Atmospheric Stilling Promotes Summer Algal Growth in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
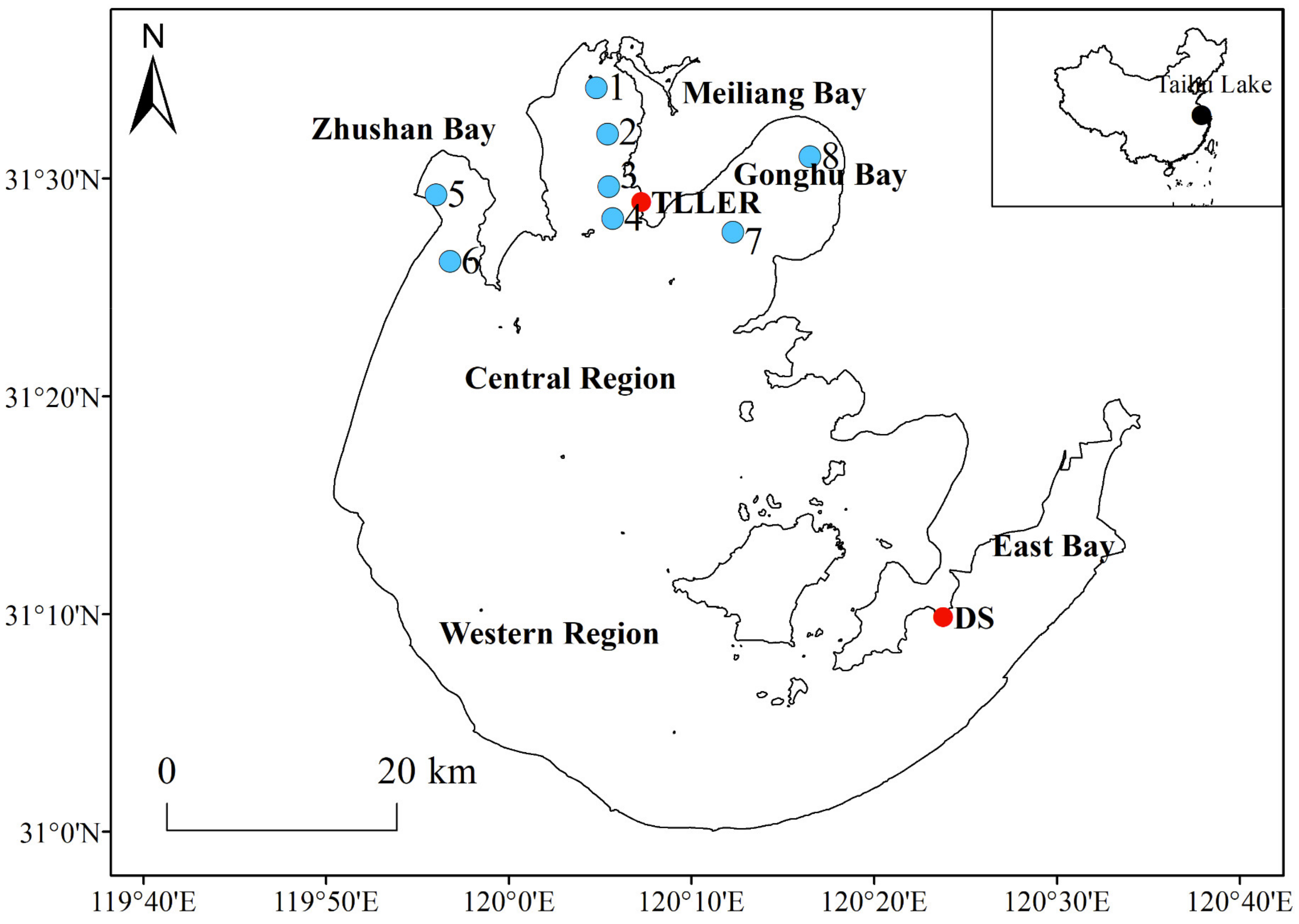
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Monitoring
2.3. Data Analyses
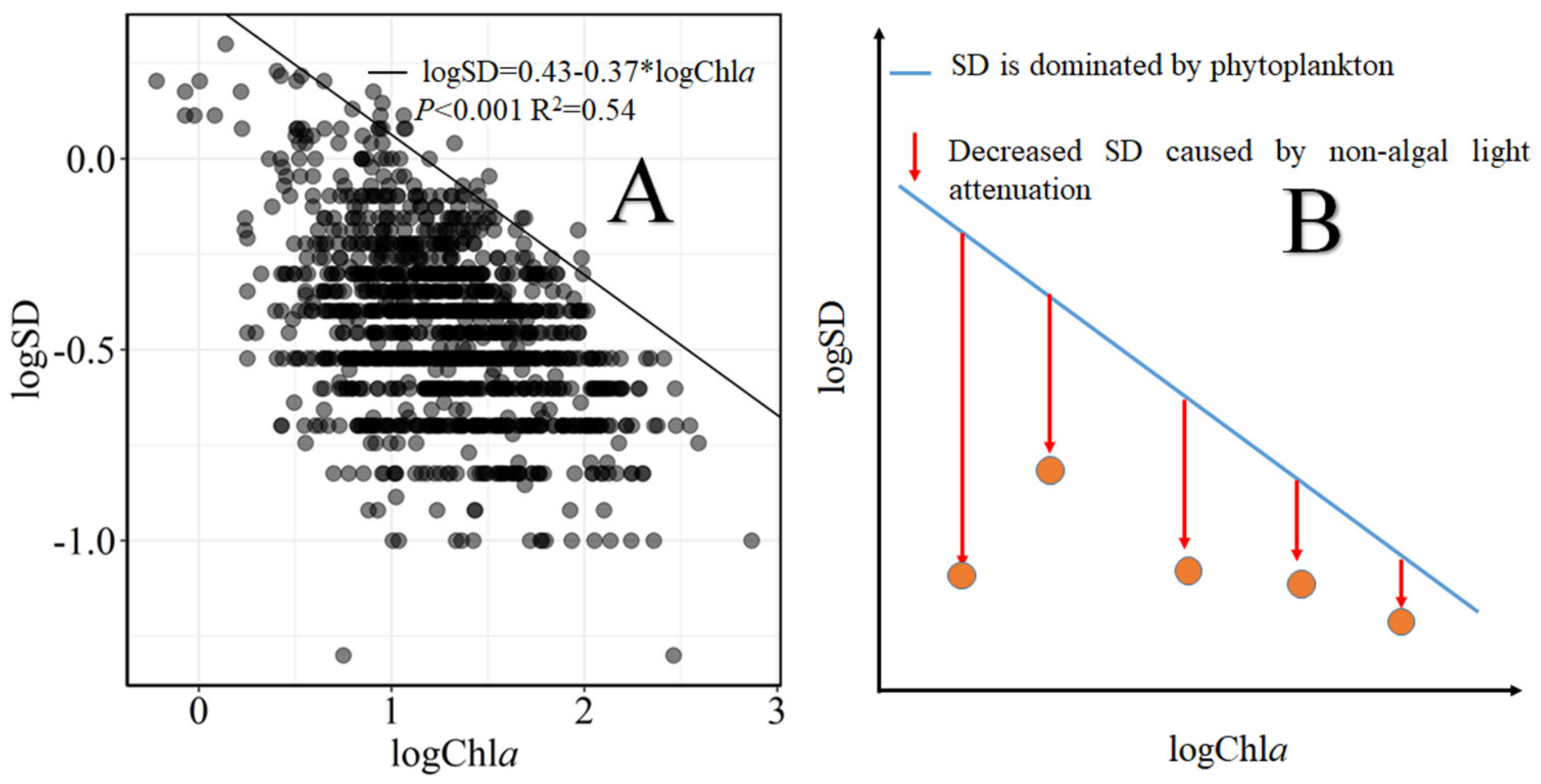
2.3.1. Quantifying the Non-Algal Light Attenuation
2.3.2. Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Spearman Correlation Analysis
2.3.4. Random Forest Model
3. Results
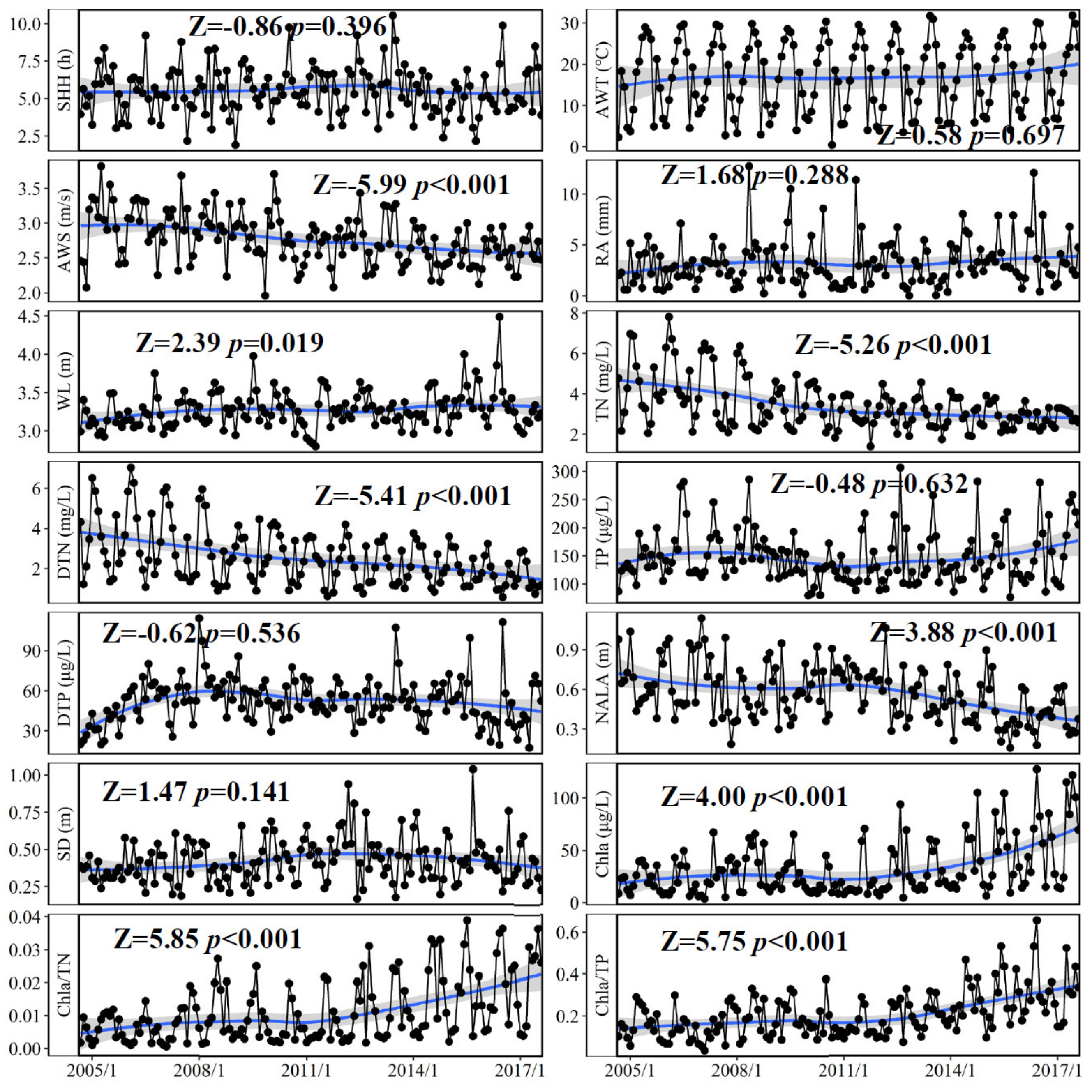
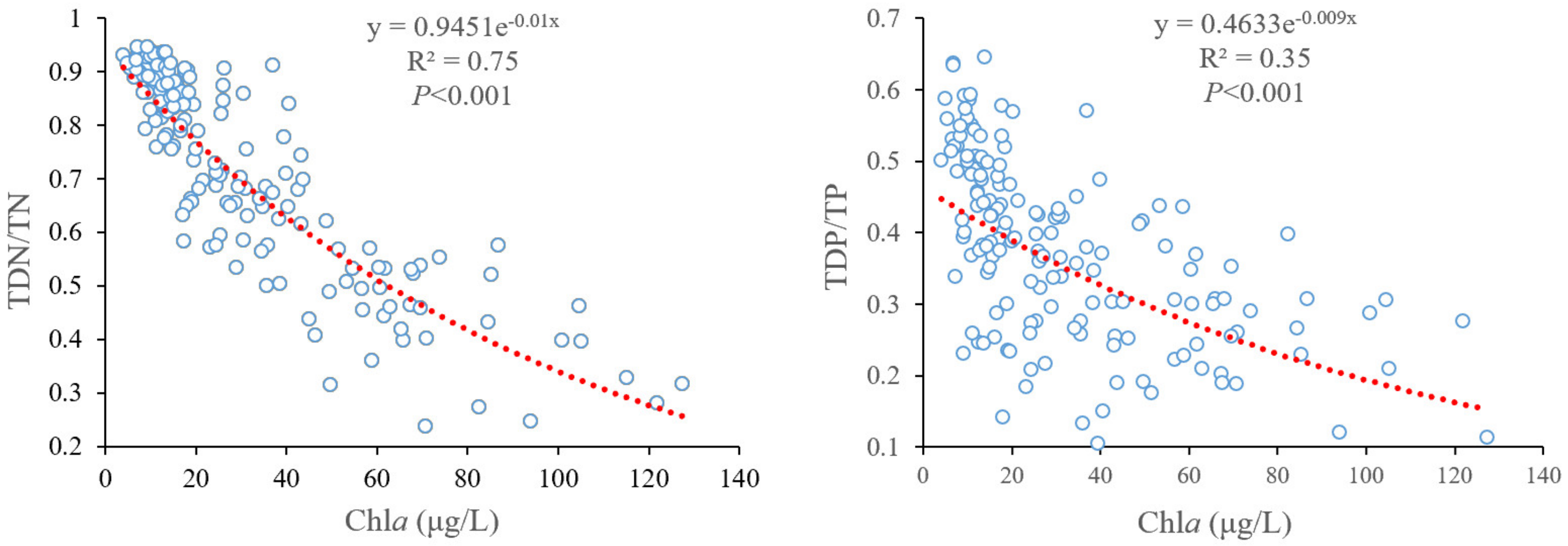
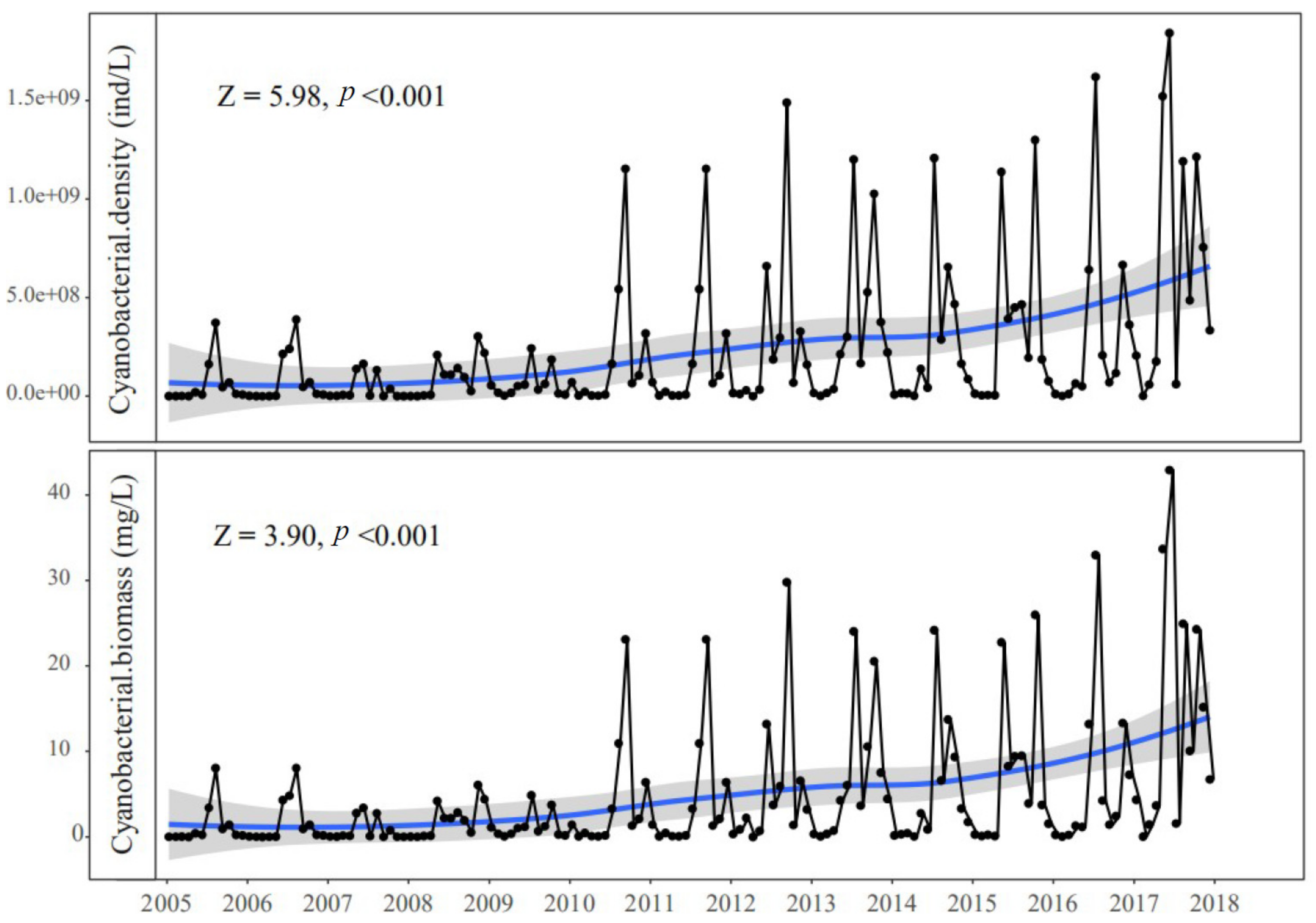
3.1. Trends in Environmental Factors and Chla Yields
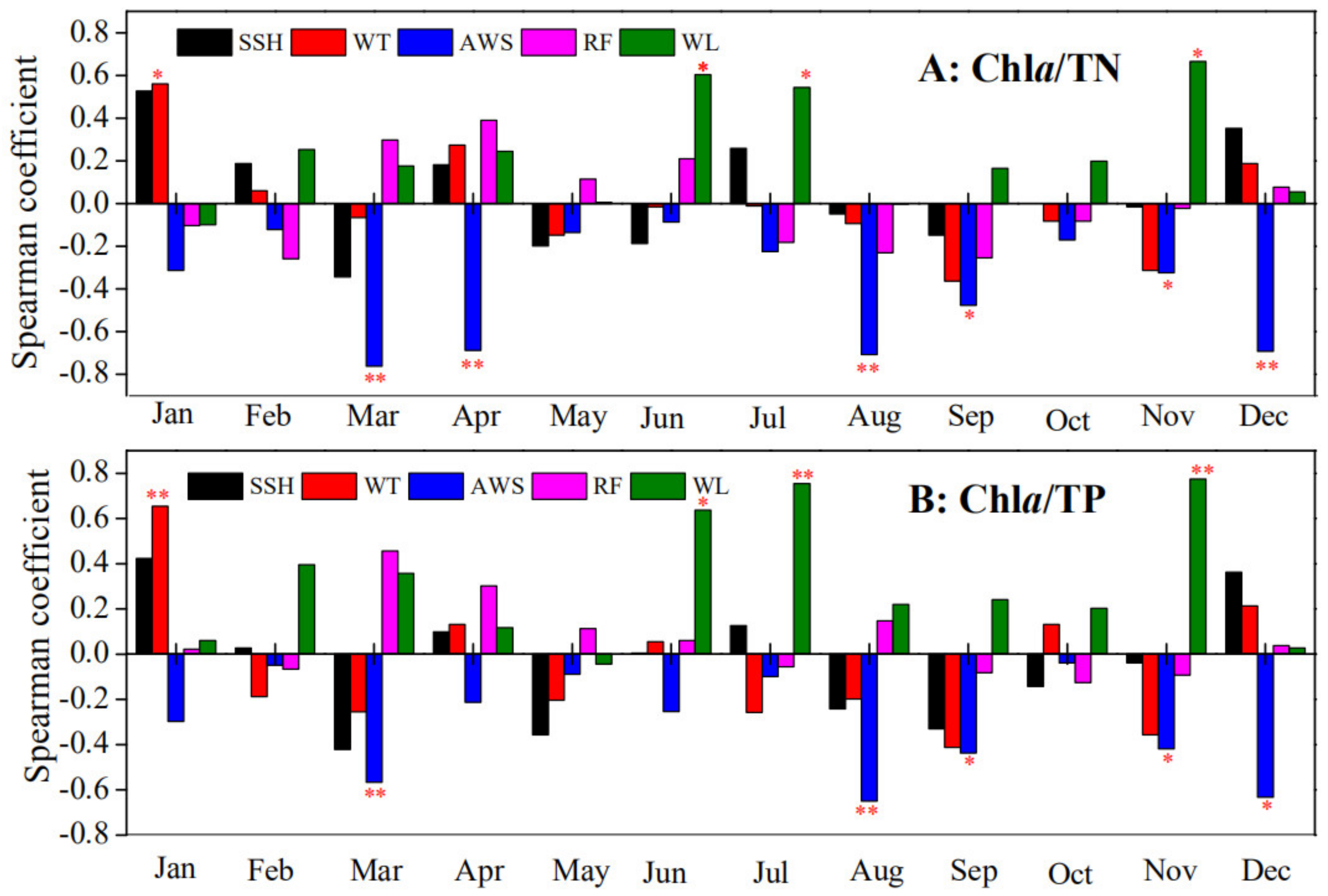
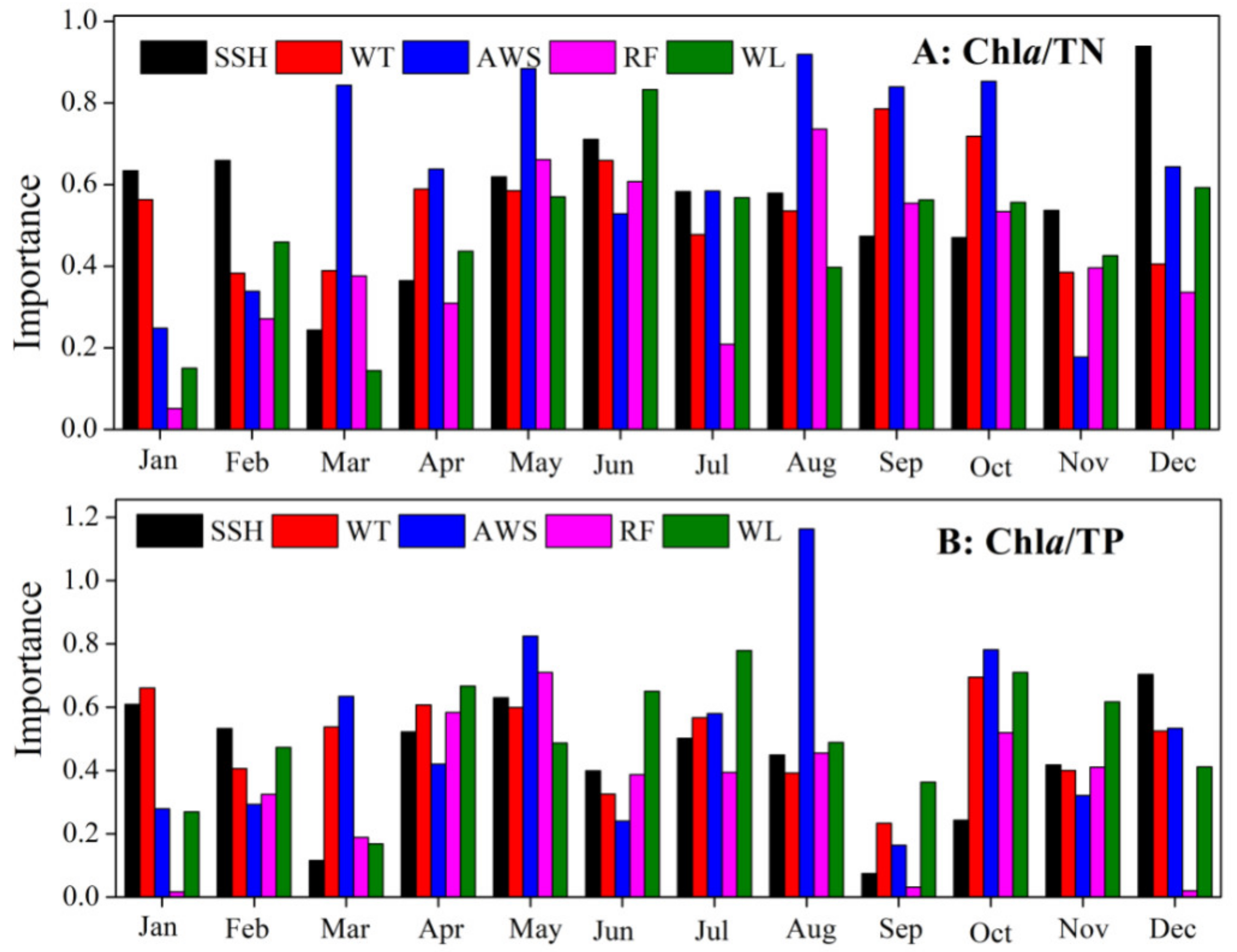
3.2. Chla Yields Driving Force
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Factors Influencing Chla Yields
4.2. Implications for Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B. Lake Taihu, China: Dynamics and Environmental Change; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to Climatic Variability and Lake Management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, A.; Bird, D.F.; Prairie, Y.T.; Lawrence, J.F. Empirical study of cyanobacterial toxicity along a trophic gradient of lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading—An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gaoa, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinlan, R.; Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Blagrave, K.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Gray, D.K.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Relationships of total phosphorus and chlorophyll in lakes worldwide. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Zou, W.; Guo, C.; Ji, P.; Da, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Changing characteristics and driving factors of trophic state of lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River in the past 30 years. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1510–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Yang, H.; Li, K.; Min, S.; Shen, R.; Zhong, C. Variation and driving factors of nutrients and chlorophyll-a concentrations in northern region of Lake Taihu, China, 2005–2017. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, R. China Aims to Turn Tide Against Toxic Lake Pollution. Science 2011, 333, 1210–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Hampel, J.J.; et al. Contributions of external nutrient loading and internal cycling to cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in Lake Taihu, China: Implications for nutrient management. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 1492–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacnik, R.; Solimini, A.G.; Andersen, T.; Tamminen, T.; Brettum, P.; Lepistö, L.; Willén, E.; Rekolainen, S. Diversity predicts stability and resource use efficiency in natural phytoplankton communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5134–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Hillebrand, H.; Heathcote, A.J.; Harpole, W.S.; Downing, J.A. Cyanobacteria dominance influences resource use efficiency and community turnover in phytoplankton and zooplankton communities. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, S.; He, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Xi, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, F.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal impacts of meteorological and geographic factors on the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus to algae in Chinese lakes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janatian, N.; Olli, K.; Cremona, F.; Laas, A.; Nõges, P. Atmospheric stilling offsets the benefits from reduced nutrient loading in a large shallow lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhu, G.; Wu, T.; Li, W.; Shi, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Caruso, A.M. The role of tropical cyclones in stimulating cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, L.; Qin, B. Long-term dynamics and drivers of phytoplankton biomass in eutrophic Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Yang, C.; He, L.-Q.-S.; Dao, G.-H.; Du, J.-S.; Han, Y.-P.; Wu, G.-X.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Hu, H.-Y. Meteorological factors and water quality changes of Plateau Lake Dianchi in China (1990–2015) and their joint influences on cyanobacterial blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Fang, C.; Jacinthe, P.-A.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Xu, X.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, L. Climatic versus Anthropogenic Controls of Decadal Trends (1983–2017) in Algal Blooms in Lakes and Reservoirs across China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Jeppesen, E.; Cai, Y.; Xu, H. Climatically-modulated decline in wind speed may strongly affect eutrophication in shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunlin, Z.; Boqiang, Q.; Guangwei, Z. Long-term changes in physical environments and potential implications for the eco-environment of Lake Taihu in the past four decades. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Paerl, H.W. Climate exerts a greater modulating effect on the phytoplankton community after 2007 in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China: Evidence from 25 years of recordings. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Xu, Z.X. Spatial–temporal characteristics of long-term trends for climate change in the Taihu Basin during 1954 to 2006. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 2009, 18, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.R.; Hubbart, J.A. NOTE: Empirical estimation of non-chlorophyll light attenuation in Missouri reservoirs using deviation from the maximum observed value in the Secchi-Chlorophyll relationship. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, B.S.; Noon, B.R. A gentle introduction to quantile regression for ecologists. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Carvalho, L.; Dudley, B.; May, L. Variation in chlorophyll a to total phosphorus ratio across 94 UK and Irish lakes: Implications for lake management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 115, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Broberg, N. Increasing algal biomass in Lake Vänern despite decreasing phosphorus concentrations: A lake-specific phenomenon? Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2014, 17, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Brookes, J.D.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Yan, W.; Wang, Z. The influence of changes in wind patterns on the areal extension of surface cyanobacterial blooms in a large shallow lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wofsy, S.C. A simple model to predict extinction coefficients and phytoplankton biomass in eutrophic waters 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, T. The effect of resuspension on algal production in a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 1991, 213, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phlips, E.J.; Aldridge, F.J.; Schelske, C.L.; Crisman, T.L. Relationships between light availability, chlorophyll a, and tripton in a large, shallow subtropical lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, C.; Diehl, S.; Schmidt, G.M. Influence of water-column depth and mixing on phytoplankton biomass, community composition, and nutrients. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gameiro, C.; Zwolinski, J.; Brotas, V. Light control on phytoplankton production in a shallow and turbid estuarine system. Hydrobiologia 2011, 669, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Qin, B.; Liu, G.; Li, Y. Long-term remote monitoring of total suspended matter concentration in Lake Taihu using 250m MODIS-Aqua data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Sharples, J.; Stroom, J.M.; Visser, P.M.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sommeijer, B. Changes in Turbulent Mixing Shift Competition for Light between Phytoplankton Species. Ecology 2004, 85, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posch, T.; Köster, O.; Salcher, M.; Pernthaler, J. Harmful filamentous cyanobacteria favoured by reduced water turnover with lake warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Maberly, S.C. Photoinhibition and the availability of inorganic carbon restrict photosynthesis by surface blooms of cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Duan, H.; Shi, X.; Yu, Y.; Kong, F. Contributions of meteorology to the phenology of cyanobacterial blooms: Implications for future climate change. Water Res. 2012, 46, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torremorell, A.; Llames, M.E.; Pérez, G.L.; Escaray, R.; Bustingorry, J.; Zagarese, H. Annual patterns of phytoplankton density and primary production in a large, shallow lake: The central role of light. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.J.; Rigler, F.H. The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes 1, 2. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.; Hall, N.S.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The persistence of cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms throughout winter in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 61, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, R.E.; Havens, K.E. Simple Graphical Methods for the Interpretation of Relationships Between Trophic State Variables. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautard, R.; Cattiaux, J.; Yiou, P.; Thépaut, J.-N.; Ciais, P. Northern Hemisphere atmospheric stilling partly attributed to an increase in surface roughness. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, W.; Zhu, G.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Guo, C.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y. Atmospheric Stilling Promotes Summer Algal Growth in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. Biology 2021, 10, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121222
Zou W, Zhu G, Xu H, Zhu M, Guo C, Qin B, Zhang Y. Atmospheric Stilling Promotes Summer Algal Growth in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121222
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Wei, Guangwei Zhu, Hai Xu, Mengyuan Zhu, Chaoxuan Guo, Boqiang Qin, and Yunlin Zhang. 2021. "Atmospheric Stilling Promotes Summer Algal Growth in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes" Biology 10, no. 12: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121222
APA StyleZou, W., Zhu, G., Xu, H., Zhu, M., Guo, C., Qin, B., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Atmospheric Stilling Promotes Summer Algal Growth in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. Biology, 10(12), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121222







