Cellulose Microfibril and Micronized Rubber Modified Asphalt Binder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
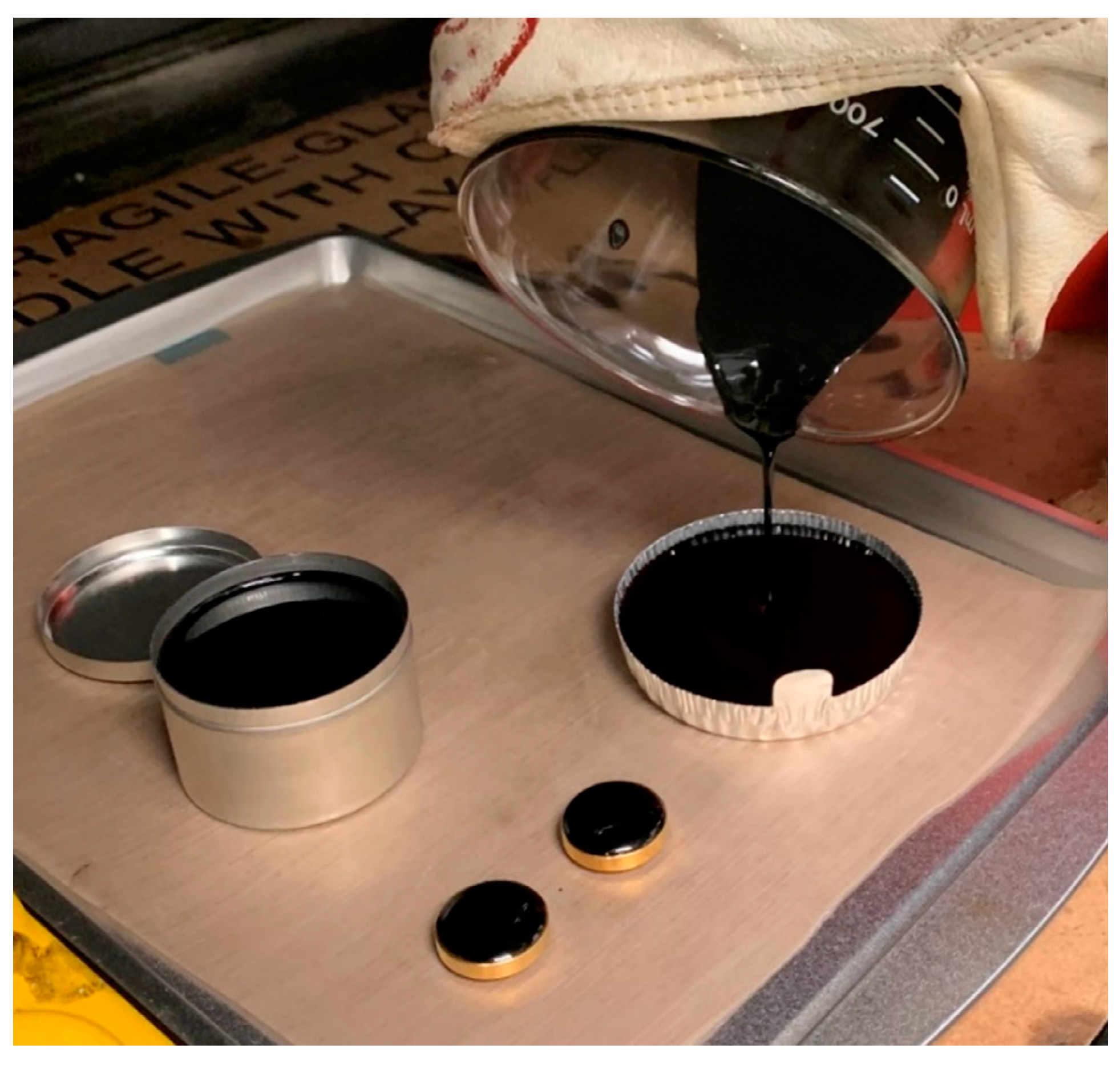
2.2. Asphalt Modification
2.3. Characterization of Modified Asphalt
3. Results and Discussion
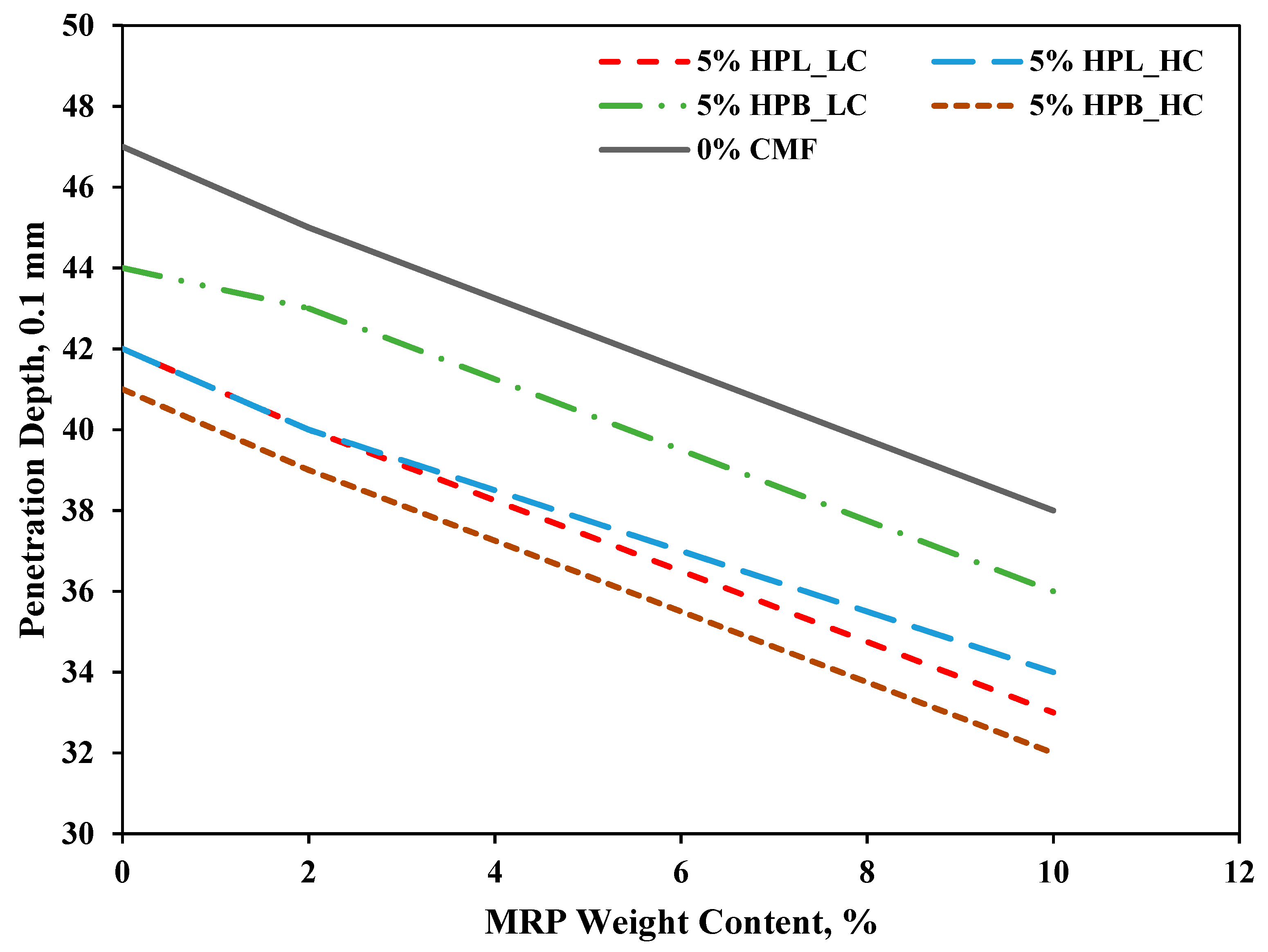
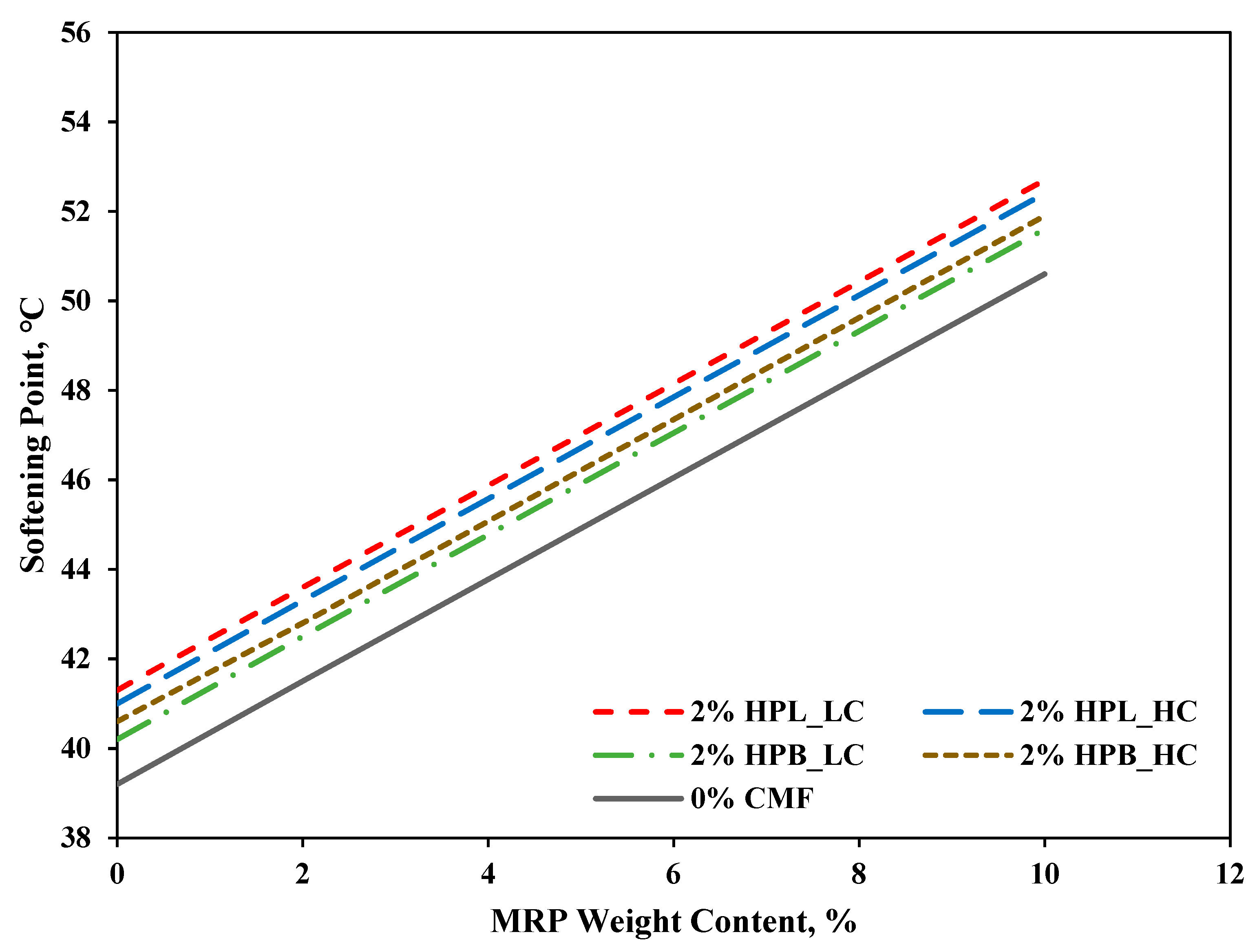
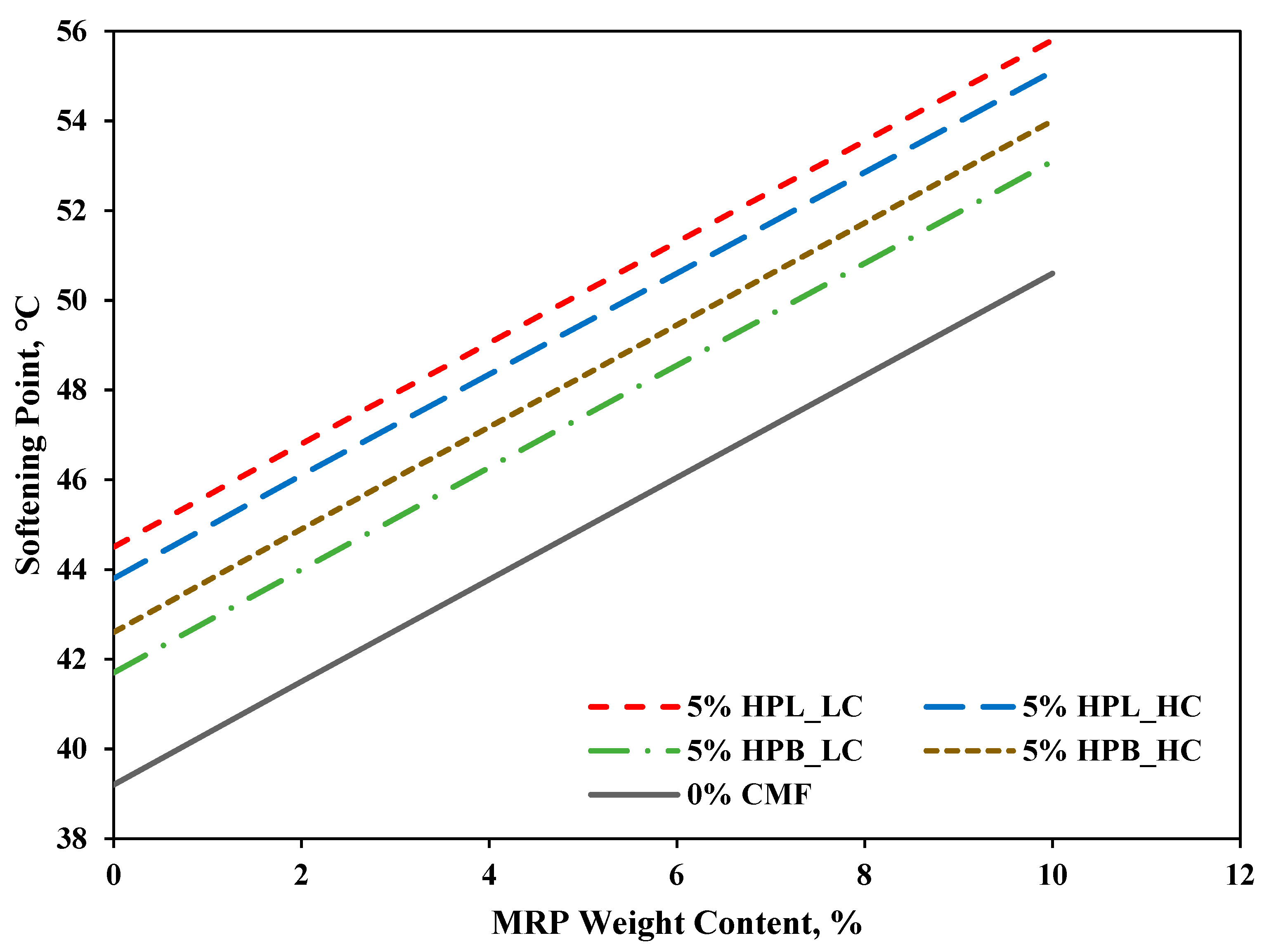
3.1. Penetration Depth and Softening Point
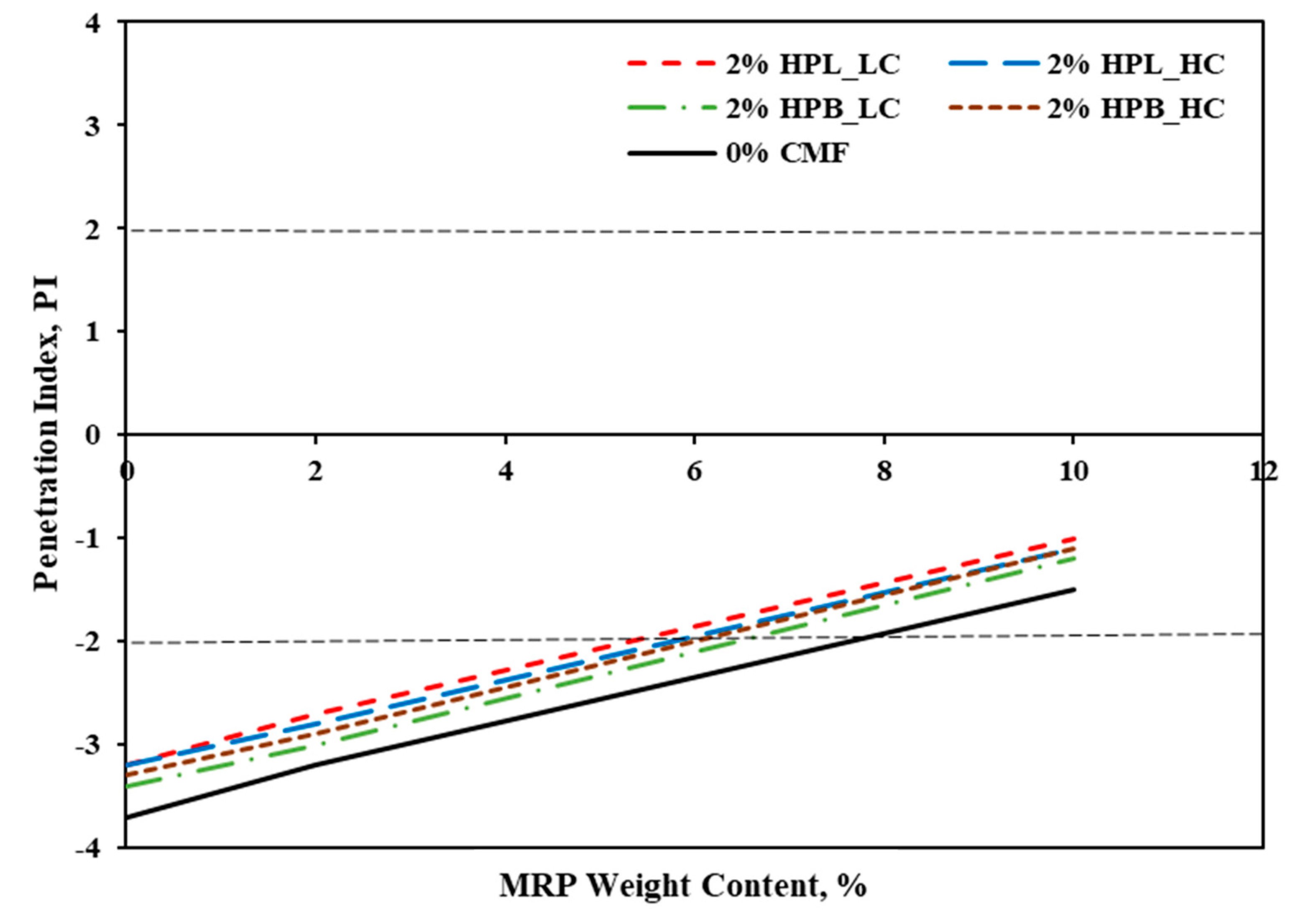
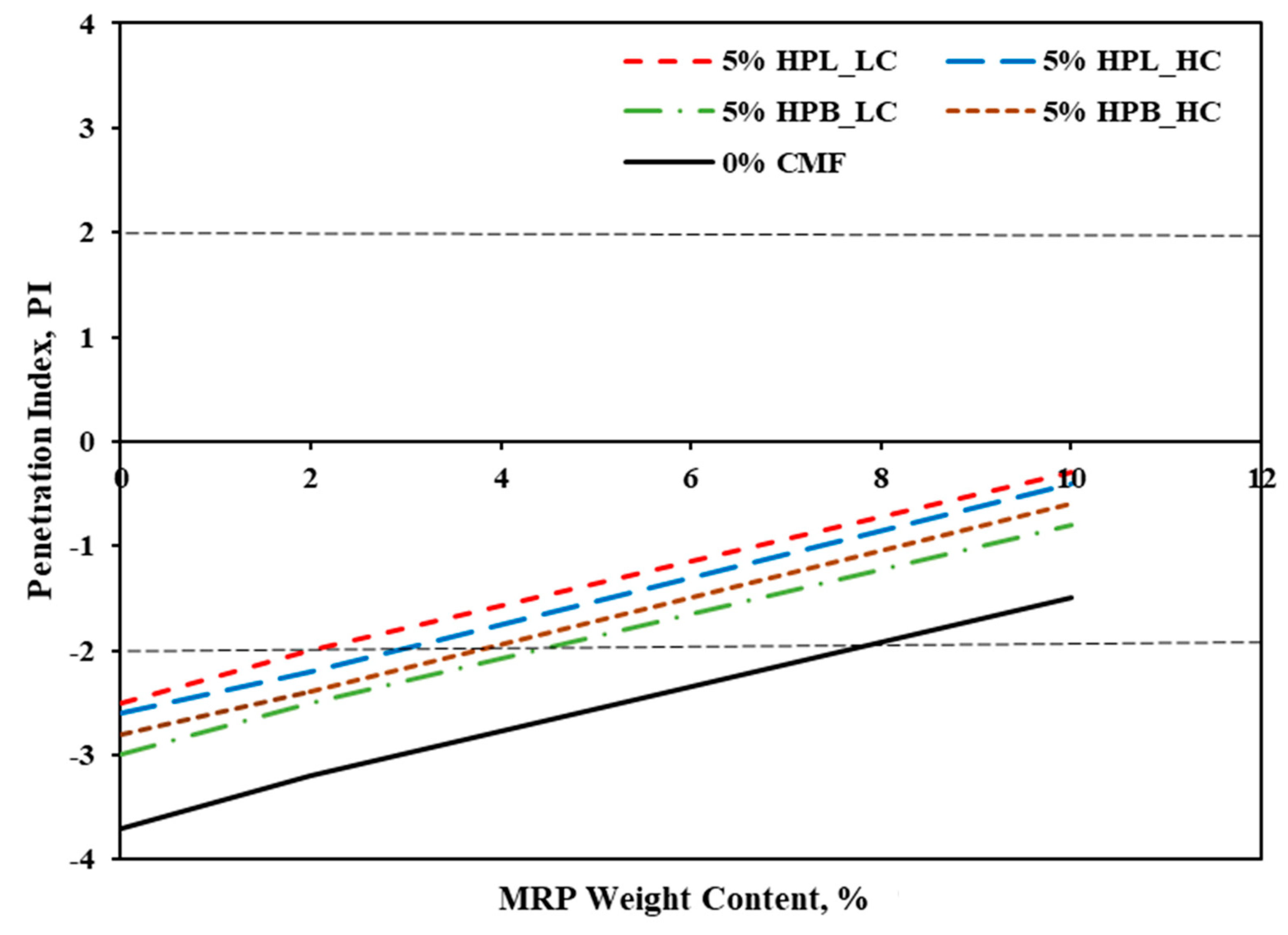
3.2. Penetration Index
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behnood, A.; Modiri Gharehveran, M. Morphology, rheology, and physical properties of polymer-modified asphalt binders. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 766–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Olek, J. Rheological properties of asphalt binders modified with styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS), ground tire rubber (GTR), or polyphosphoric acid (PPA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachovicova, Z.; Wekumbura, C.; Stastna, J.; Zanzotto, L. Creep characteristics of asphalt modified by radial styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punith, V.S.; Suresha, S.N.; Raju, S.; Bose, S.; Veeraragavan, A. Estimating Welfare Change Associated with Improvements in Urban Bicycling Facilities. J. Transp. Eng. 2015, 138, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, V.; Martínez-Boza, F.J.; Navarro, F.J.; Gallegos, C.; Pérez-Lepe, A.; Páez, A. Thermomechanical properties of bitumen modified with crumb tire rubber and polymeric additives. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, H.; Aksoy, A.; Tayfur, S.; Çelik, F. Laboratory performance comparison of the elastomer-modified asphalt mixtures. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dubabe, I.A.; Al-Abdul Wahhab, H.I.; Asi, I.M.; Ali, M.F. Polymer modification of Arab asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1998, 10, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; You, Z.; Li, L.; Goh, S.W.; Lee, C.H.; Yap, Y.K.; Shi, X. Rheological properties and chemical analysis of nanoclay and carbon microfiber modified asphalt with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.E.; Zamhari, K.A.; Hainin, M.R.; Oluwasola, E.A.; Hassan, N.A.; Yusoff, N.I.M. Engineering properties of asphalt binders containing nanoclay and chemical warm-mix asphalt additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplantz, J.S.; Yapp, M.T.; Finn, F.N. Review of Relationships between Modified Asphalt Properties and Pavement Performance. 1993. Available online: http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/shrp/SHRP-A-631.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2020).
- Köfteci, S.; Ahmedzade, P.; Kultayev, B. Performance evaluation of bitumen modified by various types of waste plastics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadri, A.A.; Roman, C.; García-Morales, M.; Guisado, F.; Moreno, E.; Partal, P. Formulation and processing of recycled-low-density-polyethylene-modified bitumen emulsions for reduced-temperature asphalt technologies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 156, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. Comparative study of asphalts modified by packaging waste EPS and waste PE. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, M.; Partal, P.; Navarro, F.J.; Gallegos, C. Effect of waste polymer addition on the rheology of modified bitumen. Fuel 2006, 85, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, M.; Chaki, T.K.; Reddy, K.S. Effect of waste plastic as modifier on thermal stability and degradation kinetics of bitumen/waste plastics blend. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 509, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Garg, R. Rheology of waste plastic fibre-modified bitumen. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2011, 12, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, M.; Borzędowska-Labuda, K.; Zalewski, S.; Janik, H. The effect of tyre rubber grinding method on the rubber-asphalt binder properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, W.; Fang, J.; Shang, S. Variance analysis and performance evaluation of different crumb rubber modified (CRM) asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2701–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.D.; Lee, S.J.; Amirkhanian, S.N.; Kim, K.W. Interaction effects of crumb rubber modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merci, A.; Urbano, A.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; Tischer, C.A.; Mali, S. Properties of microcrystalline cellulose extracted from soybean hulls by reactive extrusion. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Boufi, S.; Celli, A.; Kango, S. Nanofibrillated cellulose: Surface modification and potential applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Gastelú, G.; Barrera, G.N.; Ribotta, P.D.; Álvarez Igarzabal, C.I. Preparation and characterization of soy protein films reinforced with cellulose nanofibers obtained from soybean by-products. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebeish, A.; Farag, S.; Sharaf, S.; Shaheen, T.I. High performance fabrics via innovative reinforcement route using cellulose nanoparticles. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Jiang, S.; Farooq, A.; Naeem, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Liu, L. Structure and properties of high quality natural cellulose nano fibrils from a novel material Ficus natalensis barkcloth. J. Ind. Text. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanbakhsh, M.F.; Rashidi, A. The effect of ultrasonic waves on alpha-cellulose extraction from wheat bran to prepare alpha-cellulose nanofibers. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 111, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashjaran, A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E.; Rashidi, A.; Khajavi, R.; Rezaee, A. Overview of bio nanofabric from bacterial cellulose. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivar, A.; Kavussi, A. Rheological characteristics of SBR and NR polymer modified bitumen emulsions at average pavement temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5-05 Standard Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials. ASTM Int. 2008, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D36-06 Standard Test Method for Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus). ASTM Int. 2008, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Gawel, I.; Stepkowski, R.; Czechowski, F. Molecular interactions between rubber and asphalt. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 3044–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchoin, L.; Blanchoin, L.; Pollard, T.D.; Pollard, T.D. Mechanism of Interaction of Cement with Crumb Rubber Modifier. Biochemistry 1999, 274, 15538–15546. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Q. Experimental study of fibers in stabilizing and reinforcing asphalt binder. Fuel 2010, 89, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enieb, M.; Diab, A. Characteristics of asphalt binder and mixture containing nanosilica. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| MRP wt %, R | 0, 2, 10 |
| CMF wt %, F | 0, 2, 5 |
| CMF type | HPL_LC, HPL_HC, HPB_LC, HPB_HC |
| Number of samples | 3 × (1 + 4 + 4) = 27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, A.; Danladi, A.A.; Vallabh, R.; Yakubu, M.K.; Ishiaku, U.; Theyson, T.; Seyam, A.-F.M. Cellulose Microfibril and Micronized Rubber Modified Asphalt Binder. Fibers 2021, 9, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9040025
Li A, Danladi AA, Vallabh R, Yakubu MK, Ishiaku U, Theyson T, Seyam A-FM. Cellulose Microfibril and Micronized Rubber Modified Asphalt Binder. Fibers. 2021; 9(4):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ang, Abdu A. Danladi, Rahul Vallabh, Mohammed K. Yakubu, Umar Ishiaku, Thomas Theyson, and Abdel-Fattah M. Seyam. 2021. "Cellulose Microfibril and Micronized Rubber Modified Asphalt Binder" Fibers 9, no. 4: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9040025
APA StyleLi, A., Danladi, A. A., Vallabh, R., Yakubu, M. K., Ishiaku, U., Theyson, T., & Seyam, A.-F. M. (2021). Cellulose Microfibril and Micronized Rubber Modified Asphalt Binder. Fibers, 9(4), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9040025







