MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
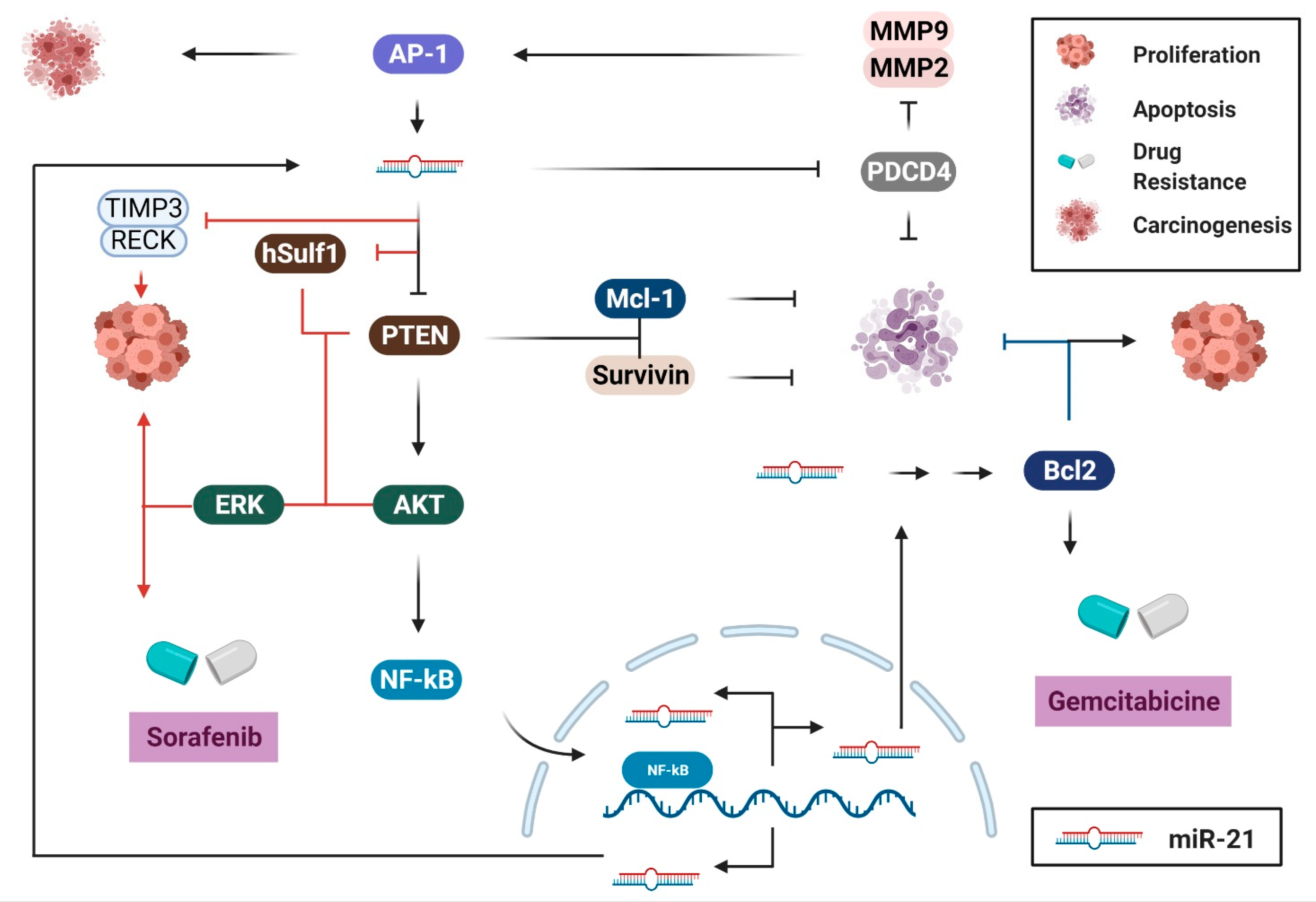
2. Biological Pathways of miR-21 in Cancers of the Digestive System
2.1. Cell Survival and Proliferation
2.2. Migration and Invasion
2.3. Immune Response, Inflammation, and Angiogenesis
3. Role of mir-21 as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker across Cancers in Digestive System
3.1. Gastric Cancer
3.1.1. MiR-21 as a Diagnostic Biomarker in Gastric Cancer
3.1.2. MiR-21 as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Gastric Cancer
3.1.3. MiR-21 as a Therapeutic Target in Gastric Cancer
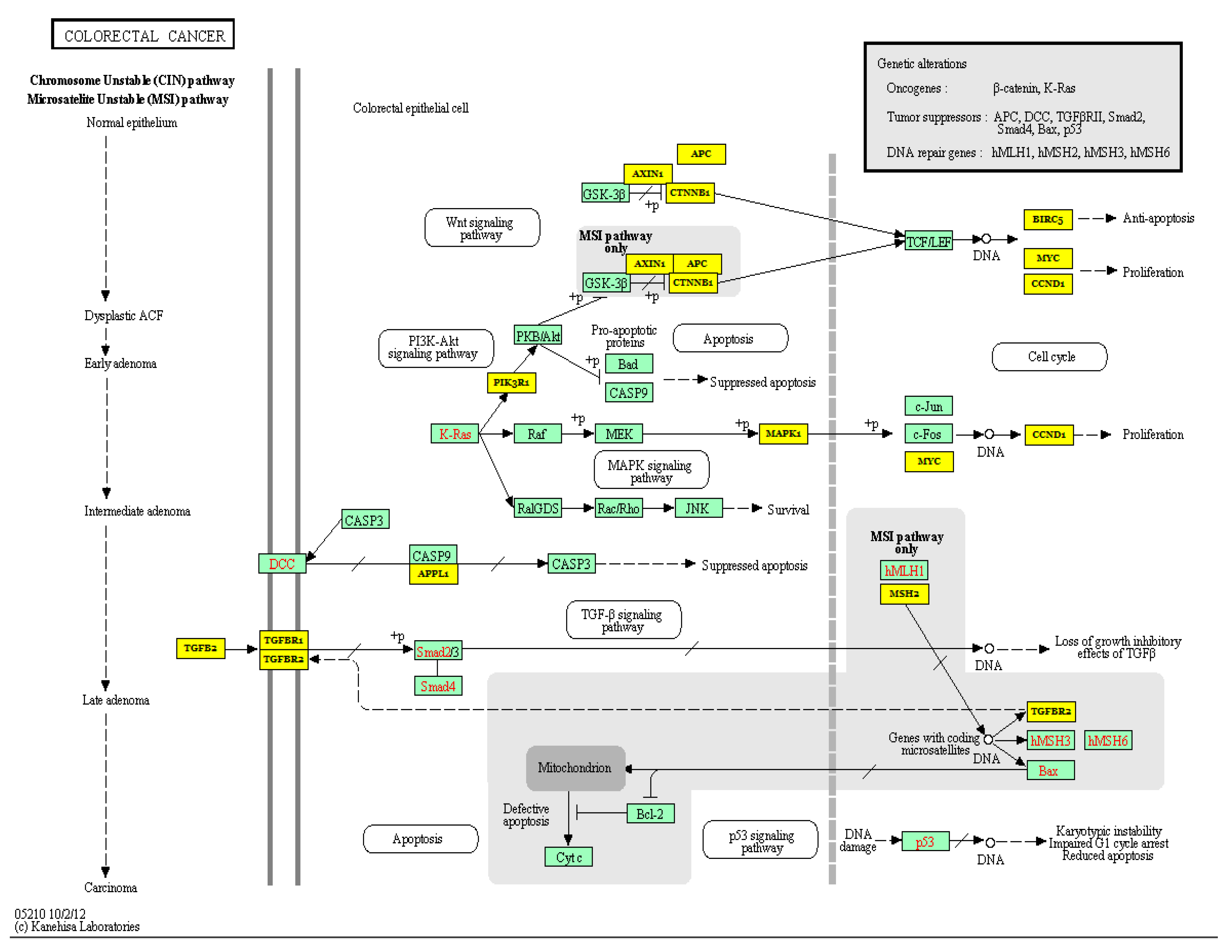
3.2. Colorectal Cancer
3.2.1. MiR-21 as a Potential Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer
3.2.2. Roles of miR-21 in Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer
3.2.3. MiR-21 as a Potential Therapeutic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer
3.3. Pancreatic Cancer
3.3.1. MiR-21 as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in Pancreatic Cancer
3.3.2. Roles of miR-21 in Chemoresistance and Regulation of Apoptosis
3.4. Liver Cancer
3.4.1. MiR-21 as a Prognostic and Diagnostic Biomarker in Liver Cancer
3.4.2. MiR-21 as a Therapeutic Target in Liver Cancer
3.5. Salivary Gland Cancer
3.5.1. MiR-21 as a Prognostic and Diagnostic Biomarker in Salivary Gland Cancer
3.5.2. MiR-21 as a Therapeutic Target in Salivary Gland Cancer
3.6. Esophageal Cancer
3.6.1. MiR-21 as a Diagnostic Biomarker in Esophageal Cancer
3.6.2. MiR-21 as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Esophageal Cancer
3.6.3. MiR-21 as a Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Cancer
4. Perspectives of miR-21 in Digestive Tract Cancers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, Z.; Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Aghajani, M.; Haji-Asgarzadeh, K.; Safarzadeh, E.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Duijf, P.H.; Baradaran, B. microRNAs in cancer stem cells: Biology, pathways, and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10002–10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Li, L.; Li, S. Circulating microRNA-21 as a biomarker for the detection of various carcinomas: An updated meta-analysis based on 36 studies. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.-G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, P.P.; Nolde, M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 467, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.Y.; Ferrajoli, A.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Calin, G.A. Calin. microRNA therapeutics in cancer—An emerging concept. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Lu, S.; Meng, L. Pleiotropic microRNA-21 in pulmonary remodeling: Novel insights for molecular mechanism and present advancements. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Nguyen, H.T.T. Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.; Güttinger, S.; Calado, A.; Dahlberg, J.E.; Kutay, U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 2004, 303, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seike, M.; Goto, A.; Okano, T.; Bowman, E.D.; Schetter, A.J.; Horikawa, I.; Mathe, E.A.; Jen, J.; Yang, P.; Sugimura, H. MiR-21 is an EGFR-regulated anti-apoptotic factor in lung cancer in never-smokers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12085–12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, X.; He, C.; Tan, G.; Li, Z.; Zhai, B.; Feng, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, H.; et al. LncRNA SNHG1 contributes to sorafenib resistance by activating the Akt pathway and is positively regulated by miR-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yu, Q.; Xin, L.; Guo, L. Circular RNA circC3P1 restrains kidney cancer cell activity by regulating miR-21/PTEN axis and inactivating PI3K/AKT and NF-kB pathways. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Dong, D.; Lun, Y.; Sun, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, G. Circular RNA circHIAT1 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cell lines through downregulation of miR-21. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.; Kontos, C.K.; Boni, T.; Bantounas, I.; Siakouli, D.; Kosmidou, V.; Vlassi, M.; Spyridakis, Y.; Tsipras, I.; Zografos, G.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-21 in colorectal cancer: ITGB4 as a novel miR-21 target and a three-gene network (miR-21-ITGΒ4-PDCD4) as predictor of metastatic tumor potential. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichevsky, A.M.; Gabriely, G. miR-21: A small multi-faceted RNA. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarswamy, R.; Volkmann, I.; Thum, T. Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalami, A.H.; Abdeahad, H.; Mesgari, M. Circulating miR-21 as a potential biomarker in human digestive system carcinoma: A systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Mao, F.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in various carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-H.; Tsao, C.-J. Emerging role of microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J. Considering exosomal miR-21 as a biomarker for cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica-Pop, C.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Magdo, L.; Raduly, L.; Gulei, D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Overview upon miR-21 in lung cancer: Focus on NSCLC. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3539–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Shastrim, A.A.; Palagani, A.; Buraschi, S.; Neill, T.; Savage, J.E.; Kapoor, A.; DeAngelis, T.; Addya, S.; Camphausen, K.; et al. miR-21 Plays a Dual Role in Tumor Formation and Cytotoxic Response in Breast Tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, F.; Gayral, M.; Lulka, H.; Buscail, L.; Cordelier, P. Targeting miR-21 for the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, K.; Fan, D. MicroRNA-21: A therapeutic target for reversing drug resistance in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wang, Z.-X.; Wang, R. MicroRNA-21: A novel therapeutic target in human cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonian, M.; Mosallayi, M.; Mirzaei, H. Circulating miR-21 as novel biomarker in gastric cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 475. [Google Scholar]
- Melnik, B.C. MiR-21: An environmental driver of malignant melanoma? J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, A.F.; Dellon, E.S.; Lund, J.; Crockett, S.D.; McGowan, C.E.; Bulsiewicz, W.J.; Gangarosa, L.M.; Thiny, M.T.; Stizenberg, K.; Morgan, D.R.; et al. Burden of gastrointestinal disease in the United States: 2012 update. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Li, A.; Olino, K.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Herman, J.M.; Schulick, R.D.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Loss of E-cadherin expression and outcome among patients with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Kostoulas, N.; Vergoulis, T.; Georgakilas, G.; Reczko, M.; Maragkakis, M.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Prionidis, K.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA miRPath v.2.0: Investigating the combinatorial effect of microRNAs in pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W498–W504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Zheng, Y. MicroRNA Roles in the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Tomuleasa, C. MicroRNA-21 stimulates gastric cancer growth and invasion by inhibiting the tumor suppressor effects of programmed cell death protein 4 and phosphatase and tensin homolog. J. B.U.ON. 2014, 19, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yusufu, A.; Tuerdi, R.; Redati, D.; Rehemutula, A.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Wang, H.-J. Expression and clinical correlation of Survivin and PTEN in gastric cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Olaru, A.V.; An, F.; Luvsanjav, D.; Jin, Z.; Agarwal, R.; Tomuleasa, C.; Popescu, I.; Alexandrescu, S.; Dima, S.; et al. MicroRNA-21 inhibits Serpini1, a gene with novel tumour suppressive effects in gastric cancer. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Han, B.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L. MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) promotes cell growth and invasion by repressing tumor suppressor PTEN in colorectal cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, L.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, M.; Weng, J.; Li, B. miR-21 promotes EGF-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by targeting Spry2. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qu, H.; Fan, Y.; Wu, C. Antagonism of miR-21 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Yan, Y.; Xu, C.; Ji, W.; Shen, S.; Xu, G.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, B.; Qian, H.; Chen, L.; et al. MicroRNA-21 suppresses PTEN and hSulf-1 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through AKT/ERK pathways. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-H.; Ge, M.-H.; Hou, X.-X.; Cao, J.; Hu, S.-S.; Lu, X.-X.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; et al. miR-21 regulates tumor progression through the miR-21-PDCD4-Stat3 pathway in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mao, W.M.; Zheng, Z.G.; Dong, Z.M.; Ling, Z.Q. Down-regulation of PTEN expression modulated by dysregulated miR-21 contributes to the progression of esophageal cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 3483–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-R.; Qi, H.-J.; Deng, D.-F.; Luo, Y.-Y.; Yang, S.-L. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12061–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C.Q.; He, J.H.; Duan, X.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ji, X.; Zang, W.Q.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.Y.; Wang, T.; et al. MiR-21 down-regulation suppresses cell growth, invasion and induces cell apoptosis by targeting FASL, TIMP3, and RECK genes in esophageal carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Becker Buscaglia, L.E.; Barker, J.R.; Li, Y. MicroRNAs in NF-κB signaling. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 3, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Wang, Y.; Sai, W.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhai, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, L. HBx-induced miR-21 suppresses cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting interleukin-12. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Varley, P.; Chang, Y.; He, X.-X.; Huang, H.; Tang, D.; Lotze, M.T.; Lin, J.; Tsung, A. High-Mobility Group Box 1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through miR-21-Mediated Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyoshi, Y.; Kamohara, H.; Karashima, R.; Sato, N.; Imamura, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Toyama, E.; Hayashi, N.; Watanabe, M.; et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Wang, C.; Li, T.; Cai, W.; Sun, J. Role of miR-21 in the growth and metastasis of human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4237–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuang, W.; Hou, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, W. Mcl-1 stabilization confers resistance to taxol in human gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82981–82990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.-P.; Chen, G. Bcl-2 Upregulation Induced by miR-21 Via a Direct Interaction Is Associated with Apoptosis and Chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-H.; Wu, X.-Y. Regarding Article ‘Bcl-2 Upregulation Induced by miR-21 Via a Direct Interaction Is Associated with Apoptosis and Chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 Pancreatic Cancer Cells’. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Kanwar, S.S.; Patel, B.B.; Oh, P.-S.; Nautiyal, J.; Sarkar, F.H.; Majumdar, A.P.N. MicroRNA-21 induces stemness by downregulating transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFβR2) in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 33, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.; Leupold, J.; Colburn, N.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, M.; Stribinskis, V.; Klinge, C.; Ramos, K.; Colburn, N.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4373–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits the malignant phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting VHL. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7215–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Sato, N.; Nabae, T.; Takahata, S.; Toma, H.; Nagai, E.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe–Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 Regulates Expression of the PTEN Tumor Suppressor Gene in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tang, Q.; Qiu, M.; Lang, N.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Bi, F. miR-21 targets the tumor suppressor RhoB and regulates proliferation, invasion and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.A. STAT3 as a central mediator of neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, L.; Wang, R.; Wei, C.; Liu, B.; Zhu, L.; Liu, P.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, S.-L.; et al. High frequency of loss of PTEN expression in human solid salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma and its implication for targeted therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11477–11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfrán-Duque, A.; Rotllan, N.; Zhang, X.; Fernández-Fuertes, M.; Ramírez-Hidalgo, C.; Araldi, E.; Daimiel, L.; Busto, R.; Fernández-Hernando, C.; Suárez, Y. Macrophage deficiency of miR-21 promotes apoptosis, plaque necrosis, and vascular inflammation during atherogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1244–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carissimi, C.; Carucci, N.; Colombo, T.; Piconese, S.; Azzalin, G.; Cipolletta, E.; Citarella, F.; Barnaba, V.; Macino, G.; Fulci, V. miR-21 is a negative modulator of T-cell activation. Biochimie 2014, 107, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraei, M.; Chaube, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Kaplan, A.; Price, N.L.; Ding, W.; Oyaghire, S.; García-Milian, R.; Mehta, S.; et al. Suppressing miR-21 activity in tumor-associated macrophages promotes an antitumor immune response. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 5518–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Neilson, J.R.; Kumar, P.; Manocha, M.; Shankar, P.; Sharp, P.A.; Manjunath, N. miRNA profiling of naive, effector and memory CD8 T cells. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhyastha, R.; Madhyastha, H.; Nurrahmah, Q.I.; Purbasari, B.; Maruyama, M.; Nakajima, Y. MicroRNa 21 elicits a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages, with exosomes functioning as delivery vehicles. Inflammation 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, F.J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.; Hennessy, E.J.; Martin, C.; O’leary, J.J.; Ruan, Q.; Johnson, D.S.; Chen, Y.; O’neill, L.A. Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.-S.; Tian, S.-S.; Lu, J.-J.; Ding, X.-H. Cardamonin Regulates miR-21 Expression and Suppresses Angiogenesis Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 501581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, L.; Xu, S.; Fu, G. MicroRNA-21 mediates the rapamycin-induced suppression of endothelial proliferation and migration. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Jing, Y.; Carpenter, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kung, H.-F.; Lai, L.; Jiang, B.-H. MiR-21 Induced Angiogenesis through AKT and ERK Activation and HIF-1a Expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E.C.; Van Doorslaer, K.; Rogler, L.E.; Rogler, C.E. Overexpression of miR-21 promotes an in vitro metastatic phenotype by targeting the tumor suppressor RHOB. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatel, C.; Malvaux, L.; Bovy, N.; Deroanne, C.; Lambert, V.; Alvarez Gonzalez, M.-L.; Colige, A.; Rakic, J.-M.; Noël, A.; Martial, J.A.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Exhibits Antiangiogenic Function by Targeting RhoB Expression in Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z.; Li, L.; Liu, M.Y.; Jin, X.B.; Mao, J.W.; Pu, Q.H.; Meng, M.J.; Chen, X.G.; Zhu, J.Y. Curcumin induces FasL-related apoptosis through p38 activation in human hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, X.; Gu, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Dai, Z.; Li, C.; et al. SERPINA3K induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells via activating the Fas/FasL/caspase-8 signaling pathway. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3244–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-S.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Gang, G.; Li, W.; Zhu, E.-D.; Luo, X.; Mao, X.-H.; Zou, Q.-M.; Yu, P.-W.; Zuo, Q.-F.; et al. Plasma microRNAs, miR-223, miR-21 and miR-218, as novel potential biomarkers for gastric cancer detection. PloS ONE 2012, 7, e41629. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Hu, P.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; He, D.; Tang, S.; Zeng, Z. Potential role of microRNA-21 in the diagnosis of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, S.; Nekouian, R.; Akbari, A.; Faraji, A.; Abbasi, V.; Agah, S. Evaluation of circulating miR-21 and miR-222 as diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujiura, M.; Ichikawa, D.; Komatsu, S.; Shiozaki, A.; Takeshita, H.; Kosuga, T.; Konishi, H.; Morimura, R.; Deguchi, K.; Fujiwara, H. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Pu, X.; Wang, J. Circulating MicroRNA-21 Is a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in Gastric Cancer. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 435656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Tsujiura, M.; Konishi, H.; Takeshita, H.; Nagata, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hirajima, S.; Arita, T.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of circulating miR-21 in the plasma of patients with gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, M.Y.; Pan, K.F.; Su, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.L.; Li, J.Y.; Yuasa, Y.; Kang, D.; Kim, Y.S.; You, W.C. Identification of serum microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Fan, Z.; Liu, F.; Zuo, J. Hsa-miR-21 and Hsa-miR-29 in Tissue as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Gastric Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q. miR-21 Is a Promising Novel Biomarker for Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 640168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, B.; Wu, C.; Ju, J. Prognostic significance of miR-181b and miR-21 in gastric cancer patients treated with S-1/Oxaliplatin or Doxifluridine/Oxaliplatin. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C. Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Cai, J.; Deng, W.; Bi, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z. Serum microRNA-21 levels are related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Park, Y.S.; Ahn, J.Y.; Do, E.J.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.E.; Jung, K.; Byeon, J.S.; Ye, B.D.; Yang, D.H.; et al. MiR 21-5p as a predictor of recurrence in young gastric cancer patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeda, N.; Iinuma, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsukahara, D.; Midorikawa, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Kumata, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Kiyokawa, T.; Fukagawa, T.; et al. Plasma exosome-encapsulated microRNA-21 and microRNA-92a are promising biomarkers for the prediction of peritoneal recurrence in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4467–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuhisa, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Yashiro, M.; Hirakawa, K.; Kosaka, T.; Makino, H.; Akiyama, H.; Kunisaki, C.; et al. Exosomal miRNAs from Peritoneum Lavage Fluid as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers of Peritoneal Metastasis in Gastric Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohzawa, H.; Kimura, Y.; Saito, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Miyato, H.; Sakuma, Y.; Horie, H.; Hosoya, Y.; Lefor, A.K.; Sata, N.; et al. Ratios of miRNAs in Peritoneal Exosomes are Useful Biomarkers to Predict Tumor Response to Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Patients with Peritoneal Metastases from Gastric Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 5057–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jeon, T.Y.; Choi, C.I.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, G.H.; Ryu, D.Y.; Lee, B.E.; Kim, H.H. Validation of circulating miRNA biomarkers for predicting lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E.C.; Verheij, M.; Allum, W.; Cunningham, D.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v38–v49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Chen, L.; Yuan, X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, G.; Ma, Y.; Shen, L. Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, G.F.; Shi, Y.F.; Xu, W. Research Progress in microRNA-Based Therapy for Gastric Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11393–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Yin, J.F.; Ji, Z.; Hong, Y.; Wu, P.; Bian, B.; Song, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Wu, F. Strengthening Gastric Cancer Therapy by Trastuzumab-Conjugated Nanoparticles with Simultaneous Encapsulation of Anti-MiR-21 and 5-Fluorouridine. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 2158–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, L.; Deng, J.; Xiong, J. miR-21-5p confers doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer cells by targeting PTEN and TIMP3. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hur, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetter, A.J.; Leung, S.Y.; Sohn, J.J.; Zanetti, K.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Yuen, S.T.; Chan, T.L.; Kwong, D.L.W.; Au, G.K.H.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profiles Associated With Prognosis and Therapeutic Outcome in Colon Adenocarcinoma. JAMA 2008, 299, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Song, W.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wei, J.-H.; Liao, Y.-J.; Lei, J.; Hu, M.; Chen, G.-Z.; Liao, B.; Lu, J.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of a microRNA signature in stage II colon cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.S.; Jørgensen, S.; Fog, J.U.; Søkilde, R.; Christensen, I.J.; Hansen, U.; Brünner, N.; Baker, A.; Møller, S.; Nielsen, H.J. High levels of microRNA-21 in the stroma of colorectal cancers predict short disease-free survival in stage II colon cancer patients. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Yang, B.; Zhai, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, K.; Wu, Z.; Cai, J. Prognostic Role of microRNA-21 in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Lei, W.; Fu, J.-C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.-H.; Xiong, J.-P. Targeting miR-21 enhances the sensitivity of human colon cancer HT-29 cells to chemoradiotherapy in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourô, S.; Mourato, C.; Velho, S.; Cardador, A.; Ferreira, M.P.; Albergaria, D.; Castro, R.E.; Maio, R.; Rodrigues, C.M.P. Potential of miR-21 to Predict Incomplete Response to Chemoradiotherapy in Rectal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 577653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Dong, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, L.; Han, D.L.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.L.; Zhang, Z.L. MicroRNA-494 sensitizes colon cancer cells to fluorouracil through regulation of DPYD. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.H.; Tian, D.; Yang, Z.C.; Li, J.L. Exosomal miR-21 promotes proliferation, invasion and therapy resistance of colon adenocarcinoma cells through its target PDCD4. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeri, N.; Gasparini, P.; Braconi, C.; Paone, A.; Lovat, F.; Fabbri, M.; Sumani, K.M.; Alder, H.; Amadori, D.; Patel, T.; et al. MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21098–21103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Hsieh, Y.Y.; Lo, H.L.; Li, A.; Chou, C.J.; Yang, P.M. In Vitro and In Silico Mechanistic Insights into miR-21-5p-Mediated Topoisomerase Drug Resistance in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A 6 microRNA Tool for Stratifying Stage II Colon Cancer of Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02466113 (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Szafranska, A.E.; Davison, T.S.; John, J.; Cannon, T.; Sipos, B.; Maghnouj, A.; Labourier, E.; Hahn, S.A. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, O.A.; Mullendore, M.; Wentzel, E.A.; López-Romero, P.; Tan, A.C.; Alvarez, H.; West, K.; Ochs, M.F.; Hidalgo, M.; Arking, D.E.; et al. A resource for analysis of microRNA expression and function in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Rieu, M.C.; Torrisani, J.; Selves, J.; Al Saati, T.; Souque, A.; Dufresne, M.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Carrère, N.; Buscail, L.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Is Induced Early in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Precursor Lesions. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodes, M.J.; Caraballo, M.; Suciu, D.; Munro, S.; Kumar, A.; Anderson, B. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microarray. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Funel, N.; Peters, G.J.; Del Chiaro, M.; Erozenci, L.A.; Vasile, E.; Leon, L.G.; Pollina, L.E.; Groen, A.; Falcone, A.; et al. MicroRNA-21 in Pancreatic Cancer: Correlation with Clinical Outcome and Pharmacologic Aspects Underlying Its Role in the Modulation of Gemcitabine Activity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4528–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-K.; Lee, E.J.; Esau, C.; Schmittgen, T.D. Antisense Inhibition of microRNA-21 or -221 Arrests Cell Cycle, Induces Apoptosis, and Sensitizes the Effects of Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2009, 38, e190–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Lang, M.; Wehbe, H.; Maheshwari, S.; Mendell, J.T.; Jiang, J.; Schmittgen, T.D.; Patel, T. Involvement of Human Micro-RNA in Growth and Response to Chemotherapy in Human Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2113–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Zhang, X.H.; Yu, X.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Cheng, X.C. MicroRNA-21 gene and cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Z.; Kusumanchi, P.; Han, S.; Liangpunsakul, S. Critical Role of microRNA-21 in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wei, F.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, H.; Sun, Q.; Yan, F.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-21 for cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene 2014, 533, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.-X.; Song, W.-J.; Li, Q.-J.; Yang, F.A.N.; Wang, D.-S.; Zhang, N.; Dou, K.-F. MicroRNA-21 regulates the migration and invasion of a stem-like population in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J. Targeting Kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) for cancer therapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M. miR-21 promotes cell migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting KLF5. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Dong, X.; Zhai, B.; Jiang, X.; Dong, D.; Li, B.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S.; Sun, X. MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28867–28881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, T.R.; Zabludoff, S.; Ahn, S.M.; Allerson, C.; Arlt, H.; Baffa, R.; Cao, H.; Davis, S.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Gaur, R.; et al. Anti-miR-21 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth via Broad Transcriptional Network Deregulation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimaru, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; Wada, H.; Tomokuni, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Marubashi, S.; Takeda, Y.; Tanemura, M.; Umeshita, K.; et al. MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to the anti-tumour effect of interferon-α/5-fluorouracil in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado-González, Ó.; Majem, B.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; López-López, R.; Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Cancer Salivary Biomarkers for Tumours Distant to the Oral Cavity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapado-González, Ó.; Majem, B.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Álvarez-Castro, A.; Santamaría, A.; Gil-Moreno, A.; López-López, R.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Human salivary microRNAs in Cancer. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintakuntlawar, A.V.; Okuno, S.H.; Price, K.A. Systemic therapy for recurrent or metastatic salivary gland malignancies. Cancers Head Neck 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalin, M.G.; Desrichard, A.; Katabi, N.; Makarov, V.; Walsh, L.A.; Lee, K.-W.; Wang, Q.; Armenia, J.; West, L.; Dogan, S.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Salivary Duct Carcinoma Reveals Actionable Targets and Similarity to Apocrine Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4623–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhaveri, K.L.; Makker, V.; Wang, X.V.; Chen, A.P.; Flaherty, K.; Conley, B.A.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Williams, P.M.; Hamilton, S.R.; Harris, L.; et al. Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in patients (pts) with HER2 amplified (amp) tumors excluding breast and gastric/gastro-esophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinomas: Results from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (MATCH) trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzrock, R.; Bowles, D.W.; Kang, H.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Hainsworth, J.; Spigel, D.R.; Bose, R.; Burris, H.; Sweeney, C.J.; Beattie, M.S.; et al. Targeted therapy for advanced salivary gland carcinoma based on molecular profiling: Results from MyPathway, a phase IIa multiple basket study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, T.; Yan, F.; Cai, W.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, X.; Sun, J. Effect of simvastatin and microRNA-21 inhibitor on metastasis and progression of human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennathur, A.; Gibson, M.K.; Jobe, B.A.; Luketich, J.D. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 2013, 381, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, B.; Ren, P.; Ye, H.; Shi, J.; Qin, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J. Circulating plasma microRNAs in the detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3303–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Ye, P.; Zhang, W.; Rao, J.; Xie, Z. Diagnostic values of salivary versus and plasma microRNA-21 for early esophageal cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2014, 34, 885–889. [Google Scholar]
- Guraya, S. Prognostic significance of circulating microRNA-21 expression in esophageal, pancreatic and colorectal cancers; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 60, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Kawaguchi, T.; Miyamae, M.; Okajima, W.; Ohashi, T.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Circulating miR-21 as an independent predictive biomarker for chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, G.; Krasna, M. Overview of esophageal cancer. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 6, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Liu, G.J.; Yuan, D.F.; Li, C.Q.; Xue, M.; Chen, L.J. Influence of exosome-derived miR-21on chemotherapy resistance of esophageal cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Li, F.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C.M.; Tuo, L.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.B.; Wang, J.S.; Shi, W.H.; Li, X. Comparison of long non-coding RNAs, microRNAs and messenger RNAs involved in initiation and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, F.; Lv, J.-H.; Liang, L.; Wang, J.-C.; Li, C.-R.; Sun, L.; Li, T. Downregulation of microRNA-21 inhibited radiation-resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.J.; Slack, F.J. A truth serum for cancer—microRNAs have major potential as cancer biomarkers. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 983–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, W.K.K.; Wu, C.W.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Yu, J.; Ng, S.S.M. MicroRNA dysregulation in colorectal cancer: A clinical perspective. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acunzo, M.; Romano, G.; Wernicke, D.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA and cancer–a brief overview. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.R. Introduction to Predictive Biomarkers: Definitions and Characteristics; Predictive Biomarkers in Oncology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, B.A.; Baras, A.S.; McCall, M.N.; Hertel, J.A.; Cornish, T.C.; Halushka, M.K. A critical evaluation of microRNA biomarkers in non-neoplastic disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89565. [Google Scholar]
- Salaspuro, M.P. Acetaldehyde, microbes, and cancer of the digestive tract. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2003, 40, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogtmann, E.; Goedert, J.J. Epidemiologic studies of the human microbiome and cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saus, E.; Iraola-Guzmán, S.; Willis, J.R.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Gabaldón, T. Microbiome and colorectal cancer: Roles in carcinogenesis and clinical potential. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 69, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrand, L.; Graham, D.Y. Microbiome and Gastric Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Tai, J.W.; Lu, L.-F. miRNA–Microbiota Interaction in Gut Homeostasis and Colorectal Cancer. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, D.G.; Williams, M.A.; Thaiss, C.A.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Raverdeau, M.; McEntee, C.; Cotter, P.D.; Elinav, E.; O’Neill, L.A.; Corr, S.C. Loss of microRNA-21 influences the gut microbiota, causing reduced susceptibility in a murine model of colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 12, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, A.; Musolino, C.; Tonacci, A.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Interactions between the MicroRNAs and microbiota in cancer development: Roles and therapeutic opportunities. Cancers 2020, 12, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.A.; Afonso, M.B.; Ramiro, R.S.; Pires, D.; Pimentel, M.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M. Host miRNA-21 promotes liver dysfunction by targeting small intestinal Lactobacillus in mice. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K.; Sugi, Y.; Narabayashi, H.; Kobayakawa, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Hosono, A.; Kaminogawa, S.; Hanazawa, S.; Takahashi, K. Commensal microbiota-induced microRNA modulates intestinal epithelial permeability through the small GTPase ARF4. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15426–15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.-Z.; Han, B.-S.; Di, J.-M.; Liu, W.-Y.; Tang, Q. Role of the brain-gut axis in gastrointestinal cancer. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 1554–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, G.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbial regulation of microRNA expression in the brain–gut axis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 48, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.T.; Kacimi, S.E.O.; Nguyen, T.L.; Suman, K.H.; Lemus-Martin, R.; Saleem, H.; Do, D.N. MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker. Biology 2021, 10, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050417
Nguyen HT, Kacimi SEO, Nguyen TL, Suman KH, Lemus-Martin R, Saleem H, Do DN. MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker. Biology. 2021; 10(5):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050417
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Ha Thi, Salah Eddine Oussama Kacimi, Truc Ly Nguyen, Kamrul Hassan Suman, Roselyn Lemus-Martin, Humaira Saleem, and Duy Ngoc Do. 2021. "MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker" Biology 10, no. 5: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050417
APA StyleNguyen, H. T., Kacimi, S. E. O., Nguyen, T. L., Suman, K. H., Lemus-Martin, R., Saleem, H., & Do, D. N. (2021). MiR-21 in the Cancers of the Digestive System and Its Potential Role as a Diagnostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Biomarker. Biology, 10(5), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050417





