Abstract
Composite fibers and films based on cellulose and betulin were spun for the first time from solutions in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide using the dry–wet jet method. The rheological properties of the composite solutions did not reveal any fundamental difference from those of the cellulose solutions. Introduction of betulin into the cellulose matrix (up to 10%) led to a decrease in the mechanical properties of the obtained fibers. The structure of the composite fibers was analyzed using SEM and X-ray diffraction methods. It was shown that the introduction of an additive into the cellulose matrix led to a decrease in the structural ordering of the cellulose. Comparative studies of the antibacterial activity of the composite films on Escherichia coli (E. coli) were carried out. The antifungal activity of the composite films was estimated using the strain of the O-97 Trichoderma viride Pers ex Fr (Gause Institute of New Antibiotics, Moscow, Russia).
1. Introduction
Over the past decade, because of a number of political and natural cataclysms, the migration of people from Asia and Africa to Europe has grown dramatically. This process is often uncontrolled. Arriving people cause new threats in the field of biological and medical security. Migrants are potential vectors of new diseases, microbes, bacteria, and fungi, including phytopathogenic ones. Dissemination of spores, mycelium, sclerotia of parasitic fungi can occur through the movement of seeds (food and planting material), houseplants, agricultural products, remnants of materials and soils on clothes, shoes, etc. [1]. This gives researchers the task of creating antifungal materials.
There is currently an increasing interest in biomaterials, which include products made of wood and cellulose. Such materials, under the influence of a number of factors, are subject to degradation processes, which lead to the development of colonies of bacteria and fungi [2]. Fungi of the genus Trichoderma activate the biodestruction of cellulosic materials and are highly active in any breeding ground [3]. Soil is one of the main places where it is possible to detect this genus of fungi with great probability [4]. Interaction between the fungus of the genus Trichoderma and cellulose reveals the ability of cellulose to undergo hydrolysis [5].
In order to prevent damage to cellulosic materials by fungal spores, they are treated with various active substances, for example, polymers, resins, or silver and copper [6].
Betulin—a pentacyclic triterpene alcohol of the lupane family—is one of the main components of birch bark [7]. Over the past ten years, interest in this substance has increased dramatically in connection with its unique antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antitumor properties, and its resistance to fungi and bacteria [8,9,10]. For example, the activity of betulin in relation to the Gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is described in works [11,12]; protective properties of betulin against bacterial pneumonia and acute lung injury are described.
In paper [8], betulin was proposed as an antifungal agent for protecting cellulose by impregnating it with a 1–3% ethanol solution. Based on the work, it was shown that the results of the proposed method remain effective for several weeks with respect to strain Aspergillus Brasiliensis.
Along with the change in antibacterial activity and fungal resistance, the use of betulin causes changes in other properties of materials; for example, the application of betulin to cellulosic material by impregnation and molding methods causes an increase in hydrophobicity and water repellency [13].
It is important to note that along with the impregnation of cellulosic materials, the preparation of composite materials is also proposed. The production of composite materials has several advantages over impregnation which is not always evenly distributed over the surface of the fiber, and less evenly in the bulk of the matrix [14]. For example, a method was described in [15] for producing packaging materials based on cellulose and zeolites that show resistance to fungi of the genus Candida.
The majority of the fibers and films are produced from cellulose through either an environmentally dangerous viscose process or an ecologically acceptable NMMO-process where N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) is used as the direct cellulose solvent [16]. Cellulose fibers spun from cellulose solutions in NMMO take, according to the classification of the international committee BISFA (International Bureau of Standardization of Man-Made Fibres (Brussels, Belgium)), the general name Lyocell [17].
As shown in a number of papers [18,19,20,21], the NMMO process allows the introduction of some additives at the dope preparation stage to obtain composite materials with the required functional and mechanical properties.
However, at the present time, there is practically no data in the literature on the production of composite fibers and films based on cellulose and betulin and on their structures, properties, or fungal resistance. This problem will be considered in this paper.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
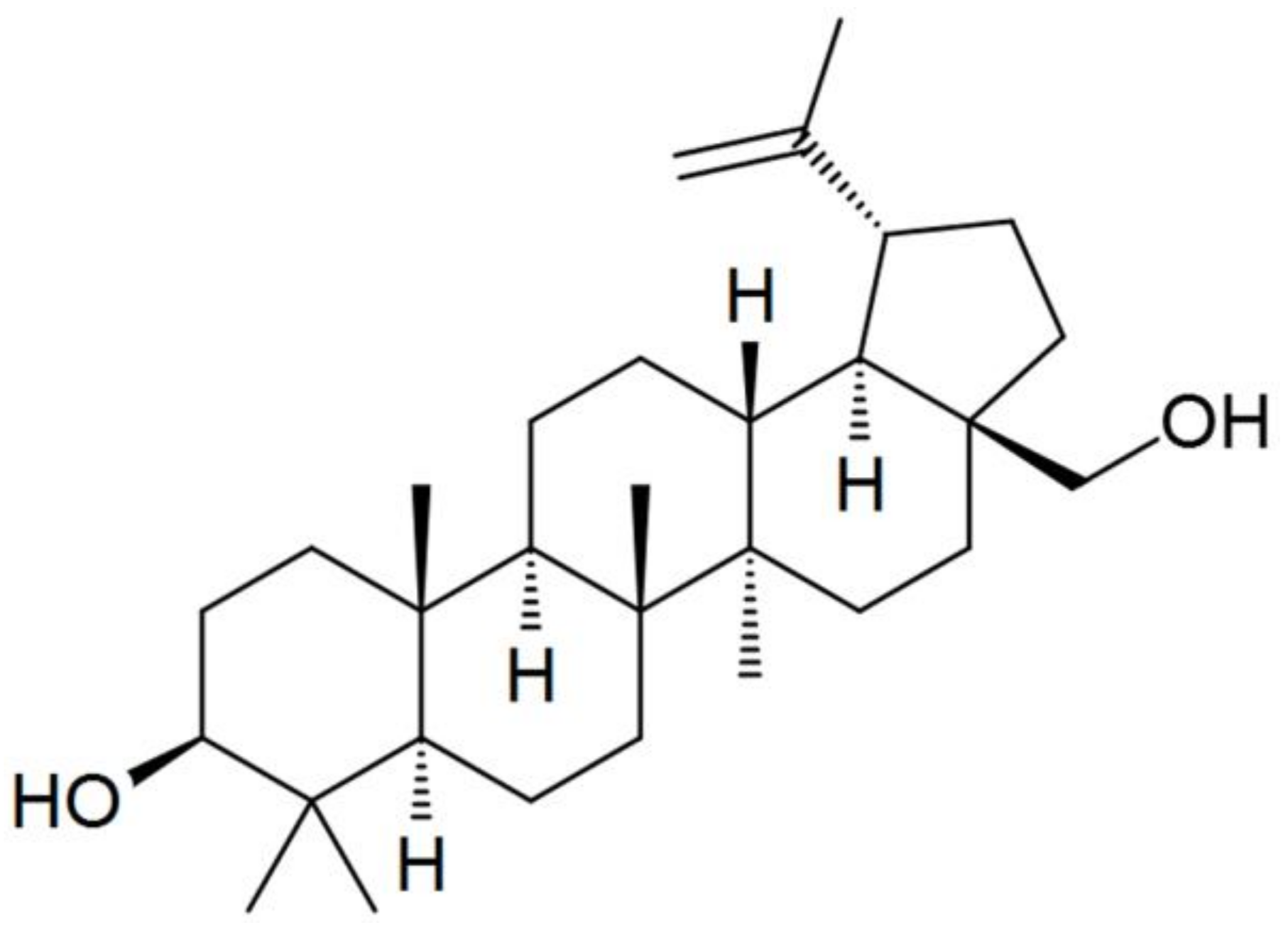
Cellulose of the Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill (BTsBK, Baykalsk, Russia) (DP = 600, H2O ~ 8%, alpha cellulose content not less than 94% (GOST 6840-78)) and N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) (Tm.p. = 120–160 °C, H2O < 10%) (Demochem, Shanghai, China) were used as the main components for solution preparation and fiber spinning. Betulin (C30H50O2, CAS No. 479-98-3, purity ~ 96%) in the form of a powder as an additive was obtained from LLC “Cortex” (Tyumen, Russia) (Figure 1).
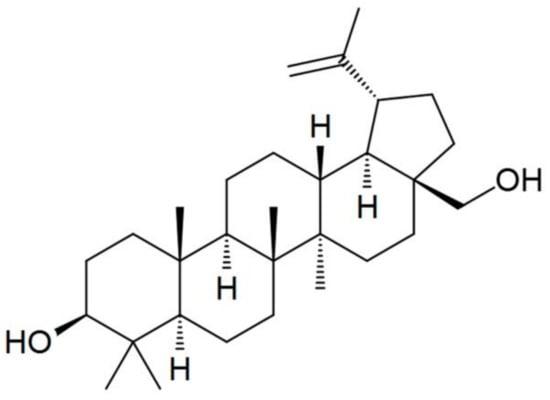
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of betulin.
2.2. Preparation of Dopes and Fiber Spinning (Films Formation)
Eighteen percent filled cellulose solutions in NMMO with betulin were prepared using a solid-phase activation method (cellulose/betulin: 95/5 and 90/10, wt %), where the cellulose–additive–solvent system was previously activated by mechanical action according to procedure [22] and converted to a viscous state by heating to a temperature of 120 °C. Thereafter, fibers were formed from the obtained solution using a dry–wet jet method on a capillary viscometer Rheoscope 1000 (CEAST, Torino, Italy) (capillary diameter 1 mm, l/d = 40) equipped with a fiber winding system. After exiting the spinneret and passing through an air gap (10 cm), the solution jets enter into an aqueous coagulation bath. The fibers were washed for several hours to ensure complete removal of NMMO. At the final stage, the fibers were dried in ambient conditions in a free state.
The films, for the evaluation of fungal resistance, were prepared from the obtained solutions using a HLCL-1000 laminator (Cheminstruments, Fairfield, OH, USA). A freshly prepared hot cellulose–additive–NMMO solution was pressed between the two anti-adhesion polyimide films. The prepared sandwich was then passed through the rollers, calibrated to the specified thickness, and heated to 120 °C. Cooling the solution layer led to the formation of a relatively strong film, which was transferred to the aqueous coagulation bath.
2.3. Rheology
The rheological properties of cellulose and filled solutions were studied on a rotational rheometer “RheoStress 600” (“Thermo Haake”, Karlsruhe, Germany), at a temperature of 120 °C and 135 °C, using a cone–plate-type operating unit with a cone diameter of 20 mm and an angle between cone and plate of 1°. Flow curves were obtained in the shear rate range of 0.001–100 s−1.
2.4. Mechanical Test
All specimens were tested using an Instron universal tensile machine (Instron, model 1122, MA, Norwood, USA) supplied with pneumatic clamps. A working length of 10 mm and an extension rate of 10 mm/min were used for all specimens. Twenty parallel tests were conducted for each kind of specimen. The fibers' diameters were measured with an optical microscope Biomed-6PO (GOST (10213.4-2002; 10213.0-2002; 10213.2-2002)) (Biomed Service, Moscow, Russia). The tensile strength, elastic modulus, and elongation at break values of all specimens were measured.
2.5. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction (WAXD)
The structure of the fibers was investigated by X-ray diffractometry using a Rigaku Rotaflex-RC unit (Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a rotating copper anode (30 kV–100 mA source operating mode, characteristic wavelength of CuKα radiation λ = 1.542 Å), horizontal D-Max/B goniometer (Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), and scintillation detector. X-ray experiments were performed at room temperature in “Bragg–Brentano” mode. To obtain the diffractograms of the fibers, parallel bundles of their fragments (~100 pieces) were used.
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Micrographs of the cellulose and composite fibers were obtained on a scanning electron microscope JSM U-3 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
2.7. Fungal and Antimicrobial Resistance Tests
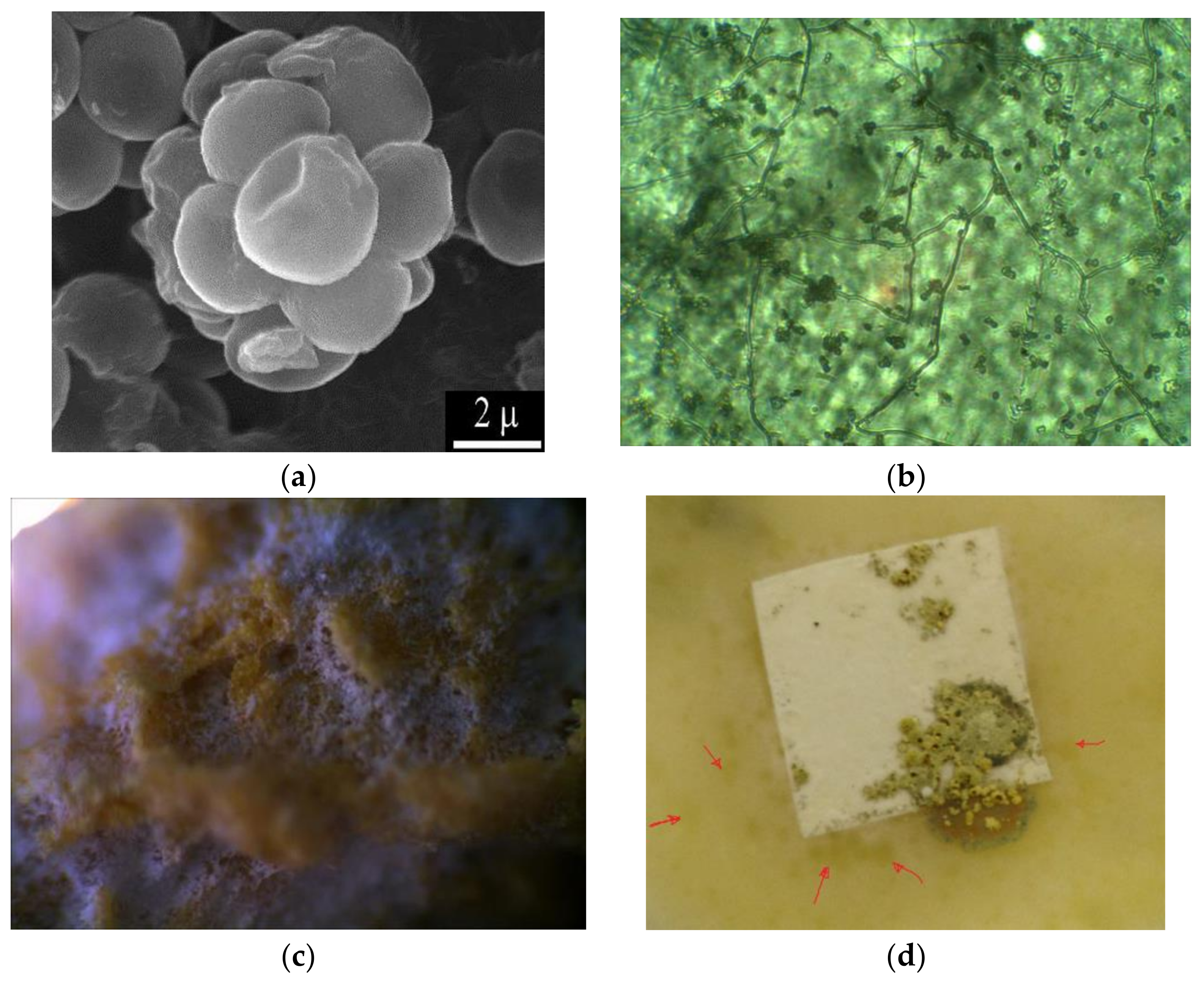
The determination of the fungal resistance was carried out in accordance with GOST 9.049-91 C. 3 1.2.3, Method 2. In assessing the fungal resistance of the material, 1 cm2 samples of composite films with a thickness of 30–40 μm were used. Samples of the material (at least 5) were cleaned of external contaminants, immersed for 1 minute in ethyl alcohol, dried, and placed in a Petri dish. To estimate fungal resistance, strain O-97 Trichoderma viride Pers. ex Fr. from the collection of cultures of the Gause Institute of New Antibiotics was used. Figure 2 shows micrographs of the Trichoderma strain and images of the damage by this strain to cellulose and its derivatives in the example of carboxymethyl cellulose.
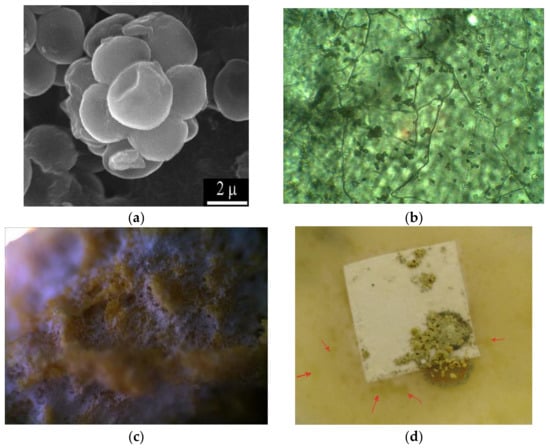
Figure 2.
Micromorphology of viable spores of the test strain Trichoderma viride Pers. ex Fr.: scanning electron microscopy (a); micromorphology of growth of T. viride on a film of carboxymethyl cellulose ((b), magnification 1350×), appearance of carboxymethyl cellulose film after 15 days of incubation with T. viride in a moist chamber (scanning light microscopy, magnification 200×, (c)); appearance of the carboxymethyl cellulose film after incubation with the T. viride strain (d).
The cultivation and storage of fungi cultures were carried out in accordance with GOST 9.048. The material of the films was infected on both sides with a spore suspension of the strain in an aqueous solution of mineral salts (according to GOST 9.048). The T. viride micromycetes grow because of the presence of salts and nutrients contained in the material. Petri dishes with samples were placed in desiccators, on the bottom of which water was poured. The desiccators were then closed and incubated in a thermostat at a temperature of 29 ± 2 °C and a relative humidity of more than 90% for 14 days. At the end of the test, the samples were removed from the Petri dishes and examined visually in scattered light at an illumination of 2000–3000 lux and microscopically at a magnification of 50–900. Fungal resistance was assessed by the intensity of fungal growth (or its suppression) according to a 6-point scale.
Antibacterial activity was tested with the disc-diffusion method in agar medium using an Escherichia coli test strain (catalog of microorganisms VKPM V-11419). For this purpose, a “lawn on the agar medium of LB (Luria–Bertrani, Difco)” was sown. On the surface of the agar plane, the disks of the tested polymer wetted with pyrogen-free water and the control discs of filter paper and bacterial cellulose wetted with a mycelium extract of macromitset Laetiporus sulphureus (L. sulphureus) were loaded. Mycelium extracts of L. sulphureus contain lipid fractions that diffuse slowly into agar. The test strain was incubated in a thermostat for 48 h at a temperature of 36 ± 1 °C [23]. Antimicrobial activity was assessed by the presence or absence of growth inhibition zones of the test strain.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Rheology
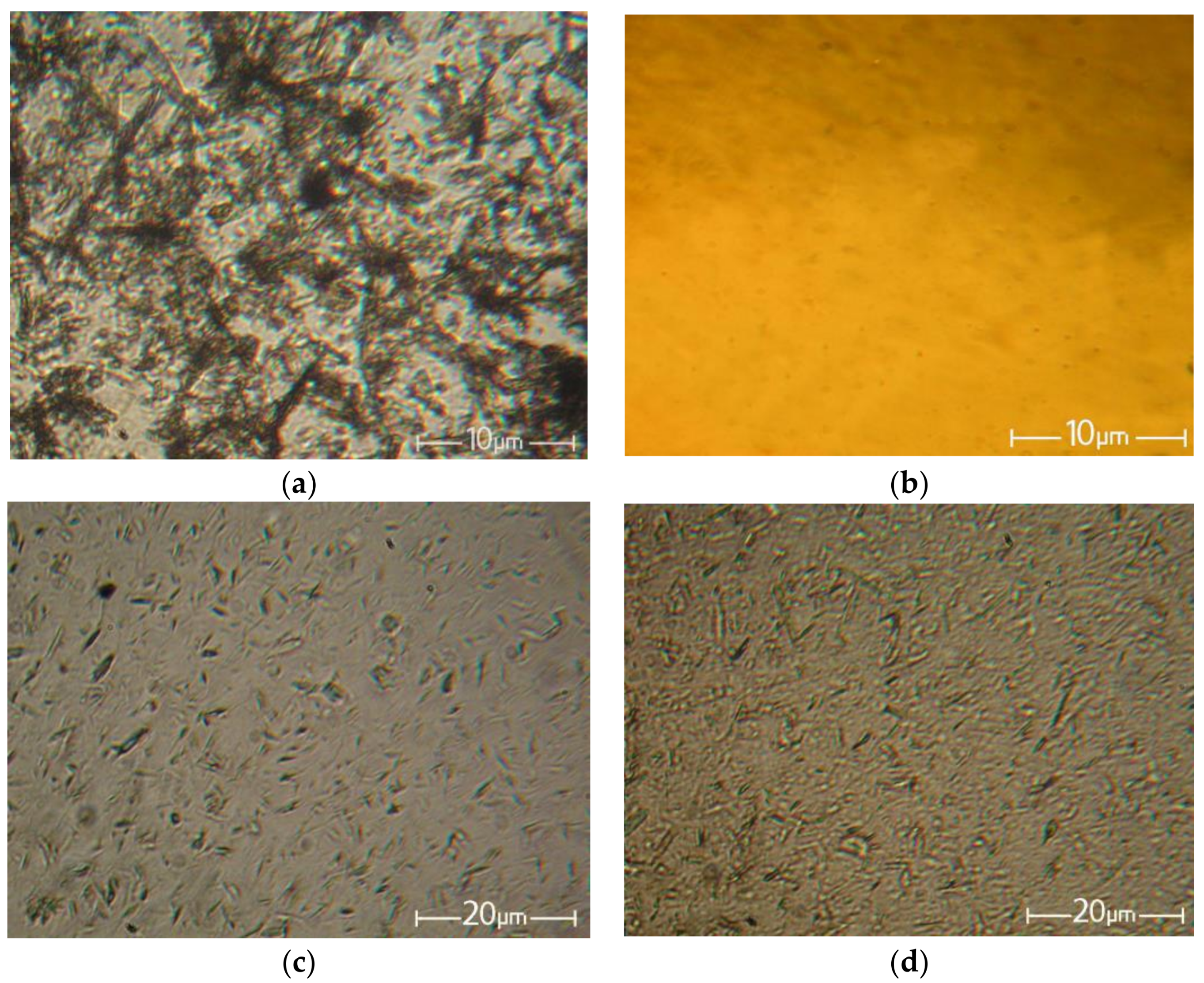
Figure 3 shows the initial betulin powder, the solution of cellulose, and the filled solutions of cellulose with betulin in the NMMO.
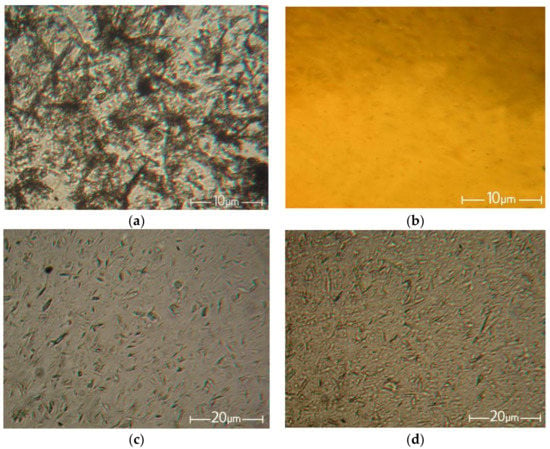
Figure 3.
Morphology of the betulin particles (a), 18% solution of cellulose in NMMO (b), and cellulose solution with betulin with a ratio of the cellulose to betulin of 95:5 (c) and 90:10 (d).
NMMO, being a suitable solvent for the dissolution of hydrophilic cellulose and a number of hydrophobic polymers, unfortunately does not show its activity toward betulin. As seen from the micrographs, the average particle size of betulin decreased during the preparation of the filled solutions from 5–15 μm to 1–5 μm for solutions with betulin contents of 5% and 10%, respectively.
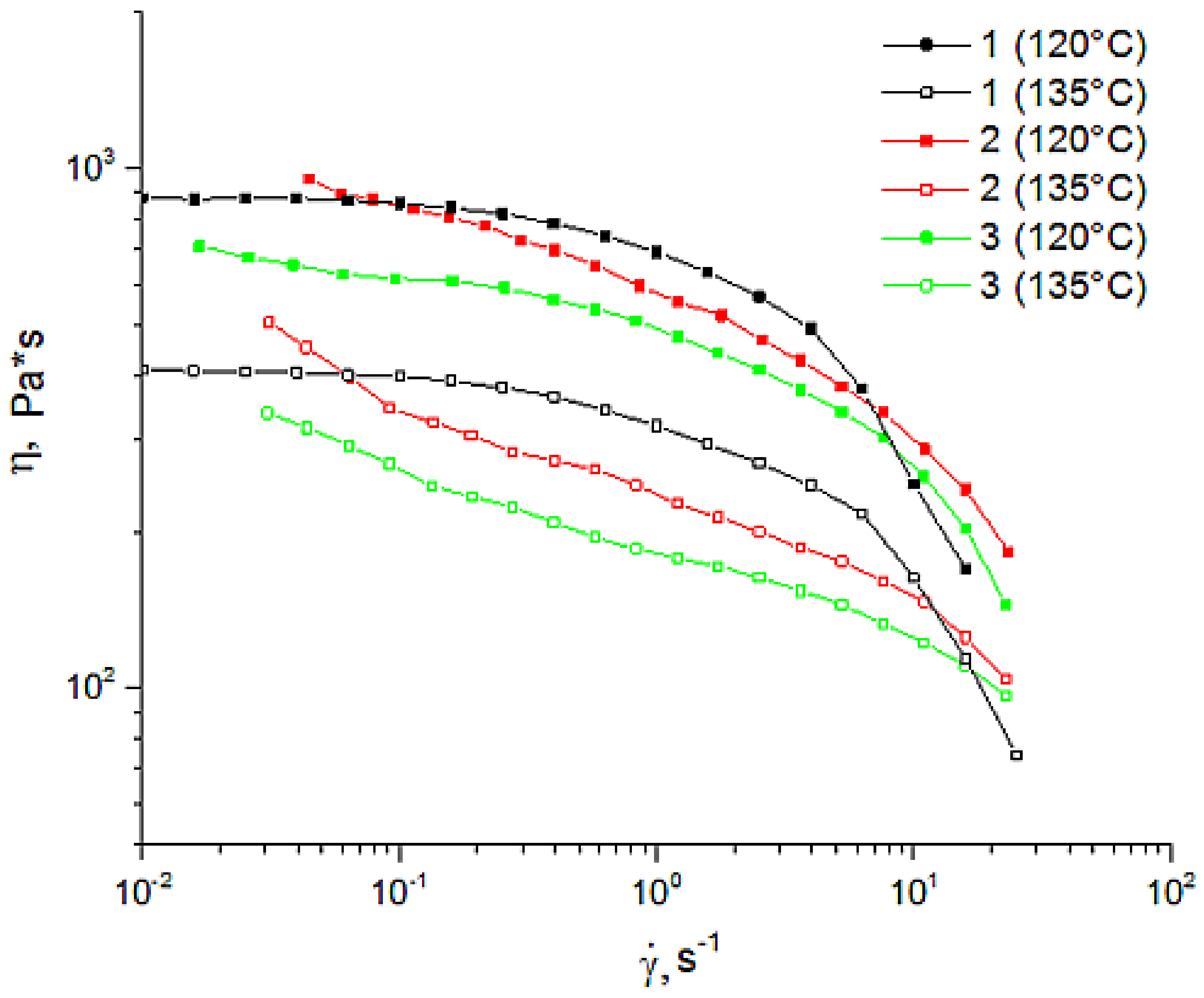
In order to determine the effect of the additive on the rheological behavior of cellulose solutions, the properties of 18% cellulose and betulin-filled solutions in NMMO were studied (Figure 4).
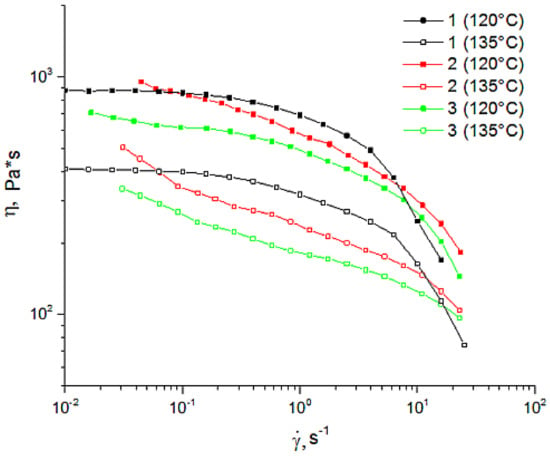
Figure 4.
Flow curves of 18% mixtures of cellulose solutions at 120 °C and 135 °C with different contents of betulin (in %): (1) 0%; (2) 5%; (3) 10%.
The flow curves obtained from the test behaved as those of non-Newtonian fluids. As for the 18% cellulose solution in NMMO, the traditional behavior with a constant viscosity at low shear rates and its decreasing with a shear rate (non-Newtonian flow) was evident. For betulin-containing solutions, the yield stress behavior typical of filled polymers was evident. A comparison of the shape of the curves (Figure 4) suggests that the flow of betulin-filled solutions is determined by the behavior of the cellulose matrix. The introduction of up to 10% of its weight of betulin led to a slight decrease in viscosity, at both temperatures (120 °C and 135 °C). Increasing the temperature up to 135 °C led to a decrease in viscosity of both cellulosic and betulin-filled solutions. The observed decrease in viscosity of solutions with an increase in the content of the composite additive appeared to be due to the violation of the system of hydrogen bonds between macromolecules of cellulose. Thus, the introduction of betulin into cellulose solutions does not lead to any significant change in rheological behavior, and, as a result, the same regimes of formation of composite fibers as in the case of cellulose can be used.
3.2. Mechanical Properties
Good mechanical properties of fibers are the determining factors for their use in the textile industry. On the basis of the data of rheological research, cellulosic and composite fibers were formed using a dry–wet jet method. The mechanical properties of the obtained fibers are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Mechanical properties of the cellulose and composite fibers.
The addition of betulin into the cellulose matrix resulted in a 10–20% reduction in strength, with the modulus increasing by more than 50%. Such an increase in the modulus of elasticity was most likely due to the introduction of a rigid filler in the cellulose matrix. At the same time, the values of the elongation at break decreased almost twofold with an increase in the content of the composite additive in the cellulose matrix of up to 10%. Thus, the optimal content of the additive, to ensure good mechanical properties of composite fibers, should not exceed 10%.
3.3. Structure
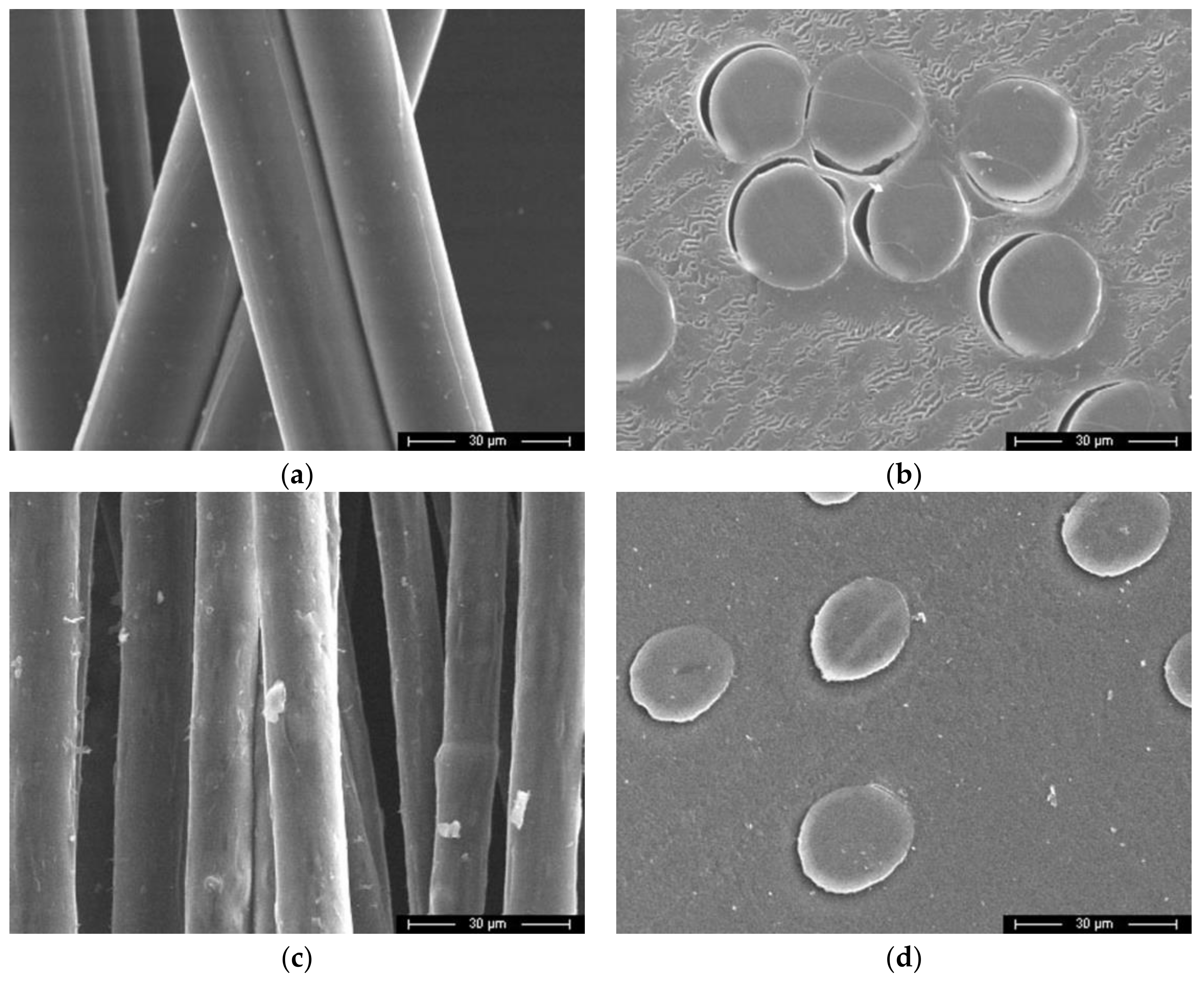
The visualization of the morphology of cellulose and composite fibers was carried out using SEM, and micrographs of the surface and the cross section are shown in Figure 5.
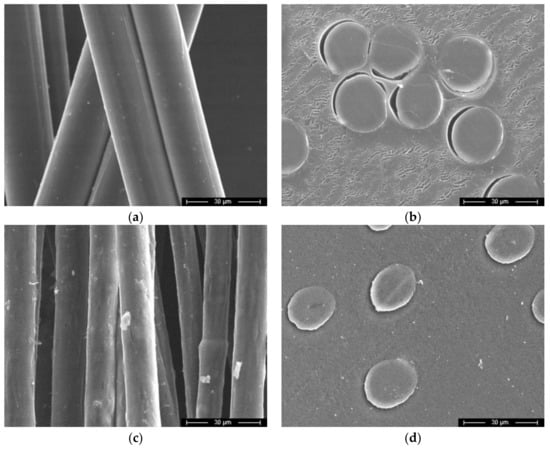
Figure 5.
Micrographs of cellulose (a,b) and composite fibers (c,d) containing 95% cellulose and 5% betulin, surface (a,c) and cross sections (b,d).
In contrast to cellulosic fibers, the composite fibers do not have a flat surface but, in some places, there are elongated craters and rips (waviness). The average composite fibers' diameter was 15 μm. In the photographs of the cross section, it is possible to observe differences in the form of the fibers, corresponding to their transformation from round to oval.
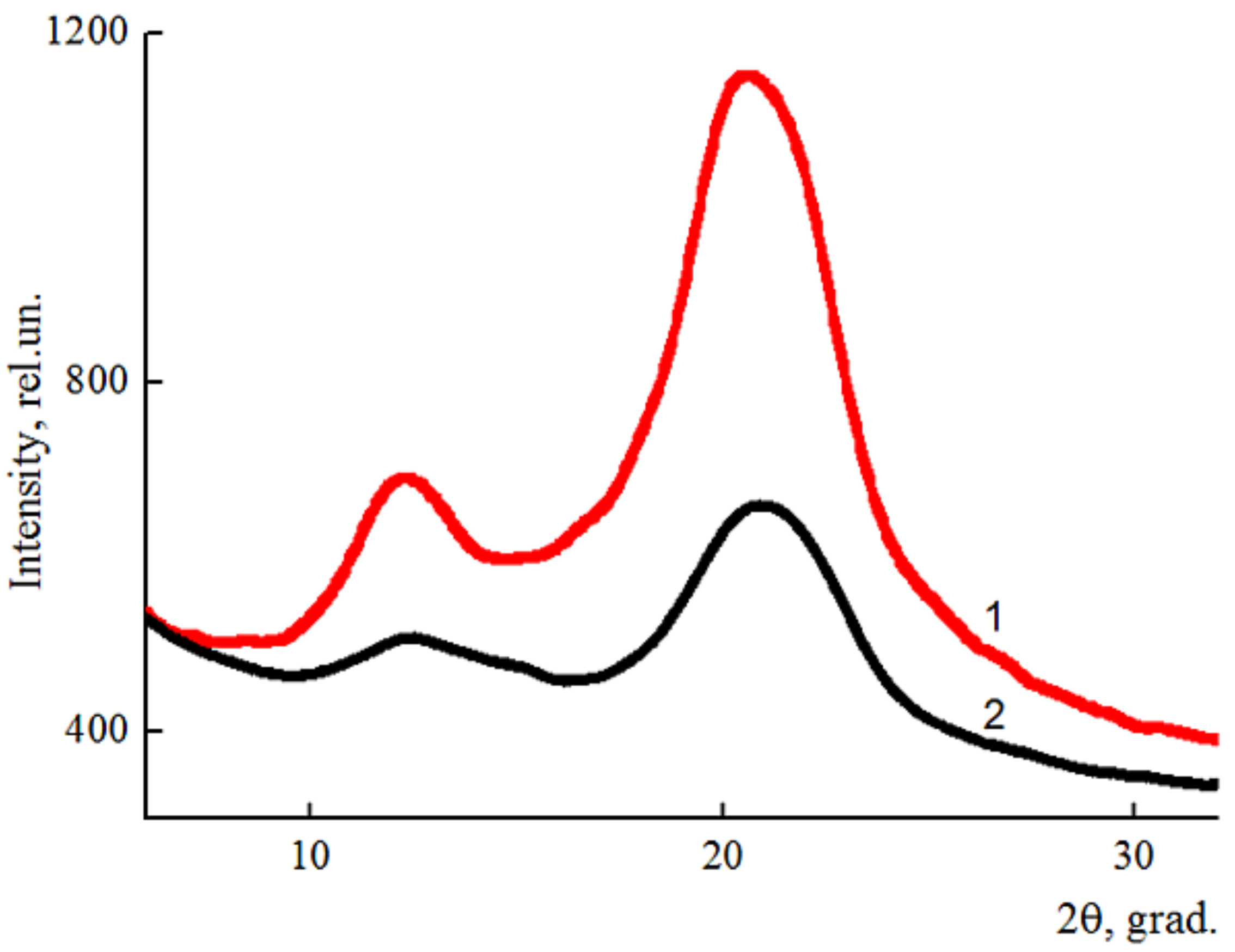
The diffractograms of cellulose and composite fibers are shown in Figure 6.
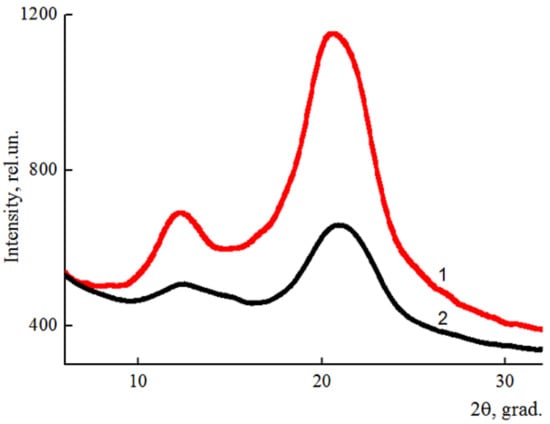
Figure 6.
Equatorial diffractograms of cellulose (1) and composite (95% cellulose + 5% betulin) (2) fibers.
The result of the addition of betulin into the cellulose matrix was a decrease in the intensity of the peaks in the equatorial diffractogram obtained for the composite fiber, and, as a result, the reduction of the degree of ordering in the system. The main peak characterizing betulin (~14.5°) is expressed as the right shoulder of the cellulose peak in the region of 2θ ~ 12° [24]. The basic basal reflexes practically did not change their position when the additive was added to the cellulose matrix and appear in the region of 2θ~12° and ~20.5°, which corresponds to the cellulose polymorph II [25,26].
3.4. Fungal Resistance
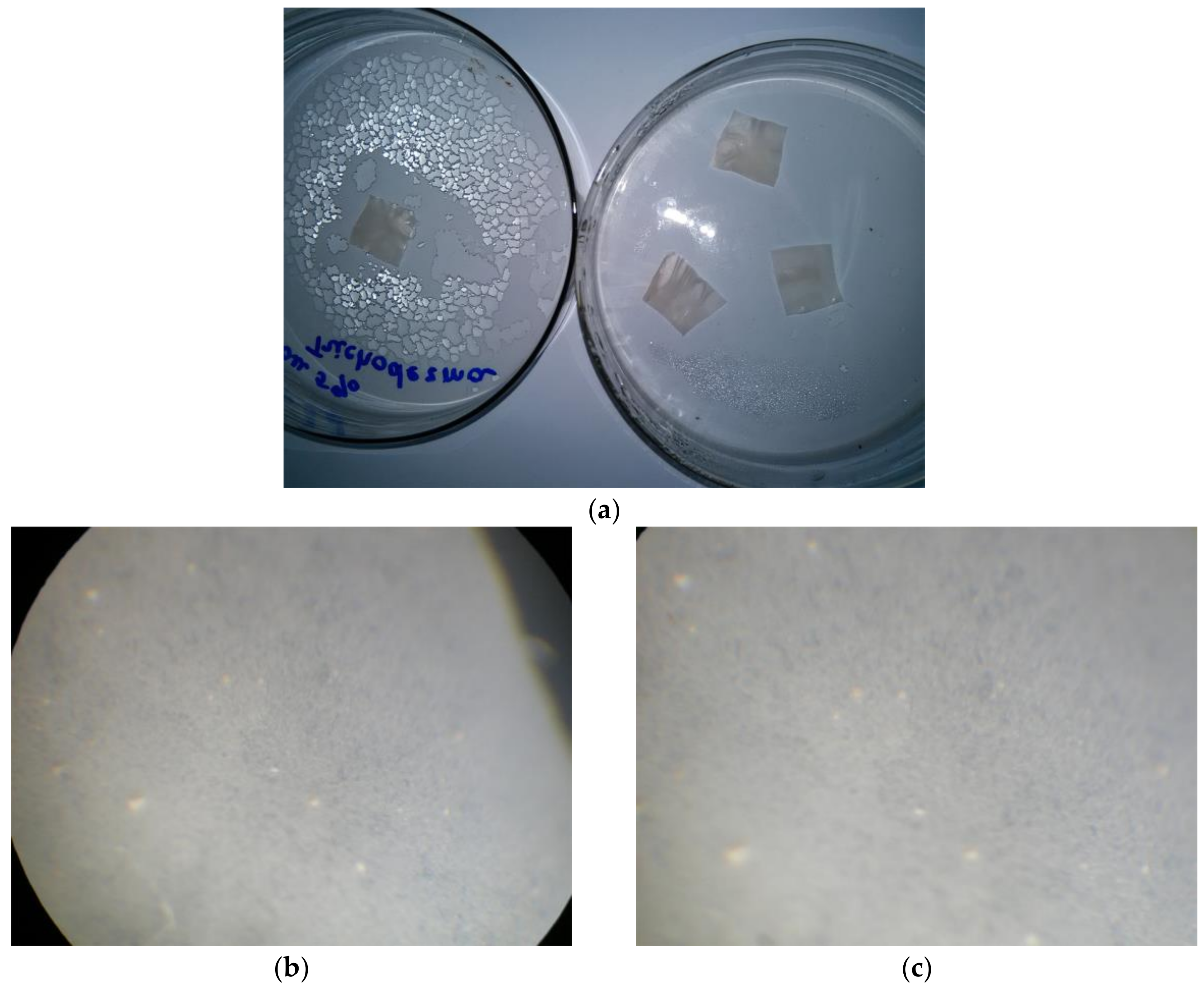
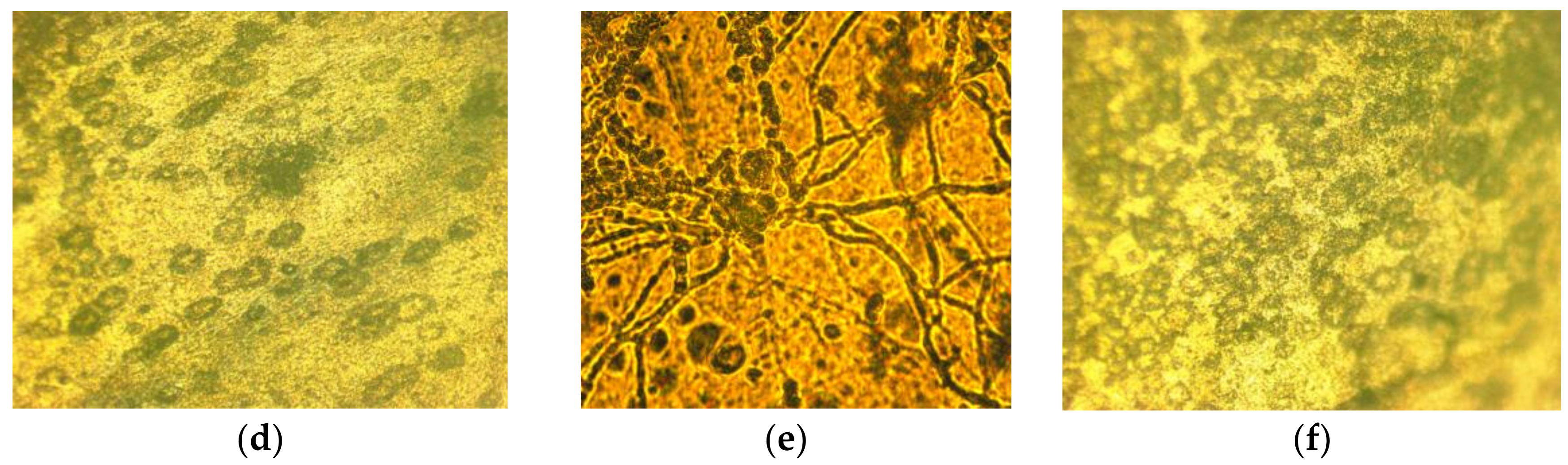
To assess the fungal resistance of the composite materials with a wet-chamber method using a T. viride strain, films containing 5% betulin were used (Figure 7).
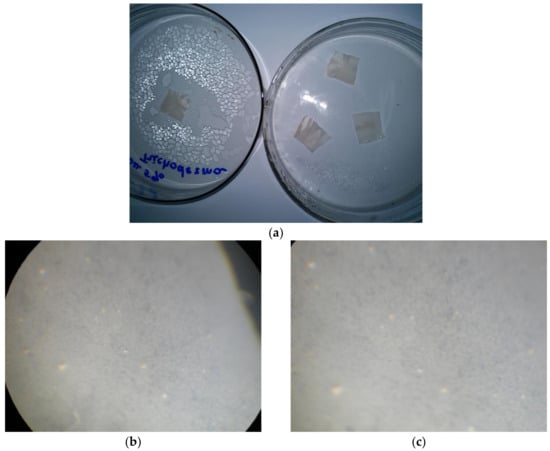
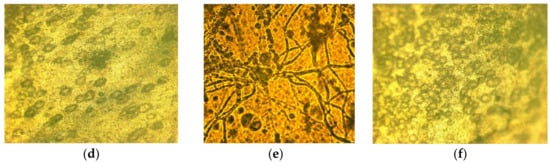
Figure 7.
Evaluation of the fungal resistance of cellulose films with the wet-chamber method using the strain T. viride Pers. ex Fr. General view (a); scanning light microscopy, magnification of 200×: (b) control (uninfected film), (c) test sample; light microscopy, 900× magnification: (d) control (uninfected film), (e) control (infected cellulose film (without betulin)), (f) test sample.
When examining samples of films on micro and macro levels, the development of mycelium of the test strain was not observed. The obtained results indicate that the material has a fungal resistance and in humid conditions does not promote the colonization of the micromycete.
Earlier in the literature, it was noted that the fibers obtained by the NMMO process are characterized by a lower speed distribution of bacteria in comparison with synthetic and cotton fibers [27]. The antimicrobial properties of composite films based on cellulose and betulin were evaluated using E. coli as an example (Figure 8).
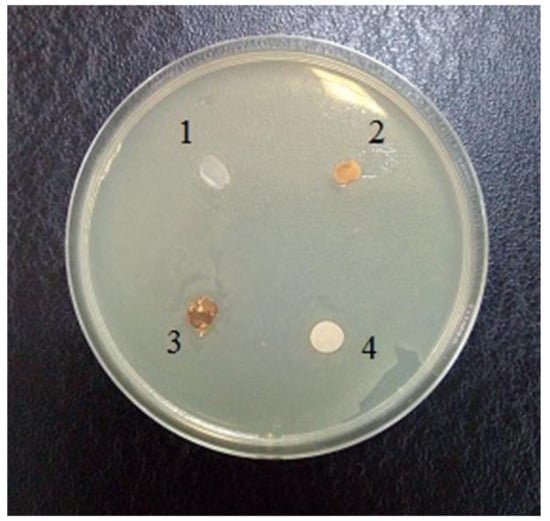
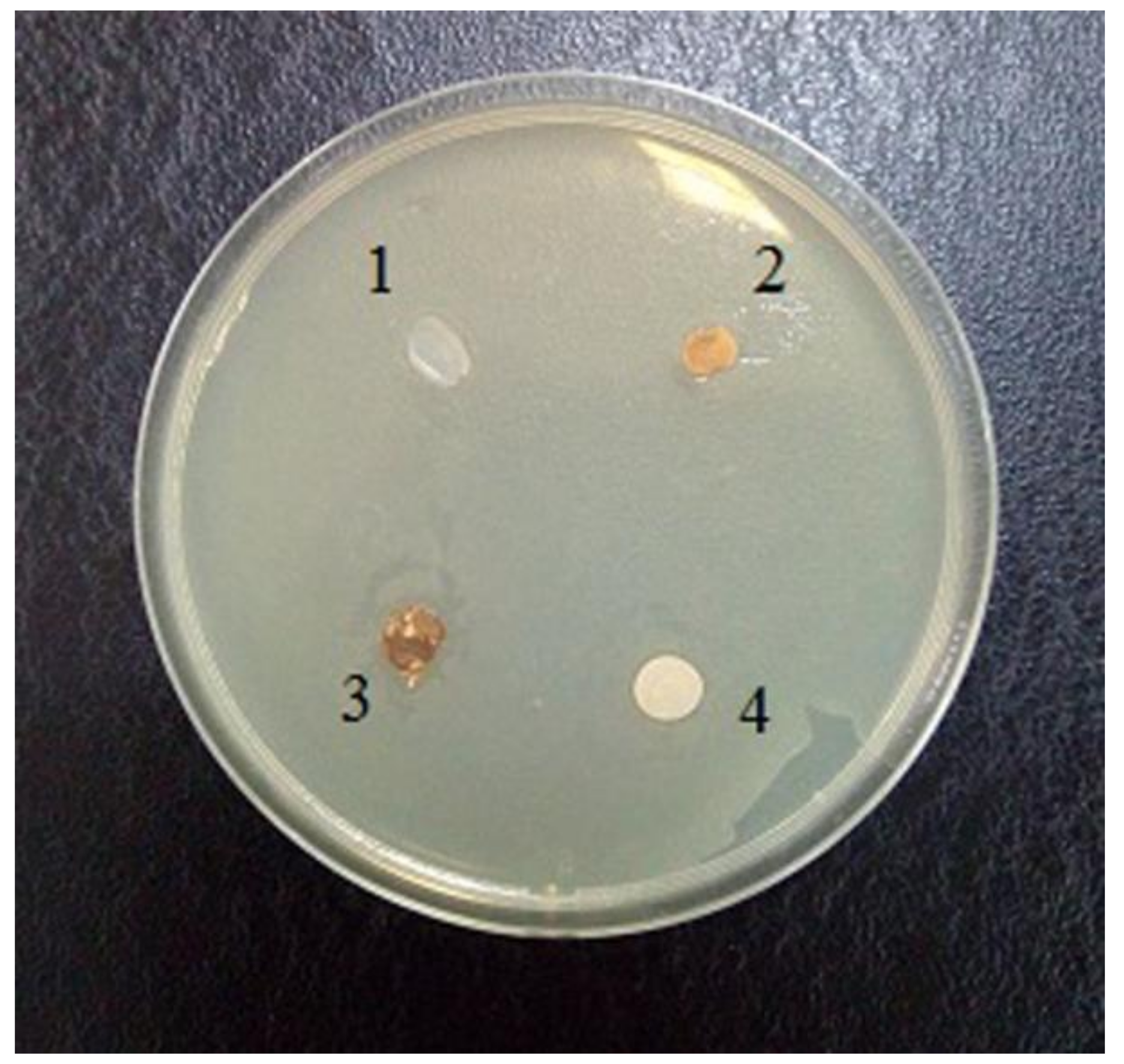
Figure 8.
Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of films with respect to Escherichia coli: 1 composite film (95% cellulose + 5% betulin), 2 filter paper, saturated with mycelium extract of Laetiporus sulphureus strain, 3 bacterial cellulose film, saturated with mycelium extract of L. sulphureus strain, 4 filter paper, wetted pyrogen-free water (control).
The evaluation of the antimicrobial activity towards the Gram-negative strain E. coli showed low activity. As can be seen in Figure 8, zones of growth inhibition are not clearly evident. This indicates the inability of the antimicrobial compounds contained in both the test material and the cellulose impregnated with L. sulphureus mycelium extract to diffuse into agar.
On the other hand, the sample remained unaffected by the bacterium, which may indicate new antibacterial properties of the composite material.
For a more detailed assessment of the fungal resistance of a material saturated with betulin, its antimicrobial activity and the ability of betulin to diffuse into agar, additional tests on a wider range of test strains are necessary, using several methods for evaluating these indices, according to GOST 9.049-91 C. 3 1.2.3.
4. Conclusions
In this study, it was shown that it is possible to form composite fibers based on cellulose and betulin from solid-phase solutions in NMMO. The resulting composite fibers have good mechanical properties and can be used for the production of textile materials. It was shown that the composite materials obtained are resistant to the T. viride strain. Further optimization of the introduction of the composite additive into the spinning solution will allow betulin to be better distributed in the cellulose matrix and, as a result, increase the mechanical parameters and antifungal properties of the final material. Further studies of the resistance to other strains of fungi will reveal promising areas of use of such materials.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Russian Science Foundation grant (No. 17-79-30108).
Author Contributions
Igor Makarov spun the fibers and wrote the paper, Gulbarshin Shambilova prepared the solutions, Markel Vinogradov performed the determination of rheological and mechanical properties, Tatyana Gromovykh and Vera Sadykova carried out the fungal and bacterial resistance experiments, Sergey Lutsenko and Nataliya Feldman set goals and analyzed the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McCance, K.L.; Huether, S.E. Pathophysiology-E-Book: The Biologic Basis for Disease in Adults and Children (Pathophysiology the Biologic Basis), 7th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2014; p. 1864. [Google Scholar]
- Voronchikhin, V.D.; Bondar, P.N. Evaluation of the fungi resistance of film-forming agents used to modify the surface of wood post 1. Fungi resistance of functional oligodenes. Hvojnye Boreal’noj Zony 2016, XXXIV, 117–120. (In Russian). Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=27541433 (accessed on 9 March 2018).
- Lazareva, S.V.; Smirnov, V.F.; Struchkova, I.V. Influence of the components of the culture medium on the phenoloxidase activity of the micromycetes Trichoderma viride and Trichderma Lignorum. Vestnik of Lobachevsky University of Nizhni Novgorod 2008, 1, 77–80. (In Russian). Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=10007939 (accessed on 9 March 2018).
- Kumar, K.; Amaresan, N.; Bhagat, S.; Madhuri, K.; Srivastava, R.C. Isolation and Characterization of Trichoderma spp. for Antagonistic Activity Against Root Rot and Foliar Pathogens. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryabin, G.K.; Golovlev, E.L.; Klesov, A.A. Problems of Bioconversion of Plant Raw Materials; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1986; p. 292. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Eremenko, A.M.; Petrik, I.S.; Smirnova, N.P.; Rudenko, A.V.; Marikvas, Y.S. Antibacterial and Antimycotic Activity of Cotton Fabrics, Impregnated with Silver and Binary Silver/Copper Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kislitsyn, A.N. Extractive substances birch bark: Isolation, composition, properties, application. Himiya Drev. 1994, 3, 3–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Li, D.; Ottenhall, A.; Ek, M. Cellulose fiber based fungal and water resistant insulation materials. Holzforschung 2017, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzubak, P.; Hajduch, M.; Vydra, D.; Hustova, A.; Kvasnica, M.; Biedermann, D.; Markova, L.; Urban, M.; Sarek, J. Pharmacological activities of natural triterpenoids and their therapeutic implications. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 394–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakova, O.B.; Giniyatullina, G.V.; Yamansarov, E.Y.; Tolstikov, G.A. Betulin and ursolic acid synthetic derivatives as inhibitors of papilloma virus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4088–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, C.; Li, C.; Deng, G. Betulin suppresses S. aureus-induced mammary gland inflammatory injury by regulating PPAR-γ in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Qui, J.; Feng, H. Betulin protects mice from bacterial pneumonia and acute lung injury. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 75, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Li, D.; Ek, M. Water repellency improvement of cellulosic textile fibers by betulin and a betulin-based copolymer. Cellulose 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I.S.; Golova, L.K.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Skvortsov, I.Yu.; Mironova, M.V.; Bermeshev, M.V. Composite fibers based on cellulose and tetraethoxysilane: Preparation, structure and properties. Fibre Chem. 2017, 49, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulovskaya, S.A.; Garas'ko, E.V.; Kuz’min, S.M.; Semenov, YA.S.; Parfenyuk, V.I. Fungicidal properties of a cellulose-based composite material with zeolite additives. Khimija Rastitel’nogo Syr’ja 2012, 3, 49–53. (In Russian). Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=18807214 (accessed on 9 March 2018).
- Golova, L.K.; Borodina, O.E.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Lyubova, T.A.; Krylova, T.B. The Solid-Phase MMO Process. Fibre Chem. 2000, 32, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenau, T.; Potthast, A.; Sixta, H.; Kosma, P. The chemistry of side reactions and byproduct formation in the system NMMO/cellulose (Lyocell process). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1763–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikova, E.P.; Golova, L.K.; Makarov, I.S.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Rheological properties of mixed solutions of cellulose and layered aluminosilicates in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2013, 55, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulichikhin, V.; Golova, L.; Makarov, I.; Bondarenko, G.; Makarova, V.; Ilyin, S.; Skvortsov, I.; Berkovich, A. Solutions of acrylonitrile copolymers in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide: Structure, properties, fiber spinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, I.S.; Golova, L.K.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Rebrov, A.V.; Berkovich, A.K.; Skvortsov, I.Yu.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Composite Fibers Based on Cellulose and Polyacrylonitrile Copolymers. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, F.; Meister, F.; Montigny, R.; Wagener, M. A New Antimicrobial ALCERU Fiber with Silver Nanoparticles. Fibers Text. East. Eur. 2007, 64, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Golova, L.K.; Romanov, V.V.; Balashova, O.B. Method for Producing a Solution for Spinning Fibers RF Patent 1645308, 1992. Available online: http://patents.su/3-1645308-sposob-polucheniya-rastvora-dlya-formovaniya-volokon.html (accessed on 9 March 2018).
- Egorov, N.S. Fundamentals of the doctrine of antibiotics. In Classical University Textbook, 6th ed.; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2004; p. 528. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mikhaylenko, M.A.; Shakhtshneyderb, T.P.; Brezgunova, M.E.; Drebuschak, V.A.; Kuznetsova, S.A.; Boldyrev, V.V. Obtaining and studying the physico-chemical properties of betulin solvates. Khimija Rastitel’nogo Syr’ja 2010, 2, 63–70. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, I.S.; Golova, L.K.; Kuznetsova, L.K.; Antonov, S.V.; Kotsyuk, A.V.; Ignatenko, V.Ya.; Kulichikhin, V.G. Influence of Precipitation and Conditioning Baths on the Structure, Morphology, and Properties of Cellulose Films. Fibre Chem. 2016, 48, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, R. Biodegradable and Sustainable Fibres; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Firgoa, H.; Schuster, K.C.; Suchomel, F.; Männer, J.; Burrow, T.; Abu-Rous, M. The Functional Properties of TENCEL®—A Current Update. Lenzing. Berichte 2006, 85, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).