.; McLean, L.; Walshaw, C.; Kemp, S.; Corrado, J.; Singh, R. Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, R.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Luperdi, S.C.; Estrada, I.; Latorre, A.; González-Jiménez, P.; Feced, L.; Bouzas, L.; Yepez, K.; Ferrando, A. Short-term neuropsychiatric outcomes and quality of life in COVID-19 survivors. J. Intern. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Li, T.; Gong, F.; Zhang, J.-S.; Li, X.-K. Predictors of health-related quality of life and influencing factors for COVID-19 patients, a follow-up at one month. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Wong, J.G.; McAlonan, G.M.; Cheung, V.; Cheung, C.; Sham, P.C.; Chu, C.-M.; Wong, P.-C.; Tsang, K.W.; Chua, S.E. Stress and psychological distress among SARS survivors 1 year after the outbreak. Can. J. Psychiatry 2007, 52, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lega, I.; Nistico, L.; Palmieri, L.; Caroppo, E.; Lo Noce, C.; Donfrancesco, C.; Vanacore, N.; Scattoni, M.L.; Picardi, A.; Gigantesco, A.; et al. Psychiatric disorders among hospitalized patients deceased with COVID-19 in Italy. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 35, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, Q. The Associated Factors of Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in Wuhan, China. Psychiatric Quarterly 2021, 92, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, A.; Balfanz, P.; Cornelissen, C.; Müller, A.; Bergs, I.; Marx, N.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Hartmann, B.; Dreher, M.; Müller, T. Follow up of patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Pulmonary and extrapulmonary disease sequelae. Respir. Med. 2020, 174, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.L.; Clark, J.R.; Orban, Z.S.; Lim, P.H.; Szymanski, A.L.; Taylor, C.; DiBiase, R.M.; Jia, D.T.; Balabanov, R.; Ho, S.U.; et al. Persistent neurologic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction in non-hospitalized Covid-19 “long haulers”. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol 2021, 8, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolache, T.T.; Benros, M.E.; Brenner, L.A. Targetable biological mechanisms implicated in emergent psychiatric conditions associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, C.M.; Louie, M.; Loeb, M.; Gold, W.L.; Muller, M.P.; de Jager, J.; Cameron, J.I.; Tomlinson, G.; Mazzulli, T.; Walmsley, S.L. One-year outcomes and health care utilization in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, A.; Beck, K.; Becker, C.; Zumbrunn, S.; Ramin-Wright, M.; Urben, T.; Quinto, A.; Schaefert, R.; Meinlschmidt, G.; Gaab, J.; et al. Psychological burden in patients with COVID-19 and their relatives 90 days after hospitalization: A prospective observational cohort study. J. Psychosom. Res. 2021, 147, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schandl, A.; Hedman, A.; Lyng, P.; Tachinabad, S.F.; Svefors, J.; Rol, M.; Geborek, A.; Franko, M.A.; Sderberg, M.; Joelsson-Alm, E.; et al. Long-term consequences in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A prospective cohort study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2021, 65, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, L.I.; Garry, K.; Prete, A.M.; Sharma, S.; Mendoza, F.; Kahan, T.; Karpel, H.; Duan, E.; Hochman, K.A.; Weerahandi, H. Six-Month Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized with Severe COVID-19. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 3772–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, J.A.; Yang, D.; Lewis, A.; Patel, P.; Medicherla, C.; Arena, V.; Fang, T.; Andino, A.; Snyder, T.; Madhavan, M.; et al. A prospective study of long-term outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19 patients with and without neurological complications. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 426, 117486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Latronico, N.; Peli, E.; Calza, S.; Rodella, F.; Novelli, M.P.; Cella, A.; Marshall, J.; Needham, D.M.; Rasulo, F.A.; Piva, S.; et al. Physical, cognitive and mental health outcomes in 1-year survivors of COVID-19-associated ARDS. Thorax 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Beck, K.; Zumbrunn, S.; Memma, V.; Herzog, N.; Bissmann, B.; Gross, S.; Loretz, N.; Mueller, J.; Amacher, S.A.; et al. Long COVID 1 year after hospitalisation for COVID-19: A prospective bicentric cohort study. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2021, 151, w30091. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Altman, M.T.; Knauert, M.P.; Pisani, M.A. Sleep disturbance after hospitalization and critical illness: A systematic review. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, P.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Rathod, S.; Elliot, K.; Thayanandan, T.; Sandle, N.; Haque, N.; Chau, S.W.; Wong, O.W.; Chan, S.S. An evaluation of the mental health impact of SARS-CoV-2 on patients, general public and healthcare professionals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 34, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiri, D.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Giuseppin, G.; Molinaro, M.; Modica, M.; Montanari, S.; Terenzi, B.; Carfì, A.; Landi, F.; Sani, G. Psychological distress after Covid-19 recovery: Reciprocal effects with temperament and emotional dysregulation. An exploratory study of patients over 60 years of age assessed in a post-acute care service. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lin, J.; Ying, W.; Zheng, C.; Tao, L.; Ying, B.; Cheng, B.; Jin, S.; Hu, B. Correlation study of short-term mental health in patients discharged after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection without comorbidities: A prospective study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrigues, E.; Janvier, P.; Kherabi, Y.; Le Bot, A.; Hamon, A.; Gouze, H.; Doucet, L.; Berkani, S.; Oliosi, E.; Mallart, E. Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e4–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.X.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Ren, L.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Hu, P.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2021, 398, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, J.A.; Lewis, A.; Melmed, K.; Lin, J.; Kondziella, D.; Helbok, R.; Yaghi, S.; Meropol, S.; Wisniewski, T.; Balcer, L. Prevalence and Predictors of Prolonged Cognitive and Psychological Symptoms Following COVID-19 in the United States. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, M.W. Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines Against COVID-19 Among Hospitalized Adults Aged≥ 65 Years—United States, January–March 2021. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Rassel, M.A.; Monayem, F.B.; Sayeed, S.J.B.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.M. Post-COVID-19 syndrome among symptomatic COVID-19 patients: A prospective cohort study in a tertiary care center of Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, S.; Shokry, D.; Gomaa, S.M. Post-COVID-19 fatigue and anhedonia: A cross-sectional study and their correlation to post-recovery period. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2021, 41, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, I.W.C.; Chu, C.M.; Pan, P.C.; Yiu, M.G.C.; Chan, V.L. Long-term psychiatric morbidities among SARS survivors. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2009, 31, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Sutin, A.R.; Daly, M.; Jones, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies comparing mental health before versus during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.; Harthi, A.; Hussein, J.; Bouchama, A.; Johani, S.; Hajeer, A.; Saeed, B.; Wahbi, A.; Saedy, A.; AlDabbagh, T. Severe neurologic syndrome associated with Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS-CoV). Infection 2015, 43, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Gong, E.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhan, J.; Wang, S.; Xie, Z. Multiple organ infection and the pathogenesis of SARS. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, N. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the brain: Potential role of the chemokine mig in pathogenesis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Shin, H.-S.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, J.L.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, H.; Won, S.-D.; Han, W. Depression as a mediator of chronic fatigue and post-traumatic stress symptoms in Middle East respiratory syndrome survivors. Psychiatry Investig. 2019, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arab-Zozani, M.; Hashemi, F.; Safari, H.; Yousefi, M.; Ameri, H. Health-related quality of life and its associated factors in COVID-19 patients. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.W.; Chang, H.H.; Kwon, K.T.; Bae, S.; Hwang, S. Significance and Associated Factors of Long-Term Sequelae in Patients after Acute COVID-19 Infection in Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 53, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquet, M.; Luciano, S.; Geddes, J.R.; Harrison, P.J. Bidirectional associations between COVID-19 and psychiatric disorder: Retrospective cohort studies of 62 354 COVID-19 cases in the USA. The Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.-X.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheung, T.; Wu, X.; Xiang, Y.-T. Posttraumatic stress symptoms and attitude toward crisis mental health services among clinically stable patients with COVID-19 in China. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 1052–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Fromson, J.A.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, H. Immediate psychological distress in quarantined patients with COVID-19 and its association with peripheral inflammation: A mixed-method study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z. Characteristics and outcomes of a sample of patients with COVID-19 identified through social media in Wuhan, China: Observational study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e20108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Kou, C.; Xu, X.; Lu, J. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmwald, K.; Galvez, N.; Ríos, M.; Kalergis, A.M. Neurologic alterations due to respiratory virus infections. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Kang, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, X. Understanding the neurotropic characteristics of SARS-CoV-2: From neurological manifestations of COVID-19 to potential neurotropic mechanisms. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Sánchez, C.M.; Díaz-Maroto, I.; Fernández-Díaz, E.; Sánchez-Larsen, Á.; Layos-Romero, A.; García-García, J.; González, E.; Redondo-Peñas, I.; Perona-Moratalla, A.B.; Del Valle-Pérez, J.A. Neurologic manifestations in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The ALBACOVID registry. Neurology 2020, 95, e1060–e1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, R.R.; Kashani, K.B.; Boire, N.A.; Constantopoulos, E.; Guo, Y.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuropathology of COVID-19: A spectrum of vascular and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)-like pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntosh, B.J.; Ji, X.; Chen, J.J.; Gilboa, A.; Roudaia, E.; Sekuler, A.B.; Gao, F.; Chad, J.A.; Jegatheesan, A.; Masellis, M.; et al. Brain structure and function in people recovering from COVID-19 after hospital discharge or self-isolation: A longitudinal observational study protocol. CMAJ Open 2021, 9, E1114–E1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Golenbock, D.; Latz, E.; Morgan, D.; Brown, R. Immediate and long-term consequences of COVID-19 infections for the development of neurological disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccioli, L.; Pensato, U.; Cani, I.; Guarino, M.; Cortelli, P.; Bisulli, F. COVID-19-associated encephalopathy and cytokine-mediated neuroinflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 860–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Padovani, A. Reply to the Letter “COVID-19-Associated Encephalopathy and Cytokine-Mediated Neuroinflammation”. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, K.; McCulloch, L.; McColl, B.W.; Elkind, M.S.; Allan, S.M.; Smith, C.J. Preceding infection and risk of stroke: An old concept revived by the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechter, K. Virus infection as a cause of inflammation in psychiatric disorders. Inflamm. Psychiatry 2013, 28, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, H.; Lazartigues, E. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in the brain: Properties and future directions. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, A.; Domingues, R.; Setz, C.; Outeiro, T.F.; Krisko, A. SARS-CoV-2: At the crossroad between aging and neurodegeneration. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortolato, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Soczynska, J.K.; Perini, G.I.; McIntyre, R.S. The involvement of TNF-α in cognitive dysfunction associated with major depressive disorder: An opportunity for domain specific treatments. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramaniyan, S.; Terrando, N. Narrative Review Article: Neuroinflammation and Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 128, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P.-H.; Ho, Y.-S.; Leung, W.K.; Goto, T.; Chang, R.C.-C. Systemic inflammation linking chronic periodontitis to cognitive decline. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R. Neuroimmune interactions: From the brain to the immune system and vice versa. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 477–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyer, E.A.; Kohn, J.N.; Hong, S. Are we facing a crashing wave of neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19? Neuropsychiatric symptoms and potential immunologic mechanisms. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.d.; De Andrade, N.; Liu, C.; Fernandes, B.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.J.; Buckley, P.; Seabolt, W.; Mellor, A.; Kirkpatrick, B. Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: Clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renna, M.E.; O’Toole, M.S.; Spaeth, P.E.; Lekander, M.; Mennin, D.S. The association between anxiety, traumatic stress, and obsessive–compulsive disorders and chronic inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Depress. Anxiety 2018, 35, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletti, S.; Leone, G.; Hoogenboezem, T.A.; Ghiglino, D.; Vai, B.; de Wit, H.; Wijkhuijs, A.J.; Locatelli, C.; Colombo, C.; Drexhage, H.A. Markers of neuroinflammation influence measures of cortical thickness in bipolar depression. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2019, 285, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Aggio, V.; Pratesi, M.L.; Greco, G.; Furlan, R. Neuroinflammation in bipolar depression. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benedetti, F.; Poletti, S.; Hoogenboezem, T.A.; Locatelli, C.; de Wit, H.; Wijkhuijs, A.J.; Colombo, C.; Drexhage, H.A. Higher baseline proinflammatory cytokines mark poor antidepressant response in bipolar disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatr. 2017, 78, e986–e993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, S.; Pearlman, D.M.; Alper, K.; Najjar, A.; Devinsky, O. Neuroinflammation and psychiatric illness. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, K.A.; Thomsen, C. The role of the innate immune system in psychiatric disorders. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 53, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. The role of inflammation in depression: From evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameron, M.J.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Danesh, A.; Muller, M.P.; Kelvin, D.J. Human immunopathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Virus Res. 2008, 133, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, N.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, C. Inflammation-related biomarkers in major psychiatric disorders: A cross-disorder assessment of reproducibility and specificity in 43 meta-analyses. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Fatima, R.; Assaly, R. Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pairo-Castineira, E.; Clohisey, S.; Klaric, L.; Bretherick, A.D.; Rawlik, K.; Pasko, D.; Walker, S.; Parkinson, N.; Fourman, M.H.; Russell, C.D. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in Covid-19. Nature 2021, 591, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Pang, J.; Ji, P.; Zhong, Z.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, J. Elevated interleukin-6 is associated with severity of COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisman, D.E.; Ronner, L.; Pinotti, R.; Taylor, M.D.; Sinha, P.; Calfee, C.S.; Hirayama, A.V.; Mastroiani, F.; Turtle, C.J.; Harhay, M.O. Cytokine elevation in severe and critical COVID-19: A rapid systematic review, meta-analysis, and comparison with other inflammatory syndromes. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohleb, E.S.; Franklin, T.; Iwata, M.; Duman, R.S. Integrating neuroimmune systems in the neurobiology of depression. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, S.; Vai, B.; Mazza, M.G.; Zanardi, R.; Lorenzi, C.; Calesella, F.; Cazzetta, S.; Branchi, I.; Colombo, C.; Furlan, R. A peripheral inflammatory signature discriminates bipolar from unipolar depression: A machine learning approach. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 105, 110136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibney, S.M.; Drexhage, H.A. Evidence for a dysregulated immune system in the etiology of psychiatric disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 900–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, L.; Carvalho, L.A.; Wijkhuijs, A.J.; Bellingrath, S.; Ruland, T.; Ambrée, O.; Alferink, J.; Ehring, T.; Drexhage, H.A.; Arolt, V. Clinical characteristics of inflammation-associated depression: Monocyte gene expression is age-related in major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 44, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, J.A.; Sabadia, S.; Lalchan, R.; Fang, T.; Flusty, B.; Millar-Vernetti, P.; Snyder, T.; Berger, S.; Yang, D.; Granger, A. A prospective study of neurologic disorders in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in New York City. Neurology 2021, 96, e575–e586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, J.A.; Valdes, E.; Huang, J.; Lewis, A.; Lord, A.S.; Zhou, T.; Kahn, D.E.; Melmed, K.; Czeisler, B.M.; Yaghi, S. Prevalence and impact of hyponatremia in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City. Crit. Care Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevets, W.C.; Savitz, J.; Trimble, M. The subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in mood disorders. CNS Spectr. 2008, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, N.A.; Brydon, L.; Walker, C.; Gray, M.A.; Steptoe, A.; Critchley, H.D. Inflammation causes mood changes through alterations in subgenual cingulate activity and mesolimbic connectivity. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howren, M.B.; Lamkin, D.M.; Suls, J. Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: A meta-analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2009, 71, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enache, D.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Markers of central inflammation in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies examining cerebrospinal fluid, positron emission tomography and post-mortem brain tissue. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, H.A.; Air, T.; Pradhan, A.; Johnston, J.; Lavretsky, H.; Stuart, M.J.; Baune, B.T. A meta-analysis of chemokines in major depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Prognostic value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with cervical cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.; Thurairajasingam, S.; Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Exploring the Role and Potential of Probiotics in the Field of Mental Health: Major Depressive Disorder. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.T.; Walsh, R.F.; Sheehan, A.E. Prebiotics and probiotics for depression and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 102, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, F.F.; de Paulo Farias, D. Psychobiotics: An emerging alternative to ensure mental health amid the COVID-19 outbreak? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.P.; Hutch, W.; Borre, Y.E.; Kennedy, P.J.; Temko, A.; Boylan, G.; Murphy, E.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Bifidobacterium longum 1714 as a translational psychobiotic: Modulation of stress, electrophysiology and neurocognition in healthy volunteers. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olaimat, A.N.; Aolymat, I.; Al-Holy, M.; Ayyash, M.; Ghoush, M.A.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Osaili, T.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Liu, S.-Q.; Shah, N.P. The potential application of probiotics and prebiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. npj Sci. Food 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttiker, P.; Weissenberger, S.; Stefano, G.B.; Kream, R.M.; Ptacek, R. SARS-CoV-2, Trait Anxiety, and the Microbiome. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, H.; Harris, J.; Lyon, E.; Beal, J.; Foey, A.D. Probiotics, prebiotics and immunomodulation of gut mucosal defences: Homeostasis and immunopathology. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1869–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, K.; Samson, R.; Dastager, S.; Dharne, M. Probiotics in the prophylaxis of COVID-19: Something is better than nothing. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, L.; Pitkäranta, A.; Korpela, R. Probiotics in respiratory virus infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purton, T.; Staskova, L.; Lane, M.M.; Dawson, S.L.; West, M.; Firth, J.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; Berk, M.; O’Neil, A. Prebiotic and probiotic supplementation and the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway: A systematic review and meta analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, C.L.; Rook, G.W.; Miller, A.H.; Begay, T.K. Role of inflammation in psychiatric disease. In Neurobiology of Brain Disorders; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 396–421. [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki, Y.; Yoshioka, N.; Nozaki, K.; Ito, H.; Oda, K.; Harada, K.; Shirawachi, S.; Asano, S.; Aizawa, H.; Yamawaki, S. Sodium butyrate abolishes lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviors and hippocampal microglial activation in mice. Brain Res. 2018, 1680, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Tóth, M.; Korecka, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Ng, L.G.; Kundu, P. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, ra158–ra263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishida, K.; Sawada, D.; Kuwano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Rokutan, K. Health benefits of Lactobacillus gasseri CP2305 tablets in young adults exposed to chronic stress: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawada, D.; Kuwano, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Hara, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Sugawara, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Rokutan, K.; Nishida, K. Daily intake of Lactobacillus gasseri CP2305 relieves fatigue and stress-related symptoms in male university Ekiden runners: A double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, V.; Thye, A.Y.-K.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Law, J.W.-F.; Johnson, D.; Ser, H.-L.; Bhuvanendran, S.; Thurairajasingam, S.; Lee, L.-H. Gut feelings in depression: Microbiota dysbiosis in response to antidepressants. Gut 2021, A49–A50. [Google Scholar]
- Tabacof, L.; Tosto-Mancuso, J.; Wood, J.; Cortes, M.; Kontorovich, A.; McCarthy, D.; Rizk, D.; Rozanski, G.; Breyman, E.; Nasr, L.; et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome negatively impacts physical function, cognitive function, health-related quality of life and participation. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 101, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottemanne, H.; Gouraud, C.; Hulot, J.S.; Blanchard, A.; Ranque, B.; Lahlou-Laforêt, K.; Limosin, F.; Günther, S.; Lebeaux, D.; Lemogne, C. Do Anxiety and Depression Predict Persistent Physical Symptoms After a Severe COVID-19 Episode? A Prospective Study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 757685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzato, S.; Ghiggia, A.; Ferraro, F.; Galante, E. Cognitive, behavioral, and psychological manifestations of COVID-19 in post-acute rehabilitation setting: Preliminary data of an observational study. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouraud, C.; Bottemanne, H.; Lahlou-Laforêt, K.; Blanchard, A.; Günther, S.; Batti, S.E.; Auclin, E.; Limosin, F.; Hulot, J.S.; Lebeaux, D.; et al. Association Between Psychological Distress, Cognitive Complaints, and Neuropsychological Status After a Severe COVID-19 Episode: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12, 725861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletti, S.; Palladini, M.; Mazza, M.G.; De Lorenzo, R.; Furlan, R.; Ciceri, F.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Benedetti, F.; Covid- Biob Outpatient Clinic, S. Long-term consequences of COVID-19 on cognitive functioning up to 6 months after discharge: Role of depression and impact on quality of life. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesl, F.; Audebert, H.; Endres, M.; Pruss, H.; Franke, C. A Neurological Outpatient Clinic for Patients With Post-COVID-19 Syndrome—A Report on the Clinical Presentations of the First 100 Patients. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, H.; Saffari, M.; Movahedi, M.; Sanaeinasab, H.; Rashidi-Jahan, H.; Pourgholami, M.; Poorebrahim, A.; Barshan, J.; Ghiami, M.; Khoshmanesh, S.; et al. A mediating role for mental health in associations between COVID-19-related self-stigma, PTSD, quality of life, and insomnia among patients recovered from COVID-19. Brain Behav 2021, 11, e02138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thye, A.Y.-K.; Law, J.W.-F.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Pusparajah, P.; Ser, H.-L.; Thurairajasingam, S.; Letchumanan, V.; Lee, L.-H. Psychological Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: Insights into Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Long COVID-19. Biology 2022, 11, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010061
Thye AY-K, Law JW-F, Tan LT-H, Pusparajah P, Ser H-L, Thurairajasingam S, Letchumanan V, Lee L-H. Psychological Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: Insights into Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Long COVID-19. Biology. 2022; 11(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleThye, Angel Yun-Kuan, Jodi Woan-Fei Law, Loh Teng-Hern Tan, Priyia Pusparajah, Hooi-Leng Ser, Sivakumar Thurairajasingam, Vengadesh Letchumanan, and Learn-Han Lee. 2022. "Psychological Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: Insights into Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Long COVID-19" Biology 11, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010061
APA StyleThye, A. Y.-K., Law, J. W.-F., Tan, L. T.-H., Pusparajah, P., Ser, H.-L., Thurairajasingam, S., Letchumanan, V., & Lee, L.-H. (2022). Psychological Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: Insights into Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Long COVID-19. Biology, 11(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010061







