The Effect of Direct and Pulsed Current in the Presence of Surfactants on the Electrodeposition of Zn–SiC Nanocomposite Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
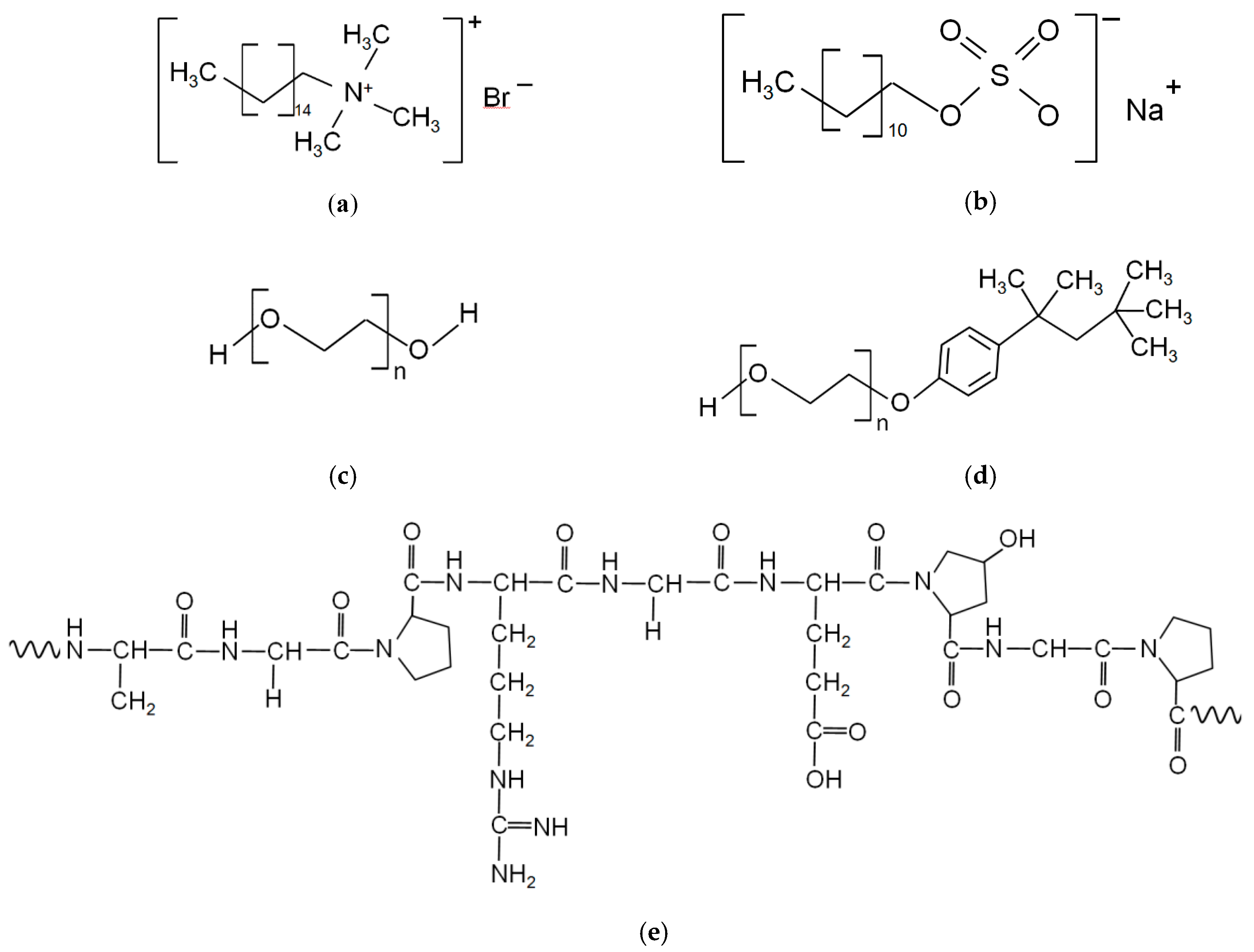
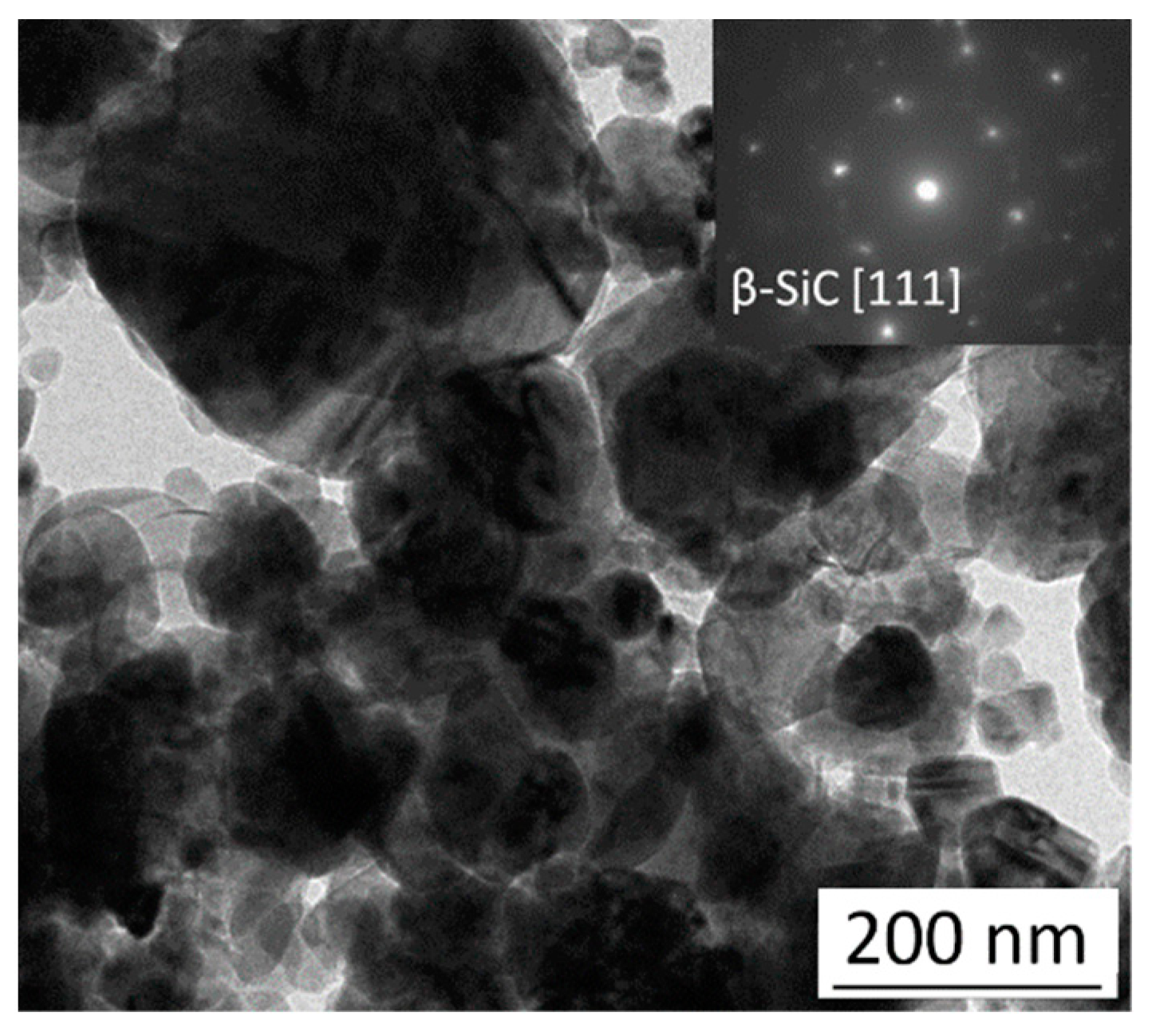
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Voltammetric Studies
3.2. Direct Current Deposition (DCD) from Zn–cit–SiC Baths
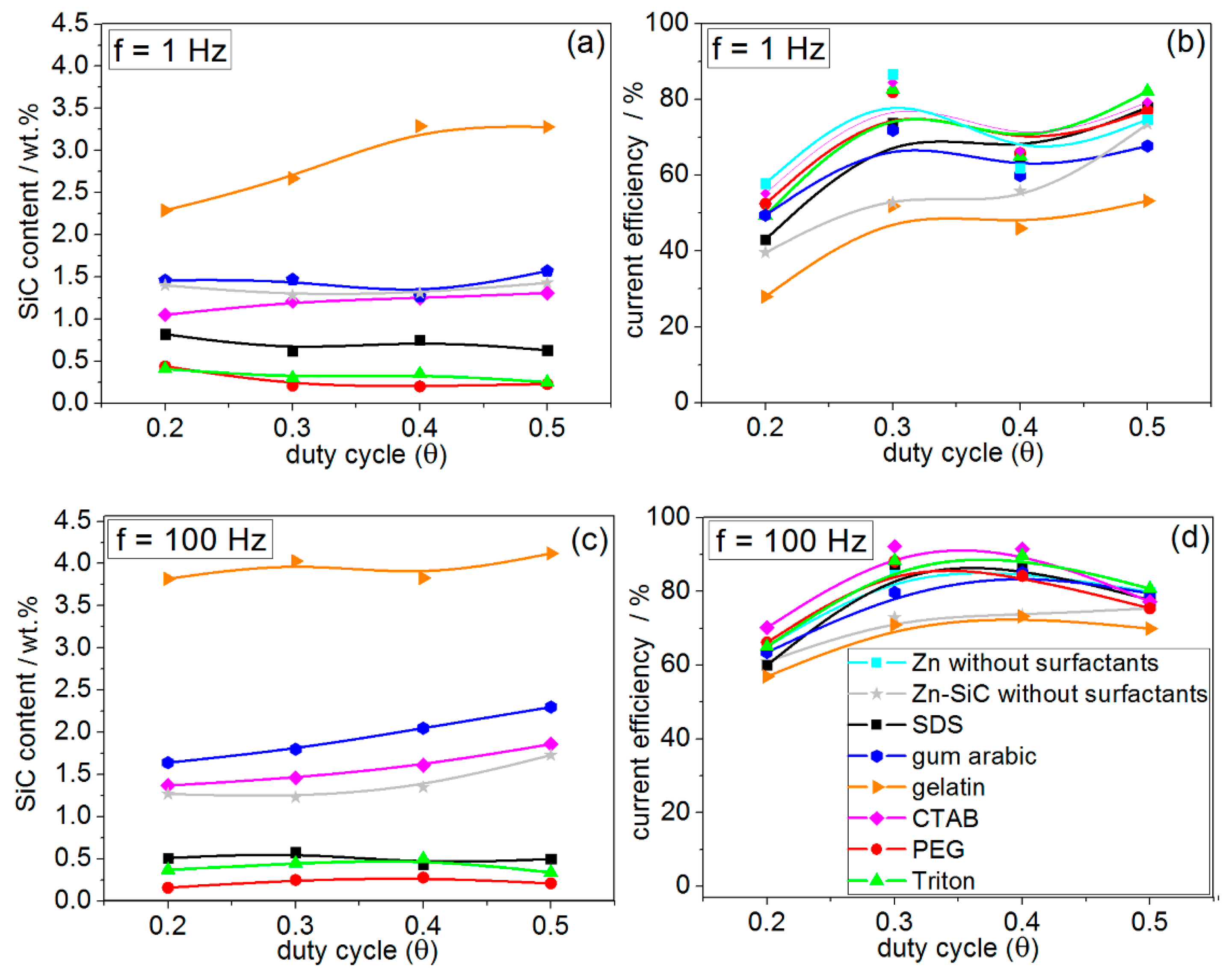
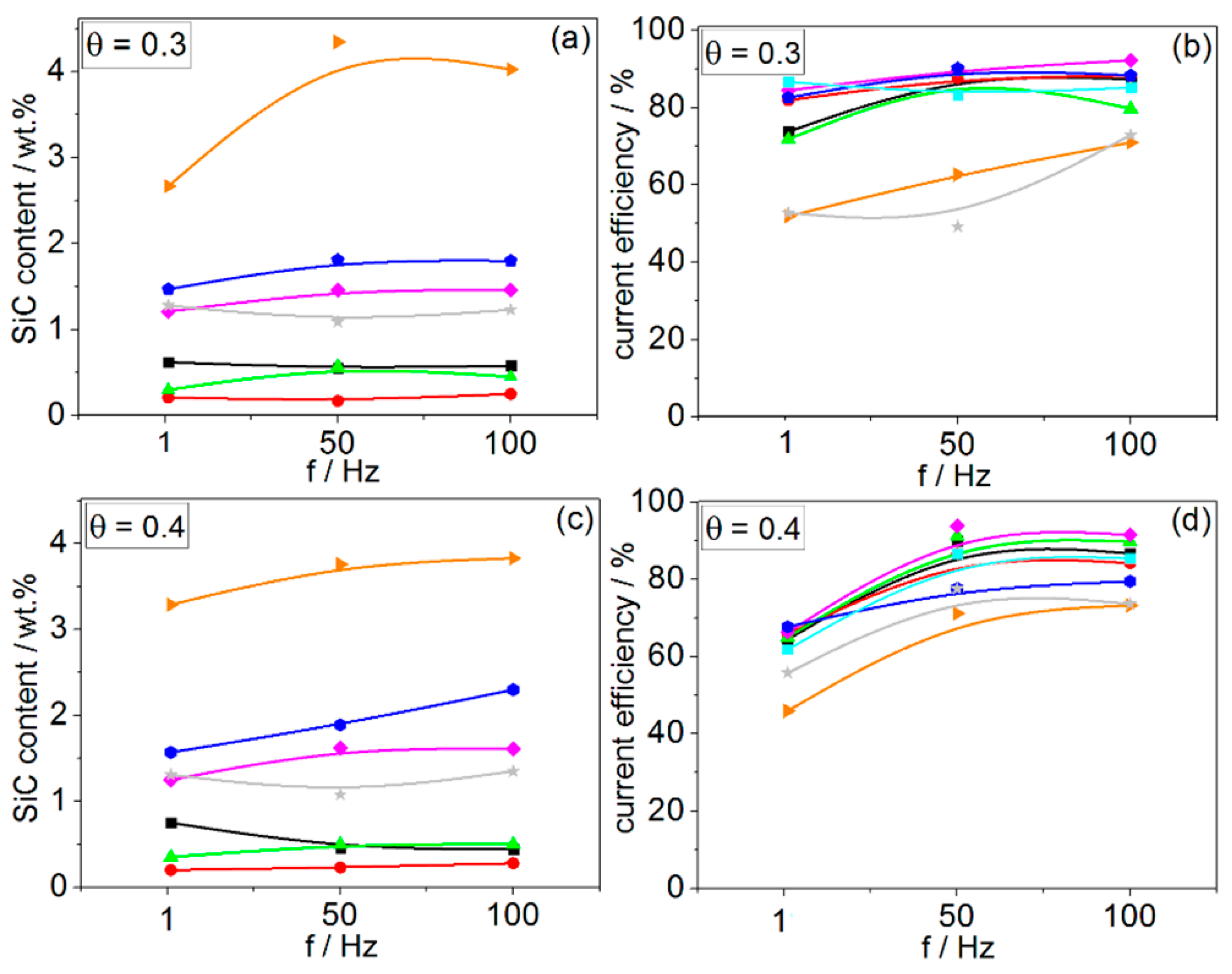
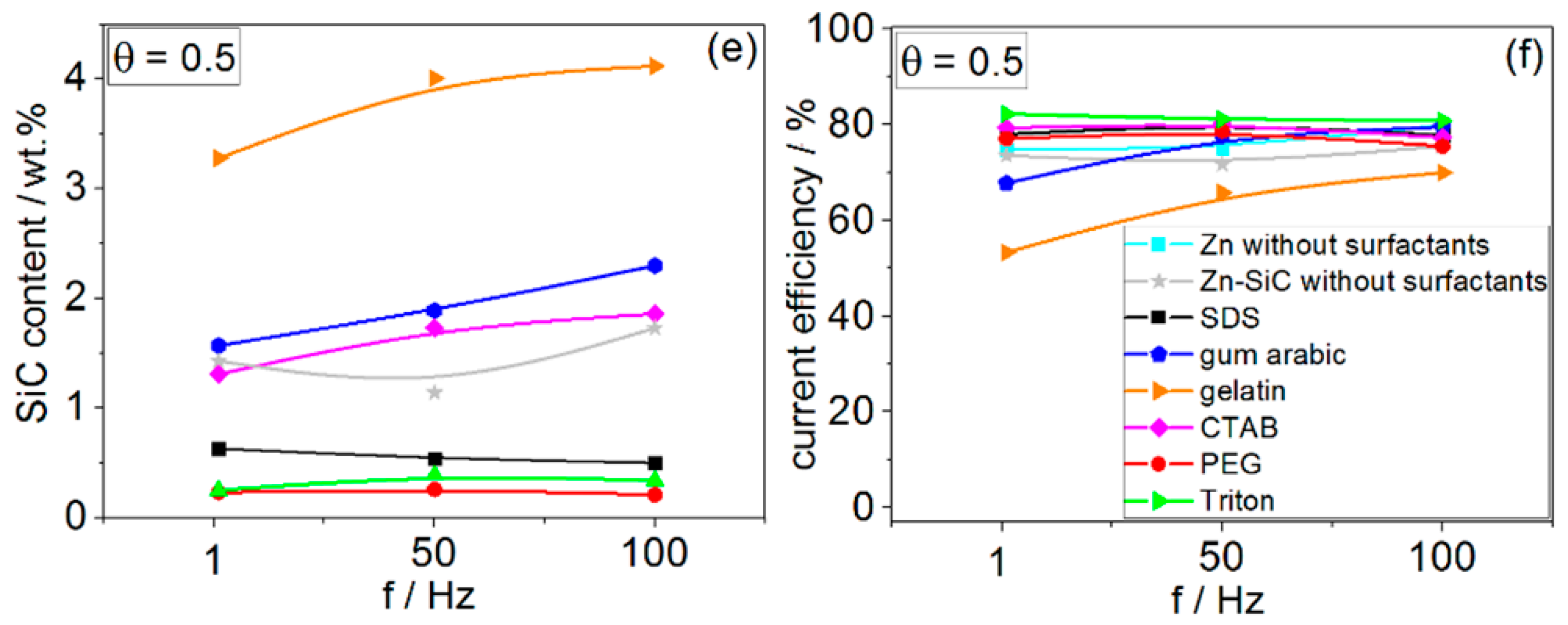
3.3. Pulsed Current Electrodeposition (PED) from Zn–cit–SiC Baths
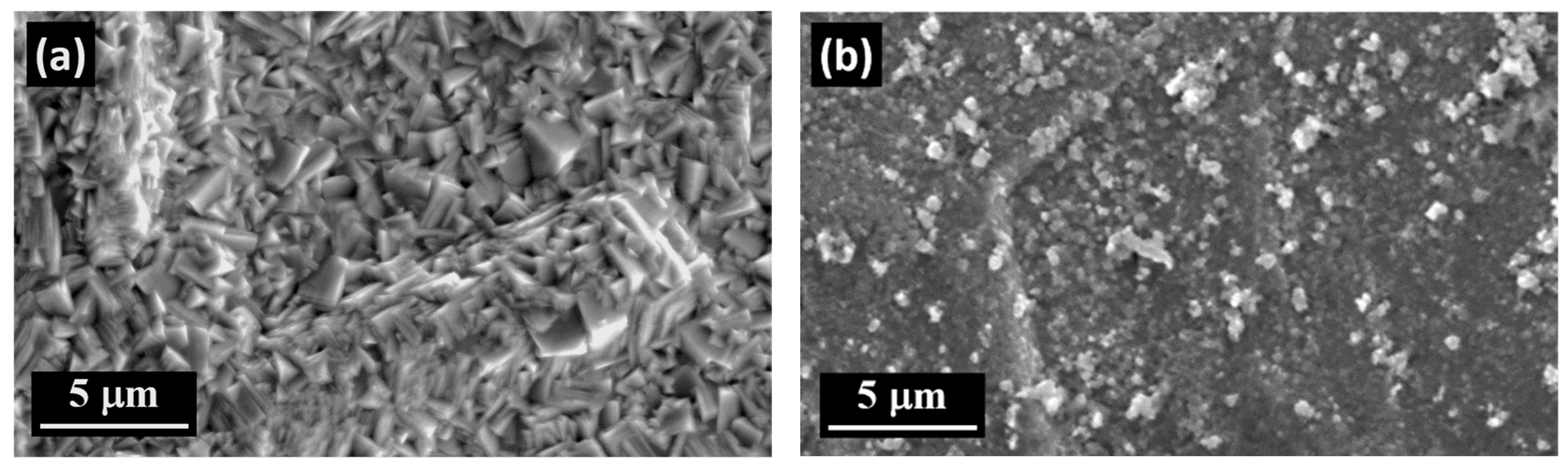
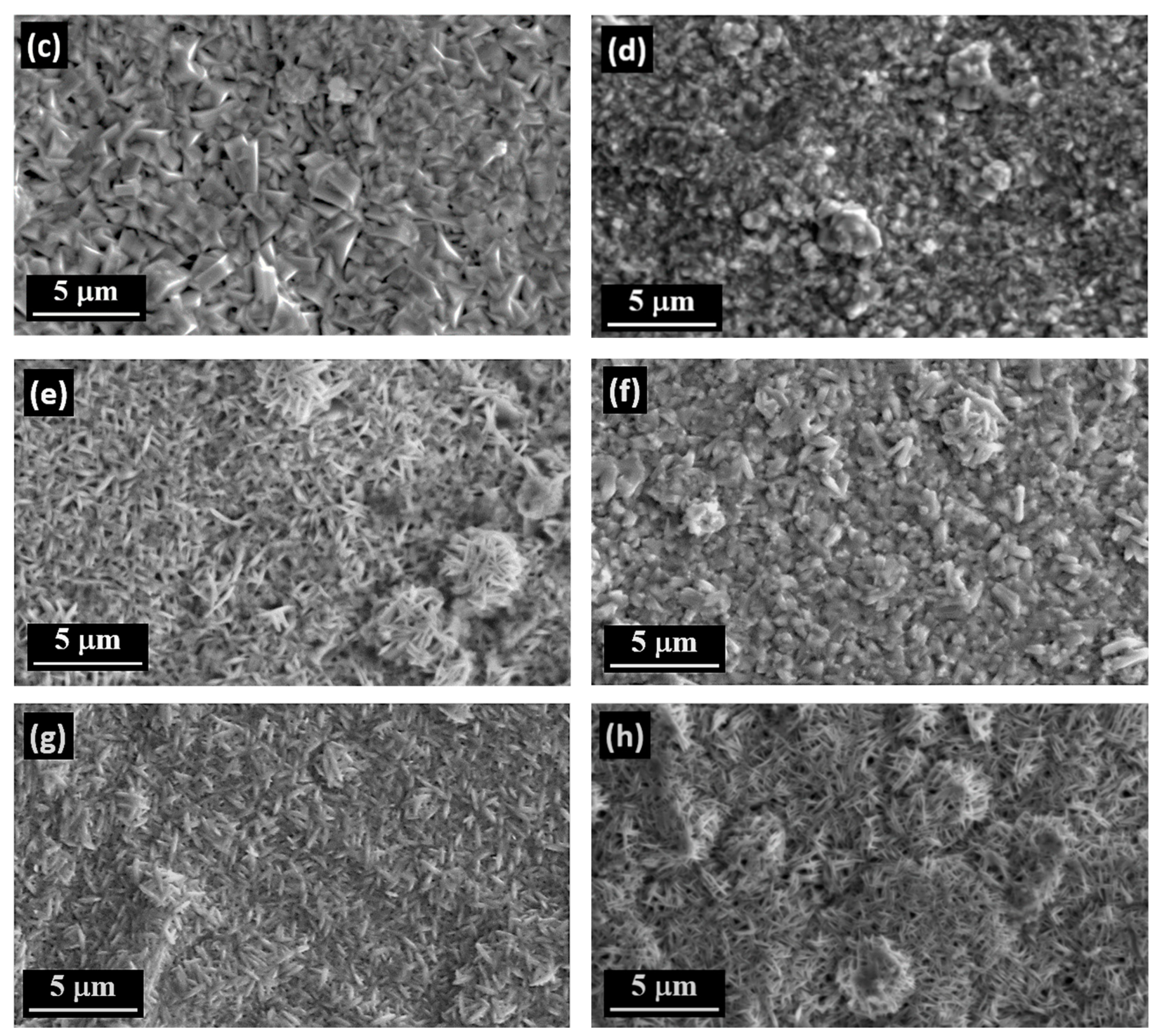
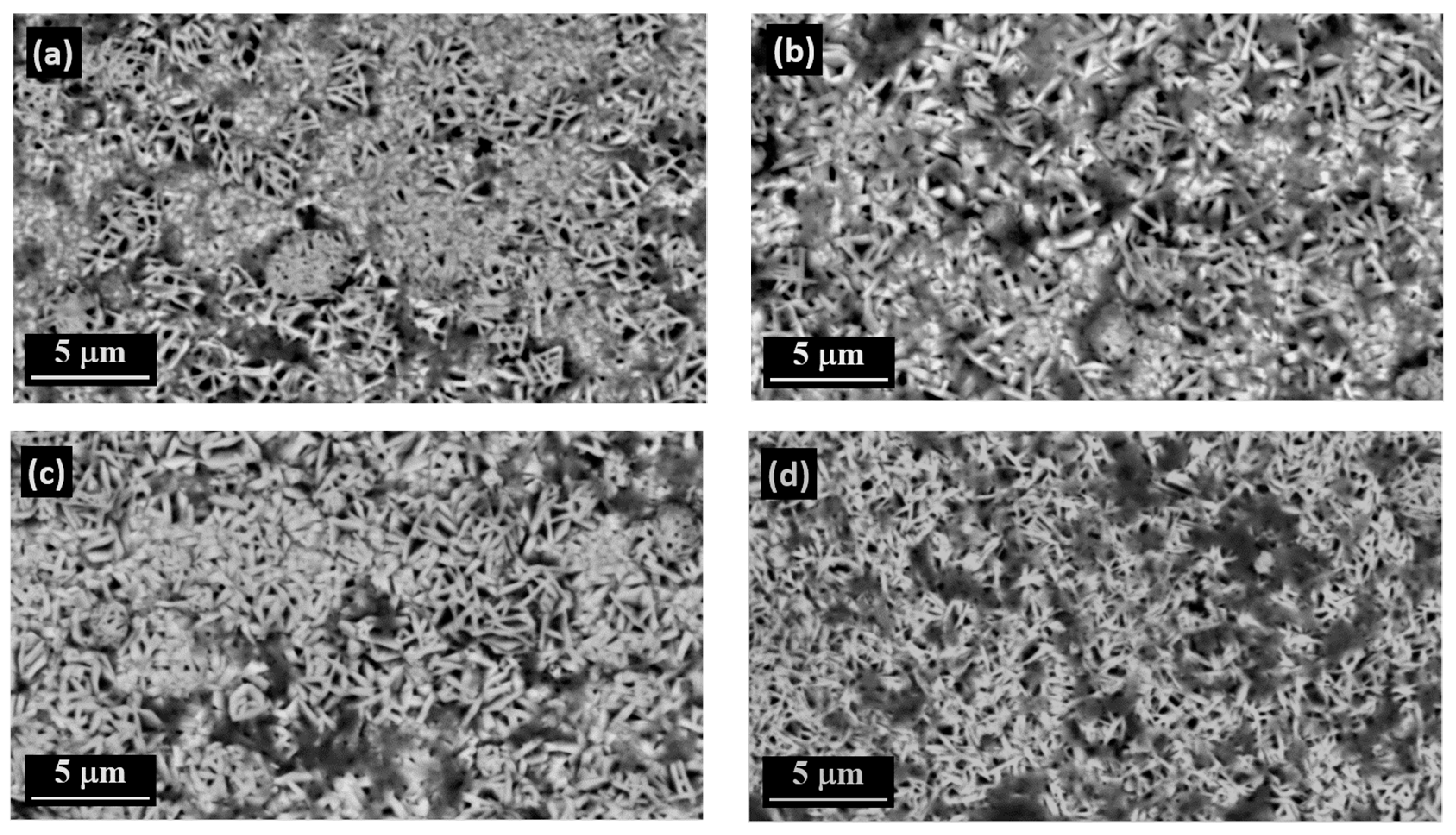
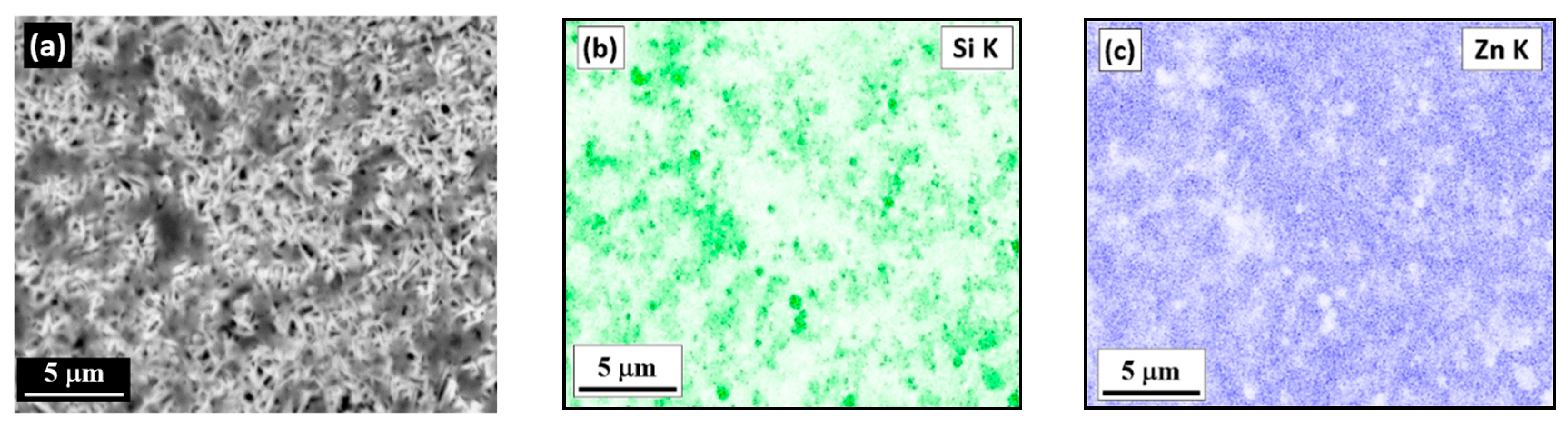
3.4. The Surface Morphology of Zn and Zn–SiC Layers
4. Conclusions
- The amount of SiC NPs incorporated in the Zn matrix is similar in both DCD and PED layers. In both cases NPs are distributed throughout the bulk of the coatings in the form of agglomerates of different sizes.
- The main advantage of PED compared to DCD is the formation of Zn–SiC layers with finer surface morphology.
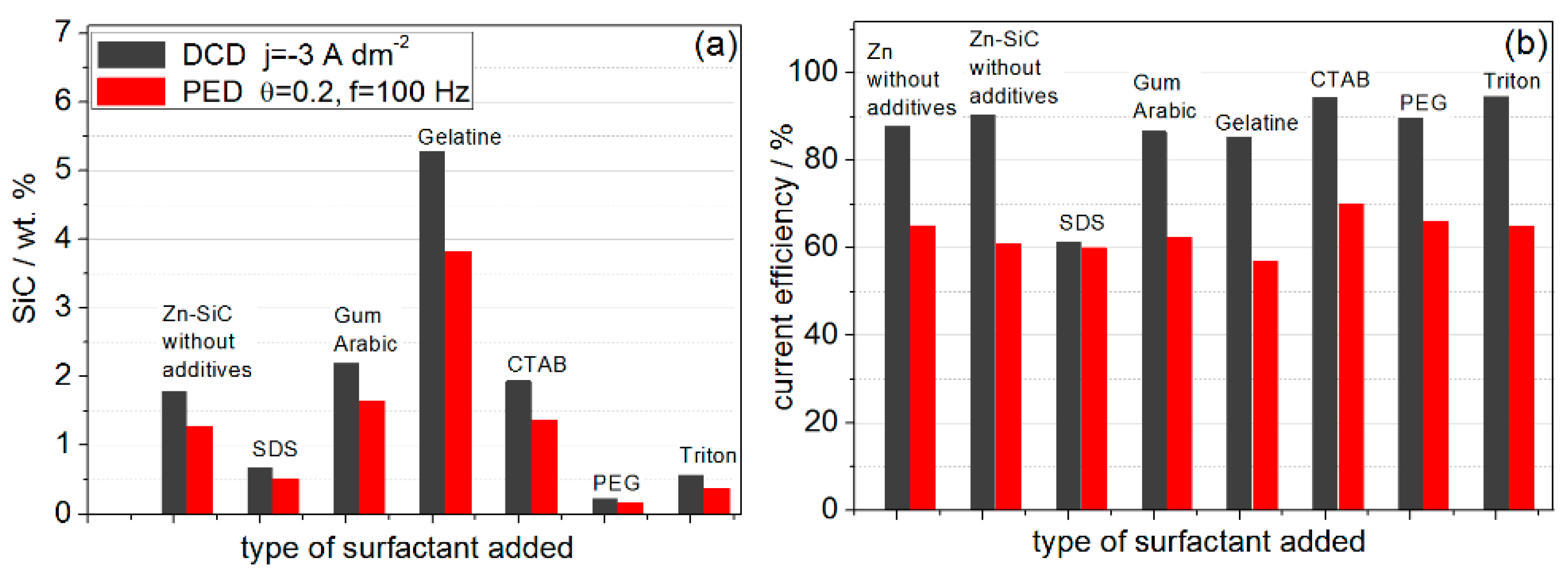
- The most significant modification of both surface morphology and SiC distribution is accomplished through the use of different types of surface-active organic compounds. The weight percentage of SiC co-deposited with Zn is also mainly affected by the type of surfactant used.
- No significant effect of PED on the SiC incorporation in the Zn matrix can be explained by activation-controlled Zn electrodeposition and SiC incorporation via the reduction of Zn–cit ions adsorbed on the SiC NPs under the studied range of process parameters. Under such conditions, during the relaxation time (toff) no deposition takes place, while the enhanced diffusion of ions from the bulk solution to the cathode surface does not influence either the Zn electrodeposition processes or SiC incorporation.
- The comparison of cyclic voltammograms obtained in cit-Zn and ci-Zn-SiC systems with various surfactants, indicate that surfactant molecules adsorb on the surface of SiC NPs, thus limiting its inhibiting effect on the Zn electrodeposition process.
- Ionic surfactants allow co-deposition of higher amounts of SiC NPs compared to non-ionic surfactants. Electrostatic forces may play a significant role in the incorporation of SiC NPs in the Zn matrix during electrodeposition from citrate baths.
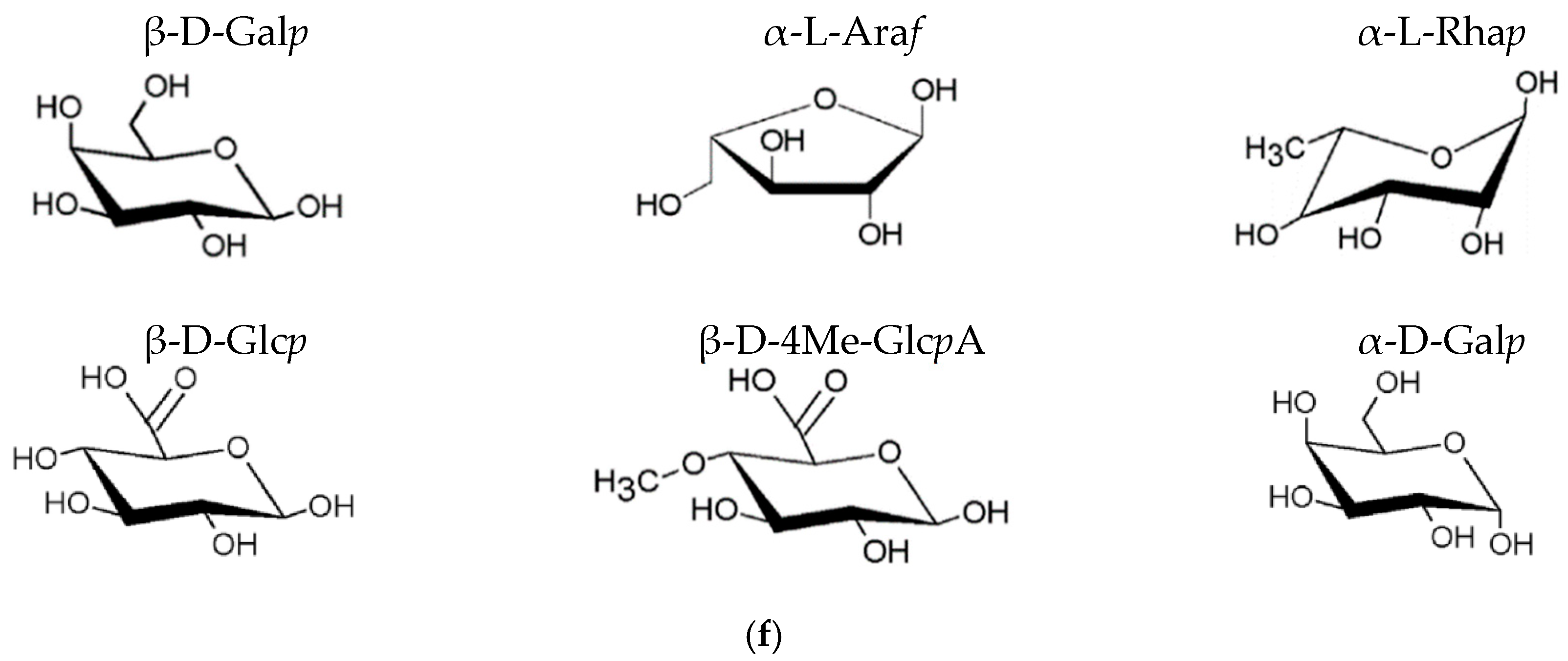
- The Zn–SiC layers obtained in the presence of cationic gelatin as well as anionic gum arabic show considerable SiC NP aggregation. A common feature of these two oppositely charged surfactants is that both are characterized by high molecular weight and a highly branched structure of molecules. Hence, the size and structure of these macromolecules may affect the agglomeration of the ceramic NPs, which then results in a higher than average content of SiC incorporated in the Zn. On the other hand, the use of cationic CTAB (with significantly lower molecular weight and relatively simpler molecular structure) results in the formation of more compact surfaces, with relatively well-dispersed SiC NPs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Physical Electrochemistry: Fundamentals, Techniques, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.B.; Singh, D.K. An overview on the preparation, characterization and properties of electrodeposited-metal matrix nanocomposites. Nanosci. Technol. 2014, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, F.; Gul, H.; Aslan, S.; Alp, A.; Akbulut, H. Effect of CTAB concentration in the electrolyte on the tribological properties of nanoparticle SiC reinforced Ni metal matrix composite (MMC) coating produced by electrodeposition. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 419, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadnejad, M.; Omidvar, H.; Javanbakht, M.; Pooladi, R.; Mozafari, A. Direct current electrodeposition of Zn and Zn-SiC nanocomposite coatings. Trans. Inst. Mater. Finish. 2014, 92, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaneyan, S.P.; Senthilvelan, T. Electro co-deposition and characterization of SiC in nickel metal matrix composite coatings on aluminium 7075. Proc. Eng. 2014, 97, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F.C.; Ponce de Leon, C. A review of the electrodeposition of metal matrix composite coatings by inclusion of particles in a metal layer: An established and diversifying technology. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2014, 92, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.K.P.; Venkatesha, T.V.; Pavithra, M.K. Development of Zn-SiC composite coatings: Electrochemical corrosion studies. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 5, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Sribalaji, M.; Wasekar, N.P.; Joshi, S.; Sundararajan, G.; Singh, R.; Keshri, A.K. Microstructural, phase evolution and corrosion properties of silicon carbide reinforced pulse electrodeposited nickel-tungsten composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, S.; Matsumara, S. Electrochemical preparation and characterization of Ni/SiC gradient deposit. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 145, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, M.D. Electrochemical deposition of nickel/SiC composites in the presence of surfactants. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 87, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Jeon, J.M. Codeposition of micro- and nano-sized SiC particles in the nickel matrix composite coatings obtained by electroplating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftou, P.; Pavlatou, E.A.; Spyrellis, N. Effect of pulse electrodeposition parameters on the properties of Ni/nano-SiC composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 5910–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobosz, I.; Rudnik, E.; Burzynska, L. Codeposition of SiC particles with electrolytic nickel. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2011, 56, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimman, P.; Pushpavanam, M.; Periasamy, V.M. Effect of Surfactant on the electrodeposition of Ni-SiC composites. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.; Sarret, M.; Benballa, M. ZnNi/SiC composites obtained from an alkaline bath. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 162, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulio, P.C.; Rodrigues, S.E.B.; Carlos, I.A. The influence of SiC and Al2O3 micrometric particles on the electrodeposition of ZnNi films and the ontainment of ZnNi-SiC and ZnNi-Al2O3 electrocomposite coatings from slightly acidic solutions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulio, P.C.; Carlos, I.A. Effects of SiC and Al2O3 particles on the electrodeposition of Zn, Co and ZnCo. I. Electrodeposition in the absence of SiC and Al2O3. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulio, P.C.; Carlos, I.A. Effect of SiC and Al2O3 particles on the electrodeposition of Zn, Co and ZnCo: Electrodeposition in the presence of SiC and Al2O3 and production of ZnCo-SiC and ZnCo-Al2O3 coatings. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Induced codeposition of alloys of tungsten, molybdenum and rhenium with transition metals. In Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Vayenas, C.G., White, R.E., Gamboa-Aldeco, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 42, p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, B.A.; Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. Microstructure and composition of pulse plated Re–Ni alloys on a rotating cylinder electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 731, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusbaum, T.; Rosen, B.A.; Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. Effect of pulse on-time and peak current density on pulse plated Re-Ni alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, D250–D255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fustes, J.; Gomes, A.; da Silva Pereira, M.I. Electrodeposition of Zn-TiO2 nanocomposite fils-effect of bath composition. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2008, 12, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, P.I.; Lekka, M.; Fedrizzi, L.; Muresan, L.M. Influence of the electrodeposition current regime on the corrosion resistance of Zn–CeO2 nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 252, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, T.; Bouzon, V.; Gomes, A.; da Silva Pereira, M.I. Pulsed-reverse current electrodeposition of Zn and Zn-TiO2 nanocomposite films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3592–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; da Silva Pereira, M.I. Pulsed electrodeposition of Zn in the presence of surfactants. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roventi, G.; Belezze, T.; Fratesi, R. Rivestimenti compositi Zn-SiC ottenuti per elettrodeposizione. Proceedings of XI AIMAT National Congress, Gaeta, Italy, 16–19 September 2012; pp. 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Roventi, G.; Belleze, T.; Fratesi, R. Electrodeposition of Zn-SiC nanocoposite coatings. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2013, 43, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadnejad, M.; Mozafari, A.; Omidvar, H.; Javanbakht, M. Preparation and corrosion resistance of pulse electrodeposited Zn and Zn-SiC nanocomposite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 300, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.E. Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelsen, P.A.; Quintanilha, R.C.; Vidotti, M.; Gorin, P.A.J.; Simas-Tosin, F.F.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C. Native and structurally modified gum arabic: Exploring the effect of the gum’s microstructure in obtaining electroactive nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 119, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, S.E.; Ebaid, A.R.; Hegazy, M.M.; Barakat, A.K. The effect of additives on Zinc deposited from Zinc sulfate solutions. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 1992, 44, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recendiz, A.; Gonzalez, I.; Nava, J.L. Current efficiency studies of the zinc electrowinning process on aluminum rotating cylinder electrode (RCE) in sulfuric acid medium: Influence of different additives. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 6880–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shan, G.; Liu, H.; Xing, J. Surface modification of γ-Al2O3 nano-particles with gum arabic and its applications in adsorption and biodesulfurization. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 6917–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Zhang, J.; An, M. Influences of SiC concentration on Sn/SiC nanocomposite electrodeposition. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Inam, F.; Heaton, A.; Brown, P.; Pijs, T.; Reece, M.J. Effects of dispersion surfactants on the properties of ceramic-carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Electrodeposition of Re-Ni alloys from aqueous solutions with organic additives. Thin Solid Films 2016, 616, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Venkatakrishna, K.; Hegde, A.C. Electroplating and characterization of Zn–Ni, Zn–Co and Zn–Ni–Co alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, A.C.; Venkatakrishna, K.; Eliaz, N. Electrodeposition of Zn–Ni, Zn–Fe and Zn–Ni–Fe alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, V.; Eliaz, N.; Hegde, A.C. Corrosion behavior of composition modulated multilayer Zn–Co electrodeposits produced using a single-bath technique. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Sridhar, T.M.; Gileadi, E. Synthesis and characterization of nickel tungsten alloys by electrodeposition. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 2893–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.K.; Dash, M.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Chiellini, E.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Moroni, L.; Dubruel, P. Cationic polymers and their therapeutic potential. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7147–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, N.; Sahoo, R.K.; Biswas, N.; Guha, A.; Kuotsu, K. Recent advancement of gelatin nanoparticles in drug and vaccine delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Hu, Y.; McClement, D.J. Competitive adsorption and displacement of anionic polysaccharides (fucoidan and gum arabic) on the surface of protein-coated lipid droplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuelli, M.A. Hydrodynamic properties of whole arabic gum. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 1, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, A.; Moron, L.E.; Ortega-Borges, R.; Meas, Y.; Trejo, G. EQCM study of the adsorption of polyethyleneglycol with different molecular weights and its coadsorption with Cl− ions on Pt in perchloric acid solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 5, 1754–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Mendez, A.; Moron, L.E.; Ortiz-Frade, L.; Meas, Y.; Ortega-Borges, R.; Trejo, G. Thermodynamic studies of PEG (Mw 20,000) adsorption onto a polycrystalline gold electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, F45–F51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, A.; Meas, Y.; Ortega-Borges, R.; Trejo, G. Thermodynamic study of PEG (Mw 20,000) adsorption in the presence of Cl-anions onto a polycrystalline gold electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, F48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.J.; Akolkar, R. Suppressing dendrite growth during zinc electrodeposition by PEG-200 additive. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D519–D523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.C.; Diaz-Arista, P.; Meas, Y.; Ortega, R.; Trejo, G. Zinc electrodeposition in the presence of polyethylene glycol 20,000. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 3686–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; da Silva Pereira, M.I. Zn electrodeposition in the presence of surfactants Part I. Voltammetric and structural studies. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Kuo, S.L.; Lee, J.L.; Ke, S.T.; Wong, C.H.; Ger, M.D. The influence of surfactant CTAB on the microstructure and material properties of Nickel microelectroforming. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 364, 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy, B.C.; Das, S.C.; Hefter, G.T.; Singh, P. Zinc electrowinning from acidic sulfate solutions: Part I: Effect of sodium lauryl sulfate. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1997, 27, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Szymkiewicz, K.; Rogal, Ł.; Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. Direct current electrodeposition of Zn-SiC nanocomposite coatings from citrate bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, D526–D535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Szymkiewicz, K.; Bobrowski, P.; Świątek, Z.; Rogal, Ł.; Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. The effect of SiC nanoparticle size on the electrodeposition of Zn–SiC nanocomposite coatings from citrate bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, D774–D782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpavanam, M.; Balakrishnan, K. Zinc-Nickel alloy deposition in the presence of citrate ions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1996, 26, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P.; Jalowiec, A.; Kowalik, R. Tin–Zinc alloy electrodeposition from aqueous citrate baths. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 240, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P. Electrodeposition of Sn–Zn and Sn–Zn–Mo layers from citrate solutions. Surf. Sci. 2013, 607, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P.; Socha, R.P. Investigation of electrochemical co-deposition of zinc and molybdenum from citrate solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 104, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Hara, A.; Bigos, A.; Ozga, P. Electrodeposition of Zn-Mn-Mo layers from citrate-based aqueous. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 202, 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.S. The influence of sorbitol on zinc film deposition, zinc dissolution process and morphology of deposits obtained from alkaline bath. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2006, 36, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.C.; Hu, C.C.; Lee, T.C. The synergistic effects of additives on improving the electroplating of Zinc under high current densities. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, D675–D681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazimierczak, H.; Szymkiewicz, K.; Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. The Effect of Direct and Pulsed Current in the Presence of Surfactants on the Electrodeposition of Zn–SiC Nanocomposite Coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9020093
Kazimierczak H, Szymkiewicz K, Gileadi E, Eliaz N. The Effect of Direct and Pulsed Current in the Presence of Surfactants on the Electrodeposition of Zn–SiC Nanocomposite Coatings. Coatings. 2019; 9(2):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9020093
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazimierczak, Honorata, Krzysztof Szymkiewicz, Eliezer Gileadi, and Noam Eliaz. 2019. "The Effect of Direct and Pulsed Current in the Presence of Surfactants on the Electrodeposition of Zn–SiC Nanocomposite Coatings" Coatings 9, no. 2: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9020093
APA StyleKazimierczak, H., Szymkiewicz, K., Gileadi, E., & Eliaz, N. (2019). The Effect of Direct and Pulsed Current in the Presence of Surfactants on the Electrodeposition of Zn–SiC Nanocomposite Coatings. Coatings, 9(2), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9020093






