Impact of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical and Thermal Expansion Properties of Fe-36Ni Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
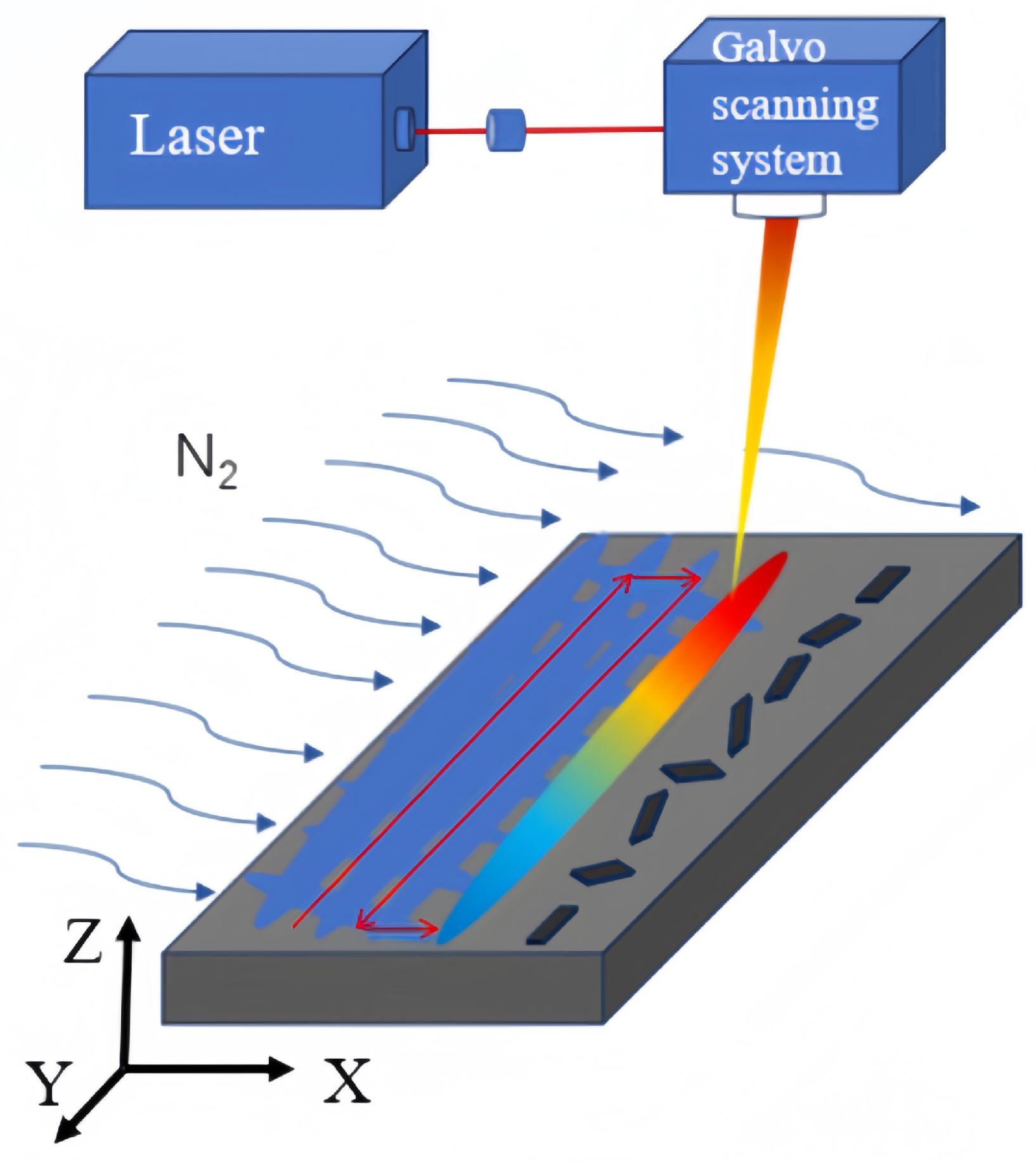
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
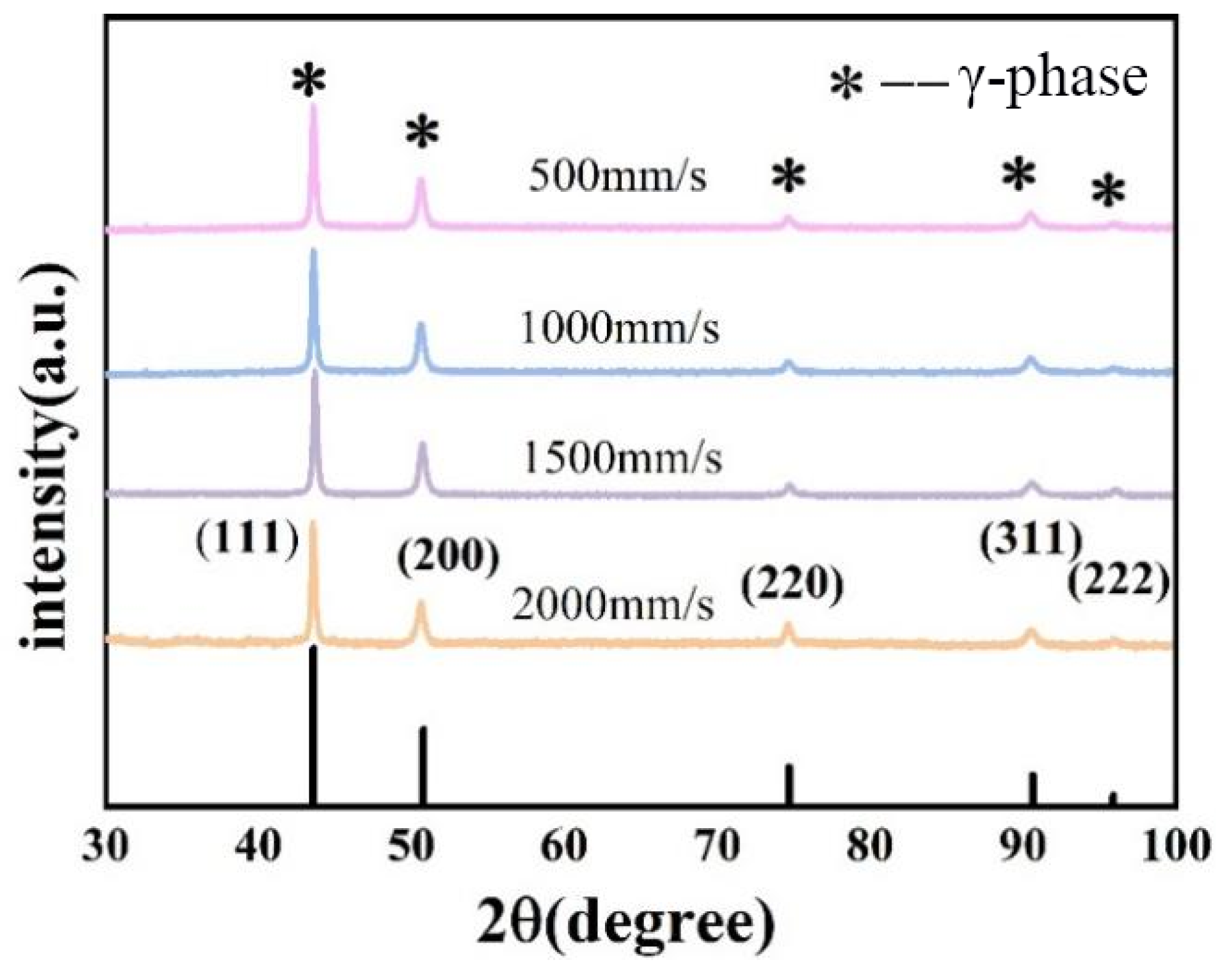
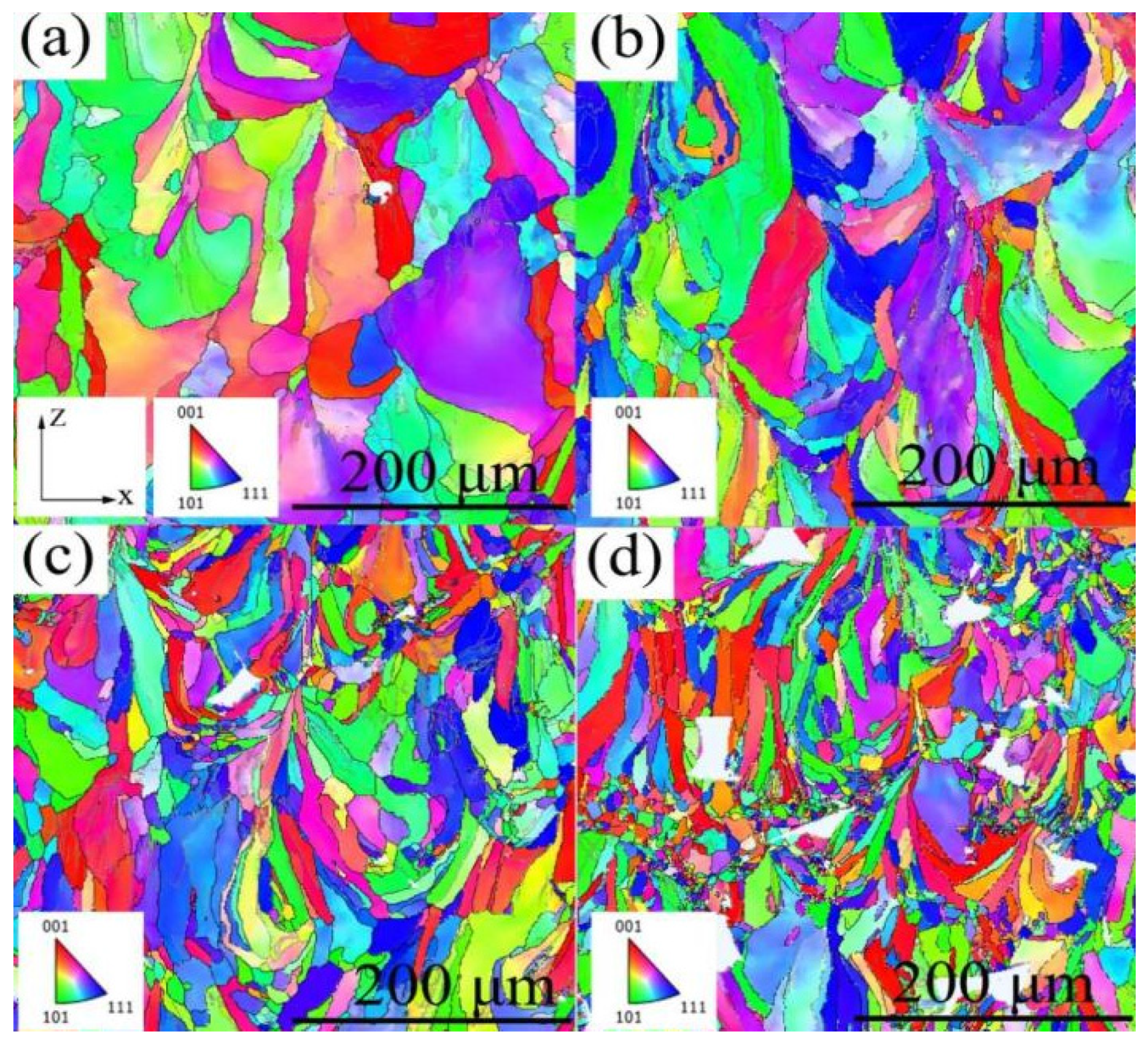
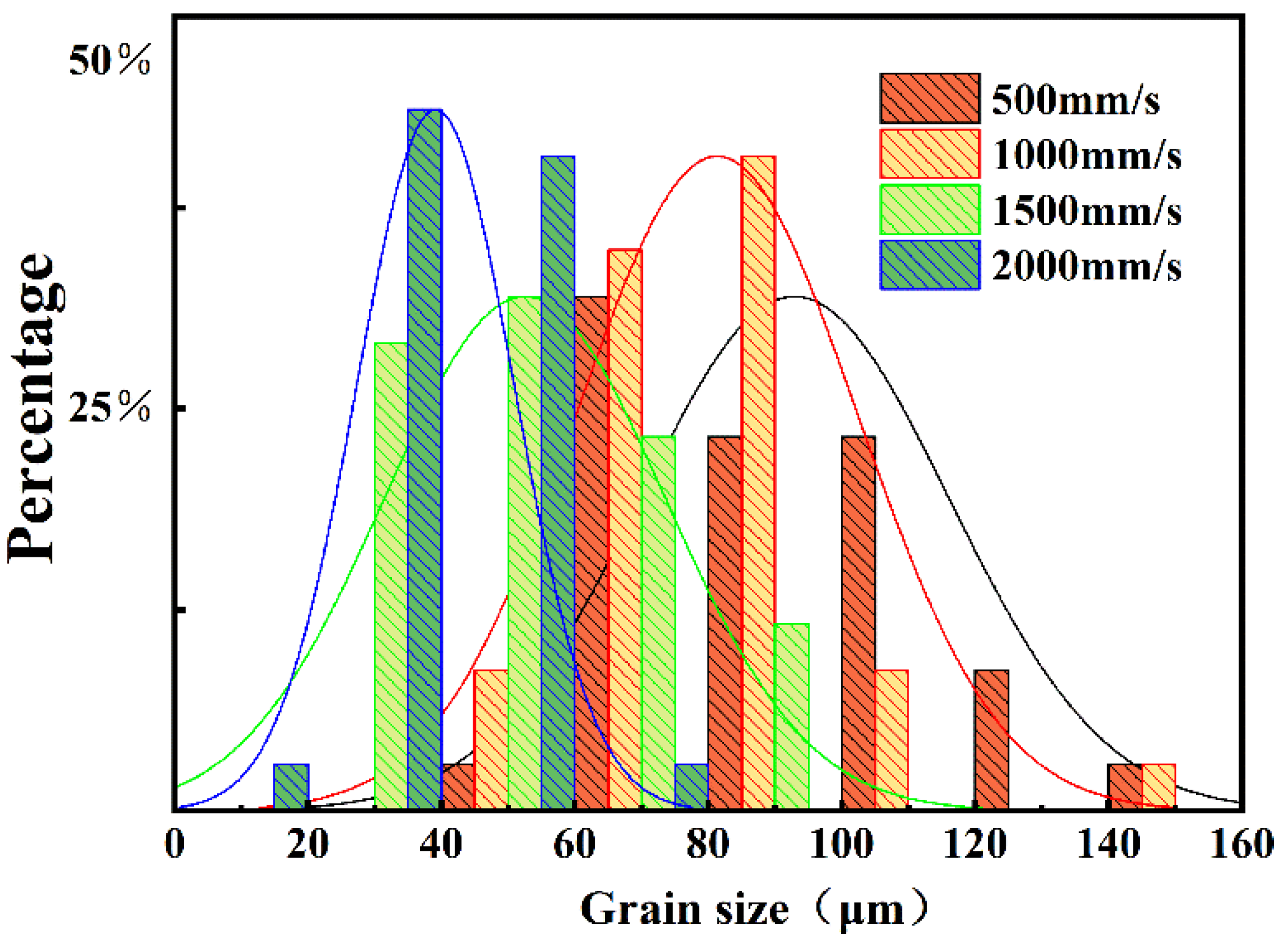
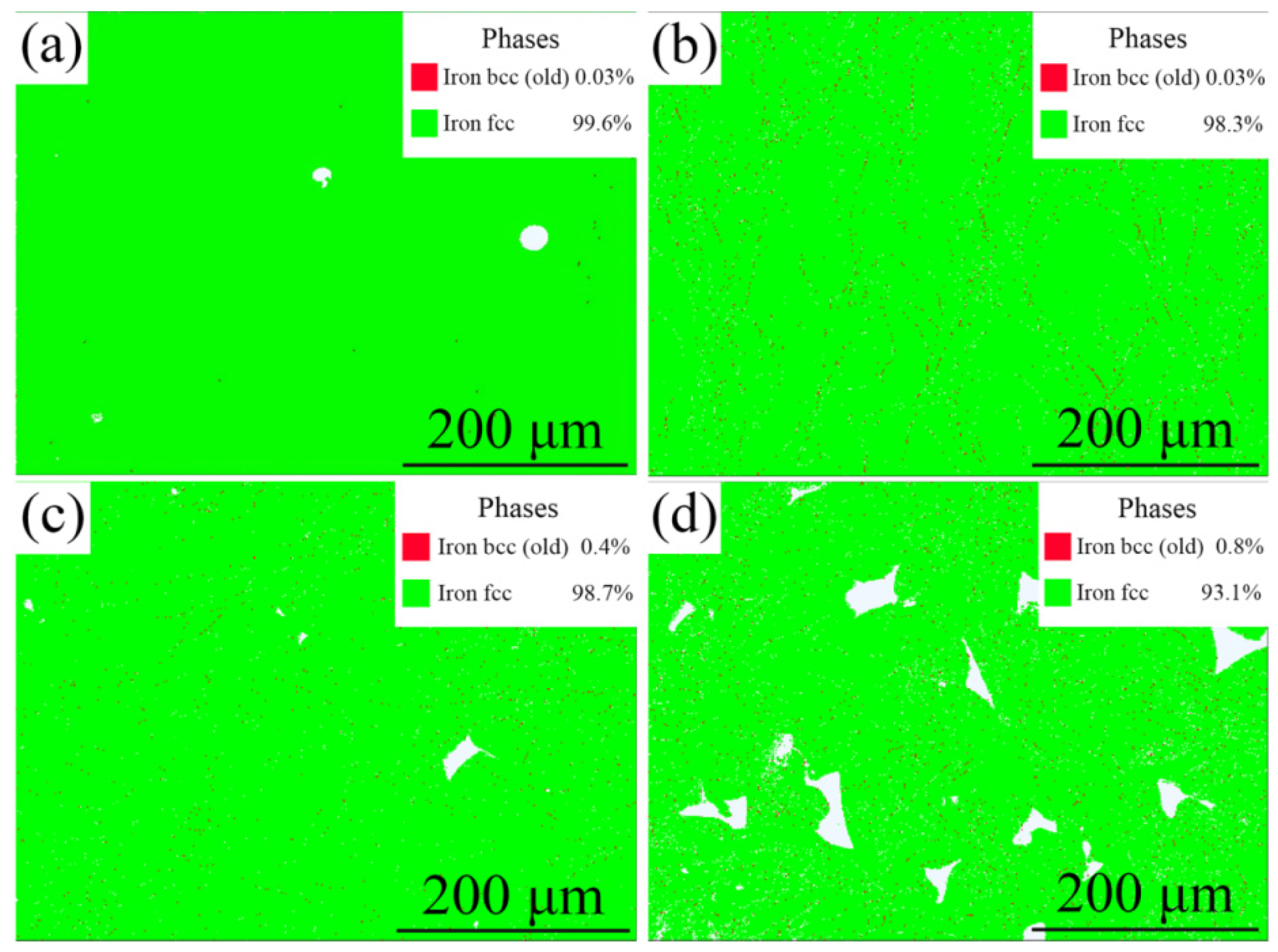
3.1. Phase and Microstructure
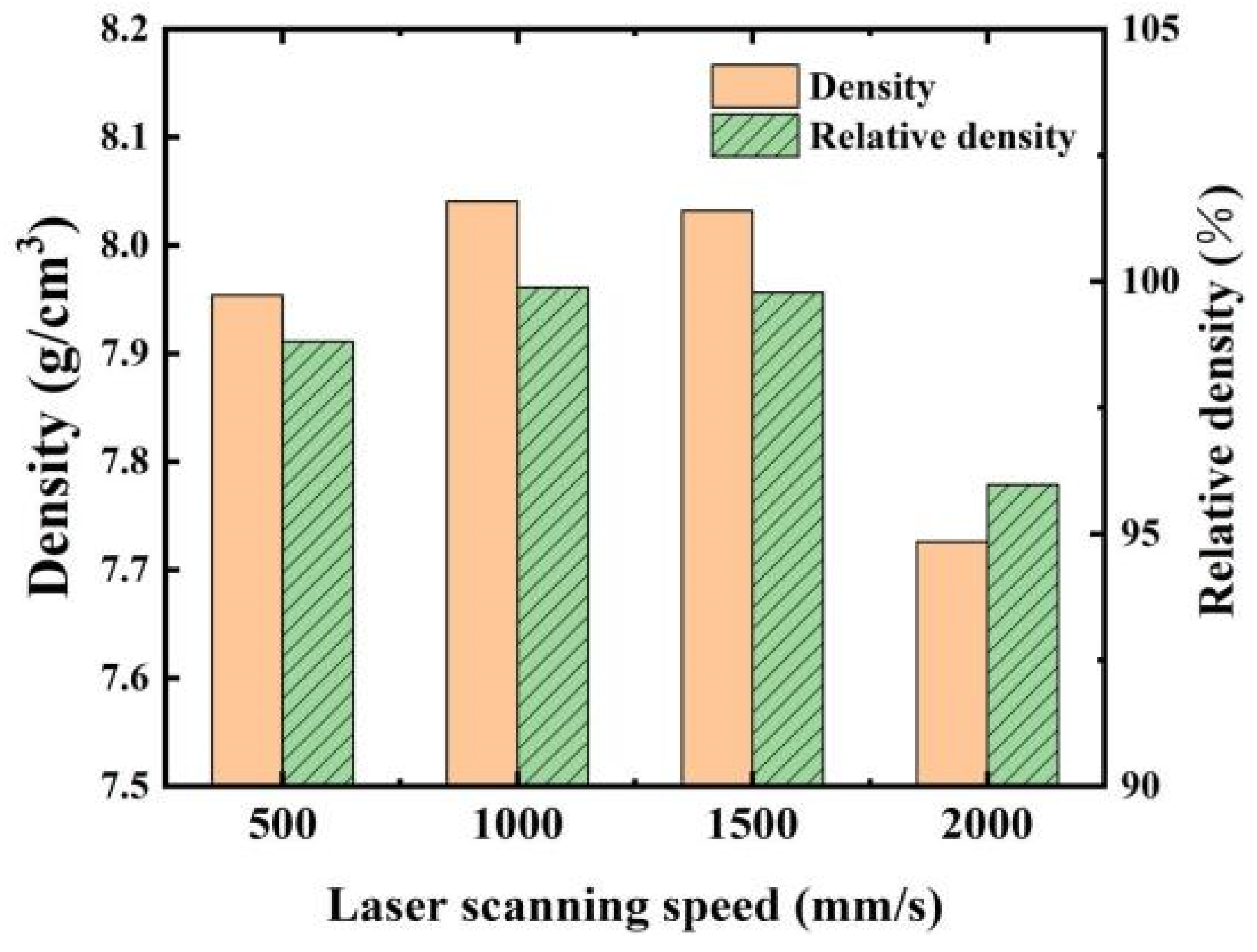
3.2. Relative Density and Mechanical Properties
3.3. Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Fe-36Ni alloy predominantly exhibits the γ-phase, with a small amount of α precipitates observed. This is primarily attributed to the formation of a supercooled region during the rapid cooling process inherent to SLM.
- (2)
- The grain size of the Fe-36Ni alloy samples decreased progressively with increasing laser scanning speed, while porosity initially decreased and subsequently increased with higher scanning speeds. The sample exhibiting the optimal microstructure was obtained at a scanning speed of 1000 mm/s.
- (3)
- At a laser scanning speed of 1000 mm/s, the Fe-36Ni alloy demonstrated the most favorable mechanical properties, with a tensile strength of approximately 439 MPa and an elongation of about 49%. This can be attributed to the superior molding quality of the SLM samples and the effects of grain refinement strengthening.
- (4)
- At a laser scanning speed of 2000 mm/s, the samples displayed the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion. This behavior is likely due to the higher defect density, such as the presence of pores, which provides additional space for the thermal expansion of adjacent microstructures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qing, H. Clarifying the role of Ce in the corrosion behavior of Fe-36Ni Invar alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2024, 30, 6536–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, J. Enhancing low thermal expansion behavior and strength via induced Zr-rich intermetallic phase in Fe-36Ni Invar alloy. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qing, H. Unveiling the influence of zirconium on the corrosion behavior of Fe-36Ni Invar alloy. Intermetallics 2024, 175, 108519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhan, X. Unraveling microstructure evolution induced mechanical responses in coaxial fiber-diode laser hybrid welded Fe–36Ni Invar alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 908, 146778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zou, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qing, H. Effects of Ce addition on mechanical properties and thermal expansion behavior of Fe-36Ni Invar alloy. Mater. Charact. 2024, 207, 113584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supekar, S.; Ghuge, R.; Shinde, M.; Manda, S.; Sivalingam, Y.; Ganesh, P.; Kumar, S.S.; Pareek, P.; Rane, S. Effect of annealing conditions on structural and magnetic properties of 36Ni-64Fe laminates. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 567, 170357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, M.; Wegener, T.; Laabs, L.; Vollmer, M.; Niendorf, T. Influence of Defects and Microstructure on the Thermal Expansion Behavior and the Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured Fe-36Ni. Materials 2024, 17, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Li, K.; Xing, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, J. Molten pool macroscopic thermodynamic analysis during selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg: Simulations and experiments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 2506–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wei, K.; Wang, T.; Feng, Q.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Ma, J.; Meng, D.; Li, J. Effect of laser scanning speed on the surface characteristics and wear resistance of TiZrAlV alloy via laser gas nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 500, 131909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Liang, H.; Xie, D.; Mao, Y.; Wang, C.; Shen, L.; Tian, Z. On the role of laser in situ re-melting into pore elimination of Ti–6Al–4V components fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 854, 156866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.; Suryanarayana, C.; Okulov, I.; Prashanth, K. Selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V: Effect of laser re-melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 805, 140558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Tang, H.B.; Tian, X.J.; Liu, D. Laser additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic aerospace components. Chin. J. Lasers 2020, 47, 0500002. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Meng, D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Microstructure evolution and vacuum tribological properties of surface nitriding layer on a TiZrAlV alloy fabricated by laser nitriding. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2023, 24, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, X.; Han, P.; Fu, H.; Dong, H.; Guo, S.; Su, R.; Li, J. Microstructure and microhardness of a novel TiZrAlV alloy by laser gas nitriding at different laser powers. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Kim, G.-H.; Kim, W.R.; Lee, T.W.; Kang, H.S.; Ham, M.J.; Choi, S.-J.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, H.T.; et al. Effect of energy density on down surface characteristics of AlSi10Mg alloy fabricated via selective laser melting. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, H.; Salarian, M.; Ma, H.; Olubamiji, A.; Vlasea, M. On thermal expansion behavior of Invar alloy fabricated by modulated laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Bai, Q. Defect formation mechanisms in selective laser melting: A review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergene, B. Farklı bağıl yoğunluklardaki Inconel 718 ve Ti6Al4V biyomedikal parçaların seçici lazer ergitme (SLE) metoduyla üretiminin simülasyonu. Gazi Üniversitesi Mühendislik Mimar. Fakültesi Derg. 2021, 37, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, C. Forming process and property of selective laser melted 4J36 invar alloy. Hot Work. Technol. 2023, 21, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Wang, P.; Yan, M.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Lu, Z. Additive manufacturing of metals: Microstructure evolution and multistage control. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 100, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tong, X.; Dong, S.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, L. Effects of process parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 24CrNiMo steel fabricated by selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 128, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeinfar, K.; Khodabakhshi, F.; Kashani-Bozorg, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Gerlich, A. A review on metallurgical aspects of laser additive manufacturing (LAM): Stainless steels, nickel superalloys, and titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1029–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W. Track trajectory, molten pool and defect characterization in NiTi single-track selective laser melting (SLM) experiments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 5210–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Mu, Y.; Yang, P.; Wu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, G. Metastable core-shell precipitation strengthened high-entropy alloys fabricated by direct energy deposition with multi-stage terrace-like slip wave toughening. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 210, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Khan, D.F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yin, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, G.; Su, J. Unveiling the cellular microstructure–property relations in martensitic stainless steel via laser powder bed fusion. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 2476–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, C. A magnesium alloy with ultrahigh Gd content manufactured by laser directed energy deposition: Heat treatment and microstructure evolution. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 175965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, L.-E.; Chua, C.-K.; Yeong, W.-Y.; Song, J.; Mapar, M.; Sing, S.-L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D. Numerical investigation and an effective modelling on the Selective Laser Melting (SLM) process with aluminium alloy 6061. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 80, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, L.; Ning, J.; Na, S.J. Effect of laser beam drift at high scanning speed on relative density, thickness and roughness of thin-walled TC11 specimen by selective laser melting. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 139, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, W.; Zeng, J.; Song, M.; Chang, S.; Zhu, C. Effect of scanning speed and laser power on formability, microstructure, and quality of 316L stainless steel prepared by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 3189–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Ke, L.; Zeng, X. Selective laser melting of Al7050 powder: Melting mode transition and comparison of the characteristics between the keyhole and conduction mode. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wei, Y.; Gao, H. Nanoscale precipitates as sustainable dislocation sources for enhanced ductility and high strength. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5204–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; He, G.; Peng, X.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. Effect of processing parameters on the microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal expansion behavior of Invar 36 alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 897, 146329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cai, B.; Ou, B.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, S. Effect of laser energy density on the phase transformation behavior and functional properties of NiTi shape memory alloy by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 176060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Peng, X.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. Microstructure evolution and corrosion behavior of Invar 36 alloy additively manufactured via laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Charact. 2024, 217, 114422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, M.; Elbestawi, M.; Veldhuis, S.C. Density and mechanical properties in selective laser melting of Invar 36 and stainless steel 316L. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 266, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Yin, R.; Tang, Y.; Liu, G.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Z. Effect of base material temper condition on precipitate evolution and mechanical properties of 2195 AlLi alloy friction stir welding joints. Mater. Charact. 2024, 209, 113712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| C | Mn | Si | Ni | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001 | 0.412 | 0.141 | 35.726 | 0.004 | 0.001 | Bal. |
| Sample ID | P (W) | V (mm/s) | h (mm) | t (mm) | Ev (J/mm)3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-500 | 240 | 500 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 120 |
| V-1000 | 240 | 1000 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 60 |
| V-1500 | 240 | 1500 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 40 |
| V-2000 | 240 | 2000 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Di, Y.; Wang, T.; Wei, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, M.; Li, J. Impact of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical and Thermal Expansion Properties of Fe-36Ni Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Coatings 2025, 15, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050572
Yang Z, Feng Z, Di Y, Wang T, Wei K, Zhang Z, Ge J, Wang J, Fan M, Li J. Impact of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical and Thermal Expansion Properties of Fe-36Ni Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050572
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zijian, Zhihao Feng, Yufei Di, Tianyu Wang, Kaimin Wei, Zhe Zhang, Junqi Ge, Jiangang Wang, Mingqiang Fan, and Jianhui Li. 2025. "Impact of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical and Thermal Expansion Properties of Fe-36Ni Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting" Coatings 15, no. 5: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050572
APA StyleYang, Z., Feng, Z., Di, Y., Wang, T., Wei, K., Zhang, Z., Ge, J., Wang, J., Fan, M., & Li, J. (2025). Impact of Scanning Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical and Thermal Expansion Properties of Fe-36Ni Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Coatings, 15(5), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050572






