A Comprehensive Review of Hot In-Place Recycling Technology: Classification, Factors Affecting Performance of Asphalt Mixtures, and Benefits Analysis
Abstract
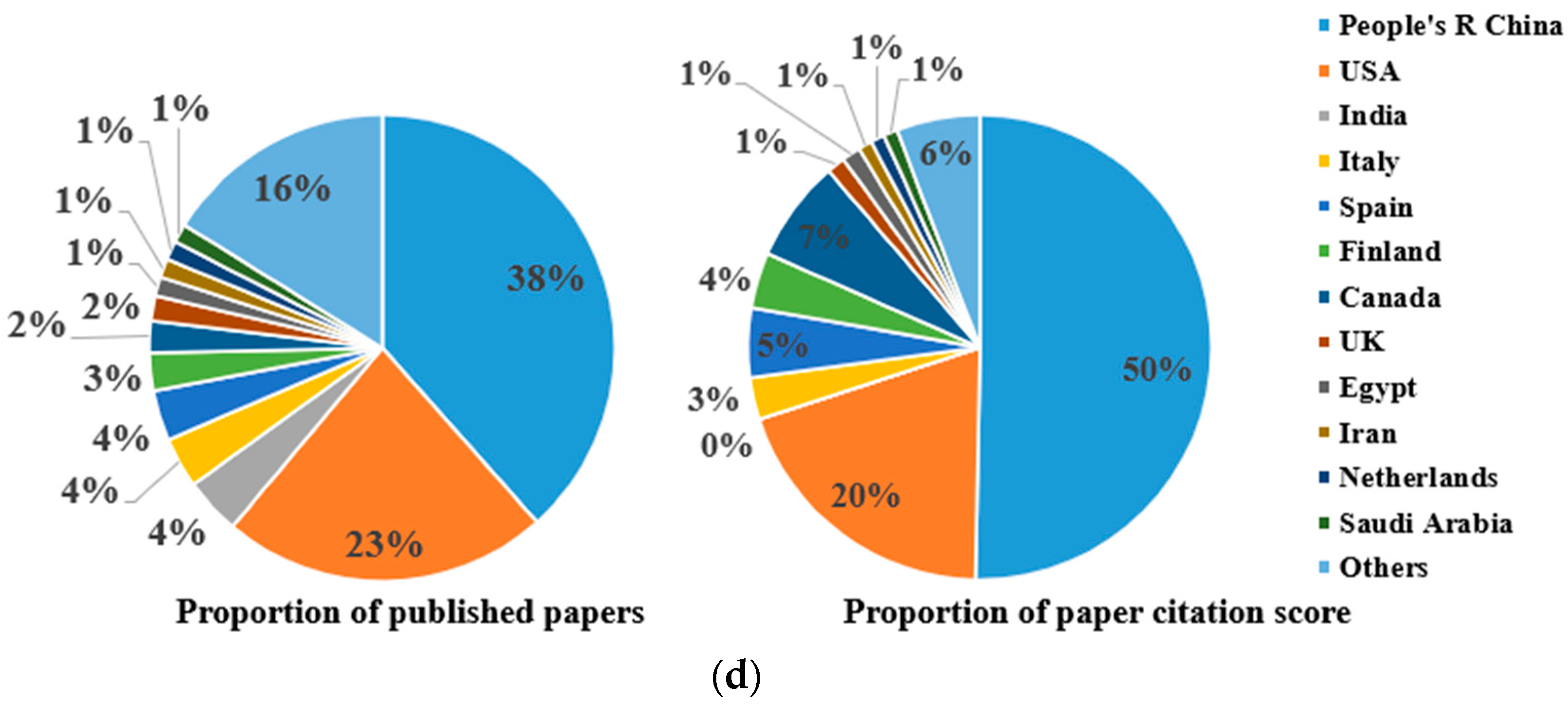
1. Introduction
2. HIR Technology Classification
2.1. Surface Recycling
- (1)
- The gradation of RAP material exhibits high uniformity, ensuring controllable post-reconstruction quality of the recycled mixture.
- (2)
- Pre-existing pavement distress (e.g., ruts and potholes) is shallow, requiring VAM incorporation below 30% of the total blend volume.
- (3)
- The surface recycling process alone can achieve compliance with design specifications without supplemental treatments.
- (4)
- The original asphalt binder exhibits moderate aging, enabling effective restoration of its performance through rejuvenation; the recycled asphalt mixture meets wear layer specifications.
2.2. Remixing
- (1)
- Significant material variability in the original asphalt surface mixture and extensive patched areas preclude achieving wear layer specifications via remixing.
- (2)
- Severe inherent gradation flaws in the original asphalt mixture prevent remixing from meeting wear layer requirements, though the recycled material remains suitable for middle surface applications.
- (3)
- The original pavement asphalt is more severely aged, making it difficult to use directly as a wear layer through rejuvenation.
2.3. Repaving
- (1)
- Significant material variability in the original asphalt surface mixture and extensive patched areas preclude achieving wear layer specifications via remixing.
- (2)
- The original asphalt surface layer is inadequate for upgraded traffic demands, necessitating an overlay with virgin asphalt mixtures for structural enhancement.
- (3)
- Severe inherent gradation flaws in the original asphalt mixture prevent repaving from meeting wear layer requirements, though the recycled material remains suitable for middle surface applications.
3. Factors Affecting the Road Performance of HIRAMs
3.1. Raw Materials
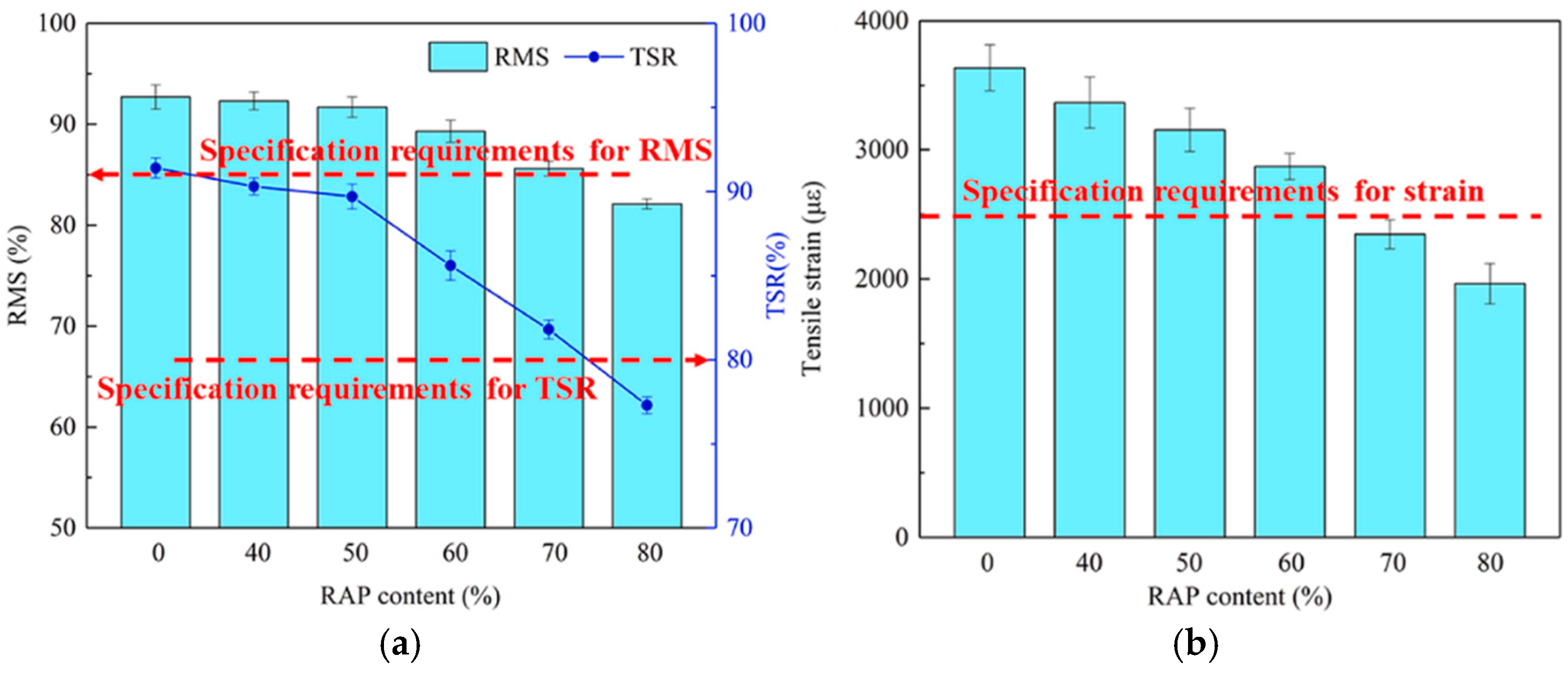
3.1.1. RAP Materials
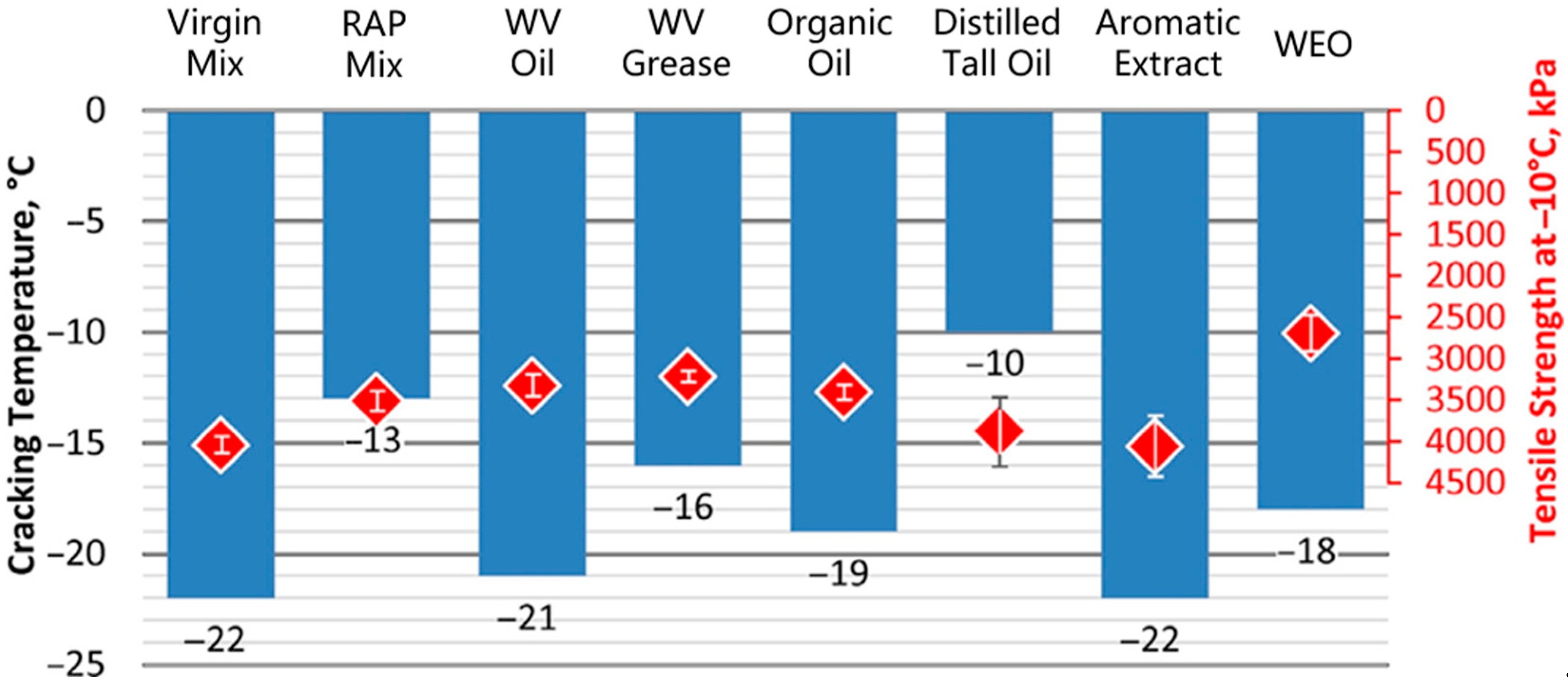
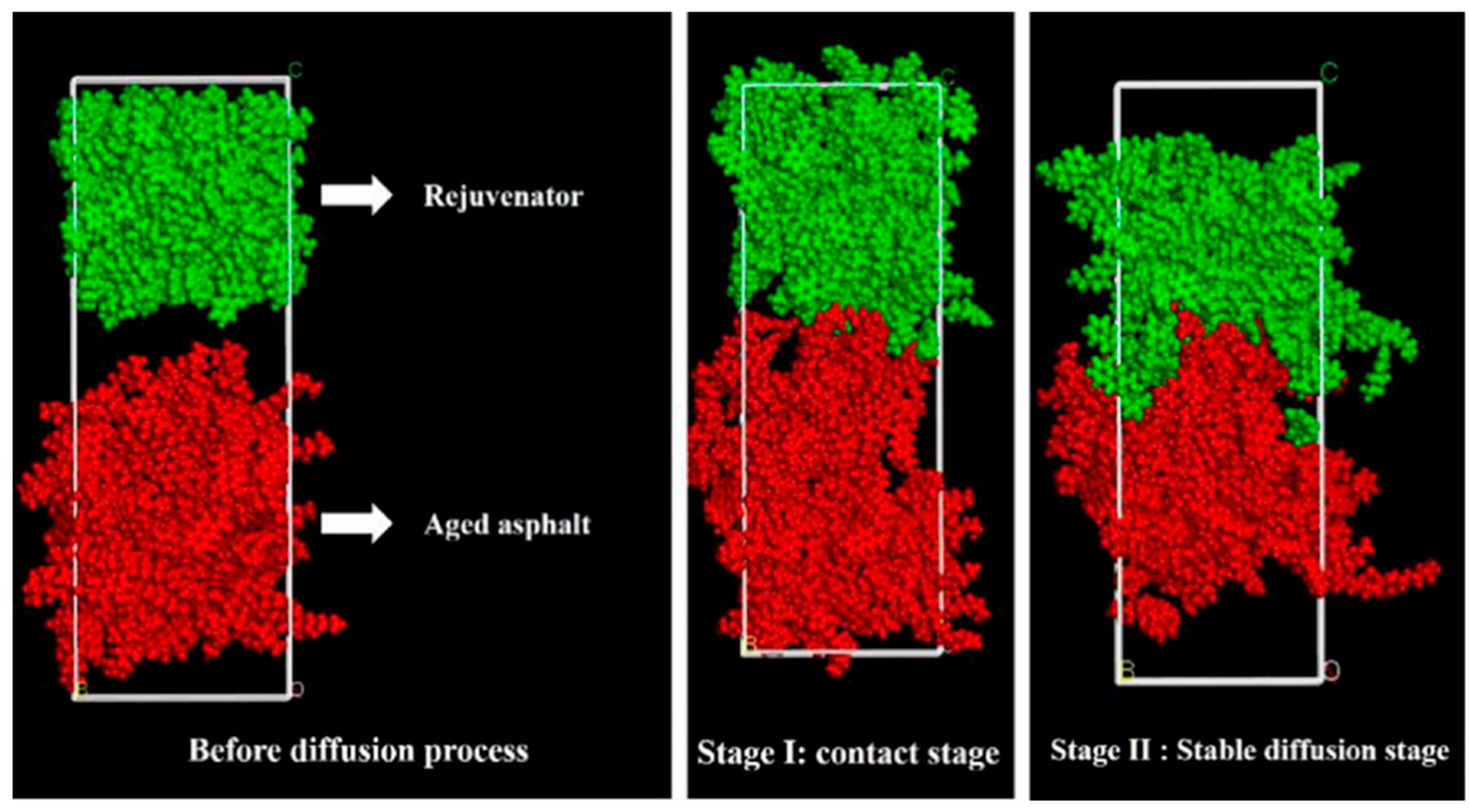
3.1.2. Rejuvenators
3.1.3. Virgin Asphalt
3.1.4. Virgin Asphalt Mixtures
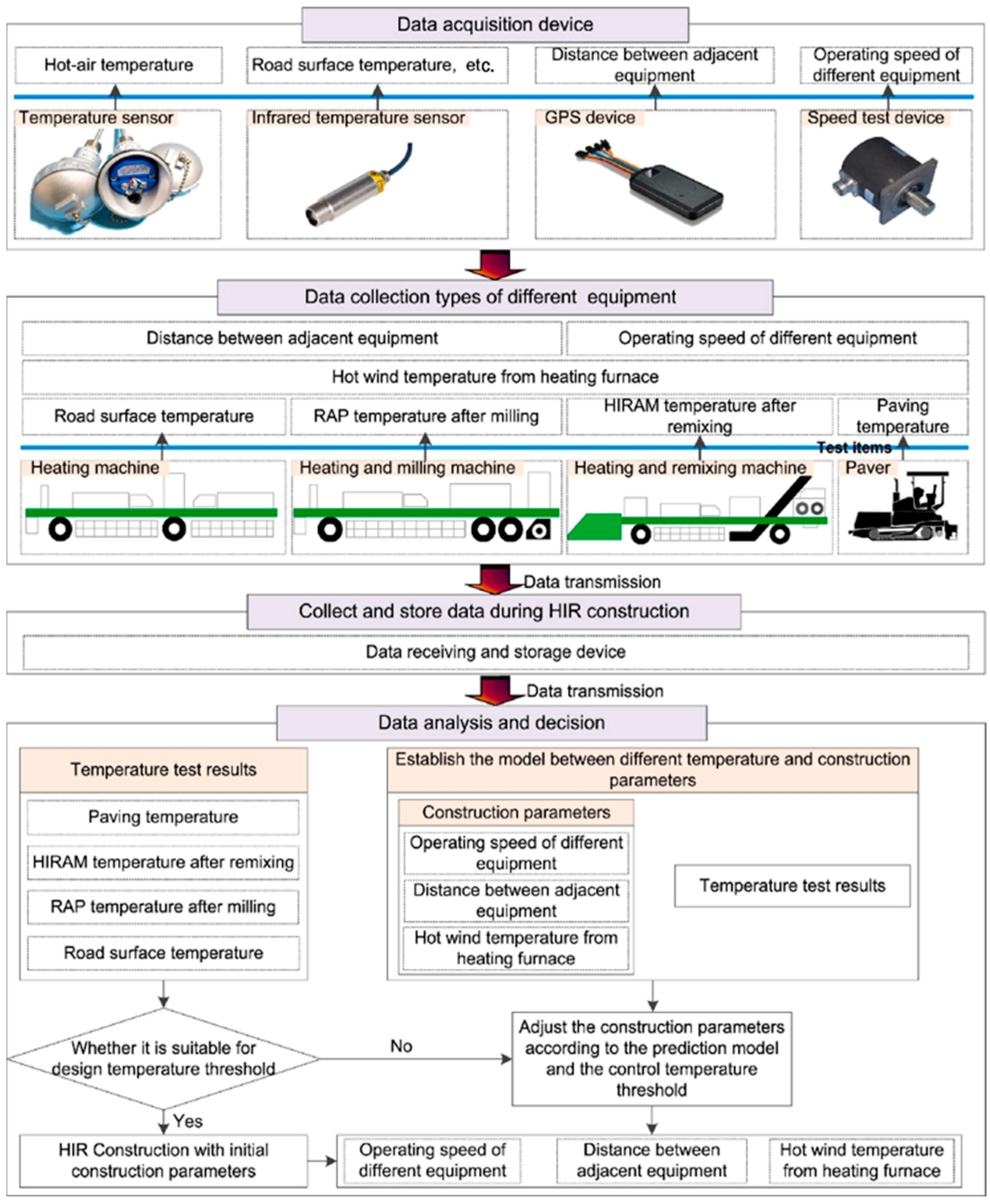
3.2. Production
3.2.1. Preheating
3.2.2. Mixing
4. Long-Term Performance of HIRAMs
5. HIR Benefits
5.1. Environment
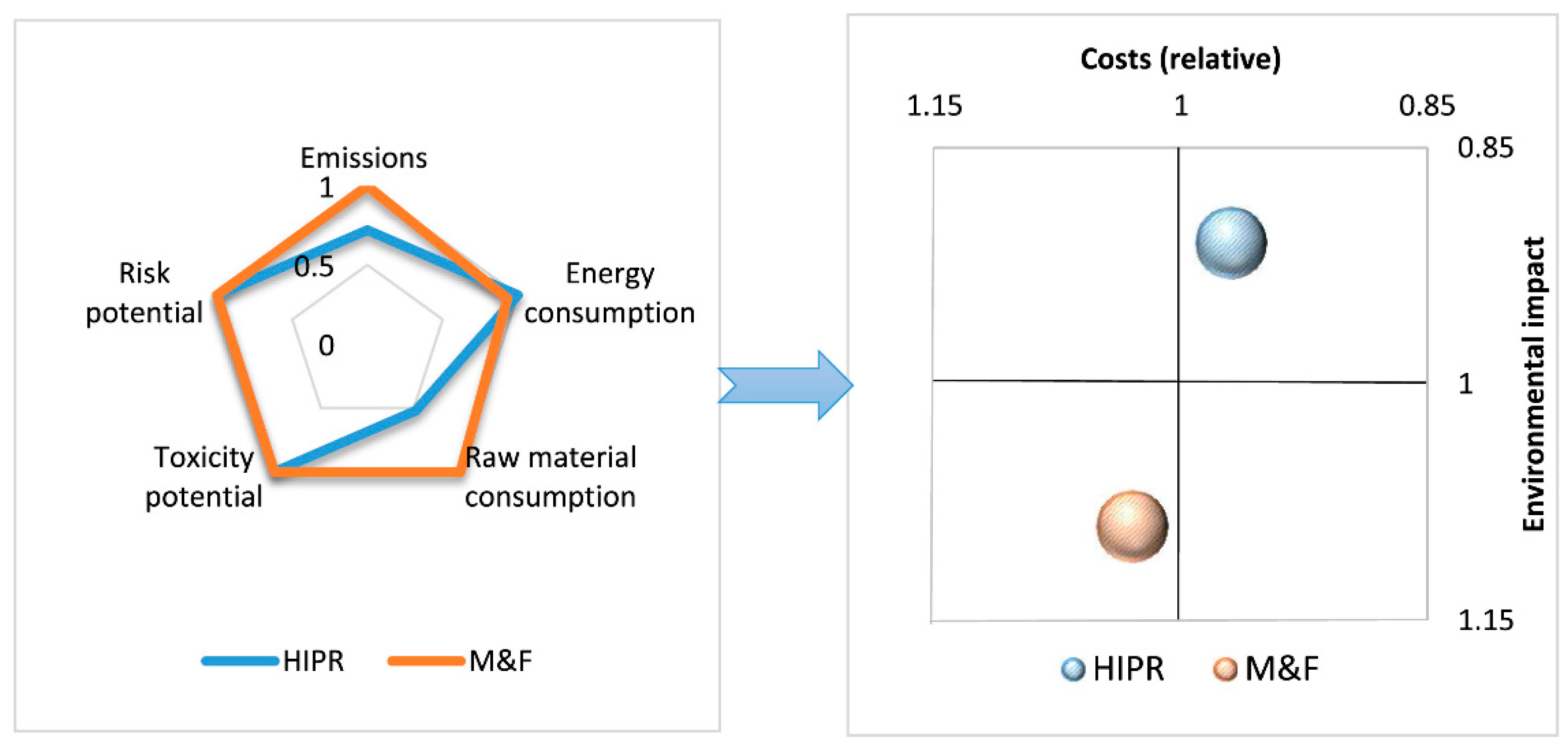
5.1.1. Comparison with Milling and Filling
5.1.2. Comparison with Thin HMA Overlay
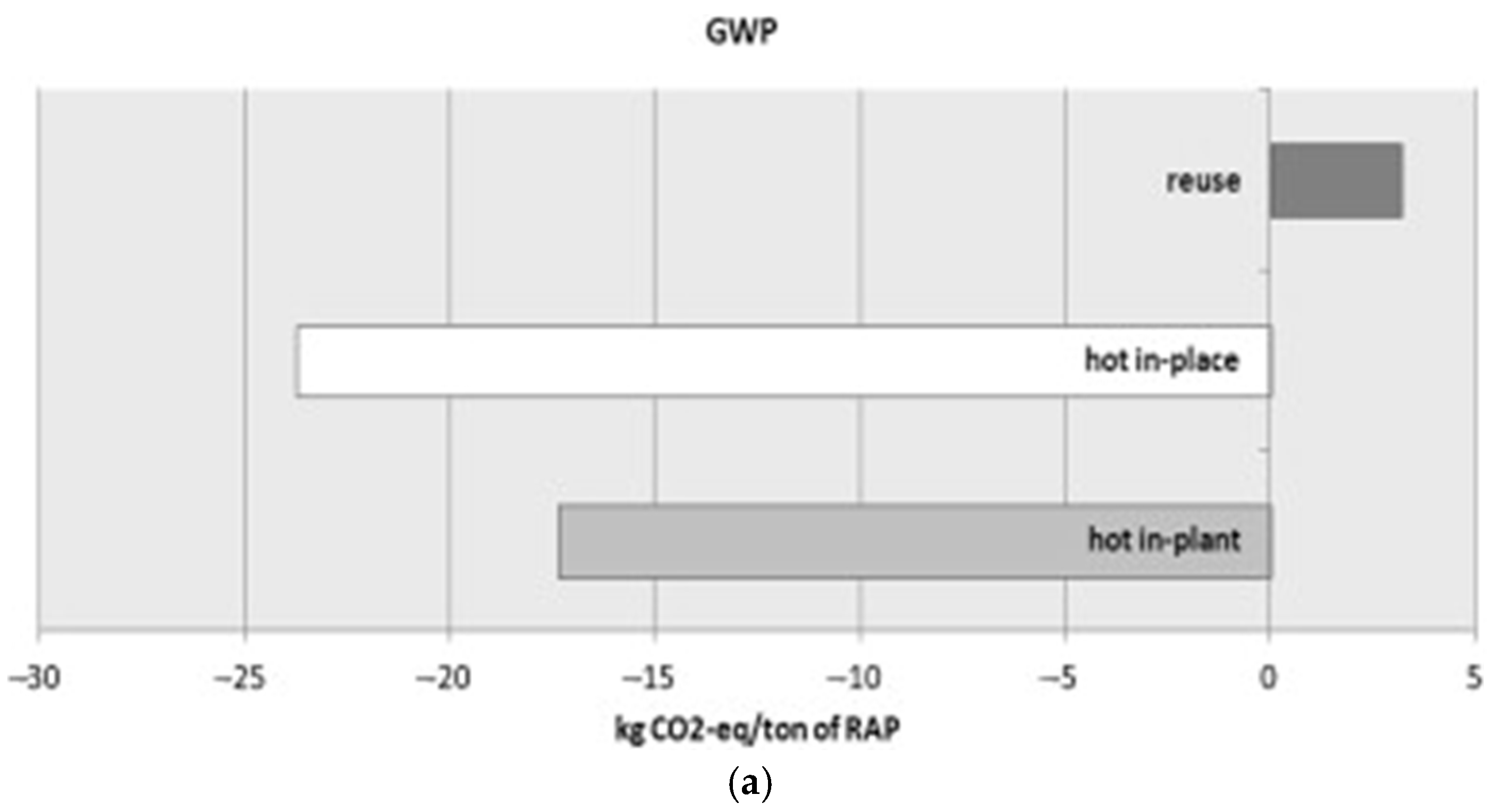
5.1.3. Comparison with Other Recycling Technology
5.1.4. Comparison Between Different HIR Technologies
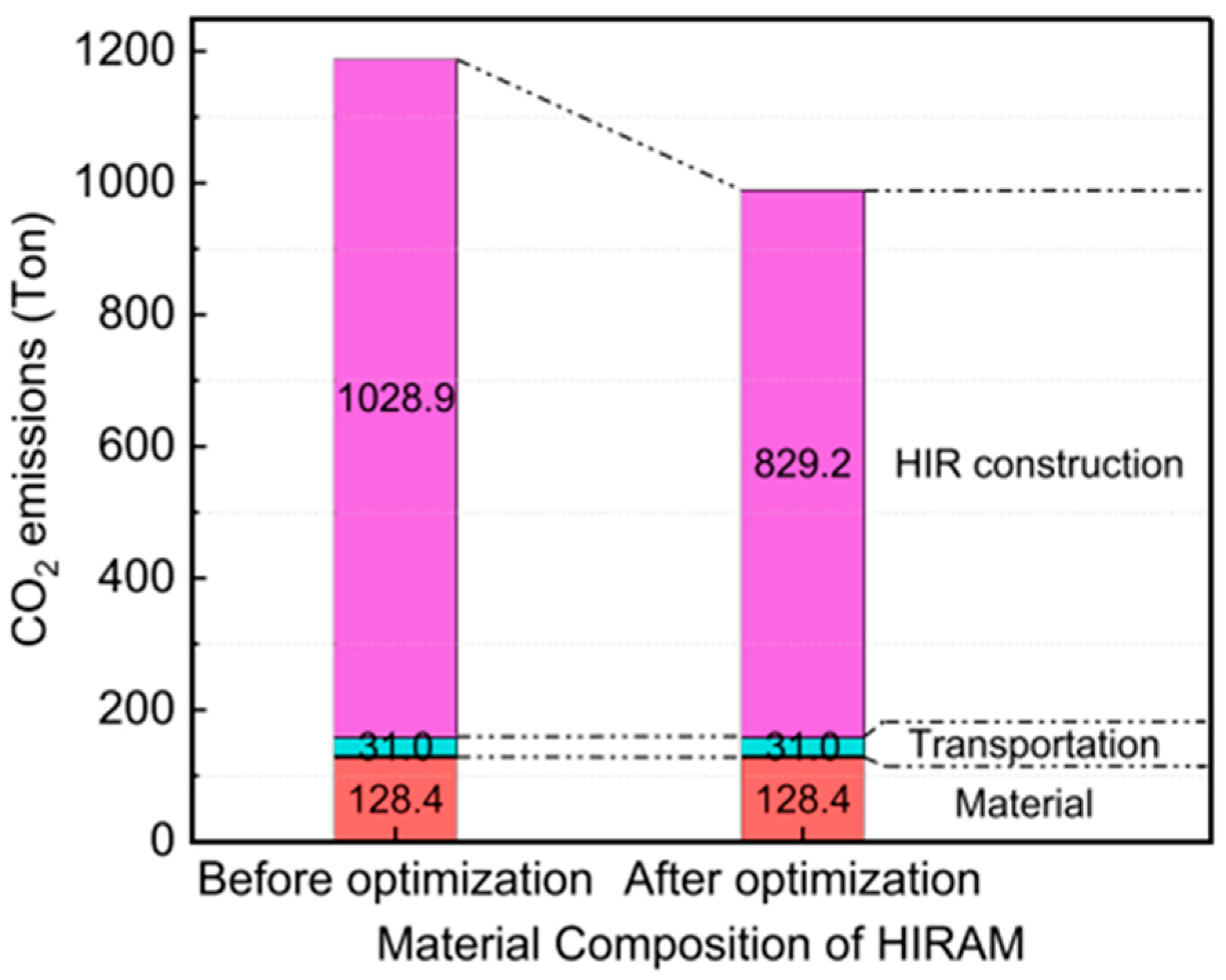
5.1.5. Optimization of HIR Environmental Benefits
5.2. Economy
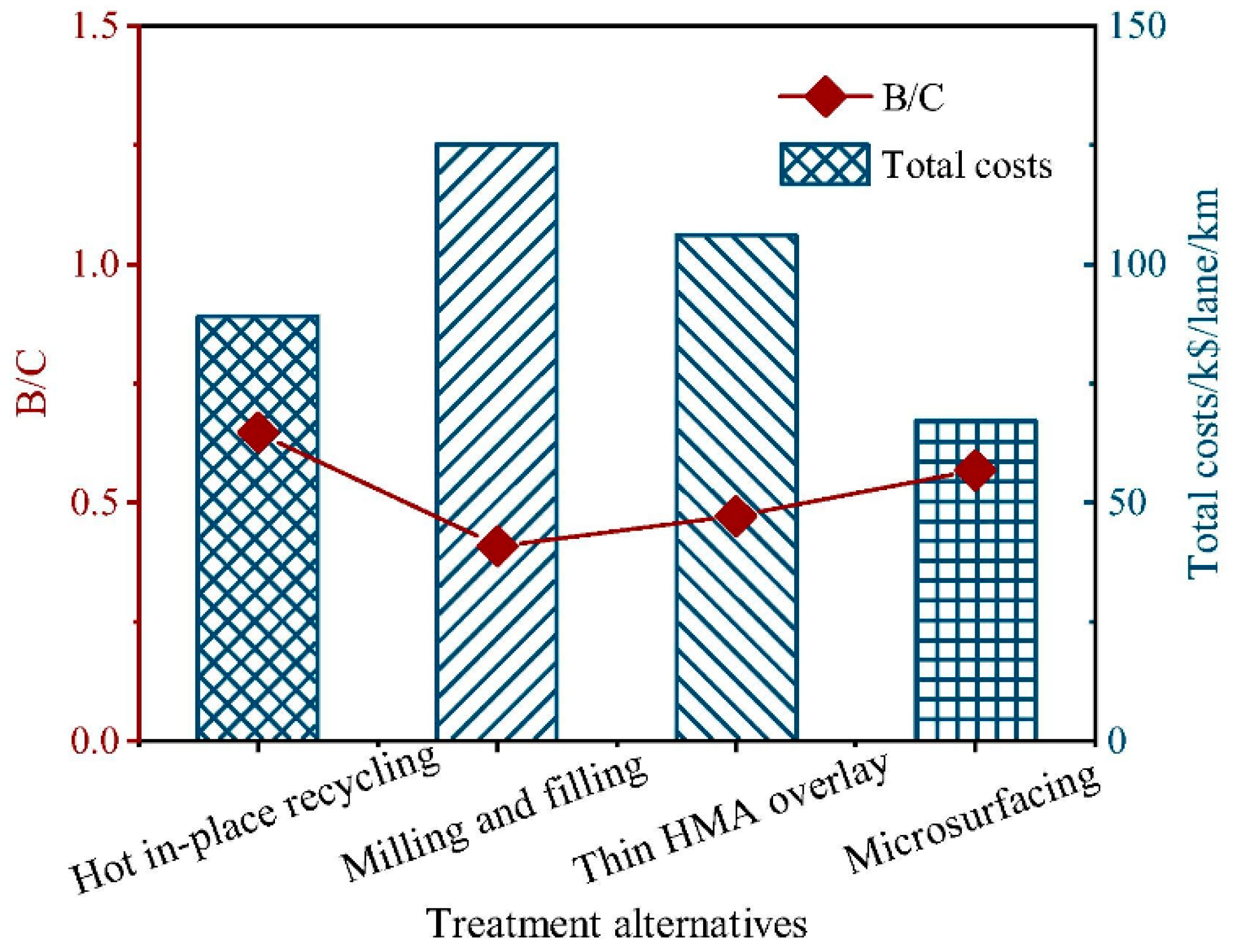
5.2.1. Comparison with Milling and Filling
5.2.2. Comparison with Thin HMA Overlay
5.2.3. Comparison with Other Recycling Technology
5.2.4. Comparison Between Different HIR Technology
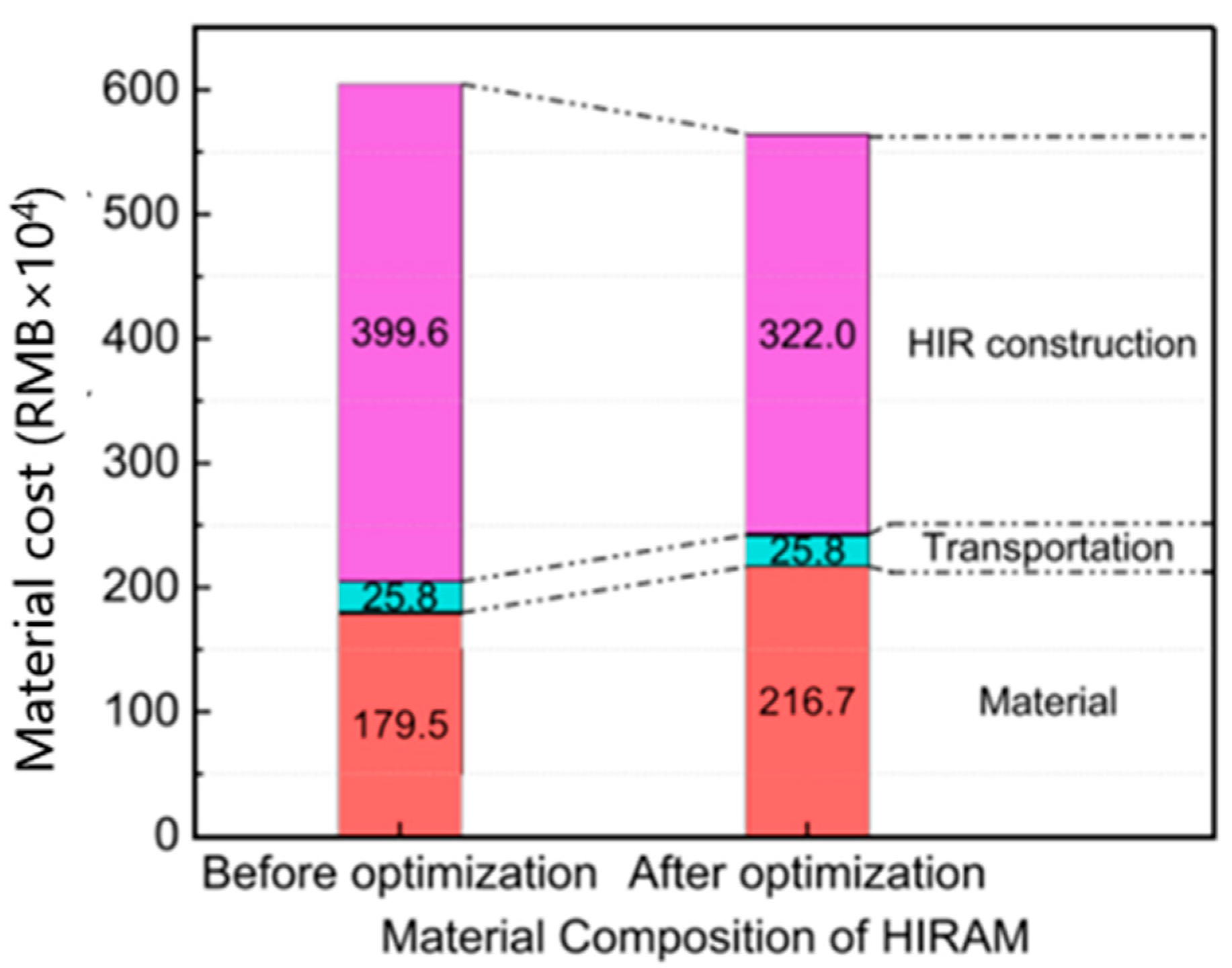
5.2.5. Optimization of HIR Economic Benefits
6. Technical Challenges and Future Research Recommendations
6.1. Applicability of HIR Technology
6.2. Key Factors Affecting the Road Performance of HIRAMs
6.2.1. Raw Materials
6.2.2. Production
6.3. Long-Term Performance of HIRAMs
6.4. HIR Benefits
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HIRAMs | Hot in-place recycling asphalt mixtures |
| HIR | Hot in-place recycling |
| RAP | Reclaimed asphalt pavement |
| VAMs | Virgin asphalt mixtures |
| HCPR | Hot central-plant recycling |
| CIR | Cold in-place recycling |
| HMA | Hot mix asphalt |
| DSR | Dynamic shear rheometer |
| TSR | Tensile strength ratio |
| WEO | Waste engine oil |
| WVO | Waste vegetable oil |
| SBR | Styrene–butadiene rubber latex |
| SBS | Styrene–butadiene-styrene block copolymer |
| M&R | Milling and filling |
| THO | Thin HMA overlay |
| BCR | Benefit–cost ratio |
References
- Dong, F.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Yu, X.; Jiang, M.M.; Guo, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Zu, Y.Z.; Ren, S.S. Regeneration mechanisms of aged SBS modified asphalt from RAP materials: Molecule structure, morphology, phase transition, and interface adhesion characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.; Frank, R. 100% recycled hot mix asphalt: A review and analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 92, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Shukla, A.; Nandra, T. Technological, environmental and economic aspects of Asphalt recycling for road construction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, M.C.; Office, J.E.; Chen, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Falchetto, A.C.; Fang, M.J.; Gu, H.R.; Han, Z.Q.; He, Z.J.; et al. Review of advanced road materials, structures, equipment, and detection technologies. J. Road Eng. 2023, 3, 370–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.Y.; Xing, C.W.; Zhu, B.H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tang, S.X.; Cheng, H.L. Comparative analysis of four styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) structure repair agents in the rejuvenation of aged SBS-modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 476, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.W.; Liu, L.P.; Jiang, W.; Shan, J.H.; Xiao, J.J.; Yuan, D.D.; Wu, W.J. Investigation of internal phases of linear SBS modified bitumen at the nanoscale using AFM PF-QNM. J. Traffic Transp. Eng.-Engl. Ed. 2023, 10, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Asphalt mixtures emission and energy consumption: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, F.P.; Zhu, X.Y.; Huang, B.S.; Wang, J.G.; Amirkhanian, S. Energy consumption and environmental impact of rubberized asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, S.Y.; Gu, X.Y. Estimation and uncertainty analysis of energy consumption and CO2 emission of asphalt pavement maintenance. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Qiao, Z.H.; Zhang, H.T. Evaluation of an economy-technology-green development system for asphalt pavement construction in China based on synergetics. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Dong, Q.; Chen, X.Q.; Gu, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, S. A comprehensive review on the fatigue resistance of recycled asphalt materials: Influential factors, correlations and improvements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magar, S.; Xiao, F.P.; Singh, D.; Showkat, B. Applications of reclaimed asphalt pavement in India-A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.C.; Han, Z.C.; Cheng, H.L.; Yang, R.K.; Yuan, J.; Jin, T. Low-temperature performance improvement strategies for high RAP content recycled asphalt mixtures: Focus on RAP gradation variability and mixing process. Fuel 2025, 387, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.C.; Yuan, J.; Jin, T.; Wang, W.Y.; Sun, Y.R.; Cheng, H.L. Investigation of performance evolution in recycled asphalt mixtures: The impact of virgin and RAP binder blending. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 469, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M.; Zhao, Y.L. Theory and Practice of Asphalt Pavement Recycling; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.P.; Yao, S.L.; Wang, J.G.; Li, X.H.; Amirkhanian, S. A literature review on cold recycling technology of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 579–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.W.; Tang, S.X.; Chang, Z.B.; Han, Z.C.; Li, H.Z.Y.; Zhu, B.H. A comprehensive review on the plant-mixed cold recycling technology of emulsified asphalt: Raw materials and factors affecting performances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Han, D.D.; Yang, T.; Tang, D.; Huang, Y.X.; Tang, N.X.; Zhao, Y.L. Field observations and laboratory evaluations of asphalt pavement maintenance using hot in-place recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, T.B.; Baaj, H. The use of rejuvenating agents in production of recycled hot mix asphalt: A systematic review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.; Nizamuddin, S.; Madapusi, S.; Giustozzi, F. Sustainable asphalt rejuvenation using waste cooking oil: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Polaczyk, P.; Zhang, M.M.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, X.; Huang, B.S. Comparative study of pavement rehabilitation using hot in-place recycling and hot-mix asphalt: Performance evaluation, pavement life prediction, and life cycle cost analysis. Transportation Research Record 2022, 2677, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Study on Application of Hot in-Place Recycling Technology in SMA-13 Pavement. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, H.J.; Cong, Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Song, L.C.; Romanovich, M. Mix ratio optimization design method for hot in-place recycled asphalt mixtures. Dyna 2020, 95, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Pan, B.F. Effect of RAP content on fatigue performance of hot-mixed recycled asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Poulikakos, L.; Frank, R. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Aliha, M.R.M.; Moniri, A.; Saghafi, Y. Crack resistance of hot mix asphalt containing different percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement and glass fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 117015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, X.M.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the diffusion and distribution of the rejuvenator for hot asphalt recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.J.; Guo, D.D.; Yuan, D.D.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, W.T. Study on the blending behavior of asphalt binder in mixing process of hot recycling. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Grzybowski, K. Life cycle of hot in-place pavement recycling case study. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2292, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.J.; Leng, Z.; Hsu, S.C. Comparative eco-efficiency analysis on asphalt pavement rehabilitation alternatives: Hot in-place recycling and milling-and-filling. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Wang, H. Life cycle assessment of asphalt pavement recycling for greenhouse gas emission with temporal aspect. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliutenko, S.; Björklund, A.; Carlsson, A. Opportunities for environmentally improved asphalt recycling: The example of Sweden. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 43, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Q.; Yang, J.G.; Gao, J.; Zheng, M.L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, L. Strategy for improving the effect of hot in-place recycling of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Tighe, S.; Zhao, G.Y.; You, Z.P. Effects of preheating conditions on performance and workability of hot in-place recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Tighe, S.; Pickel, D.; You, Z.P. Study on impact of variables to pavement preheating operation in HIR by using FEM. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.Z.; Gu, H.R.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.P.; Yue, K. Heating power control in asphalt pavement in-place hot recycling. China J. Highw. Transp. 2016, 29, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M. Road Subgrade and Pavement Engineering; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Lu, R.; Liu, N.; Wu, W.; Yuan, D. A comprehensive review on the blending condition between virgin and RAP asphalt binders in hot recycled asphalt mixtures: Mechanisms, evaluation methods, and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 398, 136515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.X.; Wei, D.B.; Zhao, J.Z.; Zhang, J.L.; Ma, Y.G. Study on low temperature cracking resistance of recycled asphalt based on glover-rowe parameter. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 38, 905–910+917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S. Research on Cracking and Fatigue Resistance of Compounded In-Situ Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixes. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.Q.; Yu, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.Y. Comparison of high temperature performance and microstructure for foamed WMA and HMA with RAP binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Z.X.; Li, W.B.; Zou, X.L. Study on waste engine oil and waste cooking oil on performance improvement of aged asphalt and application in reclaimed asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Tan, B.Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, F. Evaluation on recycling effect of a novel rejuvenator combined with fresh asphalt on field-aged SBS modified asphalt by rheological and micro characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Shoukat, T.; Yoo, P.J.; Lee, S.H. Strengthening of hybrid glass fiber reinforced recycled hot-mix asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 118947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.F.; Karimi, M.M.; Jahanbakhsh, H.; Tabatabaee, N. Cracking performance of rubberized RAP mixtures with Sasobit. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, B.; You, Z.P. The determination of mechanical performance of laboratory produced hot mix asphalt mixtures using controlled RAP and virgin aggregate size fractions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, F.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.F.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wu, S.P.; Wei, M.H.; Xie, J. Multi-scale performance evaluation and correlation analysis of blended asphalt and recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating high RAP content. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Q.; Ma, T.; Fan, J.W.; Fang, Z.Y.; Chen, T.; Zhou, Y. Experimental study of high modulus asphalt mixture containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, W.W.; Liu, K.; Lv, S.T.; Peng, X.H.; Yang, S.; Ding, S. Research on failure strength master curve and fatigue performance of asphalt mixture containing high-proportion reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Liu, G.Q.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.L. Recycling aged asphalt using hard asphalt binder for hot-mixing recycled asphalt mixture. Applied Sciences-Basel 2021, 11, 11125698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.H.; Li, X.J. Comprehensive review on the application of bio-rejuvenator in the regeneration of waste asphalt materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A. Application of rejuvenators to improve the rheological and mechanical properties of asphalt binders and mixtures: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwettmann, K.; Nytus, N.; Weigel, S.; Radenberg, M.; Stephan, D. Effects of rejuvenators on bitumen ageing during simulated cyclic reuse: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, Z.S.; Xu, M.; Feng, D.C. Mechanisms and research progress on biological rejuvenators for regenerating aged asphalt: Review and discussion. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Fan, W.Y.; Qian, C.D.; Nan, G.Z.; Erkens, S. Investigating the effects of waste oil and styrene-butadiene rubber on restoring and improving the viscoelastic, compatibility, and aging properties of aged asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; You, Z.P.; Wang, H.N.; Ye, M.X.; Yap, Y.K.; Si, C.D. The impact of bio-oil as rejuvenator for aged asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.G.; Wei, J.C.; Yao, Z.Y. Influence of different rejuvenating agents on rheological behavior and dynamic response of recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating 60% RAP dosage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.B.; Hossain, K. Waste cooking oil as an asphalt rejuvenator: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Ge, D.D.; Ju, Z.H.; Lv, S.T.; Xue, Y.H.; Xue, Y.Y.; Peng, L.C. Study on performance and mechanism of SBR and Bio-oil recycled SBS modified asphalt. Polymers 2022, 14, 14235096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashef, M.; Williams, R.C. Improving fatigue and low temperature performance of 100% RAP mixtures using a soybean-derived rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Moniri, A.; Bahri, P.; Saghafi, Y. The effect of rejuvenators on the aging resistance of recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryaee, D.; Ameri, M.; Mansourkhaki, A. Utilizing of waste polymer modified bitumen in combination with rejuvenator in high reclaimed asphalt pavement mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.T.; Fan, Q.J.; Hou, M.Y.; Mi, S.Z.; Yan, X.H. Effects of rejuvenator dosage, temperature, RAP content and rejuvenation process on the road performance of recycled asphalt mixture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15043539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Yang, T.; Chen, A.Q.; Li, X.G.; Zhao, Y.L. Determination of virgin asphalt mixture content in hot in-place recycling based on field rutting depth variability. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 05023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Bian, G.J. Investigation of aged asphalt film transfer during hot in-place recycling of asphalt pavement. In Proceedings of the Japan-China Pavement Technologies, Wuhan, China, 12–14 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Influences of preheating temperature of RAP on properties of hot-mix recycled asphalt mixture. J. Test. Eval. 2016, 44, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Polaczyk, P.; Park, H.; Jiang, X.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.S. Performance evaluation of temperature effect on hot in-place recycling asphalt mixtures. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 277, 124093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Tighe, S.; Zhao, G.Y.; You, Z.P. Effects of preheating on the rheological properties of rejuvenated asphalt binder. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.N.; Liu, B.Y.; Feng, D.C.; Li, G. Analysis of factors influencing the modulus of hot-recycled asphalt mixture with high RAP. Materials 2023, 16, 16155280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.C.; Liu, L.P.; Xing, C.W.; Liu, L.X.; Wang, H.Y. Influence of rejuvenator preheating temperature and recycled mixture’s curing time on performance of hot recycled mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Polaczyk, P.; Hu, W.; Zhang, M.M.; Huang, B.S. Quantifying the effective mobilized RAP content during hot in-place recycling techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Polaczyk, P.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, B.S. Influence of mobilized RAP content on the effective binder quality and performance of 100% hot in-place recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Ma, T.; Xu, G.J.; Fan, J.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, M. Study of the mixing between asphalt and rejuvenator in hot in-place recycled layer. J. Transp. Eng. Part B-Pavements 2023, 149, 04023005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.L.; Huang, X.M. Evaluation of dispersive performance of asphalt mixture during mixing of hot in-place recycling. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology 2011, 43, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Lv, X.C.; Zhou, Y.H.; You, Z.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Cui, Z.J.; Diab, A. Homogeneity evaluation of hot in-place recycling asphalt mixture using digital image processing technique. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 258, 120524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.P.; Li, S.Q.; Xu, X.Q.; Luo, X.P.; Liu, F. Investigation and Evaluation on Long-term Performance of Geothermal Recycled Pavement of Expressway in Guangdong Province. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng. Ed.) 2023, 47, 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.L. Analysis of Long-term Performance and Economic Benefits of Hot In-Place Recycling of Highway Asphalt Pavements. Transp. Bus. China 2021, 8, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Li, F. Analysis of short-term and long-term effects of different hot in-place recycling equipment for treating asphalt pavements. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2019, 15, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.; Ren, Q.G.; Zeng, H. Applicability evaluation of pavement recycling technology in hot and rainy areas. Shanxi Archit. 2025, 51, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurangzeb, Q.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Yang, R. Hybrid life cycle assessment for asphalt mixtures with high RAP content. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, Y. Method of mix design for hot recycled asphalt mixtures. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 584–586, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, W.; Napiah, M.; Sutanto, M.H.; Alaloul, W.S.; Khan, M.I.; Al-Sabaeei, A. Performance evaluation for rutting and moisture damage of hot asphalt mixtures using high percentage of recycled asphalt pavement material. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering for Sustainability (IConCEES), Senai, Malaysia, 19–20 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, M.M.; Li, M.; Qi, G.C.; Wang, T. Analysis of carbon emission during hot in-place recycling asphalt pavement construction. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development 2016, 33, 148–151,158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Huang, Y.; Peng, X.N.; Wang, H.X. Analysis on energy consumption and carbon emission of hot in-place recycled asphalt pavement in construction period. Journal of Chang’An University. Natural Science Edition 2022, 42, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.R.; Cai, H.Q.; Yan, J.H.; Li, H.; Li, H. Incorporating life cycle science into asphalt pavement maintenance decision making. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Congress (Trc), Beijing, China; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.G. Quantitative Research on Energy Consumption and Carbon Emission of Typical Asphalt Pavement Recycling Technologies. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Chongqing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, L.W. The Applicability Disquisition of Hot in-Place Recycling Technology in Asphalt Pavement’s Pre-Maintenance of Expressway. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W. Research on Comprehensive Strategies of Recycled Asphalt Pavement in Jiangsu Province. Master’s Thesis, Southeast University, Chongqing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.Y. Study on Post Evaluation of Prevention and Maintenance Technology of Ordinary Road in Mountainous Area. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Wang, S.Y.; Gu, X.Y.; Ni, F.J.; Liu, Q. Environmental burden evaluation of hot in-place recycling of asphalt pavement based on discrete event simulation. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2018, 65, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Environmental Impacts Evaluation of Hot in-Place Recycling of Asphalt Pavement. Master’s Thesis, Southeast University, Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Meng, X.C.; Liu, Q. Multi-objective optimisation of hot in-place recycling of asphalt pavement considering environmental impact, cost and construction quality. International Journal of Pavement Engineering 2020, 21, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
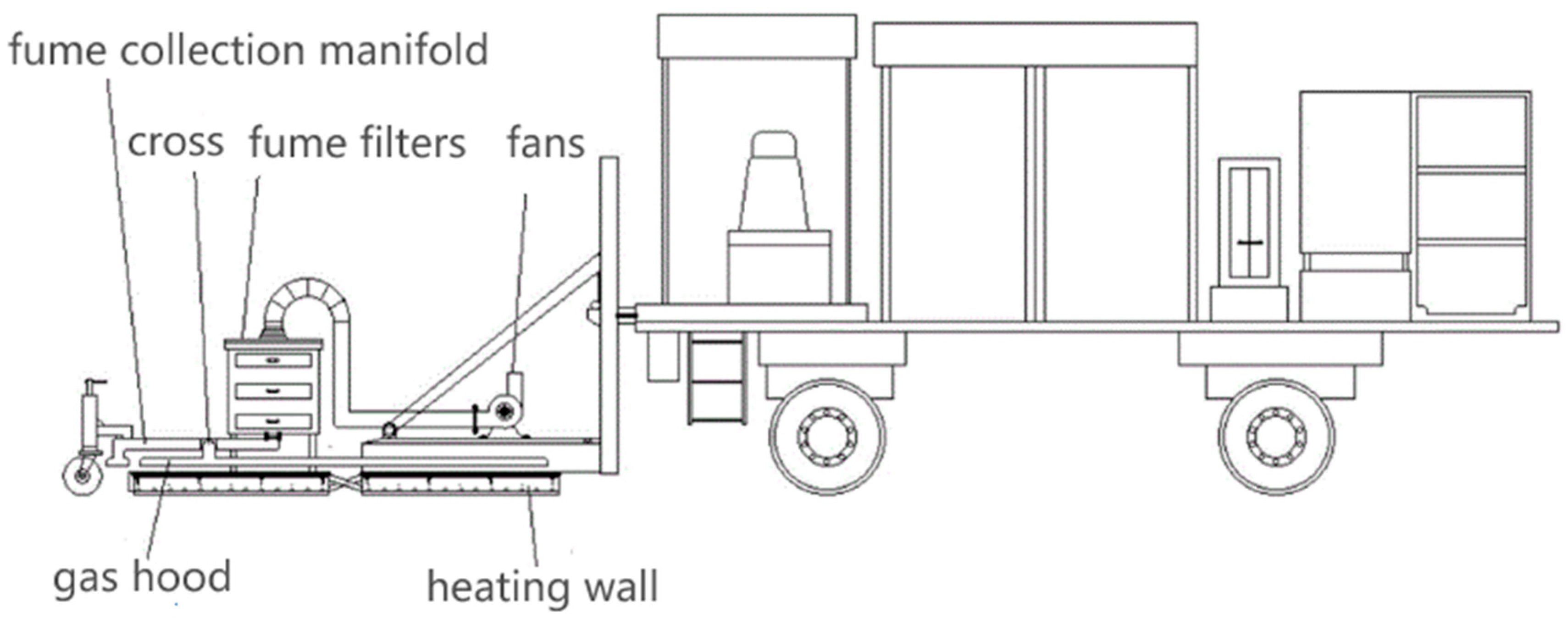
- Mo, S.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Xiong, F.; Ai, C.J.; Wang, D.W.; Tan, G.Y.A. Changes of asphalt fumes in hot-mix asphalt pavement recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.G.; Liu, X.Y.; Xie, L.Y. A Hot In-Place Recycling Asphalt Fume Treatment Device. China Patent CN210751705U, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.X. Research on Hot in-Place Recycling for Asphalt Pavement of National and Provincial Trunk Roads Based on Clean Perspective. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, V.; Freire, A.C.; Neves, J. A review on the effect of RAP recycling on bituminous mixtures properties and the viability of multi-recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R. Review of very high-content reclaimed asphalt use in plant-produced pavements: State of the art. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2015, 16, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Prozzi, J. Evaluation of recycled asphalt pavement using economic, environmental, and energy metrics based on long-term pavement performance sections. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 19, 1816–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L. Introduction to the current situation and future prospect of the asphalt pavement recycling technology. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Engineering Applications (ISDEA), Zhangjiajie, China, 6–7 November 2013; pp. 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, J. Using recycled asphalt pavement in construction of transportation infrastructure: Alaska experience. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Xie, Y.C.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhao, Y.L. Cost-effectiveness evaluation of pavement maintenance treatments using multiple regression and life-cycle cost analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.J.; Han, C.J.; Ma, T.; Huang, X.M.; Huang, R.J. Planning and benefits of comprehensive recycling stations for old asphalt materials in road network. J. Southeast Univ. (Naturnal Sci. Ed.) 2022, 52, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.Q.; Gao, J.; Yang, J.G. Optimization and benefit evaluation of construction parameters for hot in-place recycling (HIR) of asphalt pavement. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.B.; Huang, W.D.; Yan, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Sun, L.J.; Liu, L.Y. Investigating binder aging during hot in-place recycling (HIR) of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, Q.Z.; Liu, S.Y. Research on application of warm mix asphalt technology in hot in-place recycled engineering. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Civil Engineering, Architecture and Building Materials (CEABM 2013), Jinan, China, 25–26 May 2013; pp. 1655–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Bouraima, M.B.; Zhang, X.H.; Rahman, A.; Qiu, Y.J. A comparative study on asphalt binder and mixture performance of two traffic lanes during hot in-place recycling (HIR) procedure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Recycling Process | Characteristics | Features and Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| Surface recycling | Only rejuvenators need to be added. | Surface recycling is suitable for roads with little road damage and small damaged areas and can eliminate cracks and ruts in the original pavement. |
| Remixing | Rejuvenators, virgin asphalt (if necessary), and asphalt mixtures are added. | Remixing is suitable for moderately damaged pavement and can improve the material performance of old asphalt pavement, repair aging and unstable wear layers, and improve pavement strength. |
| Repaving | On the basis of the surface recycling and remixing, an abrasion layer is added. | Repaving is applicable to severely damaged roads. The rehabilitated asphalt pavement has good skid resistance, improved cross slope, and increased pavement strength. |
| Influence Factor | Performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Temperature | Moisture Susceptibility | Low Temperature | Fatigue | |||
| RAP | Content | ✓ | ✓ | ❖ | ✓ | |
| ❖ | ❖ | |||||
| Aging degree | ✓ | N/A | ❖ | N/A | ||
| Rejuvenators | Types | Mineral oil | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ❖ | ||||||
| Bio-oil | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| ❖ | ||||||
| Composite oil | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Content | Mineral oil | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Bio-oil | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| ❖ | ||||||
| Composite oil | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||
| Virgin asphalt | Types | Base asphalt | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Modified asphalt | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Content | Base asphalt | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Modified asphalt | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| VAM | Types | Continuously graded | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | N/A |
| Gap-graded | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | N/A | ||
| Content | Continuously graded | ❖ | ✓ | ✓ | N/A | |
| ❖ | ||||||
| Gap-graded | ✓ | ✓ | ❖ | N/A | ||
| ❖ | ❖ | |||||
| Production | Preheating temperature | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| ❖ | ||||||
| Mixing temperature and time | ❖ | N/A | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, C.; Li, H.; Chang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, S.; Zhu, B. A Comprehensive Review of Hot In-Place Recycling Technology: Classification, Factors Affecting Performance of Asphalt Mixtures, and Benefits Analysis. Coatings 2025, 15, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070794
Xing C, Li H, Chang Z, Cheng H, Zhang H, Tang S, Zhu B. A Comprehensive Review of Hot In-Place Recycling Technology: Classification, Factors Affecting Performance of Asphalt Mixtures, and Benefits Analysis. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070794
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Chengwei, Haozongyang Li, Zhibin Chang, Huailei Cheng, Hengji Zhang, Shixian Tang, and Bohan Zhu. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of Hot In-Place Recycling Technology: Classification, Factors Affecting Performance of Asphalt Mixtures, and Benefits Analysis" Coatings 15, no. 7: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070794
APA StyleXing, C., Li, H., Chang, Z., Cheng, H., Zhang, H., Tang, S., & Zhu, B. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of Hot In-Place Recycling Technology: Classification, Factors Affecting Performance of Asphalt Mixtures, and Benefits Analysis. Coatings, 15(7), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070794








