Piscirickettsia salmonis-Triggered Extracellular Traps Formation as an Innate Immune Response of Atlantic Salmon-Derived Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Sampling
2.2. Bacteria Culture
2.3. Obtaining a PMN-Enriched Suspension from Atlantic Salmon
2.4. Total Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
2.5. Quantification of P. salmonis-Triggered ETs
2.6. Visualization of P. salmonis-Triggered ETs
2.7. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
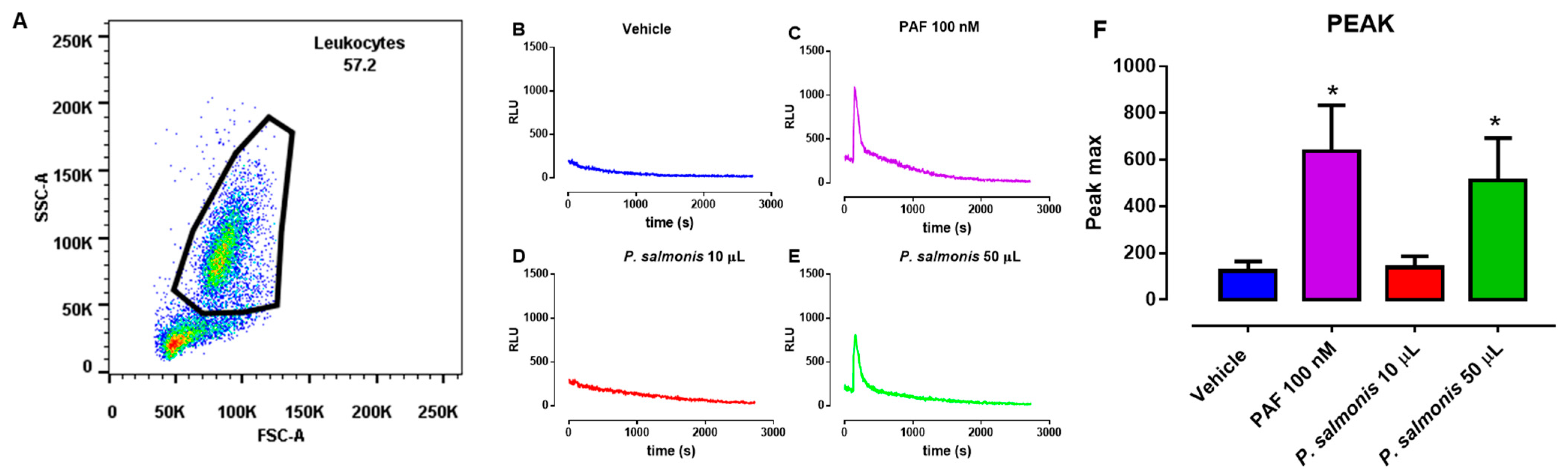
3.1. ROS Production in P. salmonis-Exposed PMN from Atlantic Salmon
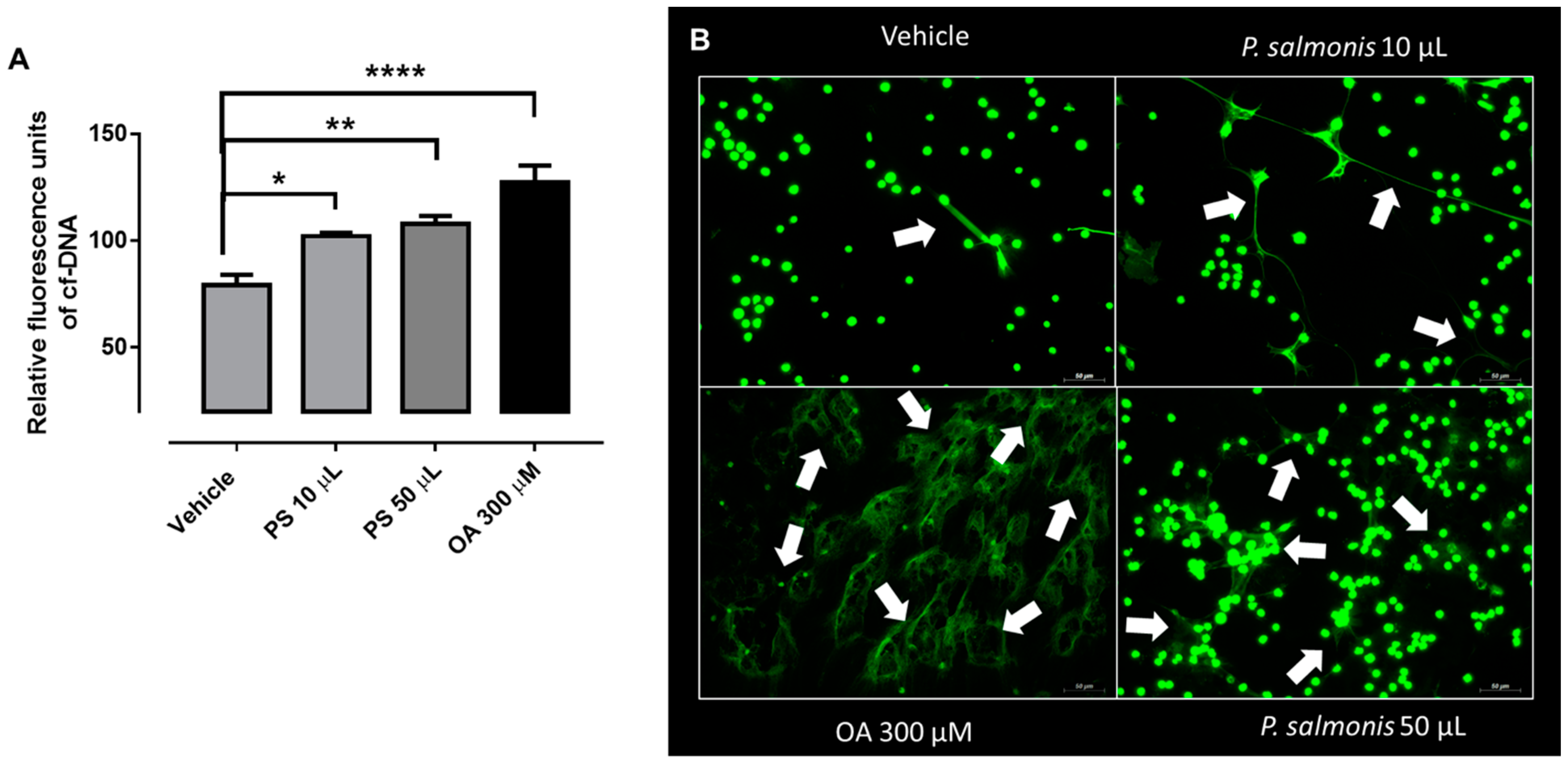
3.2. Atlantic Salmon-Derived PMN Release ETs after Exposure to P. salmonis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Latz, E.; Mills, K.H.G.; Natoli, G.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Xavier, R.J. Trained immunity: A program of innate immune memory in health and disease. Science 2016, 352, aaf1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S3–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Tao, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, S.; Xu, A. Comparative immune systems in animals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, C.T.; Dyrynda, E.A.; Gray, R.D.; Rossi, A.G.; Smith, V.J. Invertebrate extracellular phagocyte traps show that chromatin is an ancient defence weapon. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Godínez, C.; Carrero, J.C. The state of art of neutrophil extracellular traps in protozoan and helminthic infections. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wartha, F.; Henriques-Normark, B. ETosis: A novel cell death pathway. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, pe25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, C.; Caro, T.M.; Silva, L.M.R.; Ruiz, A.; Taubert, A. The intriguing host innate immune response: Novel anti-parasitic defence by neutrophil extracellular traps. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra-Blanco, R.; Silva, L.M.R.; Conejeros, I.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Pinniped- and Cetacean-Derived ETosis Contributes to Combating Emerging Apicomplexan Parasites (Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum) Circulating in Marine Environments. Biology 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães-Costa, A.B.; Nascimento, M.T.C.; Wardini, A.B.; Pinto-da-Silva, L.H.; Saraiva, E.M. ETosis: A Microbicidal Mechanism beyond Cell Death. J. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 2012, 929743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, P.; Manosalva, C.; Quiroga, J.; Belmar, I.; Álvarez, K.; Díaz, G.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Carretta, M.D.; Burgos, R.A.; et al. Oleic and Linoleic Acids Induce the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps via Pannexin 1-Dependent ATP Release and P2X1 Receptor Activation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Zychlinsky, A. NETs: A new strategy for using old weapons. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.D.; Lucas, C.D.; MacKellar, A.; Li, F.; Hiersemenzel, K.; Haslett, C.; Davidson, D.J.; Rossi, A.G. Activation of conventional protein kinase C (PKC) is critical in the generation of human neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Inflamm. (Lond.) 2013, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D.J.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Is immunity the second function of chromatin? J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; McDonald, B.; Gowing, S.; Chow, S.; Giannias, B.; Bourdeau, F.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells and promote metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, F.; Schulz, M.; Pilatz, A.; Wagenlehner, F.; Schuppe, H.-C.; Conejeros, I.; Uribe, P.; Taubert, A.; Sánchez, R.; Hermosilla, C. Increase of leucocyte-derived extracellular traps (ETs) in semen samples from human acute epididymitis patients—A pilot study. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, T.; Kotarski, F.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A.; Wrenzycki, C. Semen extender and seminal plasma alter the extent of neutrophil extracellular traps (NET) formation in cattle. Theriogenology 2021, 160, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.K.; Penagos-Tabares, F.; Muñoz-Caro, T.; Gärtner, U.; Mejer, H.; Schaper, R.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Gastropod-derived haemocyte extracellular traps entrap metastrongyloid larval stages of Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Troglostrongylus brevior. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palić, D.; Andreasen, C.B.; Ostojić, J.; Tell, R.M.; Roth, J.A. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) whole kidney assays to measure neutrophil extracellular trap release and degranulation of primary granules. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 319, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palić, D.; Ostojić, J.; Andreasen, C.B.; Roth, J.A. Fish cast NETs: Neutrophil extracellular traps are released from fish neutrophils. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, G.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Adamek, M.; Reuner, F.; Jung-Schroers, V.; Naim, H.Y.; Steinhagen, D. β-Glucan protects neutrophil extracellular traps against degradation by Aeromonas hydrophila in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, L.; Golbach, L.; Kolaczkowska, E.; Scheer, M.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M.; Chadzinska, M. Carp neutrophilic granulocytes form extracellular traps via ROS-dependent and independent pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Sun, L. Neutrophils of Scophthalmus maximus produce extracellular traps that capture bacteria and inhibit bacterial infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 56, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, A.P.; Álvarez de Haro, N.; Bron, J.E.; Desbois, A.P. Chromatin extracellular trap release in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, J.L.; Lannan, C.N.; Garces, L.H.; Larenas, J.J.; Smith, P.A. Isolation of a Rickettsiales-Like Organism from Diseased Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) in Chile. Fish Pathol. 1990, 25, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, J.L.; Hedrick, R.P. Piscirickettsia salmonis: A Gram-negative intracellular bacterial pathogen of fish. J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvitanich, J.D.; Garate, N.; Smith, C.E. The isolation of a rickettsia-like organism causing disease and mortality in Chilean salmonids and its confirmation by Koch’s postulate. J. Fish Dis. 1991, 14, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauel, M.J.; Ware, C.; Smith, P.A. Culture of Piscirickettsia salmonis on enriched blood agar. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikalsen, J.; Skjaervik, O.; Wiik-Nielsen, J.; Wasmuth, M.A.; Colquhoun, D.J. Agar culture of Piscirickettsia salmonis, a serious pathogen of farmed salmonid and marine fish. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yañez, A.J.; Silva, H.; Valenzuela, K.; Pontigo, J.P.; Godoy, M.; Troncoso, J.; Romero, A.; Figueroa, J.; Carcamo, J.G.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. Two novel blood-free solid media for the culture of the salmonid pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, M.; Enríquez, R. Piscirickettsiosis and Piscirickettsia salmonis in fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernapesca. Informe Sanitario de Salmonicultura en Centros Marinos 1er Semestre Año 2019; Sernapesca: Valparaíso, Chile, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, J.L.; Lannan, C.N.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Wood, N.D. Piscirickettsia salmonis gen. nov., sp. nov., the causative agent of an epizootic disease in salmonid fishes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1992, 42, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branson, E.J.; Diaz-Muñoz, D.N. Description of a new disease condition occurring in farmed coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch (Walbaum), in South America. J. Fish Dis. 1991, 14, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, J.W.; Alvarado, V.; Enriquez, R.; Monrás, M. The “Coho salmon syndrome” (CSS): A new disease in chilean salmon reared in sea water. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 1990, 10, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Conejeros, I.; Jara, E.; Carretta, M.D.; Alarcón, P.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) reduces respiratory burst, MMP-9 release and CD11b expression, and increases l-selectin shedding in bovine neutrophils. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, J.; Alarcón, P.; Manosalva, C.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Carretta, M.D.; Burgos, R.A. Glycolysis and mitochondrial function regulate the radical oxygen species production induced by platelet-activating factor in bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 226, 110074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Mena Huertas, S.J.; Conejeros, I.; Alarcón, P.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Eimeria bovis-triggered neutrophil extracellular trap formation is CD11b-, ERK 1/2-, p38 MAP kinase- and SOCE-dependent. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, C.; Sekkin, S. The Immune System Drugs. In Recent Advances in Fish Farms; Do, Z., Aral, F., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Magnadóttir, B. Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaï, H.C.; Rioult, D.; Bado-Nilles, A.; Delahaut, L.; Jubréaux, J.; Geffard, A.; Porcher, J.-M.; Betoulle, S. Procedures for leukocytes isolation from lymphoid tissues and consequences on immune endpoints used to evaluate fish immune status: A case study on roach (Rutilus rutilus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, J.D.; Takahashi, L.S. Oxidative stress and fish immune system: Phagocytosis and leukocyte respiratory burst activity. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 3403–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusi, S.; Rossi, F. Activation of NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils involves the phosphorylation and the translocation of cytosolic p67phox. Biochem. J. 1993, 296 Pt 2, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covantes-Rosales, C.E.; Trujillo-Lepe, A.M.; Díaz-Reséndiz, K.J.G.; Toledo-Ibarra, G.A.; Ventura-Ramón, G.H.; Ortiz-Lazareno, P.C.; Girón-Pérez, M.I. Phagocytosis and ROS production as biomarkers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) leukocytes by exposure to organophosphorus pesticides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havixbeck, J.J.; Rieger, A.M.; Wong, M.E.; Hodgkinson, J.W.; Barreda, D.R. Neutrophil contributions to the induction and regulation of the acute inflammatory response in teleost fish. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.A.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Matthei, S.M.; Hermosilla, R.; Folch, H.; Hancke, J.L. Determination of specific receptor sites for platelet activating factor in bovine neutrophils. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, N.; Alarcón, P.; Millán, C.; Burgos, R.A.; Morera, F.J.; Ojeda, J. Vincristine, carboplatin and cisplatin increase oxidative burst induced by PAF in canine neutrophils. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. In Vitro Antithrombotic Properties of Salmon (Salmo salar) Phospholipids in a Novel Food-Grade Extract. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Hoesli, S.; Roth, N.; Staedler, S.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U. Eosinophil extracellular DNA traps in skin diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn, C.; Janko, C.; Latzko, M.; Chaurio, R.; Schett, G.; Herrmann, M. Monosodium urate crystals induce extracellular DNA traps in neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils but not in mononuclear cells. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Caro, T.; Silva, L.M.R.; Ritter, C.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Besnoitia besnoiti tachyzoites induce monocyte extracellular trap formation. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4189–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, V.; Faille, D.; Marani, V.; Noël, B.; Gallais, Y.; Szely, N.; Flament, H.; Pallardy, M.; Chollet-Martin, S.; de Chaisemartin, L. Human blood monocytes are able to form extracellular traps. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzeczynska-Moncznik, J.; Wlodarczyk, A.; Banas, M.; Kwitniewski, M.; Zabieglo, K.; Kapinska-Mrowiecka, M.; Dubin, A.; Cichy, J. DNA structures decorated with cathepsin G/secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor stimulate IFNI production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 2, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanan, S.; Horibata, S.; McElwee, J.L.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Coonrod, S.A. Identification of macrophage extracellular trap-like structures in mammary gland adipose tissue: A preliminary study. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Goldmann, O.; Thulin, P.; Heinemann, K.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Rohde, M.; Medina, E. Phagocytosis-independent antimicrobial activity of mast cells by means of extracellular trap formation. Blood 2008, 111, 3070–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Kobayashi, S.D.; Quinn, M.T.; Deleo, F.R. A NET Outcome. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chi, H.; Sun, L. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps of Cynoglossus semilaevis: Production Characteristics and Antibacterial Effect. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoiber, W.; Obermayer, A.; Steinbacher, P.; Krautgartner, W.D. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Formation of Extracellular Traps (ETs) in Humans. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 702–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douda, D.N.; Khan, M.A.; Grasemann, H.; Palaniyar, N. SK3 channel and mitochondrial ROS mediate NADPH oxidase-independent NETosis induced by calcium influx. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, V.A.; Arthur, J.S.C. Subverting Toll-Like Receptor Signaling by Bacterial Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yipp, B.G.; Petri, B.; Salina, D.; Jenne, C.N.; Scott, B.N.; Zbytnuik, L.D.; Pittman, K.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Wu, K.; Meijndert, H.C.; et al. Infection-induced NETosis is a dynamic process involving neutrophil multitasking in vivo. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, R.; Gómez, F.A.; Marshall, S.H. The infection process of Piscirickettsia salmonis in fish macrophages is dependent upon interaction with host-cell clathrin and actin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, U.M.; Bron, J.E.; Brown, L.; Pourahmad, F.; Bricknell, I.R.; Thompson, K.D.; Adams, A.; Ellis, A.E. Survival and replication of Piscirickettsia salmonis in rainbow trout head kidney macrophages. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, V.; Galanti, N.; Bols, N.C.; Jiménez, V.; Paredes, R.; Marshall, S.H. Piscirickettsia salmonis induces apoptosis in macrophages and monocyte-like cells from rainbow trout. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga, A.; Aravena, P.; Pulgar, R.; Travisany, D.; Ortiz-Severín, J.; Chávez, F.P.; Maass, A.; González, M.; Cambiazo, V. Transcriptomic Changes of Piscirickettsia salmonis During Intracellular Growth in a Salmon Macrophage-Like Cell Line. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.E.; Galleguillos, M.; Díaz, S.; Machuca, A.; Carbonero, A.; Smith, P.A. Evidence of exotoxin secretion of Piscirickettsia salmonis, the causative agent of piscirickettsiosis. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Blodkamp, S.; Nizet, V. Interaction of Bacterial Exotoxins with Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Impact for the Infected Host. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, J.H.; Ruiz, A.; Zahner, H.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation as innate immune reactions against the apicomplexan parasite Eimeria bovis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahilog, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Alam, A.; Eguchi, S.; Weng, H.; Ma, D. The Role of Neutrophil NETosis in Organ Injury: Novel Inflammatory Cell Death Mechanisms. Inflammation 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.J.; Radic, M. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Double-edged swords of innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejeros, I.; Velásquez, Z.D.; Grob, D.; Zhou, E.; Salecker, H.; Hermosilla, C.; Taubert, A. Histone H2A and Bovine Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Damage of Besnoitia besnoiti-Infected Host Endothelial Cells but Fail to Affect Total Parasite Proliferation. Biology 2019, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutua, V.; Gershwin, L.J. A Review of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Disease: Potential Anti-NETs Therapeutics. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alarcon, P.; Espinosa, G.; Millan, C.; Saravia, J.; Quinteros, V.; Enriquez, R.; Henriquez, C.; Vargas-Chacoff, L.; Burgos, R.A.; Taubert, A.; et al. Piscirickettsia salmonis-Triggered Extracellular Traps Formation as an Innate Immune Response of Atlantic Salmon-Derived Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils. Biology 2021, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030206
Alarcon P, Espinosa G, Millan C, Saravia J, Quinteros V, Enriquez R, Henriquez C, Vargas-Chacoff L, Burgos RA, Taubert A, et al. Piscirickettsia salmonis-Triggered Extracellular Traps Formation as an Innate Immune Response of Atlantic Salmon-Derived Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils. Biology. 2021; 10(3):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030206
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlarcon, Pablo, Gabriel Espinosa, Catalina Millan, Julia Saravia, Vania Quinteros, Ricardo Enriquez, Claudio Henriquez, Luis Vargas-Chacoff, Rafael A. Burgos, Anja Taubert, and et al. 2021. "Piscirickettsia salmonis-Triggered Extracellular Traps Formation as an Innate Immune Response of Atlantic Salmon-Derived Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils" Biology 10, no. 3: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030206
APA StyleAlarcon, P., Espinosa, G., Millan, C., Saravia, J., Quinteros, V., Enriquez, R., Henriquez, C., Vargas-Chacoff, L., Burgos, R. A., Taubert, A., Hermosilla, C., & Morera, F. J. (2021). Piscirickettsia salmonis-Triggered Extracellular Traps Formation as an Innate Immune Response of Atlantic Salmon-Derived Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils. Biology, 10(3), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030206






