Strength Development of Bottom Ash-Based Geopolymer-Stabilized Recycled Concrete Aggregate as a Pavement Base Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
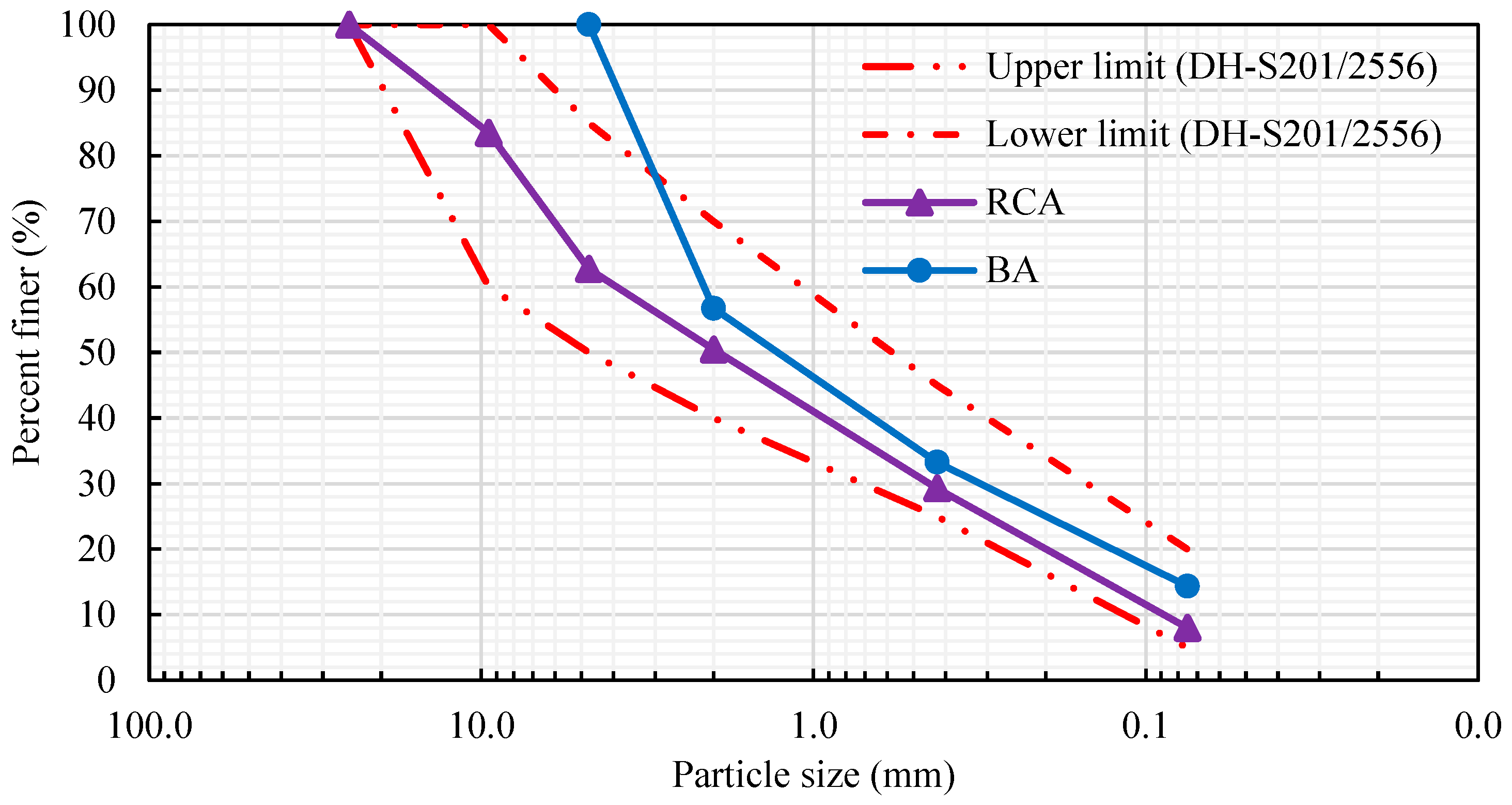
2.1. Materials
2.2. Alkaline Activator
2.3. Mix Design and Sample Preparation
3. Laboratory Experimental Program
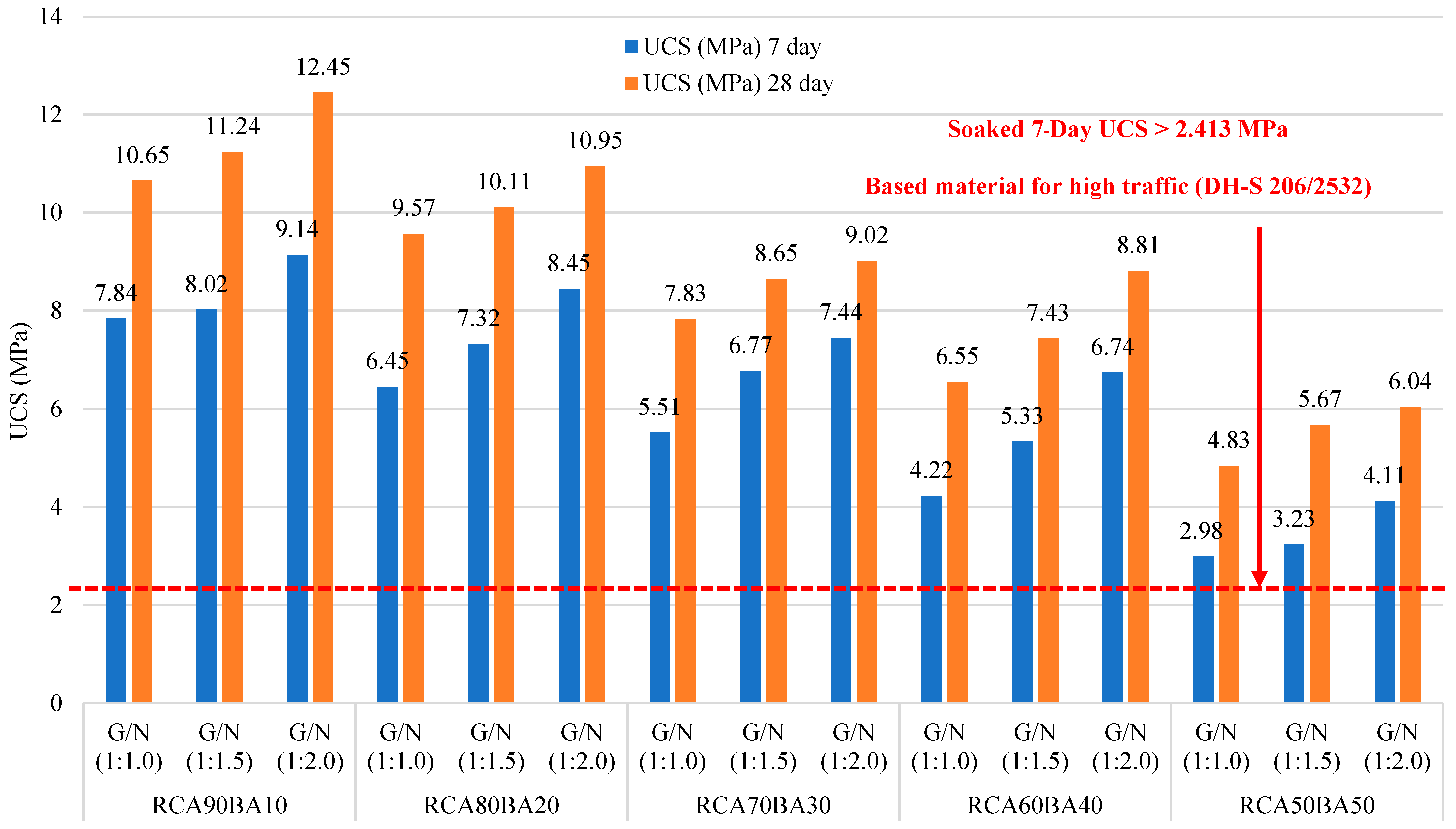
3.1. Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS)
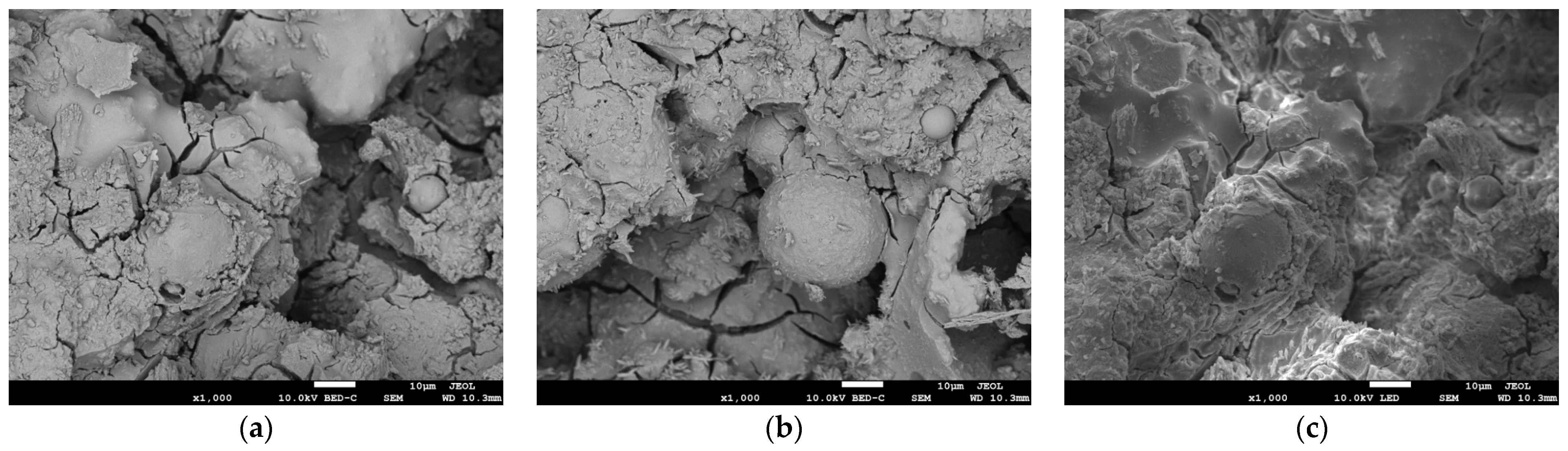
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. UCS Development
4.1.1. Strength Performance and Standard Compliance
4.1.2. Influence of RCA:BA Ratio on Strength Development
4.1.3. Alkaline Activator Optimization and Geopolymerization Mechanisms
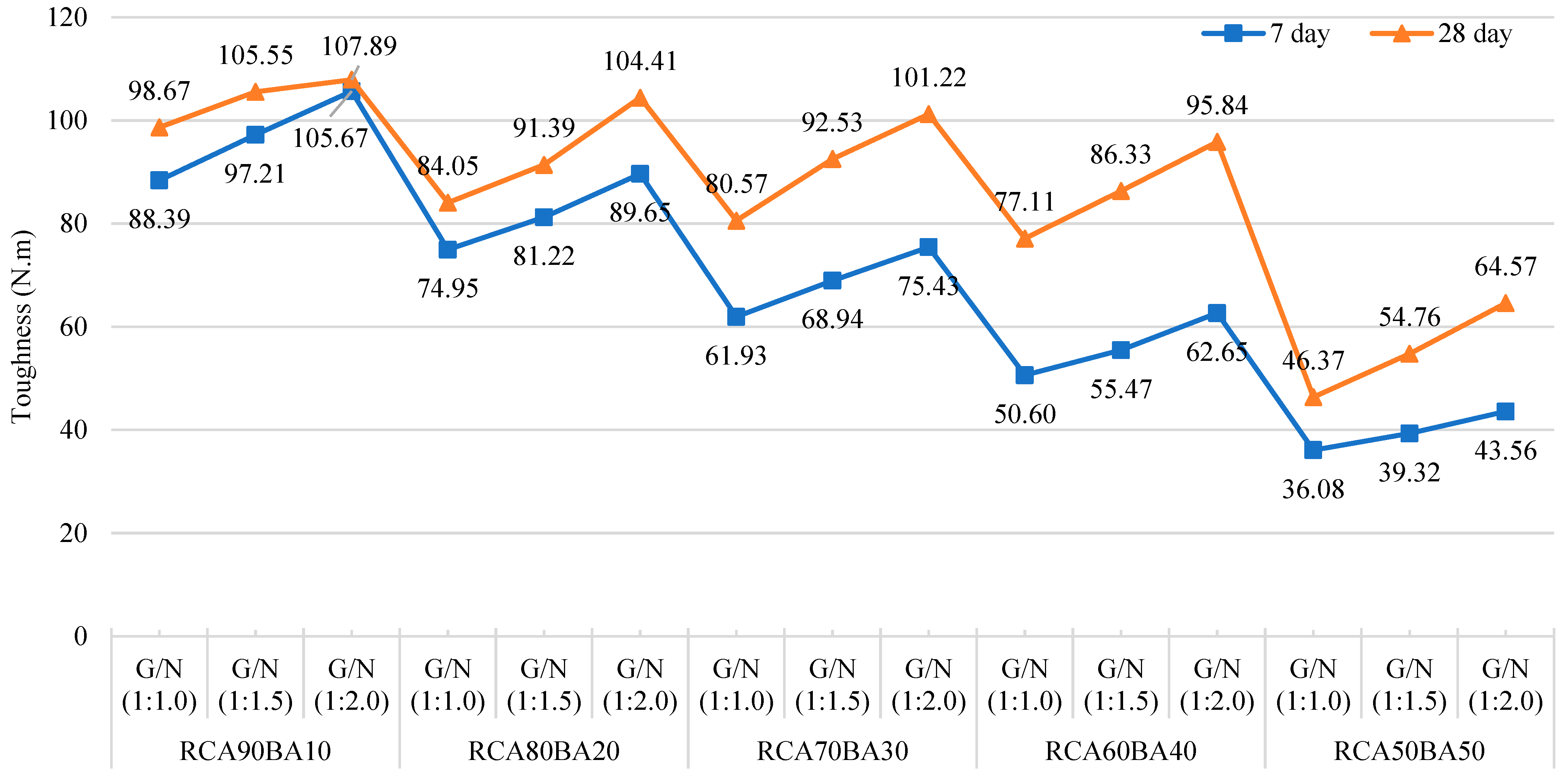
4.1.4. Toughness Properties of BA-Based Geopolymer-Stabilized RCA
4.2. Microstructural Analysis
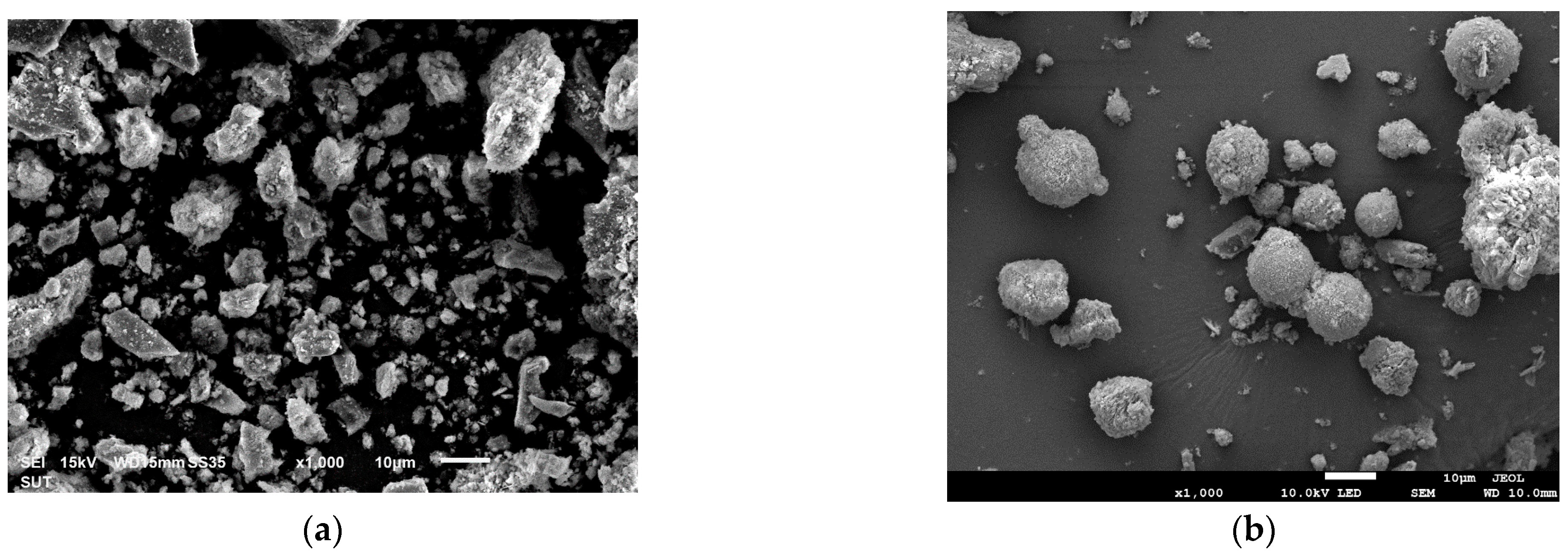
4.2.1. Microstructural Development in Systems with a Low Bottom Ash Content
4.2.2. Microstructural Development in Systems with a High Bottom Ash Content
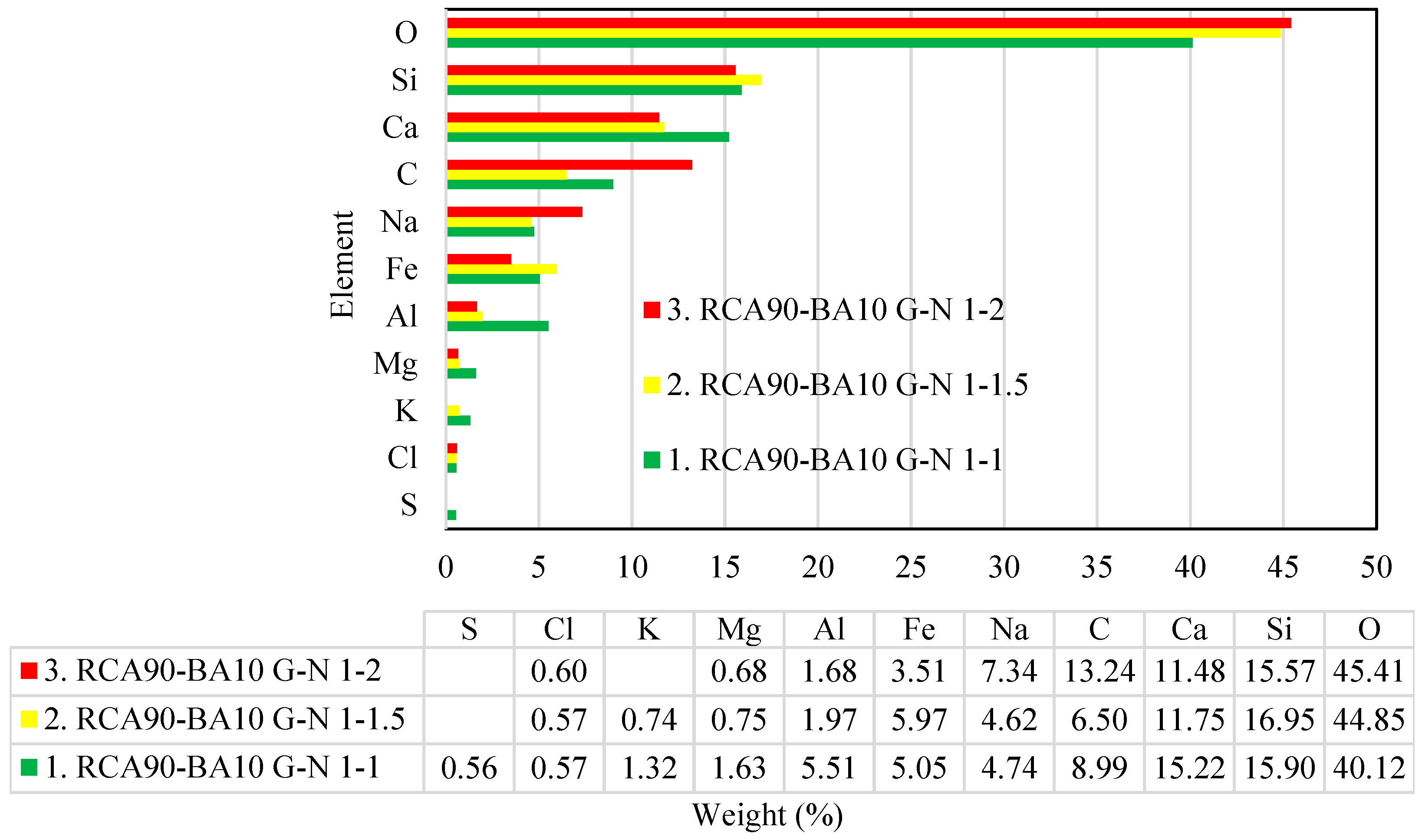
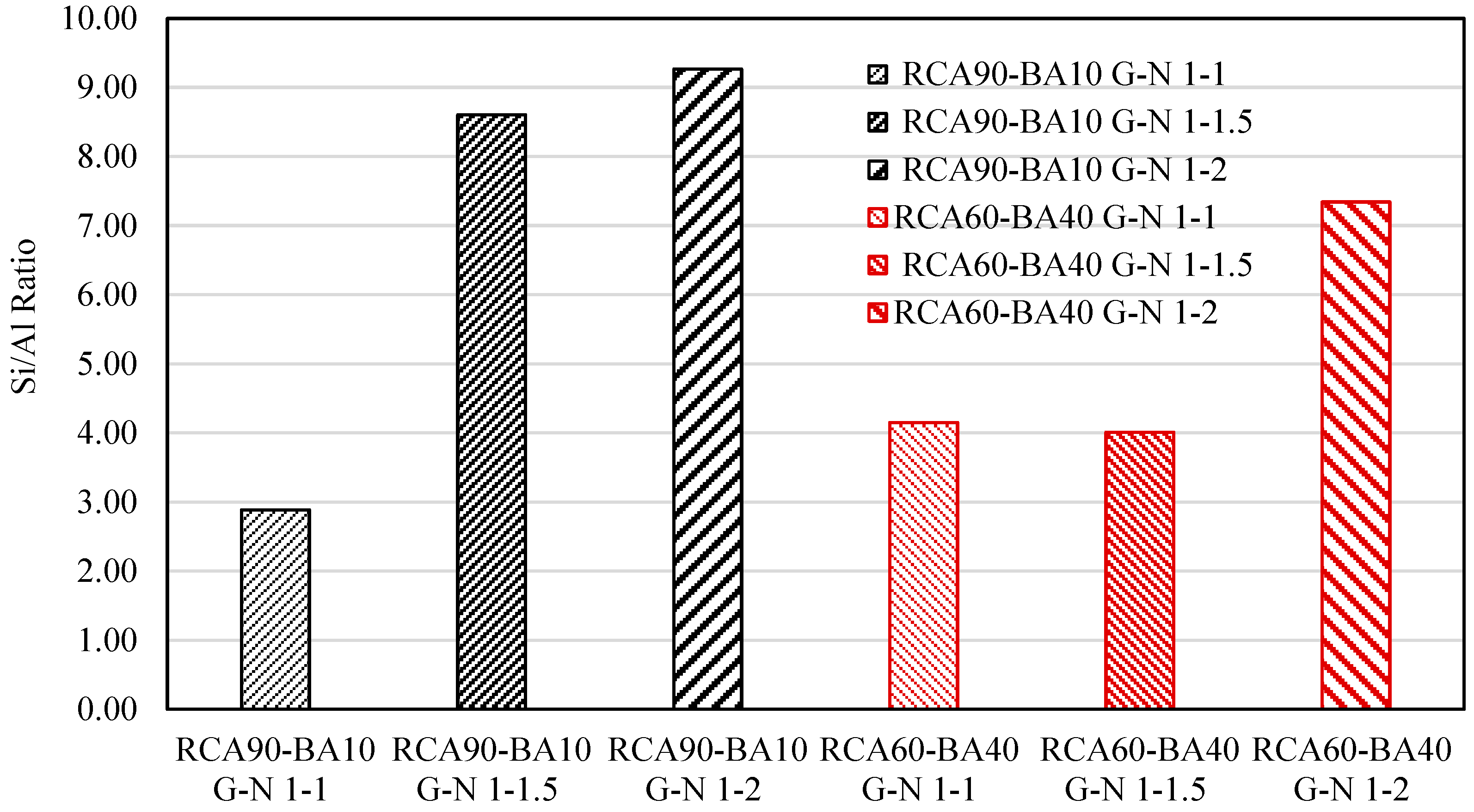
4.3. EDX Analysis
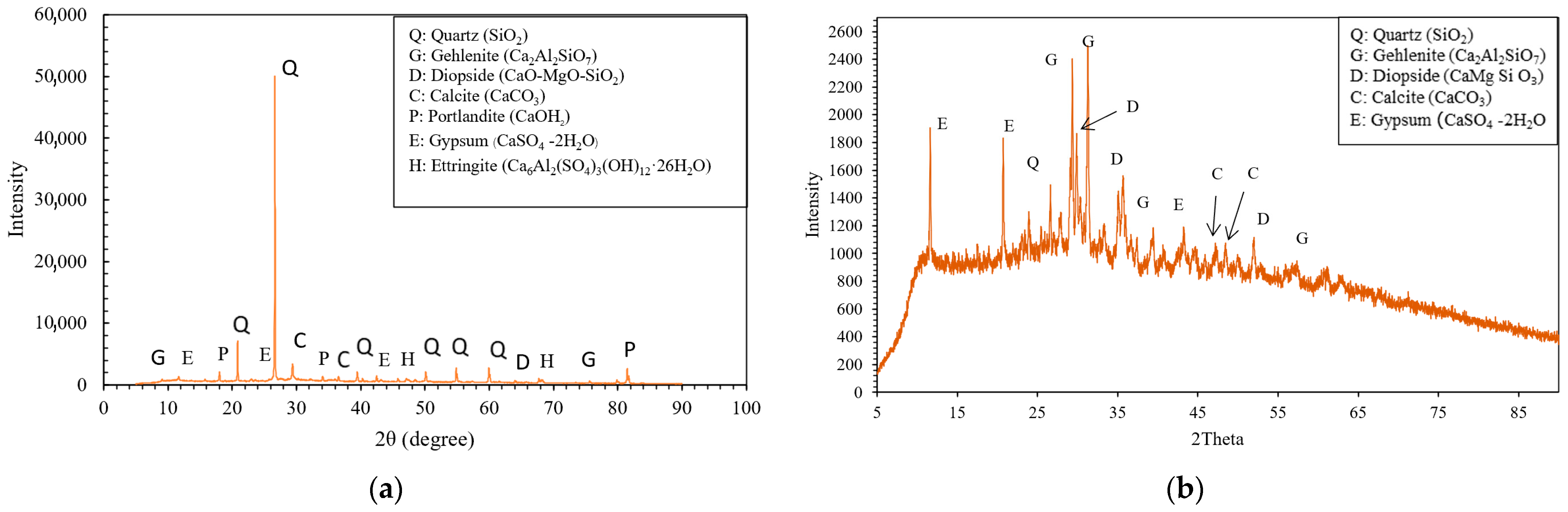
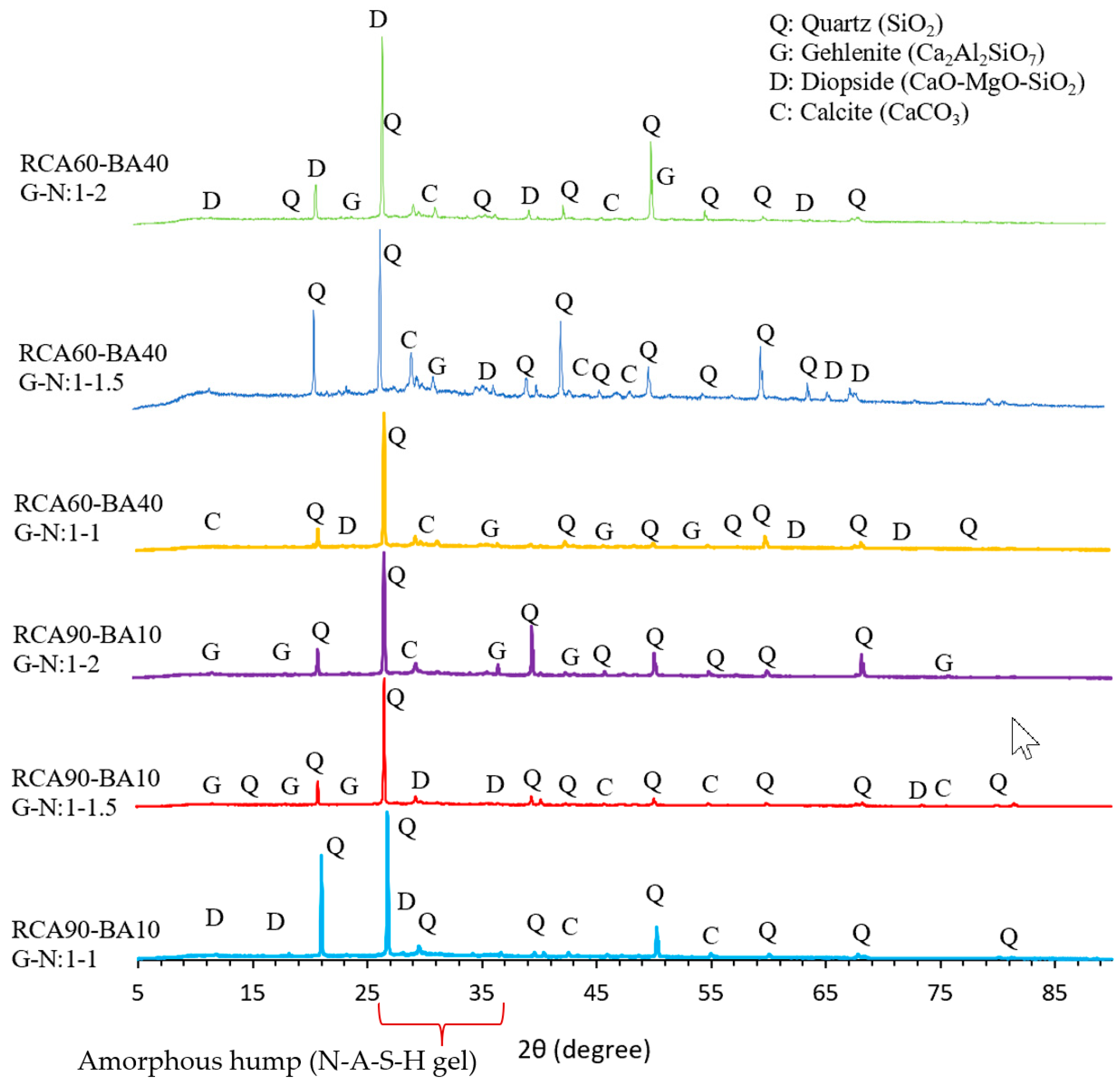
4.4. XRD Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BA | Bottom ash |
| C-A-S-H | Calcium aluminosilicate hydrate |
| C-S-H | Calcium silicate hydrate |
| DOH | Department of Highways |
| EDX | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| G/N | Sodium silicate to sodium hydroxide |
| MDD | Maximum dry density |
| N-A-S-H | Sodium aluminosilicate hydrate |
| OLC | Optimum liquid content |
| RCA | Recycled concrete aggregate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopic |
| UCS | Unconfined compressive strength |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Giunta, M. Sustainable Practices in Road Constructions: Estimation and Mitigation of Impact on Air Quality. Transp. Res. Procedia 2023, 69, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, M.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chinkulkijniwat, A.; Suddeepong, A.; Buritatum, A.; Yaowarat, T.; Choenklang, P.; Udomchai, A.; Kantatham, K. Innovations in recycled construction materials: Paving the way towards sustainable road infrastructure. Front. Built Environ. 2024, 10, 1449970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Arashpour, M.; Kodikara, J.; Guppy, R. Sustainable pavement construction: A systematic literature review of environmental and economic analysis of recycled materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Qi, L.; Hu, L.; Jiao, W.; Barbieri, D.M. Advances and development trends in eco-friendly pavements. J. Road Eng. 2021, 1, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buritatum, A.; Suddeepong, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Akkharawongwhatthana, K.; Yaowarat, T.; Hoy, M.; Bunsong, C.; Arulrajah, A. Improved performance of asphalt concretes using bottom ash as an alternative aggregate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurič, B.; Hanžič, L.; Ilić, R.; Samec, N. Utilization of municipal solid waste bottom ash and recycled aggregate in concrete. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Use of raw-state bottom ash for aggregates in construction materials. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyasangthong, S.; Yoosuk, P.; Krosoongnern, K.; Sakdinakorn, R.; Tabyang, W.; Phojan, W.; Suksiripattanapong, C. Stabilization of recycled concrete aggregate using high calcium fly ash geopolymer as pavement base material. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltue, T.; Suddeepong, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Samingthong, W.; Arulrajah, A.; Rashid, A.S.A. Strength development of recycled concrete aggregate stabilized with fly ash-rice husk ash based geopolymer as pavement base material. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.P.; Priya, N. Geopolymer as stabilising materials in pavement constructions: A review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024, 7, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Polaczyk, P.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Hu, W. Evaluation of glass powder-based geopolymer stabilized road bases containing recycled waste glass aggregate. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications; Geopolymer Institute: Saint-Quentin, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, F.; Jin, X.; Javed, M.F.; Akbar, A.; Shah, M.I.; Aslam, F.; Alyousef, R. Geopolymer concrete as sustainable material: A state of the art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Arif, M.; Shariq, M. Use of geopolymer concrete for a cleaner and sustainable environment—A review of mechanical properties and microstructure. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 704–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakka, W.P.; Lim, N.H.A.S.; Khun, M.C. A scientometric review of geopolymer concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.L.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Geopolymer foam concrete: An emerging material for sustainable construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phummiphan, I.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Rachan, R.; Arulrajah, A.; Shen, S.-L.; Chindaprasirt, P. High calcium fly ash geopolymer stabilized lateritic soil and granulated blast furnace slag blends as a pavement base material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuaklong, P.; Wongsa, A.; Sata, V.; Boonserm, K.; Sanjayan, J.; Chindaprasirt, P. Properties of high-calcium and low-calcium fly ash combination geopolymer mortar containing recycled aggregate. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoo-ngernkham, T.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Sata, V.; Hanjitsuwan, S.; Hatanaka, S. The effect of adding nano-SiO2 and nano-Al2O3 on properties of high calcium fly ash geopolymer cured at ambient temperature. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horpibulsuk, S.; Hoy, M.; Suddepong, A.; Udomchai, A.; Buritatum, A.; Yaowarat, T.; Akkharawongwhatthana, K.; Yeanyong, C.; Horpibulsuk, J.; Mobkrathok, M. A 10-Year Research on Sustainable Pavement Materials. In Recent Advances and Innovative Developments in Transportation Geotechnics: Keynote Volume ICTG 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Chalee, W.; Rattanasak, U. Comparative study on the characteristics of fly ash and bottom ash geopolymers. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, V.; Sathonsaowaphak, A.; Chindaprasirt, P. Resistance of lignite bottom ash geopolymer mortar to sulfate and sulfuric acid attack. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Behavior of low-calcium fly and bottom ash-based geopolymer concrete cured at ambient temperature. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5945–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Minjigmaa, A.; Lee, M.; Chen-Tan, N.; Van Riessen, A. Characterisation of class F fly ash geopolymer pastes immersed in acid and alkaline solutions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.K.; Lukey, G.C.; Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S. Effect of calcium silicate sources on geopolymerisation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymers: Structures, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Santa, R.A.A.B.; Padoin, N.; Soares, C.; Riella, H.G. Microstructural characteristics of geopolymer materials with twenty eight days of curing and after eight years stored at room temperature. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Lukey, G.C.; Kriven, W.M.; Van Deventer, J.S. The effect of alkali and Si/Al ratio on the development of mechanical properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 292, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer, green chemistry and sustainable development solutions. In Proceedings of the World Congress Geopolymer 2005, Saint-Quentin, France, 29 June–1 July 2005; Geopolymer Institute: Saint-Quentin, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sivasakthi, M.; Jeyalakshmi, R. Effect of change in the silica modulus of sodium silicate solution on the microstructure of fly ash geopolymers. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Dang, M.Q.; Do, T.M. Studies on compressive strength of sand stabilized by alkali-activated ground bottom ash and cured at the ambient conditions. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.B.; Subramaniam, K.V. Evaluation of sodium content and sodium hydroxide molarity on compressive strength of alkali activated low-calcium fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 81, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoti, M.; Wong, K.K.; Yang, E.-H.; Tan, K.H. Effects of Si/Al molar ratio on strength endurance and volume stability of metakaolin geopolymers subject to elevated temperature. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 5726–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, D.; Yusoff, Z.M.; Muniandy, R.; Hamid, H. Effect of stabilizers on stiffness modulus of soil layers: A review. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2013, 8, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.Q.; Hoy, M.; Suddeepong, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Kantathum, K.; Arulrajah, A. Improved mechanical and microstructure of cement-stabilized lateritic soil using recycled materials replacement and natural rubber latex for pavement applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Glendinning, S.; Fernandes, L.; Pinto, A.T. Effect of calcium content on soil stabilisation with alkaline activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjitsuwan, S.; Hunpratub, S.; Thongbai, P.; Maensiri, S.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Effects of NaOH concentrations on physical and electrical properties of high calcium fly ash geopolymer paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, G.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Alkali-activated fly ash: Effect of thermal curing conditions on mechanical and microstructural development—Part II. Fuel 2007, 86, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The geopolymerisation of alumino-silicate minerals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000, 59, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Doh, J.-H.; Dinh, H.L.; Ong, D.E.L.; Zi, G.; You, I. Effect of Si/Al molar ratio on the strength behavior of geopolymer derived from various industrial waste: A current state of the art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.L.; Revathi, V. Microstructural Properties of Alkali-Activated Metakaolin and Bottom Ash Geopolymer. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 4235–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alouani, M.; Saufi, H.; Aouan, B.; Bassam, R.; Alehyen, S.; Rachdi, Y.; El Hadki, H.; El Hadki, A.; Mabrouki, J.; Belaaouad, S.; et al. A comprehensive review of synthesis, characterization, and applications of aluminosilicate materials-based geopolymers. Environ. Adv. 2024, 16, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Development of Geopolymer Concrete from Fly Ash and Bottom Ash Mixture. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 73, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobirică, C.; Orbeci, C.; Bobirică, L.; Palade, P.; Deleanu, C.; Pantilimon, C.M.; Pîrvu, C.; Radu, I.C. Influence of red mud and waste glass on the microstructure, strength, and leaching behavior of bottom ash-based geopolymer composites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbachiya, M.; Meddah, M.S.; Ouchagour, Y. Performance of Portland/Silica Fume Cement Concrete Produced with Recycled Concrete Aggregate. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakararoj, N.; Tran, T.N.H.; Sukontasukkul, P.; Attachaiyawuth, A.; Tangchirapat, W.; Ban, C.C.; Rattanachu, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C. Effects of High-Volume bottom ash on Strength, Shrinkage, and creep of High-Strength recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, S.; Kassem, H.; Elkordi, A.; Joumblat, R. Advancing Pavement Sustainability: Assessing Recycled Aggregates as Substitutes in Hot Mix Asphalt. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
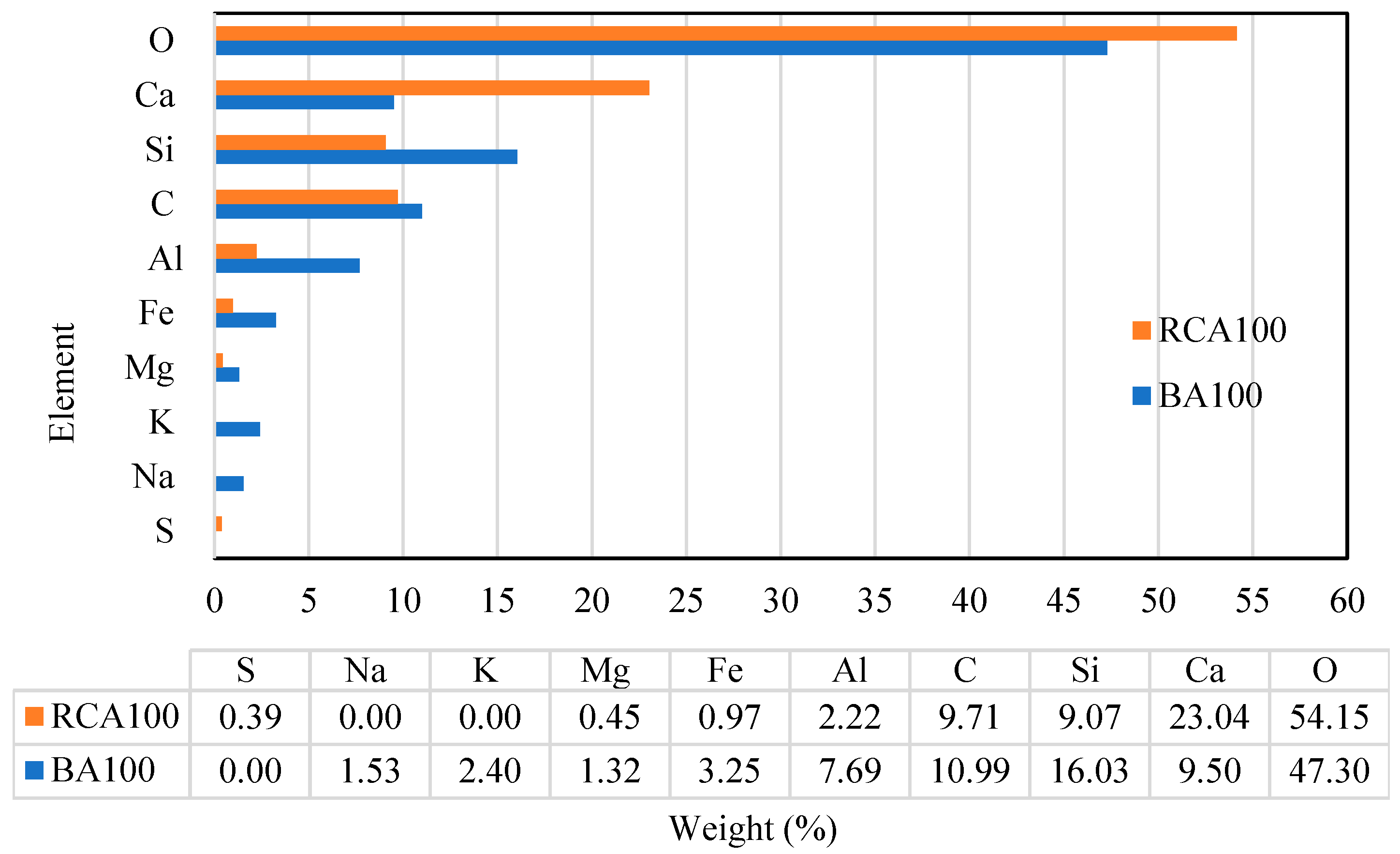

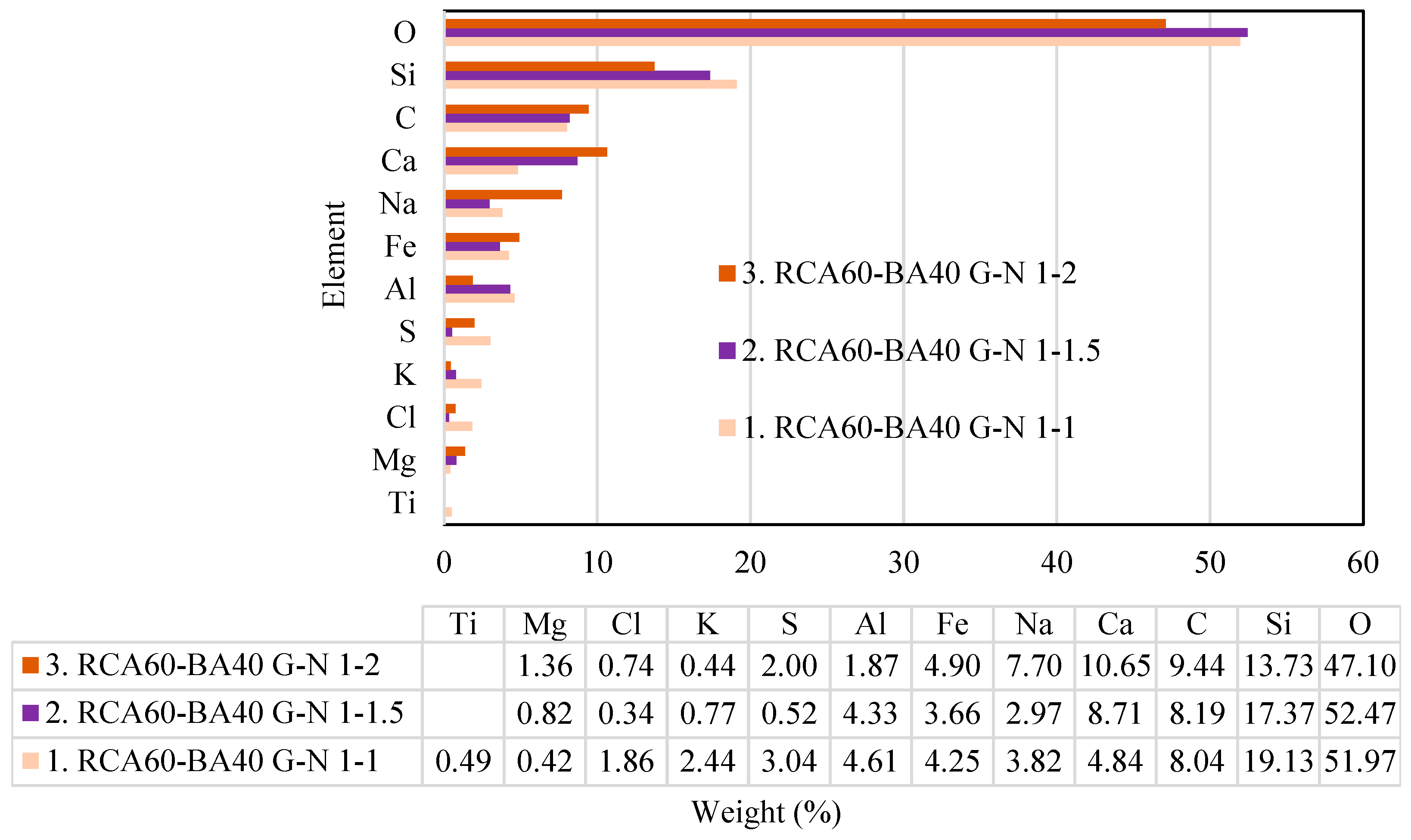
| Sample ID | Mix Ingredients |
|---|---|
| 90RCA10BA G/N 1:1.0 | 90%RCA + 10%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1) NaOH |
| 90RCA10BA G/N 1:1.5 | 90%RCA + 10%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1.5) NaOH |
| 90RCA10BA G/N 1:2.0 | 90%RCA + 10%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (2) NaOH |
| 80RCA20BA G/N 1:1.0 | 80%RCA + 20%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1) NaOH |
| 80RCA20BA G/N 1:1.5 | 80%RCA + 20%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1.5) NaOH |
| 80RCA20BA G/N 1:2.0 | 80%RCA + 20%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (2) NaOH |
| 70RCA30BA G/N 1:1.0 | 70%RCA + 30%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1) NaOH |
| 70RCA30BA G/N 1:1.5 | 70%RCA + 30%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1.5) NaOH |
| 70RCA30BA G/N 1:2.0 | 70%RCA + 30%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (2) NaOH |
| 60RCA40BA G/N 1:1.0 | 60%RCA + 40%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1) NaOH |
| 60RCA40BA G/N 1:1.5 | 60%RCA + 40%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1.5) NaOH |
| 60RCA40BA G/N 1:2.0 | 60%RCA + 40%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (2) NaOH |
| 50RCA50BA G/N 1:1.0 | 50%RCA + 50%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1) NaOH |
| 50RCA50BA G/N 1:1.5 | 50%RCA + 50%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (1.5) NaOH |
| 50RCA50BA G/N 1:2.0 | 50%RCA + 50%BA + (1) Na2SiO3 + (2) NaOH |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoy, M.; Traiyasut, C.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chinkulkijniwat, A.; Suddeepong, A.; Buritatum, A.; Yaowarat, T.; Julvorawong, M.; Savetviwat, T. Strength Development of Bottom Ash-Based Geopolymer-Stabilized Recycled Concrete Aggregate as a Pavement Base Material. Coatings 2025, 15, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080935
Hoy M, Traiyasut C, Horpibulsuk S, Chinkulkijniwat A, Suddeepong A, Buritatum A, Yaowarat T, Julvorawong M, Savetviwat T. Strength Development of Bottom Ash-Based Geopolymer-Stabilized Recycled Concrete Aggregate as a Pavement Base Material. Coatings. 2025; 15(8):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080935
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoy, Menglim, Chokchai Traiyasut, Suksun Horpibulsuk, Avirut Chinkulkijniwat, Apichat Suddeepong, Apinun Buritatum, Teerasak Yaowarat, Mantana Julvorawong, and Thanaset Savetviwat. 2025. "Strength Development of Bottom Ash-Based Geopolymer-Stabilized Recycled Concrete Aggregate as a Pavement Base Material" Coatings 15, no. 8: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080935
APA StyleHoy, M., Traiyasut, C., Horpibulsuk, S., Chinkulkijniwat, A., Suddeepong, A., Buritatum, A., Yaowarat, T., Julvorawong, M., & Savetviwat, T. (2025). Strength Development of Bottom Ash-Based Geopolymer-Stabilized Recycled Concrete Aggregate as a Pavement Base Material. Coatings, 15(8), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080935









