Study on the Embrittlement of Steel Grain Boundaries Caused by Penetration and Diffusion of Liquid Copper
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
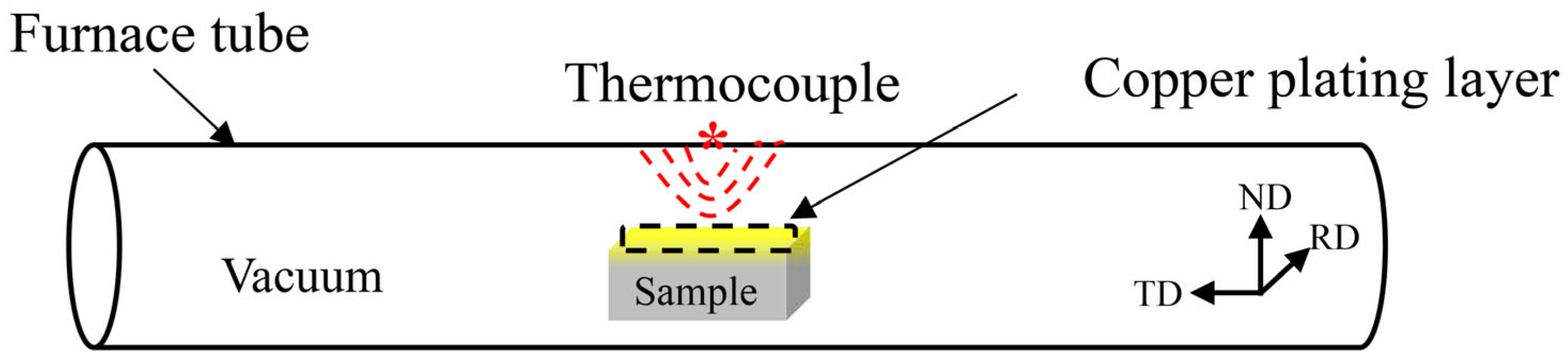
2.2. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
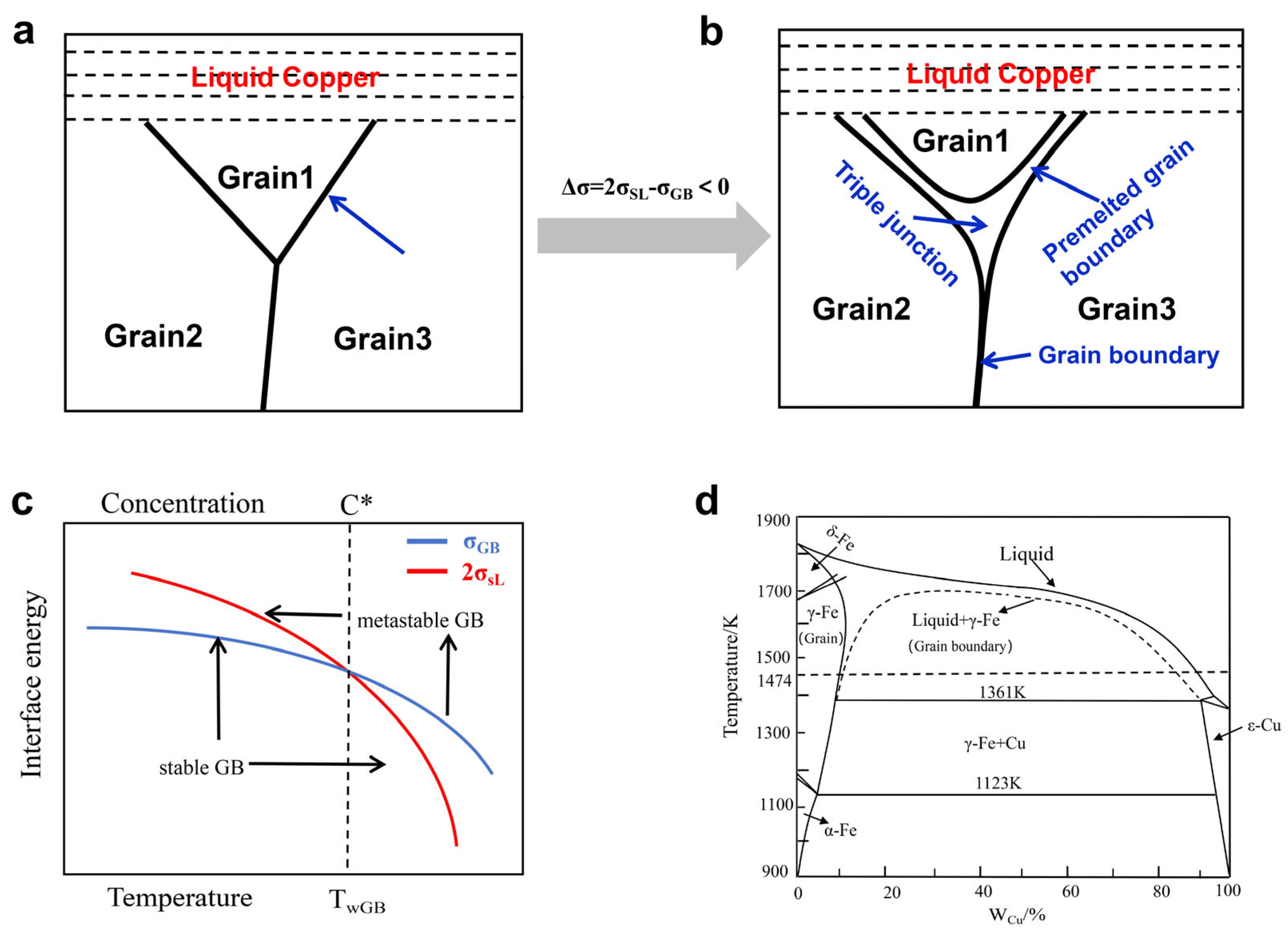
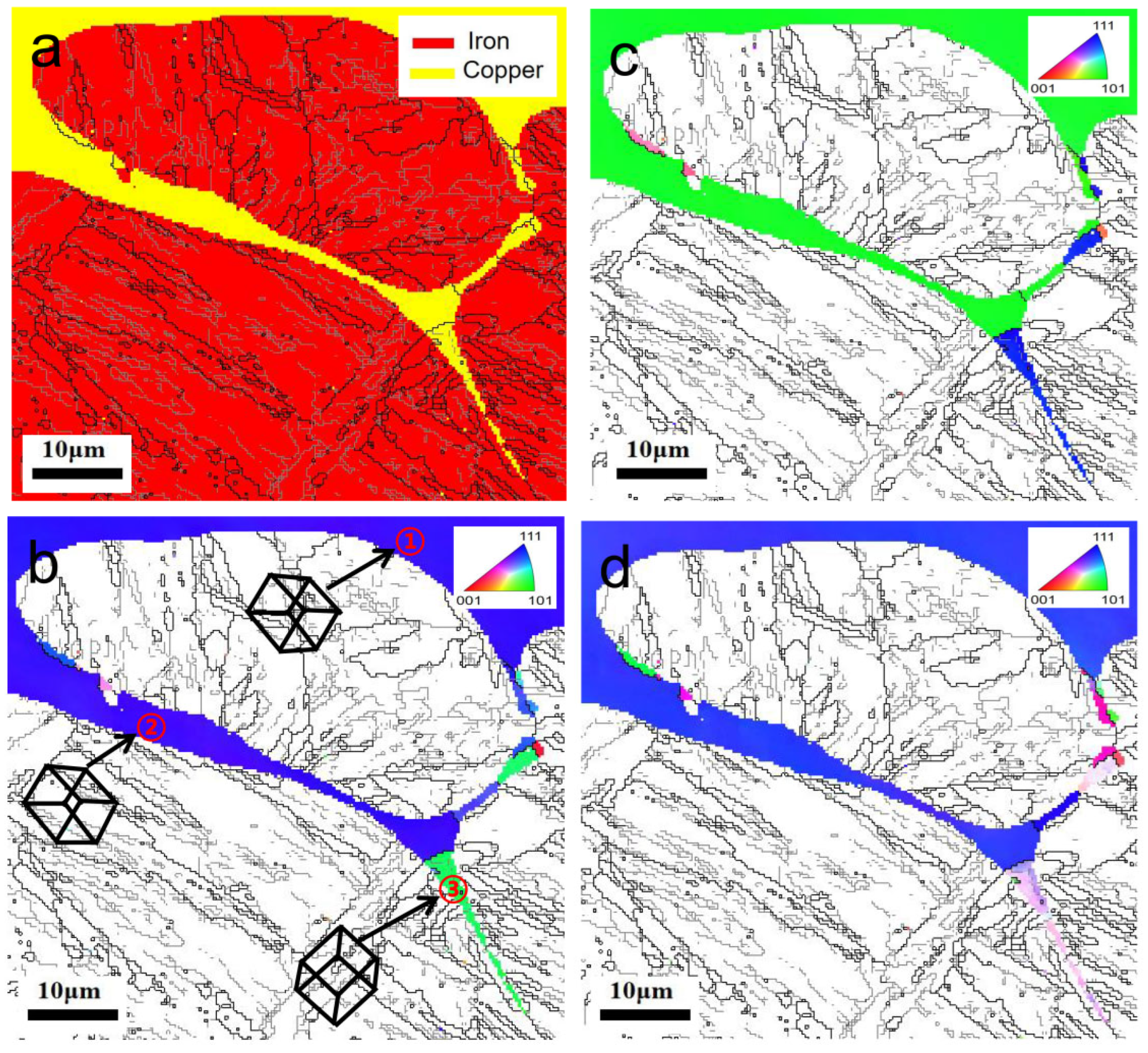
3.1. Microstructure Analysis of the Liquid Copper Penetration–Diffusion Along the GBs and TJs
3.2. Measurement of Copper Diffusion at High Temperatures and Theoretical Analysis of Its Diffusion
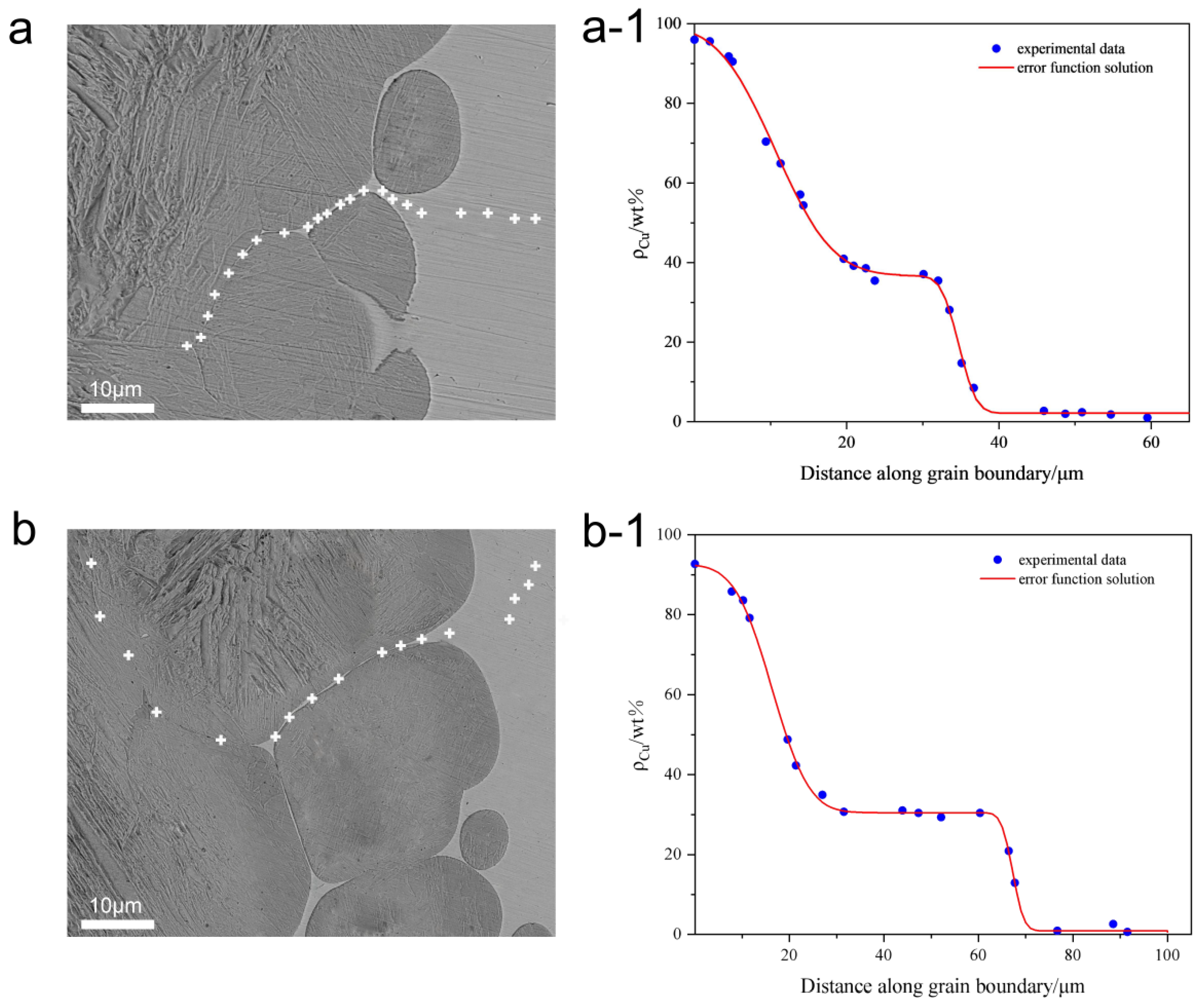
3.2.1. The Quantitative Analysis on the Base of the Diffusion Equation
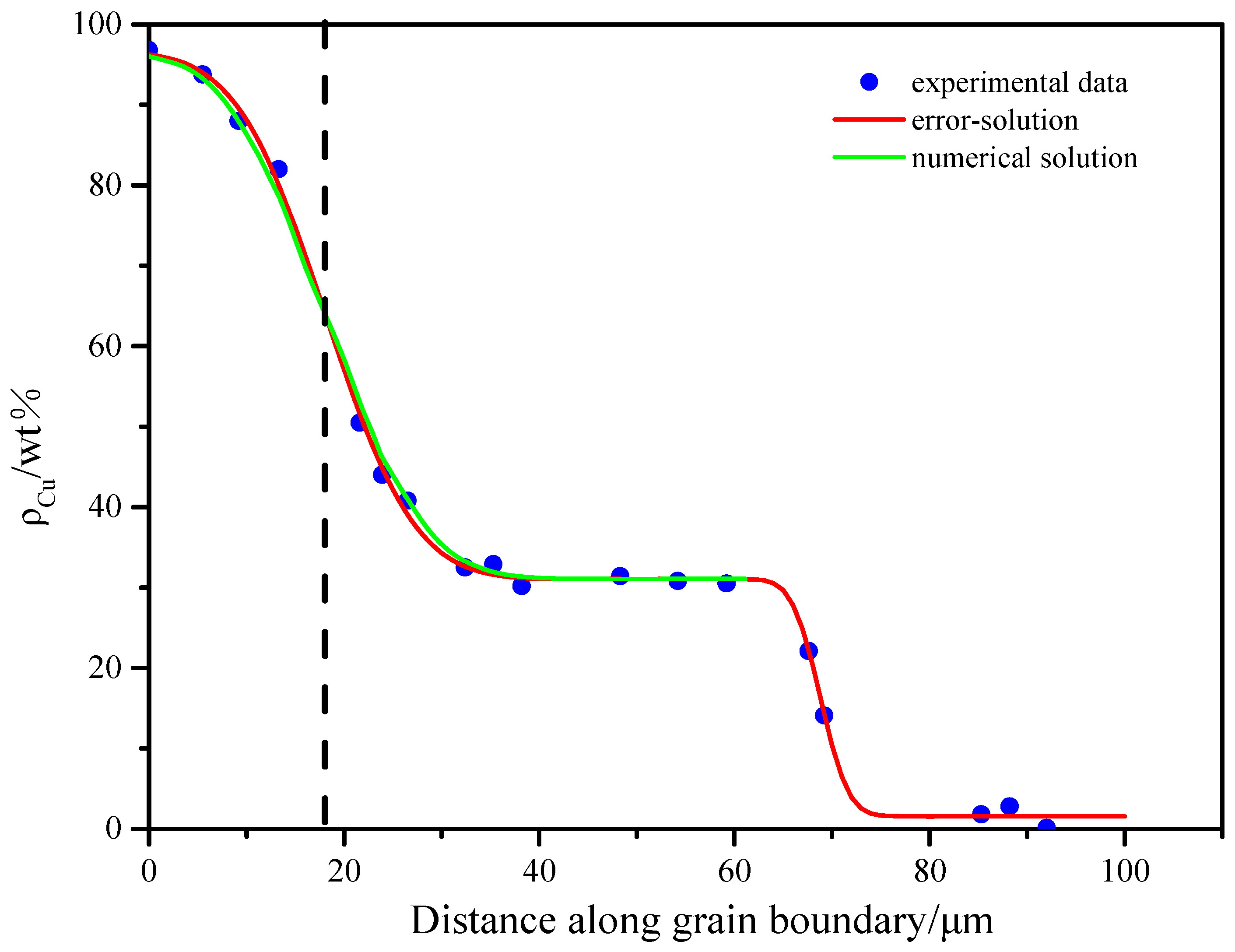
3.2.2. Quantitative Analysis on the Base of the Modified Diffusion Equation (Considering Liquid Copper Diffusion Along GBs)
3.3. Analysis of Copper Orientation at the Penetration–Diffusion Region Along Steel GBs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Symbols
| σSL | the energy of the boundary between solid and liquid phases |
| σGB | the energy of the grain boundary |
| TwGB | the wetting temperature for a GB |
| C* | the solute saturation concentrations |
| δ | the GB width |
| ρ | the concentration in the GBs |
| Db | the GB diffusion coefficient |
| D | the volume diffusion coefficient |
| x | the distance from the source surface |
| ρs | the concentration of diffusant atoms at the source surface |
| t | the diffusion time |
| Db | the GB diffusion coefficient |
| x0 | the coordinate of the Matano interfaces on the x-axis, corresponding to diffusion distance along GBs |
| ρ0 | the initial concentration of diffusant atoms; represents the coefficient related to the difference in initial composition |
| Dbi | the GB diffusion coefficients in the ith GBs phase; subscripts 1 and 2 represent the first and second parts of diffusion |
| ti | the diffusion time of the first and second stages |
| β (0 < β < 1) | the effect of liquid copper on infiltration diffusion |
References
- Kamder, M.H. Liquid Metal Embrittlement. Treatise Mater. Sci. Technol. 1983, 25, 361–459. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, V. Review of hot shortness problems in copper-containing steel. ATB Metall. 1983, 23, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Melford, D.A. The influence of residual and trace elements on hot shortness and high temperature embrittlement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1980, 295, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Habraken, L.; Lecomte-Beckers, J. Hot shortness and scaling of copper-containing steel. Mater. Sci. 1982, 45–81. [Google Scholar]
- Aramfard, M.; Deng, C. Interaction of shear-coupled grain boundary motion with crack: Crack healing, grain boundary decohesion, and sub-grain formation. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 085308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Safaei, B.; Long, H.; Chu, F.; Wei, Y. Orientation effect on intergranular fracture behaviors along symmetrical tilt grain boundaries in bcc iron. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.H. On some remarkable changes produced in iron and steel by the action of hydrogen and acids. R. Soc. 1875, 23, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, W.; McCaughey, J.; Markus, H. Embrittlement by Liquid Metals. Aeronautical 1960, 65, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, S.P. Hydrogen embrittlement and liquid-metal embrittlement in nickel single crystals. Sripta Metall. 1979, 13, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.P.; Stoner, G.E. Cleavage crystallography of liquid metal embrittled aluminum. Metall. Trans. 1991, 22, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumal, B.; Lepkova, T.; Korneva, A.; Gerstein, G.; Kogtenkova, O.; Gornakova, A. Grain Boundary Wetting by the Second Solid Phase: 20 Years of History. Metals 2023, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweinfest, R.; Paxton, A.T.; Finnis, M.W. Bismuth embrittlement of copper is an atomic size effect. Nature 2004, 432, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Razmpoosh, M.H.; Langelier, B.; Marzbanrad, E.; Zurob, H.S.; Zhou, N.; Biro, E. Atomic-scale Investigation of Liquid-Metal-Embrittlement Crack-path: Revealing Mechanism and Role of Grain Boundary Chemistry. Acta Mater. 2021, 204, 116519. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Cho, L.; Lee, C.; De Cooman, B.C. Zn Penetration in Liquid Metal Embrittled TWIP Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2016, 47, 2885–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, A.A.; Petelin, A.L.; Bokstein, B.S.; Zhevnenko, S.N.; Orelkina, D.I. The Formation of Liquid Metal Channels Network under Grain Boundary Wetting in the Cu-Bi System. Defect Diffus. 2012, 323–325, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, W.F.; Nippes, E.P.; Mushala, M.C. Copper-Contamination Cracking in the Weld Heat-Affected Zone. Weld. J. 1978, 57, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.S. Grains, Phases and Interfaces: Interpretation of Microstructures. Trans. AIME 1948, 175, 15–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, A.; Murray, J.D. Surface Hot Shortness in Low-Carbon Steel. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1956, 203, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, T. The interaction of molten copper with solid iron. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksson, H.; Hansson, K.; Olsson, A. On the mechanism of liquid copper penetration into iron grain boundaries. Scand. J. Met. 2001, 30, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X. Grain boundary premelting and activated sintering in binary refractory alloys. Mater. Sci. 2016, 93, 224108. [Google Scholar]
- Hickman, J.; Mishin, Y. Disjoining potential and grain boundary premelting in binary alloys. Phys. Rev. 2016, 93, 24108. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, M.S.; Agarwala, R.P. Diffusion of copper in iron. J. Appl. Phys. 1966, 37, 4248–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y. Migration of solidification grain boundaries and prediction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi Rad, M.; Boussinot, G.; Apel, M. Geometry of Triple Junctions during Grain Boundary Premelting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 225701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabkin, E. Grain Boundary Interdiffusion in the Case of Concentration-Dependent Grain Boundary Diffusion Coefficient. Interface Sci. 1996, 3, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellenthin, J.; Karma, A.; Plapp, M. Phase-field crystal study of grain-boundary premelting. Phys. Rev. 2018, 78, 184110. [Google Scholar]
- Lipowsky, R. Melting at grain boundaries and surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2876. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt, J.J.; Olmsted, D.; Jindal, S.; Asta, M.; Karma, A. Method for Computing Short-Range Forces between Solid-Liquid Interfaces Driving Grain Boundary Premelting. Phys. Rev. 2009, 79, 020601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cheng, H.; Asl, K.M.; Kiely, C.J.; Harmer, M.P. The Role of a Bilayer Interfacial Phase on Liquid Metal Embrittlement. Science 2011, 332, 1730–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beke, D.L.; Kaganovskii, Y.; Katona, G.L. Interdiffusion along grain boundaries diffusion induced grain boundary migration, low temperature homogenization and reactions in nanostructured thin films. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 98, 625–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishin, Y. Grain Boundary Diffusion in Metals. Phil. Mag. 1995, 1589, 337–366. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini, J.; Gas, P. Grain Boundary Diffusion in Solids: Recent Advances and Applications. Defect Diffus. Forum 1997, 143–147, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.C. Calculation of Diffusion Penetration Curves for Surface and Grain Boundary Diffusion. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishin, Y.; Herzig, C.; Bernardini, J. Gust, Grain boundary diffusion: Fundamentals to recent developments. Int. Mater. Rev. 1997, 42, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoluchowski, R. Theory of Grain Boundary Diffusion. Phys. Rev. 1952, 87, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Ratke, L. Instability of Grain Boundary Grooves due to Equilirium Grain Boundary Diffusion. Acta Metall. 1991, 39, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Herzig, C.; Mishin, Y. Diffusion in Condensed Matter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 337–366. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, A.; Laurila, T.; Vourinen, V.; Divinski, S.V. Thermodynamics, Thermodynamics, Diffusion and the Kirkendall Effect in Solids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 17, p. 446. [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin, E.; Semenov, V.N.; Shvindlerman, L.S.; Straumal, B.B. Penetration of tin and zinc along tilt grain boundary 43° in Fe-5at%Si alloy: Premelting phase transition. Acta Metall. Mater. 1991, 39, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Composition | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content% | 0.17 | 0.18 | 1.2 | 0.02 | 0.008 | 0.03 | Others |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, Y.; Wen, D.; Wang, W.; Fan, C.; Chen, K. Study on the Embrittlement of Steel Grain Boundaries Caused by Penetration and Diffusion of Liquid Copper. Coatings 2025, 15, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040408
Chu Y, Wen D, Wang W, Fan C, Chen K. Study on the Embrittlement of Steel Grain Boundaries Caused by Penetration and Diffusion of Liquid Copper. Coatings. 2025; 15(4):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040408
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Yu, Donghui Wen, Wei Wang, Changzhi Fan, and Kun Chen. 2025. "Study on the Embrittlement of Steel Grain Boundaries Caused by Penetration and Diffusion of Liquid Copper" Coatings 15, no. 4: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040408
APA StyleChu, Y., Wen, D., Wang, W., Fan, C., & Chen, K. (2025). Study on the Embrittlement of Steel Grain Boundaries Caused by Penetration and Diffusion of Liquid Copper. Coatings, 15(4), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040408






