Activity of TREK-2-like Channels in the Pyramidal Neurons of Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cytoplasmic Calcium
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.2. Electrophysiological Recordings
3. Results
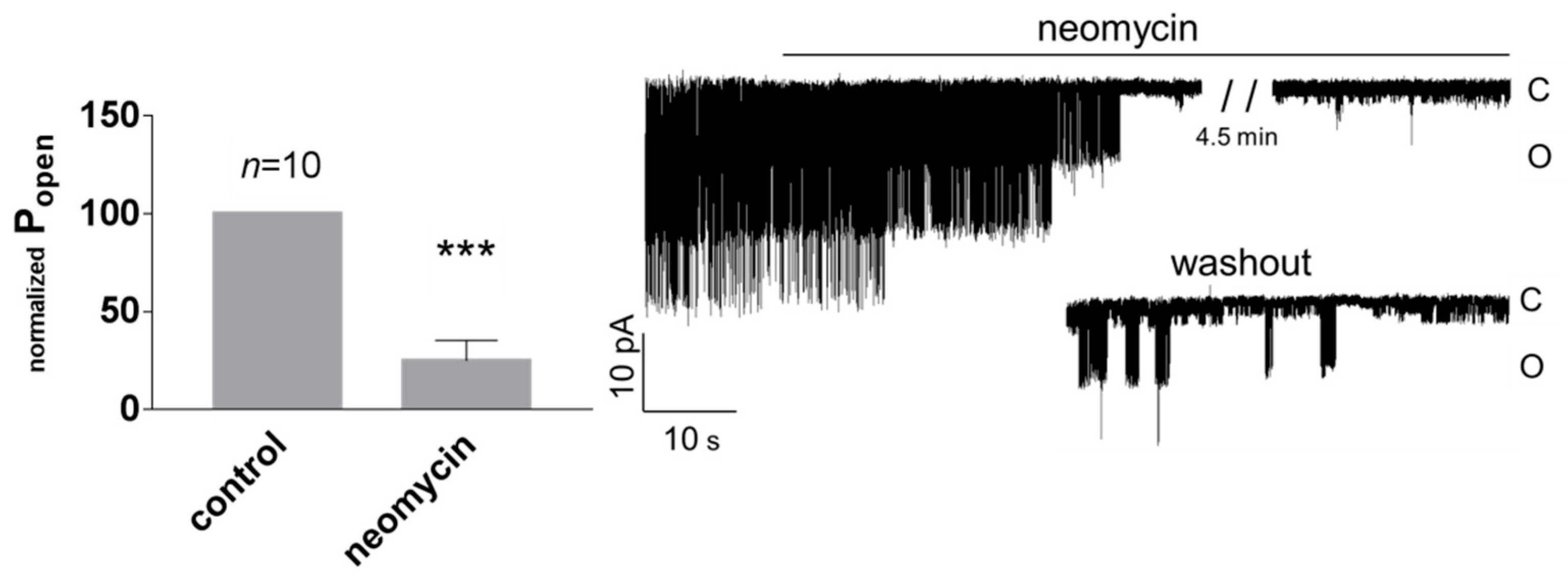
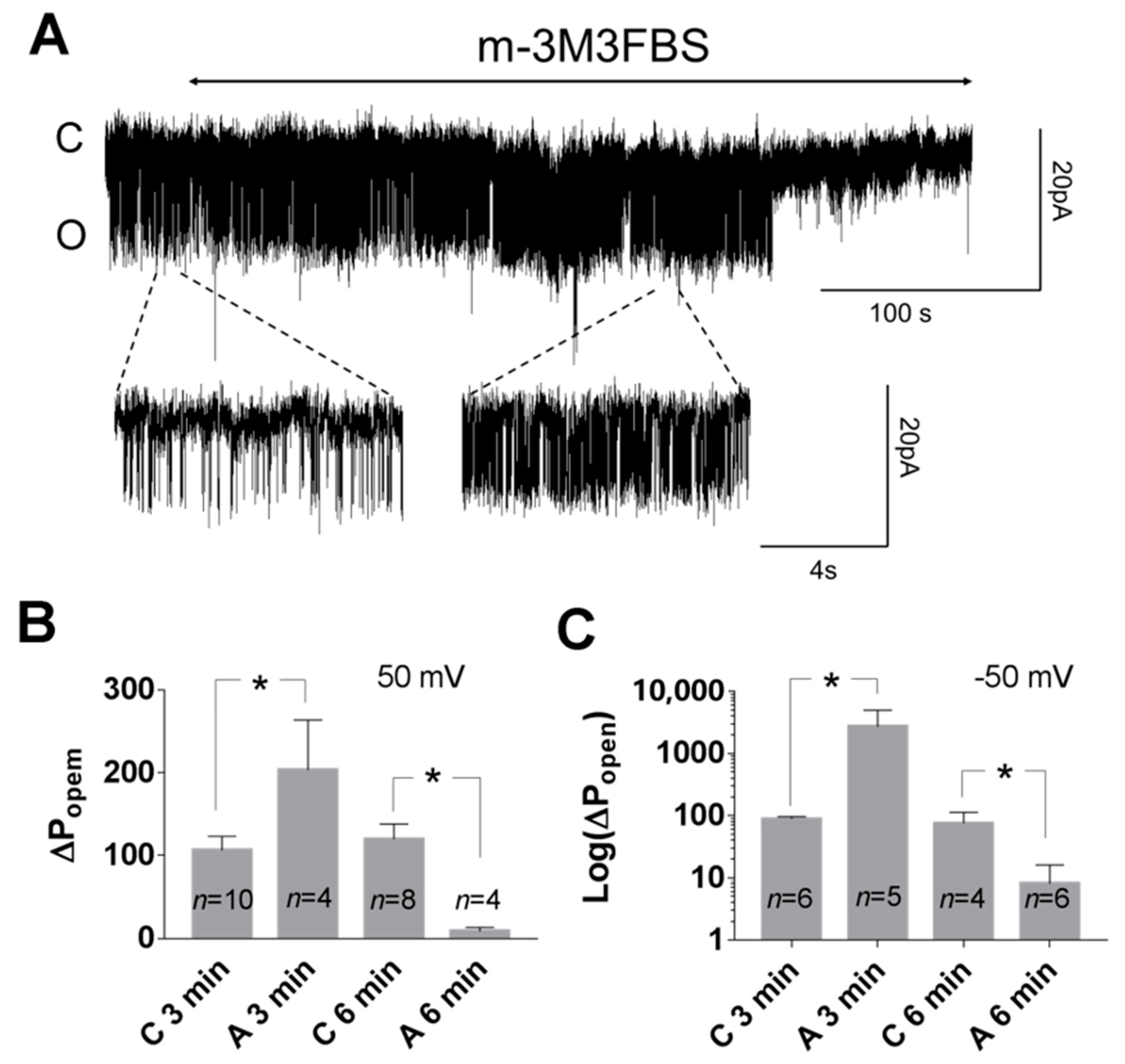
3.1. Role of Calcium in TREK-2-Like Channel Activation
3.2. Pattern of TREK-2-Like Channel Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, J.N.; Grafman, J.H. Human prefrontal cortex: Processing and representational perspectives. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobson, D.D.; Hase, Y.; Clarkson, A.N.; Kalaria, R.N. The role of the medial prefrontal cortex in cognition, ageing and dementia. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Xing, X.; Lu, H. Medial prefrontal cortex in neurological diseases. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Agarwal, P.; Ravichandiran, V. Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channel in Neurological Disorders. J. Membr. Biol. 2021, 254, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, F.; Terrenoire, C.; Romey, G.; Lazdunski, M. Human TREK2, a 2P Domain Mechano-sensitive K+Channel with Multiple Regulations by Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Lysophospholipids, and Gs, Gi, and Gq Protein-coupled Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28398–28405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heurteaux, C.; Lucas, G.; Guy, N.; El Yacoubi, M.; Thümmler, S.; Peng, X.-D.; Noble, F.; Blondeau, N.; Widmann, C.; Borsotto, M.; et al. Deletion of the background potassium channel TREK-1 results in a depression-resistant phenotype. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Sun, H.; Gong, W.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Shan, H.; Zhang, Z. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of two-pore domain potassium channel TREK-1 alters depression-related behaviors and neuronal plasticity in the hippocampus in mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thümmler, S.; Duprat, F.; Lazdunski, M. Antipsychotics inhibit TREK but not TRAAK channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djillani, A.; Mazella, J.; Heurteaux, C.; Borsotto, M. Role of TREK-1 in Health and Disease, Focus on the Central Nervous System. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Yu, B. Recent advance and possible future in TREK-2: A two-pore potassium channel may involved in the process of NPP, brain ischemia and memory impairment. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, J.A.; Fernández-Fernández, D. Tandem pore TWIK-related potassium channels and neuroprotection. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1293–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Méndez-Reséndiz, K.A.; Oviedo, N.; Murbartián, J. PKC- and PKA-dependent phosphorylation modulates TREK-1 function in naïve and neuropathic rats. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Lee, D.K.; Hong, S.-G.; Han, J.; Kang, D. Activation of TREK-1, but Not TREK-2, Channel by Mood Stabilizers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurteaux, C.; Guy, N.; Laigle, C.; Blondeau, N.; Duprat, F.; Mazzuca, M.; Lang-Lazdunski, L.; Widmann, C.; Zanzouri, M.; Romey, G.; et al. TREK-1, a K+ channel involved in neuroprotection and general anesthesia. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2684–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsotto, M.; Veyssiere, J.; Maati, H.M.O.; DeVader, C.; Mazella, J.; Heurteaux, C. Targeting two-pore domain K+channels TREK-1 and TASK-3 for the treatment of depression: A new therapeutic concept. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 172, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Choe, C.; Kim, D. Thermosensitivity of the two-pore domain K+channels TREK-2 and TRAAK. J. Physiol. 2005, 564, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brohawn, S. How ion channels sense mechanical force: Insights from mechanosensitive K2P channels TRAAK, TREK1, and TREK2. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1352, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, J.; Sandoz, G.; Lesage, F. Molecular regulations governing TREK and TRAAK channel functions. Channels 2011, 5, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.R.; Anderson, E.O.; Gracheva, E.O.; Bagriantsev, S.N. Temperature Sensitivity of Two-Pore (K2P) Potassium Channels. In Current Topics in Membranes; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 74, pp. 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi, P.; Czirják, G. Molecular Background of Leak K+ Currents: Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channels. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 559–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Jun, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Nam, J.H.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, S.J. Identification of critical amino acids in the proximal C-terminal of TREK-2 K+ channel for activation by acidic pHi and ATP-dependent inhibition. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2018, 470, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, J.T.; de Groot, B.L. Mechanism of Mechanosensitive Gating of the TREK-2 Potassium Channel. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClenaghan, C.; Schewe, M.; Aryal, P.; Carpenter, L.; Baukrowitz, T.; Tucker, S.J. Polymodal activation of the TREK-2 K2P channel produces structurally distinct open states. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 147, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Ramírez, P.; Reboreda, A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Herrera-Pérez, S.; Lamas, J.A. Contribution of KCNQ and TREK Channels to the Resting Membrane Potential in Sympathetic Neurons at Physiological Temperature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Pérez, S.; Campos-Ríos, A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Lamas, J.A. Contribution of K2P potassium channels to cardiac phys-iology and pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, J.; Patel, A.J.; Duprat, F.; Lauritzen, I.; Lazdunski, M.; Honoré, E. A phospholipid sensor controls mechanogating of the K+ channel TREK-1. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Gnatenco, C.; Bang, H.; Kim, D. Localization of TREK-2 K + channel domains that regulate channel kinetics and sensitivity to pressure, fatty acids and pHi. Pflug. Arch. 2001, 442, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingret, F.; Patel, A.J.; Lesage, F.; Lazdunski, M.; Honore, E. Mechano- or Acid Stimulation, Two Interactive Modes of Activation of the TREK-1 Potassium Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26691–26696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Soussia, I.; Choveau, F.S.; Blin, S.; Kim, E.-J.; Feliciangeli, S.; Chatelain, F.C.; Kang, D.; Bichet, D.; Lesage, F. Antagonistic Effect of a Cytoplasmic Domain on the Basal Activity of Polymodal Potassium Channels. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoz, G.; Bell, S.C.; Isacoff, E. Optical probing of a dynamic membrane interaction that regulates the TREK1 channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.N.; Pavel, M.A.; Wang, H.; Hansen, S.B. Disruption of palmitate-mediated localization; a shared pathway of force and anesthetic activation of TREK-1 channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Ramírez, P.; Reboreda, A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Herrera-Pérez, S.; Lamas, J.A. PIP2 Mediated Inhibition of TREK Potassium Currents by Bradykinin in Mouse Sympathetic Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, P.; Pawlowski, M.; Cerina, M.; Ehling, P.; Leist, M.; Meuth, P.; Aissaoui, A.; Borsotto, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Decher, N.; et al. Differential phospholipase C-dependent modulation of TASK and TREK two-pore domain K+channels in rat thalamocortical relay neurons. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murbartián, J.; Lei, Q.; Sando, J.J.; Bayliss, D.A. Sequential Phosphorylation Mediates Receptor- and Kinase-induced Inhibition of TREK-1 Background Potassium Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30175–30184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Han, J.; Kim, D. Mechanism of inhibition of TREK-2 (K2P10.1) by the Gq-coupled M3 muscarinic receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2006, 291, C649–C656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ładno, W.; Gawlak, M.; Szulczyk, P.; Nurowska, E. Kinetic properties and adrenergic control of TREK-2-like channels in rat medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 2017, 1665, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.M.; Remon, J.I.; Matavel, A.; Sui, J.L.; Keselman, I.; Medei, E.; Shen, Y.; Rosenhouse-Dantsker, A.; Logothetis, D.E. Protein Kinase A Modulates PLC-Dependent Regulation and PIP2-Sensitivity of K+Channels. Channels 2007, 1, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, J.; Patel, A.J.; Duprat, F.; Sachs, F.; Lazdunski, M.; Honore, E. Up- and down-regulation of the mechano-gated K2P channel TREK-1 by PIP2 and other membrane phospholipids. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2007, 455, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yoo, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, S.J. Inhibition of TREK-2 K+ channels by PI(4,5)P2: An intrinsic mode of regulation by intracellular ATP via phosphatidylinositol kinase. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2016, 468, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.; Jeon, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.H.; Nam, J.H.; Shin, N.H.; Kim, S.J. Triple arginine residues in the proximal C-terminus of TREK K+ channels are critical for biphasic regulation by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C312–C324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.-H.; Woo, J.; Kim, A.S.J. Dual regulatory effects of PI(4,5)P2 on TREK-2 K+ channel through antagonizing interaction between the alkaline residues (K330 and R355-357) in the cytosolic C-terminal helix. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 24, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanos, C.; Wang, M.; Han, X.; Hansen, S.B. A Soluble Fluorescent Binding Assay Reveals PIP 2 Antagonism of TREK-1 Channels. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlak, M.; Szulczyk, B.; Berłowski, A.; Grzelka, K.; Stachurska, A.; Pełka, J.; Czarzasta, K.; Małecki, M.; Kurowski, P.; Nurowska, E.; et al. Age-dependent expression of Nav1.9 channels in medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons in rats. Dev. Neurobiol. 2017, 77, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworakowska, B.; Nurowska, E.; Dołowy, K. Hydrocortisone inhibition of wild-type and αD200Q nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 92, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurowska, E.; Adamiec, M.; Dworakowska, B. Extracellular divalent ions modulate TREK-2-like channel conductance in prefrontal pyramidal neurons in rats. Med. Res. J. 2019, 4, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Schlichthörl, G.; Hirsch, J.R.; Engels, H.; Karschin, C.; Karschin, A.; Derst, C.; Steinlein, O.K.; Daut, J. Expression pattern and functional characteristics of two novel splice variants of the two-pore-domain potassium channel TREK-2. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Truell, J.; Gnatenco, C.; Kim, D. Characterization of four types of background potassium channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons. J. Physiol. 2002, 542, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.A.N.; Bockenhauer, D.; O’Kelly, I.; Zilberberg, N. Potassium leak channels and the KCNK family of two-p-domain subunits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Han, T.W.; Nassar, L.; Zubia, M.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Phosphatidylinositol-(4, 5)-bisphosphate regulates calcium gating of small-conductance cation channel TMEM16F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1667–E1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.; Bermeo, K.; Arenas, I.; Garcia, D.E. Maintenance of CaV2.2 channel-current by PIP2 unveiled by neomycin in sympathetic neurons of the rat. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 682, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myeong, J.; Park, C.-G.; Suh, B.-C.; Hille, B. Compartmentalization of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism into plasma membrane liquid-ordered/raft domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025343118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, L.F.; Hirdes, W.; Suh, B.-C.; Hilgemann, D.W.; Mackie, K.; Hille, B. Phospholipase C in Living Cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 126, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krjukova, J.; Holmqvist, T.; Danis, A.S.; Åkerman, K.E.; Kukkonen, J.P. Phospholipase C activatorm-3M3FBS affects Ca2+ homeostasis independently of phospholipase C activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Pagán, A.F.; Rivera-Aponte, D.E.; Melnik-Martínez, K.V.; Zayas-Santiago, A.; Kucheryavykh, L.Y.; Martins, A.H.; Cubano, L.A.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Eaton, M.J. Up-Regulation of TREK-2 Potassium Channels in Cultured Astrocytes Requires De Novo Protein Synthesis: Relevance to Localization of TREK-2 Channels in Astrocytes after Transient Cerebral Ischemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kucheryavykh, L.Y.; Kucheryavykh, Y.V.; Inyushin, M.; Shuba, Y.M.; Sanabria, P.; Cubano, L.A.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Eaton, M.J. Ischemia Increases TREK-2 Channel Expression in Astrocytes: Relevance to Glutamate Clearance. Open Neurosci. J. 2009, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Honoré, E. The neuronal background K2P channels: Focus on TREK1. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Vogt, V.M.; Feigenson, G.W. Multivalent Cation-Bridged PI(4,5)P2 Clusters Form at Very Low Concentrations. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2630–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, M.J.; Coutinho, A.; Fedorov, A.; Prieto, M.; Fernandes, F. Ca2+ induces PI(4,5)P2 clusters on lipid bilayers at physiological PI(4,5)P2 and Ca2+ concentrations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Collins, A.; Guo, L.; Smith-Dupont, K.B.; Gai, F.; Svitkina, T.; Janmey, P.A. Divalent Cation-Induced Cluster Formation by Polyphosphoinositides in Model Membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.; Rohacs, T.; Hansen, S.B. Tools for Understanding Nanoscale Lipid Regulation of Ion Channels. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 9Clapham, D.E. Calcium Signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipp, P.; Reither, G. Protein Kinase C: The “Masters” of Calcium and Lipid. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.M.; Shapiro, M.S. Gq-coupled muscarinic receptor enhancement of KCNQ2/3 channels and activation of TRPC channels in multimodal control of excitability in dentate gyrus granule cells. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 1566–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenburger, B.H.; Jensen, J.B.; Hille, B. Kinetics of PIP2 metabolism and KCNQ2/3 channel regulation studied with a voltage-sensitive phosphatase in living cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 2010, 135, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Ho, W.-K. Hydrogen peroxide selectively increases TREK-2 currents via myosin light chain kinases. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Książek, A.; Ładno, W.; Szulczyk, B.P.; Grzelka, K.; Szulczyk, P.J. Properties of BK-type Ca++-dependent K+ channel currents in medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons in rats of different ages. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzkiewicz-Jałowiecka, A.; Trybek, P.; Machura, Ł.; Dworakowska, B.; Grzywna, Z.J. Mechanosensitivity of the BK Channels in Human Glioblastoma Cells: Kinetics and Dynamical Complexity. J. Membr. Biol. 2018, 251, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingret, F.; Honore, E.; Lazdunski, M.; Patel, A.J. Molecular Basis of the Voltage-Dependent Gating of TREK-1, a Mechano-Sensitive K+ Channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewe, M.; Nematian-Ardestani, E.; Sun, H.; Musinszki, M.; Cordeiro, S.; Bucci, G.; de Groot, B.L.; Tucker, S.J.; Rapedius, M.; Baukrowitz, T. A Non-canonical Voltage-Sensing Mechanism Controls Gating in K2P K+ Channels. Cell 2016, 164, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulczyk, B.; Pasierski, M.; Nurowska, E. Valproic acid potently inhibits interictal-like epileptiform activity in prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 708, 134350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasierski, M.; Szulczyk, B. Capsaicin inhibits sodium currents and epileptiform activity in prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 135, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dworakowska, B.; Gawlak, M.; Nurowska, E. Activity of TREK-2-like Channels in the Pyramidal Neurons of Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cytoplasmic Calcium. Biology 2021, 10, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111119
Dworakowska B, Gawlak M, Nurowska E. Activity of TREK-2-like Channels in the Pyramidal Neurons of Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cytoplasmic Calcium. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111119
Chicago/Turabian StyleDworakowska, Beata, Maciej Gawlak, and Ewa Nurowska. 2021. "Activity of TREK-2-like Channels in the Pyramidal Neurons of Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cytoplasmic Calcium" Biology 10, no. 11: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111119
APA StyleDworakowska, B., Gawlak, M., & Nurowska, E. (2021). Activity of TREK-2-like Channels in the Pyramidal Neurons of Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cytoplasmic Calcium. Biology, 10(11), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111119



