Study on the Time-Varying Characteristics of Discharge Plasma in Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formation and Expansion of Discharge Plasmas of Micro-EDM
2.2. Equipment and Materials
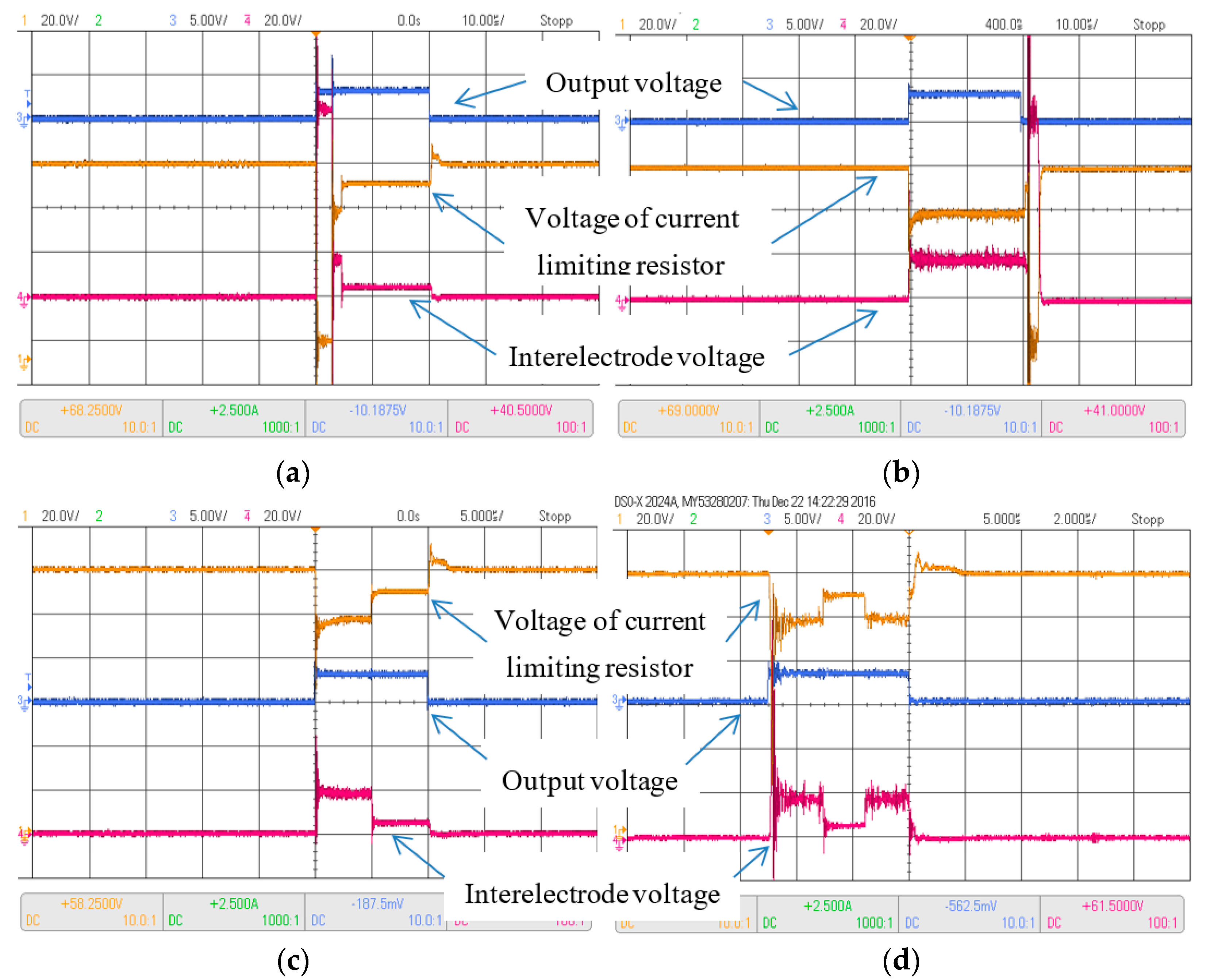
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
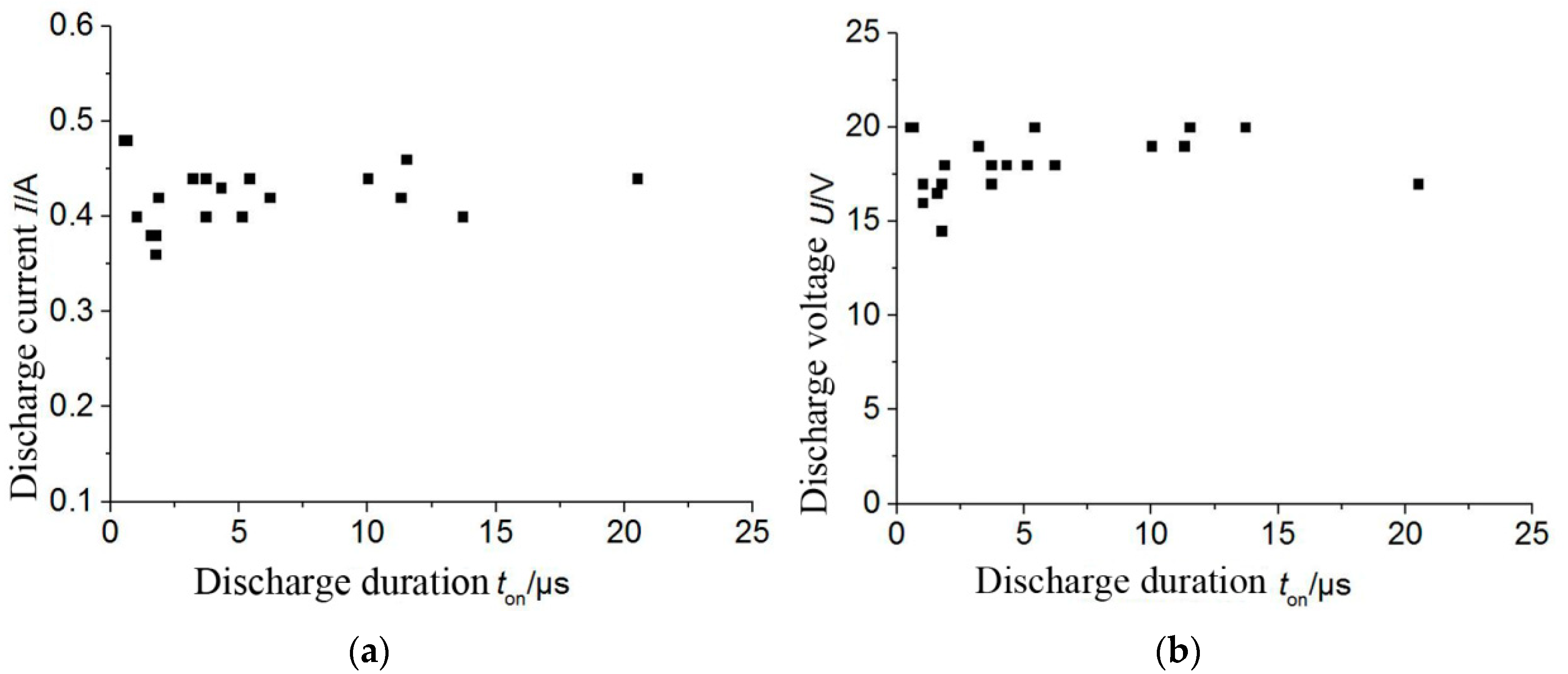
3.1. Effect of Discharge Duration on Current and Voltage
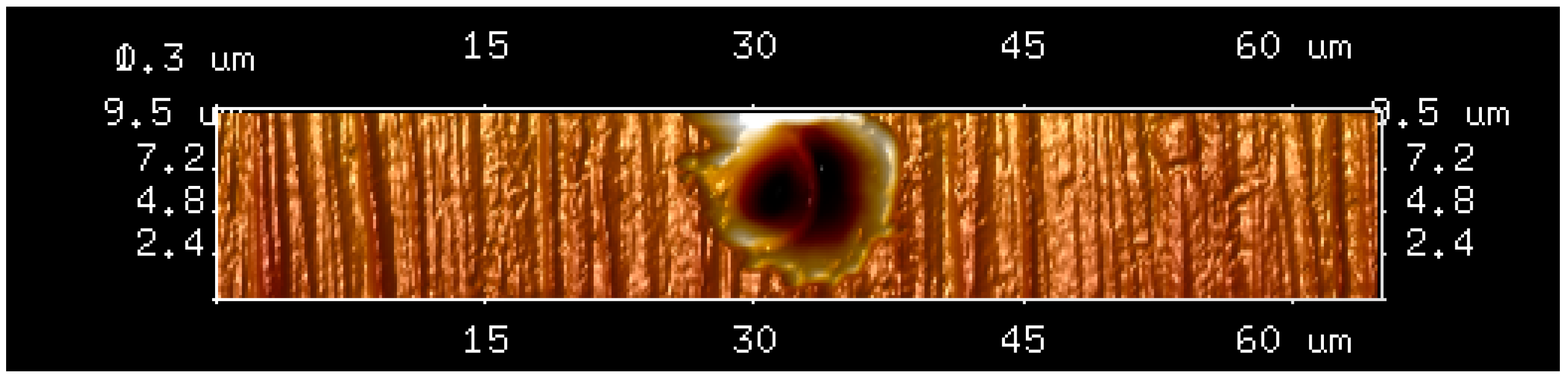
3.2. Effect of Discharge Duration on Discharge Crater Radius
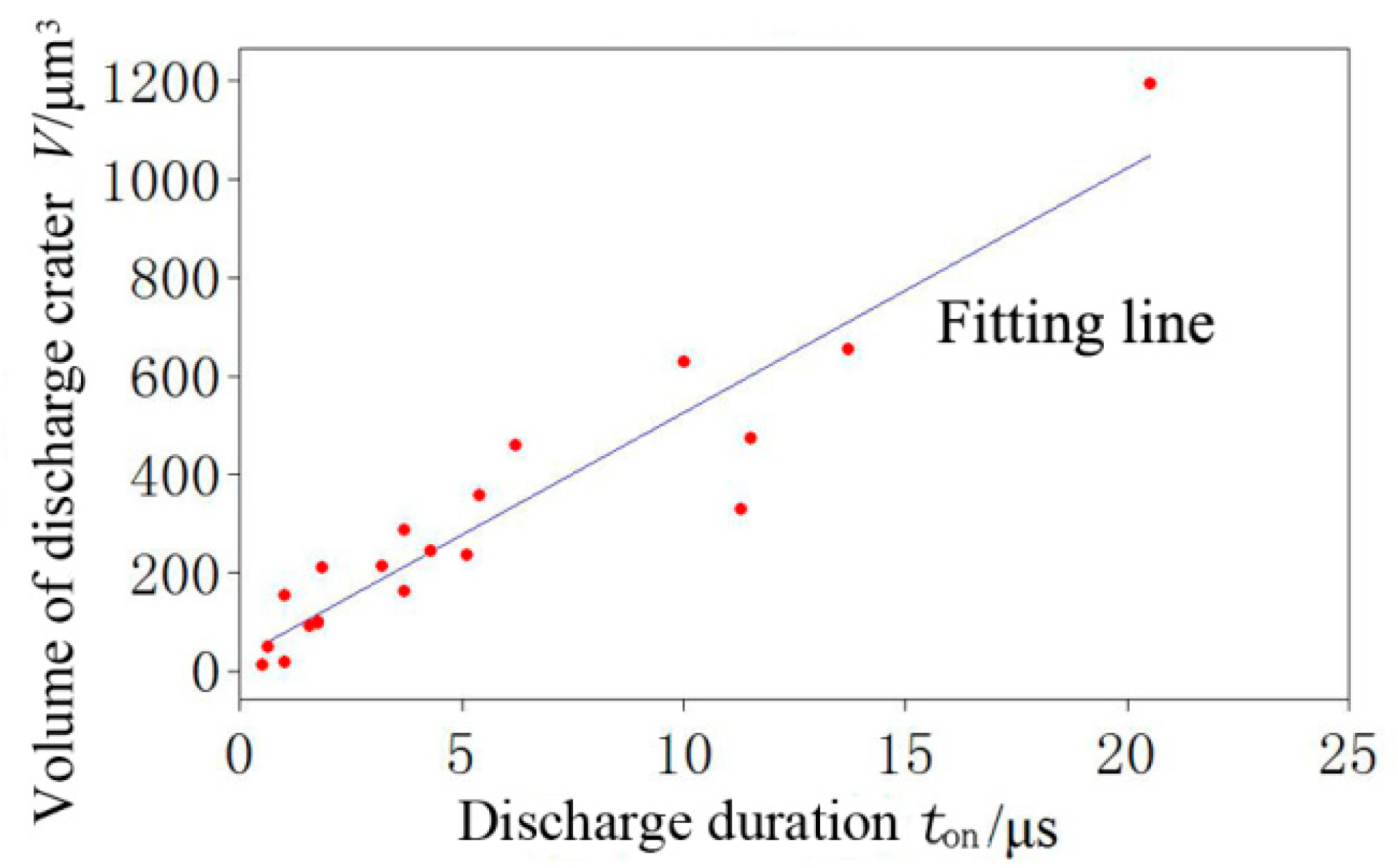
3.3. Effect of Discharge Duration on the Volume of Discharge Crater
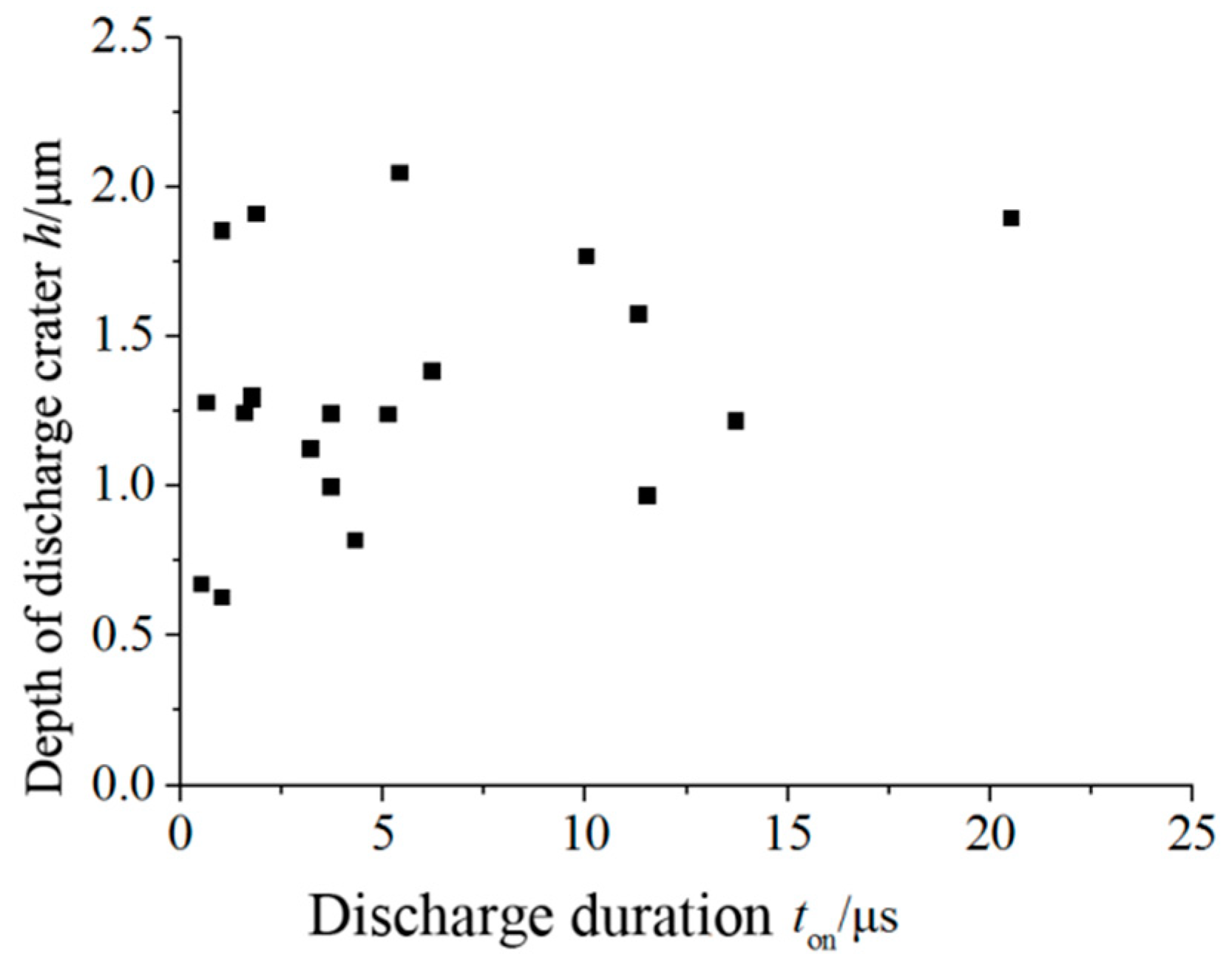
3.4. Effect of Discharge Duration on the Depth of Discharge Crater
4. Conclusions
- The expansion acceleration, internal pressure, temperature, and electron density of the discharge plasma decrease with the increase of discharge duration, while the radius and expansion velocity of the discharge plasma increase with the increase of discharge duration, and finally the discharge plasma reach the state of shape-position equilibrium.
- Discharge maintenance voltage and discharge current are not affected by discharge duration and open circuit voltage. The resistance of discharge plasma is estimated to fluctuate in the range of 38–45 Ω.
- The energy efficiency of micro-EDM is very high when discharge duration is less than 4 μs, and decreases gradually as the discharge duration increases.
- By regression analysis, the regression model of discharge crater volume variation with discharge duration is obtained. The model can be used to effectively predict the discharge crater volume when copper is used as workpiece, and can provide theoretical guidance for micro-EDM.
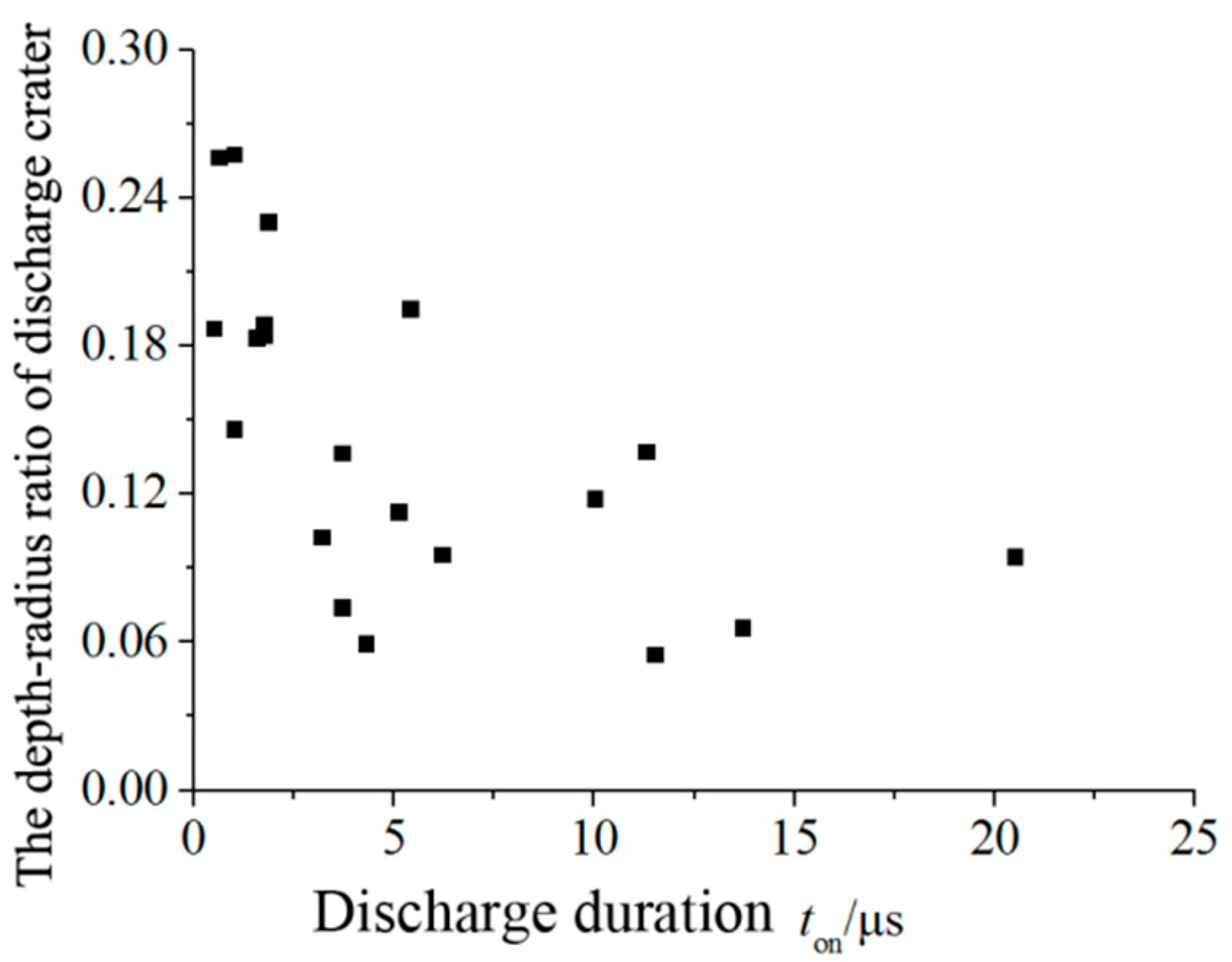
- The discharge duration has no significant effect on the discharge crater depth. As the radius of discharge crater increases, the ratio of depth to radius of discharge crater fluctuates in a larger range, and decreases gradually with the increase of discharge duration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhao, J.; Qian, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, G.; et al. Fabrication of high-performance silver mesh for transparent glass heaters via electric-field-driven microscale 3D Printing and UV-assisted microtransfer. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Feng, T.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Directly writing patterning of conductive material by high voltage induced weak electric arc machining (HV-μEAM). Coatings 2019, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouniyar, A.K.; Shandilya, P. Fabrication and experimental investigation of magnetic field assisted powder mixed electrical discharge machining on machining of aluminum 6061 alloy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 233, 2283–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Kumar, P.; Singh, P.; Hussain, M.; Das, A.; Chattopadhyaya, S. Micro-Electrical discharge machining of difficult-to-machine materials: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 233, 339–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Kumar, S. Micro-Hardness evaluation for surface alloying of H11 die steel with Cu–Cr–Ni powder metallurgy tool in electrical discharge machining. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 232, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. Review of size effects in micro electrical discharge machining. Precis. Eng. 2016, 44, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Rajurkar, K.P. Effects of surface layer of AISI 304 on micro EDM performance. Precis. Eng. 2019, 57, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanik, S.; Joshi, S.S. Modeling of a single resistance capacitance pulse discharge in micro-electro discharge machining. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2005, 127, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, A.B.M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Masaki, T.; Rahman, M.; Wong, Y.S. Analysis of micro-EDM electric characteristics employing plasma property. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Qian, J.; Wang, J.; Reynaerts, D. Simulation and experimental analysis of alternating-current phenomenon in micro-EDM with a RC-type generator. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 255, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kunieda, M.; Abe, K. EDM mechanism of single crystal SiC with respect to thermal, mechanical and chemical aspects. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 236, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.S.; Rahman, M.; Lim, H.S.; Han, H.; Ravi, N. Investigation of micro-EDM material removal characteristics using single RC-pulse discharges. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 140, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Qian, J.; Reynaerts, D. Study of alternating current flow in micro-EDM through real-time pulse counting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 231, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndaliman, M.B.; Khan, A.A.; Ali, M.Y. Influence of electrical discharge machining process parameters on surface micro-hardness of titanium alloy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 227, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assarzadeh, S.; Ghoreishi, M. Prediction of root mean square surface roughness in low discharge energy die-sinking EDM process considering the effects of successive discharges and plasma flushing efficiency. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Datta, D.; Balasubramaniam, R. Numerical modelling, simulation and fabrication of 3-D hemi-spherical convex micro features using Reverse Micro EDM. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.; Gomer, R. Field emission in liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.P.; Rahman, M.; Wong, Y.S. Modelling and experimental investigation on the effect of nanopowder-mixed dielectric in micro-electrodischarge machining of tungsten carbide. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 224, 1725–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.K. Electrostatic and hydrodynamic effects in the electrical breakdown of liquid dielectrics. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1985, EI-20, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y. A study on plasma channel expansion in micro-EDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Gao, J.; Ehn, A.; Aldén, M.; Li, Z.; Moseev, D.; Kusano, Y.; Salewski, M.; Alpers, A.; Gritzmann, P.; et al. Measurements of 3d slip velocities and plasma column lengths of a gliding arc discharge. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 044101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Machining Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Open circuit voltage (U/V) | 90, 120 |
| Capacitance (C/pF) | 1000 |
| Electrode diameter (D/μm) | 200 |
| Pulse width (ton/μs) | 1, 5, 10, 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F. Study on the Time-Varying Characteristics of Discharge Plasma in Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining. Coatings 2019, 9, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110718
Liu Q, Zhang Q, Zhang M, Yang F. Study on the Time-Varying Characteristics of Discharge Plasma in Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining. Coatings. 2019; 9(11):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110718
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingyu, Qinhe Zhang, Min Zhang, and Fazhan Yang. 2019. "Study on the Time-Varying Characteristics of Discharge Plasma in Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining" Coatings 9, no. 11: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110718
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zhang, Q., Zhang, M., & Yang, F. (2019). Study on the Time-Varying Characteristics of Discharge Plasma in Micro-Electrical Discharge Machining. Coatings, 9(11), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110718





