Abstract
With the increasing detection of antibiotics such as sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in water bodies, developing efficient and eco-friendly treatment technologies is critical. This study employs a hydrothermal impregnation method to prepare a NiFe2O4/granular activated carbon (GAC) composite catalyst, optimized for use in a proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolytic ozonation system to degrade SMX. Single-factor experiments optimized preparation conditions with a Fe:Ni molar ratio of 3:1, a GAC:Fe + Ni mass ratio of 2:1, and calcination at 500 °C for 3 h. The catalyst was characterized using XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, and FT-IR, confirming a spinel NiFe2O4 structure (crystal size ~15.2 nm) uniformly dispersed on GAC, with an Fe:Ni atomic ratio of ~2.1:1. In the PEM system, the optimized catalyst achieved a 99.15% ± 0.3% SMX degradation rate (50 mg/L) within 25 min, compared to 95.06% ± 0.6% in 30 min without a catalyst. The catalyst maintained 98.45% ± 0.5% efficiency after three cycles, demonstrating excellent stability. The synergy between GAC adsorption and NiFe2O4 catalysis, driven by Fe3+/Fe2+ redox cycling, enhances ·OH generation from ozone decomposition, boosting SMX degradation. This work provides a robust catalyst for antibiotic wastewater treatment and a foundation for scaling up catalytic ozonation.
1. Introduction
Rapid industrialization and urbanization have exacerbated water pollution, with emerging contaminants like antibiotics posing significant threats to ecosystems and human health [1]. Sulfamethoxazole (SMX), a widely used sulfonamide antibiotic, is frequently detected in surface water, groundwater, and wastewater treatment plant effluents due to its stable chemical structure and poor biodegradability, leading to bacterial resistance and ecological toxicity [2,3,4]. Conventional wastewater treatment methods, such as biological treatment and physical adsorption, exhibit limited SMX removal efficiency, failing to meet stringent discharge standards [3,5,6]. Thus, developing efficient and sustainable technologies for SMX removal is a pressing need in environmental science.
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) generate highly reactive radicals (e.g., hydroxyl radicals, ·OH) to degrade organic pollutants effectively, offering significant advantages in water treatment [7,8]. Ozonation, with its strong oxidation capacity, rapid reaction kinetics, and lack of secondary pollution, is widely applied for recalcitrant pollutant treatment [9,10]. However, standalone ozonation suffers from low selectivity and insufficient ozone utilization, limiting its practical application [10]. Proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis generates ozone in situ electrochemically, avoiding transportation and storage issues associated with traditional ozone generators while providing high ozone yield and energy efficiency [11]. Nonetheless, the utilization efficiency of PEM-generated ozone in water treatment requires improvement, making catalytic ozonation a promising strategy.
Catalytic ozonation enhances pollutant degradation by promoting ozone decomposition into ·OH radicals via catalysts [12]. Transition metal oxides, due to their high catalytic activity, low cost, and stability, are widely studied [12,13,14]. Nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4), a spinel-type composite oxide, offers excellent electrochemical properties and magnetic recoverability, making it a suitable ozonation catalyst [15]. However, standalone NiFe2O4 tends to aggregate, reducing active site availability and catalytic efficiency [16]. Supporting NiFe2O4 on high-surface-area granular activated carbon (GAC) mitigates aggregation, enhances active site exposure, and leverages GAC’s adsorption capacity to synergistically improve pollutant removal [17].
While progress has been made in preparing NiFe2O4-based catalysts for applications like photocatalytic dye degradation and electrocatalytic oxidation [17,18], their use in PEM electrolytic ozonation systems, particularly with NiFe2O4/GAC, remains underexplored. The systematic optimization of preparation conditions (e.g., Fe:Ni ratio, GAC loading, and calcination parameters) and evaluation of reusability and stability in complex water matrices are lacking [19]. This study prepares NiFe2O4/GAC via hydrothermal impregnation; optimizes its synthesis; and characterizes its crystal structure, morphology, and chemical composition using XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, and FT-IR. The catalyst’s performance in SMX degradation within a PEM ozonation system, its reusability, and its adsorption/catalysis synergy are evaluated. This work aims to develop an efficient, stable catalyst for antibiotic wastewater treatment and provide a theoretical basis for scaling up catalytic ozonation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
The instruments and reagents used are listed in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. All reagents were used as received without further purification. Instruments were calibrated per standard operating procedures to ensure data accuracy.

Table 1.
List of experimental instruments.

Table 2.
List of experimental reagents.
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. PEM Electrolytic Ozonation for SMX Degradation
The experimental setup and procedure are shown in Figure 1. The system comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, and a PEM (Nafion 117). The anode was a Ti/RuO2-IrO2 electrode, and the cathode was stainless steel. A solution containing 50 mg/L SMX (with 0.27% sodium sulfate as the electrolyte, pH 5.59 ± 0.05) was pumped into both chambers at 10 mL/min using a peristaltic pump. Under a DC power supply (current 4.3 A), the anode oxidized water to produce ozone (O3) and oxygen (O2), while the cathode reduced water to generate hydrogen (H2). The PEM facilitated H+ migration from anode to cathode, preventing O2− passage and ensuring ionic selectivity. Electrons flowed externally from the anode to the cathode to maintain charge balance.
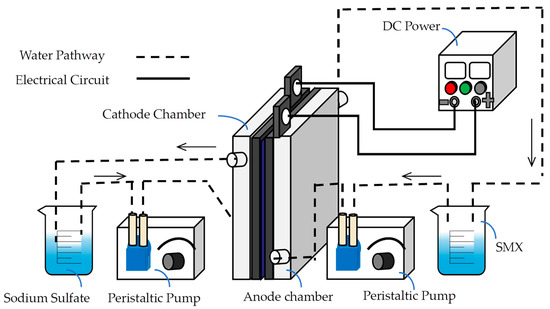
Figure 1.
Experimental flowchart.
Standalone ozonation showed limited SMX degradation efficiency. To enhance ozone utilization, 1 g of NiFe2O4/GAC catalyst was added to the anode chamber to promote ozone decomposition into ·OH, improving SMX degradation. Experimental conditions were as follows: current, 4.3 A; sodium sulfate, 0.27%; pH 5.59; and electrolysis time, 30 min, with three replicates. Without a catalyst, SMX degradation reached 95.06% ± 0.6%. Catalysts prepared under varying conditions were compared to identify optimal parameters.
For reusability tests, the optimal catalyst was recovered after each trial, washed with deionized water to neutrality (pH ≈ 7), dried at 80 °C for 3 h, and reused four times (five trials total). SMX concentrations were analyzed per trial to calculate degradation rates and assess reusability.
2.2.2. Catalyst Preparation
The hydrothermal impregnation method was selected for NiFe2O4/GAC synthesis due to its documented effectiveness in achieving the uniform dispersion of metal oxides on porous supports while preserving the structural integrity of the carrier [17,19]. NiFe2O4/GAC was prepared via hydrothermal impregnation, as depicted in Figure 2. FeCl3·6H2O, FeSO4·7H2O, and Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (total 0.02 mol) were weighed per the target Fe3+ + Fe2+:Ni2+ molar ratio, dissolved in 50 mL deionized water, and stirred until fully dissolved. Granular activated carbon (GAC, 1–2 mm, BET surface area ~800 m2/g) was added to the solution and stirred at 60 °C for 1 h in a water bath. Then, 25% ammonia solution (5–10 mL) was slowly added to adjust the pH to 9.0–10.0, followed by 1 h stirring. The Fe/Ni-loaded GAC was separated via vacuum filtration (0.45 μm membrane), washed with deionized water until neutral (pH 6.8–7.2), and dried at 80 °C for 12 h to constant weight, yielding the catalyst precursor. The precursor was calcined in a muffle furnace at set temperatures (400–700 °C) and durations (1–5 h, heating rate 5 °C∙min−1), cooled naturally, ground uniformly, and stored sealed.
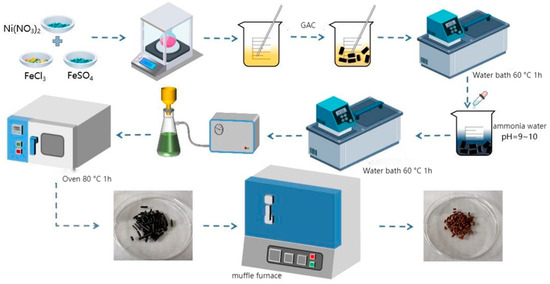
Figure 2.
Catalyst preparation flowchart.
2.2.3. Parameter Ranges for Catalyst Preparation Conditions
Single-factor experiments optimized the Fe:Ni ratio, GAC loading, calcination temperature, and time. For each test, a 1 g catalyst was added to the anode chamber and electrolyzed for 25 min (current, 4.3 A; sodium sulfate, 0.27%; pH 5.59 ± 0.05; initial SMX, 50 mg/L). SMX degradation rates were measured, with three replicates per condition.
Fe:Ni Ratio: Fixed GAC:Fe + Ni mass ratio at 1:1; calcination at 500 °C for 4 h. Fe3+ + Fe2+:Ni2+ molar ratios tested were 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, and 5:1.
GAC Loading: Using the optimal Fe:Ni ratio, GAC:Fe + Ni mass ratios were set at 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, and 4:1 and calcined at 500 °C for 4 h.
Calcination Temperature: Using optimal Fe:Ni and GAC ratios, temperatures tested were 400 °C, 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C, with 4 h calcination.
Calcination Time: Using the optimal Fe:Ni, GAC, and temperature, the times tested were 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, and 5 h.
2.3. Methods for Catalyst Characterization
2.3.1. Methods for XRD Analysis
The crystal structure was analyzed using an X-ray diffractometer (Bruker D2 Phaser, Bremen, Germany, Cu Kα, λ = 1.5406 Å). Samples were ground to 200 mesh, pressed into pellets, and scanned from 10° to 80° at 2°∙min−1. Diffraction data were compared with standard PDF cards to identify NiFe2O4 phases, with crystal size calculated via the Scherrer equation.
2.3.2. Methods for SEM Analysis
Surface morphology was observed using a scanning electron microscope (Hitachi Regulus 8100, Tokyo, Japan). Samples (<5 × 5 mm) were mounted on conductive tape, gold-coated (Quorum SC 7620, Kent, UK, 10 mA, 10 s), and imaged at 3 kV (morphology, SE2 detector) or 20 kV (EDS analysis). SEM-EDS provided qualitative and quantitative elemental distribution (Fe, Ni, C, and O).
2.3.3. Methods for TEM Analysis
Internal morphology was examined using a transmission electron microscope (JEOL JEM-2100F, Tokyo, Japan). Samples were ground, ultrasonically dispersed in ethanol for 10 min, dropped onto a 300-mesh copper grid, dried, and imaged at 200 kV. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) verified the crystal structure.
2.3.4. Methods for XPS Analysis
Surface elements and valence states were analyzed using an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (Thermo Scientific K-Alpha, MA, USA) at <2.0 × 10−7 mbar. Samples (5 × 5 mm) were tested with a 400 μm spot size, 12 kV, and 6 mA. Full scans used 150 eV pass energy (1 eV step); narrow scans used 50 eV (0.1 eV step). Binding energies were calibrated to C 1s (284.6 eV).
2.3.5. Methods for FT-IR Analysis
Chemical bonds were analyzed using a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS 20, Waltham, MA, USA). Samples were mixed with KBr (dried at 200 °C for 24 h) at 1:100, ground, and pressed into pellets. Spectra were recorded from 400 to 4000 cm−1 (4 cm−1 resolution, 32 scans) after collecting a KBr background.
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Ozone Concentration
Ozone concentration at the anode chamber outlet was measured using a portable analyzer (Luheng LH-D01F, Hangzhou, China). A 5 mL water sample was added to a cuvette containing indigo disulfonate, shaken for 40 s, and measured. After 5 min of device operation, ozone concentrations were recorded at currents of 1–5 A (Figure 3), showing a near-linear increase with current, reflecting improved electrolytic efficiency.
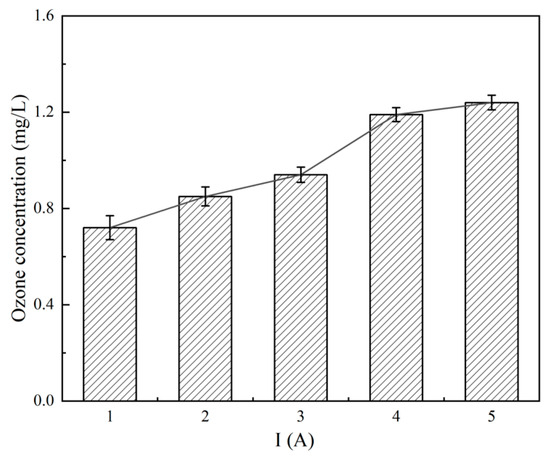
Figure 3.
Ozone concentration vs. current.
2.4.2. SMX Concentration
SMX concentrations were determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (Agilent 1260, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a C18 column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm). Mobile phase: 0.20% acetic acid aqueous solution/acetonitrile (60:40, v/v); flow rate: 1 mL/min; column temperature: 35 °C; injection volume: 10 μL; detection wavelength: 270 nm. A standard curve (Figure 4) was prepared from 0–50 mg/L SMX solutions, yielding y = 49.536x + 23.454 (R2 = 0.9998), meeting experimental requirements.
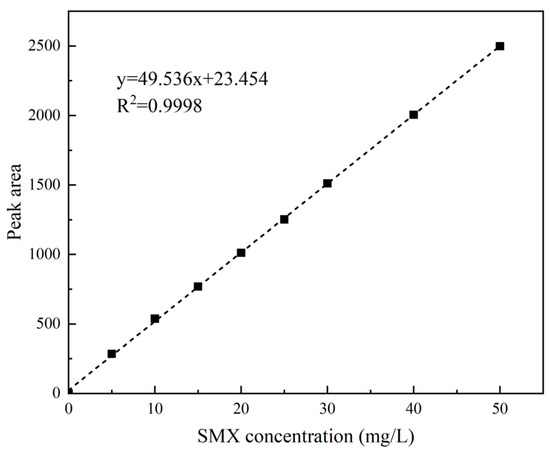
Figure 4.
SMX standard curve.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Catalyst Preparation Conditions
The Fe:Ni ratio, GAC loading, calcination temperature, and time were optimized to maximize SMX degradation (initial SMX, 50 mg/L; current, 4.3 A; sodium sulfate, 0.27%; pH 5.59 ± 0.05; catalyst, 1 g; 30 min electrolysis, with three replicates).
3.1.1. Effect of Fe:Ni Ratio
Catalysts were prepared with Fe3+ + Fe2+: Ni2+ molar ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, and 5:1 (GAC:Fe + Ni = 1:1, 500 °C, 4 h). The degradation results (Figure 5) showed SMX degradation increasing and then decreasing with higher Fe:Ni ratios. At Fe:Ni = 3:1, the 25 min degradation reached 98.02% ± 0.5%, outperforming the non-catalyzed system (95.06% ± 0.6%, 30 min) by ~5 min. Fe3+/Fe2+ redox cycling likely promoted ozone decomposition into ·OH, with Ni2+ enhancing activity as a co-catalytic site [20]. Beyond 3:1, excess Fe may cause crystal defects or uneven active site distribution on GAC, reducing efficiency [21]. EDS confirmed an Fe:Ni atomic ratio near the theoretical spinel value (~2:1) at 3:1, indicating structural stability. Thus, Fe:Ni = 3:1 was optimal.
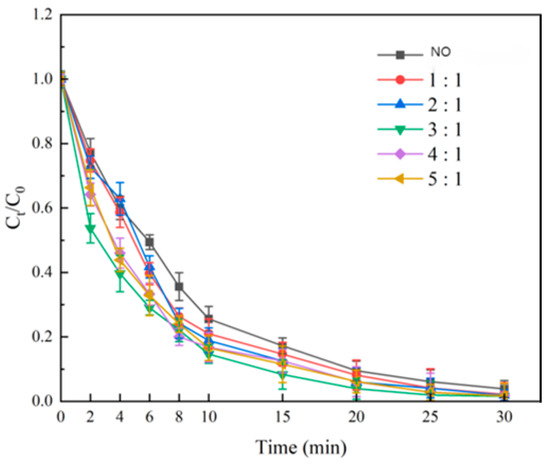
Figure 5.
Effect of Fe:Ni ratio on SMX degradation.
3.1.2. Effect of GAC Loading
Using Fe:Ni = 3:1, GAC:Fe + Ni mass ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, and 4:1 were tested (500 °C, 4 h). Degradation rates (Figure 6) increased and then decreased with GAC loading. At 2:1, 25 min degradation reached 98.93% ± 0.4%, surpassing 1:1 (96.45% ± 0.5%) and 4:1 (94.12% ± 0.6%). Initially (0–2 min), 1:1 showed the fastest rate (30.5% ± 0.8%) due to higher NiFe2O4 loading per GAC unit, concentrating active sites. Beyond 2 min, 2:1 excelled due to synergistic GAC adsorption and NiFe2O4 catalysis [21]. At 4:1, lower NiFe2O4 loading relied heavily on GAC adsorption, limiting ·OH production. Thus, GAC:Fe + Ni = 2:1 was optimal.
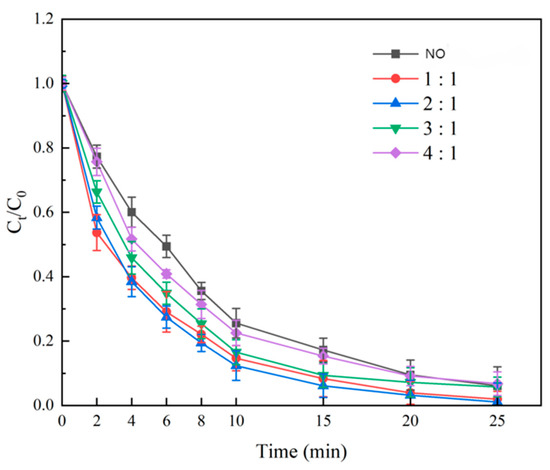
Figure 6.
Effect of GAC loading on SMX degradation.
3.1.3. Effect of Calcination Temperature
Using Fe:Ni = 3:1 and GAC:Fe + Ni = 2:1, calcination temperatures of 400 °C, 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C were tested (4 h). Degradation rates (Figure 7) peaked at 500 °C (98.93% ± 0.4% in 25 min), outperforming 400 °C (95.67% ± 0.5%) and 700 °C (94.02% ± 0.6%). At 500 °C, NiFe2O4 formed appropriately sized crystals with intact pore structures, facilitating ozone adsorption and ·OH generation [18]. At 400 °C, low crystallinity reduced active sites; at 700 °C, crystal agglomeration and pore collapse lowered efficiency. Thus, 500 °C was optimal.
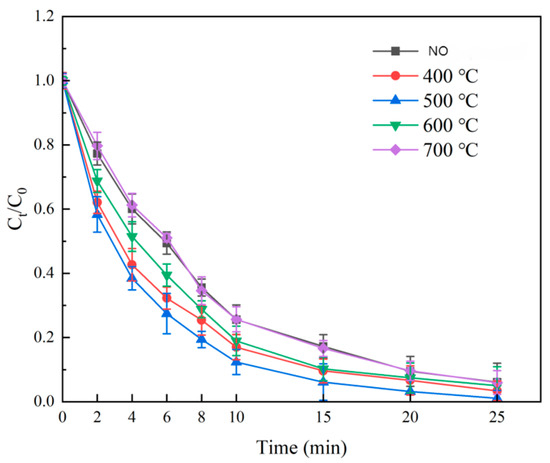
Figure 7.
Effect of calcination temperature on SMX degradation.
3.1.4. Effect of Calcination Time
Using Fe:Ni = 3:1, GAC:Fe + Ni = 2:1, and 500 °C, calcination times of 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, and 5 h were tested. Degradation rates (Figure 8) peaked at 3 h (99.15% ± 0.3% in 25 min), surpassing 1 h (94.02% ± 0.6%) and 5 h (95.65% ± 0.5%). At 3 h, NiFe2O4 formed a stable spinel structure with optimized porosity, enhancing SMX and ozone adsorption [18]. Shorter times (1–2 h) yielded incomplete crystallization, while 5 h caused crystal growth or impurity deposition, clogging pores. Thus, 3 h was optimal.
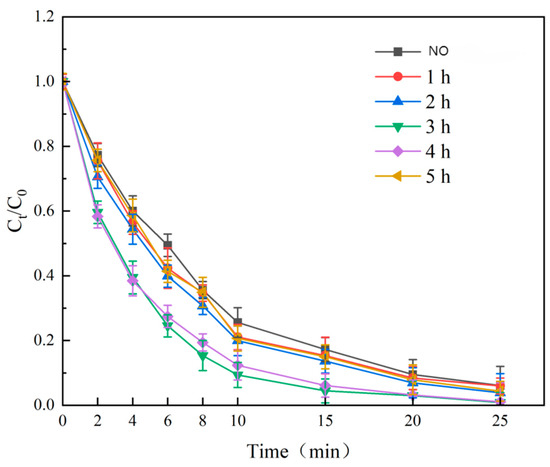
Figure 8.
Effect of calcination time on SMX degradation.
The NiFe2O4/GAC composite catalyst was optimally prepared via hydrothermal impregnation under the following conditions: Fe:Ni molar ratio (3:1), GAC:(Fe + Ni) mass ratio (2:1), and calcination at 500 °C for 3 h. Under these conditions, the catalyst achieved 99.15% ± 0.3% sulfamethoxazole (SMX, 50 mg/L) degradation in just 25 min in a PEM electrolytic ozonation system. This performance surpassed non-catalytic ozonation (95.06% ± 0.6% in 30 min) by both efficiency (+4.1%) and reaction rate (17% faster).
3.2. Multi-Technique Characterization of NiFe2O4/GAC
The optimal catalyst (Fe:Ni = 3:1, GAC:Fe + Ni = 2:1, 500 °C, 3 h) was characterized using XRD, SEM, EDS, TEM, XPS, and FT-IR to correlate structure and composition with performance.
3.2.1. XRD Characterization of NiFe2O4 Spinel Structure on GAC
XRD patterns (Figure 9, Cu Kα, λ = 1.5406 Å, 10–80°) showed peaks at 2θ = 18.4°, 30.2°, 35.6°, 43.3°, 53.8°, 57.3°, 63.0°, and 74.5°, matching NiFe2O4 spinel planes (111, 220, 311, 400, 422, 511, 440, and 533; PDF#74-2081) without significant impurities, confirming successful NiFe2O4 loading on GAC. The (311) peak yielded a crystal size of 15.2 ± 0.5 nm, indicating high crystallinity and active site exposure [22]. A weak GAC amorphous carbon peak (~26°) suggested NiFe2O4 coverage. TEM corroborated the nanocrystalline structure.
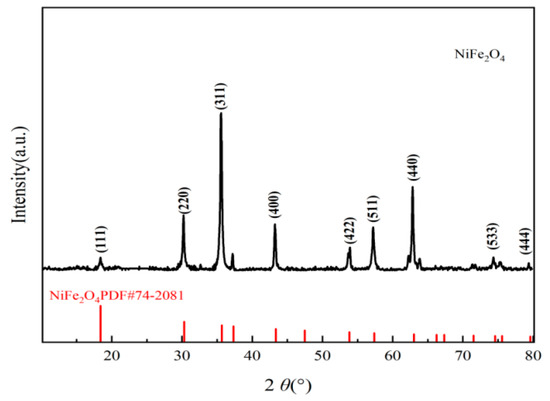
Figure 9.
XRD pattern of NiFe2O4/GAC.
3.2.2. SEM Morphological Characterization of NiFe2O4/GAC
SEM images (Figure 10, 3 kV) revealed a porous GAC surface with uniformly distributed NiFe2O4 particles, with some forming clusters. The porous structure and particle distribution favored SMX and ozone adsorption/catalysis [23]. High-magnification images show spherical NiFe2O4 particles with rough surfaces, increasing active site exposure, consistent with high degradation rates.
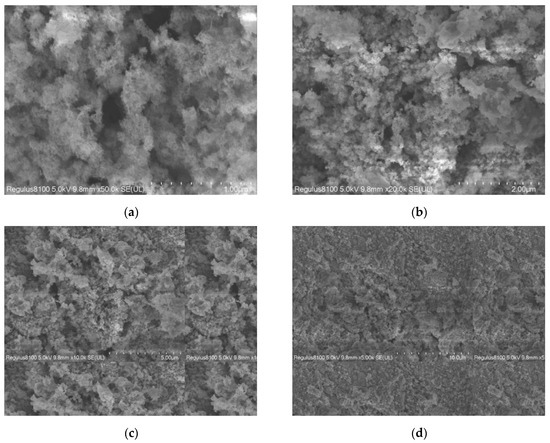
Figure 10.
SEM Images of NiFe2O4/GAC at different magnifications. (a) Low magnification morphology, (b) medium magnification morphology, (c) high magnification morphology, and (d) local amplification.
3.2.3. EDS Elemental Mapping and Quantitative Analysis of NiFe2O4/GAC
SEM-EDS mapping (Figure 11, 20 kV) showed the uniform distribution of C, O, Fe, and Ni without significant segregation (Figure 12). Quantitative EDS revealed mass fractions—C 68.5% ± 1.2%, O 21.3% ± 0.8%, Fe 7.8% ± 0.3%, Ni 2.4% ± 0.2%—with an Fe:Ni atomic ratio of ~2.1:1, close to NiFe2O4’s theoretical value, confirming successful loading [20]. C and O stemmed from GAC, Fe, and Ni from NiFe2O4, aligning with the XRD.
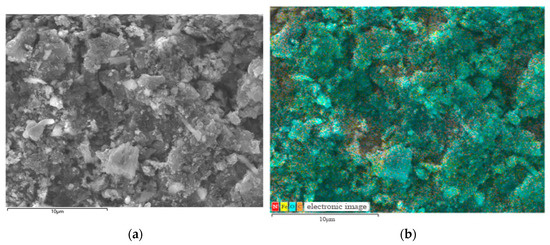
Figure 11.
SEM-EDS images of samples. (a) Electron picture; (b) hierarchical picture.
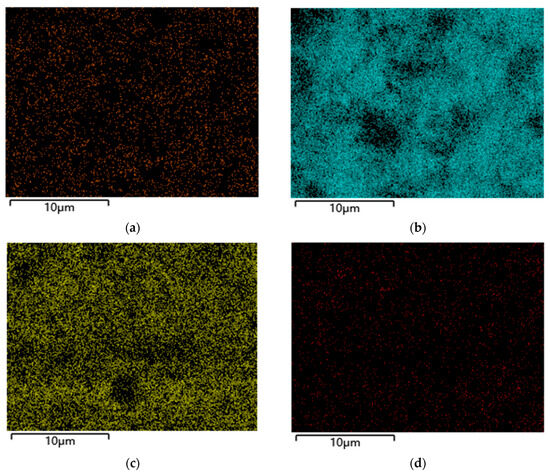
Figure 12.
EDS distribution diagram of element. (a) C, (b) O, (c) Fe, and (d) Ni.
3.2.4. TEM Structural Characterization of NiFe2O4
TEM images (Figure 13, 200 kV) show spherical NiFe2O4 particles with clear lattice fringes (0.25 nm, (311) plane), matching the XRD. Particles were uniformly distributed on GAC with some aggregation. Pore sizes of 10–20 nm facilitated molecular diffusion, supporting the spinel structure [24]. Nanocrystals and porosity enhanced ozone decomposition and SMX degradation.
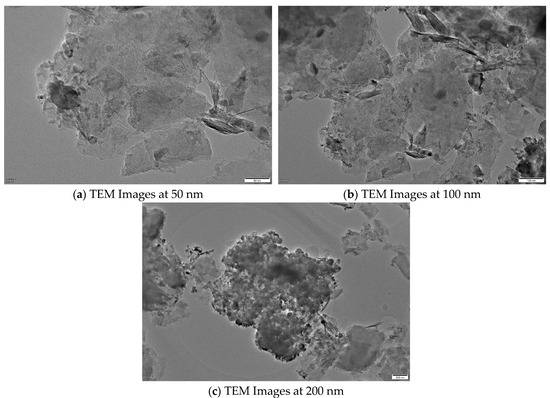
Figure 13.
TEM Images of NiFe2O4/GAC at 50, 100, and 200 nm.
3.2.5. XPS Analysis of Surface Chemical States in NiFe2O4
XPS spectra (Figure 14a) confirmed O 1s (531.1 eV), C 1s (284.6 eV), Fe 2p (710.7 eV), and Ni 2p (855.4 eV). C 1s (Figure 14b) deconvoluted into C-C (284.6 eV, 65.2%), C-O (286.1 eV, 22.5%), and O-C=O (288.2 eV, 12.3%), reflecting GAC’s carbon framework. O 1s (Figure 14c) showed lattice oxygen (530.8 eV, 48.6%) and adsorbed oxygen (531.9 eV, 51.4%), the latter aiding ·OH formation [25]. Fe 2p (Figure 14d) displayed Fe 2p3/2 (710.7 eV, Fe2+; 712.9 eV, Fe3+) and Fe 2p1/2 (724.2 eV, Fe2+; 726.3 eV, Fe3+), with an Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio of ~1.8:1, indicating redox activity. Ni 2p (Figure 14e) showed Ni 2p3/2 (855.4 eV, Ni2+) and Ni 2p1/2 (873.2 eV, Ni2+). Fe3+/Fe2+ cycling and Ni2+ synergy drove ozone decomposition, supporting high degradation rates.
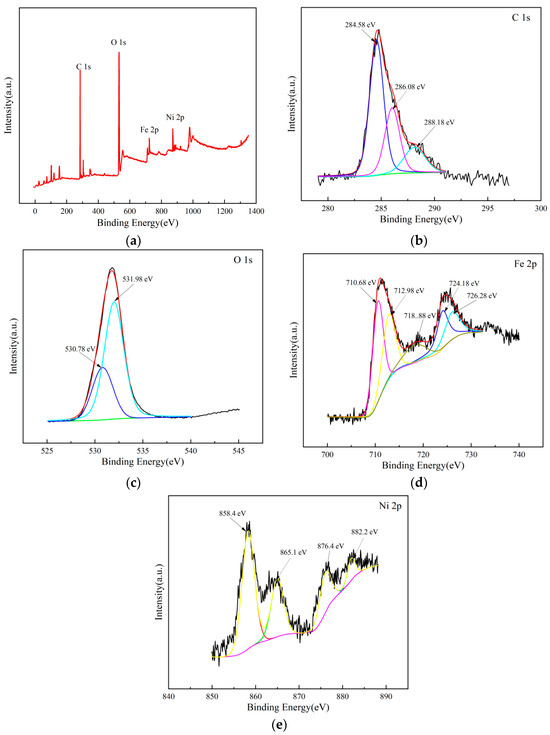
Figure 14.
XPS spectra of NiFe2O4/GAC. (a) Full scan image, (b) C 1s image, (c) O 1s image, (d) Fe 2p image, and (e) Ni 2p image.
3.2.6. FT-IR Spectroscopic Characterization of NiFe2O4
FT-IR spectra (Figure 15, 400–4000 cm−1) showed O-H stretching/bending (3432, 1634 cm−1) from adsorbed water [25] and NiFe2O4’s Fe-O/Ni-O vibrations (586, 407 cm−1), confirming spinel structure [26]. O-H and Fe-O bonds facilitated ozone adsorption/decomposition, supporting catalytic activity.
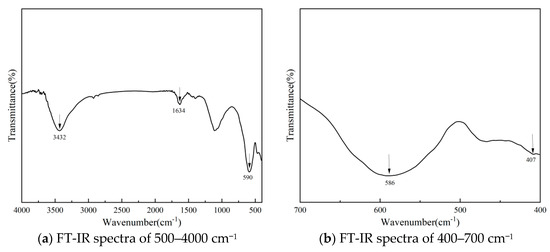
Figure 15.
FT-IR spectra of NiFe2O4/GAC.
3.3. Catalyst Reusability
The optimal catalyst was tested for reusability over five cycles (washed to pH ≈ 7 and dried at 80 °C for 3 h per cycle, with conditions as in Section 3.1). Degradation rates (Figure 16) remained stable for three cycles (98.45% ± 0.5% at cycle 3, −0.7%), dropping to 94.12% ± 0.6% (cycle 4) and 93.13% ± 0.7% (cycle 5). Efficiency decline may result from minor Fe leaching or organic deposition clogging pores [27]. Overall, the catalyst exhibited excellent reusability for long-term applications.
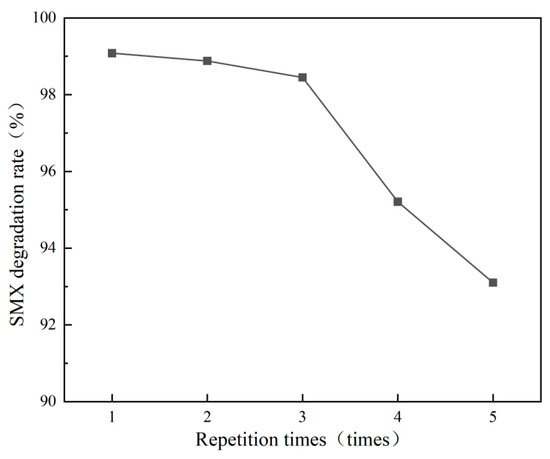
Figure 16.
Catalyst reusability.
4. Conclusions
NiFe2O4/GAC was successfully prepared via hydrothermal impregnation using FeCl3·6H2O, FeSO4·7H2O, and Ni(NO3)2·6H2O. Optimized via single-factor experiments and characterized comprehensively, the catalyst excelled in PEM electrolytic ozonation for SMX degradation, yielding the following:
Optimal Conditions: Fe:Ni = 3:1, GAC:Fe + Ni = 2:1, 500 °C, 3 h. SMX (50 mg/L) degradation reached 99.15% ± 0.3% in 25 min, 4.1% higher and 5 min faster than without a catalyst (95.06% ± 0.6%, 30 min). Balanced Fe3+/Fe2+ cycling and Ni2+ synergy, coupled with GAC’s high surface area (~650 m2/g), enhanced adsorption and catalysis.
Structure and Performance: XRD and TEM confirmed spinel NiFe2O4 (~15.2 nm) uniformly loaded on GAC. SEM/EDS showed regular particles (20–50 nm) and uniform elemental distribution (Fe:Ni~2.1:1). XPS revealed Fe3+/Fe2+ (1.8:1) and Ni2+ coexistence, with Fe3+/Fe2+ cycling promoting ·OH generation and GAC adsorption enriching SMX.
Reusability: After three cycles, degradation remained at 98.45% ± 0.5%, dropping to 95.33% ± 0.7% by cycle 5, indicating robust stability. Minor Fe leaching and pore-clogging caused slight declines, addressable via optimized recovery.
NiFe2O4/GAC demonstrates high efficiency in PEM ozonation for SMX removal, offering a viable solution for antibiotic wastewater treatment. Future work could explore its performance in complex water matrices, optimize electrolysis for energy efficiency, or use molecular simulations to elucidate SMX degradation pathways, paving the way for scaled-up catalytic ozonation.
Author Contributions
X.X.: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, validation, visualization, methodology, and conceptualization. B.W.: writing—review and editing and visualization. X.R.: writing—review and editing and visualization. Y.Y.: writing—review and editing and methodology. B.Z.: methodology, conceptualization, validation, visualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Innovative Training Program for College Students of Jiangsu University (No. 202410299039Z).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors affirm that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Leung, K.S.-Y.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging contaminants: A One Health perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbehn, R.K.; Michels, C.; Soares, H.M. Antibiotics in wastewater: From its occurrence to the biological removal by environmentally conscious technologies. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Microbial Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole in the Environment: A Review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3573–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalakova, P.; Cizmas, L.; McDonald, T.J.; Marsalek, B.; Feng, M.; Sharma, V.K. Occurrence and Toxicity of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Lens, P.N.L. Biotransformation of Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) by Aerobic Granular Sludge: Removal Performance, Degradation Mechanism and Microbial Response. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasannamedha, G.; Kumar, P.S. A Review on Contamination and Removal of Sulfamethoxazole from Aqueous Solution Using Cleaner Techniques: Present and Future Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Oturan, M.A. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: Advances in formation and detection of reactive species and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaya, V.; Rekhate, J.K. Srivastava. Recent advances in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for treatment of wastewater- A review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Pishbin, E. Ozone-based advanced oxidation processes in water treatment: Recent advances, challenges, and perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 3531–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Peña, M.; Pérez, J.A.B.; Llanos, J.; Saez, C.; Barrera-Díaz, C.E.; Rodrigo, M.A. Electrochemical generation of ozone using a PEM electrolyzer at acidic pHs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 267, 118672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, E.; AMU-Darko, J.N.-O.; Yakubu, S.; Fapohunda, F.O.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Advanced catalytic ozonation for degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants―A review. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, C.; Hazarika, K.K.; Bharali, P. Transition metal oxide nanocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2018, 1, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cen, L.; Deng, K.; Mo, W.; Hajime, H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, P.; Shangguan, W.; Huang, H.; Einaga, H. Boosting Benzene’s Ozone Catalytic Oxidation at Mild Temperatures over Highly Dispersed Ag-Doped Mn3O4. Catalysts 2024, 14, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, P.; Cheng, Y.; Mo, Y.; Luo, X.; Liu, P.; Guo, R.; Liu, X. Recent progress on NiFe2O4 spinels as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 946, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingale, A.A.; Kagne, R.P.; Sargar, A.M. NiFe2O4@PPA-DABCO: A novel magnetically separable bifunctional nanocatalyst for the synthesis of 2, 2´-(Arylmethylene) bis(3-hydroxy-5, 5-dimethyl-2-cyclohexene-1-one) derivatives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2025, 27, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, J.; Senthil, M.; Madhan, D.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Al-onazi, W.A. Fabrication of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon as novel composites for high efficient ultra violet-light photocatalysis for degradation of aqueous organic pollutants. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 144, 110995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, N.; Aftab, K.; Jannat, F.T.; Siddique, Z. Electrocatalytic performance of modified NiFe2O4/rGO composite deposited on fluorine-doped tin oxide electrode using polyvinylidene fluoride binder. J. Mater. Res. 2025, 40, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, P.; Murugan, A.; Siva, V.; Shameem, A.; Chinnaiah, K.; Thangarasu, S.; Bahadur, S.A. Optimization of NiFe2O4 by different facile synthetic approaches and investigations on structural and electrochemical properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 160, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibimarkani, H.; Abram, S.-L.; Buzanich, A.G.; Prinz, C.; Sahre, M.; Hodoroaba, V.-D.; Radnik, J. In-depth analysis of FeNi-based nanoparticles for the oxygen evolution reaction. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termezi, M.F.A.; Ahmad, S.I.; Yusoff, M.H.M. Effect of Fe and Ni Loading in Fe-Ni Supported on Activated Carbon Catalyst on Glycerol Acetylation to Acetins. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2025, 10, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulemana, H.; Yi, C.; Nawaz, M.I.; Zhang, B.; Yi, R.; Zhang, J.; Nkudede, E. Synthesis and characterization of nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nano-catalyst films for ciprofloxacin degradation. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 8376–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.T.; Duong, A.T.T.; Bui, N.D.; Ngo, V.T.M.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Tran, G.T.; Van Tran, T. Synthesis of magnetic NiFe2O4/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalysts for boosting dye degradation performance under visible-light irradiation. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 7, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, P.B.; Maddani, K.I.; Gumaste, M.R. Gadolinium-Doped Nickel Ferrite (NiFe2O4) Nanoparticles: Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Characterization. Phys. Solid State 2025, 67, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftyurek, E.; Li, Z.; Schierbaum, K. Adsorbed Oxygen Ions and Oxygen Vacancies: Their Concentration and Distribution in Metal Oxide Chemical Sensors and Influencing Role in Sensitivity and Sensing Mechanisms. Sensors 2022, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.; Panigrahi, U.K.; Chakravarty, S.; Hussain, S.; Mallick, P. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of NiO/NiFe2O4 nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, T.; Fang, X.; Xue, Z.; Huang, H.; Ren, H. Synergistic iron enhanced aerogel and peracetic acid for degradation of emerging organic contaminants. Npj Clean Water 2024, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).