Characteristics of Neurokinin-3 Receptor and Its Binding Sites by Mutational Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance and Growth
2.2. NKB & NKF Peptide Synthesis
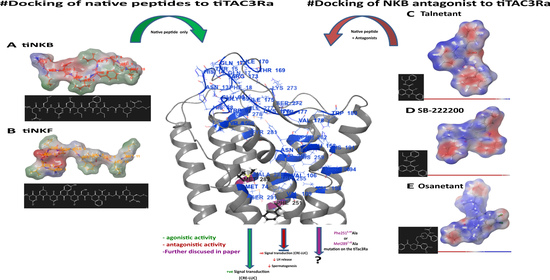
2.3. Structure Prediction, Homology Modelling and Molecular Docking
2.4. Construction of F251A and M289A tiTac3Ra Expression Vector
2.5. Construction of tiTac3Ra Fused to GFP
2.6. Receptor Transactivation Assay
2.7. ELISAs for the Measurement of Tilapia FSH LH and GH
2.8. In Vivo Effect of Non-Peptide NKB Antagonists
2.9. In Vivo Effect of NKB Antagonist on Sperm Production in Tilapia
2.10. Testicular Histology and Quantification of Cell Composition
2.11. 11-Ketotestosterone (11-KT) Analysis
3. Results
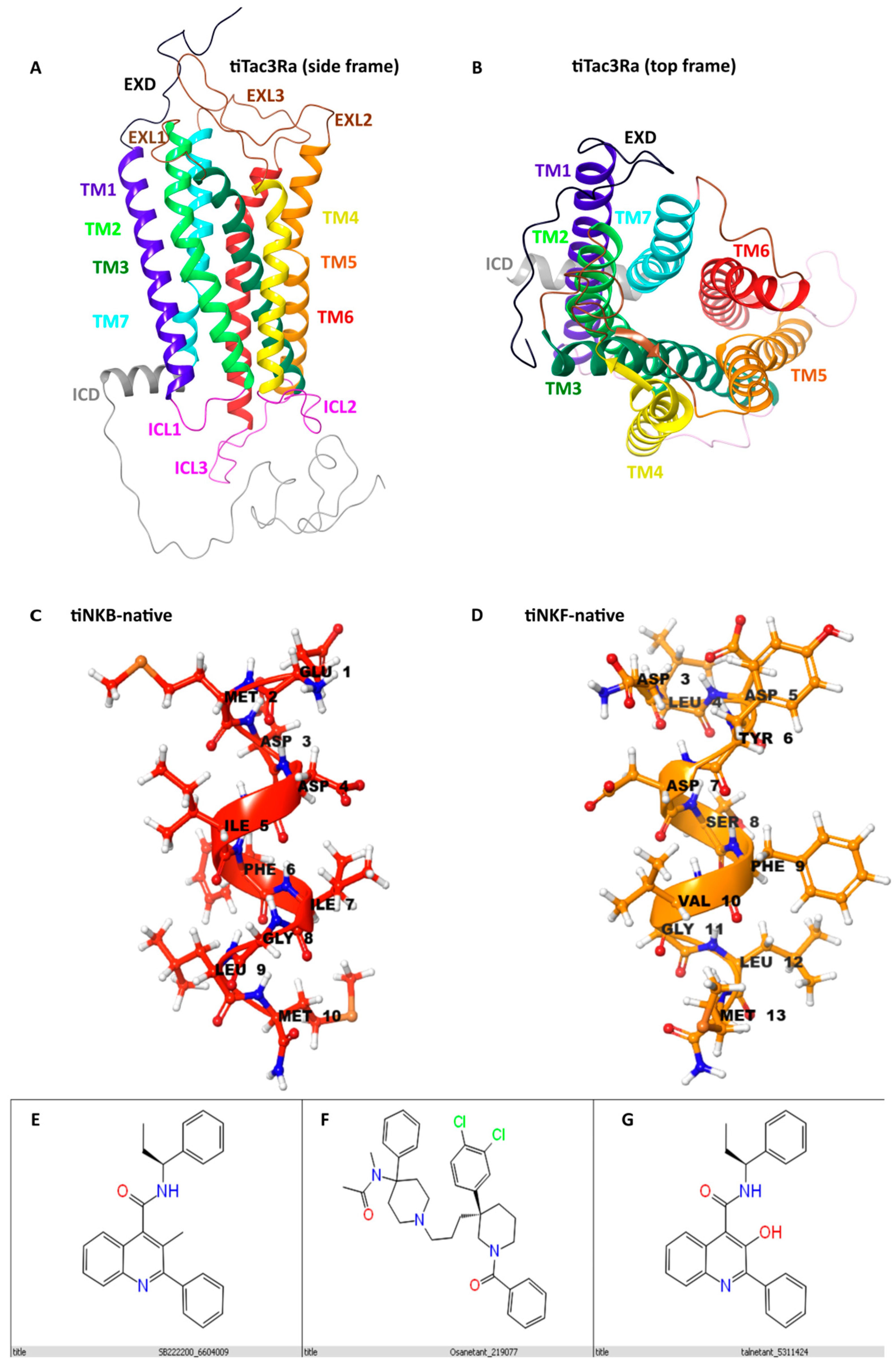
3.1. Homology Modelling
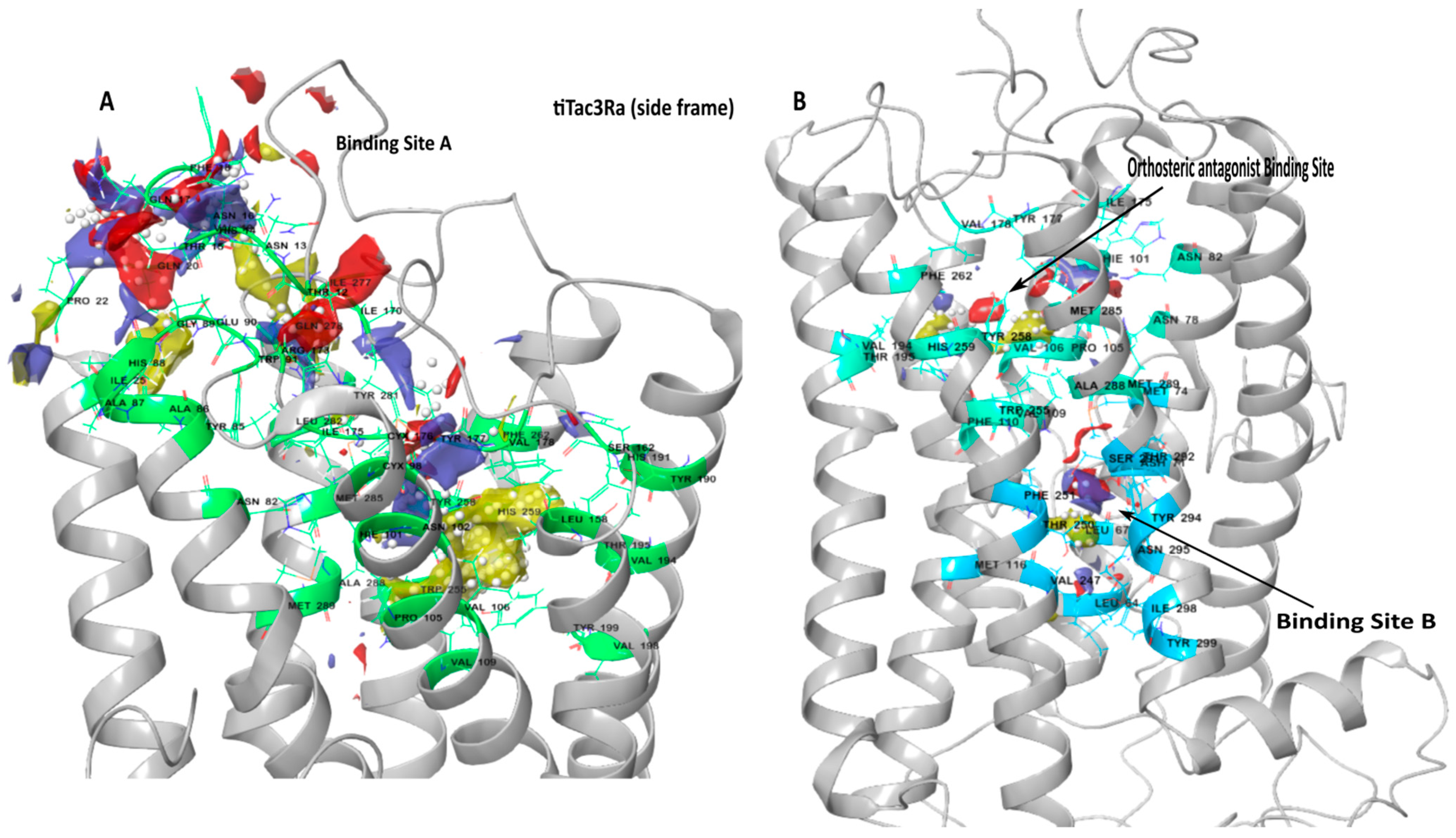
3.2. Binding Site Detection
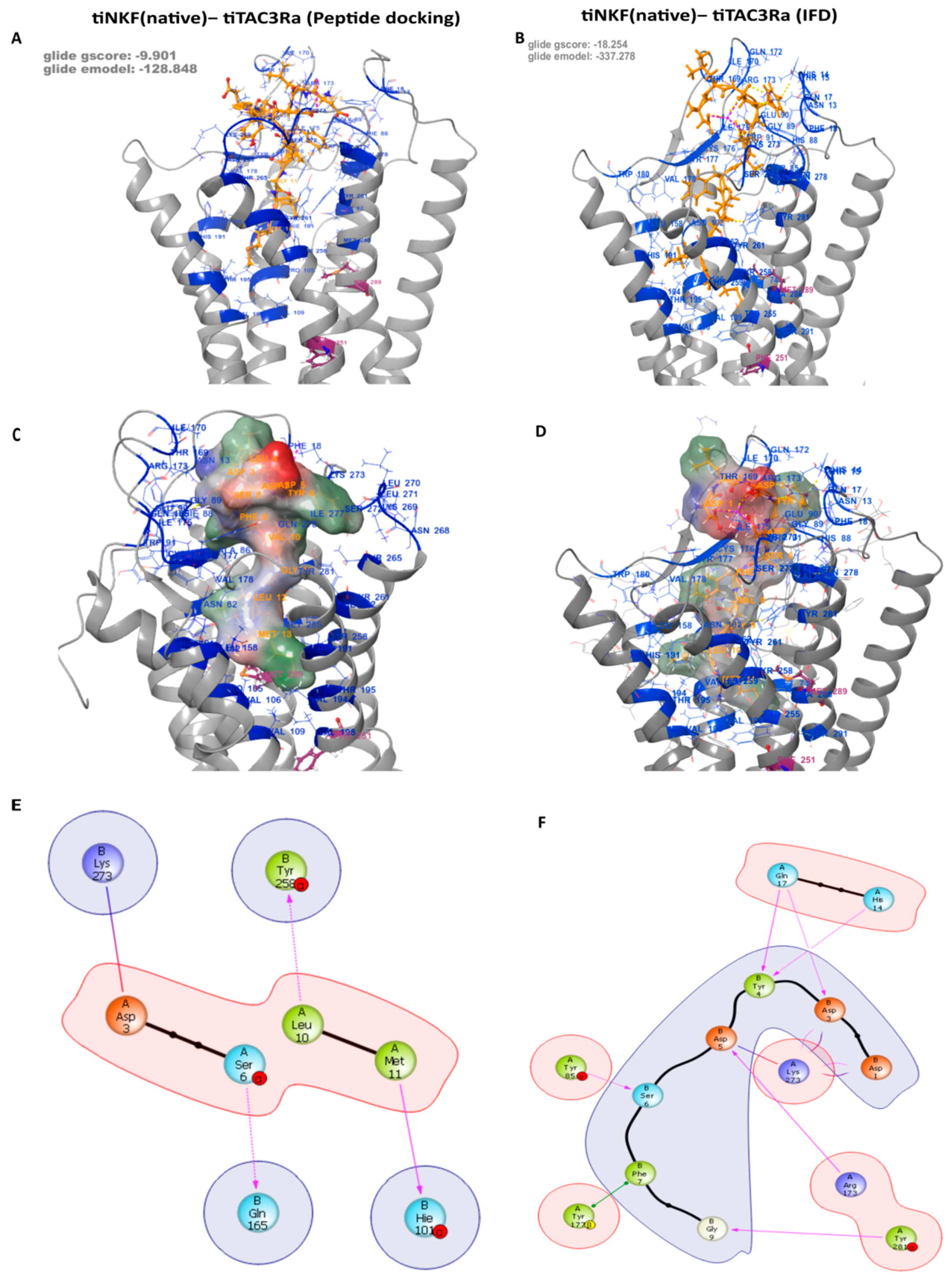
3.3. Peptide Docking and Induced Fit Docking
| Residue on NKF | Specific Interactions with Residue on tiTac3Ra | Position on tiTac3Ra |
|---|---|---|
| B:1:Asp | 1× hb, 1× salt bridge to A:273:Lys | EXL3 |
| B:3:Asp | 1× hb, 2× clash to A:17:Gln | EXD |
| 1× hb, 1× salt bridge to A:273:Lys | EXL3 | |
| B:4:Tyr | 1× hb to A:14:His | EXD |
| 1× hb to A:17:Gln | EXD | |
| 2× clash to A:90:Glu | EXL1 | |
| B:5:Asp | 2× hb, 1× clash to A:173:Arg | EXL2 |
| 1× salt bridge, 2× clash to A:273:Lys | EXL3 | |
| B:6:Ser | 1× hb to A:85:Tyr | TM2 |
| B:7:Phe | 1× pi stack to A:177:Tyr | EXL2 |
| B:9:Gly | 1× hb to A:281:Tyr | TM7 |
| B:11:Met | 1× clash to A:258:Tyr | TM6 |
| Residue on NKF | Specific Interactions with Residue on tiTac3Ra | Position on tiTac3Ra |
|---|---|---|
| B:3:Asp | 1× hb, 1× clash to A:17:Gln | EXD |
| 1× clash to A:170:Ile | EXL2 | |
| 1× salt bridge, 1× clash to A:273:Lys | EXL3 | |
| B:4:Asp | 1× hb to A:173:Arg | EXL2 |
| 1× hb to A:273:Lys | EXL3 | |
| B:5:Ile | 2× clash to A:272:Ser | EXL3 |
| B:6:Phe | 1× hb to A:173:Arg | EXL2 |
| 1× hb to A:272:Ser | EXL3 | |
| B:7:Ile | 1× clash to A:18:Phe | EXD |
| 1× clash to A:173:Arg | EXL2 | |
| B:8:Gly | 1× hb to A:177:Tyr | EXL2 |
| B:9:Leu | 1× clash to A:85:Tyr | TM2 |
| 1× hb to A:281:Tyr | TM7 | |
| B:10:Met | 1× hb to A:177:Tyr | EXL2 |
| 2× clash to A:261:Tyr | TM6 | |
| 4× clash to A:262:Phe | TM6 | |
| 1× clash to A:265:Thr | TM6 |
3.4. Residue Mutation Analysis
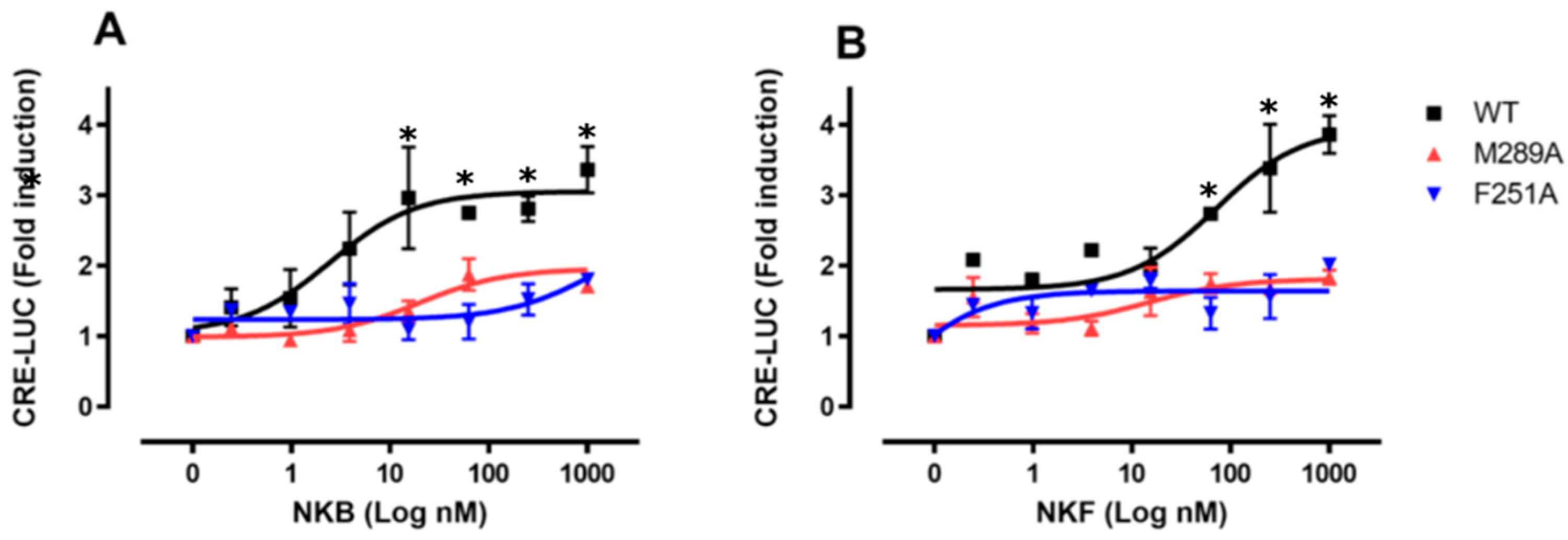
3.5. In Vitro Luciferase Assay for Peptide Induced Activity
3.6. Antagonist Binding and Activity
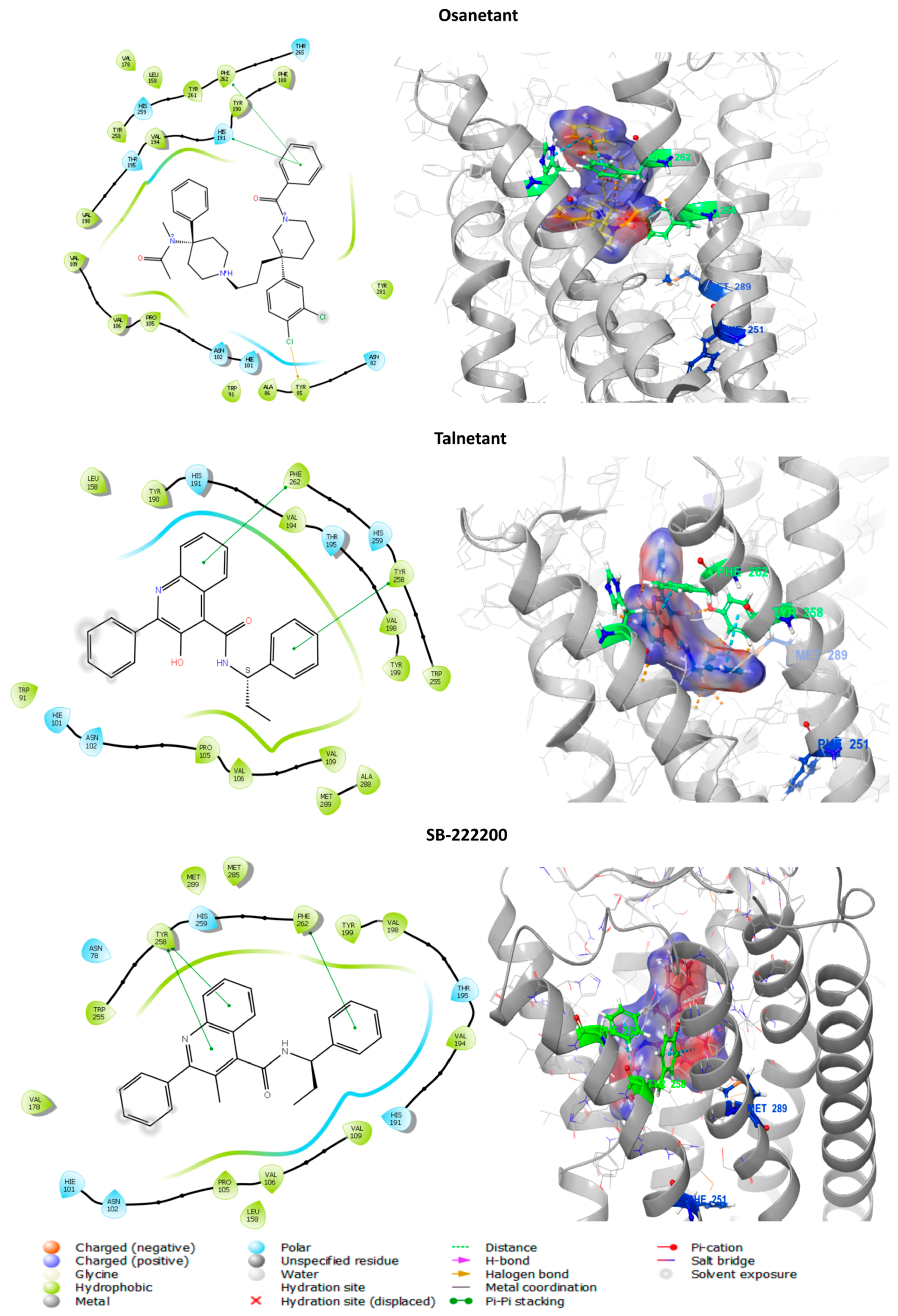
3.6.1. In Silico Binding of Antagonist to tiTac3Ra
3.6.2. In Vitro Luciferase Assay of Antagonist Activity
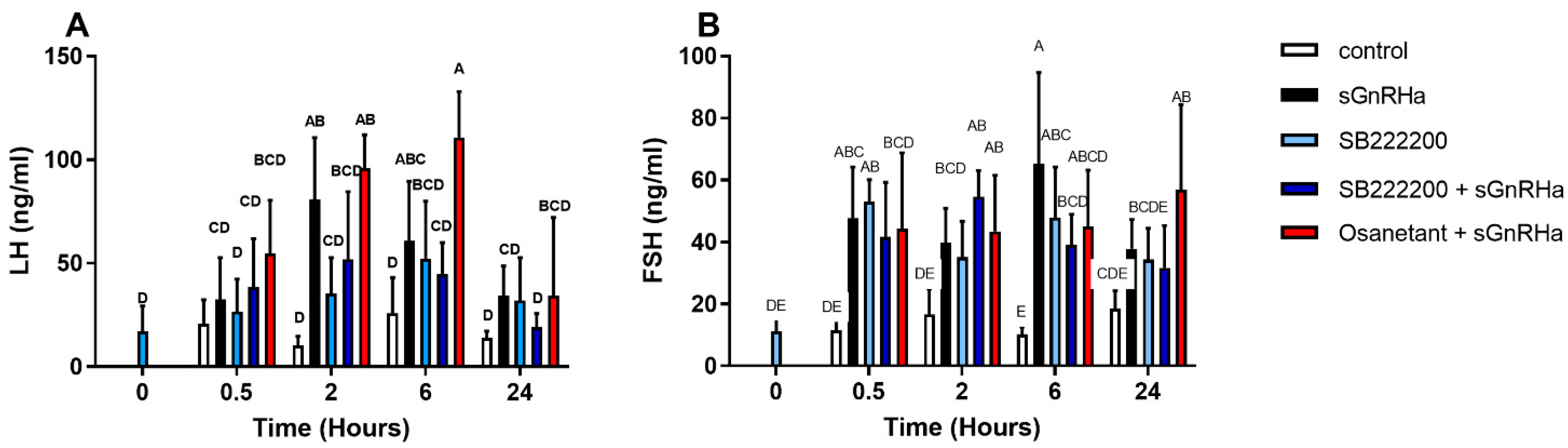
3.6.3. In Vivo Effect of Antagonist Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levavi-Sivan, B.; Bogerd, J.; Mañanós, E.; Gómez, A.; Lareyre, J. Perspectives on fish gonadotropins and their receptors. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 412–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avitan, A.; Zelinger, E.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Homologous desensitization and visualization of the tilapia GnRH type 3 receptor. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 153, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, M.; Zelinger, E.; Zohar, Y.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Architecture of GnRH-Gonadotrope-Vasculature Reveals a Dual Mode of Gonadotropin Regulation in Fish. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4163–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ball, J. Hypothalamic control of the pars distalis in fishes, amphibians, and reptiles. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1981, 44, 135–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, Y.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A.; Elizur, A.; Kah, O. Neuroendocrinology of reproduction in teleost fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothilf, Y.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A.; Sagrillo, C.A.; Selmanoff, M.; Chen, T.T.; Kah, O.; Elizur, A.; Zohar, Y. Three Forms of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in a Perciform Fish (Sparus aurata): Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid Characterization and Brain Localization1. Biol. Reprod. 1996, 55, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, S.A.; Kasten, T.L.; Bond, C.T.; Adelman, J.P.; Fernald, R.D. Three gonadotropin-releasing hormone genes in one organism suggest novel roles for an ancient peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8363–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biran, J.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Endocrine Control of Reproduction, Fish. In Encyclopedia of Reproduction; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 362–368. [Google Scholar]
- Topaloglu, A.K.; Kotan, L.D. Molecular causes of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 22, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, L.; Aguilar, E.; Dieguez, C.; Millar, R.P.; Tena-Sempere, M. Kisspeptins and Reproduction: Physiological Roles and Regulatory Mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1235–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhar, I.; Ogawa, S.; Kitahashi, T. RFamide peptides as mediators in environmental control of GnRH neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 98, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roux, N.; Genin, E.; Carel, J.-C.; Matsuda, F.; Chaussain, J.-L.; Milgrom, E. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to loss of function of the KiSS1-derived peptide receptor GPR54. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10972–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seminara, S.B.; Messager, S.; Chatzidaki, E.E.; Thresher, R.R.; Acierno, J.S.; Shagoury, J.K.; Bo-Abbas, Y.; Kuohung, W.; Schwinof, K.M.; Hendrick, A.G.; et al. The GPR54 gene as a regulator of puberty. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parhar, I.S.; Ogawa, S.; Sakuma, Y. Laser-Captured Single Digoxigenin-Labeled Neurons of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Types Reveal a Novel G Protein-Coupled Receptor (Gpr54) during Maturation in Cichlid Fish. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 3613–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbison, A.E. The Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Pulse Generator. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3723–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, D.; Ogawa, S.; Yin, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shuisheng, L.; Parhar, I.S.; Lin, H.; et al. The kiss/kissr Systems Are Dispensable for Zebrafish Reproduction: Evidence from Gene Knockout Studies. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajo, M.; Kanda, S.; Karigo, T.; Takahashi, A.; Akazome, Y.; Uenoyama, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Oka, Y. Evolutionally Conserved Function of Kisspeptin Neuronal System Is Nonreproductive Regulation as Revealed by Nonmammalian Study. Endocrinology 2017, 159, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loy, T.; Vandersmissen, H.P.; Poels, J.; Van Hiel, B.; Verlinden, H.; Broeck, J.V. Tachykinin-related peptides and their receptors in invertebrates: A current view. Peptides 2010, 31, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, N.M. Hemokinins and endokinins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biran, J.; Palevitch, O.; Ben-Dor, S.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Neurokinin Bs and neurokinin B receptors in zebrafish-potential role in controlling fish reproduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10269–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, G.; Liu, X.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Goldfish neurokinin B: Cloning, tissue distribution, and potential role in regulating reproduction. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 221, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biran, J.; Golan, M.; Mizrahi, N.; Ogawa, S.; Parhar, I.S.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Direct Regulation of Gonadotropin Release by Neurokinin B in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Endocrinology 2014, 155, 4831–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Neurokinin B signaling in hermaphroditic species, a study of the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 260, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, A.; Lafont, A.-G.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Tostivint, H.; Kamech, N.; Dufour, S.; Rousseau, K. Tachykinin-3 Genes and Peptides Characterized in a Basal Teleost, the European Eel: Evolutionary Perspective and Pituitary Role. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zmora, N.; Wong, T.-T.; Stubblefield, J.; Levavi-Sivan, B.; Zohar, Y. Neurokinin B regulates reproduction via inhibition of kisspeptin in a teleost, the striped bass. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.; Smith, J.; Coolen, L.; De Oliveira, C.V.R.; Shirazi, M.R.J.; Pereira, A.; Iqbal, J.; Caraty, A.; Ciofi, P.; et al. Kisspeptin Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Ewe Express Both Dynorphin A and Neurokinin B. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5752–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.M.; Gottsch, M.L.; Chavkin, C.; Okamura, H.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Regulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Secretion by Kisspeptin/Dynorphin/Neurokinin B Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Mouse. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 11859–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, Y.; Nakada, T.; Murata, K.; Ohkura, S.; Mogi, K.; Navarro, V.M.; Clifton, D.K.; Mori, Y.; Tsukamura, H.; Maeda, K.-I.; et al. Neurokinin B and Dynorphin A in Kisspeptin Neurons of the Arcuate Nucleus Participate in Generation of Periodic Oscillation of Neural Activity Driving Pulsatile Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Secretion in the Goat. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3124–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.M.; Coolen, L.M.; Porter, D.T.; Goodman, R.L.; Lehman, M.N. KNDy Cells Revisited. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3219–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizrahi, N.; Gilon, C.; Atre, I.; Ogawa, S.; Parhar, I.S.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Deciphering Direct and Indirect Effects of Neurokinin B and GnRH in the Brain-Pituitary Axis of Tilapia. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, S.; Akazome, Y.; Mitani, Y.; Okubo, K.; Oka, Y. Neuroanatomical Evidence That Kisspeptin Directly Regulates Isotocin and Vasotocin Neurons. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobar, S.; Servili, A.; Espigares, F.; Gueguen, M.-M.; Brocal, I.; Felip, A.; Gómez, A.; Carrillo, M.; Zanuy, S.; Kah, O. Expression of Kisspeptins and Kiss Receptors Suggests a Large Range of Functions for Kisspeptin Systems in the Brain of the European Sea Bass. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grone, B.P.; Maruska, K.P.; Korzan, W.J.; Fernald, R.D. Social status regulates kisspeptin receptor mRNA in the brain of Astatotilapia burtoni. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 169, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somoza, G.M.; Mechaly, A.S.; Trudeau, V.L. Kisspeptin and GnRH interactions in the reproductive brain of teleosts. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 298, 113568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buell, G.; Schulz, M.; Arkinstall, S.; Maury, K.; Missotten, M.; Adami, N.; Talabot, F.; Kawashima, E. Molecular characterisation, expression and localisation of human neurokinin-3 receptor. FEBS Lett. 1992, 299, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, R.F. Social behavior in context: Hormonal modulation of behavioral plasticity and social competence. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2009, 49, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurevich, M.; Tal-Gan, Y.; Klein, S.; Barda, Y.; Levitzki, A.; Gilon, C. Novel method for the synthesis of urea backbone cyclic peptides using new Alloc-protected glycine building units. J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. COFACTOR: An accurate comparative algorithm for structure-based protein function annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W471–W477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: Fully automated protein structure prediction in CASP8. Proteins 2009, 77 (Suppl. 9), 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blom, N.S.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasits, U.; Ahrens, C.; Müller, S.; Wollscheid, B. Protter: Interactive protein feature visualization and integration with experimental proteomic data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashkenazy, H.; Abadi, S.; Martz, E.; Chay, O.; Mayrose, I.; Pupko, T.; Ben-Tal, N. ConSurf 2016: An improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W344–W350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biran, J.; Ben-Dor, S.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Molecular Identification and Functional Characterization of the Kisspeptin/Kisspeptin Receptor System in Lower Vertebrates1. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 79, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander-Cohen, L.; Bohm, B.; Hausken, K.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Ontogeny of the specificity of gonadotropin receptors and gene expression in Carp. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarau, H.M.; Griswold, D.E.; Bush, B.; Potts, W.; Sandhu, P.; Lundberg, D.; Foley, J.J.; Schmidt, D.B.; Webb, E.F.; Martin, L.D.; et al. Nonpeptide tachykinin receptor antagonists. II. Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic profile of SB-222200, a central nervous system penetrant, potent and selective NK-3 receptor antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Aizen, J.; Kasuto, H.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Development of specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determining LH and FSH levels in tilapia, using recombinant gonadotropins. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2007, 153, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, P.; Eliahu, N.; Ofir, M.; Levavi-Sivan, B.; Smal, J.; Rentier-Delrue, F.; Yaron, Z. The effects of gonadal development and sex steroids on growth hormone secretion in the male tilapia hybrid (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1995, 14, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, J.; Kasuto, H.; Golan, M.; Zakay, H.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Tilapia Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Immunochemistry, Stimulation by Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone, and Effect of Biologically Active Recombinant FSH on Steroid Secretion1. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 76, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasuto, H.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Production of biologically active tethered tilapia LHbetaalpha by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 140, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levavi-Sivan, B.; Safarian, H.; Rosenfeld, H.; Elizur, A.; Avitan, A. Regulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)-Receptor Gene Expression in Tilapia: Effect of GnRH and Dopamine1. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heyrati, F.P.; Amiri, B.M.; Dorafshan, S. Effect of GnRHa injection on milt volume in recently stripped rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e487–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, E.K.; Shaun, M.G. Coral Point Count with Excel extensions (CPCe): A Visual Basic program for the determination of coral and substrate coverage using random point count methodology. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, R.W.; de Franca, L.R.; Lareyre, J.J.; Le Gac, F.; Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Nobrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; Canning, B.; Coulson, J.; Dombrowsky, E.; Douglas, S.D.; Fong, T.M.; Heyward, C.Y.; Leeman, S.E.; Remeshwar, P. Tachykinin receptors (version 2019.4) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. IUPHAR/BPS Guide Pharmacol. CITE 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Lu, M.; Liu, D.; Yang, L.; Yi, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Frimurer, T.M.; Wang, M.-W.; et al. Human substance P receptor binding mode of the antagonist drug aprepitant by NMR and crystallography. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöppe, J.; Ehrenmann, J.; Klenk, C.; Rucktooa, P.; Schütz, M.; Doré, A.S.; Plückthun, A. Crystal structures of the human neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with clinically used antagonists. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, J.F.; Noinaj, N.; Shibata, Y.; Love, J.; Kloss, B.; Xu, F.; Gvozdenovic-Jeremic, J.; Shah, P.; Shiloach, J.; Tate, C.; et al. Structure of the agonist-bound neurotensin receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 490, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandrashekaran, I.; Rao, G.S.; Cowsik, S.M. Molecular Modeling of the Peptide Agonist-Binding Site in a Neurokinin-2 Receptor. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjiwale, A.D.; Rao, G.S.; Cowsik, S.M. Molecular Modeling of Neurokinin B and Tachykinin NK3 Receptor Complex. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malherbe, P.; Bissantz, C.; Marcuz, A.; Kratzeisen, C.; Zenner, M.-T.; Wettstein, J.G.; Ratni, H.; Riemer, C.; Spooren, W. Me-Talnetant and Osanetant Interact within Overlapping but Not Identical Binding Pockets in the Human Tachykinin Neurokinin 3 Receptor Transmembrane Domains. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1736–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labrou, N.E.; Bhogal, N.; Hurrell, C.R.; Findlay, J.B. Interaction of Met297 in the Seventh Transmembrane Segment of the Tachykinin NK2 Receptor with Neurokinin A. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37944–37949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Labroska, V.; Qin, S.; Darbalaei, S.; Wu, Y.; Yuliantie, E.; Xie, L.; Tao, H.; Cheng, J.; et al. G protein-coupled receptors: Structure- and function-based drug discovery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, R.; Martini, A.; Navarro, V.; Castellano, J.M.; Dieguez, C.; Aguilar, E.; Pinilla, L.; Tena-Sempere, M. Novel signals for the integration of energy balance and reproduction. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 254–255, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayen, A.; Goswami, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, C. NMR evidence of GM1-induced conformational change of Substance P using isotropic bicelles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grisshammer, R. The quest for high-resolution G protein-coupled receptor–G protein structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6971–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995, 25, 366–428. [Google Scholar]
- Isberg, V.; de Graaf, C.; Bortolato, A.; Cherezov, V.; Katritch, V.; Marshall, F.; Mordalski, S.; Pin, J.-P.; Stevens, R.; Vriend, G.; et al. Generic GPCR residue numbers—Aligning topology maps while minding the gaps. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turku, A.; Schihada, H.; Kozielewicz, P.; Bowin, C.-F.; Schulte, G. Residue 6.43 defines receptor function in class F GPCRs. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, R.L.; Hileman, S.M.; Nestor, C.; Porter, K.L.; Connors, J.M.; Hardy, S.L.; Millar, R.P.; Cernea, M.; Coolen, L.; Lehman, M. Kisspeptin, Neurokinin B, and Dynorphin Act in the Arcuate Nucleus to Control Activity of the GnRH Pulse Generator in Ewes. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4259–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, G.L.; Hoveyda, H.R.; Clarke, I.; Ramaswamy, S.; Plant, T.M.; Rose, C.; Millar, R.P. The NK3 Receptor Antagonist ESN364 Interrupts Pulsatile LH Secretion and Moderates Levels of Ovarian Hormones Throughout the Menstrual Cycle. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4214–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maruska, K.P.; Levavi-Sivan, B.; Biran, J.; Fernald, R.D. Plasticity of the Reproductive Axis Caused by Social Status Change in an African Cichlid Fish: I. Pituitary Gonadotropins. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravina, C.; Seda, M.; Pinto, F.; Orea, A.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Pintado, C.; Candenas, M. A role for tachykinins in the regulation of human sperm motility. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Primer | Position | Sequence (5′ 3′) | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| tiTac3Ra -F251A-F | 732 | GATTGTTGTAGTGGTGACGGCCGCCCTCTGTTGGCTGCCAT | F251A mutation |
| tiTac3Ra- F251A-R | 732 | ATGGCAGCCAACAGAGGGCGGCCGTCACCACTACAACAATC | F251A mutation |
| tiTac3Ra- M289A-F | 843 | CCTGTCGATCATGTGGCTTGCAGCCAGTTCCACCATGTACAACC | M289A mutation |
| tiTac3Ra- M289A-R | 843 | GGTTGTACATGGTGGAACTGGCTGCAAGCCACATGATCGACAGG | M289A mutation |
| Binding Site | Involved Amino Acid on tiTac3Ra |
|---|---|
| Binding pocket A | Thr12, Asn13, His14, Thr15, Asn16, Gln17, Phe18, Val19, Gln20, Pro22, Ile25, Asn82, Tyr85, Ala86, Ala87, His88, Gly89, Glu90, Trp91, Cys98, His101, Asn102, Pro105, Val106, Val109, Leu158, Ser162, Ile170, Arg173, Ile175, Cys176, Tyr177, Val178, Tyr190, His191, Val194, Thr195, Val198, Tyr199, Trp255, Tyr258, His259, Phe262, Ile277, Gln278, Tyr281, Leu282, Met285, Ala288, Met289. |
| Binding pocket B | Leu64, Leu67, Asp71, Met74, Met116, Val247, Thr250, Phe251, Ser291, Thr292, Tyr294, Asn295, Ile298, Tyr299. |
| Orthosteric Antagonist binding pocket | Asn78, Phe82, His101, Pro105, Val106, Val109, Phe110, Ile175, Tyr177, Val178, Val194, Thr195, Trp255,Tyr258, His259, Phe262, Met285, Ala288, Met289. |
| NKB | NKF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation | WT | F251A | M289A | WT | F251A | M289A |
| EC50 (nM) | 2.48 ± 0.05 | X | X | 65.22 ± 18.43 | X | X |
| Min effective dose (nM) | 0.316 | X | X | 0.316 | X | X |
| Max effect (Luc fold activation) | 3.36 ± 0.46 | 2.0 ± 0.32 | 1.71 ± 0.46 | 3.87 ± 0.38 | 1.99 ± 0.04 | 1.84 ± 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atre, I.; Mizrahi, N.; Levavi-Sivan, B. Characteristics of Neurokinin-3 Receptor and Its Binding Sites by Mutational Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100968
Atre I, Mizrahi N, Levavi-Sivan B. Characteristics of Neurokinin-3 Receptor and Its Binding Sites by Mutational Analysis. Biology. 2021; 10(10):968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100968
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtre, Ishwar, Naama Mizrahi, and Berta Levavi-Sivan. 2021. "Characteristics of Neurokinin-3 Receptor and Its Binding Sites by Mutational Analysis" Biology 10, no. 10: 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100968
APA StyleAtre, I., Mizrahi, N., & Levavi-Sivan, B. (2021). Characteristics of Neurokinin-3 Receptor and Its Binding Sites by Mutational Analysis. Biology, 10(10), 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10100968