Spider Silk/Polyaniline Composite Wire
Abstract
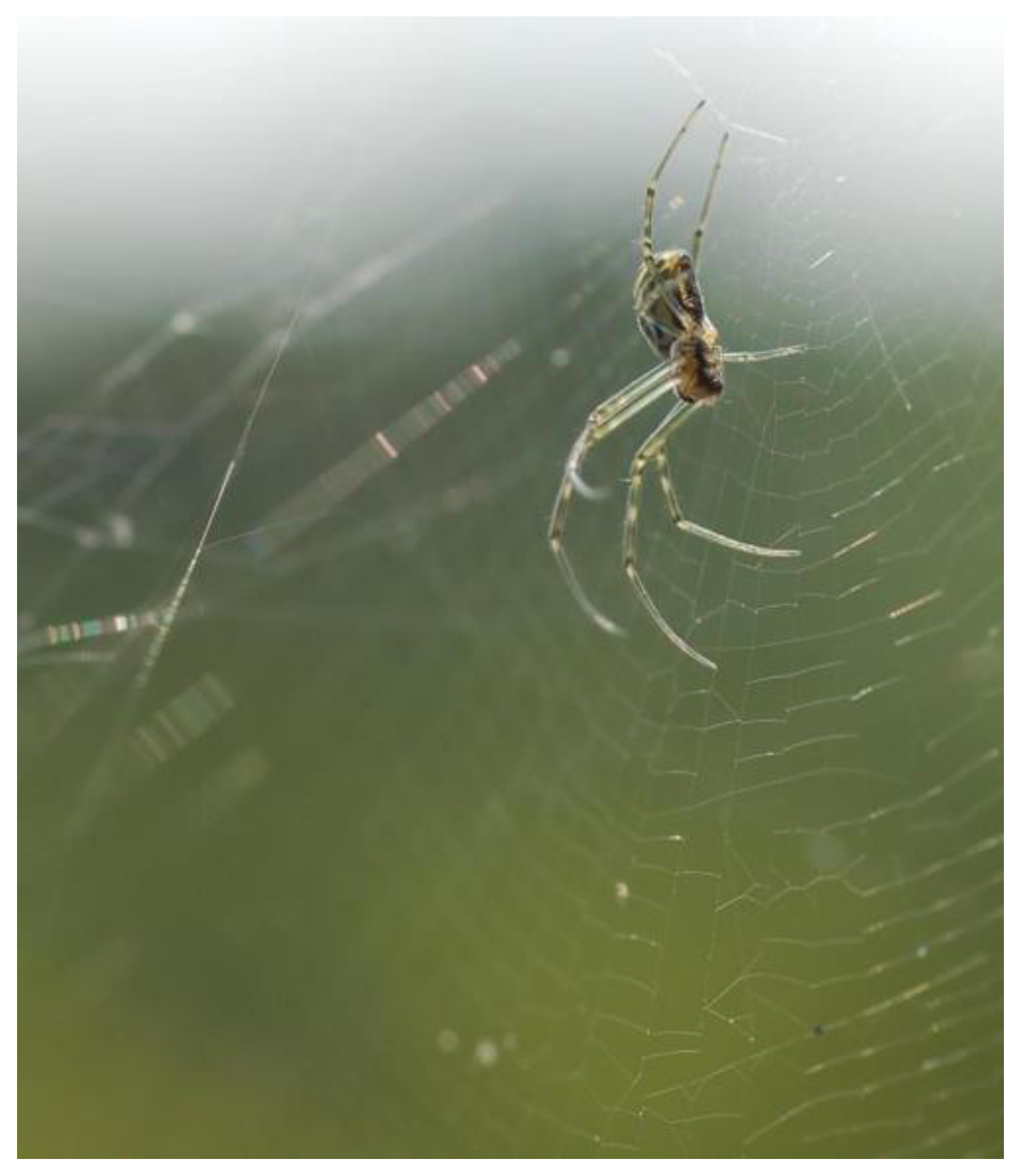
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Spider Silk
2.2. Polymerization of Aniline in the Presence of Spider Silk
3. Results and Discussion
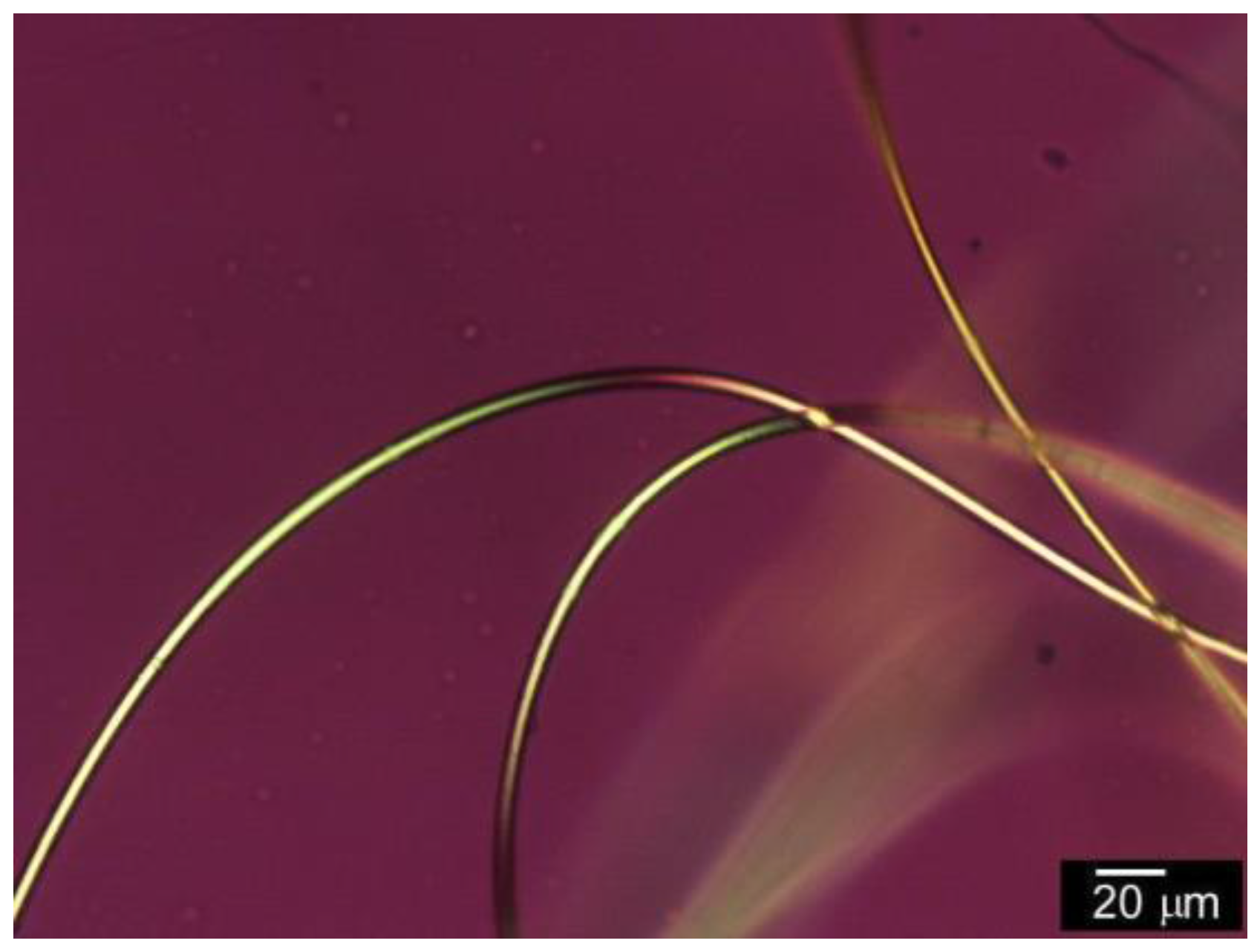
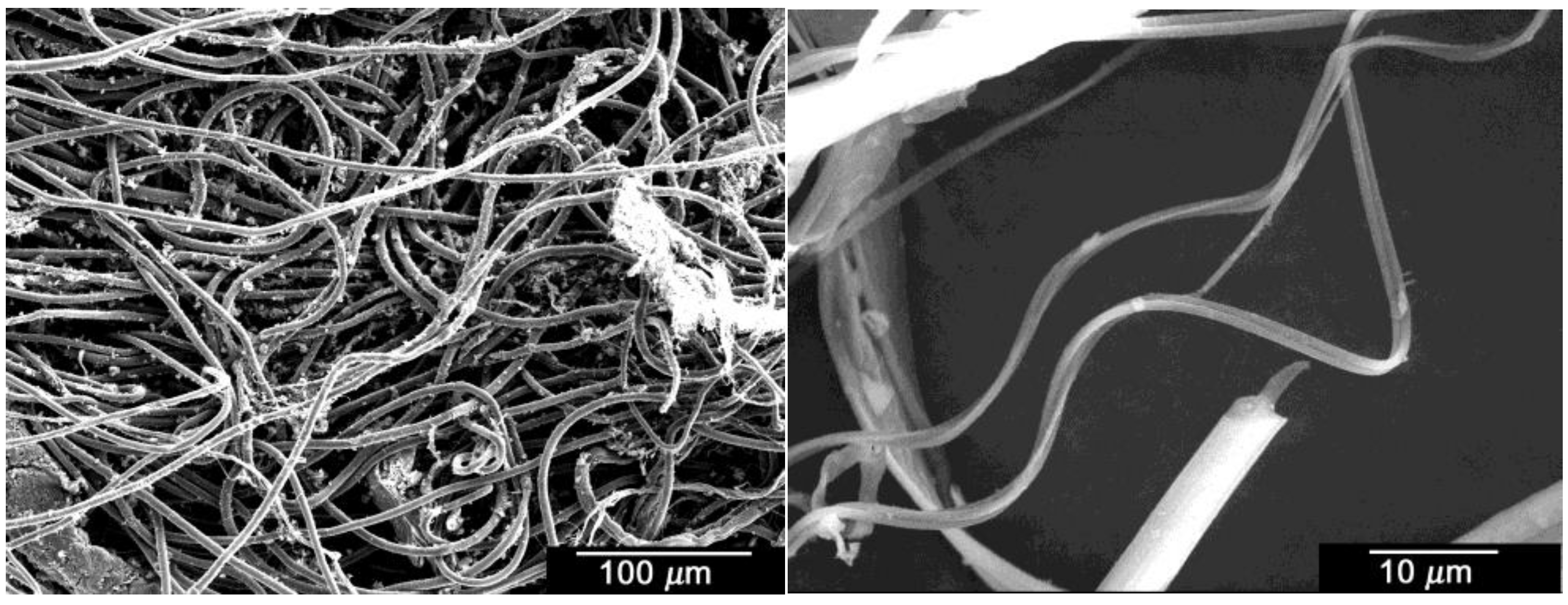
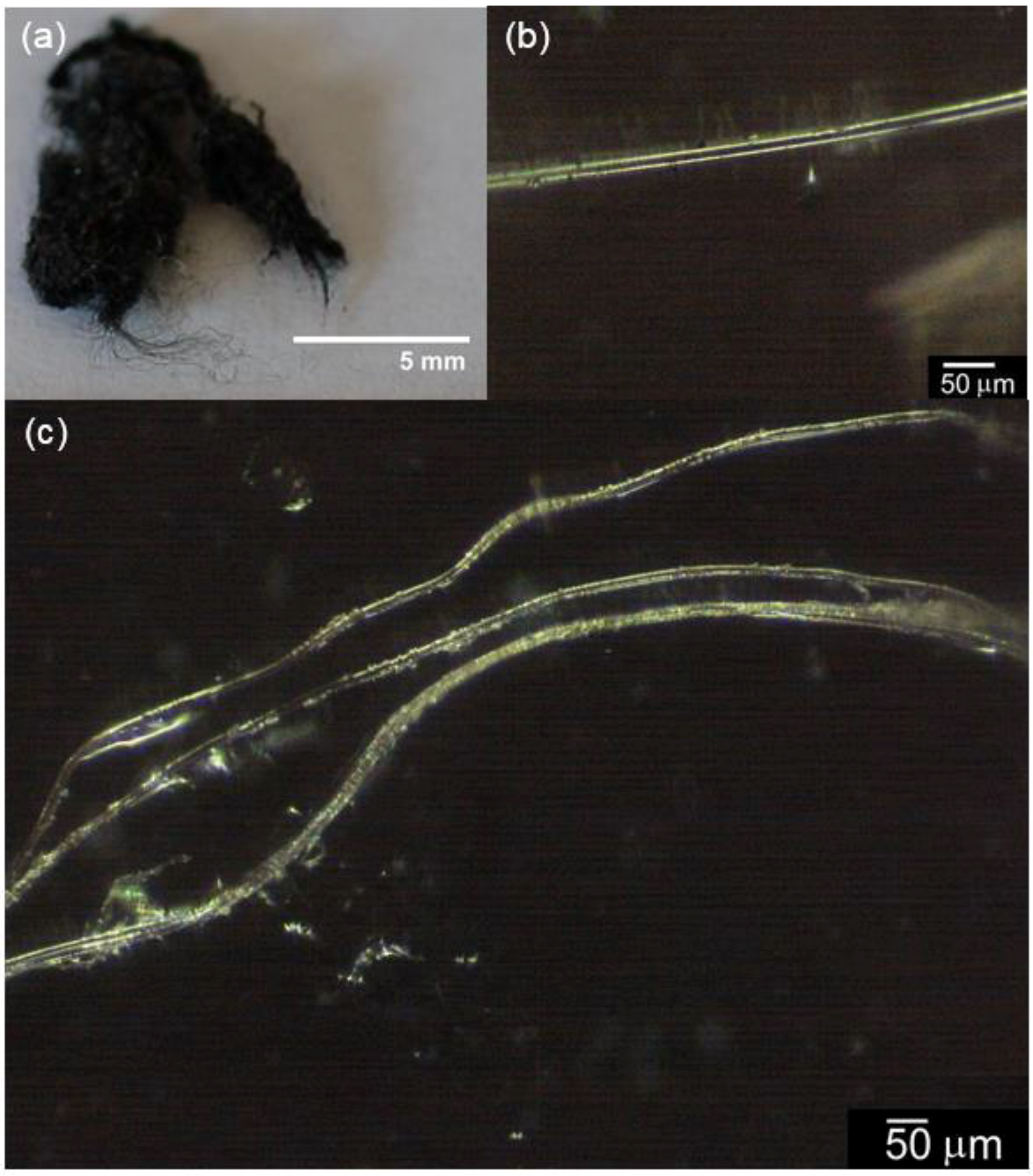
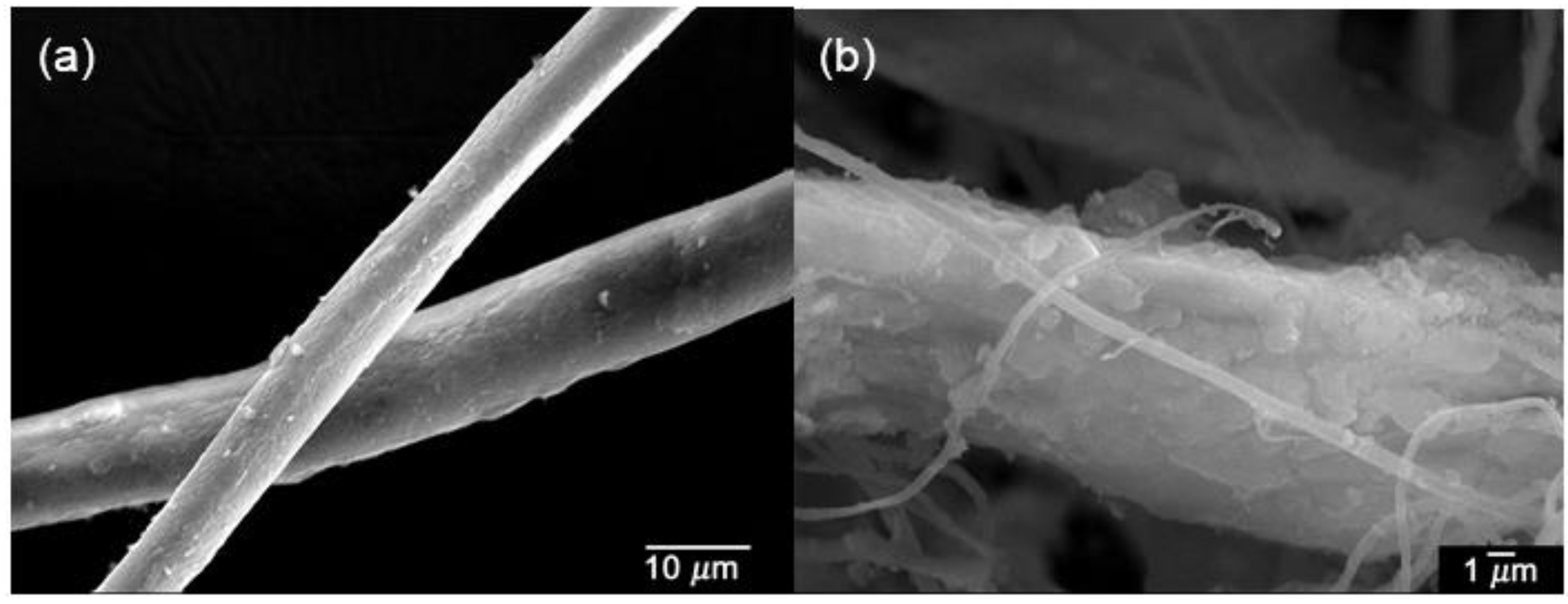
3.1. Surface Observation
3.2. Infrared Absorption
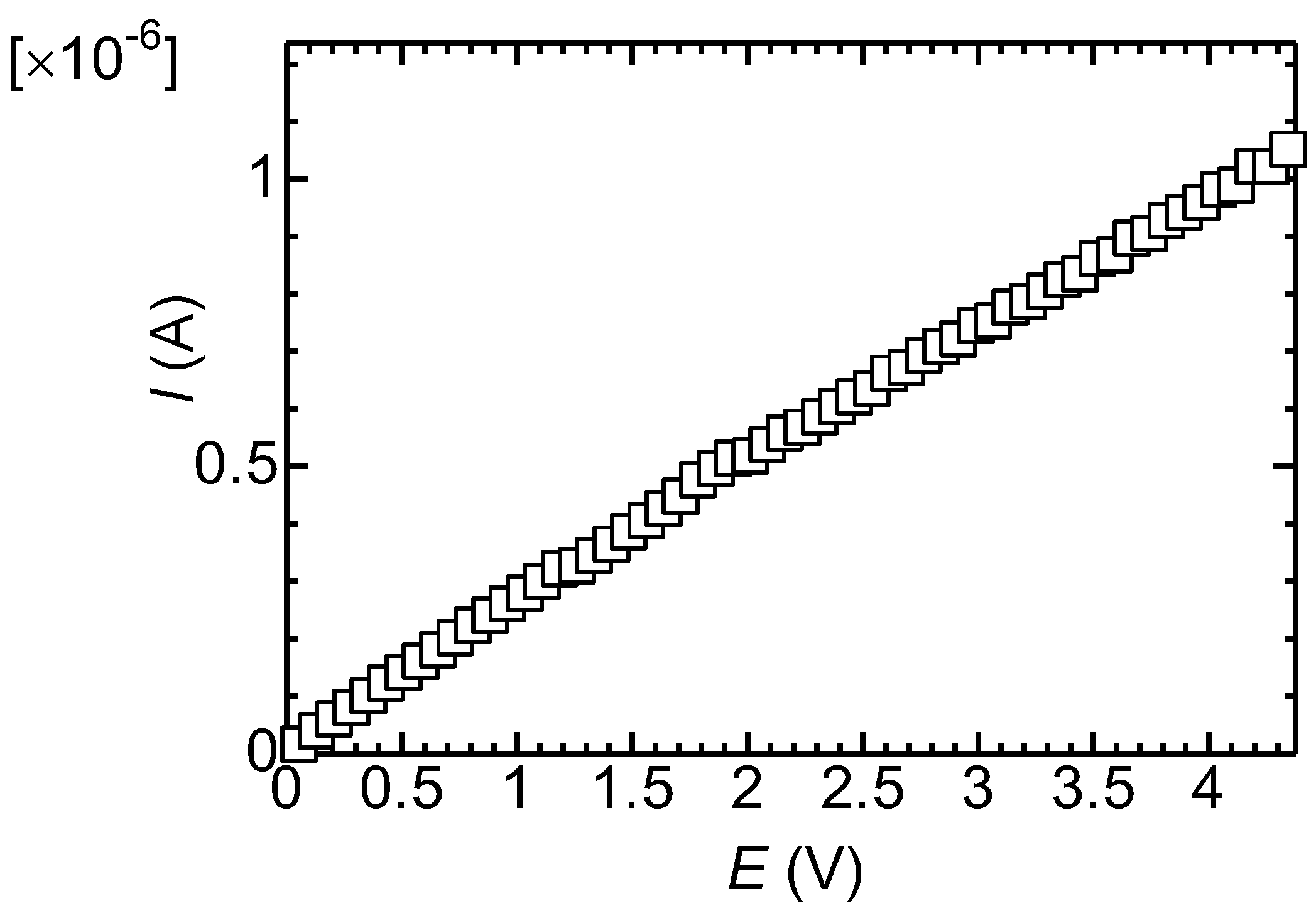
3.3. Electrical Properties
4. Conclusions
Techniques
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osaki, S. Spider silk as mechanical lifeline. Nature 1996, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humenik, M.; Smith, A.M.; Scheibel, T. Recombinant spider silks—Biopolymers with potential for future applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 640–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, Y.; Sezutsu, H.; Nakajima, K.; Tamada, Y.; Kojima, K. High-toughness silk produced by a transgenic silkworm expressing spider (araneus ventricosus) dragline silk Protein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teulé, F.; Miao, Y.G.; Sohn, B.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hull, J.J.; Fraser, M.J., Jr.; Lewis, R.V.; Jarvis, D.L. Silkworms transformed with chimeric silkworm/spider silk genes spin composite silk fibers with improved mechanical properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.-X.; Qian, Z.-G.; Ki, C.S.; Park, Y.H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Lee, S.Y. Native-sized recombinant spider silk protein produced in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli results in a strong fiber. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14059–14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futahashi, R.; Okamoto, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Zhong, Y.S.; Iwanaga, M.; Mita, K.; Fujiwara, H. Genome-wide identification of cuticular protein genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, C.; Hedhammar, M.; Feinstein, R.; Nordling, K.; Kratz, G.; Johansson, J.; Huss, F.; Rising, A. Tissue response to subcutaneously implanted recombinant spider silk: An in vivo study. Materials 2009, 2, 1908–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, E.; Saleh, W.R.; Lebedev, V.; Acquah, S.F.A.; Laukhin, V.; Alamo, R.G.; Brooks, J.S. Carbon nanotubes on a spider silk scaffold. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhu, H. Natural silk fibroin/polyaniline (core/shell) coaxial fiber: Fabrication and application for cell proliferation. Compos. Sci. Tech. 2013, 77, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet-Mercier, F.; Lefèvre, T.; Auger, M.; P’ezolet, M. Evidence by infrared spectroscopy of the presence of two types of b-sheets in major ampullate spider silk and silkworm silk. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, I.; Jing, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, F. Infrared spectra of soluble polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1988, 24, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

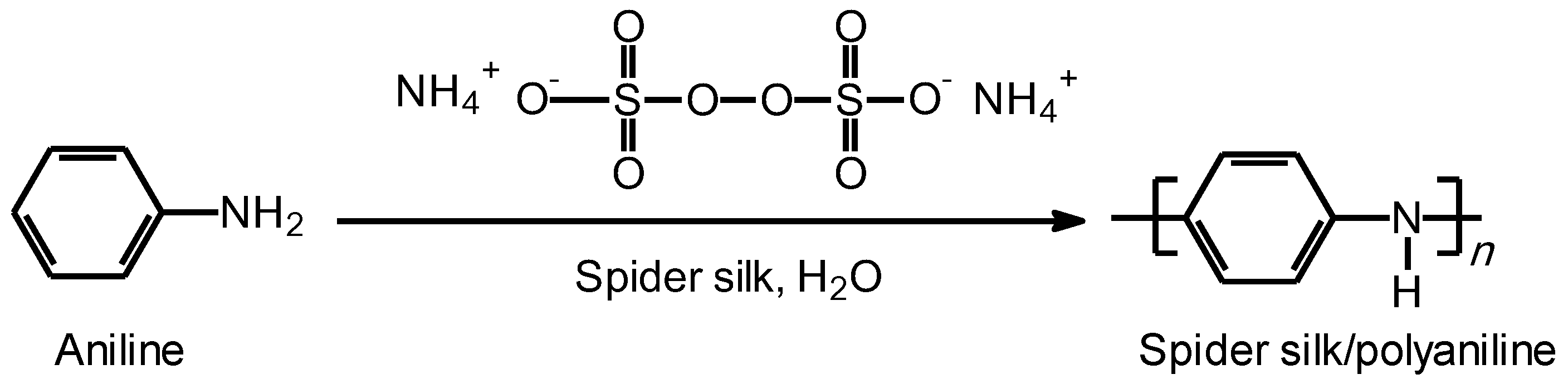

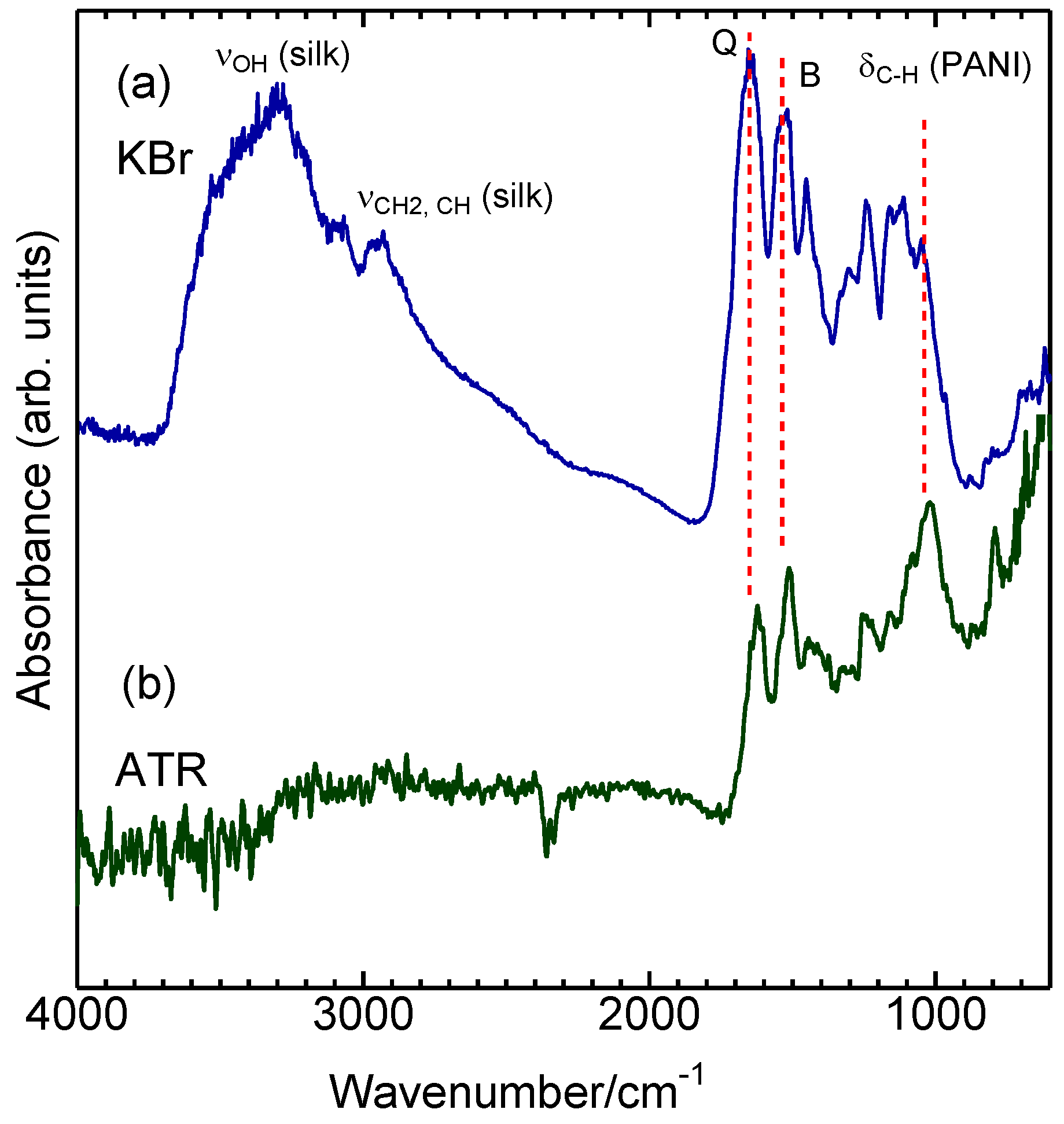

| Assignment | KBr a | ATR b |
|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | ||
| OH str. c | 3304 | - |
| CH and CH2 | 2950 | - |
| Quinoid | 1660 | 1623 |
| Benzenoid | 1532 | 1515 |
| Str. c of benzene ring | 1451 | 1452 |
| C–N str. in BBB | 1241 | 1253 |
| C–H ip d on 1,2,4-ring | 1049 | 1028 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goto, H.; Kikuchi, R.; Wang, A. Spider Silk/Polyaniline Composite Wire. Fibers 2016, 4, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020012
Goto H, Kikuchi R, Wang A. Spider Silk/Polyaniline Composite Wire. Fibers. 2016; 4(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoto, Hiromasa, Ryosuke Kikuchi, and Aohan Wang. 2016. "Spider Silk/Polyaniline Composite Wire" Fibers 4, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020012
APA StyleGoto, H., Kikuchi, R., & Wang, A. (2016). Spider Silk/Polyaniline Composite Wire. Fibers, 4(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020012






