Optimized Control of Hot-Working Parameters in Hot-Forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Medium-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Initial Material
2.2. Hot Compression Experiments
2.3. Phase and Microstructure Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
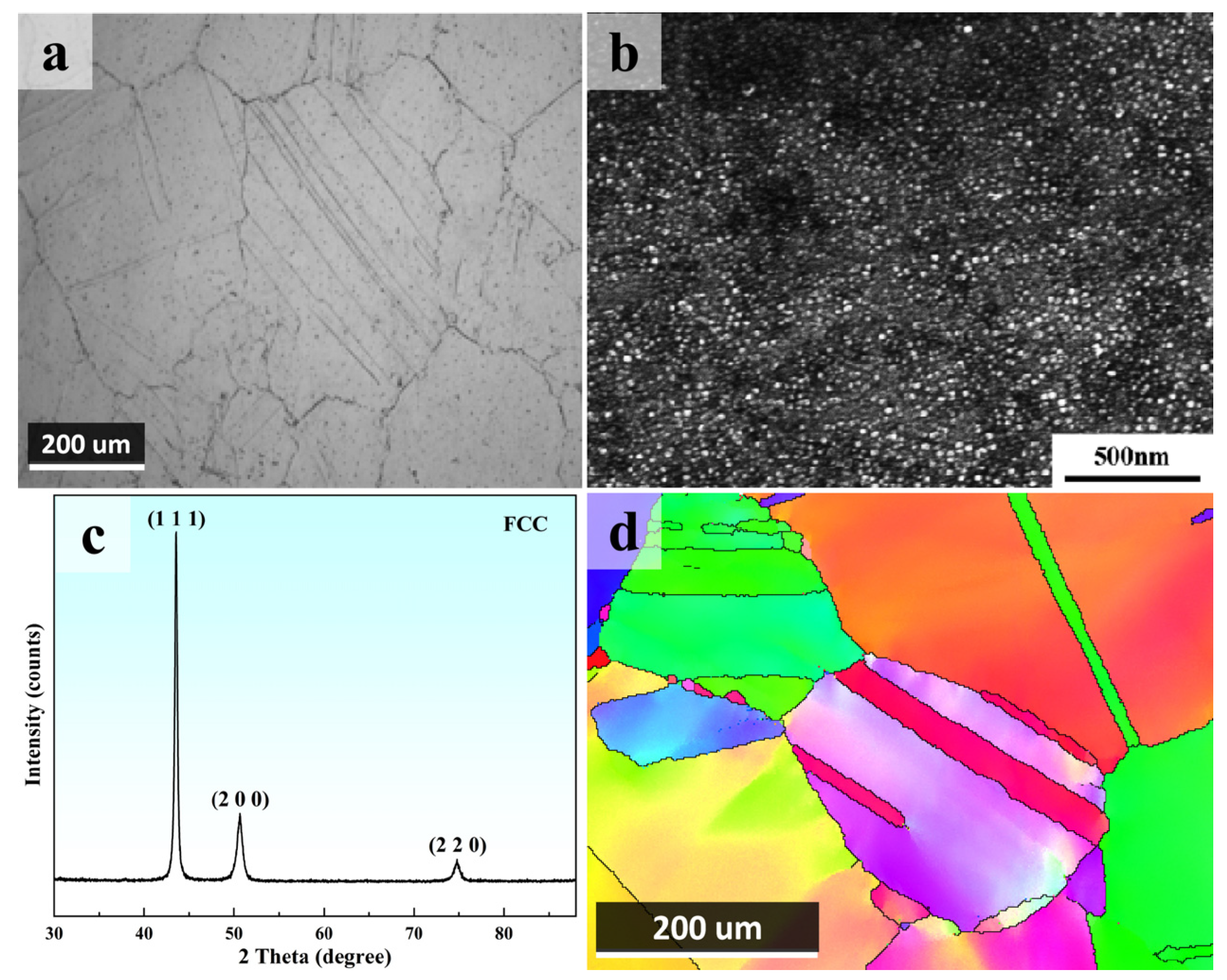
3.1. Initial Structure
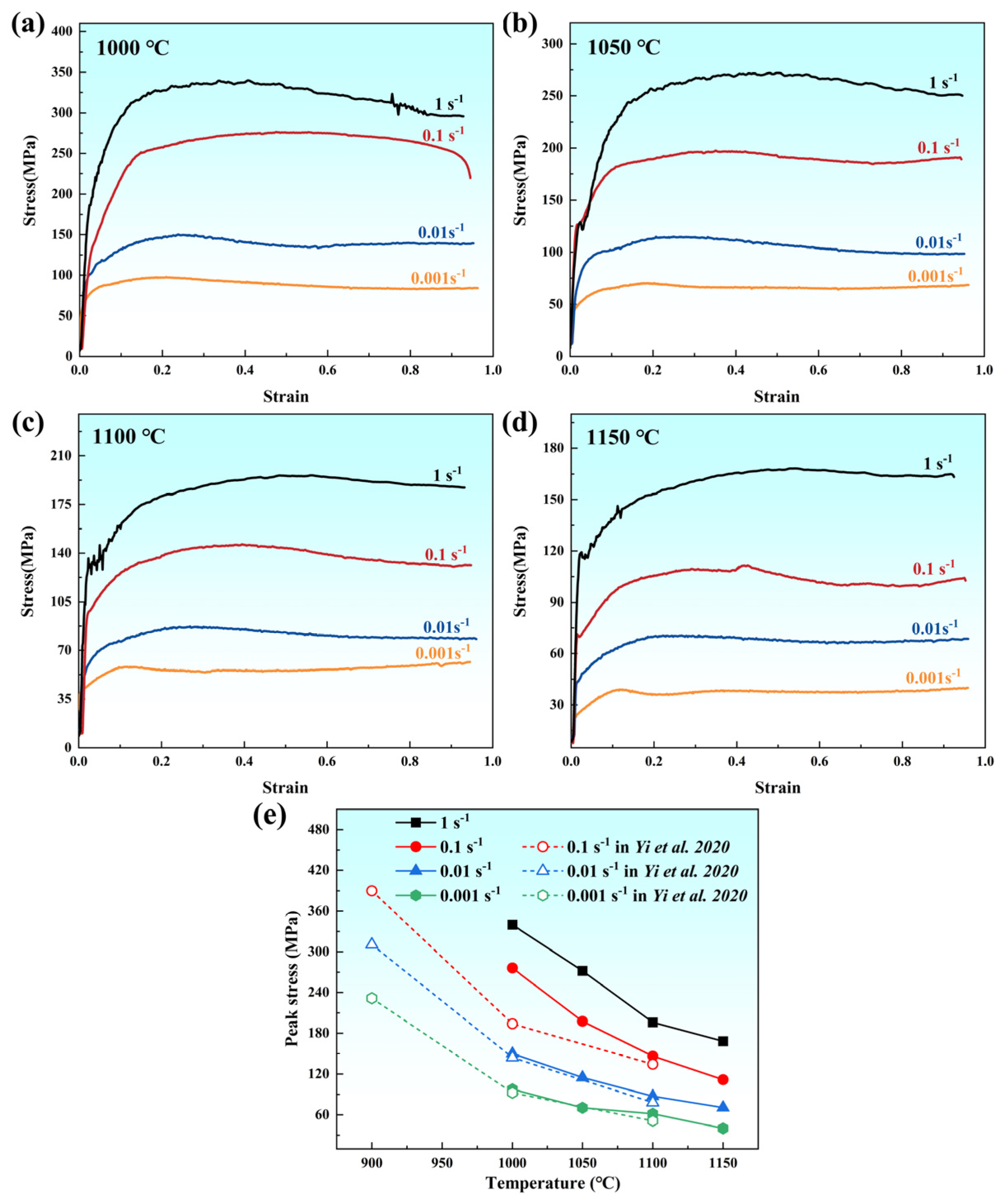
3.2. High-Temperature Plastic Flow Behavior
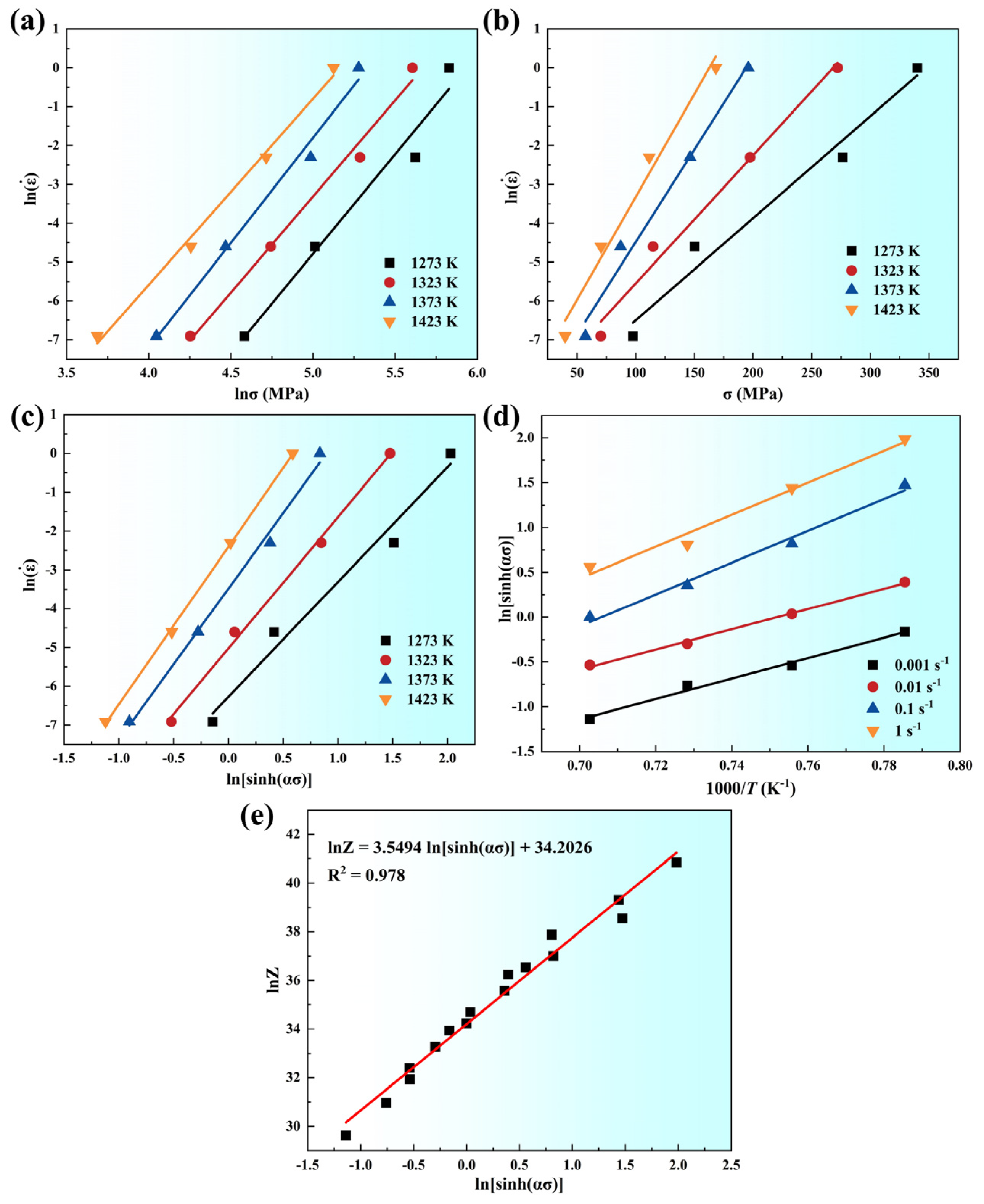
3.3. Constitutive Law Construction
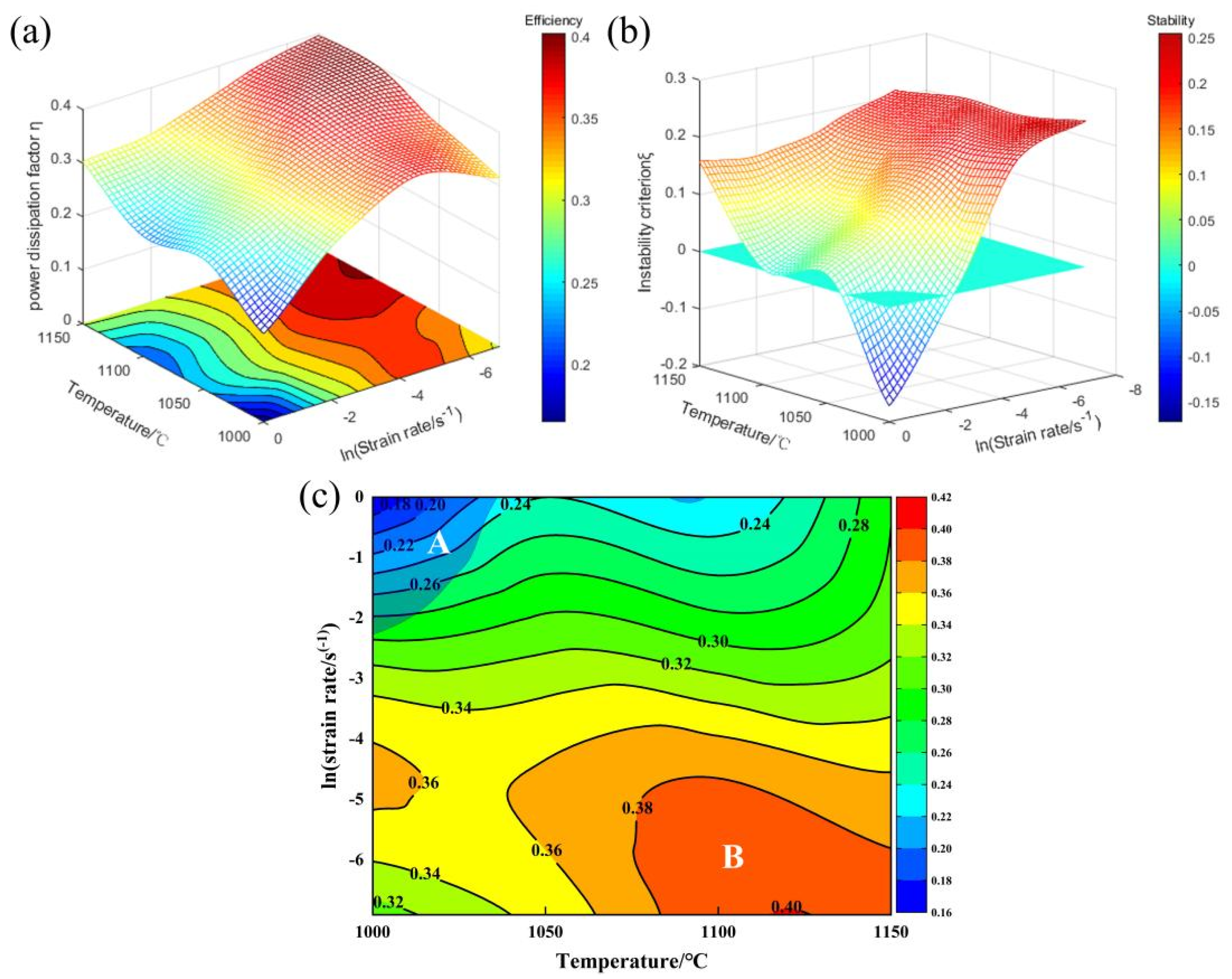
3.4. Processing Maps
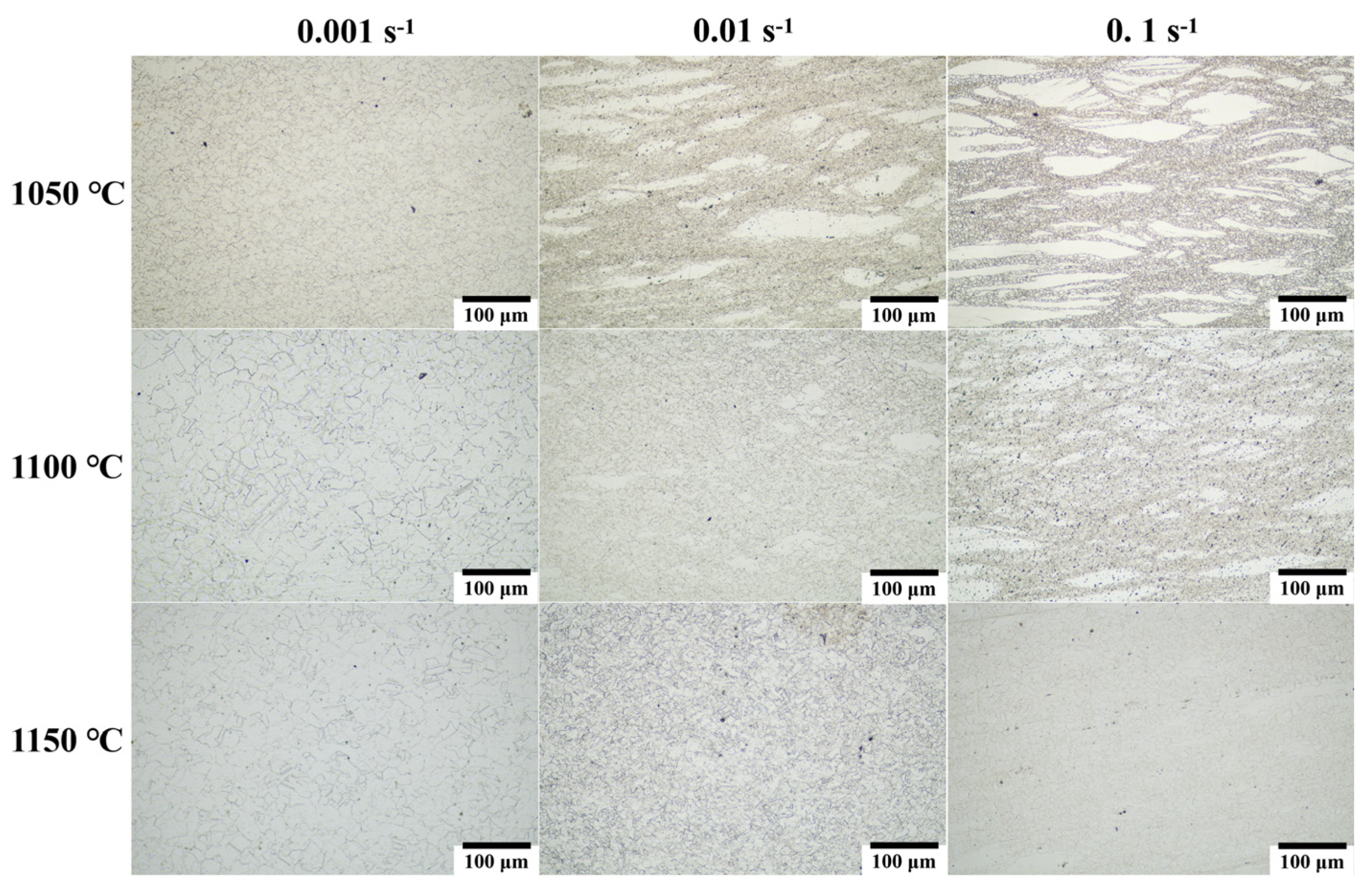
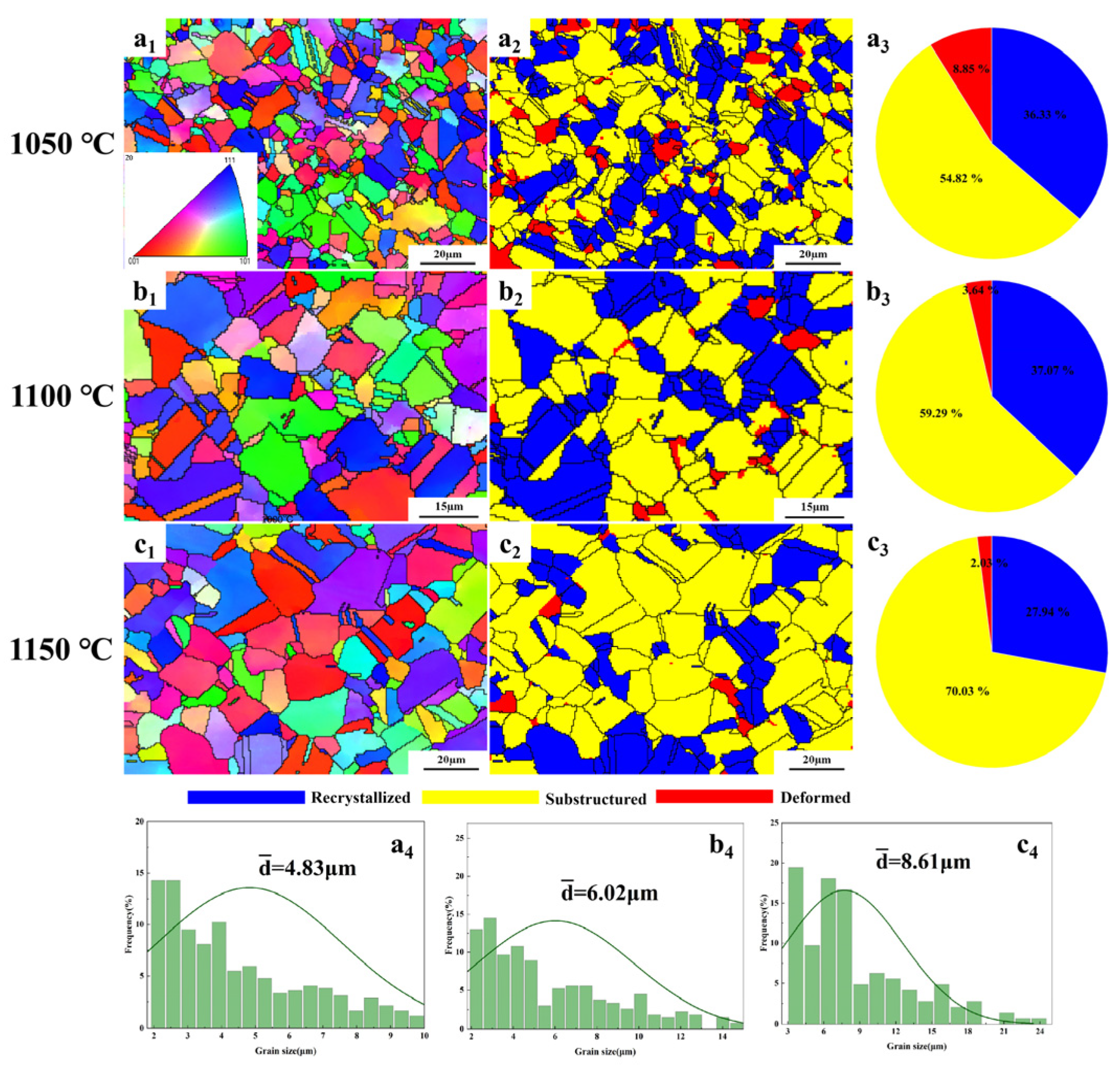
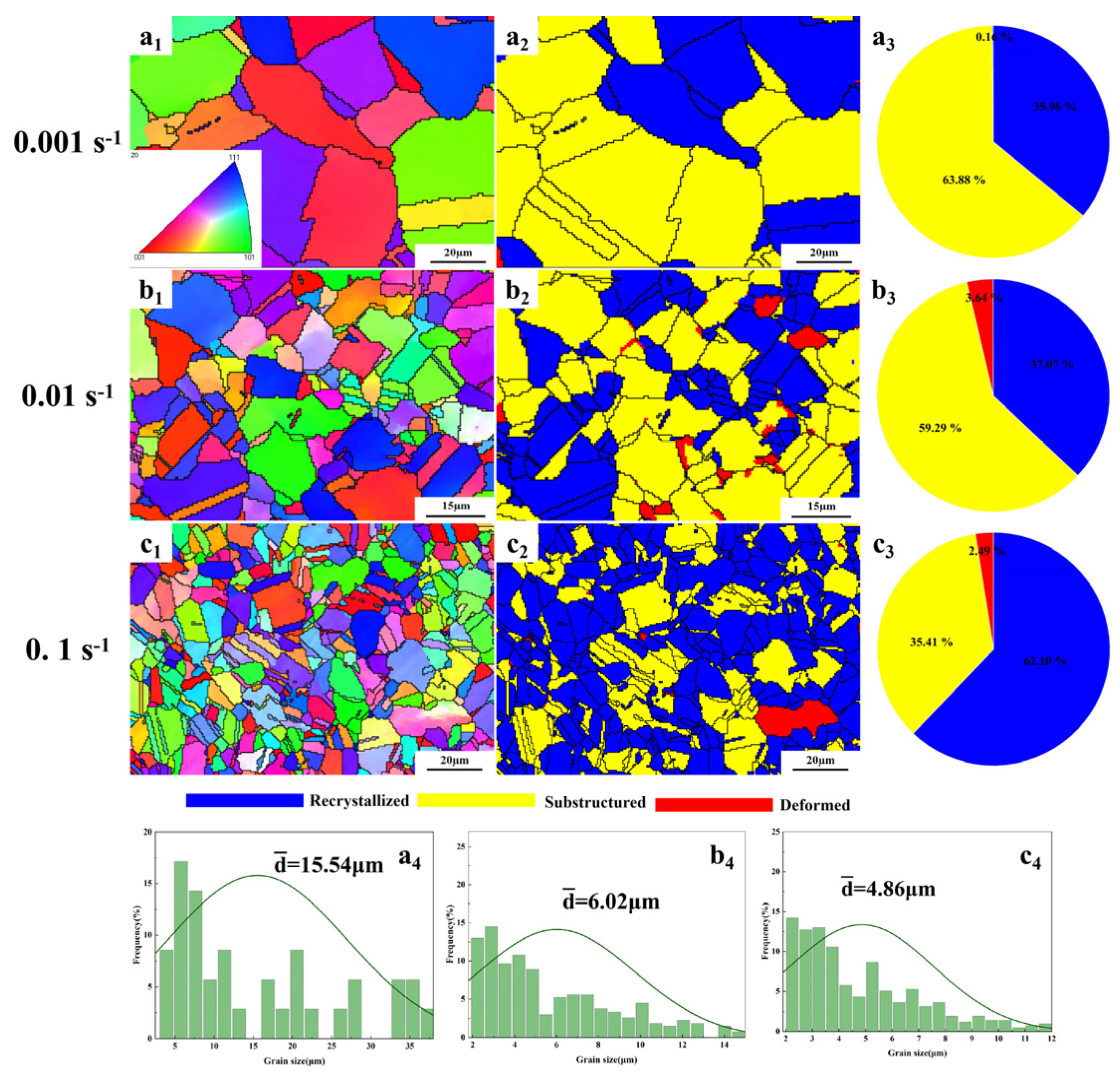
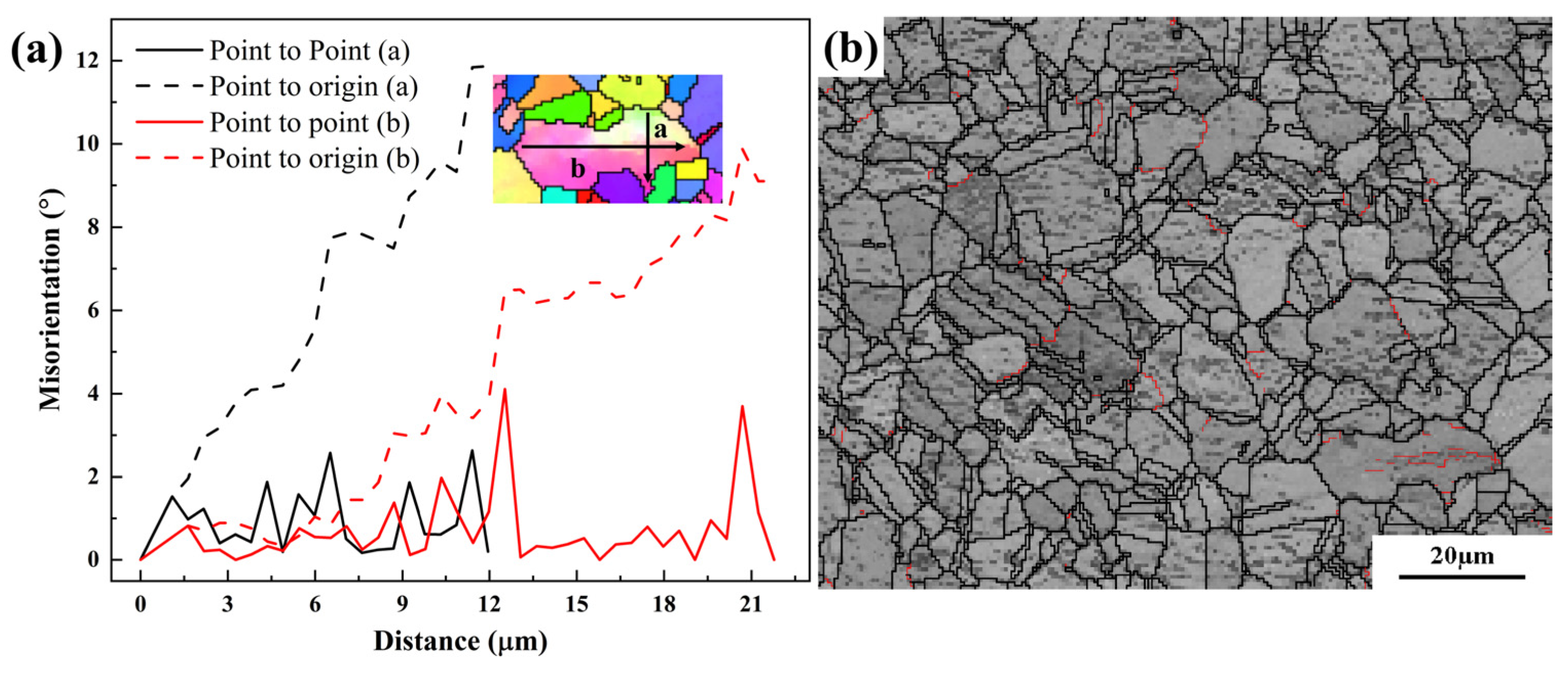
3.5. Recrystallization Behavior
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The hot-forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 MEA showed a fully equiaxed grain structure with an average grain size of about 200~300 μm. Additionally, the initial structure showed no obvious texture, indicating sufficient DRX during hot-forging.
- (2)
- Based on the stress–strain data, the peak stress of the as-forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 MEA at high strain rates was found to be higher than that of its homogenized counterpart. The constitutive equation was established as , yielding a thermal activation energy of 433.19 kJ/mol.
- (3)
- Considering the hot-processing map and DRX characteristics, the optimal processing window for the hot-forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 MEA was identified at 1100 °C with a strain rate of 0.1 s−1. The dominant DRX mechanism at the optimal hot-working condition was confirmed to be CDRX. These findings offer valuable guidelines for developing efficient forming processes for (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 MEA, which is essential for its engineering applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A. Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yu, Q.; Kabra, S.; Jiang, M.; Forna-Kreutzer, P.; Zhang, R.; Payne, M.; Walsh, F.; Gludovatz, B.; Asta, M. Exceptional Fracture Toughness of CrCoNi-Based Medium- and High-Entropy Alloys at 20 Kelvin. Science 2022, 378, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Ritchie, R.O.; Meyers, M.A. Mechanical Properties of High-Entropy Alloys with Emphasis on Face-Centered Cubic Alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 102, 296–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A Fracture-Resistant High-Entropy Alloy for Cryogenic Applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Chen, X.; Ameyama, K. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance of CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy Using Heterogeneous Structure Design. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Pang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, T. Al0.3CrxFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloys with High Corrosion Resistance and Good Mechanical Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 860, 158436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.-T.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-Y. High-Entropy Alloys in Electrocatalysis: From Fundamentals to Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 8319–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, S. High-Entropy Alloys for Electrocatalysis: Design, Characterization, and Applications. Small 2022, 18, 2104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Z.U.; Khalid, M.Y.; ur Rehman, E.; Ullah, S.; Atif, M.; Tariq, A. A review on laser cladding of high-entropy alloys, their recent trends and potential applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 225–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Thurston, K.V.; Bei, H.; Wu, Z.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Exceptional Damage-Tolerance of a Medium-Entropy Alloy CrCoNi at Cryogenic Temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, T.; Tong, Y.; Wang, J.; Luan, J.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, D.; Yang, A.; Hu, C.; Liu, C. Heterogeneous Precipitation Behavior and Stacking-Fault-Mediated Deformation in a CoCrNi-Based Medium-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 138, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xue, H.; Liu, G.; Sun, J. Achieving Excellent Strength-Ductility Synergy in Twinned NiCoCr Medium-Entropy Alloy via Al/Ta Co-Doping. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 87, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Nieh, T.; An, K.; Lu, Z. A Precipitation-Hardened High-Entropy Alloy with Outstanding Tensile Properties. Acta Mater. 2016, 102, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Chen, D.; Han, B.; Wang, J.; Feng, R.; Yang, T.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, W.; Shimizu, Y. Outstanding Tensile Properties of a Precipitation-Strengthened FeCoNiCrTi0.2 High-Entropy Alloy at Room and Cryogenic Temperatures. Acta Mater. 2019, 165, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.H.; Li, W.P.; Chang, H.T.; Yang, T.; Duan, G.S.; Wu, B.L.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, F.R.; Liu, C.T.; Chuang, W.S.; et al. Dual Heterogeneous Structures Lead to Ultrahigh Strength and Uniform Ductility in a Co-Cr-Ni Medium-Entropy Alloy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.C.; Fan, D.; Bian, Y.L.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, N.B.; Lu, L.; Cai, Y.; Luo, S.N. Effect of Minor Elements Al and Ti on Dynamic Deformation and Fracture of CoCrNi-Based Medium-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 884, 145535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Okotete, E.A. Recrystallization Mechanisms and Microstructure Development in Emerging Metallic Materials: A Review. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiaraj, G.D.; Pukenas, A.; Skrotzki, W. Texture Formation in Face-Centered Cubic High-Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.-L.; Wei, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, M.-Y.; Yang, K.; Kato, H. Hot Deformation and Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of CoCrNi and (CoCrNi)94Ti3Al3 Medium Entropy Alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleti, R.R.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Zhao, L.; Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Tsuji, N. Hot Deformation Behavior of CoCrFeMnNi FCC High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhao, Y.; Gan, B.; Sheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, L. Mechanism of Grain Refinement in an Equiatomic Medium-Entropy Alloy CrCoNi During Hot Deformation. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Park, H.; Park, K.; Na, T.; Kim, W. High-Temperature Deformation Mechanisms and Processing Maps of Equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, H.J.; Ryan, N. Constitutive Analysis in Hot Working. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 322, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, C.; Tegart, W.M. Hot Workability. Int. Metall. Rev. 1972, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, C.; Hollomon, J.H. Effect of Strain Rate upon Plastic Flow of Steel. J. Appl. Phys. 1944, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y. Processing Maps: A Status Report. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y. Recent Advances in the Science of Mechanical Processing. Indian J. Technol. 1990, 28, 435–451. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Logé, R.E. A Review of Dynamic Recrystallization Phenomena in Metallic Materials. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 548–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, A.G.; Barnett, M. Microstructural Development During Hot Working of Mg-3Al-1Zn. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xin, W.; Ma, T.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Zhu, D. Hot Deformation Behavior and Dynamic Recrystallization of Dual-Phase (CrCoNi)94Al3Ta3 Medium Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Region | Co | Cr | Ni | Al | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | 31.33 | 31.33 | 31.33 | 3 | 3 |
| DR | 33.77 | 31.69 | 29.98 | 2.48 | 2.08 |
| IR | 20.80 | 10.45 | 42.24 | 13.82 | 12.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, A.; Lu, J.; Xin, W.; Ma, T.; Wang, X.; Su, Y. Optimized Control of Hot-Working Parameters in Hot-Forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Medium-Entropy Alloy. Coatings 2025, 15, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060706
Li A, Lu J, Xin W, Ma T, Wang X, Su Y. Optimized Control of Hot-Working Parameters in Hot-Forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Medium-Entropy Alloy. Coatings. 2025; 15(6):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060706
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ao, Jiebo Lu, Wenjie Xin, Tengfei Ma, Xiaohong Wang, and Yunting Su. 2025. "Optimized Control of Hot-Working Parameters in Hot-Forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Medium-Entropy Alloy" Coatings 15, no. 6: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060706
APA StyleLi, A., Lu, J., Xin, W., Ma, T., Wang, X., & Su, Y. (2025). Optimized Control of Hot-Working Parameters in Hot-Forged (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Medium-Entropy Alloy. Coatings, 15(6), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060706





