Comparative Study of Ni-Sn Alloys Electrodeposited from Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquids in Direct and Pulsed Current
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
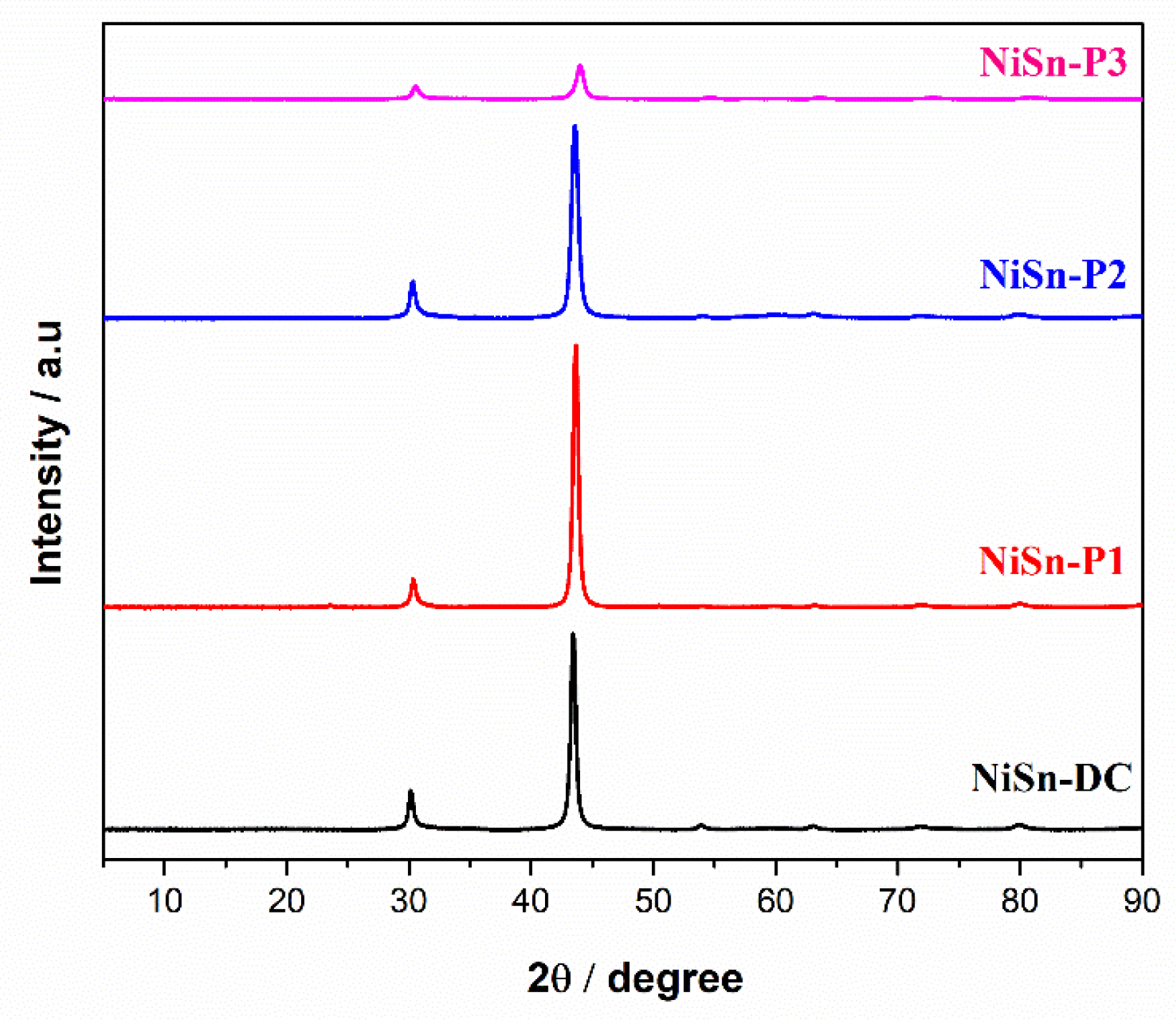
3.1. Direct Current Electrodeposition of Nickel-Tin Alloys
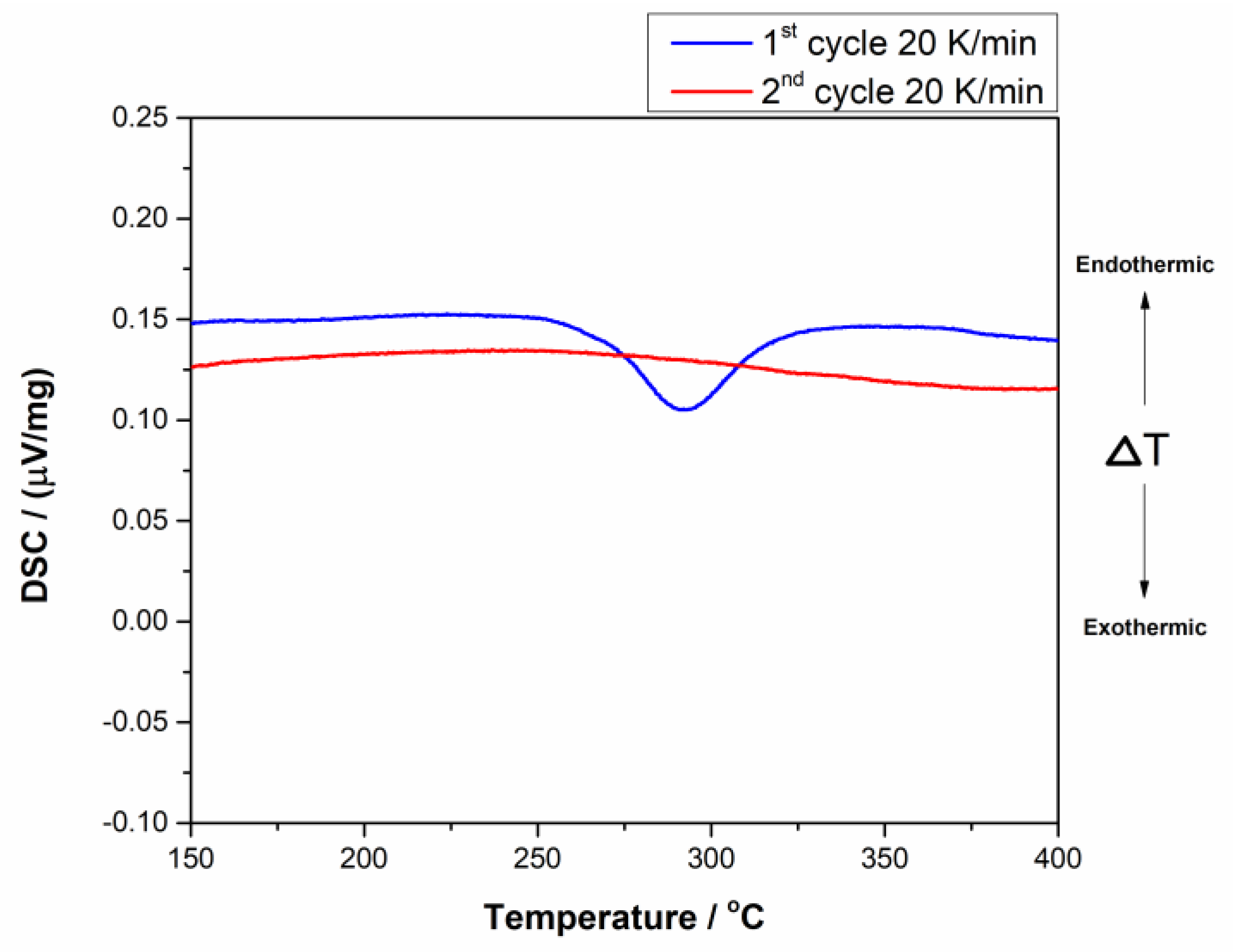
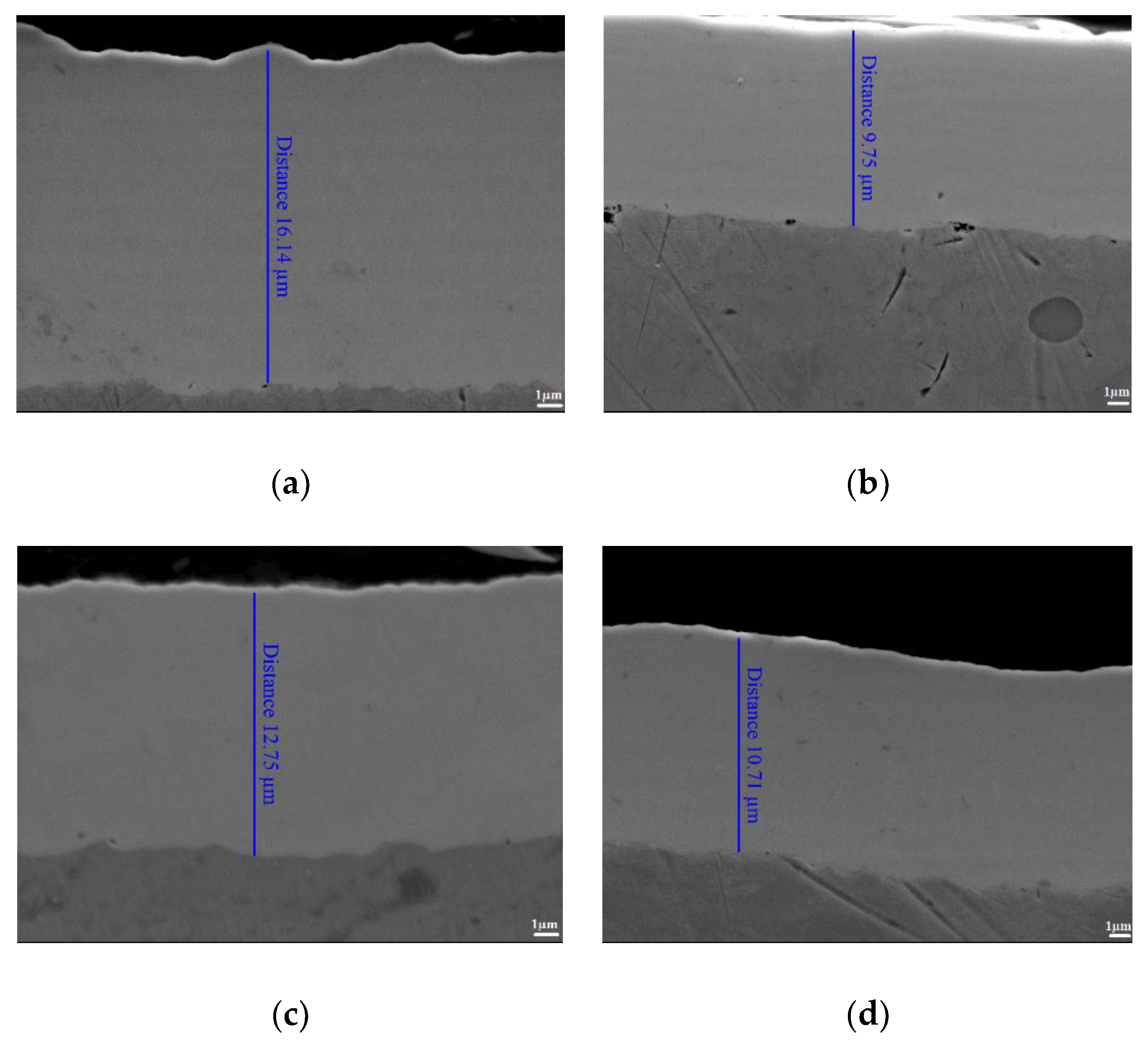
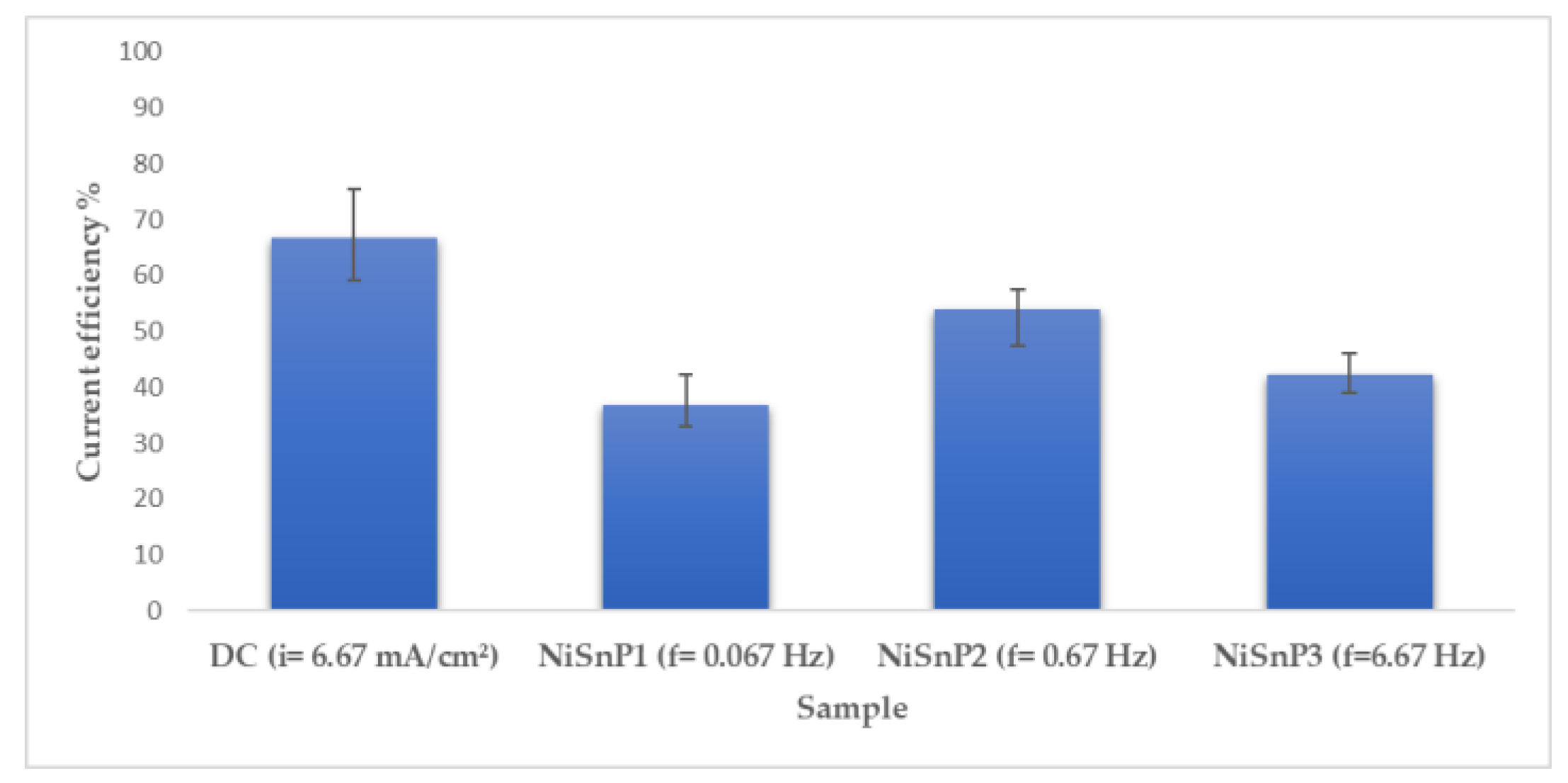
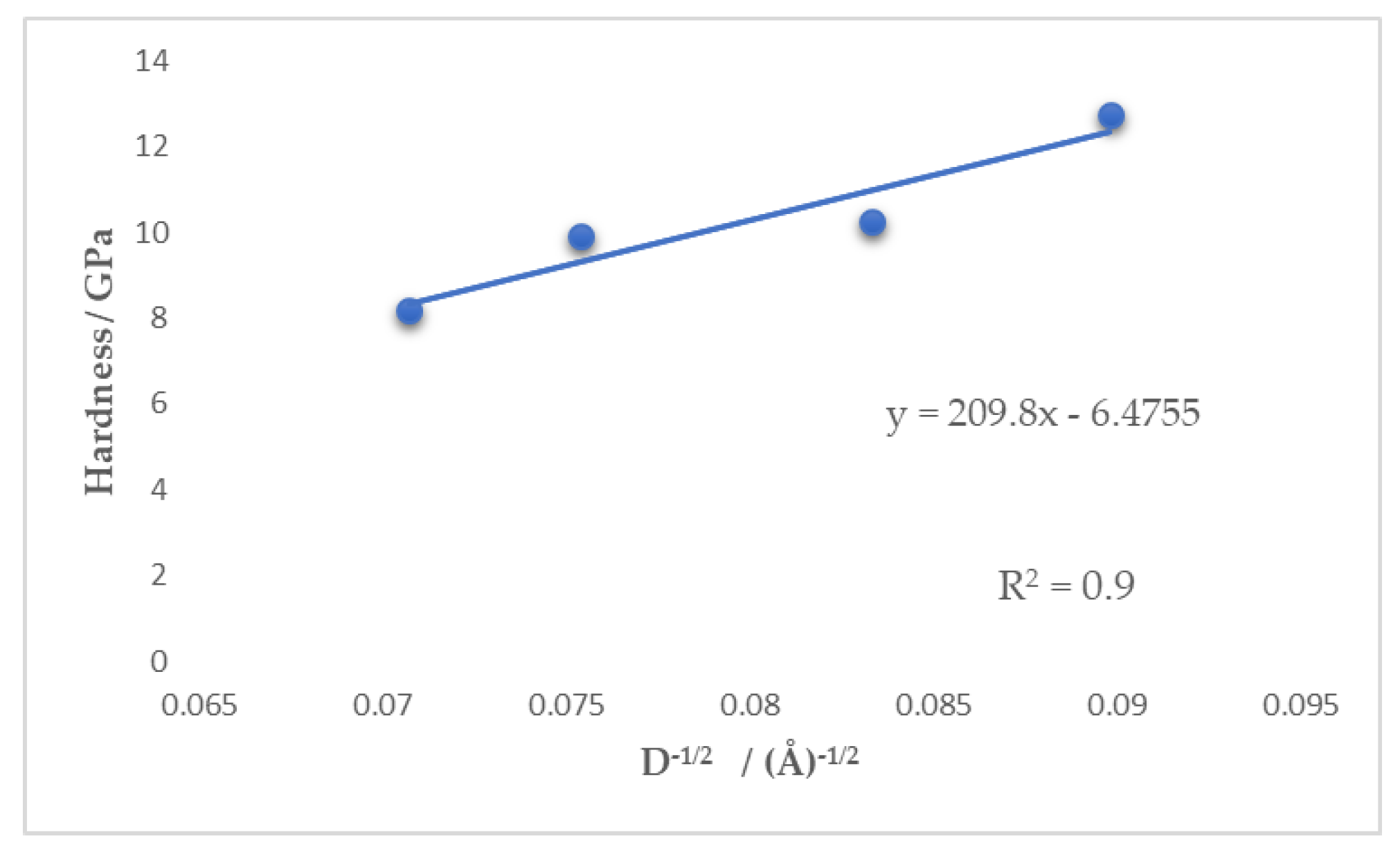
3.2. Pulse Current Electrodeposition of Nickel-Tin Alloys
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stuttle, C.J. The electrodeposition of tin coatings from deep eutectic solvents and their subsequent whiskergrowth. Ph.D. Thesis, Loughborough University, Loughborough, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jalota, S. Tin-nickel alloy plating. Met. Finish. 2002, 100, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E.; Włoch, G.; Czernecka, A. The influence of potential-current conditions on the electrodeposition of Ni-Sn alloys from acidic chloride-sulphate solution. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parkinson, N. The electrodeposition of bright tin-nickel alloy plate. Trans. IMF 1950, 27, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Formation of metastable phases by the plating method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 179–180, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellesen, M.S.; Moller, P. The electrochemical deposition of tin-nickel alloys and the corrosion properties of the coating. Plating Surf. Finish. 2005, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Nobel, F.; Ostrow, B.D.; Learonal Inc. Limiting tin sludge formation in tin or tin/lead electroplating solutions. US Patent 5066367 Appl. 07/585768, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Roy, S. Codeposition of Cu-Sn from ethaline deep eutectic solvent. Electrochim. Acta. 2015, 183, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheed, R. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheed, R.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2002, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.; Bell, T.; Handa, S.; Stoddart, B. O-acetylation of cellulose and monosaccharides using a zinc based ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; McKenzie, K.; Obi, S. Solubility of metal oxides in deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez de María, P.; Maugeri, Z. Ionic liquids in biotransformations: From proof-of-concept to emerging deep-eutectic-solvents. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.; McKenzie, K. Application of ionic liquids to the electrodeposition of metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, A.; Pölzler, M.; Gollas, B. Zinc electrodeposition from a deep eutectic system containing choline chloride and ethylene glycol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, D328–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerens, K.; Matthijs, E.; Chmielarz, A.; Van der Bruggen, B. The use of ionic liquids based on choline chloride for metal deposition: A green alternative? J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, 3245–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D. Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquids, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; McKenzie, K.; Ryder, K. Electrodeposition of zinc–tin alloys from deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 599, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.; Pereira, C.; Silva, A. The effect of complex agents on the electrodeposition of tin from deep eutectic solvents. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 2012, 1, D5–D7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.; Salomé, S.; Pereira, C.; Fernando Silva, A. Zn–Sn electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents containing EDTA, HEDTA, and Idranal VII. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, A.; Costovici, S.; Anicai, L.; Visan, T. Studies of cathodic processes during NiSn alloy deposition using choline chloride based ionic liquids. Metal. Int. 2009, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Anicai, L.; Petica, A.; Costovici, S.; Prioteasa, P.; Visan, T. Electrodeposition of Sn and NiSn alloys coatings using choline chloride based ionic liquids—evaluation of corrosion behavior. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 114, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharmachi, I.; Dhouibi, L.; Berçot, P.; Rezrazi, M. Pulse plating as an alternative approach to improve Ni-Co alloys properties coated from a bath with a low nickel content. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 1670–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanauskas, R.; Gudavičiūtė, L.; Ščit, O.; Bučinskienė, D.; Juškėnas, R. Pulse plating effect on composition and corrosion properties of zinc alloy coatings. Trans. IMF 2008, 86, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raub, C.; Knödler, A. The electrodeposition of gold by pulse plating. Gold Bull. 1977, 10, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolova, M.; Böck, R. Electrodeposition of Pd from a deep eutectic solvent system: Effect of additives and hydrodynamic conditions. Trans. IMF 2019, 97, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fan, C.; Chen, Y.; Lou, J.; Yan, L. Pulse current electrodeposition of Al from an AlCl3-EMIC ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5478–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispas, A.; Bund, A. Pulse plating of tantalum from 1-butyl-1-methyl-pyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide ionic liquids. Trans. IMF 2012, 90, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Zanella, C.; Deflorian, F. Effect of pulse current on the electrodeposition of copper from choline chloride-ethylene glycol. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooksby, H. An X-ray study of tin-nickel electrodeposits. Trans. IMF 1950, 27, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Nano Plating—Microstructure Formation Theory of Plated Films and a Database of Plated Films; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, Nederland, 2004; pp. 630–640. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C. Structure of electrodeposited equiatomic tin-nickel alloy. J. AppL. Phys. 1980, 51, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. A study of the current efficiency decrease accompanying short pulse time for pulse plating. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1989, 136, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Clarke, M. Structure and thermal stability of tin-nickel alloys electrodeposited from acid baths. Trans. IMF 1968, 46, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.; Wilson, A. Scherrer after sixty years: A survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. AppL. Crystallogr. 1978, 11, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicenzo, A.; Bonelli, S.; Cavallotti, P. Pulse plating of matt tin: Effect on properties. Trans. IMF 2010, 88, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, T.; Manty, B.; Mcdaniel, P. Pulse plating of chromium-molybdenum coatings. Plating Surf. Finish. 1980, 67, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Paatsch, W. Zinc Deposition by pulse plating. Galvanotechnik 1980, 71, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Wang, S.; Walsh, F. Electrodeposition of nanocrystalline nickel–cobalt binary alloy coatings: A review. Trans. IMF 2015, 93, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Honma, H. Micro-fabrication technologies on recent packaging. In Electrochemical Technology Applications in Electronics; Romankiw, L.T., Ed.; Electrochemical Society Proc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, S.; Rajasekaran, N. Pulse electrodeposition of tin from sulphate bath. Surf. Eng. 2009, 25, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
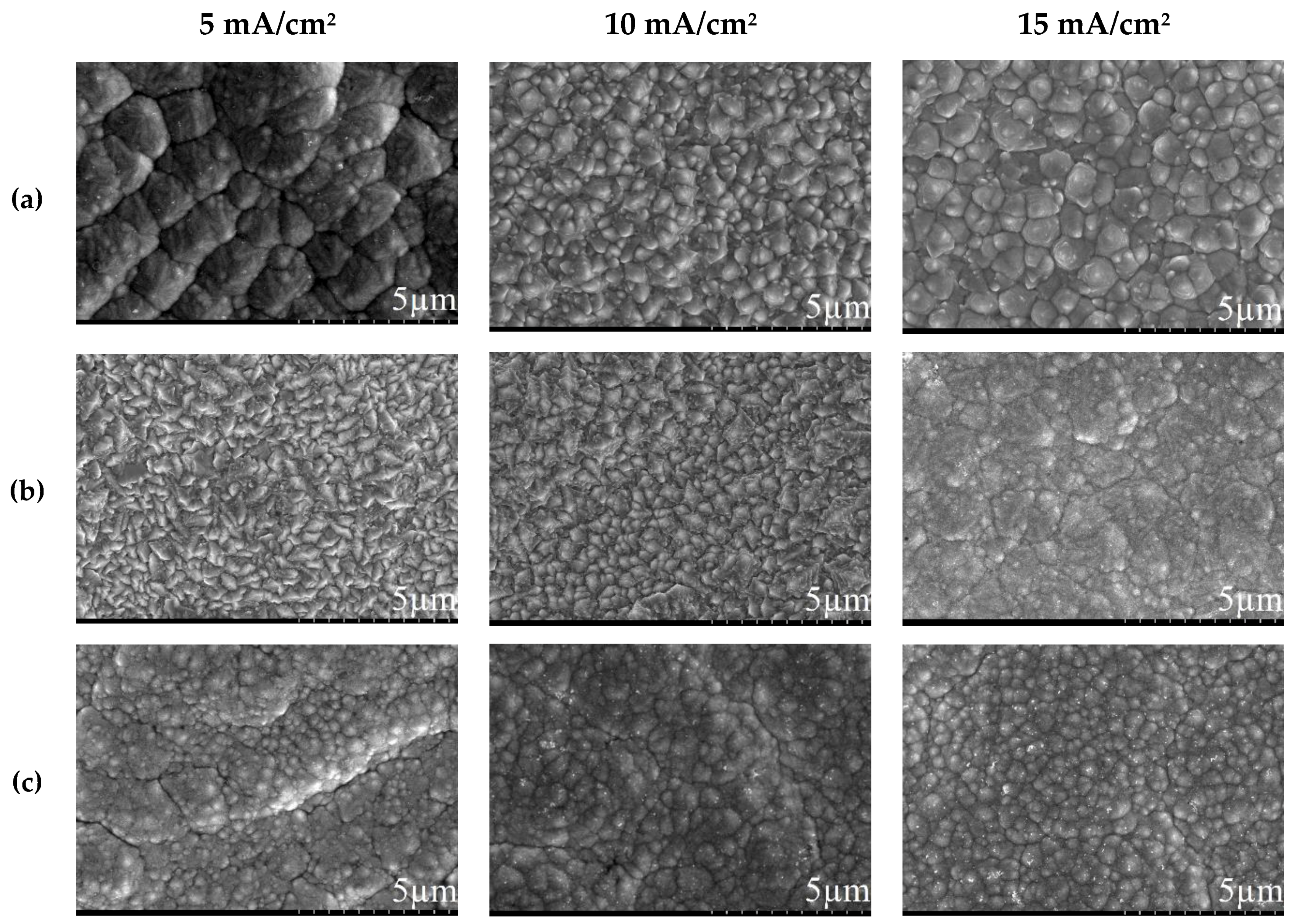
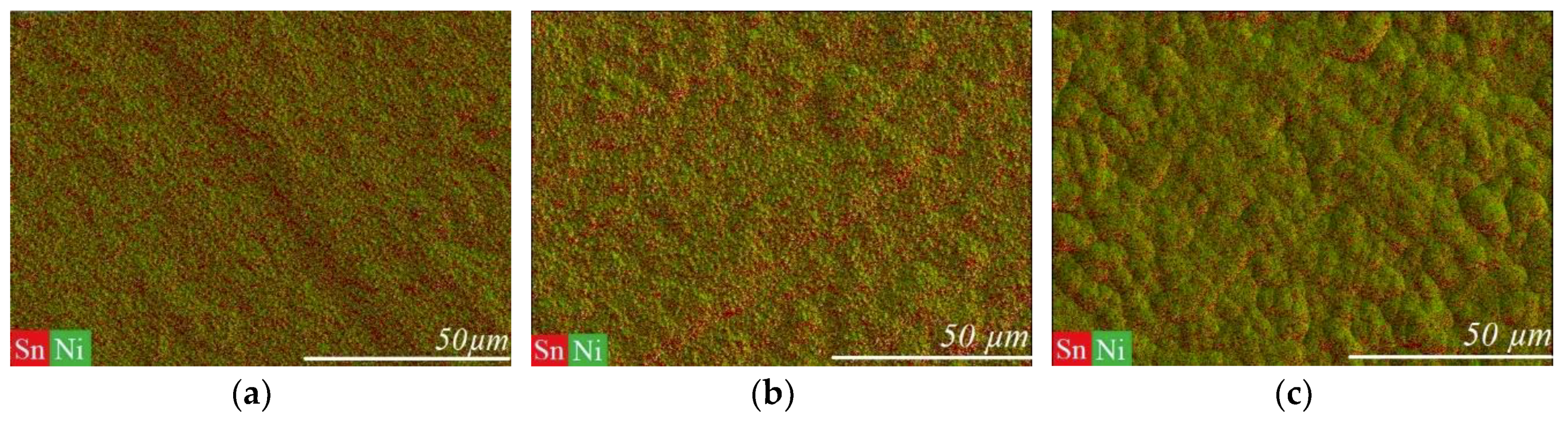
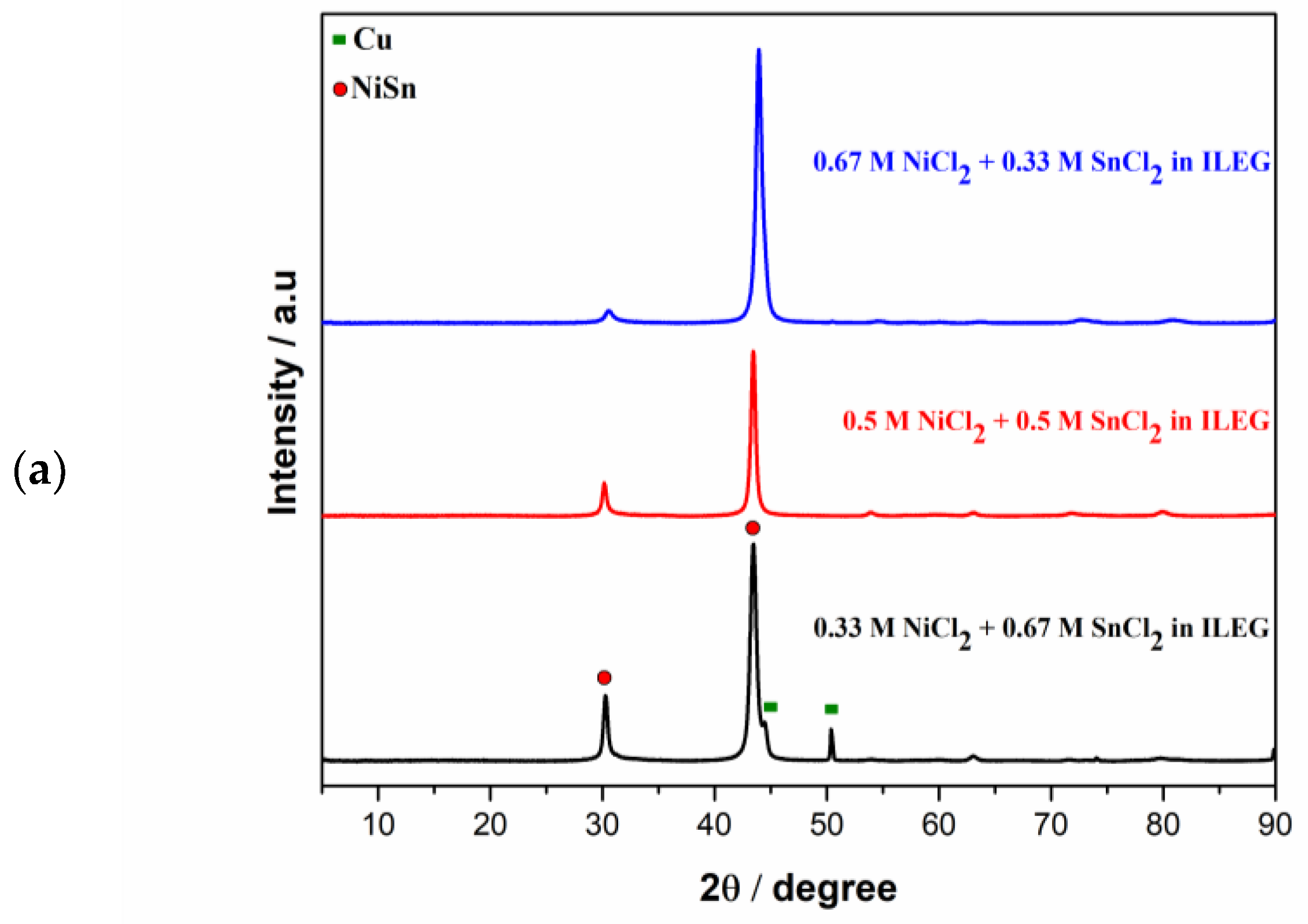


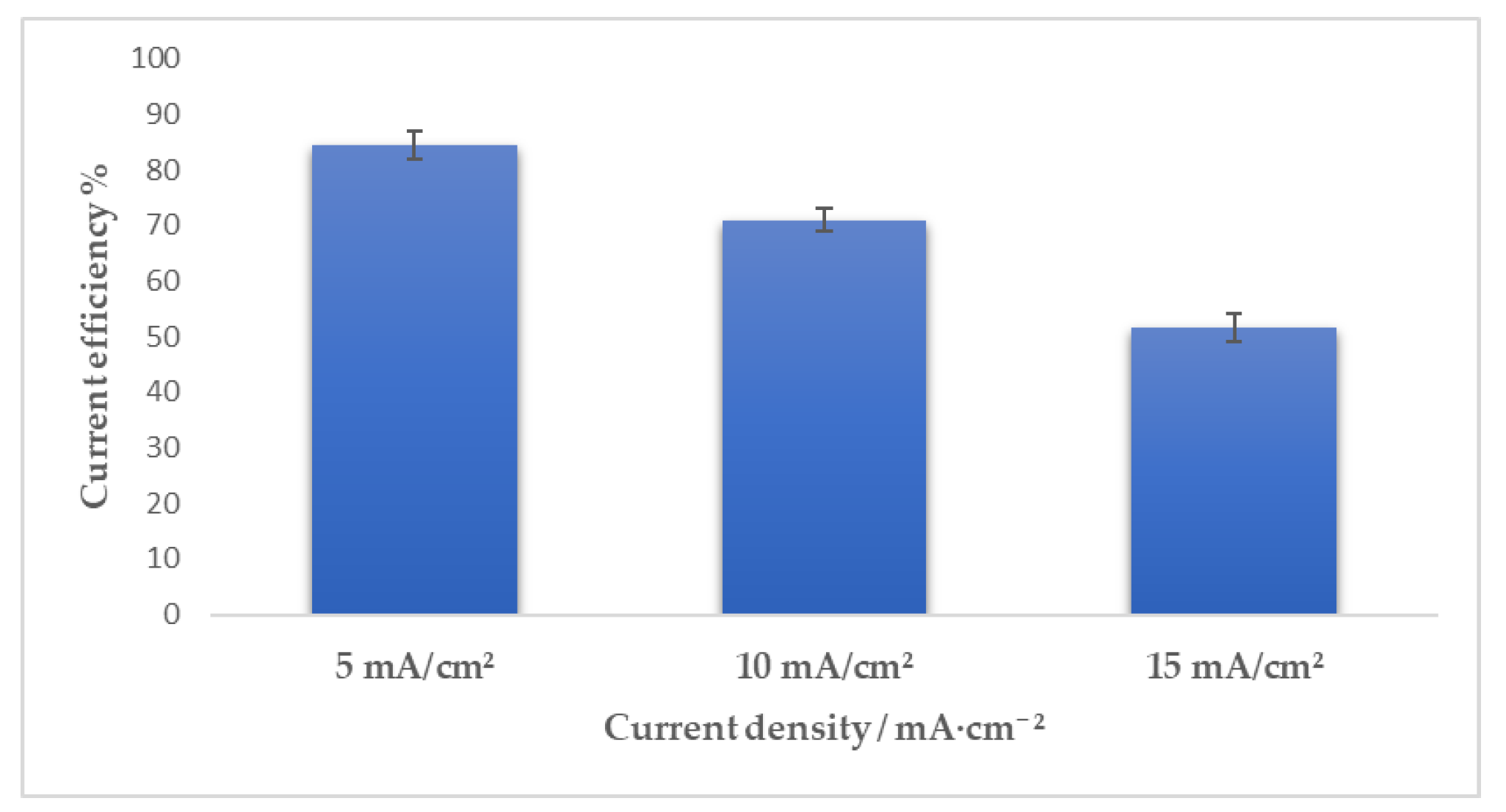


| System Type | Metal Salt, mol/L |
|---|---|
| ILEG-NiSn1 | 0.33 M NiCl2·6H2O + 0.67 M SnCl2·2H2O |
| ILEG-NiSn2 | 0.5 M NiCl2·6H2O + 0.5 M SnCl2·2H2O |
| ILEG-NiSn3 | 0.67 M NiCl2·6H2O + 0.33 M SnCl2·2H2O |
| Electrolyte | wt.% Ni (Average) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mA/cm2 | 10 mA/cm2 | 15 mA/cm2 | |
| ILEG-NiSn1 | 32.71 ± 0.65 | 32.24 ± 0.91 | 32.38 ± 1.17 |
| ILEG-NiSn2 | 30.86 ± 0.5 | 30.07 ± 0.27 | 31.18 ± 1.27 |
| ILEG-NiSn3 | 35.84 ± 0.87 | 31.90 ± 1.48 | 33.82 ± 1.06 |
| Electrolysis Parameter | NiSn-DC | NiSn-P1 | NiSn-P2 | NiSn-P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| On- and off-time durations of the pulse | - | TON = 5000 ms TOFF = 10,000 ms | TON = 500 ms TOFF = 1000 ms | TON = 50 ms TOFF = 100 ms |
| Frequency (Hz) | - | F = 0.067 Hz | F = 0.67 Hz | F = 6.7 Hz |
| Duty cycle | - | θ = 0.33 | θ = 0.33 | θ = 0.33 |
| Current density (average density) | I = 6.67 mA/cm2 | iav = 6.67 mA/cm2 | iav = 6.67 mA/cm2 | iav = 6.67 mA/cm2 |
| Film Properties | NiSn-DC | NiSn-P1 | NiSn-P2 | NiSn-P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness at 20 mN load (GPa) | 8.18 ± 0.42 | 9.92 ± 0.46 | 10.24 ± 0.67 | 12.73 ± 0.75 |
| Reduced Modulus (GPa) | 156.60 ± 3.05 | 154.20 ± 12.07 | 141.40 ± 17.72 | 149.71 ± 8.04 |
| Alloy composition (wt. %) | 33.54% Ni + 66.46% Sn | 32.81% Ni + 67.19% Sn | 30.44% Ni + 69.56% Sn | 35.09% Ni + 64.91% Sn |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosoiu, S.P.; Pantazi, A.G.; Petica, A.; Cojocaru, A.; Costovici, S.; Zanella, C.; Visan, T.; Anicai, L.; Enachescu, M. Comparative Study of Ni-Sn Alloys Electrodeposited from Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquids in Direct and Pulsed Current. Coatings 2019, 9, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120801
Rosoiu SP, Pantazi AG, Petica A, Cojocaru A, Costovici S, Zanella C, Visan T, Anicai L, Enachescu M. Comparative Study of Ni-Sn Alloys Electrodeposited from Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquids in Direct and Pulsed Current. Coatings. 2019; 9(12):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120801
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosoiu, Sabrina Patricia, Aida Ghiulnare Pantazi, Aurora Petica, Anca Cojocaru, Stefania Costovici, Caterina Zanella, Teodor Visan, Liana Anicai, and Marius Enachescu. 2019. "Comparative Study of Ni-Sn Alloys Electrodeposited from Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquids in Direct and Pulsed Current" Coatings 9, no. 12: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120801
APA StyleRosoiu, S. P., Pantazi, A. G., Petica, A., Cojocaru, A., Costovici, S., Zanella, C., Visan, T., Anicai, L., & Enachescu, M. (2019). Comparative Study of Ni-Sn Alloys Electrodeposited from Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquids in Direct and Pulsed Current. Coatings, 9(12), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9120801








