Abstract
In recent years, interest in HEAs has increased exponentially due to their extraordinary properties, especially for wear- and corrosion-resistant applications. However, the main problem involves correctly selecting the HEA composition required for a specific application, as most of the data are scattered throughout the literature, and only a limited number of models accurately predict the properties. Therefore, a database of 415 HEA alloys (bulk) and coatings obtained using thermal spray (TS) techniques has been created, compiled from scientific studies over the past 20 years. This tool collects information on physical, mechanical, and chemical properties, with a particular emphasis on corrosion and wear resistance. This facilitates material comparison and selection according to the needs of a specific application. In particular, the database highlights how composition and deposition technique also affect performance, identifying CoCrFeNi (CGS and in bulk) as a promising candidate for simultaneous wear and corrosion resistance.
1. Introduction
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have generated great interest in the research sector since the beginning of the 2000s, with the work of Cantor et al. and Yeh et al. standing out [1,2]. These types of alloys, composed of five or more main elements in nearly equal proportions (typically between 5 and 35 at.%), exhibit excellent mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical properties [3,4,5]. The primary reason for this is the high entropy configuration, which results in the formation of a solid and stable single-phase structure, providing them with better performance than traditional alloys [6]. Among all the characteristics, wear and corrosion resistance are the most outstanding and desired for the widest range of applications. These enable continuous improvement in industries dealing with these issues, improving performance and extending the components’ service life, increasing the potential for industrial applications [7]. Therefore, they are perfect candidates for industries that require high resistance to temperatures, wear, and corrosion (aerospace, chemical, and energy); excellent mechanical resistance for high-performance parts (automotive and tools); durability combined with biocompatibility (biomedical); and high conductivity and electrical stability (electronics) [8,9].
Similarly, these properties have also favored their implementation as coatings to enhance the surface properties of various components [6]. These coatings are often applied using thermal spray techniques, such as Cold Gas Spray (CGS), High-Velocity Oxy-Fuel (HVOF), Flame Spray (FS), or Atmospheric Plasma Spray (APS) [10]. This technology has certain advantages, including its low cost, simplicity of use, scalability, and great industrial potential, as well as its minimal impact on the matrix [6]. Recent studies also emphasize the wear and corrosion resistance of these alloys, in this case, those deposited by laser cladding [11]. As with thermal spray coatings, laser cladding coatings also depend on the deposition parameters.
Despite the excellent behavior of HEAs, selecting the right one for a specific application remains a significant challenge. This is primarily because of the large number of possible element combinations and their effect on the final material properties [12]. Researchers have also developed models that enable the prediction of the hardness of these alloys as a function of their composition. Elements such as Al, Ti, Mo, Cr, and V increase the hardness, and, similarly, the addition of C improves wear resistance [13]. Difficulties in predicting phase stability also complicate the creation of computer simulation models. Although some models and simulations already exist (for example, artificial neural network algorithms [14,15], multi-scale simulation methods [16], and empirical models [17]), it is important to understand their limitations. These models require the prior existence of large databases and experimental validations, and present accuracy and scalability problems linked to high computational cost [18]. Additionally, in the context of coatings, other factors, such as the particle size of the powder, morphology, and coating method selection, are critical for their final microstructure, porosity, adhesion, and overall properties [10,19].
To address this problem and facilitate the selection of HEAs and HEA coatings obtained by TS, researchers at the University of Barcelona have developed a new database, compiling information from the last 20 years and highlighting important physical, mechanical, and chemical properties. The main objective of this database is to provide a useful and accessible tool for materials comparison and selection (bulk HEAs and HEA coatings) according to the user’s needs and the required application, with a particular focus on wear and corrosion resistance. By utilizing data from various studies, this resource will bridge the gap between the industrial and research sectors. Unlike other previous databases, which focus mainly on the mechanical properties of bulk HEAs, this database also includes coatings and integrates critical properties such as corrosion and wear resistance. It also differentiates between different deposition techniques, crystal structures, and other parameters, allowing for direct comparison between different techniques and compositions and thus facilitating material selection.
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Acquisition and Key Parameters
The data were obtained from the collection of studies published about HEAs’ bulk and coatings from 2004 to 2024, covering a total of 415 materials. Each material was characterized based on a set of attributes categorized as numerical and discrete (Table 1), which cover the most critical aspects of HEAs’ performance for different applications, facilitating the material selection through data quantification and comparison. To ensure the consistency of data from different sources for each alloy, the recorded values were cross-checked with at least two publications, whenever possible. In addition, in case of different values, the values entered into the database corresponded to a range of values or an average value. The experimental conditions were recorded whenever possible. For the corrosion test results, data from a 3.5% NaCl environment were always selected. However, due to methodological differences, it was not possible to perform a complete normalization for the wear resistance results. Instead, data from the material used for the test were included in the database for reference during comparison.

Table 1.
Classification of attributes for material records.
The selected properties enable the evaluation of the material’s resistance to different stresses and environments, a key factor in high-strength and high-mechanical-contact applications. They also increase service life, reduce maintenance costs, and facilitate the correlation between the type of structure and the expected properties. Similarly, the type of coating also influences the material’s performance and its applications.
The database was created using Ansys Granta Constructor software (Ansys GRANTA, ANSYS, Inc., Cambridge, UK, 2021) based on data collected from the literature. It was organized into two main branches: bulk HEAs and HEA coatings. Additionally, bulk HEAs were divided into five families according to composition (Al-Co-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni system and derivatives, Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni system and derivatives, light metal base, refractory metal base, and other HEAs), and HEA coatings were divided into four families according to the coating deposition technique (Arc Plasma Spray-APS, Cold Gas Spray-CGS, Flame Spray-FS, and High Velocity Oxy Fuel-HVOF). Finally, within the different techniques, the materials were grouped according to their main components (AlCoCrFeNi, AlCoCrFeNiTi, AlCoCrFeNiSi, AlCoCrFeNiSiTi, AlCoCrFeMo, AlCoCrNiMo, CoCrFeNi, CoCrFeNiMn, CoCrFeNiNb, CoCrFeNiMo, and TiNbMoMnFe). Figure 1 shows the organization of the different HEAs.
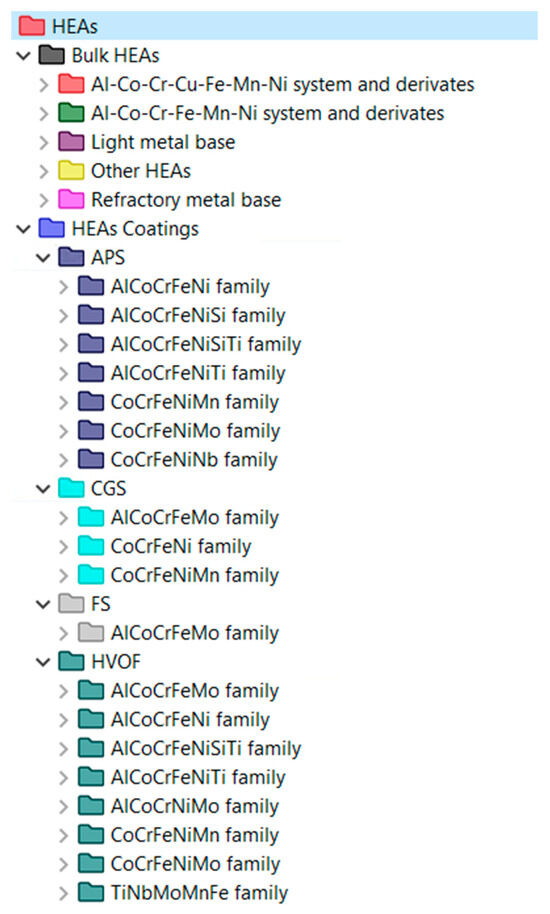
Figure 1.
Classification of HEA materials in the HEA database.
2.2. Database Records
The database created by Gorsse et al. [20] was used as the main source of information for the bulk HEAs, compiling data corresponding to density, crystalline structure, hardness, compressive or tensile strength, elongation, and Young’s modulus. This was in addition to the information on wear and corrosion resistance obtained from the investigations of Zirari and Trabadelo [21] and Shi et al. [22]. In the case of coatings, as the information was obtained from different studies, Table 2 compiles all the data collected. In addition to basic characterization information such as structure, type of coating, and mechanical properties, the search focused on wear and corrosion resistance properties.

Table 2.
Technical data on the mechanical strength, wear, and corrosion resistance of HEA coatings.
3. Results: HEA Database Representation
The new database presents graphical results that help with selecting the best HEAs and the best HEA coating depending on the requirements, constraints, and free variables. Different colors represent the different nature, group, or family of the materials. If the bubble is a dot, this means that there is a single data point in the reviewed literature or there is consistency among the data available in the literature. If the bubble is longer in one axis (X), the other axis (Y), or even in both axes (X-Y), this means that there is more than one value available in the literature. We did not discern the data included in the database; we just considered the data reported in the literature.
The representation of hardness versus density is crucial to relate these materials to their potential applications in terms of wear resistance or corrosion resistance. The hardness varies between 100 HV and 900 HV, and the density varies between 5.25 g/cm3 and 13.5 g/cm3.
Figure 2a shows that most HEAs have an average density of 5.5–8.5 g/cm3, and a wide hardness range from 100 to 900 HV. Achieving this wide range of hardnesses is one of the reasons why these materials are so useful for different applications. As a result, researchers have developed models that allow the hardness of these alloys to be predicted based on their composition [12]. It was thus established that elements such as Al, Ti, Mo, Cr and V increase the hardness of the alloy, while others such as Ni, Cu, Co, Mn and Hf weaken it. This behavior can be observed in the graph, where the highest hardness values are associated with HEAs rich in Al, Cr, and Mo (particularly those in the AlCoCrCuFeMnNi and AlCoCrFeMnNi systems) as well as with other compositions containing elements like V and Ti.
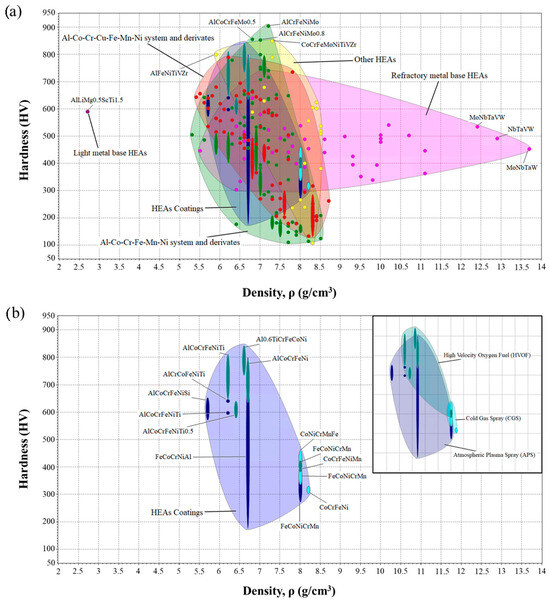
Figure 2.
Hardness as a function of density for: (a) the whole HEA database, (b) HEA coatings.
This type of material offers advantages in applications such as automotive, structural materials, cutting tools and high-temperature components. Furthermore, it was observed that refractory HEAs with elements such as Mo, Nb, Ta, and W have very high densities. These compositions provide greater resistance to high temperatures, ideal for applications in steam turbines [54]. On the other hand, light metal base HEAs contain low-density elements (<5 g/cm3) such as Al, Mg, Si, Ca and Li [55]. This type of HEA is very interesting for fields involving structural materials, such as aerospace or automotive.
Regarding coatings (see Figure 2b), it was seen that HVOF coatings are harder, even when comparing HEAs with the same composition. This is because when the powders are deposited at high temperatures and speeds, the coatings obtained are quite dense and have low porosity, which makes them harder [56,57]. Then there is the group of APS coatings, with a slightly lower hardness, since the particle deposition speed is lower, which increases porosity [57]. Finally, CGS coatings have a hardness between 300 and 450 HV. CGS operates at lower temperatures, which prevents the formation of hard oxide phases that contribute to increased hardness and limits the appearance of hardening by precipitation or other thermally induced reinforcement mechanisms [7]. Although limited in comparison with other systems, some recent studies have explored cold-sprayed Al-rich HEA, demonstrating their potential to improve hardness and wear resistance [25,58]. These studies highlight the need for further research to fully characterize their performance under different processing conditions.
Almost no studies have been carried out on this type of coating with powders rich in elements such as Al, which makes the material harder.
Another important mechanical property of HEAs, which is crucial for its implementation, is the Young’s modulus (E), which can fluctuate within a very wide range compared to other alloys. The Young modulus varies between 30 MPa and 260 MPa.
In addition, E can be very different from the modulus of any of the constituent elements [59]. Figure 3 shows that there is a linear relationship between the density of these alloys and their stiffness in tension, especially for HEAs in the AlCoCrFeMnNi and AlCoCrCuFeMnNi systems.
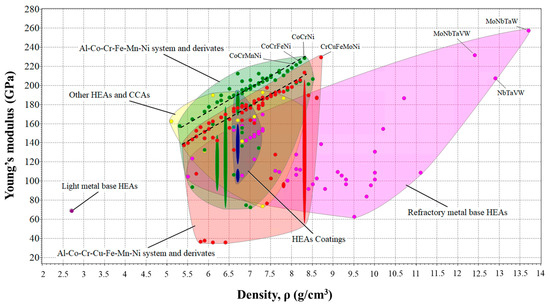
Figure 3.
Young’s modulus as a function of density for the whole HEA database.
The high stiffness of HEAs in these groups is noteworthy, particularly those containing elements such as Cr, Ni, Co, and Fe. Likewise, the highest values were those of the refractory materials, thanks to the presence of elements such as W, which also gave them greater density. On the other hand, HEAs based on light metals or with a high Al content exhibited lower Young’s modulus values, which indicates that they are more flexible and more easily deformed.
Furthermore, the type of crystalline structure has a significant effect on the mechanical properties of these high-entropy alloys [60]. In general, HEAs with an FCC structure are more ductile and can deform before fracturing. BCCs, on the other hand, are more resistant and harder. Thus, dual-phase HEAs with a BCC + FCC structure make it possible to obtain a type of material that combines these properties. Figure 4 summarizes the effect of the structure type on the physical and mechanical properties of HEAs. It was observed that the hardest HEAs had BCC structures or a structures that were a combination of FCC + BCC.
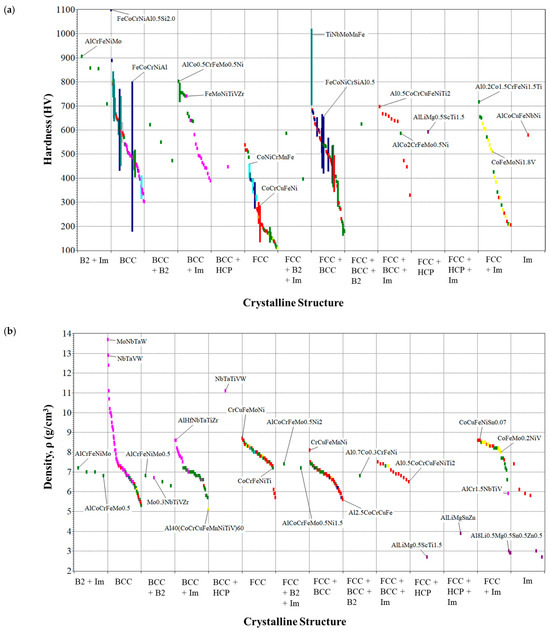
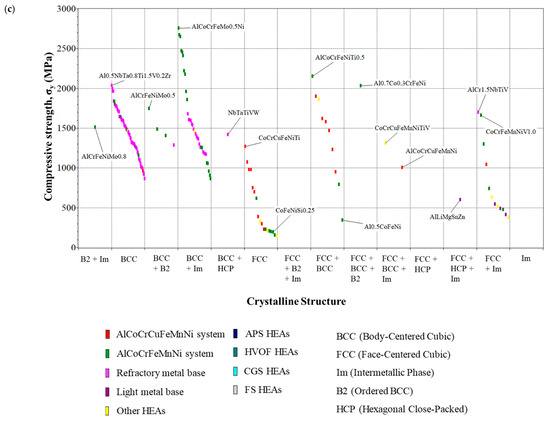
Figure 4.
(a) Hardness, (b) density, and (c) compressive strength as functions of crystalline structure for the whole HEA database.
Likewise, the highest density HEAs were those with BCC crystalline structure and derivative structures, which corresponded to the refractory materials. These were also the ones that achieved the highest compressive strength values, although it is worth mentioning that some HEAs from the AlCoCrFeMnNi and AlCoCrCuFeMnNi systems had an FCC + BCC structure.
Regarding coatings, as mentioned above, wear and corrosion resistance allow a wide variety of applications for these materials. Figure 5 shows the volume wear rate and corrosion current density of these materials as functions of density, as well as the corrosion and wear resistance grade as a function of the values obtained.
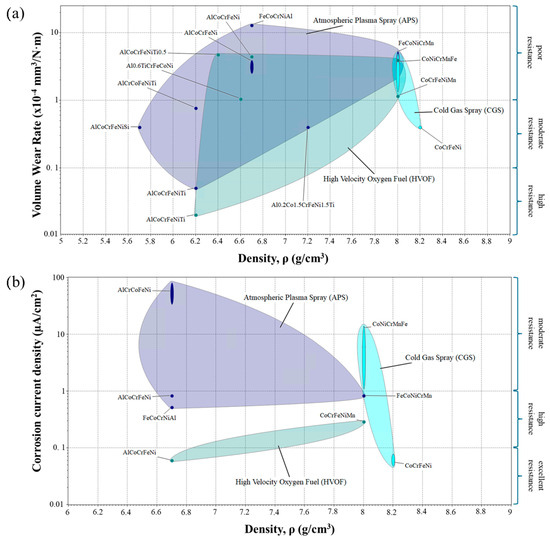
Figure 5.
(a) Volume wear rate, and (b) corrosion current density as functions of density for HEA coatings [Y-axes are shown on a logarithmic scale to better visualize the range of values].
Wear resistance is a property that can vary significantly depending on the material used in the test, the conditions, and the environment. In addition, performance may also differ depending on the intended application. HEAs, thanks to their much higher hardness than other alloys, are twice as resistant to wear than conventional alloys [4]. However, this is not the case when the material is deposited as a coating. Thereby, additions of elements such as Al and Ti also increase the wear resistance of HEAs, as well as ceramic oxide coatings (e.g., Al2O3, Cr2O3, TiO2) [4,61]. For all the values collected for the database, it has been established that values lower than 10−4 mm3/Nm are usually considered indicative of good wear resistance [62]. Although this value may vary depending on test conditions, it provides a useful benchmark for comparing the performance of HEAs.
To determine the corrosion current density (Icorr), in all cases, a solution of 3.5 wt.% NaCl at room temperature was used. The calculation of this value for a material indicates the corrosion level, based on the values resulting from the work of the RILEM TC 154 EMC committee [63]. Thus, Icorr values greater than 1 μA/cm2 indicate a high–moderate degree of corrosion, values between 0.1 and 1 indicate an improvement in corrosion resistance, and values below 0.1 reflect negligible corrosion penetration in the material under study. It was observed that HVOF coatings showed better corrosion resistance than APS coatings. CGS coatings, on the other hand, showed values ranging from moderate to excellent resistance.
4. Applications
4.1. Wear Resistance
In the scenario of selecting a coating material for wear resistance, Figure 6a shows that there are several options that are convenient for this approach, depending on the coating technique used to apply it. If APS is applied, the most wear-resistant material is FeCoNiCrSiAl0.5. However, when applying CGS, the most convenient material is CoCrFeNi. Nevertheless, Al0.6TiCrFeCoNi is the most suitable material for resisting wear degradation if HVOF is applied. Finally, the FS technique has been underexplored in the context of HEA coatings for wear resistance, as there is a limited amount of information in the literature. Therefore, a conclusive evaluation of its performance cannot be conducted. For a better comparison, the bulk alloys are also shown in Figure 6b to determine the effect of coating deposition on this property. It was observed that the majority of HEAs with good corrosion resistance are those that contain AlCoCrFeMnNi and AlCoCrCuFeMnNi and their derivatives. The one HEA with the best wear resistance result is CoCrFeMnNiC0.6. This demonstrates that the results for coatings are in a similar range to those for bulk alloys.
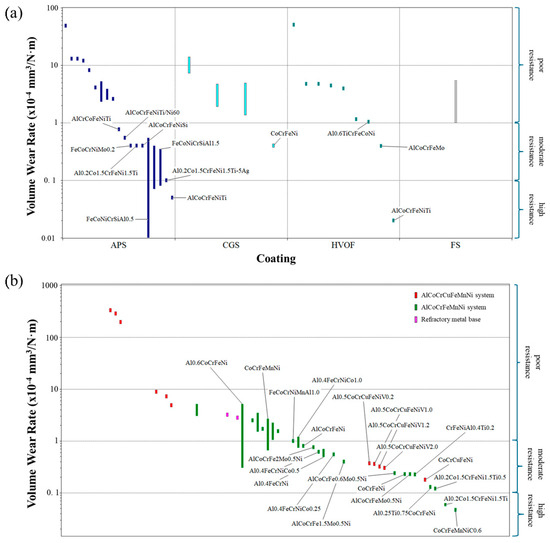
Figure 6.
Wear resistance of coating material available in the new database for (a) HEA coatings and (b) bulk HEAs [Y-axes are shown on a logarithmic scale to better visualize the range of values].
4.2. Corrosion Resistance
In the scenario of selecting a coating material for corrosion resistance, Figure 7a shows that there are several materials with potential for use in resisting corrosion. For this approach, depending on the coating technique used to apply the coating, there are several options. If APS is applied, the most corrosion-resistant coating is (CoCrFeNi)95Nb5. However, when applying CGS, the most suitable material is CoCrFeNi. This is the same coating as those existing in the database, applying CGS with the best properties against wear conditions. Nevertheless, AlCoCrNiMo and AlCoCrMo0.5Ni are the most suitable materials for resisting wear degradation when HVOF is applied. Finally, again, the lack of available data on flame spray coatings in corrosive conditions suggests that this method remains insufficiently studied. Therefore, no definitive conclusions can be drawn, and further research is needed. Regarding bulk alloy performance, the highest corrosion resistance is exhibited by alloys from the AlCoCrFeMnNi composition and its derivatives, as well as certain refractory alloys. In this context, CoCrFeNi appears to be the most corrosion-resistant material. When comparing these results with those of the coatings, a comparable level of corrosion resistance is observed (see Figure 7b).
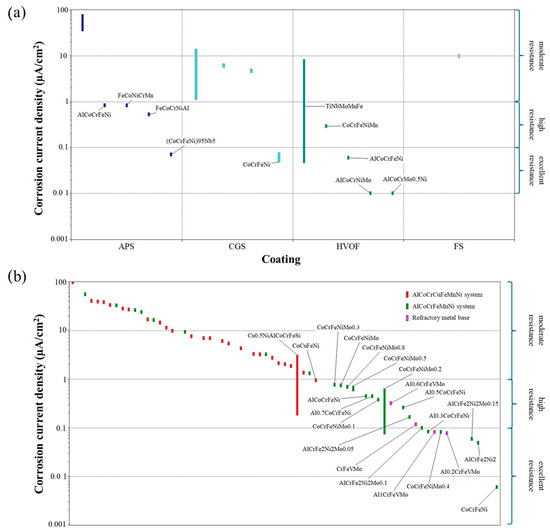
Figure 7.
Corrosion resistance of coating material available in the new database for (a) HEA coatings and (b) bulk HEAs [Y-axes are shown on a logarithmic scale to better visualize the range of values].
4.3. Corrosion and Wear Resistance
In the scenario of selecting a material for corrosion and wear resistance at the same time, there are several bulk and coatings available, as shown in Figure 8. The corrosion resistance versus wear resistance of available HEA materials is summarized as follows: the upper left quadrant shows poor wear resistance and good corrosion resistance, the upper right quadrant shows poor wear resistance and moderate corrosion resistance, the lower left quadrant shows good wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and the lower right quadrant shows good wear resistance and moderate corrosion resistance. Therefore, the coating in the lower left quadrant is the best candidate, exhibiting superior simultaneous corrosion and wear resistance—in this case, CoCrFeNi sprayed by CGS, and AlCoCrFeNi and CoCrFeNi in bulk. This means that the application of CoCrFeNi as a cold spray coating exhibits hardly any loss of corrosion and wear resistance compared to the same bulk material.
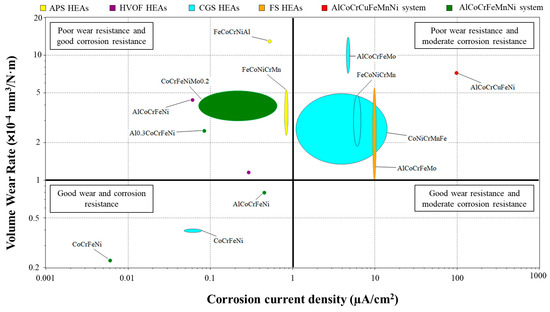
Figure 8.
Wear resistance vs. corrosion resistance of HEA materials available in the new database [Y-axis is shown on a logarithmic scale to better visualize the range of values].
Additionally, the upper right quadrant displays the worst materials for corrosion-wear resistance.
Finally, the upper left quadrant includes materials with good corrosion resistance but inadequate wear resistance. These include APS coatings (FeCoCrNiAl and FeCoNiCrMn), bulk alloys (Al0.3CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeNiMo0.2), and HVOF coatings (AlCoCrFeNi and CoCrFeNiMn). It is important to highlight that HVOF coatings achieve better results than their APS-deposited counterparts. Remarkably, there are few data for simultaneous corrosion and wear performance in the database, and this analysis is based on the collected data.
5. Conclusions
This work has focused on the development of a database of 415 HEA bulks and coatings, aiming to facilitate their selection according to their material properties (physical, mechanical, and chemical) and the desired application, especially those requiring high wear and corrosion resistance. The results obtained, based on the compilation of different bibliographic sources, suggest the following key conclusions:
- Composition and microstructure directly affect the material’s properties. BCC or FCC + BCC structures are harder and more compressive-resistant, while FCC structures are more ductile. Likewise, adding elements such as Al, Ti, Mo, Cr, and V also increases hardness. This enables the design of alloys with properties that adapt to the industry’s requirements.
- In terms of coatings, the deposition technique has a significant influence on performance. HVOF coatings tend to be harder and denser because of flame temperatures and deposition speeds. On the other hand, APS coatings, due to their greater porosity, are slightly softer. Finally, CGS coatings have the lowest values and need more optimization.
- The wear resistance of HEAs is generally high compared to that of commercial alloys, highlighting the good results of the AlCoCrFeMnNi and AlCoCrCuFeMnNi systems. The best bulk material is CoCrFeMnNiC0.6. However, this can change depending on the coating deposition parameters. Likewise, adding elements such as Al or Ti and ceramic oxides improves resistance, and FeCoNiCrSiAl0.5 is the best coating sprayed by APS, CoCrFeNi is the best HEA sprayed by CGS, and Al0.6TiCrFeCoNi is the best HEA sprayed by HVOF.
- The corrosion resistance of HEA coatings is excellent compared to that of other materials, indicating greater stability in aggressive environments. The best materials are those with a composition of AlCoCrFeMnNi and derivatives, the most superior of these being the CoCrFeNi alloy. Regarding coatings, HVOF coatings obtained better results than APS coatings; meanwhile, CGS coatings exhibit an intermediate range of values. Therefore, CoCrFeN is the best HEA for corrosion resistance sprayed by APS, CoCrFeNiMn is the best HEA sprayed by CGS, and CoNiCrMnFe is the best HEA obtained by HVOF.
- If there is a need for both corrosion and wear resistance at the same time, the main HEA candidate with the highest potential reported in the literature is CoCrFeNi. However, the number of HEA compositions currently in development is increasing exponentially, and these conclusions will need to be updated in the near future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.B.-C., G.C., C.B. and S.D.; Methodology, L.B.-C., G.C., C.B. and S.D.; Software, L.B.-C., C.B. and S.D.; Validation, L.B.-C., G.C. and S.D.; Formal analysis, L.B.-C., G.C. and C.B.; Investigation, L.B.-C., G.C., C.B. and S.D.; Resources, S.D.; Data curation, S.D.; Writing—original draft, L.B.-C.; Writing—review & editing, G.C., C.B. and S.D.; Supervision, C.B. and S.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Catalan Government for the quality accreditation given to their research group DIOPMA and SDT, respectively (2021 SGR 00708 and 2021 SGR 00512). DIOPMA is a certified agent TECNIO in the category of technology developers from the Government of Catalonia. This work has been partially funded by the Spanish government PID2021-123511OB-C32 (MICINN/FEDER, UE). This work couldn’t be carried out without the support of “Thermodust” project (no. 101046835) funded by the “Horizon Europe” framework programme, CDTI and NextGeneration EU funds for the Bioenergy project MIP-20221004, and COBRAIN project funded by the European Union under the GA no. 101092211.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagini, M.; Murty, B.S. Advanced High-Entropy Alloys: A Next Generation Materials. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2024, 9, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, V.; Xavior, A. Development of high entropy alloys (HEAs): Current trends. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracle, D.B. High entropy alloys as a bold step forward in alloy development. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Research and Application Progress of High-Entropy Alloys. Coatings 2023, 13, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran Nair, R.; Supekar, R.; Morteza Javid, S.; Wang, W.; Zou, Y.; McDonald, A.; Mostaghimi, J.; Stoyanov, P. High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Deposited by Thermal Spraying: A Review of Strengthening Mechanisms, Performance Assessments and Perspectives on Future Applications. Metals 2023, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartita, R.; Ionita, D.; Demetrescu, I. A Modern Approach to HEAs: From Structure to Properties and Potential Applications. Crystals 2024, 14, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, V.E.; Shlyarova, Y.A.; Konovalov, S.V.; Vorob’ev, S.V.; Peregudov, O.A. Application of High-Entropy Alloys. Steel Transl. 2021, 51, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, A.; Anupam, A.; Murty, B.S.; Berndt, C.C.; Kottada, R.S.; Ang, A.S.M. Thermal Spray High-Entropy Alloy Coatings: A Review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2020, 29, 857–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y. Microhardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of AlxCrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy coatings on aluminum by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Pan, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y. Predicting the hardness of high-entropy alloys based on compositions. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 112, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, W.; Yu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhou, L. The Role of Carbon in Wear Resistance of CoCrFeNiTi0.5 High-Entropy Alloy Layer. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Yi, S.; Kim, J.; Shin, B.; Hyun, S. High-Entropy Alloys Properties Prediction Model by Using Artificial Neural Network Algorithm. Metals 2021, 11, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.-J. A neural network model for high entropy alloy design. npj Comput. Mater. 2023, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Simulation and Calculation for Predicting Structures and Properties of High-Entropy Alloys; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Sun, M.; Bai, M.; Lin, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, W. A hybrid prediction frame for HEAs based on empirical knowledge and machine learning. Acta Mater. 2022, 228, 117742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.A.; Ranganathan, R. Recent advances in modelling structure-property correlations in high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 204, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R. (Ed.) Surface Engineering for Corrosion and Wear Resistance; ASM International: Detroit, MI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Nguyen, M.H.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B. Database on the mechanical properties of high entropy alloys and complex concentrated alloys. Data Brief 2018, 21, 2664–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirari, T.; Trabadelo, V. A review on wear, corrosion, and wear-corrosion synergy of high entropy alloys. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Liaw, K. Corrosion-Resistant High-Entropy Alloys: A Review. Metals 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supekar, R.; Nair, R.B.; McDonald, A.; Stoyanov, P. Sliding wear behavior of high entropy alloy coatings deposited through cold spraying and flame spraying: A comparative assessment. Wear 2023, 516–517, 204596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Nair, R.B.; Supekar, R.; McDonald, A.; Chromik, R.R.; Moreau, C.; Stoyanov, P. Enhanced wear resistance of AlCoCrFeMo high entropy coatings (HECs) through various thermal spray techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 477, 130311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Perumal, G.; McDonald, A. Effect of Microstructure on Wear and Corrosion Performance of Thermally Sprayed AlCoCrFeMo High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, N.; Liu, M.; Qiao, Z.; Yi, G.; Yao, Q.; Zhao, G.; Xie, E.; Wang, Q. Microstructure and tribological behavior of a novel atmospheric plasma sprayed AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy matrix self-lubricating composite coatings. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, A.; Anupam, A.; Luzin, V.; Schulz, C.; Hall, C.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S. Multiscale mechanical performance and corrosion behaviour of plasma sprayed AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 854, 157140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Prashanth, K.; Zhang, N.; Ma, X.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, G. Frictional Wear and Corrosion Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Synthesized by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying. Entropy 2020, 22, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, N.; Radhika, N.; Sathishkumar, M.; Saleh, B. Characterisation and property evaluation of High Entropy Alloy coating on 316L steel via thermal spray synthesis. Tribol. Int. 2023, 185, 108525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, A.; Singh, S.; Anupam, A.; King, H.J.; Schulz, C.; Hall, C.; Munroe, P.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S. Nano- and micro-mechanical properties and corrosion performance of a HVOF sprayed AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 912, 165000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Fu, M.; Xiong, W. Microstructural Evolution of AlCoCrFeNiSi High-Entropy Alloy Powder during Mechanical Alloying and Its Coating Performance. Materials 2018, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.-K.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C. Microstructure and tribological properties of plasma sprayed FeCoNiCrSiAlx high entropy alloy coatings. Wear 2020, 448–449, 203209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Zhang, N.; Guan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Microstructure and properties of laser re-melting FeCoCrNiAl0.5Six high-entropy alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yeh, J.-W. Thermal sprayed high-entropy NiCo0.6Fe0.2Cr1.5SiAlTi0.2 coating with improved mechanical properties and oxidation resistance. Intermetallics 2017, 89, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Murakami, H.; Yeh, J.-W.; Yeh, A.-C.; Shimoda, K. On the study of thermal-sprayed Ni0.2Co0.6Fe0.2CrSi0.2AlTi0.2 HEA overlay coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 316, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbel, M.; Lindner, T.; Kohrt, C.; Lampke, T. Processing of AlCoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy by atmospheric plasma spraying. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 181, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.-H.; Xiong, W.; Liu, C.; Lu, S.; Fu, M. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Atmospheric Plasma-Sprayed AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloy Coating. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 5513–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbel, M.; Lindner, T.; Mehner, T.; Lampke, T. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Produced by HVOF. Coatings 2017, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbel, M.; Lindner, T.; Lampke, T. High-temperature wear behaviour of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 coatings produced by HVOF. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Feng, Z.; Xiong, W. Microstructure, Microhardness, and Wear Resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi/Ni60 Coating by Plasma Spraying. Coatings 2018, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, D. Microstructure and Tribological Properties of Plasma-Sprayed Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti-Ag Composite Coating from 25 to 750 °C. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bobzin, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, L.; Oete, M.; Königstein, T.; Tan, Z.; He, D. Wear behavior of HVOF-sprayed Al0.6TiCrFeCoNi high entropy alloy coatings at different temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallimanalan, A.; Babu, S.K.; Muthukumaran, S.; Murali, M.; Gaurav, V.; Mahendran, R. Corrosion behaviour of thermally sprayed Mo added AlCoCrNi high entropy alloy coating. Mater. Today 2020, 27, 2398–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Hui, X.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, S.; et al. Microstructures, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloys coating on AZ91 Mg alloy prepared by cold spray. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 925, 166698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, J.; Vackel, A.; Whetten, S.; Melia, M.; Kustas, A.B. Structure Evolution and Corrosion Performance of CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy Coatings Produced via Plasma Spray and Cold Spray. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-K.; Tan, H.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C. Microstructure and wear behavior of FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy coating deposited by plasma spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfouche, M.M.; Alidokht, S.A.; Grandy, L.; Aghasibeig, M.; Mauzeroll, J.; Chromik, R.R. Microstructural, Micromechanical, Wear, and Corrosion Properties of Cold Spray and Laser-Assisted Cold Spray CrMnCoFeNi Cantor HEA Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2024, 34, 550–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvello, A.; Cavaliere, P.; Yin, S.; Lupoi, R.; Cano, I.G.; Dosta, S. Microstructural, Mechanical and Wear Behavior of HVOF and Cold-Sprayed High-Entropy Alloys (HEAs) Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 118–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Li, W.; Song, B.; Yan, X.; Kuang, M.; Xu, Y.; Wen, K.; Lupoi, R. Deposition of FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy (HEA) coating via cold spraying. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 35, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Alidokht, S.A.; Sharifi, N.; Roy, A.; Harrington, K.; Stoyanov, P.; Chromik, R.R.; Moreau, C. Microstructural and Tribological Behavior of Thermal Spray CrMnFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Xu, L. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of FeCoCrNiMo0.2 High Entropy Coatings Prepared by Air Plasma Spray and the High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Spray Processes. Coatings 2017, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qi, W.; Xie, L.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of (CoCrFeNi)95Nb5 High-Entropy Alloy Coating Fabricated by Plasma Spraying. Materials 2019, 12, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhijith, N.V.; Kumar, D.; Kalyansundaram, D. Development of Single-Stage TiNbMoMnFe High-Entropy Alloy Coating on 304L Stainless Steel Using HVOF Thermal Spray. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Ma, C. Advances in High-Temperature Molten Salt-Based Carbon Nanofluid Research. Energies 2023, 16, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, V.; Yu, Z.G.; Chen, S.; Tan, T.L.; Aitken, Z.; Zhang, Y.-W. First principles-based design of lightweight high entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksa, M.; Turunen, E.; Suhonen, T.; Varis, T.; Hannula, S.-P. Optimization and Characterization of High Velocity Oxy-fuel Sprayed Coatings: Techniques, Materials, and Applications. Coatings 2011, 1, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, U.; Kumari, E. Applications of Thermal Spray Coatings: A Review. J. Therm. Spray Eng. 2024, 4, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikbakht, R.; Alidokht, S.A.; Bessette, S.; Gauvin, R.; Chromik, R.R. New insights on bonding mechanism of FCC and BCC high entropy alloy microparticles upon supersonic impact using micromechanical adhesion test. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 483, 130752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Science and Technology in High-Entropy Alloys. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Q.Y.; Li, W.; Li, D.Y. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and wear behavior of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy and AlCrFeNi medium-entropy alloy with WC addition. Wear 2023, 522, 204701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM International. ASM Handbook: Friction, Lubrication, and Wear Technology; ASM International: Detroit, MI, USA, 1992; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C.; Alonso, C. Test methods for on-site corrosion rate measurement of steel reinforcement in concrete by means of the polarization resistance method. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).