Surface Properties of Retrieved Cementless Femoral Hip Endoprostheses Produced from a Ti6Al7Nb Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Implants/Stems
2.2. Wettability
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopuy (SEM) Analysis
2.4. Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Surface Analysis
2.4.1. AES Analysis
2.4.2. XPS Analysis
2.5. Corrosion-Resistance Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wettability and Roughness
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. Surface Analyses by AES and XPS Measurements
3.3.1. AES Analysis
3.3.2. XPS Analysis
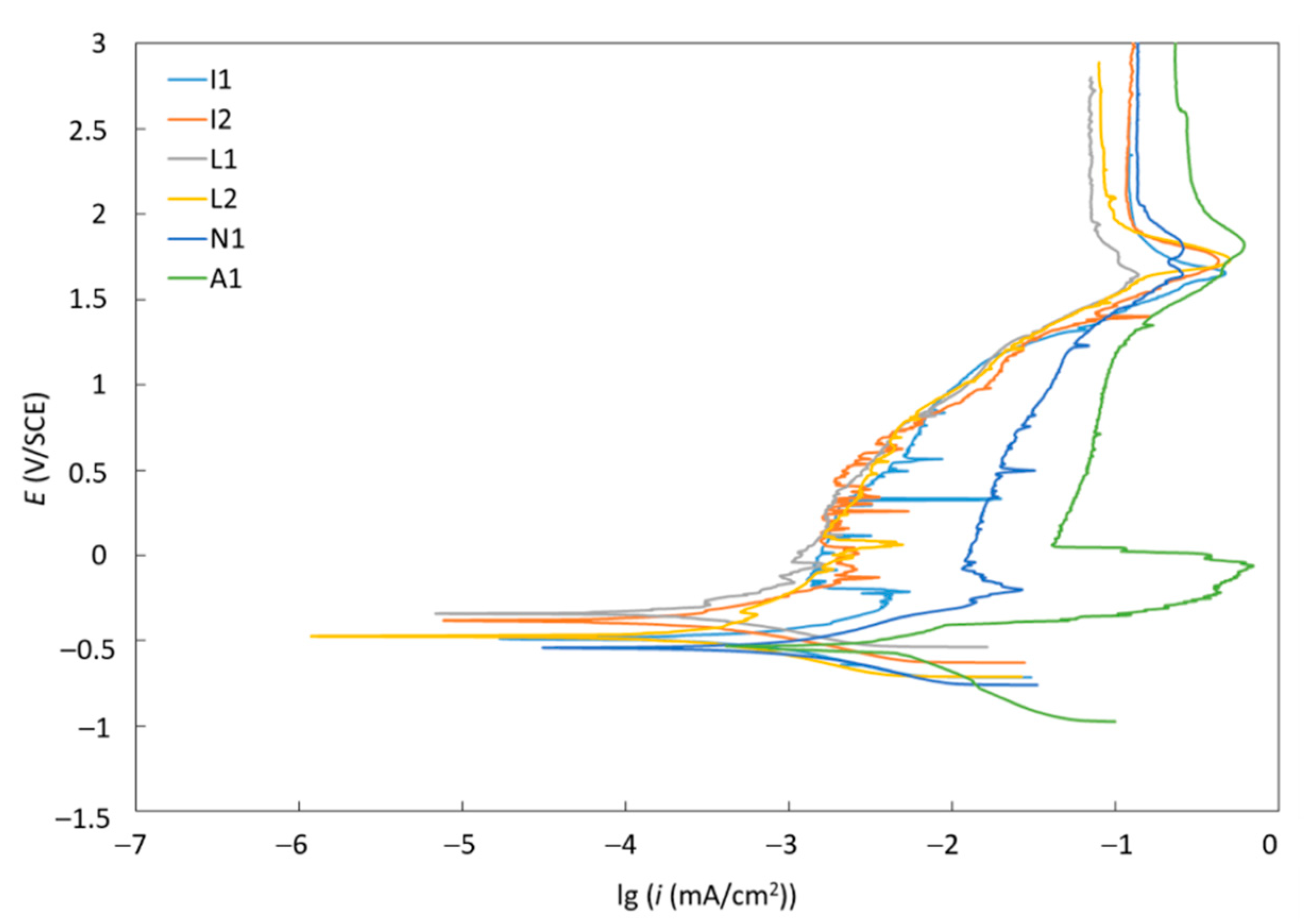
3.4. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merola, M.; Affatato, S. Materials for Hip Prostheses: A Review of Wear and Loading Considerations. Matererials 2019, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, M.J. Standard Handbook of Biomedical Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yaszemski, M.J.; Trantolo, D.J.; Levandrowski, K.U.; Hasirci, V.; Altobelli, D.E. Biomaterials in Orthopedics; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jenko, M.; Gorenšek, M.; Godec, M.; Hodnik, M.; Šetina, B.; Donik, Č.; Grant, J.T.; Dolinar, D. Surface chemistry and microstructure of metallic biomaterials for hip and knee endoprostheses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittig, C.; Textor, M.; Spencer, N.D.; Wieland, M.P.; Vallotton, H. Surface characterization of implant materials, cp Ti, Ti-6Al-7Nb and Ti-6Al-4 V with different pretreatments. J. Mater. Sci. - Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzakala, A.; Sluzalska, K.; Dercz, G.; Maciej, A.; Kazek, A.; Szade, J.; Winiarski, A.; Dudek, M.; Michalska, J.; Tylko, G. Characterisation of bioactive films on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Electrochim. Acta. 2013, 104, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundfeldt, M.; Carlsson, L.V.; Johansson, C.B.; Thomsen, P.; Gretzer, C. Aseptic loosening, not only a question of wear: a review of different theories. Acta Orthop. 2006, 77, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. The significance of infection related to orthopedic devices and issues of antibiotic resistance. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, E.M.; Bi, Y.; Ragab, A.A.; Goldberg, V.M.; Nalepka, J.L.; Seabold, J.M. Does endotoxin contribute to aseptic loosening of orthopedic implants? J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Dimitriou, R.; Parvizi, J.; Babis, G.C. Biology of implant osseointegration. J. Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2009, 9, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Baier, R.E.; Meyer, A.E.; Tannenbaumd, R.; Boyana, B.D.; Schwartz, Z. Effect of cleaning and sterilization on titanium implant surface properties and cellular response. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Wieland, M.; Schwartz, Z.; Zhao, G.; Rupp, F.; Geis, G.J.; Schedle, A.; Broggini, N.; Bornstein, M.M.; Buser, D. Potential of chemically modified hydrophilic surface characteristics to support tissue integration of titanium dental implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 88, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. Underlying mechanisms at the bone–biomaterial interface. J. Cell. Biochem. 1994, 56, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostu, D.; Lucaciu, O.; Berce, C.; Lucaciu, D.; Cosma, D. Current methods of preventing aseptic loosening and improving osseointegration of titanium implants in cementless total hip arthroplasty: a review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2104–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausemo, B.; Lausmaa, J. Biomaterial and implant surface – on the role of cleanliness, contamination, and preparation procedures. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 1988, 22, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpadi, D.V.; Weimer, J.J.; Lemons, J.E. Effect of passivation and dry heat-sterilization on surface energy and topography of unalloyed titanium implants. Colloids Surfs. A 1998, 135, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaunay, C.; Bonnomet, F.; North, J.; Jobard, D.; Cazeau, C.; Kempf, J.F. Grit-Blasted Titanium Femoral Stem in Cementless Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: a study 5- to 10-year multicenter study. J. Arthroplasty 2001, 16, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göske, J.; Uter, W.; Ulrich, H.U.; Kachler, W.; Zeiler, G.; Schuh, A. Surface Characterization of Corundum Blasted Implants in Hip Arthroplasty. Microsc. Microanal. 2004, 18, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Alla, R.K.; Ginjupalli, K.; Upadhya, N.; Shammas, M.; Ravi, R.K.; Sekhar, R. Surface Roughness of Implants: A Review. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs. 2011, 25, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.Y.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Tsoi, J.K.H. Residual Contaminations of Silicon-Based Glass, Alumina and Aluminum Grits on a Titanium Surface After Sandblasting. Silicon 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, D.; Parvizi, J. Biological response to prosthetic debris. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphel, M.; Holodniy, S.B.; Goodman, S.C.; Heilshorn, C. Multifunctional coatings to simultaneously promote osseointegration and prevent infection of orthopaedic implants. Biomaterials 2016, 84, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristina, A.G. Biomaterial-centered infection: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. Science 1987, 237, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfest, D.M.D.; Coelho, P.G.; Kang, B.S.; Sul, T.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of osseointegrated implant surfaces: materials, chemistry and topography. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—a review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodnik, M. Biomaterials for Hip and Knee Endoprosthesis. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Materials and Technology, Slovenj Gradec, Slovenia, 28 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM F1295-05 Standard Specification for Wrought Titanium-6 Aluminum-7 Niobium Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R56700). Available online: https://infostore.saiglobal.com/store/details.aspx/details.aspx?ProductID=249286 (accessed on 10 June 2017).
- Briggs, D.; Grant, T.J. Surface Analysis by Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Surface Spectra; IM Publications: Manchester, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kenton, W.D.; Childs, B.A.; Carlson, A.; Lori, A.; La Vannier, J.F.; Moulder, D.F. Handbook of Auger Electron Spectroscopy; Physical Electronics: Eden Prarie, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Moulder, J.F.; Sobol, P.E. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Physical Electronics: Eden Prarie, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G102 – 89 (2015) Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/G102 (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Avsec, K.; Jenko, M.; Godec, M.; Vesel, A.; Mozetič, M.; Gorenšek, M.; Kocjančič, B.; Dolinar, D. Effect of autoclave or plasma oxygen gaseous sterilization on surface properties of Ti6Al7Nb alloy femoral stems. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Biomaterials, Portoroz, Slovenia, 16–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dolinar, D.; Jenko, M.; Črtalič, B.; Andolšek Črtalič, M.; Godec, M.; Kocjančič, B.; Gorenšek, M.; Oblak, Č. Grit-blasted surfaces of Ti6Al7Nb alloy cementless hip endoprosthesis. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Biomaterials, Portoroz, Slovenia, 16–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rüger, M.; Gensior, T.J.; Herren, C.; VonWalter, M.; Ocklenburg, C.; Marx, R. The removal of Al2O3 particles from grit-blasted titanium implant surfaces: Effects on biocompatibility, osseointegration and interface strength in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2010, 7, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cör, A. Wear particles and lymphocytes in tissue around failed joint prostheses. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Biomaterials, Portoroz, Slovenia, 16–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
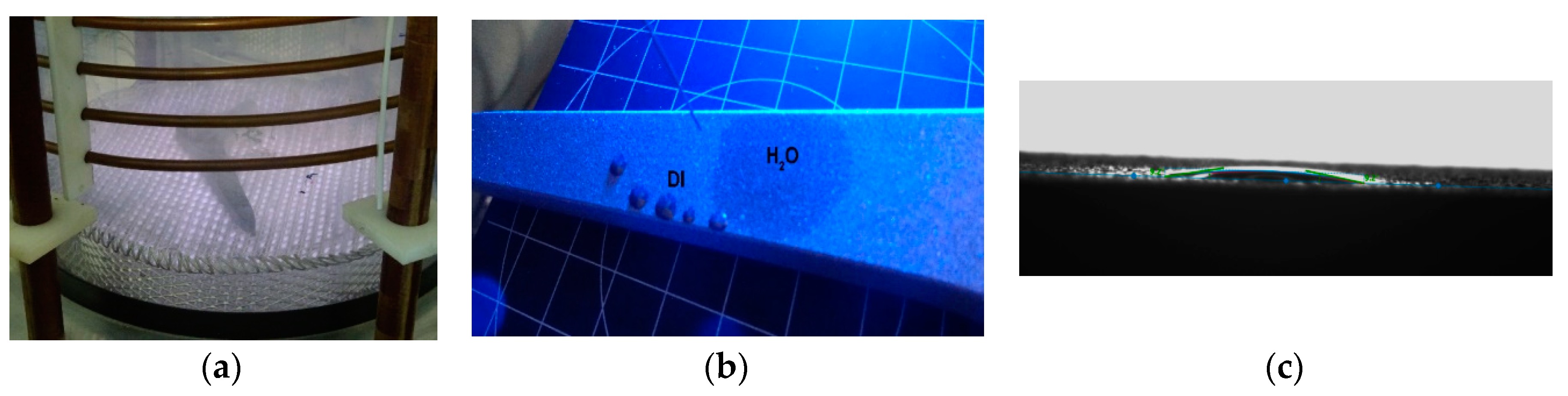
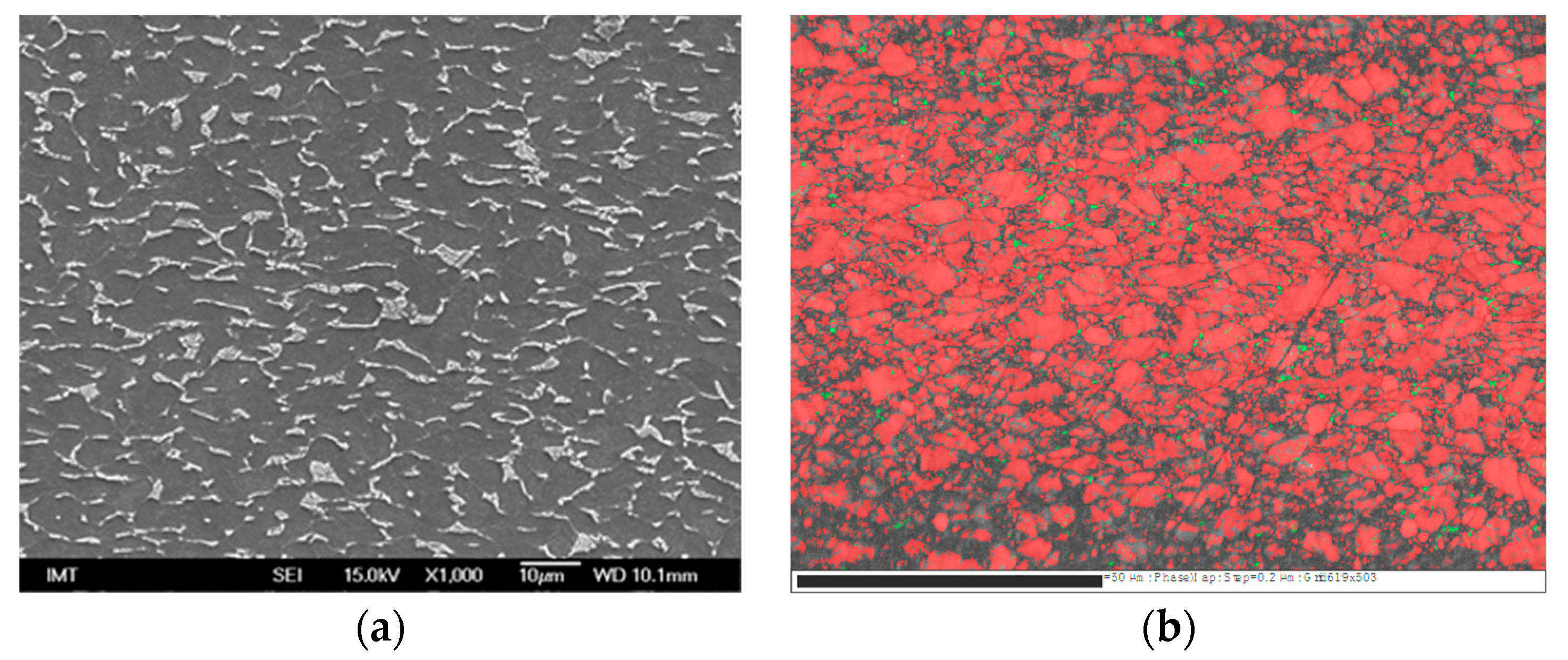
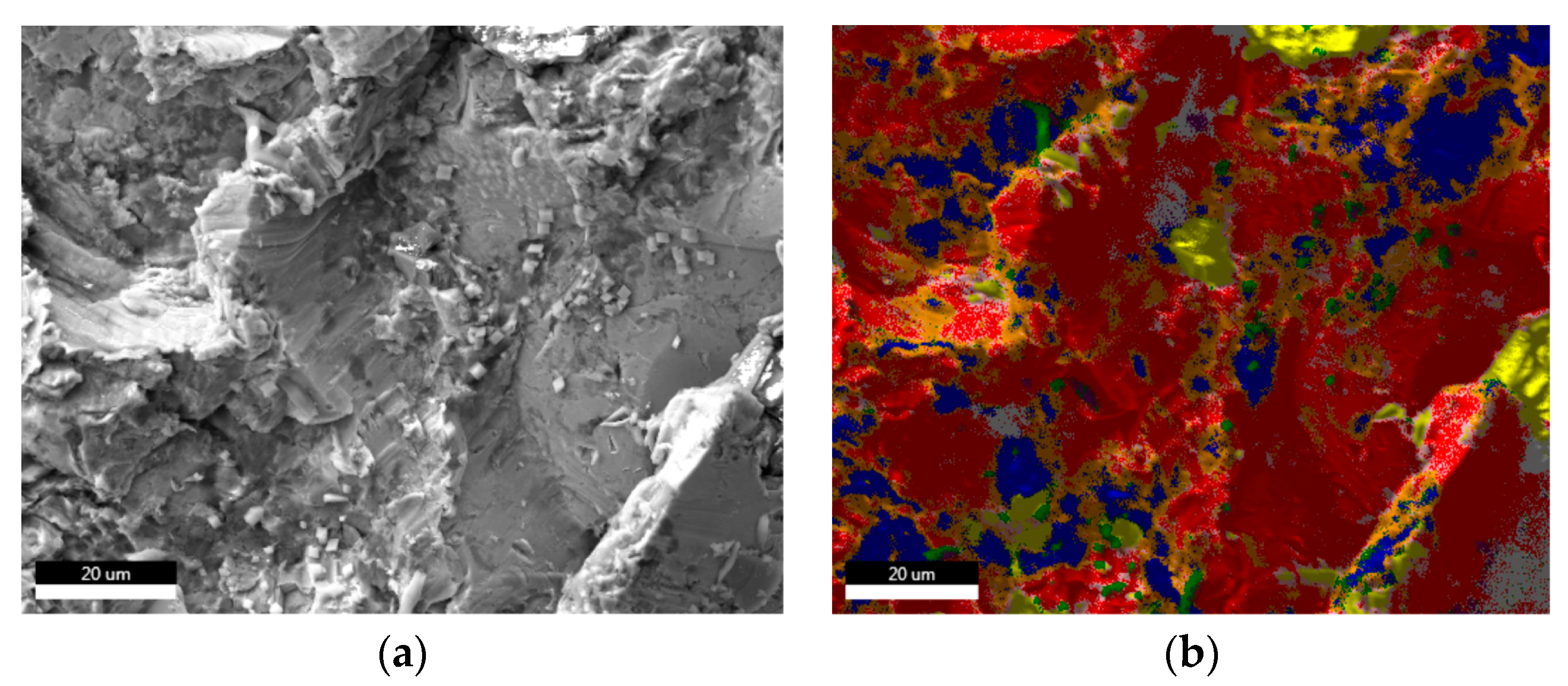
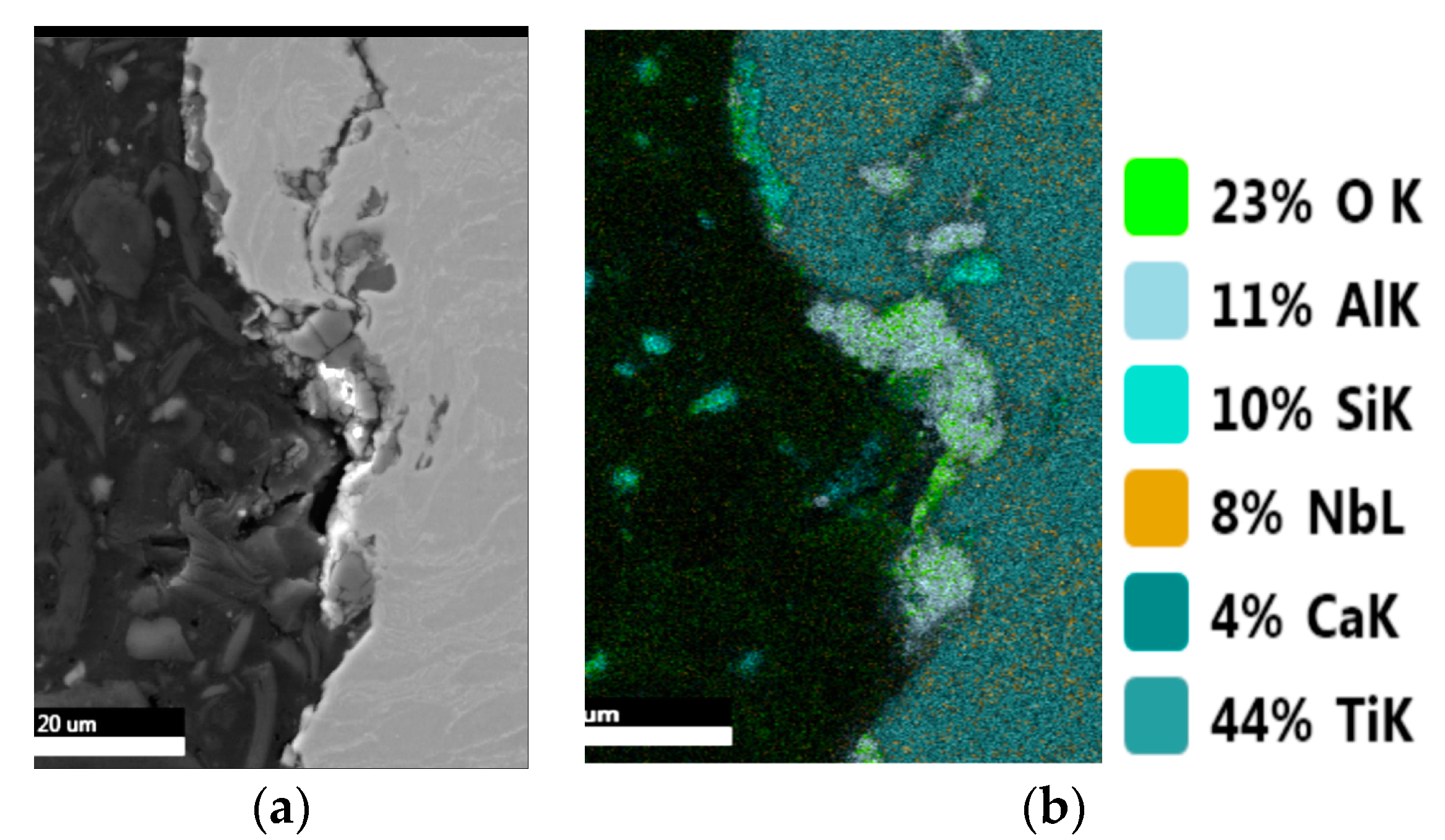
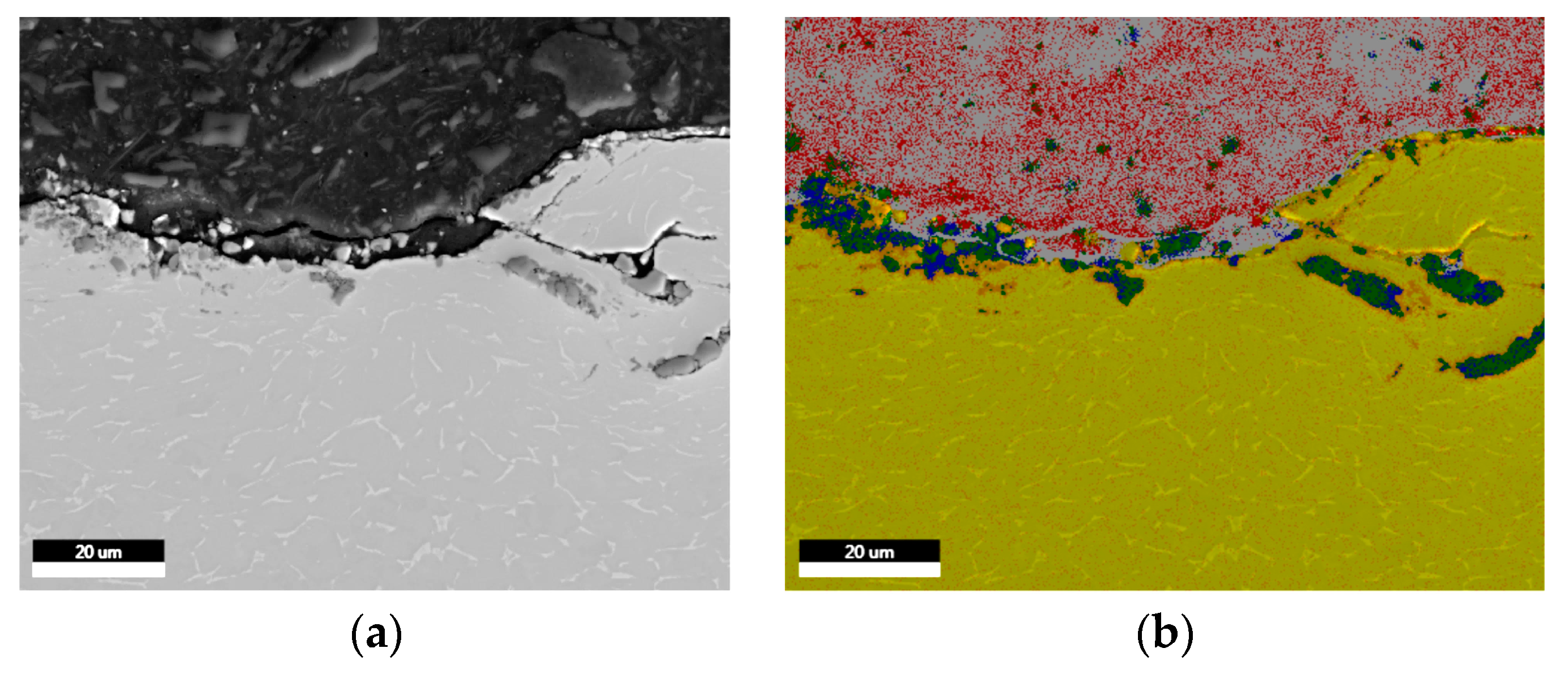
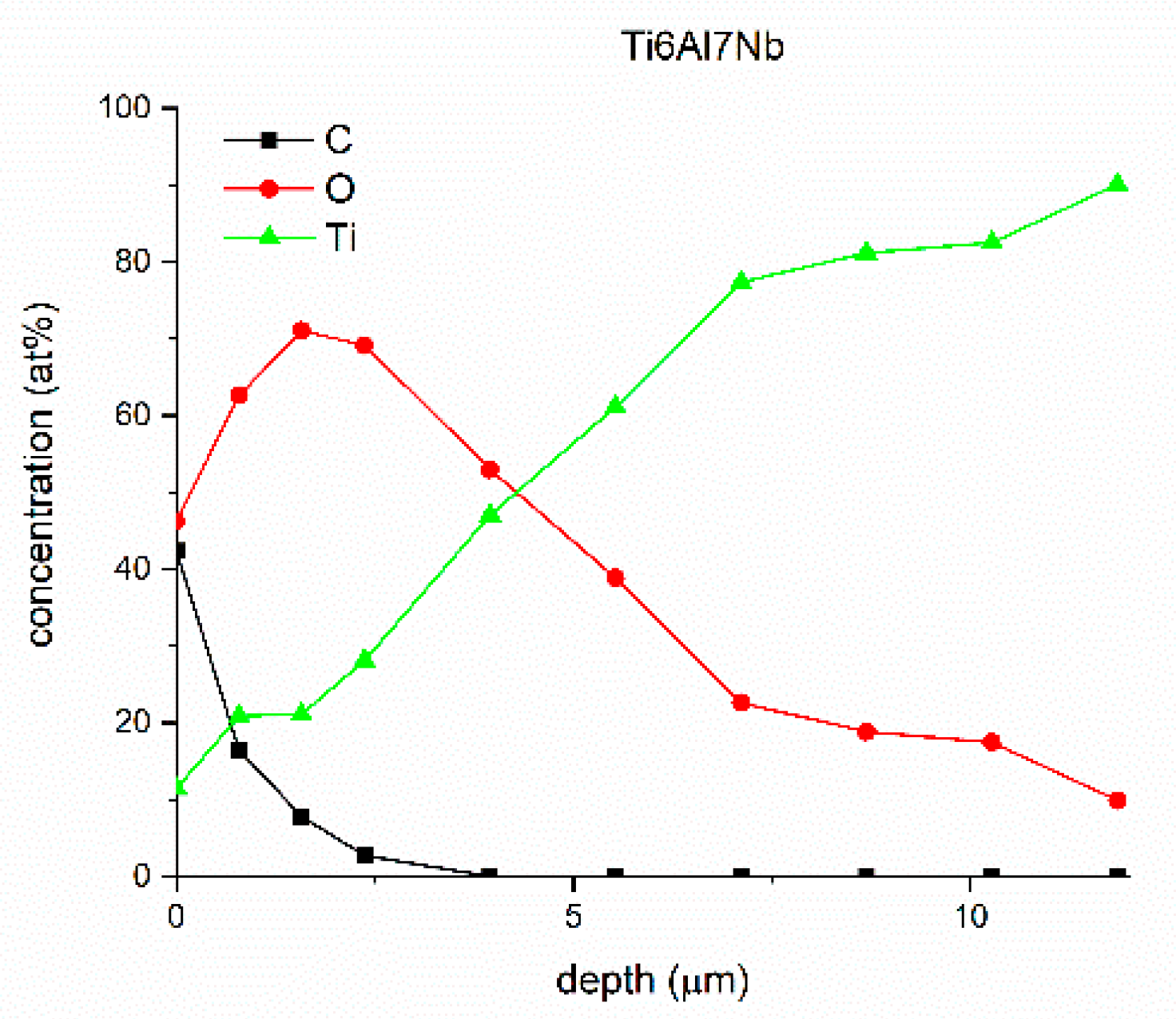
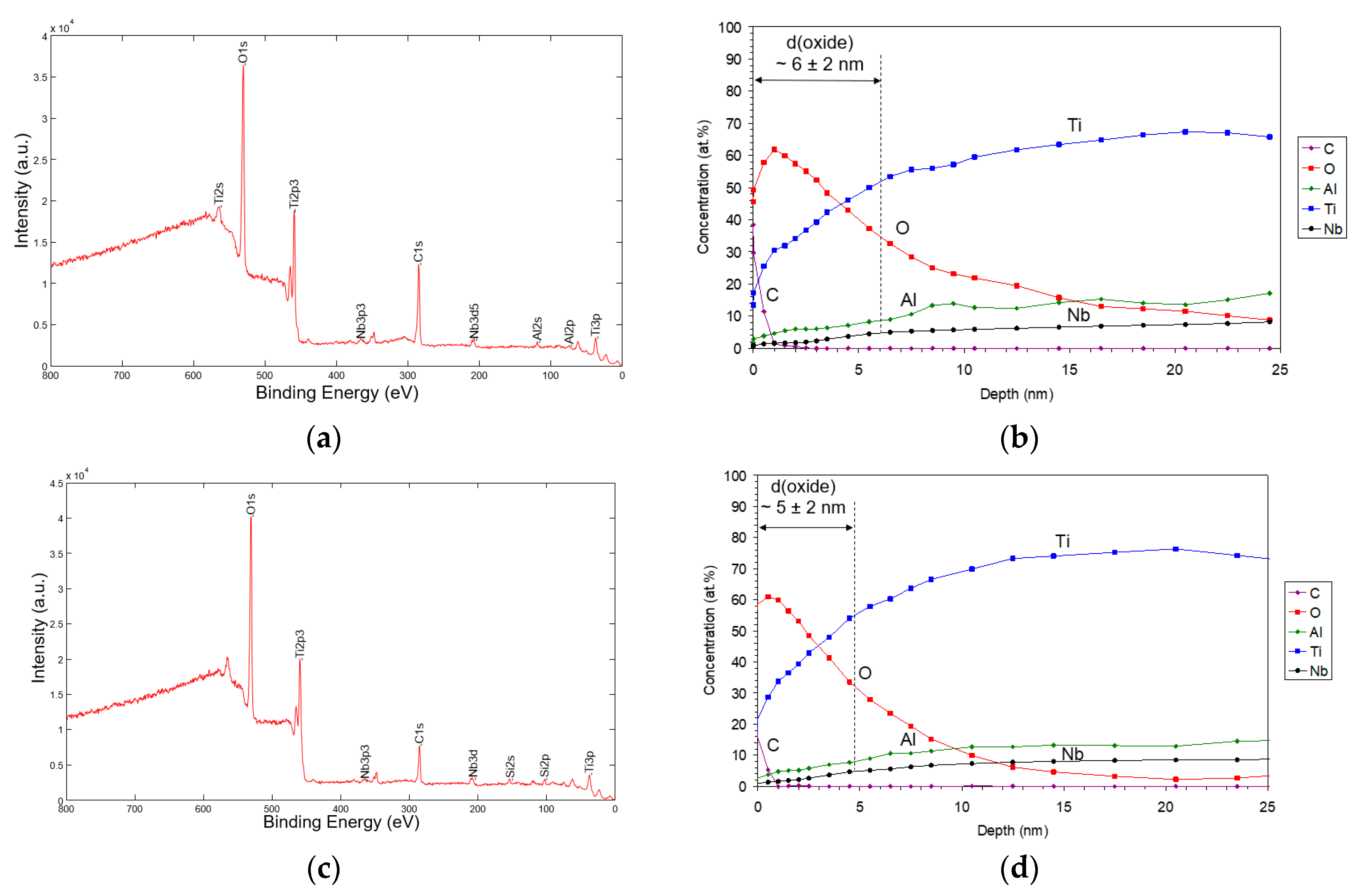
| Sample | Sa [µm] | Before Sterilization | After Sterilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implant N1 | θ [°] | θ [°] | |
| Site 1 | 5.209 | 116.3 | 66.5 (49–85) |
| Site 2 | 5.884 | 114.8 | 73.7 |
| Site 3 | 5.570 | 115.9 | 36.8 |
| Sample | Sa [µm] | θ [o] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | Neck | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 82.5 ± 1.5 |
| middle | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 80.4 ± 2.1 | |
| Root | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 81.3 ± 1.4 | |
| b | Neck | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 82.1 ± 2.1 |
| middle | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 86.9 ± 1.3 | |
| Root | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 91.6 ± 1.9 | |
| c | Neck | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 80.4 ± 1.9 |
| middle | 4.5± 0.2 | 70.6 ± 1.8 | |
| Root | 4.4 ± 0.1 | 75.7 ± 1.4 | |
| Sample | Contact Angle of Water (°) | Contact Angle of DI (°) | Surface Energy (mN/m) | Dispersive Component (mN/m) | Polar Component (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Used hip A-S 16 | <1° | 29.5 ± 2.9 | 78.5 ± 1.8 | 44.4 ± 1.2 | 34.1 ± 0.7 |
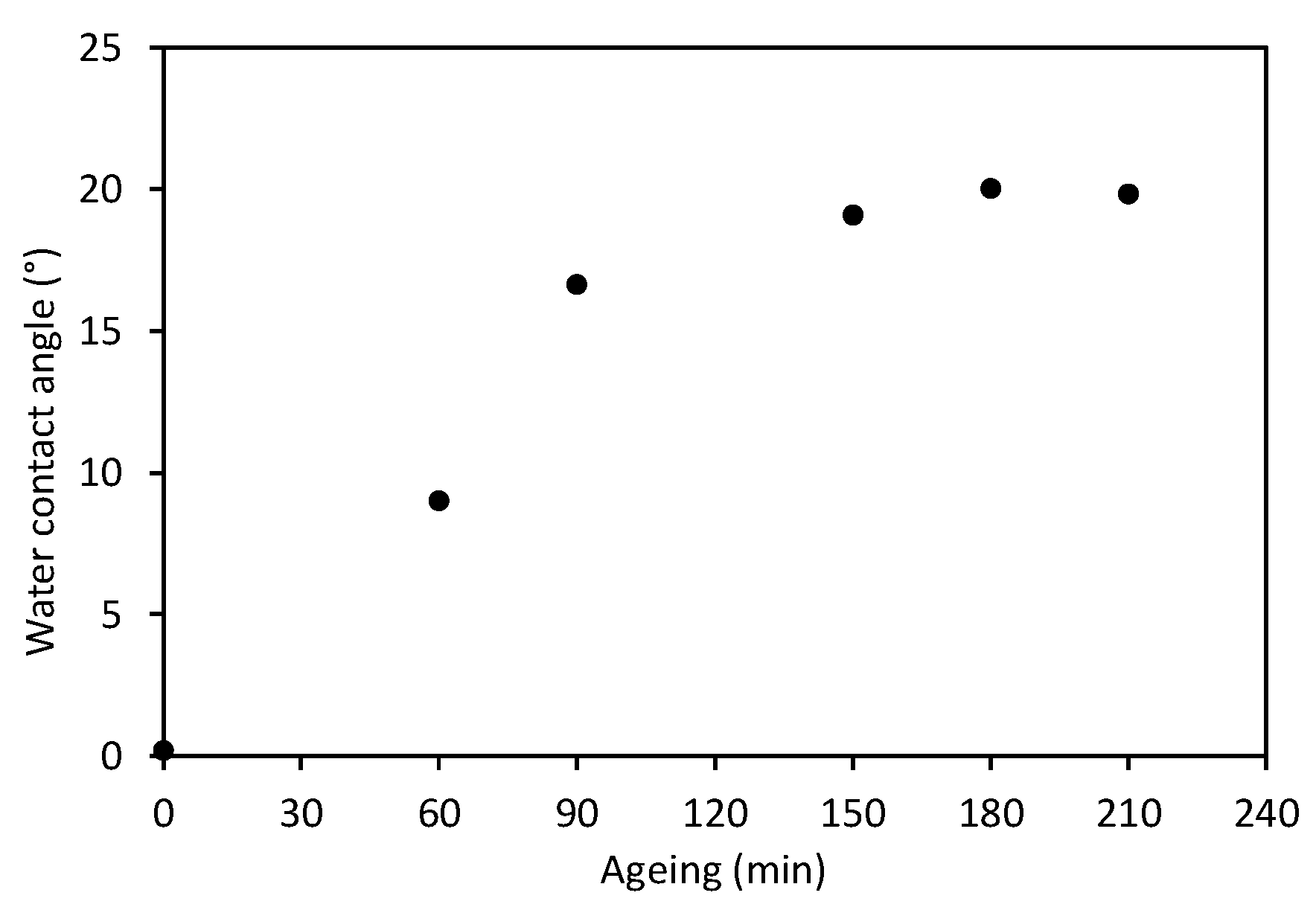
| Ageing Time (min) | Water Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| 60 | 9.03 ± 0.5 |
| 90 | 16.6 ± 2.0 |
| 150 | 19.1 ± 1.4 |
| 180 | 20.0 ± 1.2 |
| 210 | 19.8 ± 0.8 |
| Material | Ecorr (mV) | icorr (µm/cm2) | vcorr (µm/year) | Rp (kΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | −527.41 | 1.18 | 10.26 | 10.5 |
| I1 | −487.62 | 0.87 | 7.56 | 68.7 |
| I2 | −368.87 | 0.24 | 2.10 | 142.7 |
| L1 | −324.74 | 0.15 | 1.32 | 148.2 |
| L2 | −473.57 | 0.32 | 2.80 | 135.8 |
| N1 | −539.60 | 0.98 | 8.52 | 39.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avsec, K.; Jenko, M.; Conradi, M.; Kocijan, A.; Vesel, A.; Kovač, J.; Godec, M.; Belič, I.; Šetina Batič, B.; Donik, Č.; et al. Surface Properties of Retrieved Cementless Femoral Hip Endoprostheses Produced from a Ti6Al7Nb Alloy. Coatings 2019, 9, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120868
Avsec K, Jenko M, Conradi M, Kocijan A, Vesel A, Kovač J, Godec M, Belič I, Šetina Batič B, Donik Č, et al. Surface Properties of Retrieved Cementless Femoral Hip Endoprostheses Produced from a Ti6Al7Nb Alloy. Coatings. 2019; 9(12):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120868
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvsec, Klemen, Monika Jenko, Marjetka Conradi, Aleksandra Kocijan, Alenka Vesel, Janez Kovač, Matjaž Godec, Igor Belič, Barbara Šetina Batič, Črtomir Donik, and et al. 2019. "Surface Properties of Retrieved Cementless Femoral Hip Endoprostheses Produced from a Ti6Al7Nb Alloy" Coatings 9, no. 12: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120868
APA StyleAvsec, K., Jenko, M., Conradi, M., Kocijan, A., Vesel, A., Kovač, J., Godec, M., Belič, I., Šetina Batič, B., Donik, Č., Gorenšek, M., Kocjančič, B., & Dolinar, D. (2019). Surface Properties of Retrieved Cementless Femoral Hip Endoprostheses Produced from a Ti6Al7Nb Alloy. Coatings, 9(12), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120868










