Tailoring Characteristics of PEDOT:PSS Coated on Glass and Plastics by Ultrasonic Substrate Vibration Post Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental
2.2. Characterizations
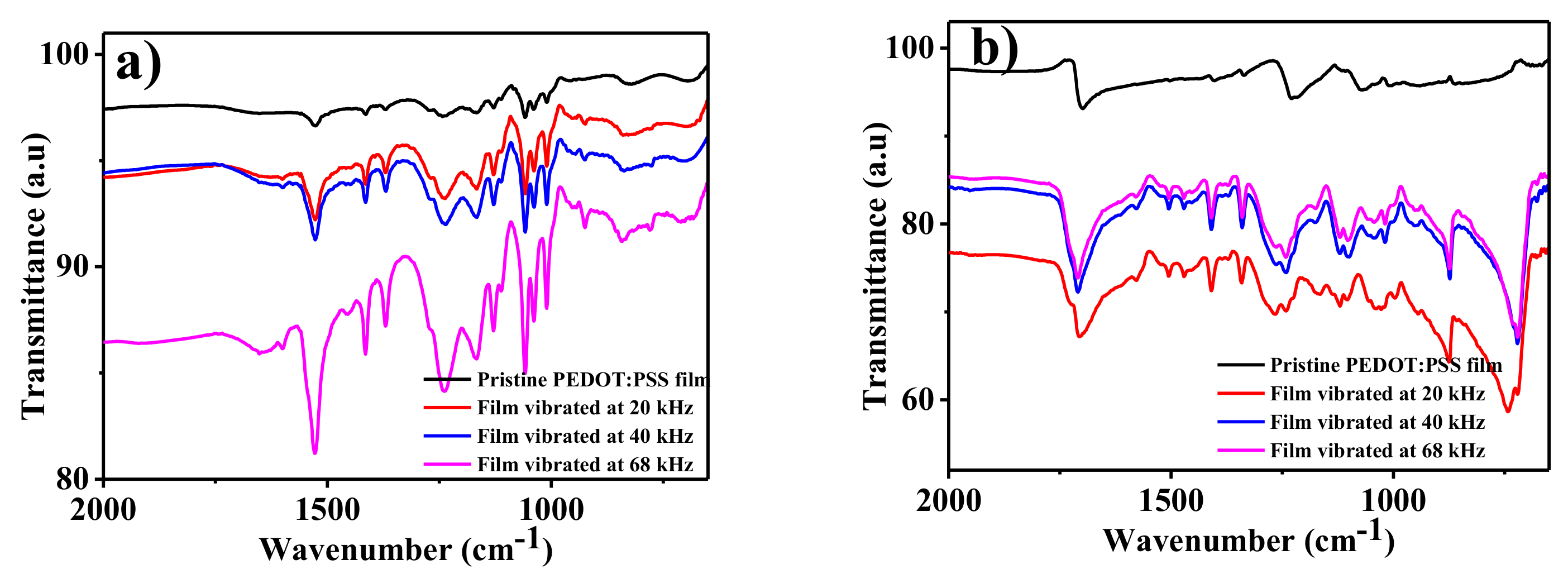
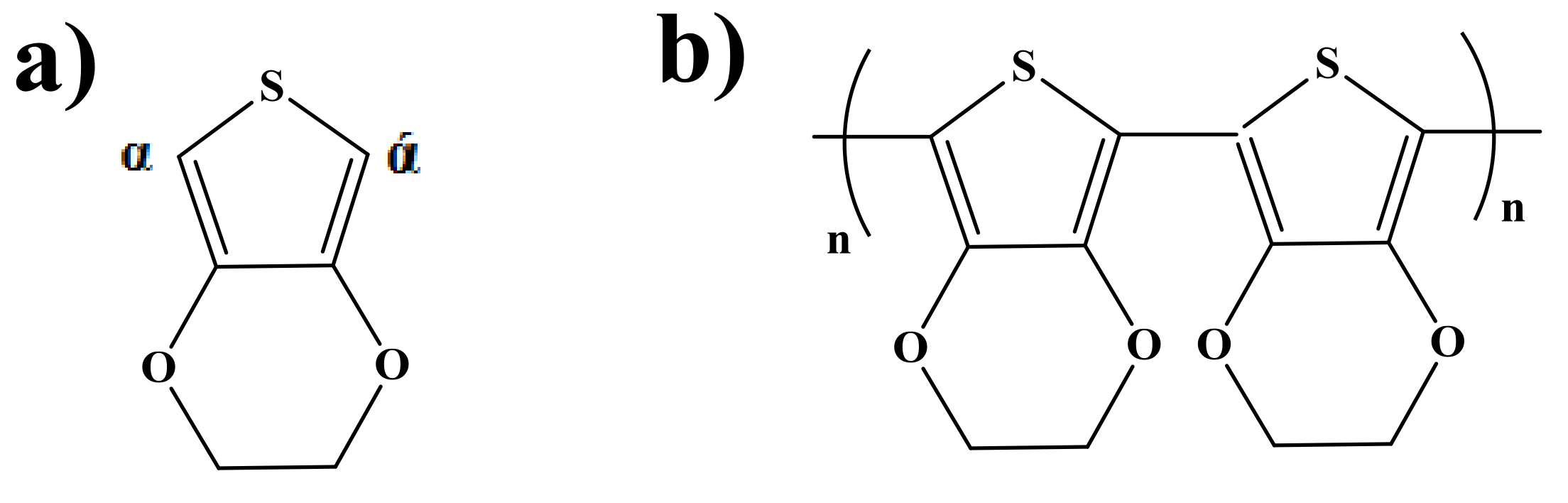
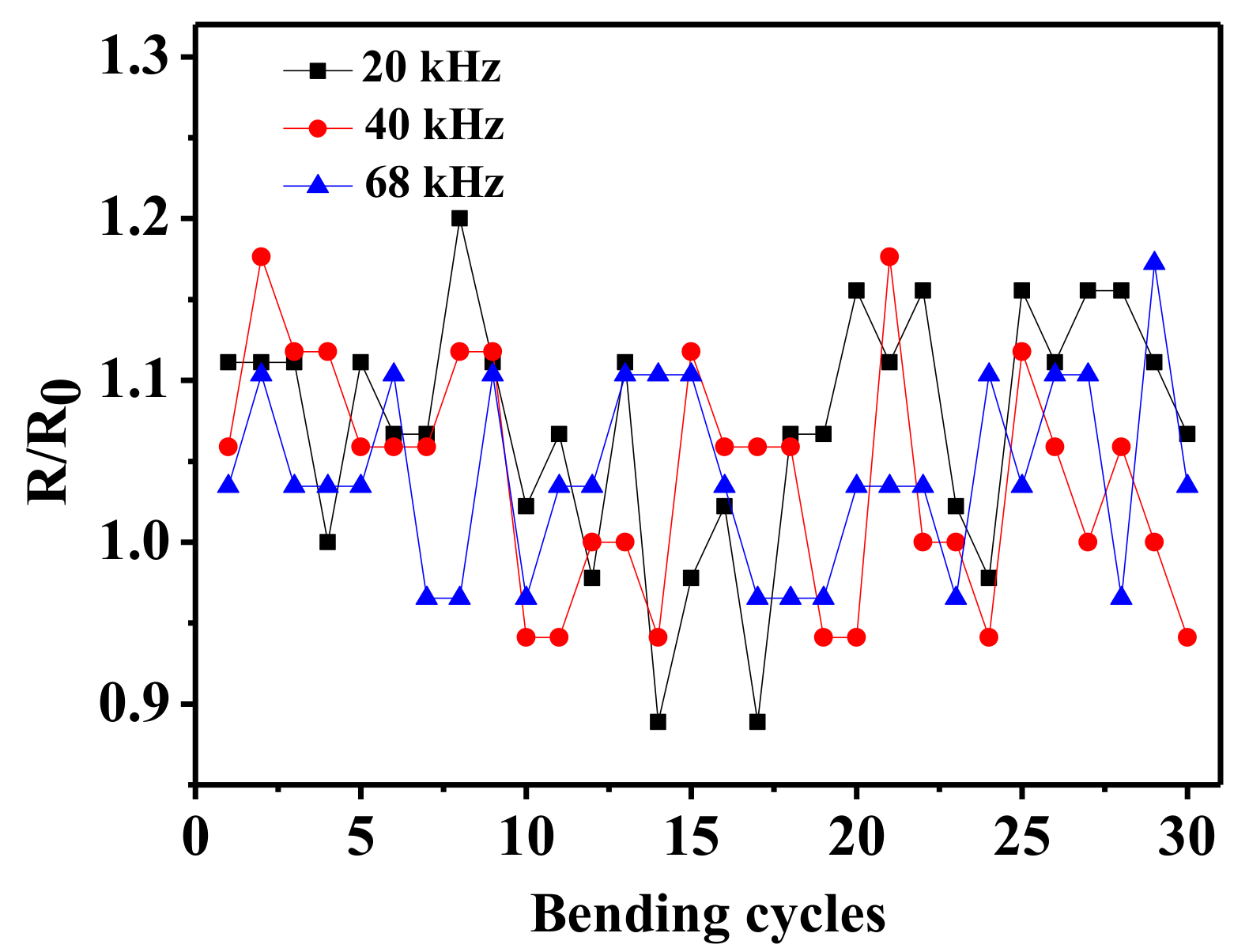
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslamian, M. Inorganic and organic solution-processed thin film devices. Nano-Micro Lett. 2017, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotheim, T.A.; Reynolds, J. Conjugated Polymers: Theory, Synthesis, Properties, and Characterization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Das, T.K.; Prusty, S. Review on conducting polymers and their applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, H.; Louis, E.J.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Chiang, C.K.; Heeger, A.J. Synthesis of electrically conducting organic polymers: Halogen derivatives of polyacetylene,(CH)x. J. Chem. Soci. Chem. Commun. 1977, 16, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, D.; Isikgor, F.H.; Ouyang, J. Review on application of PEDOTs and PEDOT: PSS in energy conversion and storage devices. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4438–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendaal, L.; Jonas, F.; Freitag, D.; Pielartzik, H.; Reynolds, J.R. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) and its derivatives: Past, present, and future. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickert, J.; Sun, H.; Palumbiny, C.; Hesse, H.C.; Schmidt-Mende, L. Spray-deposited PEDOT:PSS for inverted organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 2371–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Kang, H.; Kim, G.; Kim, N.; Lee, K. Controlled electro-spray deposition of highly conductive PEDOT: PSS films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 98, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Dou, L.; Hong, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, Y. Recent trends in polymer tandem solar cells research. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1909–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, N.; Muhammad, N.M.; Ali, A.; Jo, J.; Choi, K.-H. Characterization of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) thin film deposited through electrohydrodynamic atomization technique. Mater. Lett. 2012, 83, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, U.; Müller, E.; Naujoks, N.; Dual, J. Microscopical investigations of PEDOT:PSS thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, S.; Birgerson, J.; Crispin, X.; Greczynski, G.; Osikowicz, W.; Van Der Gon, A.D.; Salaneck, W.R.; Fahlman, M. The effects of solvents on the morphology and sheet resistance in poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–polystyrenesulfonic acid (PEDOT–PSS) films. Synth. Met. 2003, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medford, A.J.; Lilliedal, M.R.; Jørgensen, M.; Aarø, D.; Pakalski, H.; Fyenbo, J.; Krebs, F.C. Grid-connected polymer solar panels: Initial considerations of cost, lifetime, and practicality. Opt. Express 2010, 18, A272–A285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, F.C.; Gevorgyan, S.A.; Alstrup, J. A roll-to-roll process to flexible polymer solar cells: Model studies, manufacture and operational stability studies. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5442–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, F.C.; Tromholt, T.; Jørgensen, M. Upscaling of polymer solar cell fabrication using full roll-to-roll processing. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchmeyer, S.; Reuter, K. Scientific importance, properties and growing applications of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemerink, M.; Timpanaro, S.; De Kok, M.; Meulenkamp, E.; Touwslager, F. Three-dimensional inhomogeneities in PEDOT: PSS films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 18820–18825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. PEDOT: PSS films with significantly enhanced conductivities induced by preferential solvation with cosolvents and their application in polymer photovoltaic cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4927–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Lee, K. Heat-treatment-induced enhancement in the optical spectra of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(stylenesulfonate) films. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2005, 46, 973–976. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Falco, A.; Loch, M.; Lugli, P.; Scarpa, G. Spray coated indium-tin-oxide-free organic photodiodes with PEDOT: PSS anodes. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, J.G.; Worfolk, B.J.; Maloney, S.A.; Hauger, T.C.; Elias, A.L.; Buriak, J.M.; Harris, K.D. Spray coated high-conductivity PEDOT: PSS transparent electrodes for stretchable and mechanically robust organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 110, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-K.; Hwang, W.-J.; Eun, K.; Choa, S.-H.; Na, S.-I.; Kim, H.-K. Mechanical flexibility of transparent PEDOT:PSS electrodes prepared by gravure printing for flexible organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 3269–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, F.; Xie, Y.; Gao, S.; Eslamian, M. Morphology, conductivity, and wetting characteristics of PEDOT:PSS thin films deposited by spin and spray coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 338, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M.; Newton, J.E. Spray-on PEDOT:PSS and P3HT:PCBM thin films for polymer solar cells. Coatings 2014, 4, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, F.C. Fabrication and processing of polymer solar cells: A review of printing and coating techniques. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, J.; Lee, D.; Joo, J. Enhancement of electrical conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(4-styrenesulfonate) by a change of solvents. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Chu, C.W.; Chen, F.C.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y. High-conductivity poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(styrene sulfonate) film and its application in polymer optoelectronic devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardes, A.M.; Janssen, R.A.; Kemerink, M. A morphological model for the solvent-enhanced conductivity of PEDOT: PSS thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Influence of doped PEDOT:PSS on the performance of polymer solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 2763–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Du, D.; Ouyang, J. PEDOT: PSS films with metallic conductivity through a treatment with common organic solutions of organic salts and their application as a transparent electrode of polymer solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11629–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Du, D.; Yu, Z.; Li, P.; Xia, Y.; Ouyang, J. Significant enhancement in the thermoelectric properties of PEDOT:PSS films through a treatment with organic solutions of inorganic salts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23204–23211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ahmadian-Yazdi, M.-R.; Eslamian, M. Investigation of morphology and physical properties of modified PEDOT:PSS films made via in-situ grafting method. Synth. Met. 2015, 209, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosgueritchian, M.; Lipomi, D.J.; Bao, Z. Highly conductive and transparent PEDOT:PSS films with a fluorosurfactant for stretchable and flexible transparent electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döbbelin, M.; Marcilla, R.; Salsamendi, M.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Carrasco, P.M.; Pomposo, J.A.; Mecerreyes, D. Influence of ionic liquids on the electrical conductivity and morphology of PEDOT:PSS films. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2147–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Weigandt, K.M.; Uhrig, D.; Alsayed, A.; Badre, C.; Hough, L.; Muthukumar, M. Scattering studies on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)–polystyrenesulfonate in the presence of ionic liquids. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8989–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Xiao, S.; Tan, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. High-performance polymer solar cells realized by regulating the surface properties of PEDOT:PSS interlayer from ionic liquids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27018–27025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badre, C.; Marquant, L.; Alsayed, A.M.; Hough, L.A. Highly conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) films using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetracyanoborate ionic liquid. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2723–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Soltani-Kordshuli, F.; Eslamian, M. Progress in emerging solution-processed thin film solar cells–part I: Polymer solar cells. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistie, D.A.; Ibrahem, M.A.; Wang, P.-C.; Chu, C.-W. Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS treated with formic acid for ITO-free polymer solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabihi, F.; Eslamian, M. Substrate vibration-assisted spray coating (SVASC): Significant improvement in nano-structure, uniformity, and conductivity of PEDOT:PSS thin films for organic solar cells. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2015, 12, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Eslamian, M. Improving uniformity and nanostructure of solution-processed thin films using ultrasonic substrate vibration post treatment (SVPT). Ultrasonics 2016, 67, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zabihi, F.; Eslamian, M. Fabrication of highly reproducible polymer solar cells using ultrasonic substrate vibration posttreatment. J. Photonics Energy 2016, 6, 045502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, F.; Ahmadian-Yazdi, M.-R.; Eslamian, M. Fundamental study on the fabrication of inverted planar perovskite solar cells using two-step sequential substrate vibration-assisted spray coating (2S-SVASC). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, M.; Eslamian, M.; Soltani-Kordshuli, F.; Zabihi, F. Controlled wetting/dewetting through substrate vibration-assisted spray coating (SVASC). J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2016, 13, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani-kordshuli, F.; Zabihi, F.; Eslamian, M. Graphene-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite thin films fabricated by conventional and substrate vibration-assisted spray coating (SVASC). Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zabihi, F.; Eslamian, M. Improved functionality of PEDOT: PSS thin films via graphene doping, fabricated by ultrasonic substrate vibration-assisted spray coating. Synth. Met. 2016, 222, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M. Excitation by acoustic vibration as an effective tool for improving the characteristics of the solution-processed coatings and thin films. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 113, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fan, Z.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Qiu, S.; Zabihi, F.; Eslamian, M.; Chen, Q. A solution processable flexible transparent conductive graphene/PEDOT:PSS film fabricated by spin and blade coating. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. (Sci.) 2018, 23, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeke, J.D.N. Fundamentals and Applications of Ultrasonic Waves, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimzadeh, A.; Eslamian, M. On evaporation of thin liquid films subjected to ultrasonic substrate vibration. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 83, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J. “Secondary doping” methods to significantly enhance the conductivity of PEDOT:PSS for its application as transparent electrode of optoelectronic devices. Displays 2013, 34, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Kugler, T.; Keil, M.; Osikowicz, W.; Fahlman, M.; Salaneck, W.R. Photoelectron spectroscopy of thin films of PEDOT–PSS conjugated polymer blend: A mini-review and some new results. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2001, 121, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Amy, F.; Kahn, A. Spectroscopic study on sputtered PEDOT·PSS: Role of surface PSS layer. Org. Electron. 2006, 7, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, F.S.; Choi, H.H.; Cheong, I.W.; Kim, J.H. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of PEDOT:PSS nanofilms by a chemical dedoping process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6532–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaroni, R.; Logdlund, M.; Stafstrom, S.; Salaneck, W.R. The poly-3-hegxylthiophene/NOPF6 systems: A photoelectron spectroscopy study of electronic structural changes induced by the charge transfer in the solid state. Chem. Phys. 1990, 93, 4433. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaganesh, S.V.; Mathiyarasu, J.; Phani, K.; Yegnaraman, V. Chemical synthesis of PEDOT–Au nanocomposite. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wei, B.; Kuo, C.-c.; Pathak, S.; Farrell, B.; Martin, D.C. Enhanced PEDOT adhesion on solid substrates with electrografted P(EDOT-NH2). Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.E.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Snook, G.A. Storing energy in plastics: A review on conducting polymers & their role in electrochemical energy storage. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 11611–11626. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, C.; Vlandas, A.; Malliaras, G.G.; Senez, V. Wettability of PEDOT:PSS films. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 5146–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
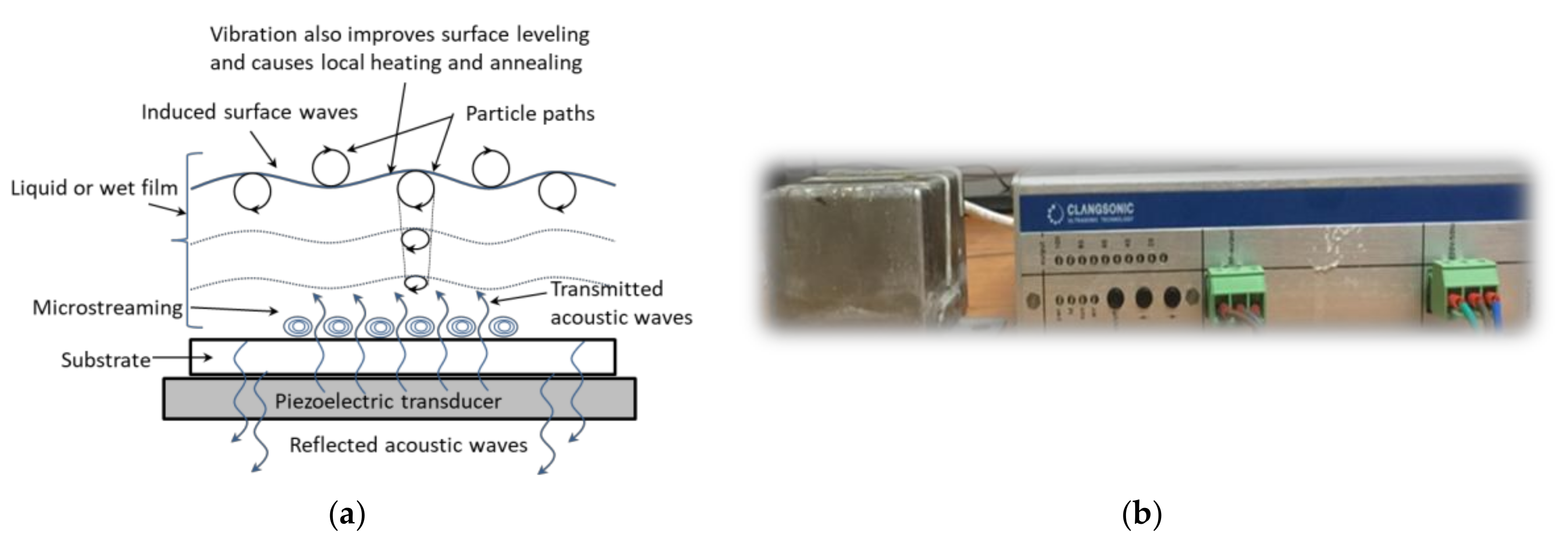
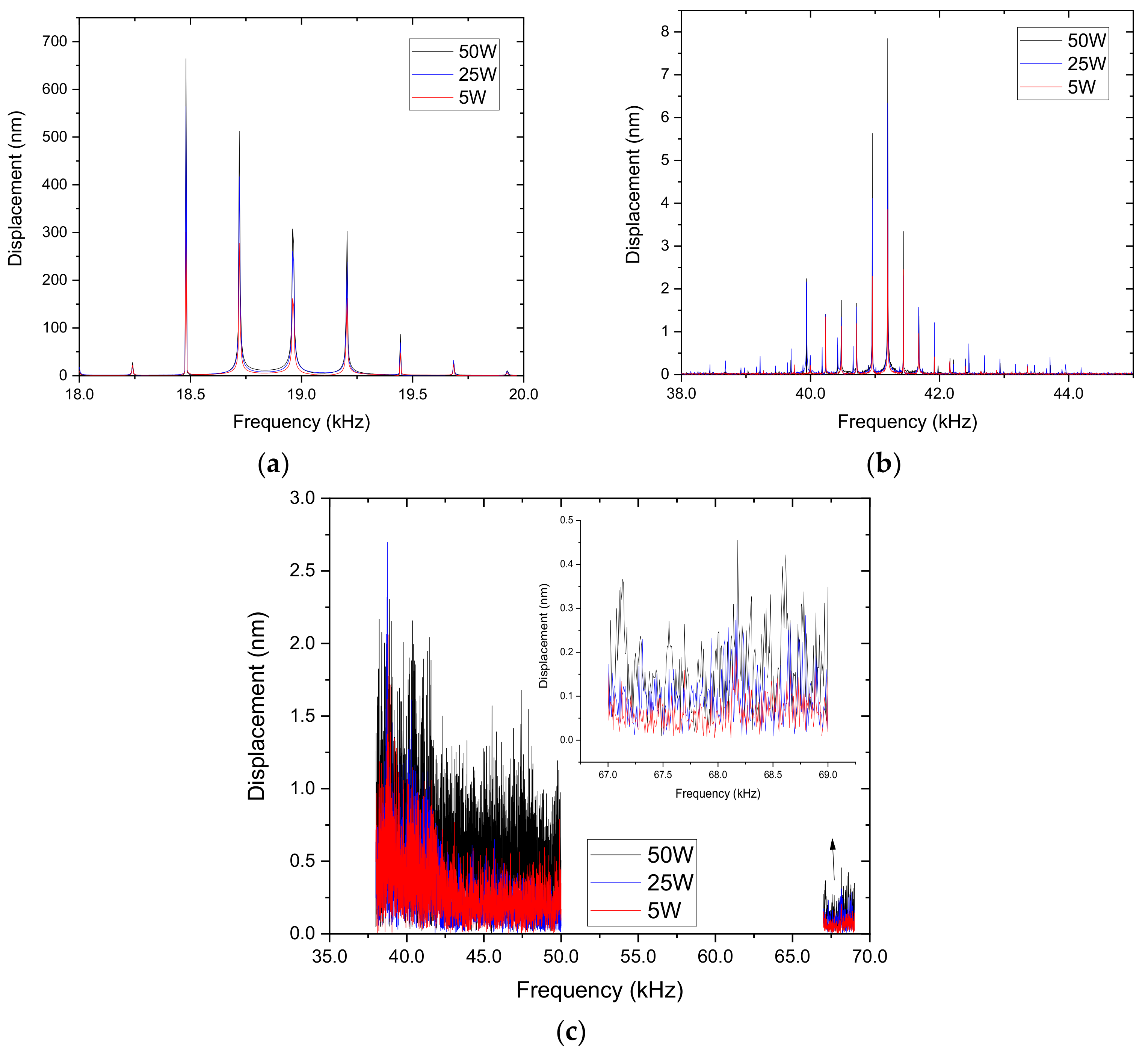
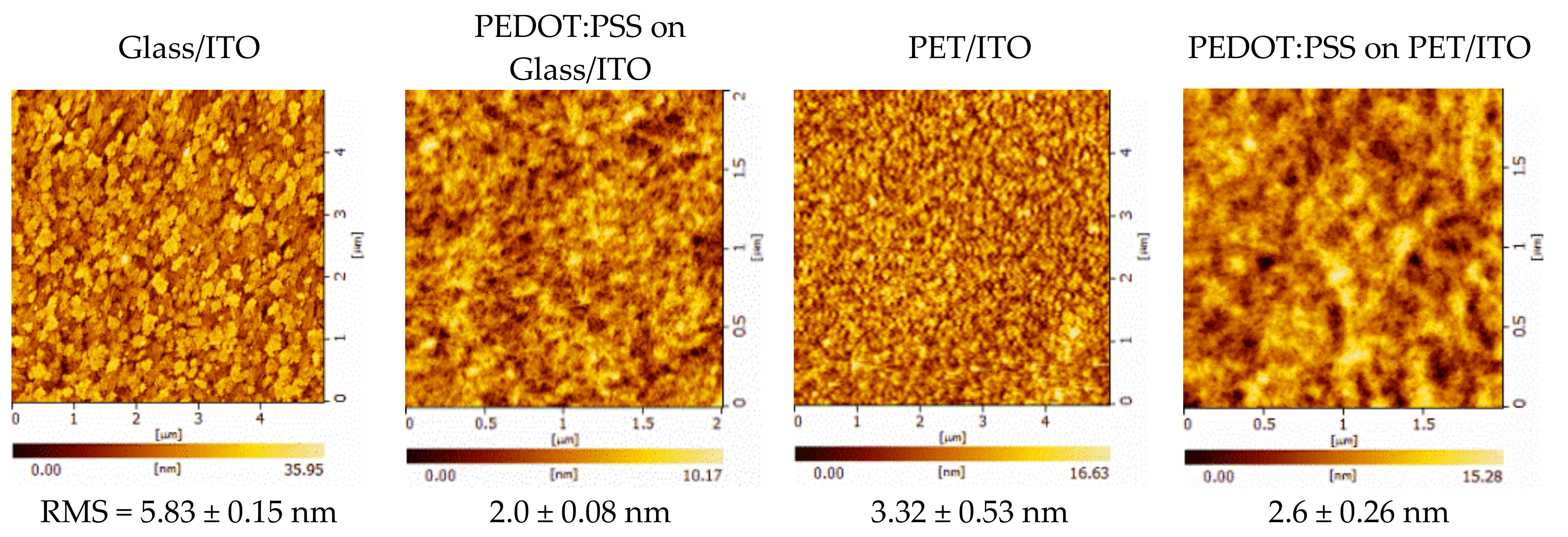
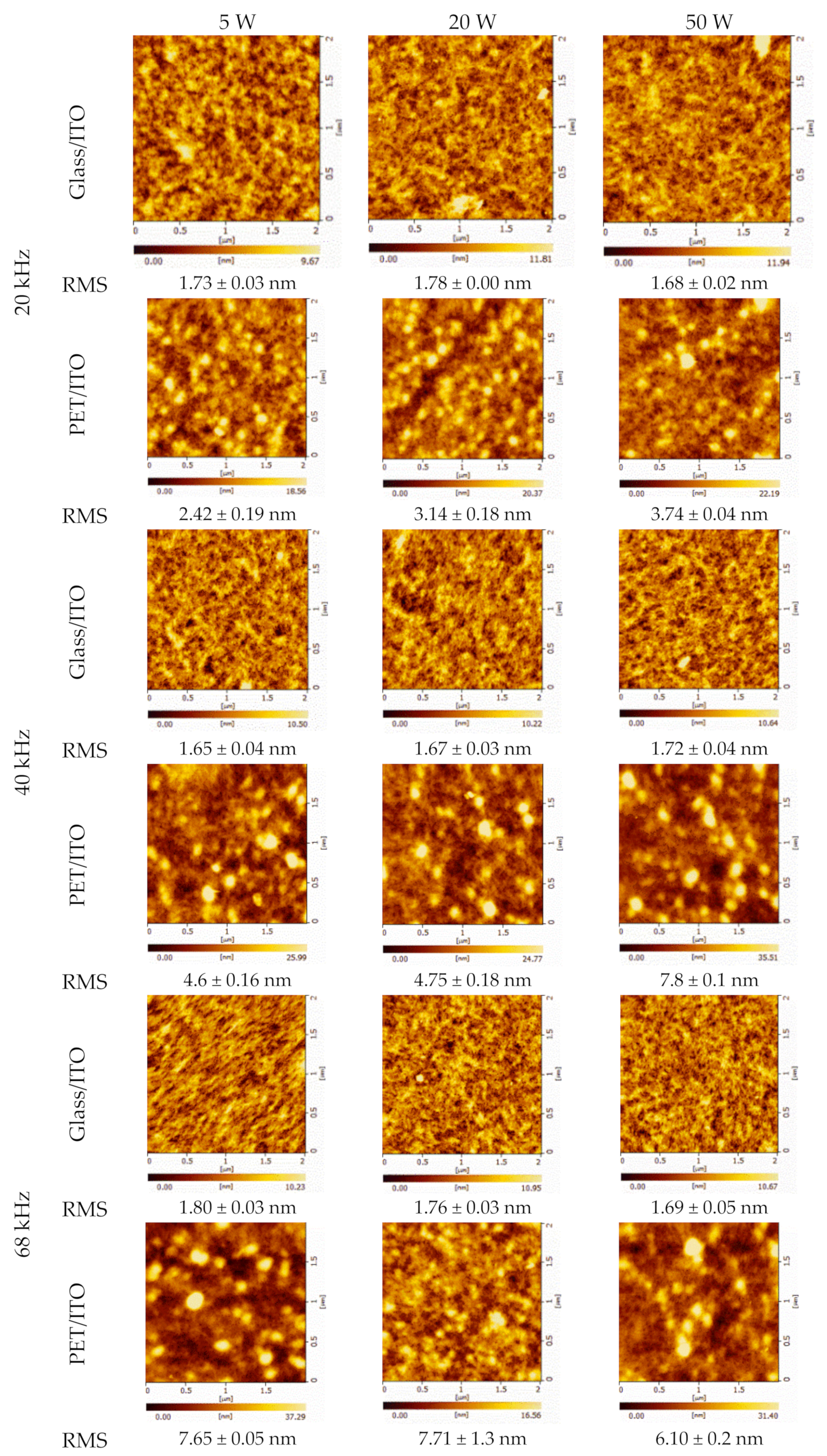
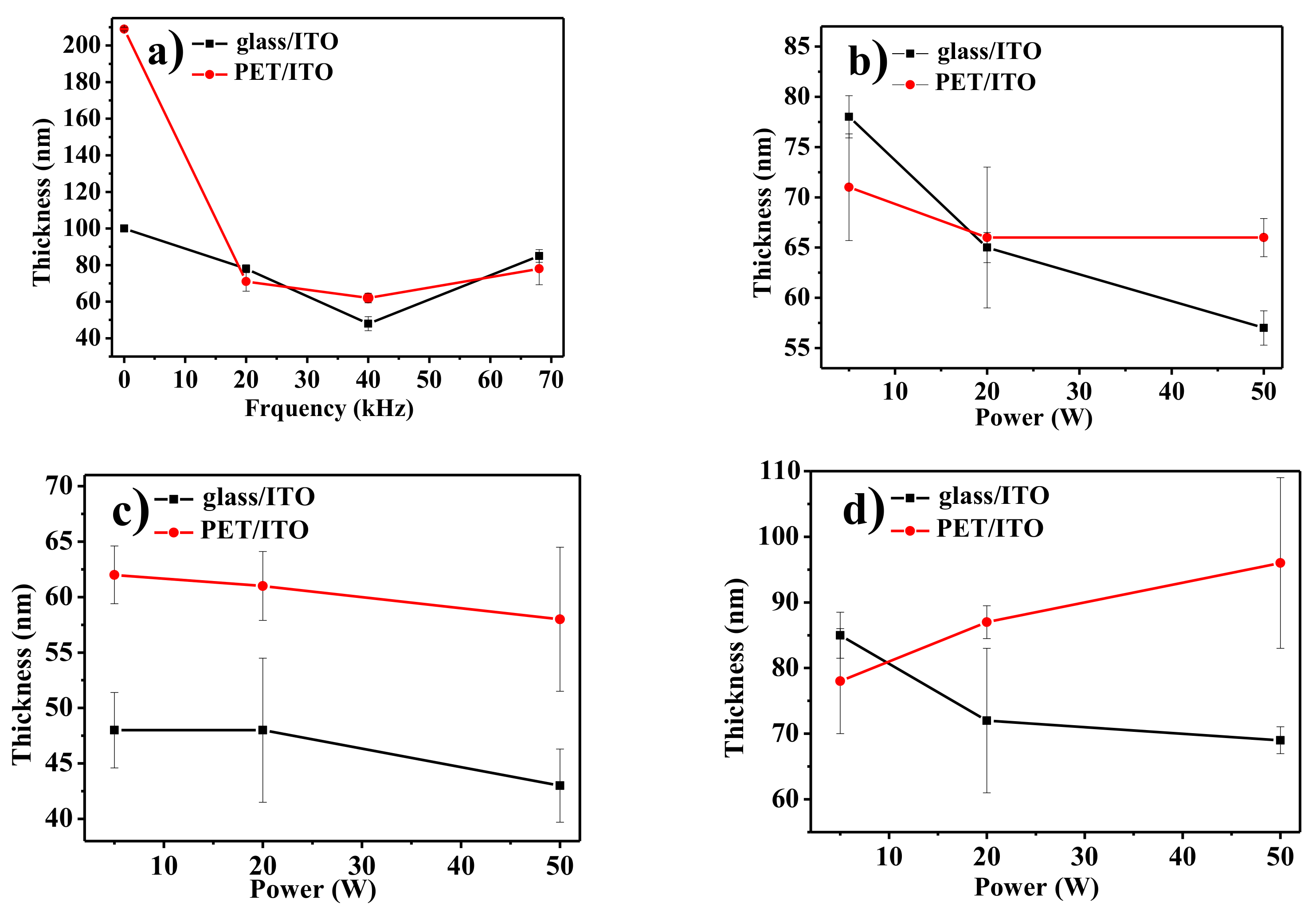
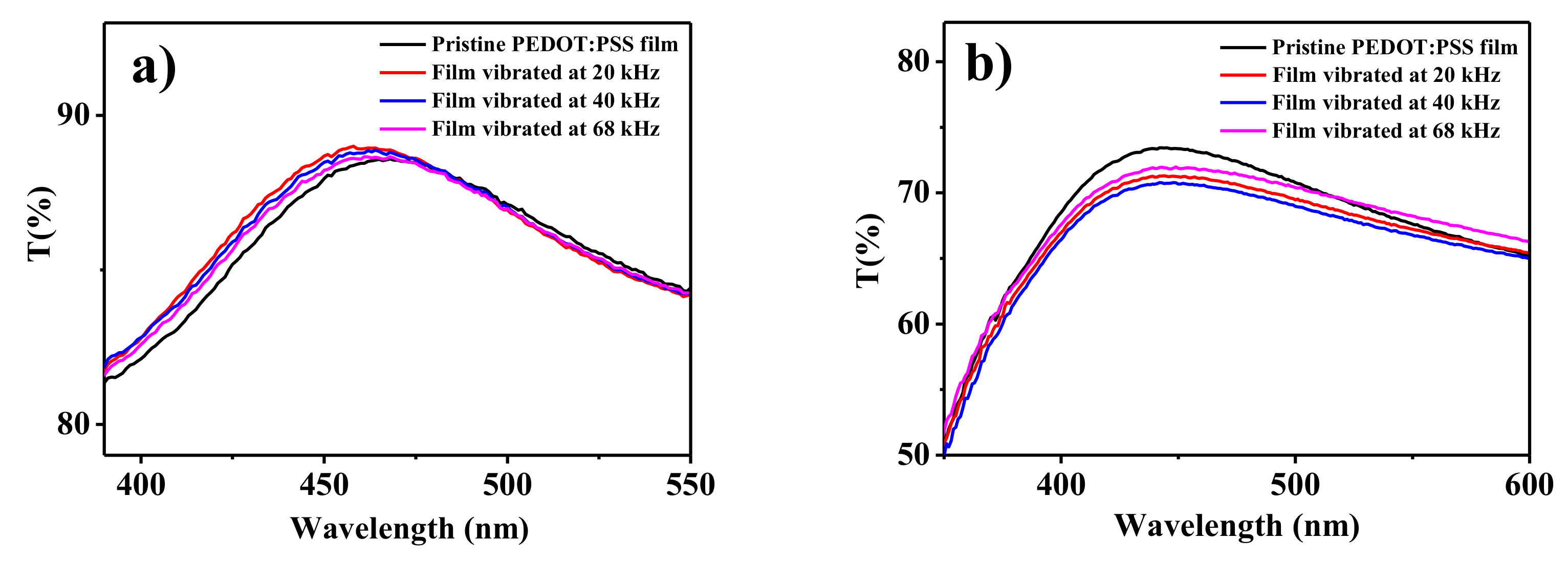
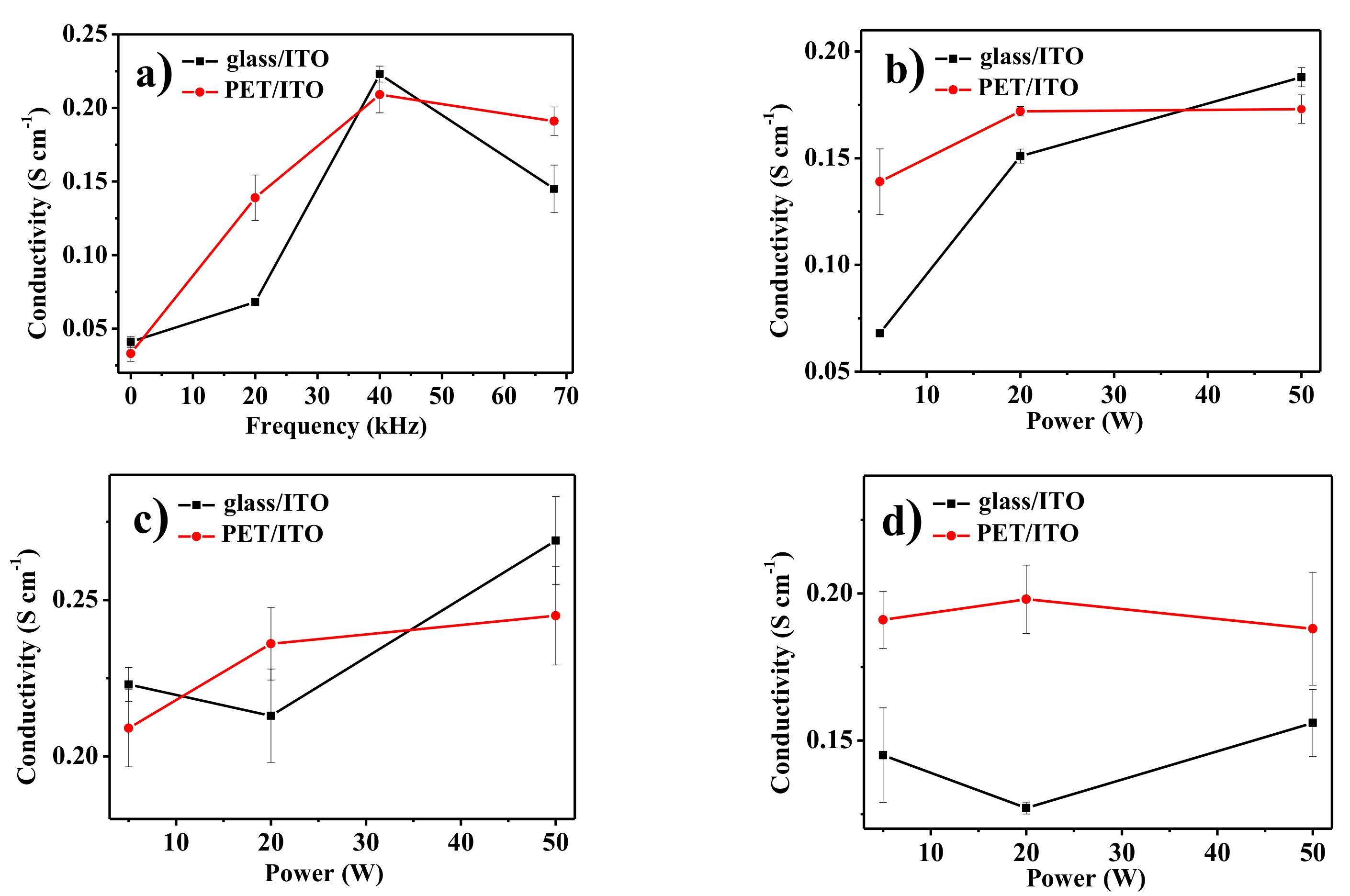
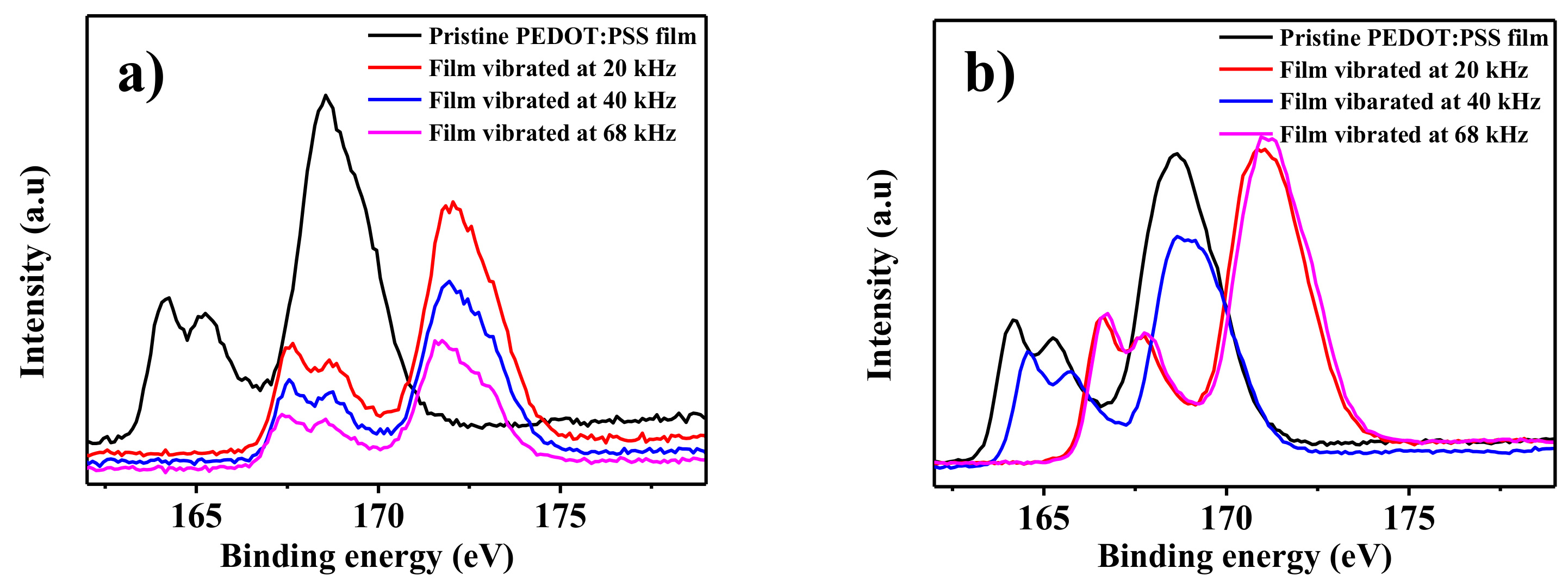
| Nominal Frequency (kHz) | Power (W) | Resonance Frequency (kHz) |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 5 | 300 @ 18.48 |
| 20 a | 517 @18.48 | |
| 25 | 563 @ 18.48 | |
| 50 | 664 @ 18.48 | |
| 40 | 5 | 3.85 @ 41.20 |
| 20 a | 5.78 @ 41.20 | |
| 25 | 6.40 @ 41.20 | |
| 50 | 7.84 @ 41.20 | |
| 68 | 5 | 2.06 @ 38.80 b |
| 20 a | 2.51 @ 38.76 b | |
| 25 | 2.70 @ 38.75 b | |
| 50 | 2.30 @ 38.89 b | |
| 5 | 0.02 @ 68.16 | |
| 20 a | 0.22 @ 68.17 | |
| 25 | 0.31 @ 68.17 | |
| 50 | 0.46 @ 68.18 |
| Frequency (kHz) | On Glass/ITO (°) | On PET/ITO (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Pristine |  | 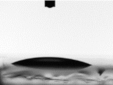 |
| 24.5 ± 3.1 | 22.3 ± 0.6 | |
| 20 | 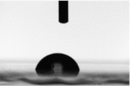 |  |
| 75.9 ± 5.4 | 49.3 ± 0.3 | |
| 40 | 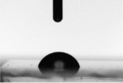 | 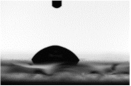 |
| 68.0 ± 3.8 | 51.5 ± 4.5 | |
| 68 | 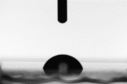 | 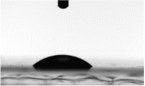 |
| 67.4 ± 4.1 | 43.4 ± 2.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gholampour, N.; Brian, D.; Eslamian, M. Tailoring Characteristics of PEDOT:PSS Coated on Glass and Plastics by Ultrasonic Substrate Vibration Post Treatment. Coatings 2018, 8, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100337
Gholampour N, Brian D, Eslamian M. Tailoring Characteristics of PEDOT:PSS Coated on Glass and Plastics by Ultrasonic Substrate Vibration Post Treatment. Coatings. 2018; 8(10):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100337
Chicago/Turabian StyleGholampour, Nadia, Dominikus Brian, and Morteza Eslamian. 2018. "Tailoring Characteristics of PEDOT:PSS Coated on Glass and Plastics by Ultrasonic Substrate Vibration Post Treatment" Coatings 8, no. 10: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100337
APA StyleGholampour, N., Brian, D., & Eslamian, M. (2018). Tailoring Characteristics of PEDOT:PSS Coated on Glass and Plastics by Ultrasonic Substrate Vibration Post Treatment. Coatings, 8(10), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100337





