Temperature-Induced Formation of Lubricous Oxides in Vanadium Containing Iron-Based Arc Sprayed Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
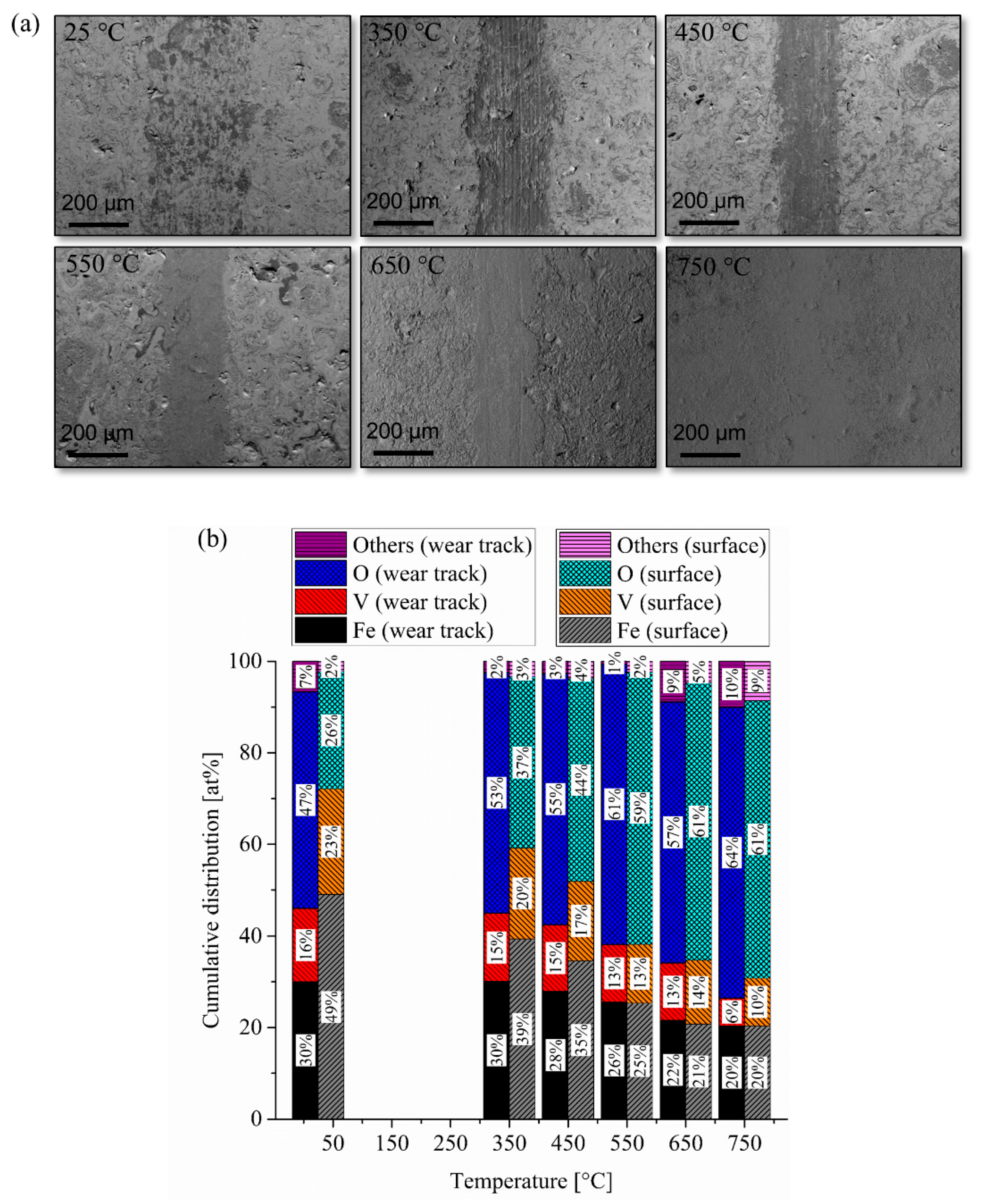
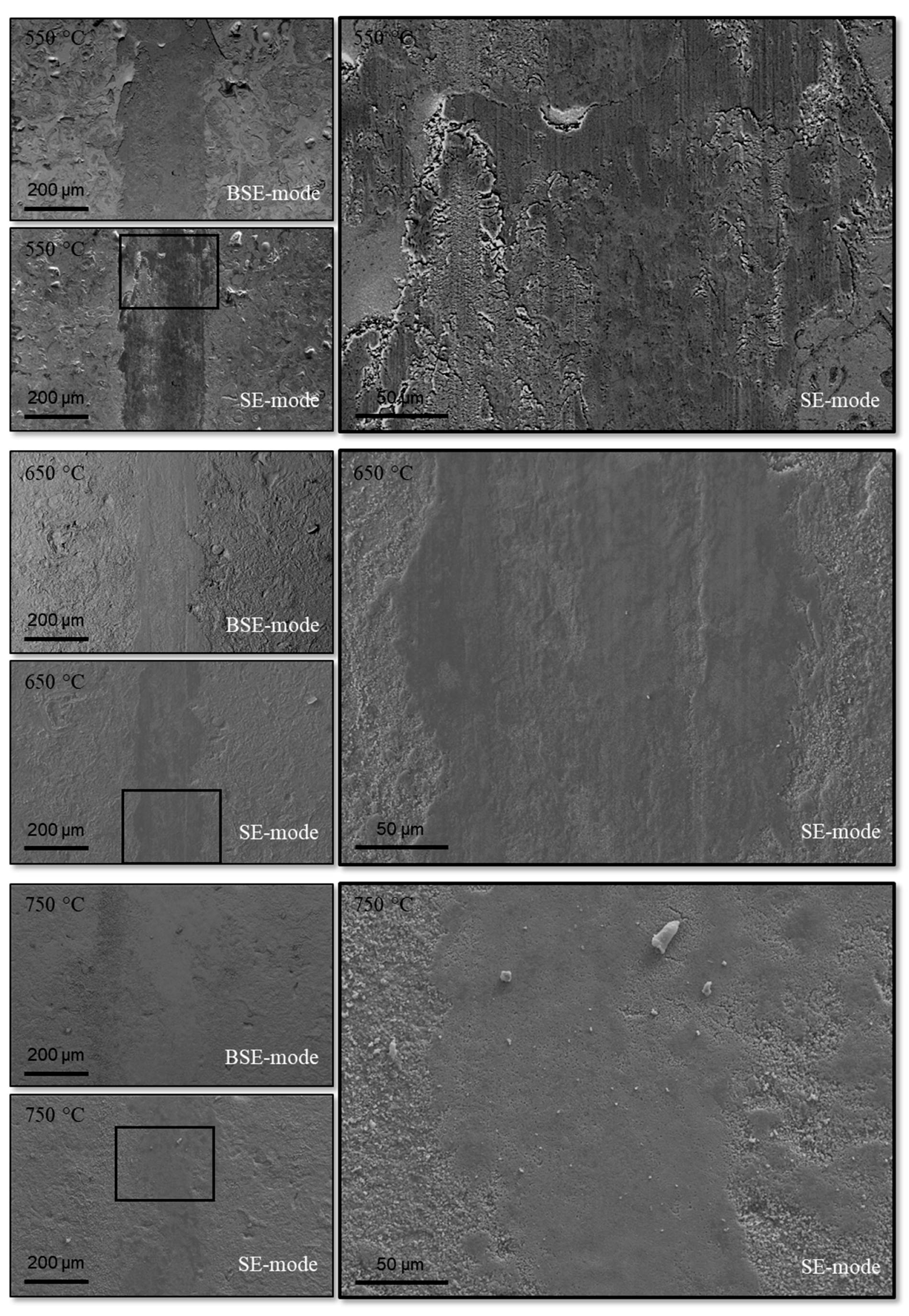
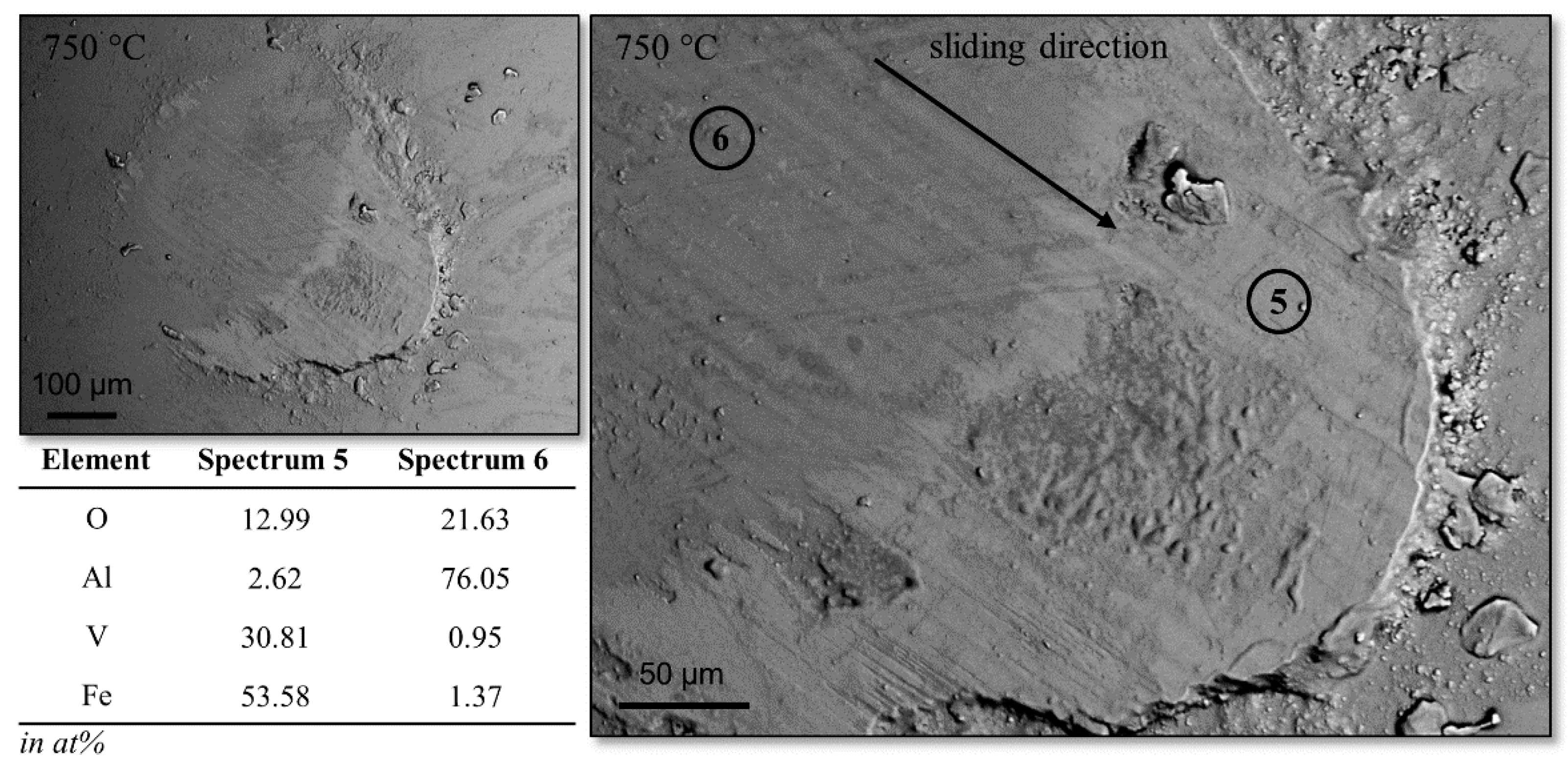
3.1. Tribological Investigation
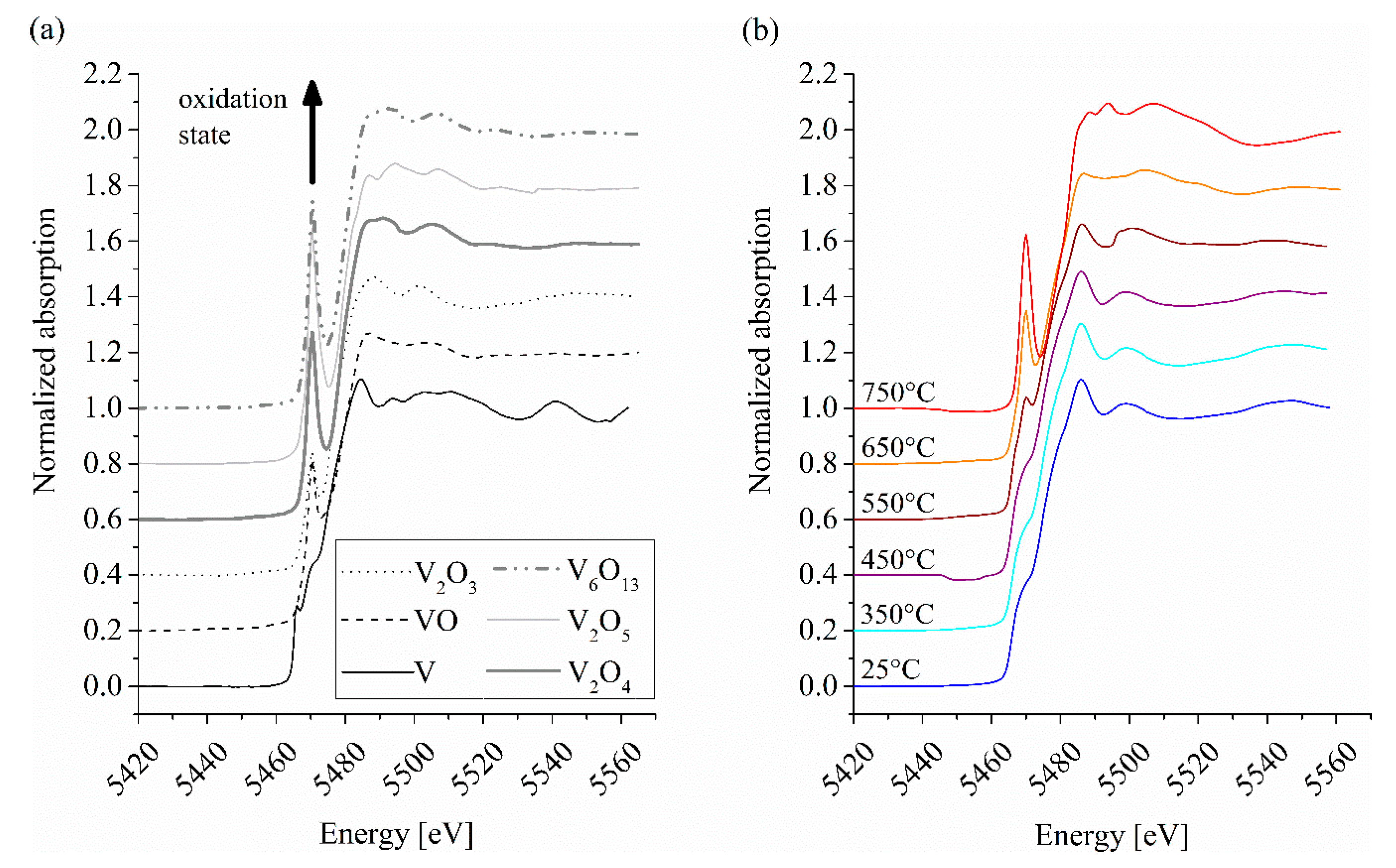
3.2. XANES Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woydt, M.; Skopp, A.; Dörfel, I.; Witke, K. Wear Engineering Oxides/Antiwear Oxides©. Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, R.; Mitterer, C. Vanadium containing self-adaptive low-friction hard coatings for high-temperature applications: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 228, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnara, R.H. Hochtemperaturaktive HPPMS-Verschleißschutzschichten durch Bildung reibmindernder Magnéli-Phasen im System (Cr,Al,X)N. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hochschule Aachen, Aachen, Germany, January 2016. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann, B.; Klemm, M.; Horn, S.; Woydt, M. Switching adhesion forces bycrossing the metal-insulator transition in Magneli-type vanadium oxide crystals. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeswinkel, T.; Music, D.; Schneider, J.M. Ab initio calculations of the structure and mechanical properties of vanadium oxides. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 145404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamsal, C.; Ravindra, N.M. Optical properties of vanadium oxides-an analysis. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 6341–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryha, E.; Rutqvist, E.; Nyborg, L. Stoichiometric vanadium oxides studied by XPS. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 44, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharton, V. Solid State Electrochemistry I: Fundamentals, Materials and their Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Woydt, M.; Skopp, A.; Dörfel, I.; Witke, K. Wear engineering oxides/anti-wear oxides. Wear 1998, 218, 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lugscheider, E.; Bärwulf, S.; Barimani, C. Properties of tungsten and vanadium oxides deposited by MSIP-PVD process for self-lubricating applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 120–121, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugscheider, E.; Knotek, O.; Bobzin, K.; Bärwulf, S. Tribological properties, phase generation and high temperature phase stability of tungsten- and vanadium-oxides deposited by reactive MSIP-PVD process for innovative lubrication applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 133–134, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbiński, W.; Suszko, T.; Sienicki, W.; Warcholiński, B. Tribological properties of silver- and copper-doped transition metal oxide coatings. Wear 2003, 254, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernardou, D.; Louloudakis, D.; Spanakis, E.; Katsarakis, N.; Koudoumas, E. Electrochemical properties of vanadium oxide coatings grown by hydrothermal synthesis on FTO substrates. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louloudakis, D.; Vernardou, D.; Spanakis, E.; Katsarakis, N.; Koudoumas, E. Electrochemical properties of vanadium oxide coatings grown by APCVD on glass substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 230, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lee, J.W.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Sun, D. Towards hard yet self-lubricious CrAlSiN coatings. J. Alloy. Comp. 2015, 618, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, F.; Loureiro, A.; Polcar, T.; Cavaleiro, A. The effect of increasing V content on the structure, mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of Ti-Si-V-N films deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2014, 289, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Bagcivan, N.; Ewering, M.; Brugnara, R.H.; Theiss, S. DC-MSIP/HPPMS (Cr,Al,V)N and (Cr,Al,W)N thin films for high-temperature friction reduction. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, R.; Neidhardt, J.; Mitterer, C.; Schaffer, B.; Hutter, H.; Kaindl, R.; Sartory, B.; Tessadri, R.; Lechthaler, M.; Polcik, P. Oxidation and diffusion processes during annealing of AlCrVN hard coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2008, 26, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Chiu, W.T.; Hung, J.P. Mechanical properties and high temperature oxidation of CrAlSiN/TiVN hard coatings synthesized by cathodic arc evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 303 Pt A, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lee, J.W.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Self-lubricating CrAlN/VN multilayer coatings at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Temperature dependent friction and wear of magnetron sputtered coating TiAlN/VN. Wear 2011, 271, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Li, F.; Zhao, D. Improvement of tribological performance of CrN coating via multilayering with VN. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 231, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.K.; Baik, Y.J. Increase of hardness and oxidation resistance of VN coating by nanoscale multilayered structurization with AlN. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2528–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Kokalj, D.; Stangier, D.; Paulus, M.; Sternemann, C.; Tolan, M. Investigation on the oxidation behavior of AlCrVxN thin films by means of synchrotron radiation and influence on the high temperature friction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriedt, H.A. The O–V (Oxygen-Vanadium) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1989, 10, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschej, K.; Mayrhofer, P.H.; Kathrein, M.; Polcik, P.; Mitterer, C. A new low-friction concept for Ti1−xAlxN based coatings in high-temperature applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188–189, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yu, S.F.; Yan, N.; Xing, S.L.; Huang, L.B. Effect of vanadium and niobium on abrasive behaviour of arc sprayed 4Cr13 coatings. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 395, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PL 40933 EN 07 PPG SmartArc® Gun Parts List (EN). Available online: https://www.oerlikon.com/metco/en/products-services/coating-equipment/thermal-spray/spray-guns/spray-guns-arc/ppg/ (accessed on 27 December 2018).
- Tillmann, W.; Hagen, L.; Kokalj, D.; Paulus, M.; Tolan, M. A study on the tribological behavior of vanadium-doped arc sprayed coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2017, 26, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation of European Producers of Abrasives. FEPA Grains Standards. Available online: https://www.fepa-abrasives.com/abrasive-products/grains (accessed on 27 December 2018).
- Newbery, A.P.; Grant, P.S.; Neiser, R.A. The velocity and temperature of steel droplets during electric arc spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 195, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, W. Effect of the long-term heat treatment on the cyclic oxidation behavior of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline coatings prepared by high-velocity arc spray process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, D.; Feng, Y.; Liang, X. Microstructure and fracture toughness of the FePSiB-based amorphous/nanocrystalline coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 696, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, V.A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.; Walter, P.; Susini, J. A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim. Acta B 2007, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poumellec, B.; Marucco, J.F.; Touzelin, B. X-ray-absorption near-edge structure of titanium and vanadium in (titanium,vanadium) dioxide rutile solid solutions. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 35, 2284–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfilyev, V.; Moshkovich, A.; Lapsker, I.; Laikhtman, A.; Rapoport, L. The effect of vanadium content and temperature on stick–slip phenomena under friction of CrV(x)N coatings. Wear 2013, 307, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, I.; Shipway, P. Wear by hard particles. In Tribology, 2nd ed.; Hutchings, I., Shipway, P., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 165–236. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.; Lytle, F.W.; Messmer, R.P.; Maylotte, D.H. K−edge absorption spectra of selected vanadium compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 5596–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurand, P.; Rose, J.; Briois, V.; Salome, M.; Proux, O.; Nassif, V.; Olivi, L.; Susini, J.; Hazemann, J.L.; Bottero, J.Y. New methodological approach for the vanadium K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure interpretation: Application to the speciation of vanadium in oxide phases from steel slag. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5101–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, J.A.; Wandzilak, A.; Maganas, D.; Wurster, N.I.C.; Hugenbruch, S.; Kowalska, J.K.; Pollock, C.J.; Lima, F.A.; Finkelstein, K.D.; DeBeer, S. Experimental and theoretical correlations between vanadium K-edge X-ray absorption and Kβ emission spectra. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 21, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Yamashita, H.; Tsuchitani, R.; Funabiki, T.; Yoshida, S. X-ray absorption (EXAFS/XANES) study of supported vanadium oxide catalysts. Structure of surface vanadium oxide species on silica and (γ-alumina at a low level of vanadium loading. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1988, 84, 2987–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Darma, S.; Kaufholz, M.; Mangold, S.; Doyle, S.; Ulrich, S.; Leiste, H.; Stuber, M.; Baumbach, T. Composition-dependent structure of polycrystalline magnetron-sputtered V-Al-C-N hard coatings studied by XRD, XPS XANES and EXAFS. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuli, G.; Paris, E.; Mungall, J.; Romano, C.; Dingwell, D. V oxidation state and coordination number in silicate glasses by XAS. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.R.; Karner, J.; Papike, J.; Delaney, J.S.; Shearer, C.; Newville, M.; Eng, P.; Rivers, M.; Dyar, M.D. Vanadium K edge XANES of synthetic and natural basaltic glasses and application to microscale oxygen barometry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, S.; Smyrl, W.H.; Berrettoni, M.; Tossici, R.; Rosolen, M.; Marassi, R.; Decker, F. XAS and electrochemical characterization of lithium intercalated V2O5 xerogels. Solid State Ion. 1996, 90, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Farges, F.; Petit, P.E.; Brown, G.E.J.; Martin, F. Oxidation state and coordination of Fe in minerals: An Fe K-XANES spectroscopic study. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Partzsch, G.M.; Bernhardt, R.; Lattard, D. Determination of the iron oxidation state in basaltic glasses using XANES at the K-edge. Chem. Geol. 2004, 213, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, P.-E.; Farges, F.; Wilke, M.; Solé, V.A. Determination of the iron oxidation state in Earth materials using XANES pre-edge information. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2001, 8, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farges, F. Ab initio and experimental pre-edge investigations of the Mn K-edge XANES in oxide-type materials. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 155109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehr, J.J.; Albers, R.C. Theoretical approaches to x-ray absorption fine structure. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2000, 72, 621–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


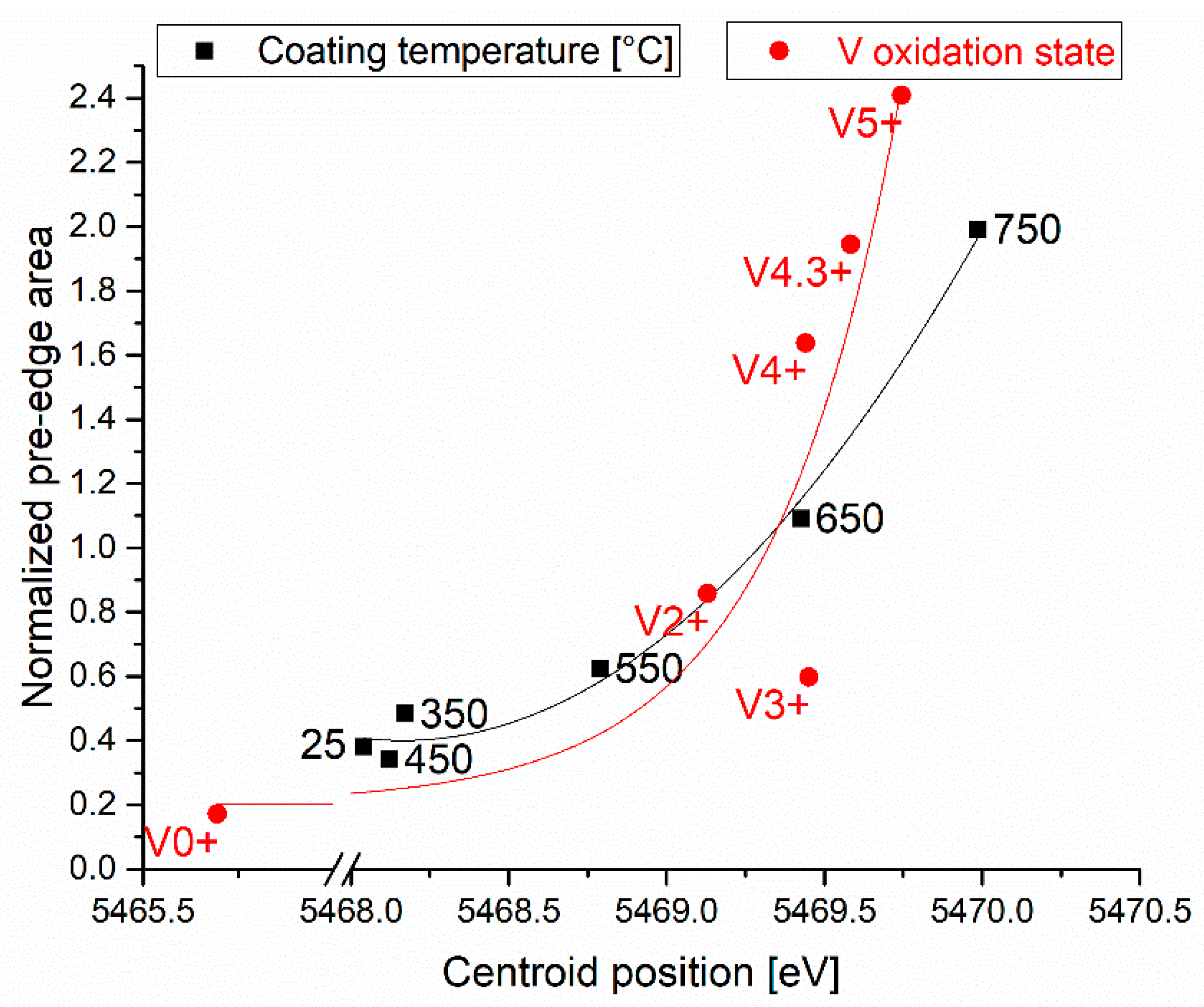
| Phase | Oxidation-State | Pre-Edge | Main-Edge Position (eV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized Intensity | Position (eV) | |||
| V | 0 | 0.29 | 1 | 9.5 |
| VO | 2 | 0.62 | 5.5 | 8.7 |
| V2O3 | 3 | 0.44 | 5.5 | 10.8 |
| V2O4 | 4 | 0.67 | 5.5 | 13.2 |
| V6O13 | 4.3 | 0.75 | 5.5 | 14.4 |
| V2O5 | 5 | 0.85 | 5.5 | 13.8 |
| Coating Temperature (°C) | Pre-Edge | Main-Edge Position (eV) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized Intensity | Position (eV) | ||
| 25 | 0.39 * | 5 * | 9.5 |
| 350 | 0.39 * | 5 * | 9.5 |
| 450 | 0.43 * | 5 * | 9.5 |
| 550 | 0.47 | 5 | 9.8 |
| 650 | 0.57 | 5 | 11.6 |
| 750 | 0.74 | 5 | 12.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tillmann, W.; Hagen, L.; Kokalj, D.; Paulus, M.; Tolan, M. Temperature-Induced Formation of Lubricous Oxides in Vanadium Containing Iron-Based Arc Sprayed Coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010018
Tillmann W, Hagen L, Kokalj D, Paulus M, Tolan M. Temperature-Induced Formation of Lubricous Oxides in Vanadium Containing Iron-Based Arc Sprayed Coatings. Coatings. 2019; 9(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleTillmann, Wolfgang, Leif Hagen, David Kokalj, Michael Paulus, and Metin Tolan. 2019. "Temperature-Induced Formation of Lubricous Oxides in Vanadium Containing Iron-Based Arc Sprayed Coatings" Coatings 9, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010018
APA StyleTillmann, W., Hagen, L., Kokalj, D., Paulus, M., & Tolan, M. (2019). Temperature-Induced Formation of Lubricous Oxides in Vanadium Containing Iron-Based Arc Sprayed Coatings. Coatings, 9(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010018




