Clinical and Biological Characteristics of Medullary and Extramedullary Plasma Cell Dyscrasias
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
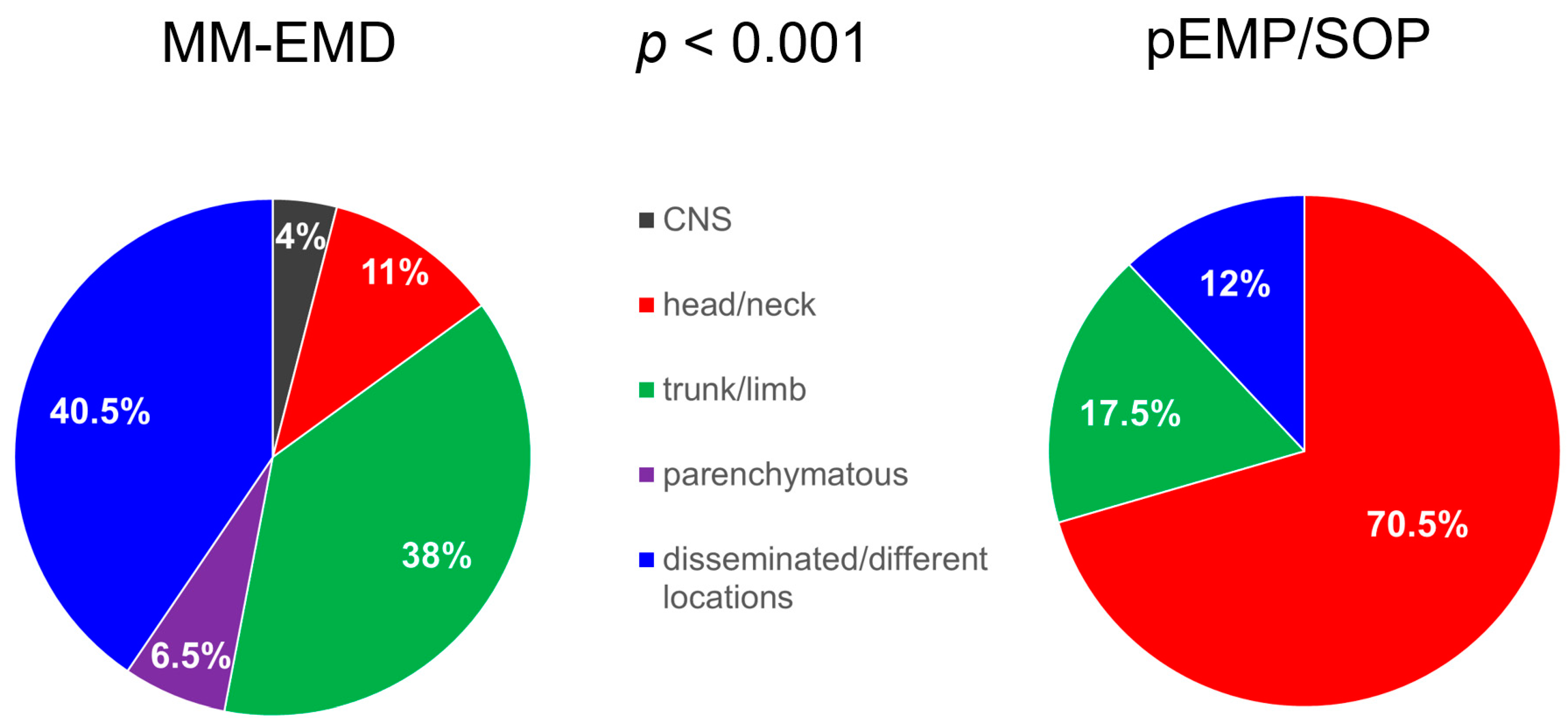
2.1. Patients
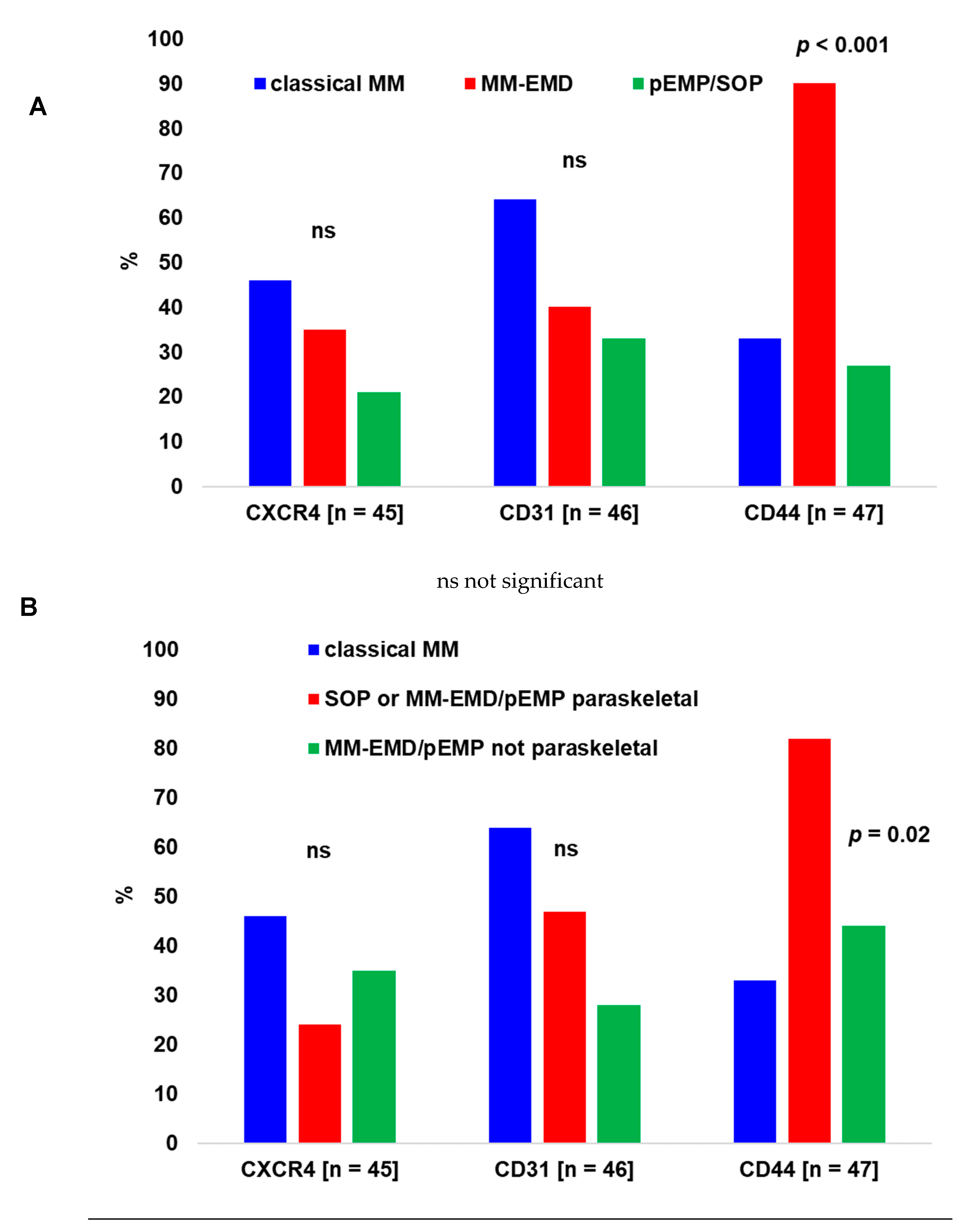
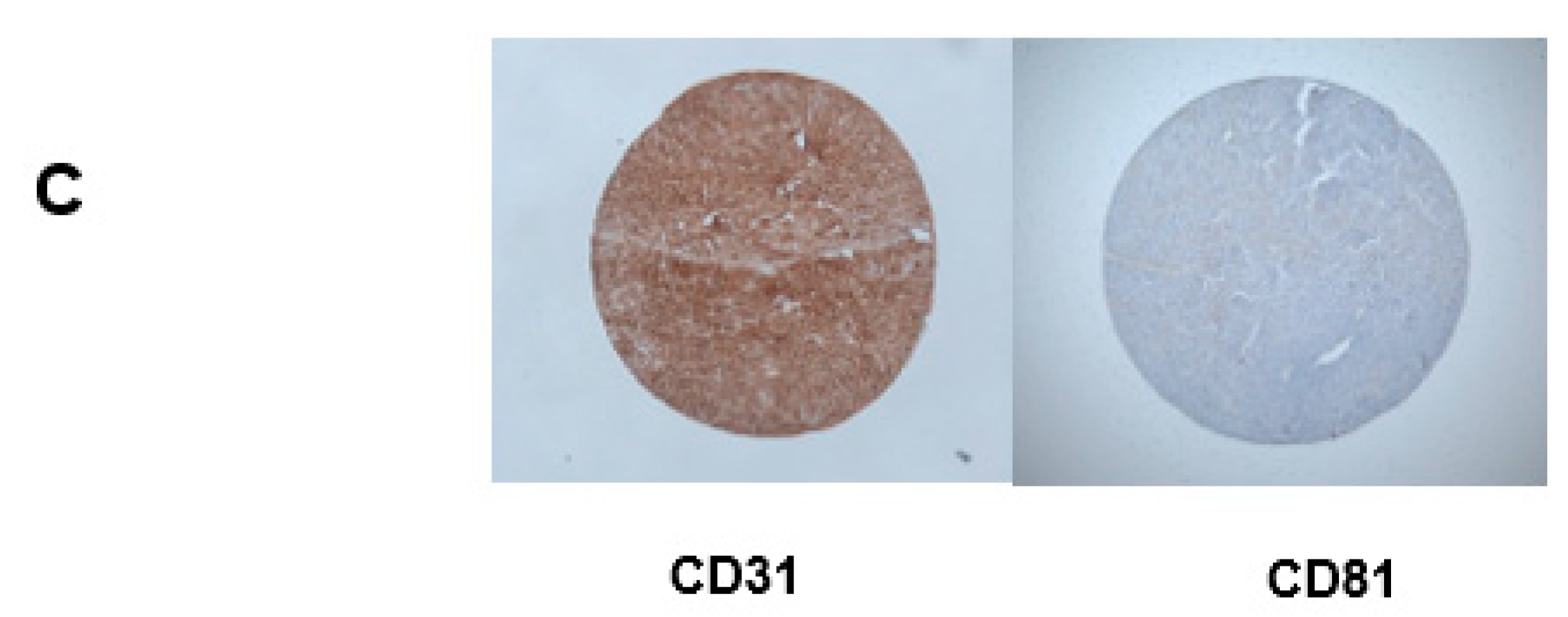
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
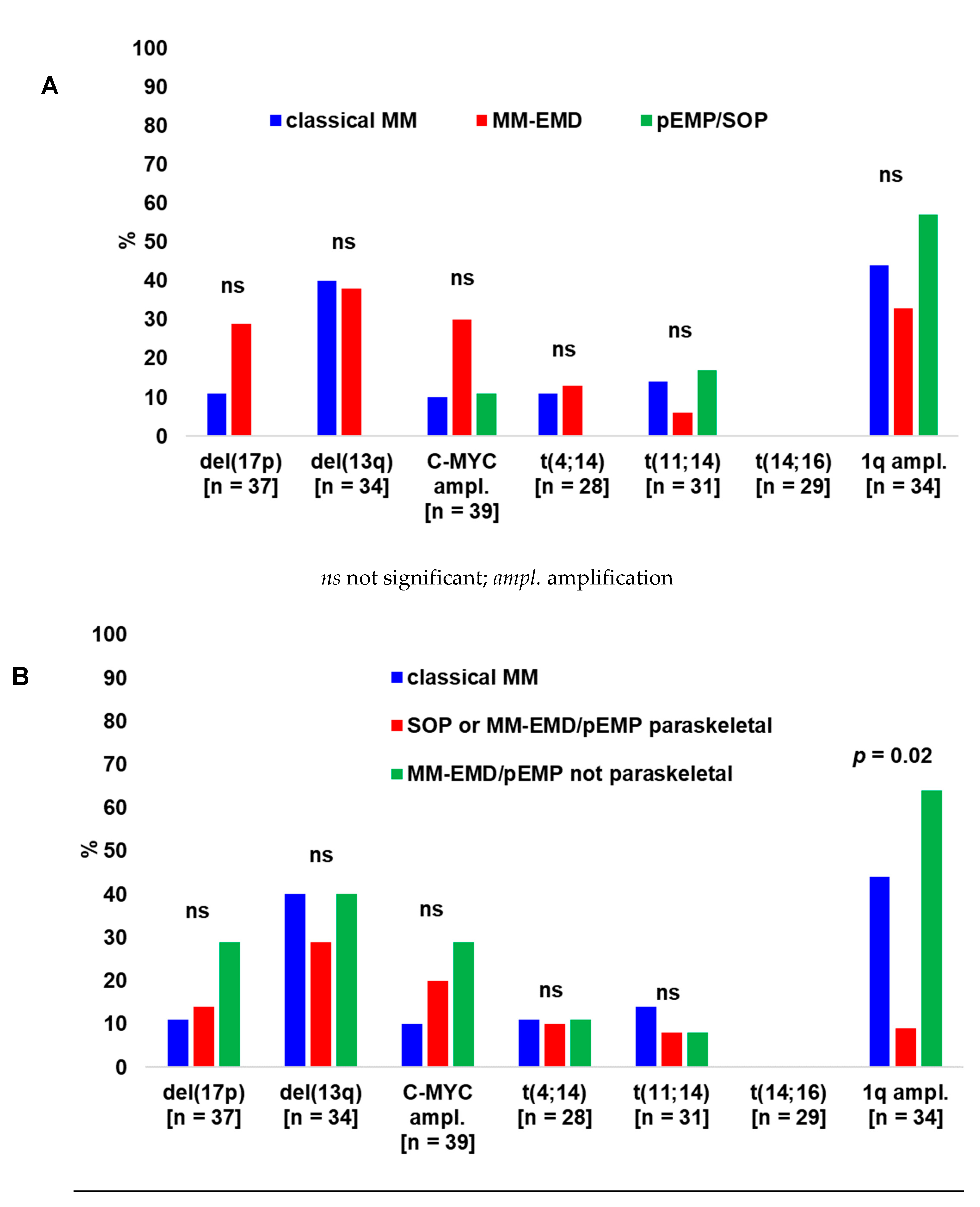
2.3. Cytogenetics
2.4. Treatment and Outcome
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Definitions and Statistics
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Cytogenetics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bladé, J.; Fernández de Larrea, C.; Rosiñol, L.; Cibeira, M.T.; Jiménez, R.; Powles, R. Soft-tissue plasmacytomas in multiple myeloma: Incidence, mechanisms of extramedullary spread, and treatment approach. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3805–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caers, J.; Paiva, B.; Zamagni, E.; Leleu, X.; Bladé, J.; Kristinsson, S.Y.; Touzeau, C.; Abildgaard, N.; Terpos, E.; Heusschen, R.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and response assessment in solitary plasmacytoma: Updated recommendations from a European Expert Panel. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varettoni, M.; Corso, A.; Pica, G.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Pascutto, C.; Lazzarino, M. Incidence, presenting features and outcome of extramedullary disease in multiple myeloma: A longitudinal study on 1003 consecutive patients. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Heuck, C.; Mitchell, A.; Szymonifka, J.; Nair, B.; Hoering, A.; Alsayed, Y.; Waheed, S.; Haider, S.; Restrepo, A.; et al. Extramedullary disease portends poor prognosis in multiple myeloma and is over-represented in high-risk disease even in the era of novel agents. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pour, L.; Sevcikova, S.; Greslikova, H.; Kupska, R.; Majkova, P.; Zahradova, L.; Sandecka, V.; Adam, Z.; Krejci, M.; Kuglik, P.; et al. Soft-tissue extramedullary multiple myeloma prognosis is significantly worse in comparison to bone-related extramedullary relapse. Haematologica 2014, 99, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vande Broek, I.; Vanderkerken, K.; van Camp, B.; van Riet, I. Extravasation and homing mechanisms in multiple myeloma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, J.; O’steen, L.; Morris, C.G.; Kirwan, J.M.; Mendenhall, W.M. Long-term Outcomes After Definitive Radiation Therapy for Solitary Plasmacytoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Mishima, Y.; Sacco, A.; Moschetta, M.; Tai, Y.-T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Reagan, M.R.; Huynh, D.; Kawano, Y.; et al. CXCR4 Regulates Extra-Medullary Myeloma through Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition-like Transcriptional Activation. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahl, I.M.S.; Rasmussen, T.; Kauric, G.; Husebekk, A. Differential expression of CD56 and CD44 in the evolution of extramedullary myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 116, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, M.; Aljawai, Y.; Morgan, E.A.; Gannon, M.; Laubach, J.; Roccaro, A.M.; Varga, C.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Paba-Prada, C.; Schlossman, R.; et al. Incidence and clinical features of extramedullary multiple myeloma in patients who underwent stem cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Govender, D.; Harilal, P.; Dada, M.; Chetty, R. CD31 (JC70) expression in plasma cells: An immunohistochemical analysis of reactive and neoplastic plasma cells. J. Clin. Pathol. 1997, 50, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plocharczyk, E.; Wakely, P.E. CD31 expression in plasmacytic/plasmablastic lesions. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 17, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, B.; Gutiérrez, N.-C.; Chen, X.; Vídriales, M.-B.; Montalbán, M.-Á.; Rosiñol, L.; Oriol, A.; Martínez-López, J.; Mateos, M.-V.; López-Corral, L.; et al. Clinical significance of CD81 expression by clonal plasma cells in high-risk smoldering and symptomatic multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Expression of CD81 and CD117 in plasma cell myeloma and the relationship to prognosis. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5920–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tohami, T.; Drucker, L.; Shapiro, H.; Radnay, J.; Lishner, M. Overexpression of tetraspanins affects multiple myeloma cell survival and invasive potential. FASEB J. 2007, 3, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.F.; Zhao, S.; Tibshirani, R.; Luo, R.F.; Zhao, S.; Tibshirani, R.; Myklebust, J.H.; Sanyal, M.; Fernandez, R.; Gratzinger, D.; et al. CD81 protein is expressed at high levels in normal germinal center B cells and in subtypes of human lymphomas. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasche, L.; Bernard, C.; Topp, M.S.; Kapp, M.; Duell, J.; Wesemeier, C.; Haralambieva, E.; Maeder, U.; Einsele, H.; Knop, S. Features of extramedullary myeloma relapse: High proliferation, minimal marrow involvement, adverse cytogenetics: A retrospective single-center study of 24 cases. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billecke, L.; Murga Penas, E.M.; May, A.M.; Engelhardt, M.; Nagler, A.; Leiba, M.; Schiby, G.; Kröger, N.; Zustin, J.; Marx, A.; et al. Cytogenetics of extramedullary manifestations in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besse, L.; Sedlarikova, L.; Greslikova, H.; Kupska, R.; Almasi, M.; Penka, M.; Jelinek, T.; Pour, L.; Adam, Z.; Kuglik, P.; et al. Cytogenetics in multiple myeloma patients progressing into extramedullary disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 2016, 97, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bink, K.; Haralambieva, E.; Kremer, M.; Ott, G.; Beham-Schmid, C.; de Leval, L.; Peh, S.C.; Laeng, H.R.; Jütting, U.; Hutzler, P.; et al. Primary extramedullary plasmacytoma: Similarities with and differences from multiple myeloma revealed by interphase cytogenetics. Haematologica 2008, 93, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, N.; Yeung, J.; Chang, H. p53 nuclear accumulation is associated with extramedullary progression of multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisterer, W.; Bechter, O.; Hilbe, W.; Driel, M.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Thaler, J.; Bloem, A.C.; Günthert, U.; Stauder, R. CD44 isoforms are differentially regulated in plasma cell dyscrasias and CD44v9 represents a new independent prognostic parameter in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2001, 25, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, P.; Eppinger, S.; Schöpflin, C.; Stehle, G.; Munzert, G.; Döhner, H.; Schmid, M. CD44v6, a target for novel antibody treatment approaches, is frequently expressed in multiple myeloma and associated with deletion of chromosome arm 13q. Haematologica 2005, 90, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Tang, Y.; Bi, C.-F.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, W.-Q.; Yang, Q.-P.; Zou, L.-Q.; Liu, W.-P. Extraosseous (extramedullary) plasmacytomas: A clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 32 Chinese cases. Diagn. Pathol. 2011, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Jens Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, A.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Oliva, S.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Goldschmidtt, H.; Rosinol, L.; Richardson, P.; Caltagirone, S.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Facon, T.; et al. Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma: A Report From International Myeloma Working Group. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MM without EMD (at Different Time Points Studied) (n = 18) | MM with EMD (at Any Studied Time Point) (n = 49) | pEMP/SOP (at Diagnosis) (n = 20) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (n = 87) | 60 (44–89) | 63 (40–84) | 61 (19–76) | ns |
| Gender | ns | |||
| Male | 11 (61%) | 31 (69%) | 12 (60%) | |
| Female | 7 (39%) | 14 (31%) | 8 (40%) | |
| Isotype | ns | |||
| IgG | 10 (59%) | 26 (54%) | 7 (44%) | |
| IgA | 4 (23.5%) | 14 (29%) | 3 (19%) | |
| Light chain | 3 (17.5%) | 8 (17%) | 6 (37%) | |
| Light chain type | ns | |||
| Kappa | 11 (65%) | 31 (66%) | 14 (74%) | |
| Lambda | 6 (35%) | 16 (34%) | 5 (26%) | |
| Durie & Salmon stage | ns | |||
| I | 4 (25%) | 6 (13.5%) | - | |
| II | 2 (12.5%) | 3 (7%) | - | |
| III | 10 (62.5%) | 35 (79.5%) | - | |
| A | 13 (76.5%) | 30 (88%) | - | |
| B | 4 (23.5%) | 4 (12%) | - | |
| Serum concentrations at diagnosis | ||||
| Creatinine | 73 (41–487) | 91 (50–200) | 57 (47–84) | 0.05 |
| (µmol/L, n = 44) | ||||
| ß2 microglobulin | 3.5 (1.4–10.8) | 2.5 (1.4–13.1) | 2.0 (1.1–7.2) | ns |
| (mg/L, n = 41) | ||||
| Calcium | 2.3 (1.7–4.1) | 2.3 (2.0–4.0) | 2.4 (2.1–3.8) | ns |
| (mmol/L, n = 46) | ||||
| LDH (U/L, n = 43) | 155 (83–271) | 188 (80–3284) | 165 (143–2244) | ns |
| % BM PC at diagnosis (MM, n = 44) | 40 (10–95) | 30 (0–100) | - | ns |
| % of KI-67+ cells (MM-EMD/pEMP/SOP samples, n = 30) | - | 38 (5–90) | 30 (5–100) | ns |
| Year of diagnosis (n = 87) * | 2005 | 2008 | 2007 | ns |
| (1996–2009) | (1996–2013) | (1994–2011) | ||
| Time of follow-up, months (n = 83) | 49 (13–79) | 35 (1–204) | 50 (3–152) | ns |
| Mortality rate (n/evaluated patients) | 9/18 (50%) | 22/46 (48%) | 2/19 (11%) | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janjetovic, S.; Lohneis, P.; Nogai, A.; Balci, D.; Rasche, L.; Jähne, D.; Bokemeyer, C.; Schilling, G.; Blau, I.W.; Schmidt-Hieber, M. Clinical and Biological Characteristics of Medullary and Extramedullary Plasma Cell Dyscrasias. Biology 2021, 10, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070629
Janjetovic S, Lohneis P, Nogai A, Balci D, Rasche L, Jähne D, Bokemeyer C, Schilling G, Blau IW, Schmidt-Hieber M. Clinical and Biological Characteristics of Medullary and Extramedullary Plasma Cell Dyscrasias. Biology. 2021; 10(7):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070629
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanjetovic, Snjezana, Philipp Lohneis, Axel Nogai, Derya Balci, Leo Rasche, Doris Jähne, Carsten Bokemeyer, Georgia Schilling, Igor Wolfgang Blau, and Martin Schmidt-Hieber. 2021. "Clinical and Biological Characteristics of Medullary and Extramedullary Plasma Cell Dyscrasias" Biology 10, no. 7: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070629
APA StyleJanjetovic, S., Lohneis, P., Nogai, A., Balci, D., Rasche, L., Jähne, D., Bokemeyer, C., Schilling, G., Blau, I. W., & Schmidt-Hieber, M. (2021). Clinical and Biological Characteristics of Medullary and Extramedullary Plasma Cell Dyscrasias. Biology, 10(7), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070629







