Uncertainty of the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) sin2 ψ Technique in Measuring Residual Stresses of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Hard Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure and Stress Calculation
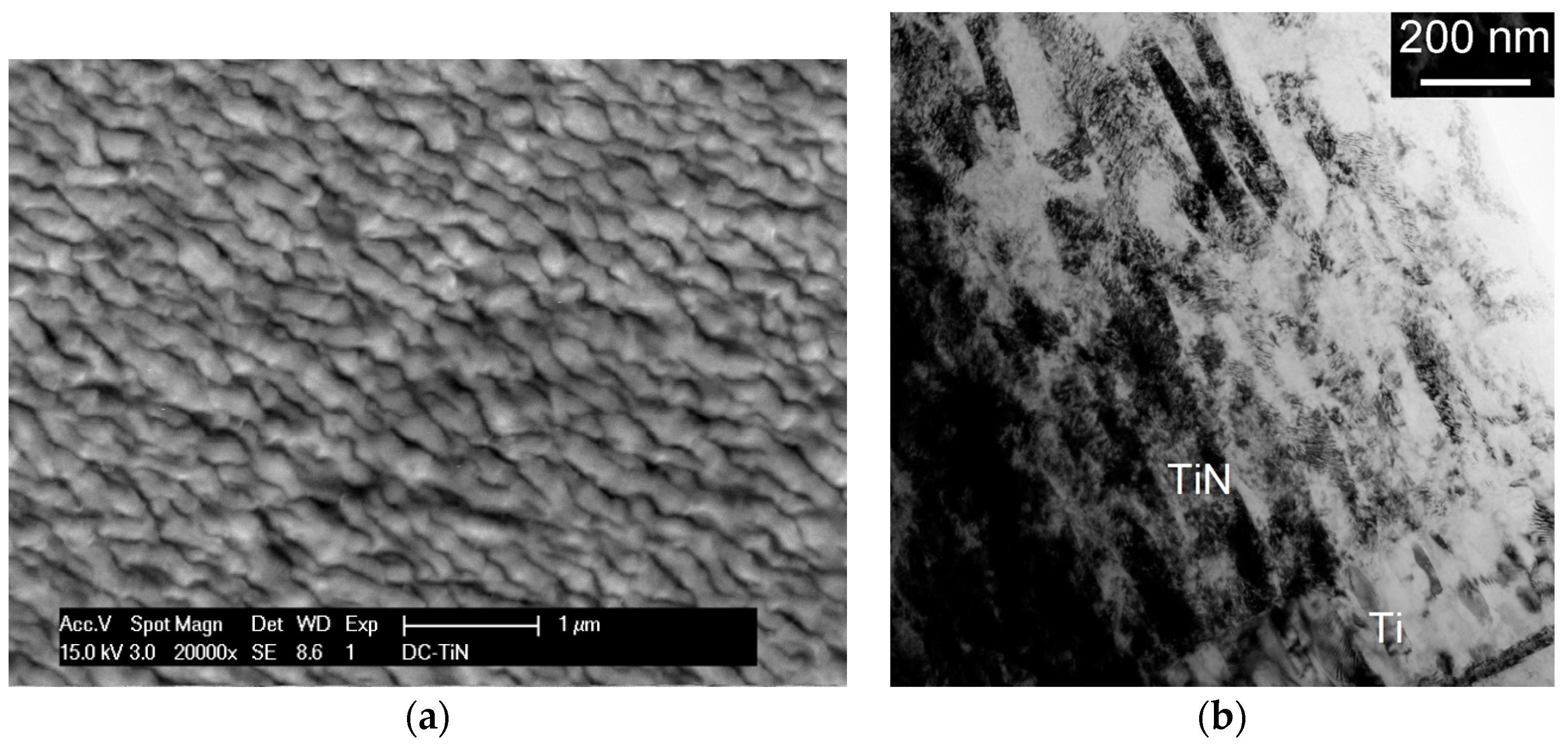
2.1. The Sample Material
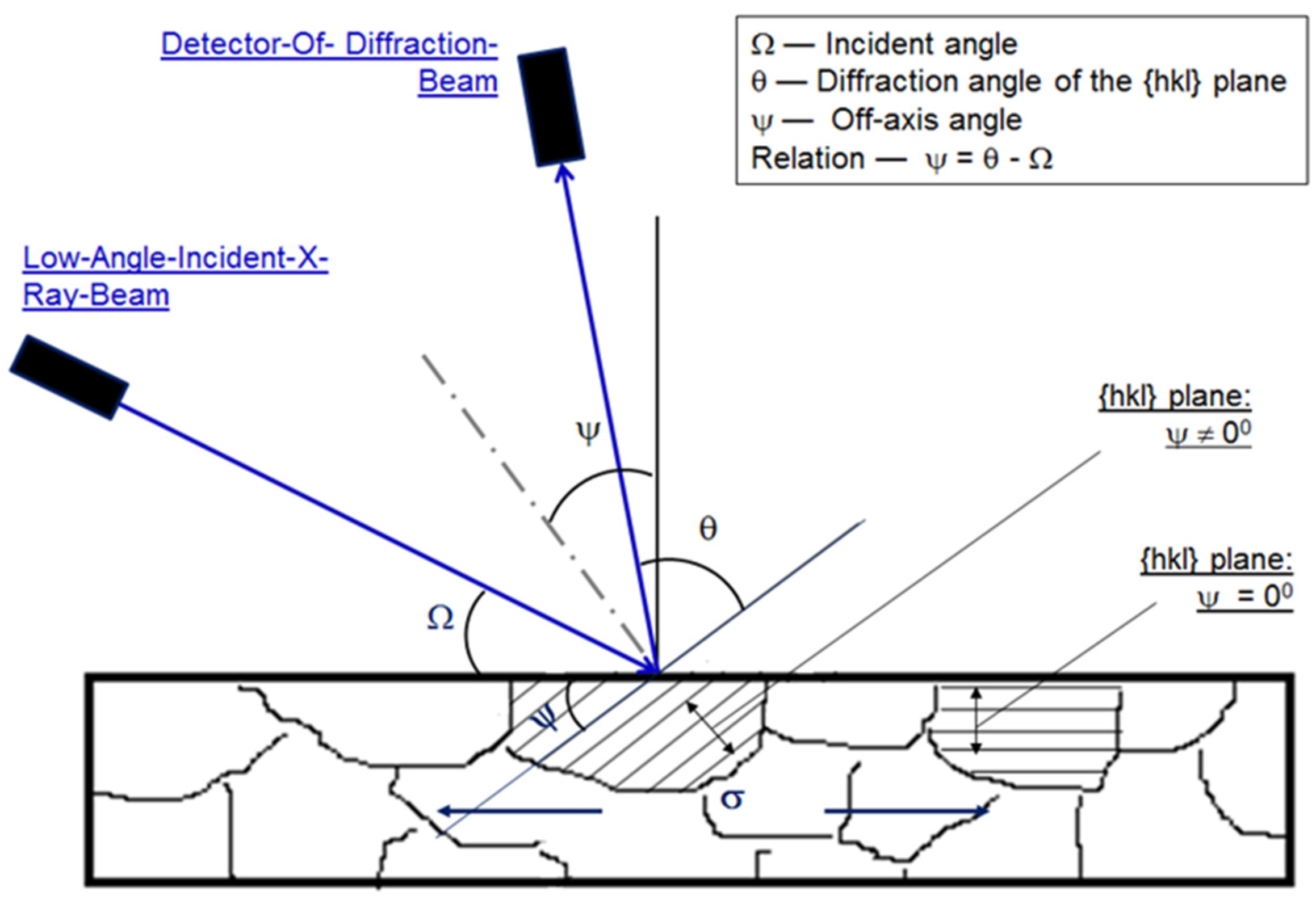
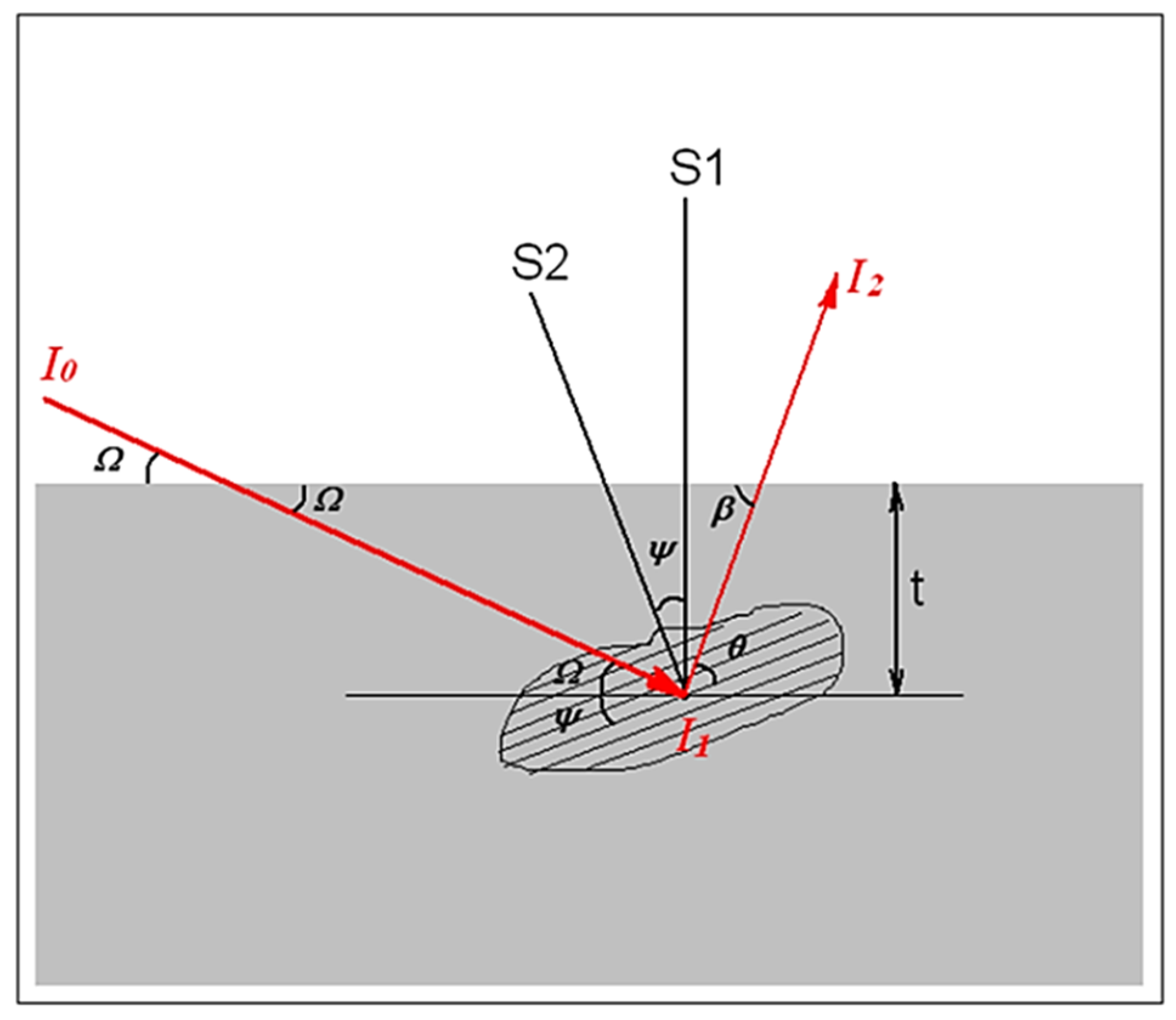
2.2. XRD Experiments
2.3. Calculation of Residual Stresses
3. Results and Discussion
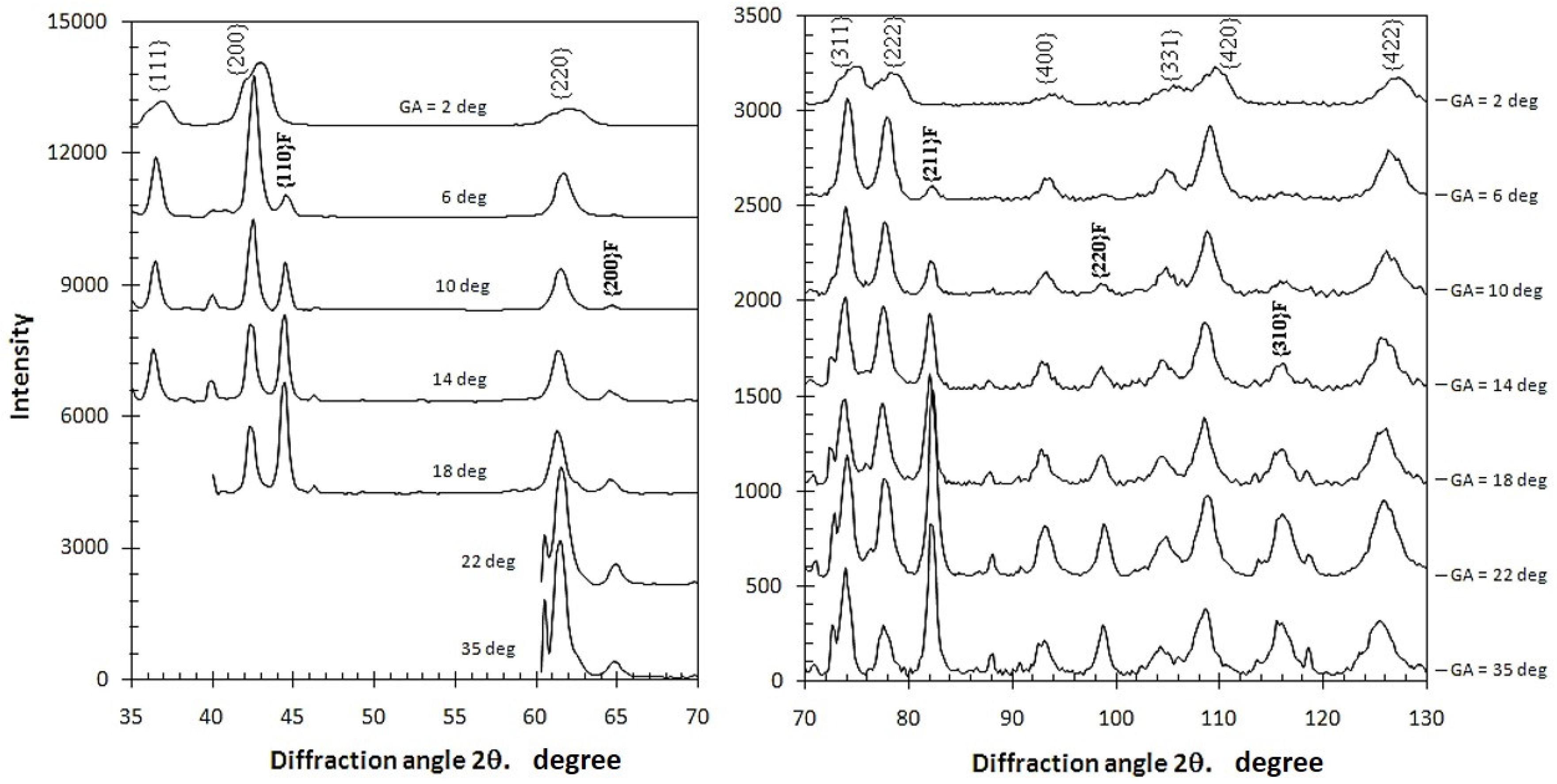
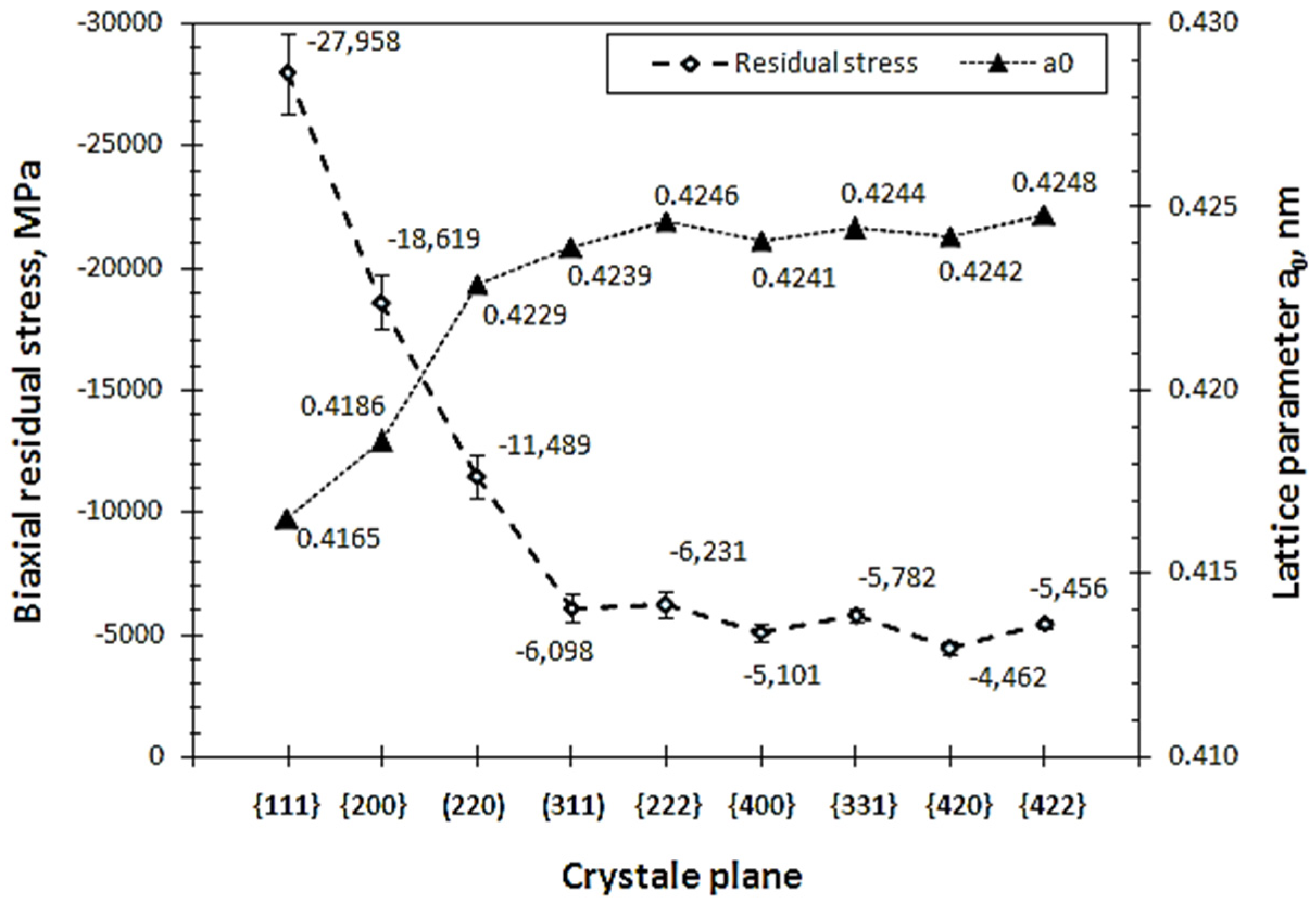
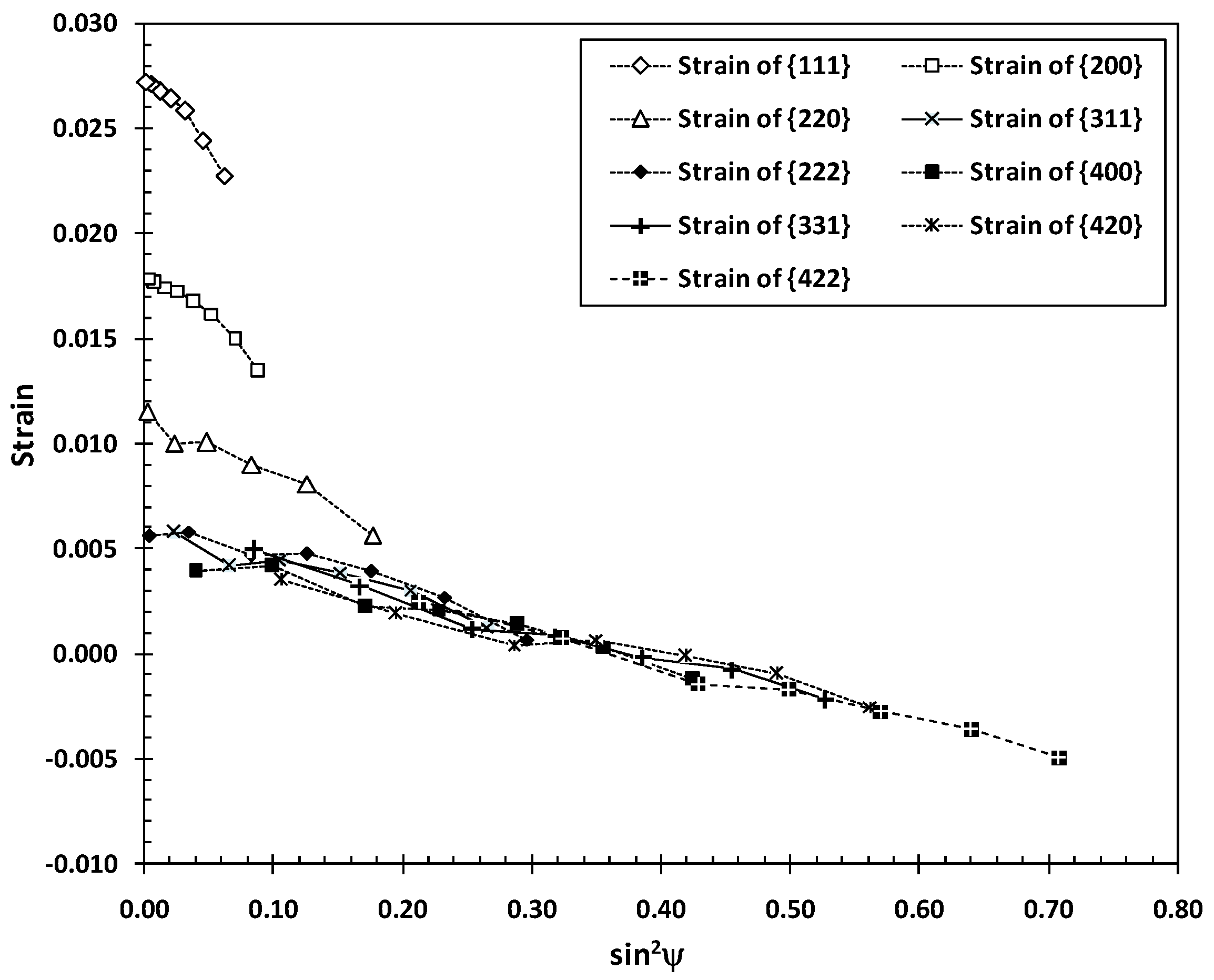
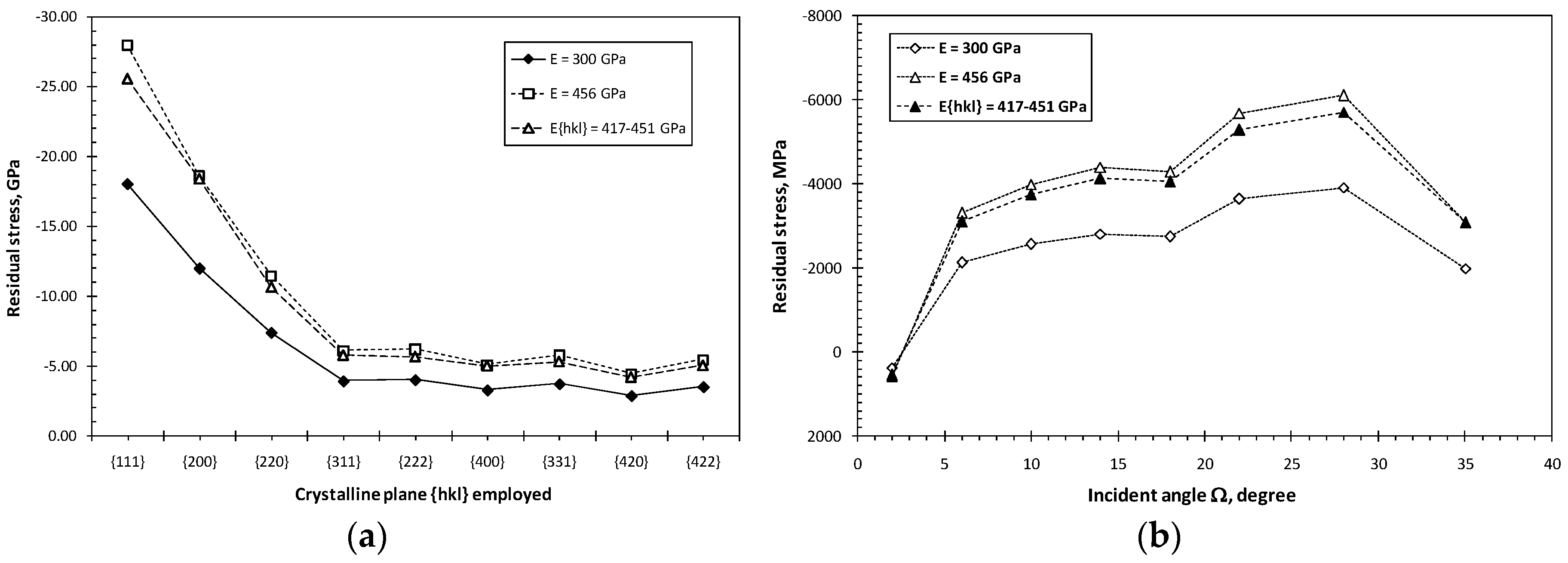
3.1. Residual Stresses Measured under the {hkl} Mode
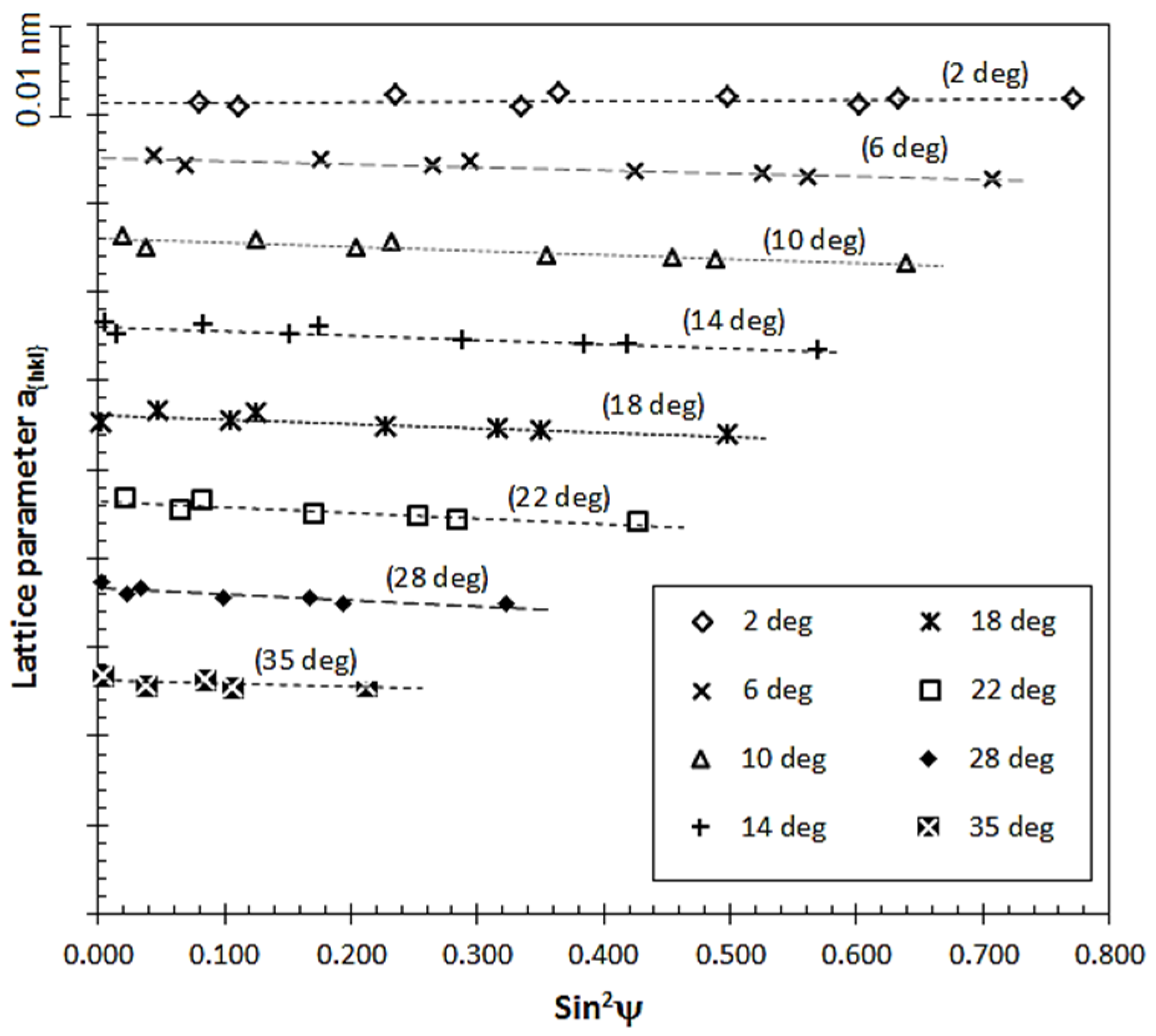
3.2. Residual Stresses Measured under the GIXRD Mode
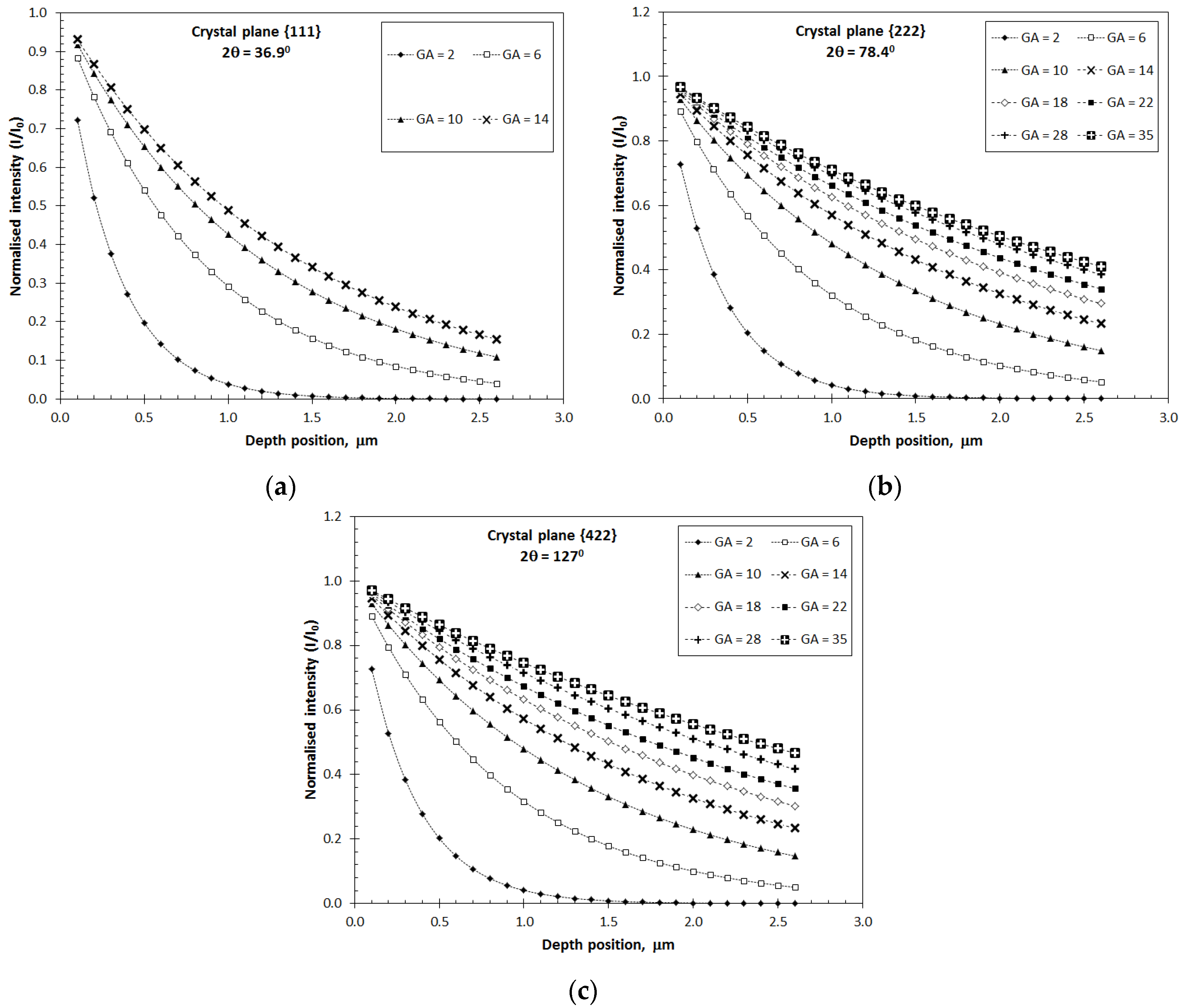
3.3. Effect of X-ray Attenuation on the Results of Residual Stress Calculation
3.4. Effect of Anisotropic Elastic Modulus on the Calculated Residual Stress Values
4. Conclusions
- The incident Ω angle has decisive influence on the effective X-ray penetration that the penetration increases significantly with the increase of the Ω angle. On the other hand, for a given Ω angle, the effect of the employed diffraction angle 2θ, i.e., the {hkl} crystalline plane, is negligible.
- When measuring using the conventional d-sin2 ψ mode, it is necessary to select a lattice plane of high diffraction angle. The results present the approximate estimation of overall residual stress over the depth of effective X-ray penetration. In the case of TiN coating, as shown in the current study, the residual stresses measured from the diffraction peaks of high-index planes from {311} to {422} are comparable to each other. On the other hand, measurements from the low-index planes {111}, {200} and {220} give rise to extraordinarily high values.
- When measuring using the GIXRD mode, the calculated residual stress depends strongly on the X-ray penetration depth as predominantly determined by the incident Ω angle. This method helps determine a depth profile of residual stress in a coating of heterogeneous growth structure.
- The anisotropy of elastic modulus has a certain influence on the calculation of residual stress, while the influence is not pronounced as compared to the incident Ω angle.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001; p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Noyan, I.C.; Cohen, J.B. Residual Stress—Measurement by Diffraction and Interpretation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 117–163. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, S.G.; Rek, Z.U.; Yalisove, S.M.; Bilello, J.C. Analysis of thin film stress measurement techniques. Thin Solid Films 1997, 301, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Fry, A.T.; Holdway, P.; Kandil, F.A.; Shackleton, J.; Suominen, L. Measurement Good Practice Guide No. 52. Determination of Residual Stresses by X-ray Diffraction—Issue 2; National Physical Laboratory: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Portinha, A.; Teixeira, V.; Carneiro, J.; Beghi, M.G.; Bottani, C.E.; Franco, N.; Vassen, R.; Stoever, D.; Sequeira, A.D.L. Residual stresses and elastic modulus of thermal barrier coatings graded in porosity. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188–189, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardi, P.; Polonioli, P.; Ferrari, S. Residual stress in stabilized zirconia thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 1994, 253, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.O.; Achenbach, J.D.; Mirkarimi, P.B.; Shinn, M.; Barnett, S.A. Elastic constants of single-crystal transition-metal nitride films measured by line-focus acoustic microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.J.; Jagner, M.; Sproul, W.D.; Rudnik, P.J. The residual stress in TiN films deposited onto cemented carbide by high-rate reactive sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1989, 39–40, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaeyhaegens, C.; Knuyt, G.; Stals, L.M. Study of the residual macroscopic stress in TiN coatings deposited on various steel types (TuSA1). Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 74–75, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, B. Residual stress analysis on TiN film fabricated by plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition process. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2013, 297, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, F.; Stock, H.-R.; Mayr, P. Examination of residual stress, morphology and mechanical properties of sputtered TiN films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1992, 54–55, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, A.; Houtte, P.V.; Meert, B.; Quaeyhaegens, C. Assessment of different X-ray stress measuring techniques for thin titanium nitride coatings. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2000, 33, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, U.; Ligot, J.; Lamparter, P.; Vermeulen, A.C.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Stress analysis of polycrystalline thin films and surface regions by X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2005, 38, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benegra, M.; Lamas, D.G.; de Rapp, M.E.F.; Mingolo, N.; Kunrath, A.O.; Souza, R.M. Residual stresses in titanium nitride thin films deposited by direct current and pulsed direct current unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2006, 494, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypek, S.J.; Baczmanski, A.; Ratuzek, W.; Kusior, E. New approach to stress analysis based on grazing-incident X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.B.; Wadsworth, I.; Münz, W.D.; Kuzel, R., Jr.; Valvoda, V. Structure and stress of TiAlN/CrN superlattice coatings as a function of CrN layer thickness. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 116–119, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzel, C. X-ray stress analysis in presence of gradients and texture. Adv. X-ray Anal. 2001, 44, 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M.J.; Dias, A.M.; Gergaud, P.; Lebrun, J.L. A methodology development for the study of near surface stress gradients. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2000, 287, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegou, S.; Christiansen, T.L.; Klaus, M.; Genzel, C.; Somers, M.A.J. Determination of composition, residual stress and stacking fault depth profiles in expanded austenite with energy-dispersive diffraction. Thin Solid Films 2013, 530, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machunze, R.; Janssen, G.C.A.M. Stress and strain in titanium nitride thin films. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 5888–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, G.C.A.M.; Kamminga, J.D. Stress in hard metal films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3086–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; He, J. Ab-initio calculation of elastic constants of TiN. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, J.A. X-ray elastic-constants and residual-stress of textured titanium nitride coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1992, 54, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadias, G. Stress and preferred orientation in nitride-based PVD coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Jones, A.H. High-precision determination of residual stress of polycrystalline coatings using optimised XRD-sin2ψ technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yang, S.; Cooke, K.E. Hybrid HIPIMS and CFUBMS deposition of TiN coatings: Deposition rate, structure and tribological properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 236, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwen, M.V.; Kamminga, J.D.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Diffraction stress analysis of thin films: Modeling and experimental evaluation of elastic constants and grain interaction. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 1904–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Lewis, D.B.; Hovsepian, P.E.; Münz, W.-D. Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction investigation of the microstructure of nano-scale multilayers TiAlN/VN grown by unbalanced magnetron deposition. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Adibi, F.; Greene, J.E.; Hultman, L.; Sundgren, J.E. Average energy deposited per atom—A universal parameter for described ion-assisted film growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.W. Stress in thin films: The relevance of grain boundaries and impurities. Thin Solid Films 1976, 34, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.D.; Clemans, B.M. Crystallite coalescence: A mechanism for intrinsic tensile stresses in thin films. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, L.B.; Chason, E. Model for stress generated upon contact of neighbouring islands on the surface of a substrate. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 4866–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, G.C.A.M. Critical review: Stress and strain in polycrystalline thin films. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6654–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Lattice Plane | E [GPa] |
|---|---|
| {111}, {222} | 417 |
| {200}, {400} | 451 |
| {111}, {222} | 424 |
| {200}, {400} | 434 |
| Ω | {111} | {200} | Ω | {220} | {311} | {222} | {400} | {331} | {420} | {422} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 36.93 | 42.96 | 2 | 62.16 | 74.74 | 78.35 | 93.85 | 105.75 | 109.55 | 127.00 |
| 4 | 36.62 | 42.67 | 6 | 61.71 | 74.07 | 77.87 | 93.39 | 105.01 | 109.07 | 126.54 |
| 6 | 36.56 | 42.61 | 10 | 61.55 | 73.92 | 77.69 | 93.20 | 104.80 | 108.82 | 126.23 |
| 8 | 36.51 | 42.55 | 14 | 61.49 | 73.85 | 77.57 | 93.08 | 104.71 | 108.69 | 126.04 |
| 10 | 36.49 | 42.53 | 18 | 61.41 | 73.80 | 77.50 | 92.99 | 104.56 | 108.56 | 125.81 |
| 12 | 36.49 | 42.50 | 22 | 61.42 | 73.82 | 77.51 | 92.98 | 104.51 | 108.60 | 125.75 |
| 14 | 36.46 | 42.50 | 28 | 61.31 | 73.69 | 77.40 | 92.75 | 104.21 | 108.37 | 125.26 |
| 16 | 36.46 | 42.49 | 35 | – | – | 77.42 | 92.77 | 103.96 | 108.11 | 124.88 |
| 18 | – | 42.48 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Parameters | {111} | {200} | {220} | {311} | {222} | {400} | {331} | {420} | {422} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (10−2) | −3.06 | −2.05 | −1.28 | −0.68 | −0.70 | −0.57 | −0.65 | −0.50 | −0.61 |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| σ (MPa) | −17,999 | −11,974 | −7383 | −3917 | −4002 | −3276 | −3713 | −2865 | −3504 |
| Δσ (MPa) | 1667 | 1083 | 809 | 611 | 535 | 340 | 276 | 292 | 184 |
| a0 (nm) | 0.4152 | 0.4178 | 0.4224 | 0.4236 | 0.4243 | 0.4239 | 0.4241 | 0.424 | 0.4246 |
| Incident Angle | 2 | 6 | 10 | 14 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 35 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (10−3) | 0.64 | −3.70 | −4.46 | −4.91 | −4.78 | −6.34 | −6.82 | −3.46 |
| R2 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.8 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.29 |
| σ (MPa) | 579 | −3313 | −3994 | −4394 | −4280 | −5677 | −6103 | −3097 |
| Δσ (MPa) | 759 | 588 | 723 | 845 | 1172 | 1215 | 1633 | 2783 |
| a0 (nm) | 0.4215 | 0.4239 | 0.4244 | 0.4245 | 0.4246 | 0.4242 | 0.4244 | 0.4251 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Yang, S. Uncertainty of the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) sin2 ψ Technique in Measuring Residual Stresses of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Hard Coatings. Coatings 2017, 7, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080128
Luo Q, Yang S. Uncertainty of the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) sin2 ψ Technique in Measuring Residual Stresses of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Hard Coatings. Coatings. 2017; 7(8):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080128
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Quanshun, and Shicai Yang. 2017. "Uncertainty of the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) sin2 ψ Technique in Measuring Residual Stresses of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Hard Coatings" Coatings 7, no. 8: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080128
APA StyleLuo, Q., & Yang, S. (2017). Uncertainty of the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) sin2 ψ Technique in Measuring Residual Stresses of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Hard Coatings. Coatings, 7(8), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080128





