Repetitive Sequence Distribution on Saguinus, Leontocebus and Leontopithecus Tamarins (Platyrrhine, Primates) by Mapping Telomeric (TTAGGG) Motifs and rDNA Loci
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Material
2.2. Karyotype Analysis
2.3. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridisation (FISH) and C-Banding
2.4. Microscopic Analysis and Imaging Processing
3. Results
3.1. Karyotype Analysis
3.2. C-Banding and CMA3 Staining
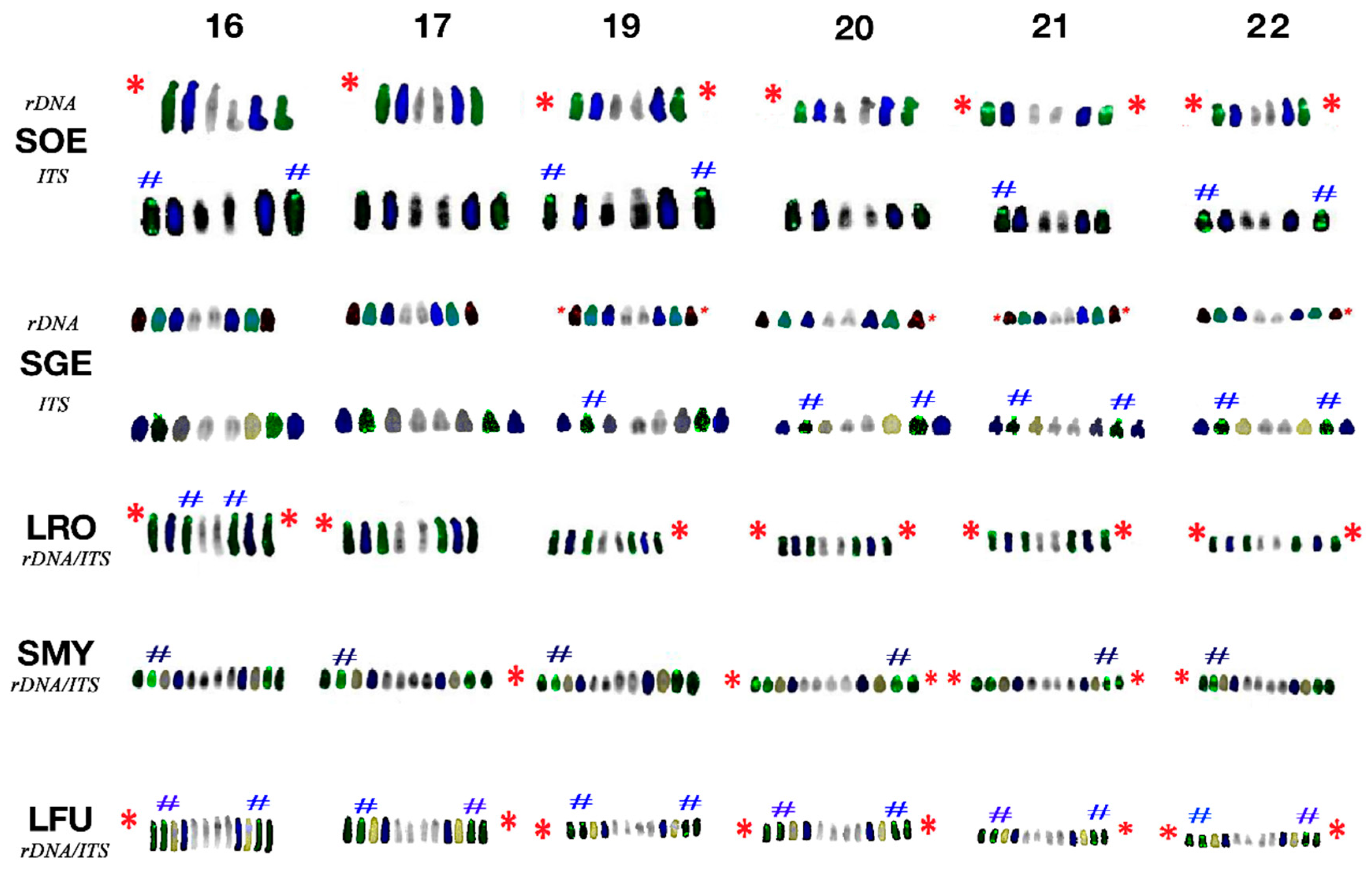
3.3. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridisation with an rDNA Probe
3.4. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridisation with (TTAGGG)n Probe
4. Discussion
4.1. Karyotypic Variability in 2n = 46 Tamarins
4.2. C-Banding Pattern Variation on Smaller Autosomes
4.3. Topology of rDNA Loci
4.4. Telomere Distribution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Statement of Ethics
References
- Garbino, G.S.; Martins-Junior, A.M. Phenotypic evolution in marmoset and tamarin monkeys (Cebidae, Callitrichinae) and a revised genus-level classification. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 118, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Ortiz, L. Molecular phylogenetics of the Callitrichidae with an emphasis on the marmosets and Callimico. In The Smallest Anthropoids; Ford, S.M., Porter, L.M., Davis, L.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Matauschek, C.; Roos, C.; Heymann, E.W. Mitochondrial phylogeny of tamarins (Saguinus Hoffmannsegg, 1807) with taxonomic and biogeographic implications for the S. nigricollis species group. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2011, 144, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelman, P.; Johnson, W.E.; Roos, C.; Seuanez, H.N.; Horvath, J.E.; Moreira, M.A.M.; Kessing, B.; Pontius, J.; Roelke, M.; Rumpler, Y.; et al. A molecular phylogeny of living primates. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, J.C.; Lynch Alfaro, J.W.; Rylands, A.B.; Alfaro, M.E. Biogeography of the marmosets and tamarins (Callitrichidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 82, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benirschke, K.; Brownhill, L.E. Further observations on marrow chimerism in marmosets. Cytogenetics 1962, 1, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, M.T.; Ma, N.S.F.; Jones, T.C. Chromosome banding patterns and nucleolar organizing regions in three species of Callitrichidae (Saguinus oedipus, Saguinus fuscicollis and Callithrix jacchus). J. Med. Primatol. 1978, 7, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutrillaux, B.; Couturier, J.; Viegas-Pequignot, E. Evolution chromosomique des platyrrhiniens. Mammalia 1986, 50, 57–81. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, S.M.M.d.M.; de Souza Barros, R.M. Cytogenetic study of the genus Saguinus (Callithrichidae, Primates). Braz. J. Genet. 1997, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C. Chromosome studies of Saguinus midas niger (Callitrichidae, Primates) from Tucurui, Para, Brazil: Comparison with the karyotype of Callithrix jacchus. Am. J. Primatol. 1988, 14, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamachi, C.; Pieczarka, J.; Schwarz, M.; Barros, R.; Mattevi, M. Chromosomal similarities and differences between tamarins, Leontopithecus and Saguinus (Platyrrhini, Primates). Am. J. Primatol. 1997, 43, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C.; Muniz, J.A.; Barros, R.M.; Mattevi, M.S. Proposed chromosomal phylogeny for the South American primates of the Callitrichidae family (Platyrrhini). Am. J. Primatol. 1999, 49, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neusser, M.; Stanyon, R.; Bigoni, F.; Wienberg, J.; Muller, S. Molecular cytotaxonomy of New World monkeys (Platyrrhini)—Comparative analysis of five species by multi-color chromosome painting gives evidence for a classification of Callimico goeldii within the family of Callitrichidae. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2001, 94, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbault-Serreau, M.; Bonnet-Garnier, A.; Richard, F.; Dutrillaux, B. Chromosome painting comparison of Leontopithecus chrysomelas (Callitrichine, Platyrrhini) with man and its phylogenetic position. Chromosome Res. 2004, 12, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanyon, R.; Giusti, D.; Araújo, N.P.; Bigoni, F.; Svartman, M. Chromosome painting of the red-handed tamarin (Saguinus midas) compared to other Callitrichinae monkeys. Genome 2018, 61, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, F.; Sineo, L.; Ishida, T. Taxonomic identification of Aotus (Platyrrhinae) through cytogenetics. Identificazione tassonomica di Aotus (Platyrrhinae) mediante la citogenetica. J. Biol. Res. 2015, 88, 65–66. [Google Scholar]
- Scardino, R.; Milioto, V.; Proskuryakova, A.A.; Serdyukova, N.A.; Perelman, P.L.; Dumas, F. Evolution of the human chromosome 13 synteny: Evolutionary rearrangements, plasticity, human disease genes and cancer breakpoints. Genes 2020, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Singchat, W.; Jehangir, M.; Suntronpong, A.; Panthum, T.; Malaivijitnond, S.; Srikulnath, K. Dark matter of primate genomes: Satellite DNA repeats and their evolutionary dynamics. Cells 2020, 9, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, F.; Cuttaia, H.; Sineo, L. Chromosomal distribution of interstitial telomeric sequences in nine neotropical primates (Platyrrhini): Possible implications in evolution and phylogeny. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2016, 54, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, S.; Schillaci, O.; Sineo, L.; Dumas, F. Distribution of interstitial telomeric sequences in primates and the pygmy tree shrew (Scandentia). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 151, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoleni, S.; Rovatsos, M.; Schillaci, O.; Dumas, F. Evolutionary insight on localization of 18S, 28S rDNA genes on homologous chromosomes in Primates genomes. Comp. Cytogenet. 2018, 12, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milioto, V.; Vlah, S.; Mazzoleni, S.; Rovatsos, M.; Dumas, F. Chromosomal localization of 18S–28S rDNA and (TTAGGG)n sequences in two south african dormice of the genus Graphiurus (Rodentia: Gliridae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2019, 158, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Herrera, A.; Nergadze, S.G.; Santagostino, M.; Giulotto, E. Telomeric repeats far from the ends: Mechanisms of origin and role in evolution. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 122, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swier, V.J.; Anwarali Khan, F.A.; Baker, R.J. Do time, heterochromatin, NORs, or chromosomal rearrangements correlate with distribution of interstitial telomeric repeats in Sigmodon (cotton rats)? J. Hered. 2012, 103, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, F.; Mazzoleni, S. Neotropical primate evolution and phylogenetic reconstruction using chromosomal data. Eur. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scardino, R.; Mazzoleni, S.; Rovatsos, M.; Vecchioni, L.; Dumas, F. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of the Sicilian endemic pond turtle Emys trinacris and the yellow-bellied slider Trachemys scripta scripta (Testudines, Emydidae). Genes 2020, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baicharoen, S.; Hirai, Y.; Srikulnath, K.; Kongprom, U.; Hirai, H. Hypervariability of nucleolus organizer regions in Bengal slow lorises, Nycticebus bengalensis (Primates, Lorisidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 149, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H. Chromosome dynamics regulating genomic dispersion and alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs). Cells 2020, 9, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfaty, D.M.B.; Carvalho, N.D.M.; Gross, M.C.; Gordo, M.; Schneider, C.H. Differential chromosomal organization between Saguinus midas and Saguinus bicolor with accumulation of differences in the repetitive sequence DNA. Genetica 2017, 145, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyne, J.; Baker, R.J.; Hobart, H.H.; Hsu, T.C.; Ryder, O.A.; Ward, O.G.; Moyzis, R.K. Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma 1990, 99, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Altmanová, M.; Johnson Pokorná, M. Interstitial telomeric motifs in squamate reptiles: When the exceptions outnumber the rule. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, M.F.; Stanyon, R.; Smith, D.G.; Sineo, L. High-resolution chromosomes of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Am. J. Primatol. 1985, 9, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levan, A.; Fredga, K.; Sandberg, A.A. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 1964, 52, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemskaya, N.A.; Kulemzina, A.I.; Beklemisheva, V.R.; Biltueva, L.S.; Proskuryakova, A.A.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Perelman, P.L.; Graphodatsky, A.S. A combined banding method that allows the reliable identification of chromosomes as well as differentiation of AT-and GC-rich heterochromatin. Chromosome Res. 2018, 26, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, F.; Sineo, L. The evolution of human synteny 4 by mapping sub-chromosomal specific probes in Primates. Caryologia 2014, 67, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernàndez, R.; Barragàn, M.; Bullejos, M.; Marchal, J.; Diaz de la Guardia, R.; Sanchez, A. New C-band protocol by heat denaturation in the presence of formamide. Hereditas 2002, 137, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


| Family | Latin Name | Sex ♂/♀ | Cell Type | Acknowledgements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cebidae | Saguinus Oedipus SOE | ♀ | fibroblast cell line | Melody Roelke (Frederick National Laboratory of Cancer Research, Leidos Biomedical Research, Frederick, MD, USA), June Bellizzi and Director Richard Hann (Catoctin Wildlife Park and Zoo, Thumont, MD, USA) |
| S. geoffroyi SGE | ♂ | |||
| S. mystax SMY | ♂/♀ | |||
| Leontocebus fuscicollis LFU | ♂/♀ | |||
| Leontopithecus rosalia LRO | ♂/♀ | Dr. Stephen O’Brien, Mary Tompson (Laboratory of Genomic Diversity, National Cancer Institute, Frederick MD, USA), Dr. Mitchell Bush; National Zoological Park, Washington, DC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceraulo, S.; Perelman, P.L.; Mazzoleni, S.; Rovatsos, M.; Dumas, F. Repetitive Sequence Distribution on Saguinus, Leontocebus and Leontopithecus Tamarins (Platyrrhine, Primates) by Mapping Telomeric (TTAGGG) Motifs and rDNA Loci. Biology 2021, 10, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090844
Ceraulo S, Perelman PL, Mazzoleni S, Rovatsos M, Dumas F. Repetitive Sequence Distribution on Saguinus, Leontocebus and Leontopithecus Tamarins (Platyrrhine, Primates) by Mapping Telomeric (TTAGGG) Motifs and rDNA Loci. Biology. 2021; 10(9):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090844
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeraulo, Simona, Polina L. Perelman, Sofia Mazzoleni, Michail Rovatsos, and Francesca Dumas. 2021. "Repetitive Sequence Distribution on Saguinus, Leontocebus and Leontopithecus Tamarins (Platyrrhine, Primates) by Mapping Telomeric (TTAGGG) Motifs and rDNA Loci" Biology 10, no. 9: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090844
APA StyleCeraulo, S., Perelman, P. L., Mazzoleni, S., Rovatsos, M., & Dumas, F. (2021). Repetitive Sequence Distribution on Saguinus, Leontocebus and Leontopithecus Tamarins (Platyrrhine, Primates) by Mapping Telomeric (TTAGGG) Motifs and rDNA Loci. Biology, 10(9), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090844







