Qualitative and Quantitative Resistance against Early Blight Introgressed in Potato
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Generation of Populations
2.3. Ploidy Determination
2.4. Production of Inoculum from A. solani
2.5. Early Blight Testing
3. Results
3.1. Genotypes with Promising Levels of Resistance to Early Blight Are Identified in Wild Solanum Germplasm
3.2. Resistant Wild Solanum Genotypes Can Be Crossed to Susceptible S. tuberosum
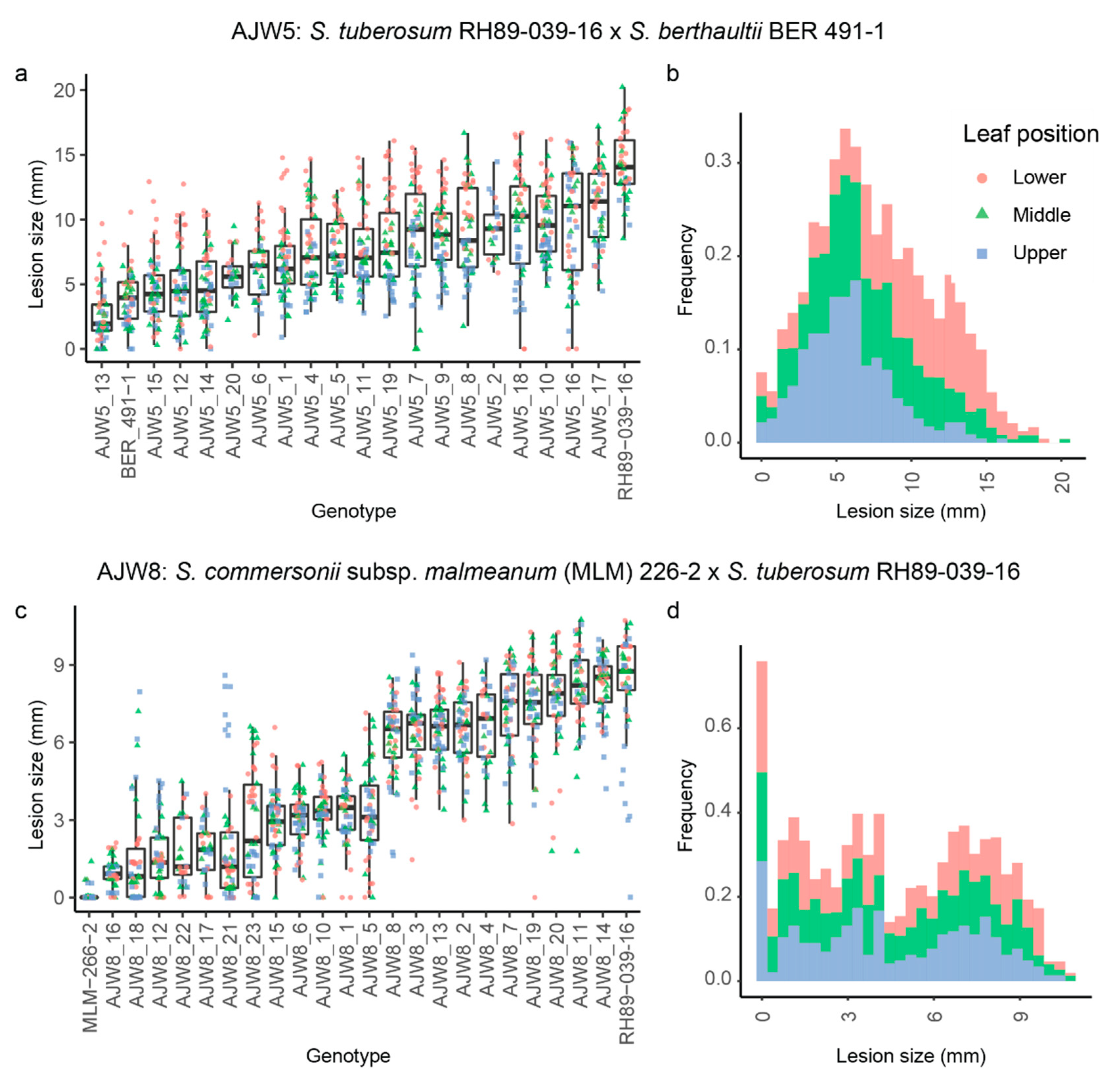
3.3. Progeny from MLM 266-2 ×RH89-039-16 Is Triploid
3.4. Resistance to A. solani Is Inherited in Two Distinct Modes in Progeny of Wild Solanum × S. tuberosum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christ, B.; Maczuga, S. The effect of fungicide schedules and inoculum levels on early blight severity and yield of potato. Plant Dis. 1989, 73, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotem, J. The Genus Alternaria: Biology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shtienberg, D.; Bergeron, S.; Nicholson, A.; Fry, W.; Ewing, E. Development and evaluation of a general model for yield loss assessment in potatoes. Phytopathology 1990, 80, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, J.; Hall, R.; Hofstra, G. Effects of cultivar resistance, leaf wetness duration and temperature on rate of development of potato early blight. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1985, 65, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussey, M.; Stevenson, W. A leaf disk assay for detecting resistance to early blight caused by Alternaria solani in juvenile potato plants. Plant Dis. 1991, 75, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, H.S.; Zambolim, L.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Paul, P.A.; Pádua, J.G.; Ribeiro Júnior, J.I.; Júnior, N.; Antonio, F.; Rosado, A.W. Field resistance of potato cultivars to foliar early blight and its relationship with foliage maturity and tuber skin types. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2014, 39, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, B. Effect of disease assessment method on ranking potato cultivars for resistance to early blight. Plant Dis. 1991, 75, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuley, I.K.; Nielsen, B.J. Evaluation of models to control potato early blight (Alternaria solani) in Denmark. Crop. Prot. 2017, 102, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, K.L.; Miles, T.D.; Wharton, P.S. Assessing fungicide resistance in populations of Alternaria in Idaho potato fields. Crop. Prot. 2013, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landschoot, S.; Carrette, J.; Vandecasteele, M.; De Baets, B.; Höfte, M.; Audenaert, K.; Haesaert, G. Boscalid-resistance in Alternaria alternata and Alternaria solani populations: An emerging problem in Europe. Crop. Prot. 2017, 92, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardigan, M.A.; Laimbeer, F.P.E.; Newton, L.; Crisovan, E.; Hamilton, J.P.; Vaillancourt, B.; Wiegert-Rininger, K.; Wood, J.C.; Douches, D.S.; Farré, E.M.; et al. Genome diversity of tuber-bearing Solanum uncovers complex evolutionary history and targets of domestication in the cultivated potato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9999–E10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, M.; Spooner, D.M. DNA from herbarium specimens settles a controversy about origins of the European potato. Am. J. Bot. 2008, 95, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M.; Ghislain, M.; Simon, R.; Jansky, S.H.; Gavrilenko, T. Systematics, diversity, genetics, and evolution of wild and cultivated potatoes. Bot. Rev. 2014, 80, 283–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleeshouwers, V.G.; Finkers, R.; Budding, D.; Visser, M.; Jacobs, M.M.; van Berloo, R.; Pel, M.; Champouret, N.; Bakker, E.; Krenek, P.; et al. SolRgene: An online database to explore disease resistance genes in tuber-bearing Solanum species. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodewald, J.; Trognitz, B. Solanum resistance genes against Phytophthora infestans and their corresponding avirulence genes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, P.J.; de Vos, L.; Bijsterbosch, G.; Woudenberg, J.H.; Visser, R.G.; van der Linden, G.; Vleeshouwers, V.G. A rapid method to screen wild Solanum for resistance to early blight. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 154, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansky, S.; Simon, R.; Spooner, D. A test of taxonomic predictivity: Resistance to early blight in wild relatives of cultivated potato. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Jansky, S. Resistance to Alternaria solani in hybrids between a Solanum tuberosum haploid and S. raphanifolium. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, K.G.; Qu, X. Late blight and early blight resistance from Solanum hougasii introgressed into Solanum tuberosum. Am. J. Potato Res. 2016, 93, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, A.; Jansky, S.; Halterman, D. Germplasm release: Three potato clones incorporating combined resistances to early blight from S. palustre and late blight from S. bulbocastanum into a S. tuberosum background. Am. J. Potato Res. 2015, 92, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanneman, R.E. Assignment of Endosperm Balance Numbers to the tuber-bearing Solanums and their close non-tuber-bearing relatives. Euphytica 1993, 74, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, M.; Peloquin, S. Origin and evolution of cultivated tetraploid potatoes via 2n gametes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1982, 61, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carputo, D.; Barone, A. Ploidy level manipulations in potato through sexual hybridisation. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2005, 146, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiero, P.; Mazzella, C.; Vilaró, F.; Speranza, P.; de Jong, H. Pairing analysis and in situ hybridisation reveal autopolyploid-like behaviour in Solanum commersonii × S. tuberosum (potato) interspecific hybrids. Euphytica 2017, 213, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansky, S.H.; Charkowski, A.O.; Douches, D.S.; Gusmini, G.; Richael, C.; Bethke, P.C.; Spooner, D.M.; Novy, R.G.; De Jong, H.; De Jong, W.S.; et al. Reinventing potato as a diploid inbred line–based crop. Crop. Sci. 2016, 56, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhout, P.; Meijer, D.; Schotte, T.; Hutten, R.C.; Visser, R.G.; van Eck, H.J. Towards F 1 hybrid seed potato breeding. Potato Res. 2011, 54, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, B.J.; Haynes, K. Inheritance of resistance to early blight disease in a diploid potato population. Plant Breed. 2001, 120, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odilbekov, F.; Selga, C.; Ortiz, R.; Chawade, A.; Liljeroth, E. QTL mapping for resistance to early blight in a tetraploid potato population. Agronomy 2020, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuley, I.K.; Nielsen, B.J.; Labouriau, R. Resistance status of cultivated potatoes to early blight (Alternaria solani) in Denmark. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beever, R.E.; Bollard, E.G. The nature of the stimulation of fungal growth by potato extract. Microbiology 1970, 60, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuredo, O.; Seijo, M.C.; Fernández-González, M.; Iglesias, I. Effects of meteorological factors on the levels of Alternaria spores on a potato crop. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2011, 55, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; v4.02; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; v1.2.5033; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Olsder, J.; Hermsen, J.T. Genetics of self-compatibility in dihaploids of Solanum tuberosum L. I. breeding behaviour of two self-compatible dihaploids. Euphytica 1976, 25, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, B.; Mu, D.; Ni, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.P.; Ipcho, S.V. Arabidopsis pathology breathes new life into the necrotrophs-vs.-biotrophs classification of fungal pathogens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2004, 5, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denby, K.J.; Kumar, P.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Identification of Botrytis cinerea susceptibility loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2004, 38, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazebrook, J. Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorang, J.M.; Sweat, T.A.; Wolpert, T.J. Plant disease susceptibility conferred by a “resistance” gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14861–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, E.D.; Bennetzen, J.L. Pathogen corruption and site-directed recombination at a plant disease resistance gene cluster. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faris, J.D.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.; Lu, S.; Reddy, L.; Cloutier, S.; Fellers, J.P.; Meinhardt, S.W.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Xu, S.S.; et al. A unique wheat disease resistance-like gene governs effector-triggered susceptibility to necrotrophic pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13544–13549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, T.L.; Meinhardt, S.W.; Faris, J.D. The Stagonospora nodorum-wheat pathosystem involves multiple proteinaceous host-selective toxins and corresponding host sensitivity genes that interact in an inverse gene-for-gene manner. Plant J. 2007, 51, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.-C.; Oliver, R.P.; Solomon, P.S.; Moffat, C.S. Proteinaceous necrotrophic effectors in fungal virulence. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.; Kaliff, M.; Dewaele, E.; Persson, M.; Dixelius, C. RLM3, a TIR domain encoding gene involved in broad-range immunity of Arabidopsis to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J. 2008, 55, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.; Li, C.; Park, H.-J.; González, J.; Wang, J.; Dandekar, A.M.; Turgeon, B.G.; Cheng, L. Sorbitol modulates resistance to Alternaria alternata by regulating the expression of an NLR resistance gene in apple. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1562–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M.; Fajardo, D.; Bryan, G.J. Species limits of Solanum berthaultii Hawkes and S. tarijense Hawkes and the implications for species boundaries in Solanum sect. Petota. Taxon 2007, 56, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, Z. Screening of Solanum species against Alternaria solani. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 1985, 6, 180–182. [Google Scholar]
- Colon, L.; Jansen, R.; Budding, D. Partial resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) in hybrid progenies of four South American Solanum species crossed with diploid S. tuberosum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1995, 90, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, R. Genetic characterization and mapping of partial resistance to early blight in diploid potato. Ph.D Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hutten, R.C.B.; Schippers, M.G.M.; Hermsen, J.G.T.; Ramanna, M.S. Comparative performance of FDR and SDR progenies from reciprocal 4×-2× crosses in potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1994, 89, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.-H.; Kim, J.-B.; Hutten, R.C.; van Eck, H.J.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G. Genetic positioning of centromeres using half-tetrad analysis in a 4 ×–2 × cross population of potato. Genetics 2007, 176, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversano, R.; Contaldi, F.; Ercolano, M.R.; Grosso, V.; Iorizzo, M.; Tatino, F.; Xumerle, L.; Dal Molin, A.; Avanzato, C.; Ferrarini, A.; et al. The Solanum commersonii Genome Sequence Provides Insights into Adaptation to Stress Conditions and Genome Evolution of Wild Potato Relatives. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 954–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carputo, D.; Barone, A.; Cardi, T.; Sebastiano, A.; Frusciante, L.; Peloquin, S.J. Endosperm balance number manipulation for direct in vivo germplasm introgression to potato from a sexually isolated relative (Solanum commersonii Dun.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12013–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carputo, D.; Garreffa, P.; Mazzei, M.; Monti, L.; Cardi, T. Fertility of somatic hybrids Solanum commersonii (2×, 1EBN) (+) S. tuberosum haploid (2×, 2EBN) in intra- and inter-EBN crosses. Genome 1998, 41, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupe, F.; Witek, K.; Verweij, W.; Śliwka, J.; Pritchard, L.; Etherington, G.J.; Maclean, D.; Cock, P.J.; Leggett, R.M.; Bryan, G.J. Resistance gene enrichment sequencing (RenSeq) enables reannotation of the NB-LRR gene family from sequenced plant genomes and rapid mapping of resistance loci in segregating populations. Plant J. 2013, 76, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Armstrong, M.; Baker, K.; Wouters, D.; Visser, R.G.; Wolters, P.J.; Hein, I.; Vleeshouwers, V.G. RLP/K enrichment sequencing; a novel method to identify receptor-like protein (RLP) and receptor-like kinase (RLK) genes. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
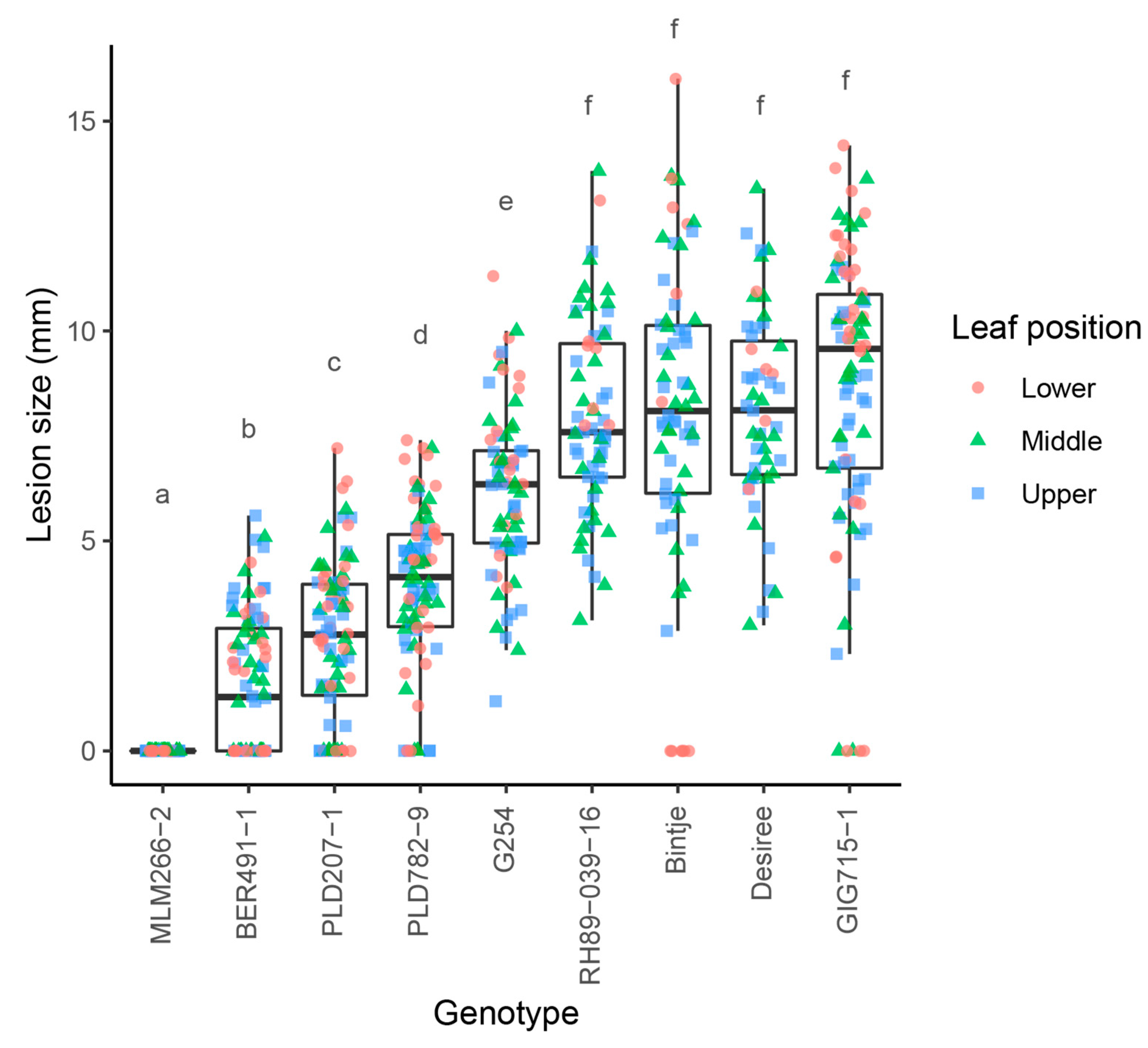

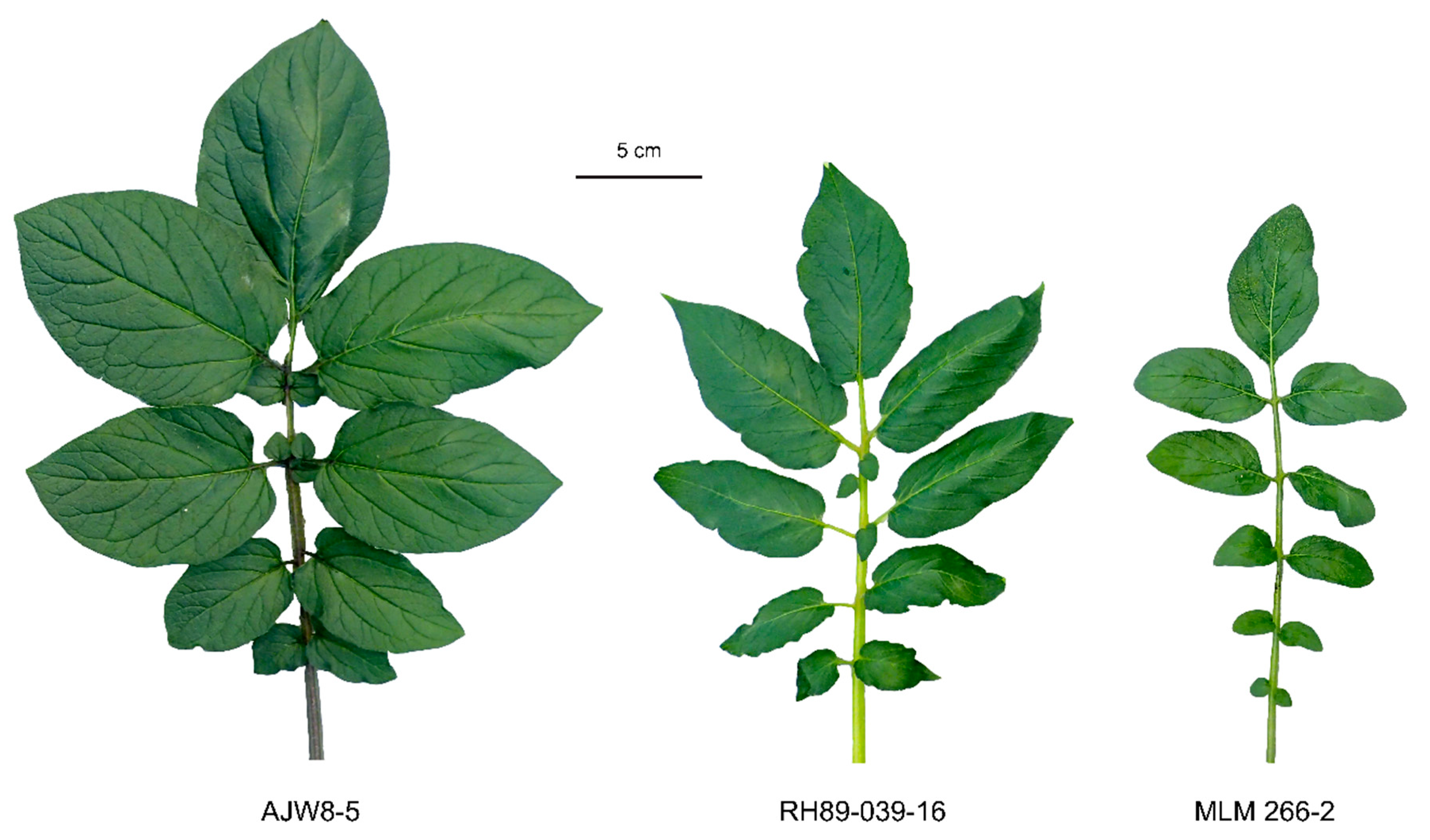
| Scheme | Genotype | Ploidy | EBN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solanum commersonii subsp. malmeanum (MLM) | 266-2 | 2× | 1 EBN |
| Solanum berthaultii (BER) | 491-1 | 2× | 2 EBN |
| Solanum polyadenium (PLD) | 207-1 | 2× | 2 EBN |
| Solanum polyadenium (PLD) | 782-9 | 2× | 2 EBN |
| Solanum tuberosum | G254 a | 2× | 2 EBN |
| Solanum tuberosum | RH89-039-16 b | 2× | 2 EBN |
| Solanum tuberosum | Bintje | 4× | 4 EBN |
| Solanum tuberosum | Désirée | 4× | 4 EBN |
| Solanum microdontum subsp. gigantophyllum (GIG) | 715-1 | 2× | 2 EBN |
| Cross | Mother | × | Father | Berries | Seeds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AJW5 | RH89-039-16 (2 EBN) | × | BER 491-1 (2 EBN) | 11 | ~400 |
| AJW6 | G254 (2 EBN) | × | BER 491-1 (2 EBN) | 18 | ~1000 |
| AJW8 | MLM 266-2 (1 EBN) | × | RH89-039-16 (2 EBN) | 166 | 59 |
| AJW9 | MLM 266-2 (1 EBN) | × | G254 (2 EBN) | 20 | 0 |
| Genotype | Ploidy |
|---|---|
| AJW8-1 | 3× |
| AJW8-2 | 3× |
| AJW8-3 | 3× |
| AJW8-4 | 3× |
| AJW8-5 | 3× |
| AJW8-6 | 3× |
| AJW8-7 | 3× |
| AJW8-8 | 3× |
| AJW8-10 | 3× |
| AJW8-11 | 4× |
| AJW8-12 | 3× |
| AJW8-13 | 3× |
| AJW8-14 | 3× |
| AJW8-15 | 3× |
| AJW8-16 | 3× |
| AJW8-17 | 3× |
| AJW8-18 | 3× |
| AJW8-20 | 3× |
| AJW8-21 | 3× |
| AJW8-22 | 3× |
| MLM 266-2 | 2× |
| RH89-039-16 | 2× |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolters, P.J.; Wouters, D.; Kromhout, E.J.; Huigen, D.J.; Visser, R.G.F.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A. Qualitative and Quantitative Resistance against Early Blight Introgressed in Potato. Biology 2021, 10, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090892
Wolters PJ, Wouters D, Kromhout EJ, Huigen DJ, Visser RGF, Vleeshouwers VGAA. Qualitative and Quantitative Resistance against Early Blight Introgressed in Potato. Biology. 2021; 10(9):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090892
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolters, Pieter J., Doret Wouters, Emil J. Kromhout, Dirk Jan Huigen, Richard G. F. Visser, and Vivianne G. A. A. Vleeshouwers. 2021. "Qualitative and Quantitative Resistance against Early Blight Introgressed in Potato" Biology 10, no. 9: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090892
APA StyleWolters, P. J., Wouters, D., Kromhout, E. J., Huigen, D. J., Visser, R. G. F., & Vleeshouwers, V. G. A. A. (2021). Qualitative and Quantitative Resistance against Early Blight Introgressed in Potato. Biology, 10(9), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090892







