Coatings Applied to the Optimization of Portulaca oleracea L. Seed Pellet Formulation Based on Mixture Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
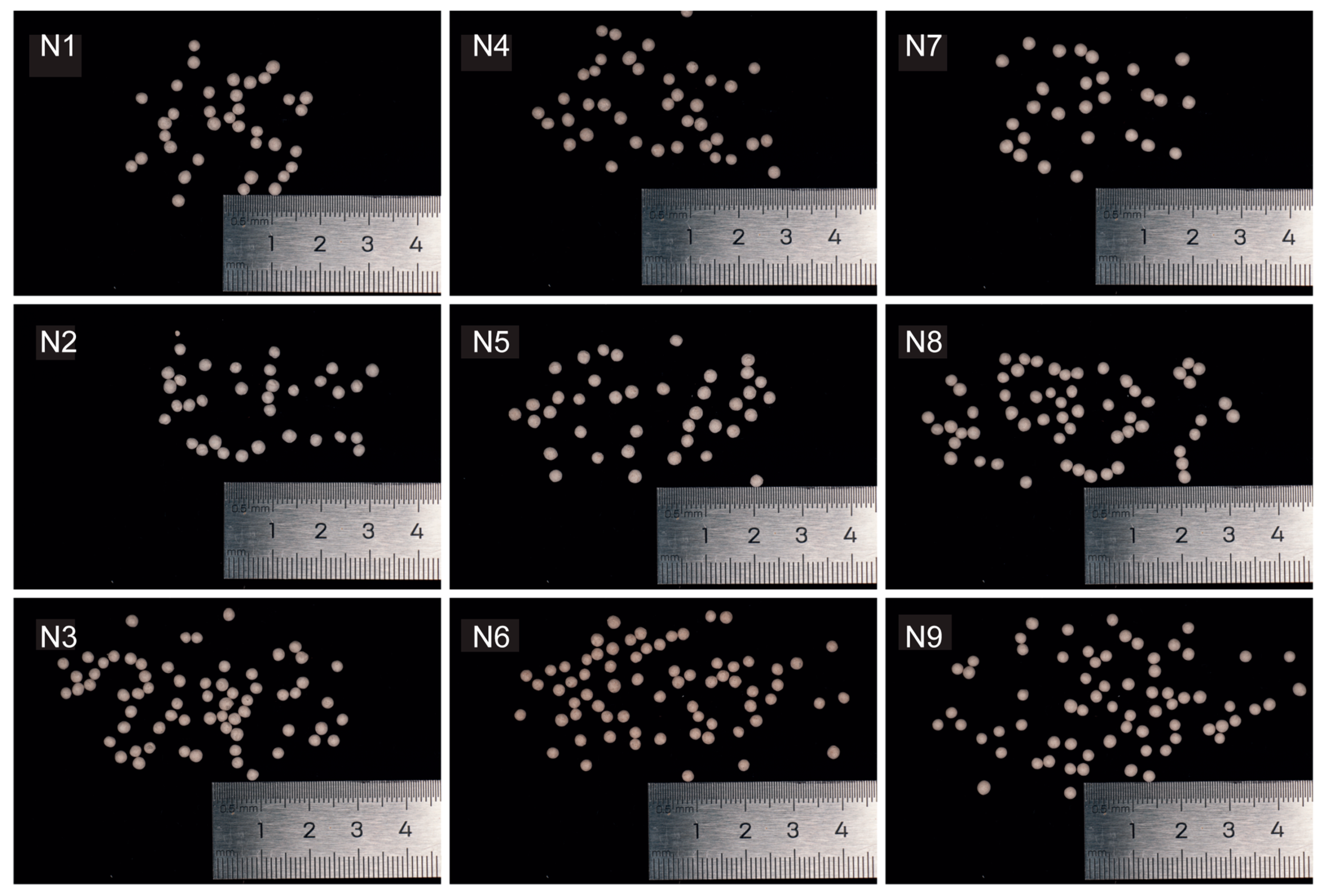
2.3. Physical Shape of Pellet Granulated Seeds of Portulaca oleracea
2.4. Germination Index of Pelletized Seeds
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Different Filler Ratios on the Physical Properties of Granulated P. oleracea Seeds
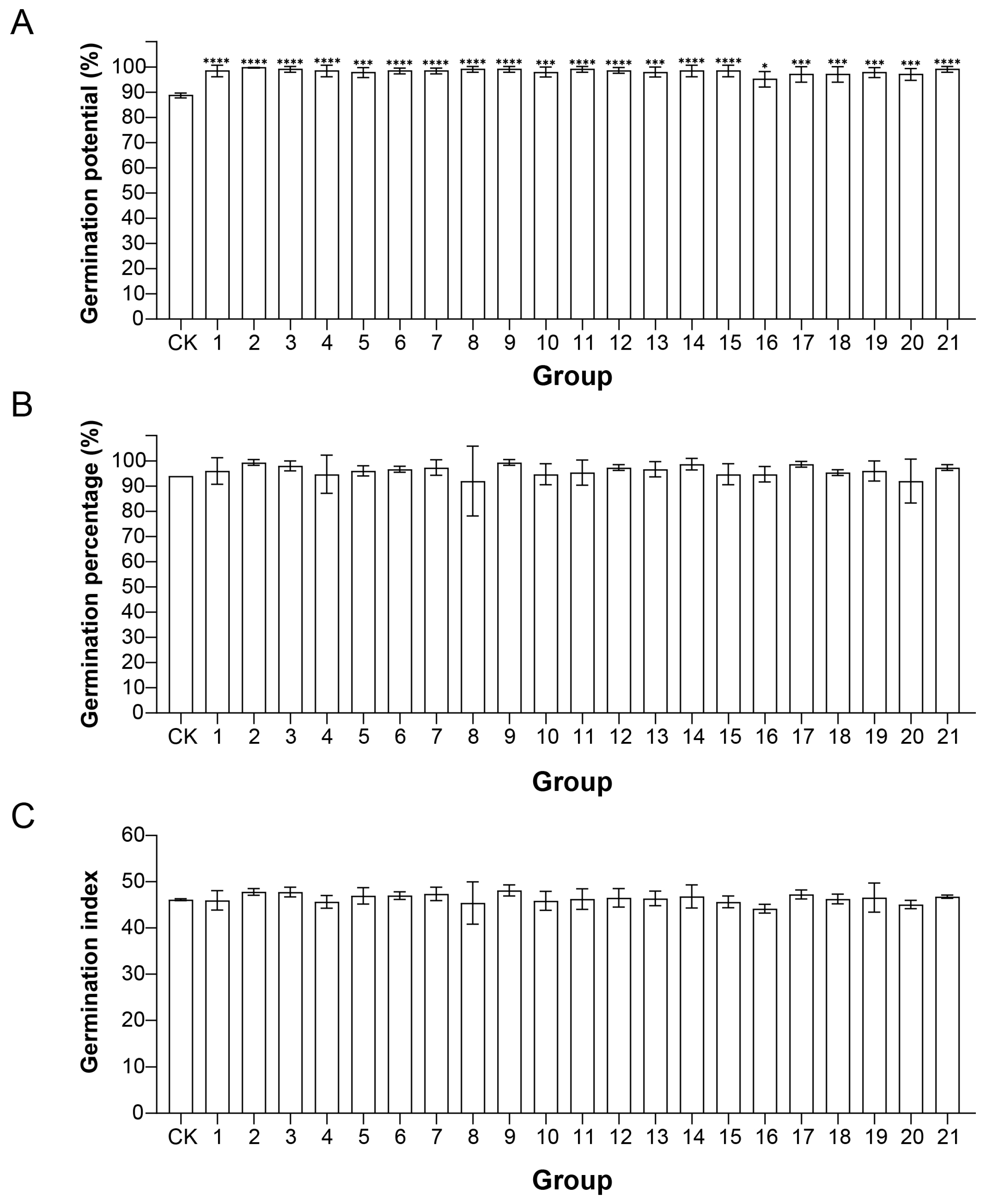
3.2. Impact of Different Filler Ratios on Seed Germination Performance
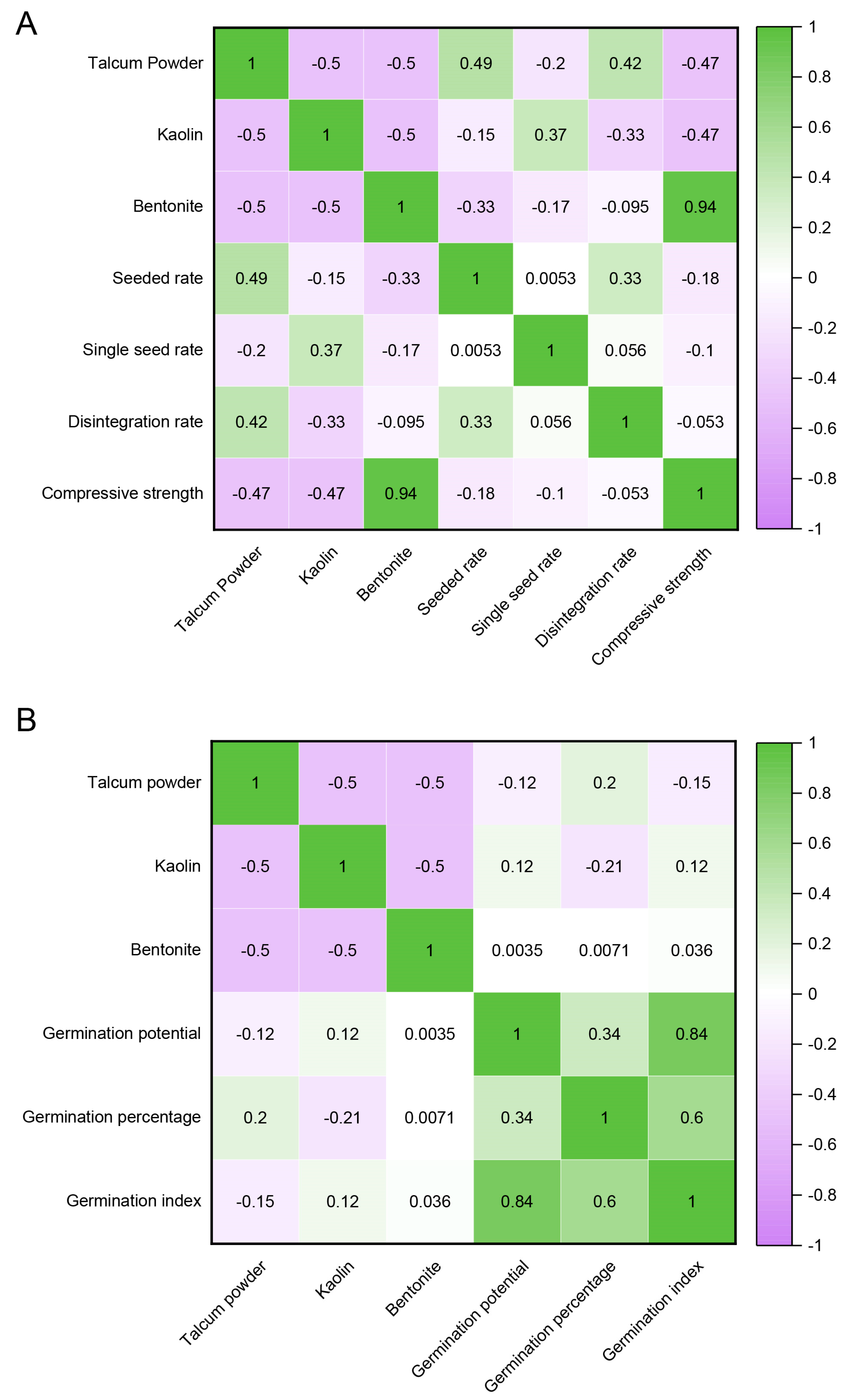
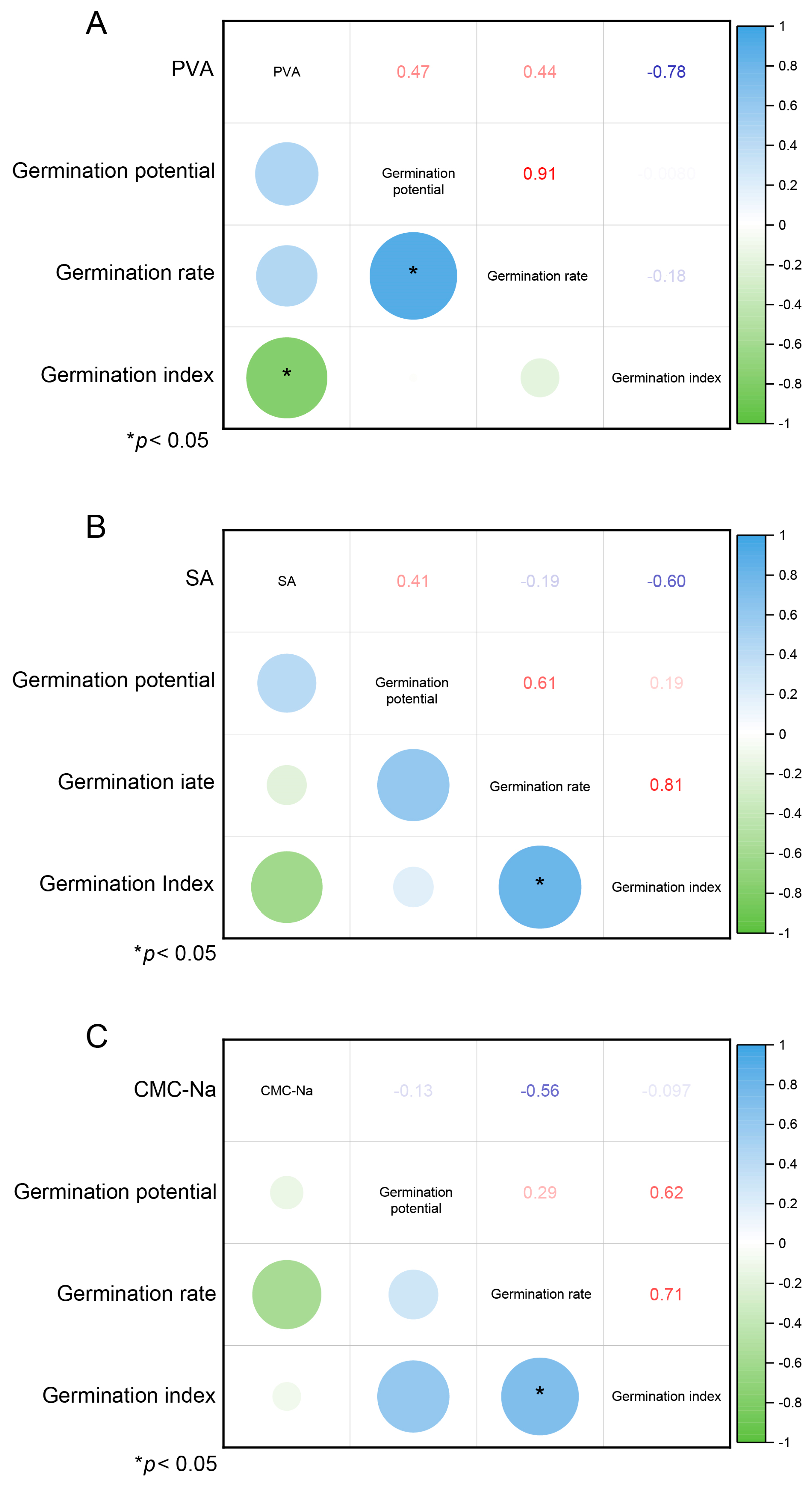
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between the Proportion of Filler, the Physical Shape, and the Germination Shape of Pelletized Seeds
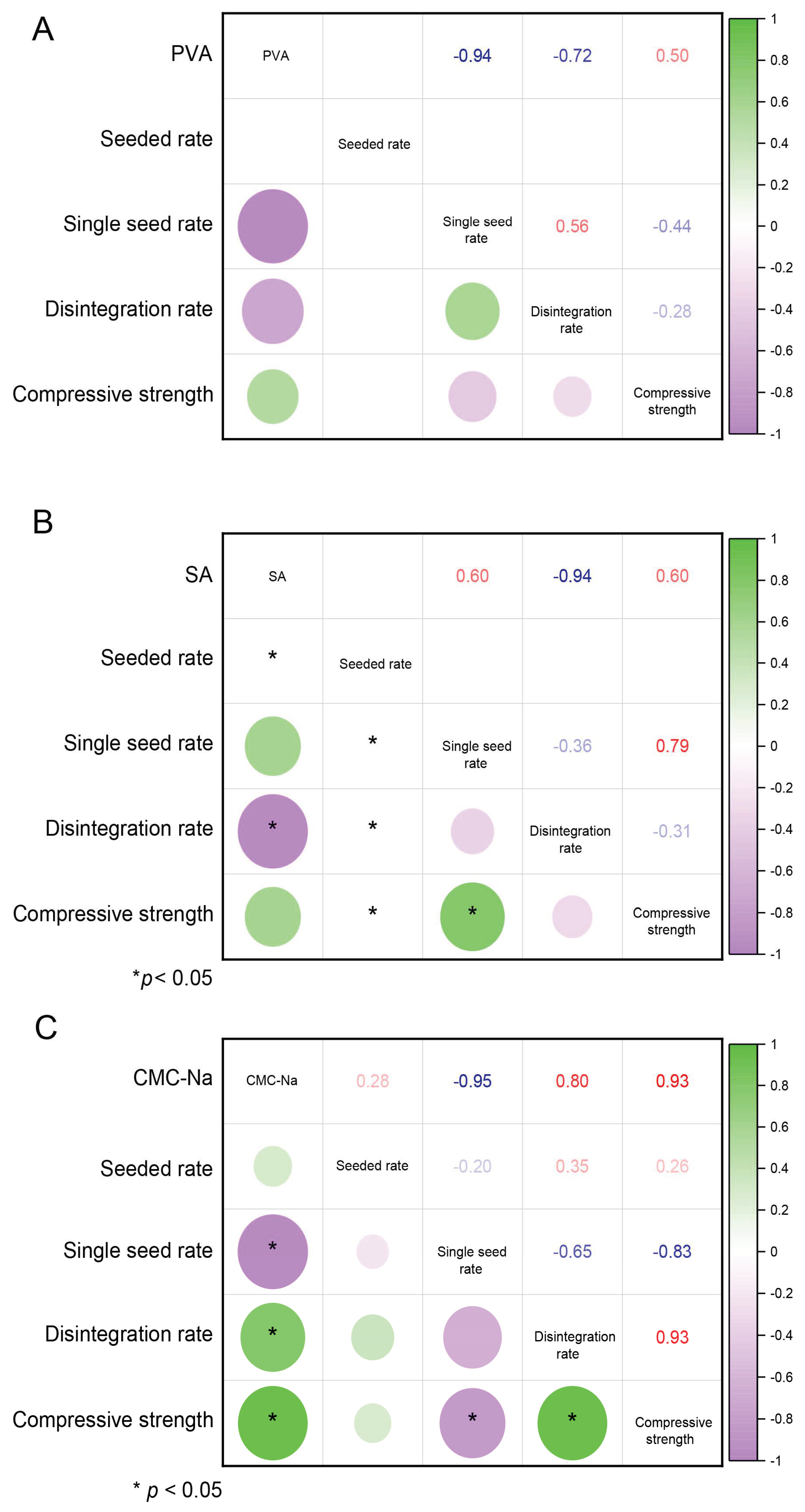
3.4. Effects of Different Binders and Their Concentrations on the Physical Properties of Pellet Granulation
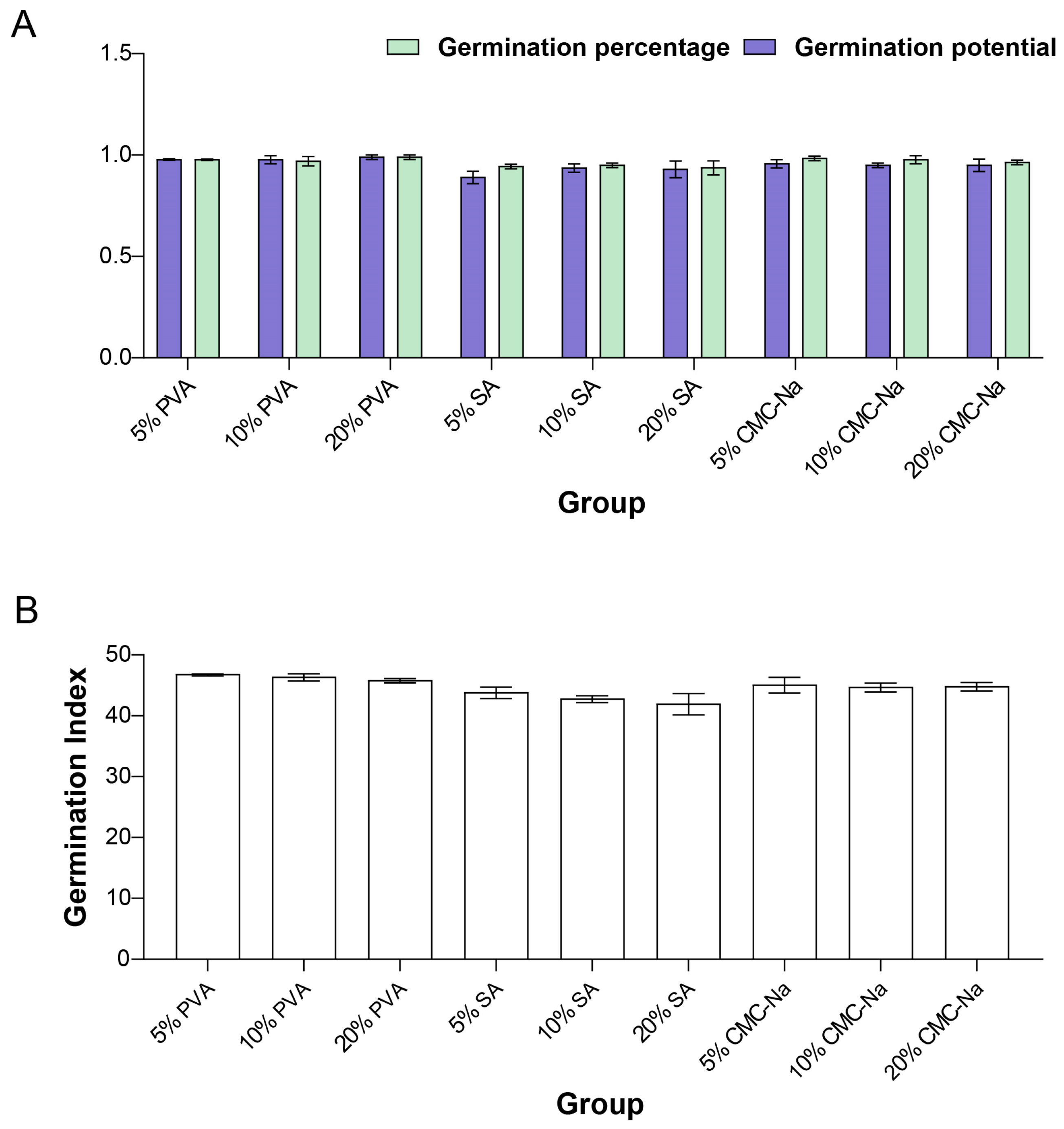
3.5. Impact of Different Binding Agents and Their Concentrations on Seed Germination Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, M.A.; Juraimi, A.S.; Rafii, M.Y.; Hamid, A.A.; Uddin, M.K.; Alam, M.Z.; Latif, M.A. Genetic improvement of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) and its future prospects. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 7395–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, R.M.; Andreo, C.S.; Lara, M.V. Deciphering the mechanisms involved in Portulaca oleracea (C4) response to drought: Metabolic changes including crassulacean acid-like metabolism induction and reversal upon re-watering. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Ben, C.; Todd, C.D.; Shi, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X. Comparative proteomic analysis of the thermotolerant plant Portulaca oleracea acclimation to combined high temperature and humidity stress. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 3605–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Yan, G.; Hua, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, W.; Liang, Z.; Chao, Q.; Hibberd, J.M.; Jiao, Y.; et al. Gene duplications facilitate C4-CAM compatibility in common purslane. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 2622–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, T.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Melili, M.G.; Stefano, V.D.; Sciacca, F.; Pagliaro, A.; Scandurra, R.B.; Virzi, N.; Gentile, C.; Palumbo, M. Improvement of Fatty Acid Profile in Durum Wheat Breads Supplemented with Portulaca oleracea L. Quality Traits of Purslane-Fortified Bread. Foods 2020, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P.; Norman, H.A.; Gillaspy, E.; Duke, J.A. Common purslane: A source of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P.; Salem, N., Jr. Purslane: A terrestrial source of omega-3 fatty acids. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-L.; Liang, X.; Gao, P.-Y.; Li, L.-Z.; Song, S.-J. Chemical Constituents of Portulaca oleracea. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 760–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in Research on Chemical Components and Antibacterial Activities of Portulaca oleracea L. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 359–371. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Li, D.; Meng, X.; Suna, Y.; Liua, R.; Sun, T. Review of isolation, purification, structural characteristics and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Portulaca oleracea L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Jia, H.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Re Zeng, C.; Yu, M. Research progress on alkaloids from whole herb of Portulaca oleracea L. Drug Eval. Res. 2020, 43, 1174–1182. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Nur, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, S.; RamaKrishna, S.; Berto, F. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties of Herbal Materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xin, H.; Rahman, K.; Wang, S.; Peng, C.; Zhang, H. Portulaca oleracea L.: A review of phytochemistry and pharmacological effects. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 925631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, P.G.d.; Rosenthal, A.; Ayres, E.M.M.; Teodoro, A.J. Potential Functional Food Products and Molecular Mechanisms of Portulaca oleracea L. on Anticancer Activity: A Review. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7235412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xia, T.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Lai, L.; Xu, S.; Yue, X.; Xin, H. A review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology and potential uses of Portulaca oleracea L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Liua, Y.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Ji, G.; Xu, H. Therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of digestive inflammatory cancer transformation: Portulaca oleracea L. as a promising drug. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 327, 117999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.-I.K. Effects of Portulaca oleracea L. seeds in treatment of type-2 diabetes mellitus patients as adjunctive and alternative therapy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wen, H.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Yang, C.; Tu, Y.; Li, N.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, A.; et al. Clinical observation on effects of skin care products containing extract from purslane and licorice in patients with sensitive skin. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 38, 364–366. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.; He, L.; Xiang, L.; Luo, D.; Li, L.; Hao, F. Clinical observation of skin care products containing papain and purslane in treatment of acne vulgaris. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 38, 352–354. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Long, C. Study on functions of purslane and evaluation of its safety. China Surfactant Deterg. Cosmet. 2018, 48, 88–93+108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, T.; Zheng, F.; Yue, H.; Dai, Y. Progress on the application and efficacy of Portulaca oleracea L. in cosmetics. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 2023, 40, 820–832. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, M.M.; Heikal, Y.M.; Bonanomi, G. Phytoremediation efficiency of Portulaca oleracea L. naturally growing in some industrial sites, Dakahlia District, Egypt. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subpiramaniyam, S. Portulaca oleracea L. for phytoremediation and biomonitoring in metal-contaminated environments. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X. Study of the effects of pretreatments on seed germination of the medicinal plant Portulaca oleracea L. J. Southwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 32, 69–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yun, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Lu, C. Provenance Identification and Comparison of Biological Characteristics and Ecological Adaptabilities Between the Wild and Cultivated Types of Purslane. Seed 2016, 35, 6–10+14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.G.; Amirkhani, M.; Hill, D.a.H. Modern Seed Technology. Agriculture 2021, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Han, L. Current status and prospects of seed pelleting research in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 605–615. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J.; Wang, W.; Peng, S.; Nie, L. Seed Pelleting with Calcium Peroxide Improves Crop Establishment of Direct-seeded Rice under Waterlogging Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-q.; Li, J.-g.; Xue, H.; Wang, X.-f. Super absorbent polymer seed coatings promote seed germination and seedling growth of Caragana korshinskii in drought. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2017, 18, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Ma, X.; Hou, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X. Experimental Study on the Pelleting and Coating Performance of Red Clover Seeds. Coatings 2024, 14, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornish, E.; Arnold, H.; Fehmi, J. Review of seed pelletizing strategies for arid land restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntam, D.; Permpoonsinsup, W.; Surin, P. The Application of a Hybrid Model Using Mathematical Optimization and Intelligent Algorithms for Improving the Talc Pellet Manufacturing Process. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussainova, B.; Tazhkenova, G.; Kazarinov, I.; Nurlybayeva, A.; Lamichova, A.; Kusepova, L.; Mashan, T.; Tantybayeva, B.; Saurbayeva, B.; Seitbekova, G.; et al. Comparative Study of the Physico-Chemical Properties of Sorbents Based on Natural Bentonites Modified with Iron (III) and Aluminium (III) Polyhydroxocations. Coatings 2023, 13, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddarai, E.M.; Mouzahim, M.E.; Boussen, R.; Bellaouchou, A.; Guenbour, A.; Zarrouk, A. Chitosan-kaolinite clay composite as durable coating material for slow release NPK fertilizer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Yimamu, A.; Nurehemaiti, H. Screening of Seed Coating Materials for Kochia prostrata. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2021, 58, 352–360. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, P.B.; Vieira, H.D.; Guimarães, C.P. Physiological potential of stylosanthes cv. Campo Grande seeds coated with different materials. J. Seed Sci. 2015, 37, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, F.; Ma, C.; Wei, Z.; Long, W. Bonding Mechanism and Process Characteristics of Special Polymers Applied in Pelletizing Binders. Coatings 2022, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Han, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, F.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y. Sodium Alginate–Montmorillonite Composite Film Coatings for Strawberry Preservation. Coatings 2024, 14, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ruiz, A.A.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; Orozco-Carmona, V.M.; Devora-Isiordia, G.E.; Villegas-Peralta, Y.; Álvarez-Sánchez, J. Chitosan and Its Derivatives as a Barrier Anti-Corrosive Coating of 304 Stainless Steel against Corrosion in 3.5% Sodium Chloride Solution. Coatings 2024, 14, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, L.; Zang, J.; Duan, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X. Study on seed pelleting and performance of welsh onion (Allium fistulosum L.). Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2022, 24, 1236–1247. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Cai, Z.; Jiao, X.; Wang, H. Effect of seed pelletization on agronomic characters and yield of Codonopsis pilosula. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2022, 57, 82–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, T.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J. Seed Granulation of Chinese Herbal Medicine in China: A Review. Mod. Chin. Med. 2021, 23, 1299–1303. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Qiao, H.; Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, R.; Wei, J.; Ma, S.; et al. Current Situation and Consideration on Pesticides Application in Production of Chinese Herbal Medicine. Mod. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 263–270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, L.; Ma, X.; Song, J.; Liu, Z. Numerical simulation method of seed pelletizing: Increasing seed size by powder adhesion. Powder Technol. 2024, 444, 119991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, I.; Javed, T.; Amirkhani, M.; Taylor, A.G. Modern Seed Technology: Seed Coating Delivery Systems for Enhancing Seed and Crop Performance. Agriculture 2020, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangsopa, J.; Hynes, R.K.; Siri, B. Lettuce seeds pelleting: A new bilayer matrix for lettuce (Lactuca sativa) seeds. Seed Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Afzal, I. Impact of seed pelleting on germination potential, seedling growth and storage of tomato seed. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1273, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikhao, P.; Taylor, A.G.; Marino, E.T.; Catranis, C.M.; Siri, B. Development of seed agglomeration technology using lettuce and tomato as model vegetable crop seeds. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 184, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetiyanon, K.; Wittaya-Areekul, S.; Plianbangchang, P. Film coating of seeds with Bacillus cereus RS87 spores for early plant growth enhancement. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanfar, S.; Modarres-Sanavy, S.A.M. Crop protection by seed coating. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2005, 70, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- O’Callaghan, M. Microbial inoculation of seed for improved crop performance: Issues and opportunities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5729–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Javaid, A.; Ashraf, M. The role of mycorrhizae and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in improving crop productivity under stressful environments. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malusá, E.; Sas-Paszt, L.; Ciesielska, J. Technologies for beneficial microorganisms inocula used as biofertilizers. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 491206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.J.; Wang, J.C.; Hu, J.-J.; Tian, Y.X.; Hu, W.M.; Zhu, S.J. A novel fluorescent dual-labeling method for anti-counterfeiting pelleted tobacco seeds. Seed Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.G.; Harman, G. Concepts and Technologies of Selected Seed Treatments. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1990, 28, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atefeh, H.; Amin, S.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Hamidreza, B.; Ali, M.; Ramin, P.; Bahman, F.N.; Peter, P.; Javed, A.M.; Al, O.S.; et al. Efficacy of biological agents and fillers seed coating in improving drought stress in anise. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 955512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesch, R.W.; Archer, D.W.; Spokas, K. Can using polymer-coated seed reduce the risk of poor soybean emergence in no-tillage soil? Field Crops Res. 2012, 125, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.G.; Allen, P.S.; Bennett, M.A.; Bradford, K.J.; Burris, J.S.; Misra, M.K. Seed enhancements. Seed Sci. Res. 1998, 8, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Tian, L.; Wu, F.; Xie, H. Seed Pelleting Technique and Status of its Researching and Application. Mod. Agric. Equip. 2006, 48–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Di, J.; Lv, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. Preparation and Performance of PE-HD/Wheat Straw Composites Filled by Mineral Fillers. China Plast. 2021, 35, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Lang, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M. Preparation and Performance Study of Red Mud-High-Grade Kaolin-Silica Fume-Cement-Desulfurisation Gypsum Multi-Component Sealing Materials. J. China Coal Soc. 2025, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Bai, D. Effects of pod pre-treatments on the germination traits of Hedysarum polybotrys seeds. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2015, 24, 159–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z. Research progress of plant seed size and seedling growth strategies. Agric. Dev. Equip. 2015, 32–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Group | Talcum Powder | Kaolin | Bentonite |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.00% | 40.0% | 60.0% |
| T2 | 100% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| T3 | 20.0% | 80.0% | 0.00% |
| T4 | 40.0% | 20.0% | 40.0% |
| T5 | 40.0% | 0.00% | 60.0% |
| T6 | 0.00% | 60.0% | 40.0% |
| T7 | 20.0% | 20.0% | 60.0% |
| T8 | 80.0% | 20.0% | 0.00% |
| T9 | 0.00% | 80.0% | 20.0% |
| T10 | 0.00% | 20.0% | 80.0% |
| T11 | 60.0% | 20.0% | 20.0% |
| T12 | 60.0% | 40.0% | 0.00% |
| T13 | 20.0% | 0.00% | 80.0% |
| T14 | 80.0% | 0.00% | 20.0% |
| T15 | 40.0% | 40.0% | 20.0% |
| T16 | 40.0% | 60.0% | 0.00% |
| T17 | 20.0% | 40.0% | 40.0% |
| T18 | 0.00% | 100% | 0.00% |
| T19 | 20.0% | 60.0% | 20.0% |
| T20 | 60.0% | 0.00% | 40.0% |
| T21 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, W. Coatings Applied to the Optimization of Portulaca oleracea L. Seed Pellet Formulation Based on Mixture Design. Coatings 2025, 15, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030341
Sun J, Liu F, Xu Y, Hu W. Coatings Applied to the Optimization of Portulaca oleracea L. Seed Pellet Formulation Based on Mixture Design. Coatings. 2025; 15(3):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030341
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jinhua, Fen Liu, Yanqin Xu, and Weiming Hu. 2025. "Coatings Applied to the Optimization of Portulaca oleracea L. Seed Pellet Formulation Based on Mixture Design" Coatings 15, no. 3: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030341
APA StyleSun, J., Liu, F., Xu, Y., & Hu, W. (2025). Coatings Applied to the Optimization of Portulaca oleracea L. Seed Pellet Formulation Based on Mixture Design. Coatings, 15(3), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030341







