Benefits of Surface-Modified Steel Fibers on Enhancing the Mechanical Properties in Cement Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mixture Proportioning Design
2.2. Surface Modification Process
2.3. Surface Morphology and Elemental Composition
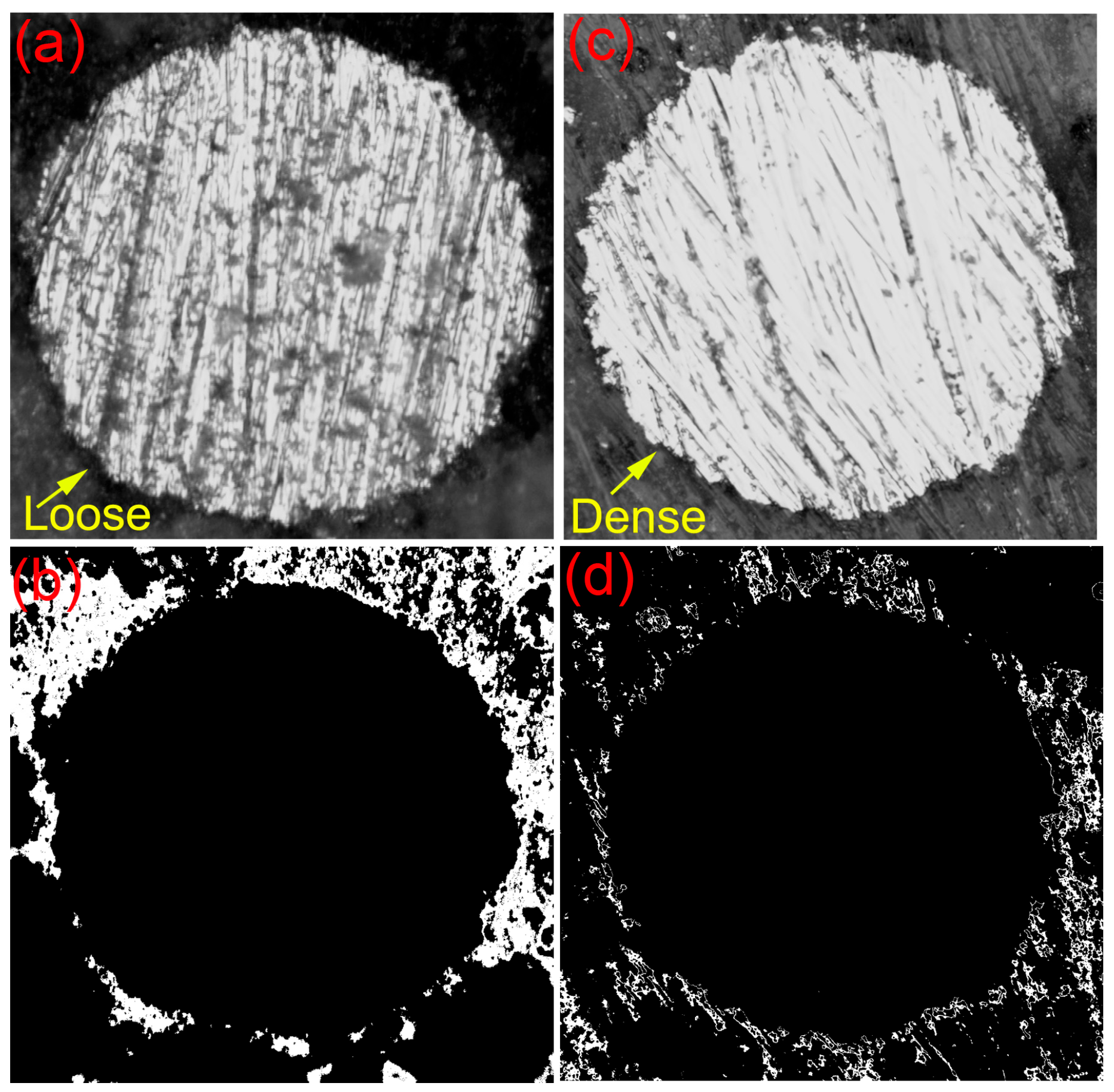
2.4. Binary Data Analysis of Microscope
2.5. Microhardness Test
2.6. Flexural and Compression Strength Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Topography
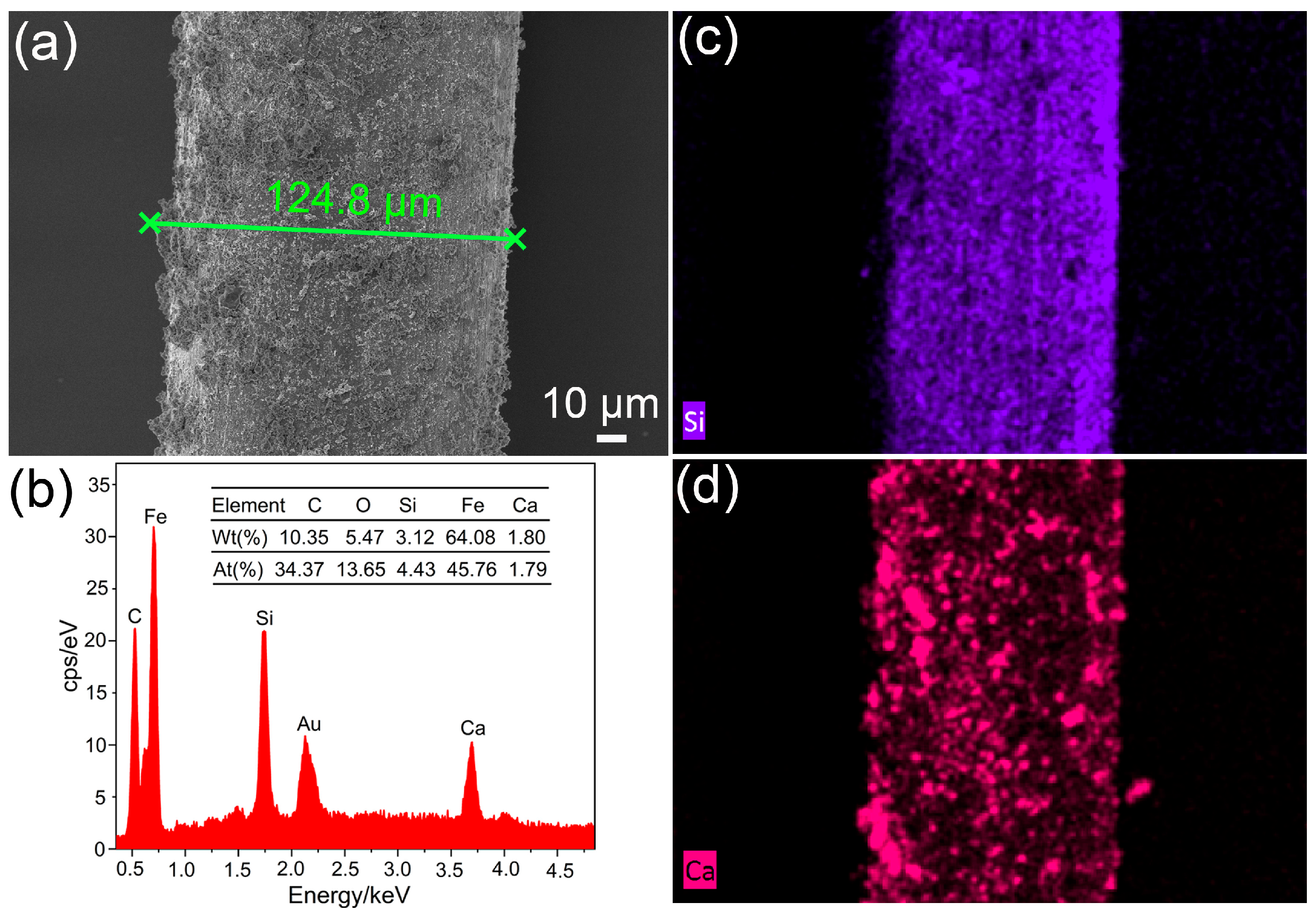
3.2. Microstructure of the Fiber–Matrix Interface
3.3. Microhardness of the Specimen
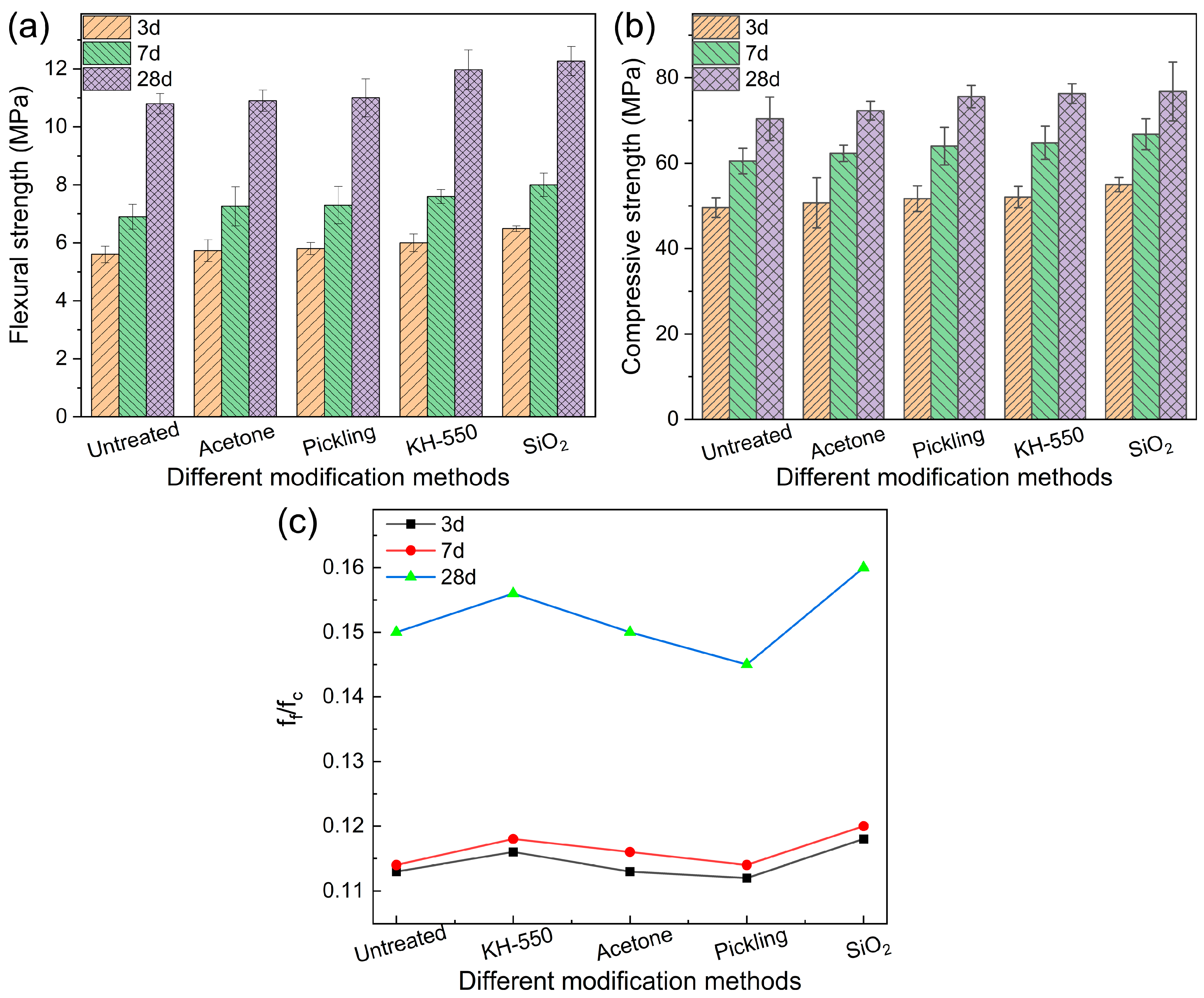
3.4. Flexural and Compression Strength
3.5. Economic and Environmental Comparison Between the Different Surface Treatments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balagopal, V.; Panicker, A.S.; Arathy, M.; Sandeep, S.; Pillai, S.K. Influence of fibers on the mechanical properties of cementitious composites-a review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Kanstad, T.; Jacobsen, S.; Ji, G. Bonding property between fiber and cementitious matrix: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 378, 131169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Neto, J.T.; Ribeiro Soares Junior, P.R.; Reis, E.D.; de Souza Maciel, P.; Gomes, P.C.C.; Gouveia, A.M.C.; da Silva Bezerra, A.C. Fiber-reinforced cementitious composites: Recent advances and future perspectives on key properties for high-performance design. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2025, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ju, J.W.; Chen, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, Z. Characterizing and analyzing the residual interfacial behavior of steel fibers embedded into cement-based matrices after exposure to high temperatures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 191, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Nitric acid-modified amorphous alloy fiber and its effects on mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.; Kim, S.; Yoo, D.-Y. Reinforcing effect of surface-modified steel fibers in ultra-high-performance concrete under tension. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Wei, H.; Liu, T.; Zou, D.; Li, Y.; Qin, R. Interfacial technology for enhancement in steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite from nano to macroscale. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 636–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, T.; Zuo, S.; Yao, H. Utilization of novel stranded steel fiber to enhance fiber–matrix interface of cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.; Kim, S.; Yoo, D.-Y. Benefits of chemically treated steel fibers on enhancing the interfacial bond strength from ultra-high-performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Sun, D.; Banthia, N.; Jiang, Z. Nano-engineering steel fiber for UHPC: Implication for varying cryogenic and elevated exposure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 156, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, P.; Sun, J.; Chen, A. Influence of fibers on tensile behavior of ultra-high performance concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 430, 136432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, S.; Yoo, D.-Y. Surface modification of steel fibers using chemical solutions and their pullout behaviors from ultra-high-performance concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fu, X.; Chung, D. A comparative study of the wettability of steel, carbon, and polyethylene fibers by water. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Cai, L.; Kainuma, S. Hybrid-Acid Pickling Method for Enhancing Adhesion and Durability at CFRP–Steel Bonded Interface. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 296, 112221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wei, H.; Zhou, A.; Zou, D.; Jian, H. Multiscale investigation on tensile properties of ultra-high performance concrete with silane coupling agent modified steel fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 111, 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Yu, Z.; Wei, H.; Tam, L.-h.; Liu, T.; Zou, D. Understanding the toughening mechanism of silane coupling agents in the interfacial bonding in steel fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 44163–44171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Luan, C.; Yuan, L.; Du, P.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J. Investigation on the effect of silane coupling agent treatment of steel fibers on the durability of UHPC. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Xiao, H.; Du, J.; Liu, M.; Li, H. Interfacial microstructure and bond strength of nano-SiO2-coated steel fibers in cement matrix. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Xiao, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, M.; Li, H. Effects of brass coating and nano-SiO2 coating on steel fiber–matrix interfacial properties of cement-based composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 189, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, S.; Bentur, A.; Mindess, S. Microhardness testing of cementitious materials. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1996, 4, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). National Standards of the Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Casagrande, C.A.; Cavalaro, S.H.P.; Repette, W.L. Ultra-high performance fibre-reinforced cementitious composite with steel microfibres functionalized with silane. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xiao, H.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Sun, L. Improved interfacial strength of SiO2 coated carbon fiber in cement matrix. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 91, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, M.S.; Jain, A. Concrete Technology (Theory and Practice), 8th ed.; S. Chand Publishing: New Delhi, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, M.; Yang, E.-H.; Schlangen, E. Distribution of porosity surrounding a microfiber in cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Dong, Y.; Jin, M.; Liu, J. A multi-scale study of enhancing mechanical property in ultra-high performance concrete by steel-fiber@ nano-silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 128069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Xiao, H.; Du, J.; Li, C.; Cai, W.; Liu, M. Effect of the water/cement ratio on the improvement of pullout behaviors using nano-SiO2 modified steel fiber and the micro mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xiao, H.; Liu, M.; Feng, J. Carbon fiber surface nano-modification and enhanced mechanical properties of fiber reinforced cementitious composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, A.; Parthiban, V.; Parvathi, N.S.; Sowndarya, S. Crack-bridging and strengthening prospects of nanofibers in the cement composite–A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Akbulut, Z.F.; Tawfik, T.A.; Smarzewski, P.; Guler, S. Advancing Hybrid Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Performance, Crack Resistance Mechanism, and Future Innovations. Buildings 2025, 15, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantilli, A.P.; Frigo, B.; Dehkordi, F.M. Relationship between flexural strength and compressive strength in concrete and ice. In Current Perspectives and New Directions in Mechanics, Modelling and Design of Structural Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Raveendran, N.; Krishnan, V. Engineering performance and environmental assessment of sustainable concrete incorporating nano silica and metakaolin as cementitious materials. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Properties | Fiber Diameter (mm) | Fiber Length (mm) | Aspect Ratio | Tensile Strength of Fiber (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight steel fiber | 0.12 | 8 | 66.7 | 2850 |
| Water-to-Binder Ratio | Mix Design (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Silica Sand | Water | Fly Ash | Steel Fiber Content | Water Reducer | |
| 0.3 | 1062 | 625 | 375 | 188 | 30.1 | 3.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, X.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Qi, M.-l. Benefits of Surface-Modified Steel Fibers on Enhancing the Mechanical Properties in Cement Matrix. Coatings 2025, 15, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060682
Tan X, Li M, Zhao L, Pan Y, Zhang P, Qi M-l. Benefits of Surface-Modified Steel Fibers on Enhancing the Mechanical Properties in Cement Matrix. Coatings. 2025; 15(6):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060682
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Xuxiang, Minghua Li, Liandi Zhao, Yichuan Pan, Peina Zhang, and Mei-li Qi. 2025. "Benefits of Surface-Modified Steel Fibers on Enhancing the Mechanical Properties in Cement Matrix" Coatings 15, no. 6: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060682
APA StyleTan, X., Li, M., Zhao, L., Pan, Y., Zhang, P., & Qi, M.-l. (2025). Benefits of Surface-Modified Steel Fibers on Enhancing the Mechanical Properties in Cement Matrix. Coatings, 15(6), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060682






