Enhanced Erosion Resistance of Cr3C2-TiC-NiCrCoMo Coatings: Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Erosion Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A mathematical model for calculating the erosion rate of particle-eroded coating surfaces was established to describe the changing rule of the erosion characteristics of coatings with the erosion angle and coating properties.
- (2)
- Erosion experiments were conducted to evaluate the erosion rates of the coatings at various impact angles, investigating the effect of nano-TiC addition on erosion behavior, which validated the accuracy of the mathematical model.
- (3)
- The erosion surface morphology and microstructure of the coating were analyzed. The influence of nano-TiC on the erosion resistance, inter-phase fracture, and erosion mechanisms of the coatings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Powder and Coating Preparation
2.2. Microstructure and Phase Composition
2.3. High-Velocity Erosion Systems and Calculation of Erosion Rates
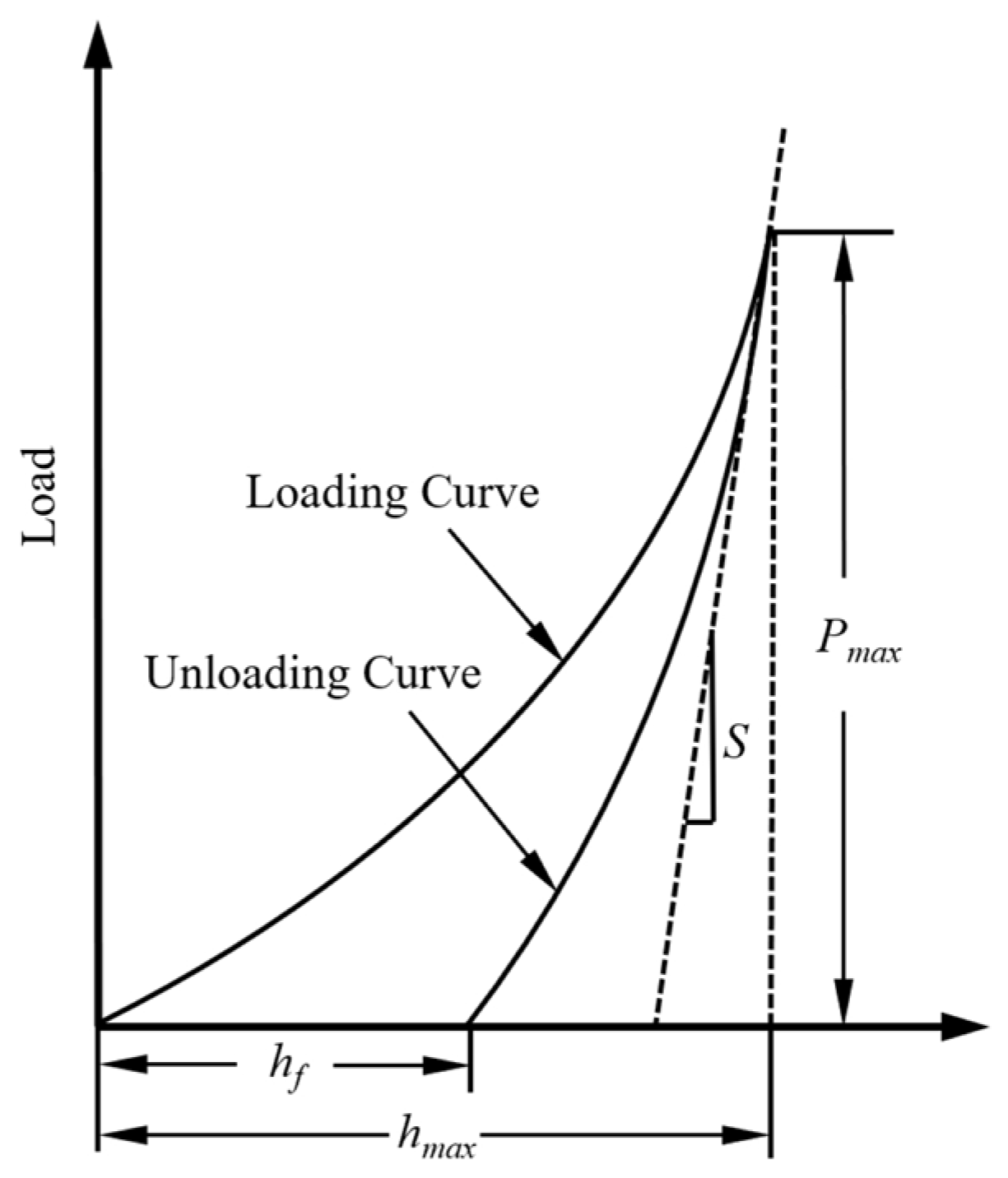
2.4. Coating Modulus of Elasticity and Yield Strength
2.5. Modeling of Coating Erosion Rate
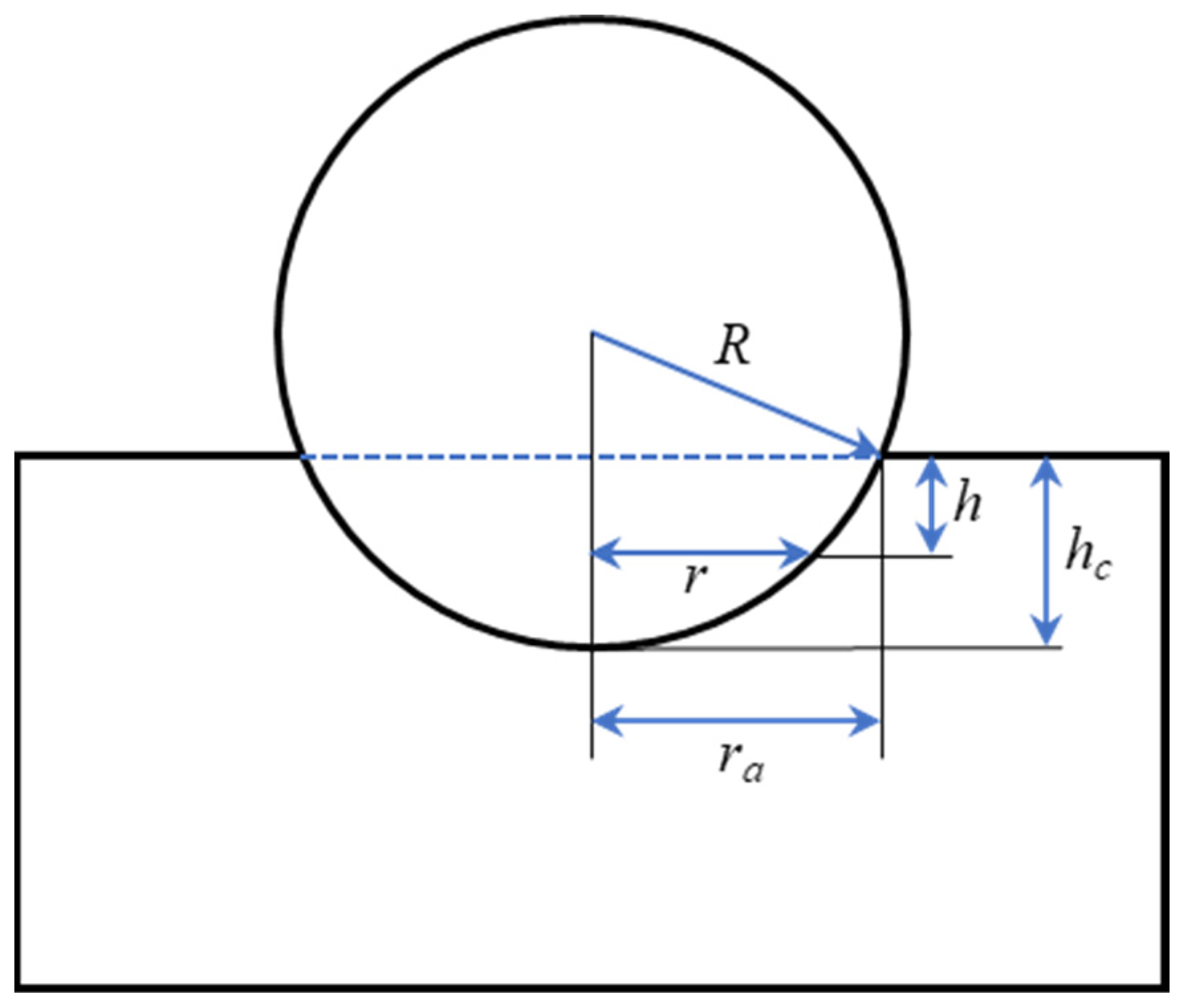
2.5.1. Elastic Compression Stage
2.5.2. Plastic Compression Stage
2.5.3. Resilient Recovery Phase
2.5.4. Calculation of Total Erosion Rate and Parameter Correction
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Coating Morphology and Phase Composition
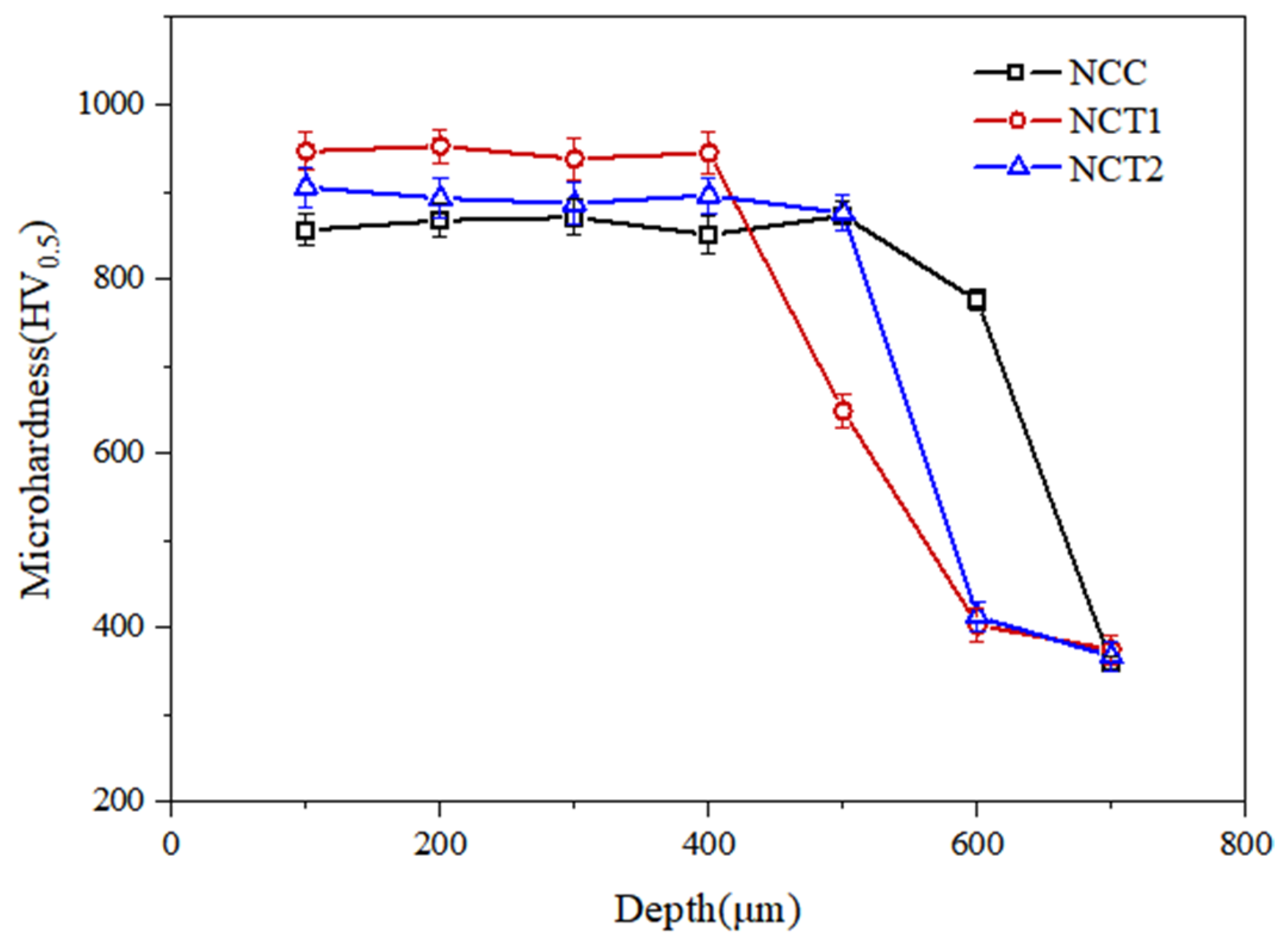
3.2. Microhardness and Tensile Bond Strength
3.3. Erosion Rate of Coating
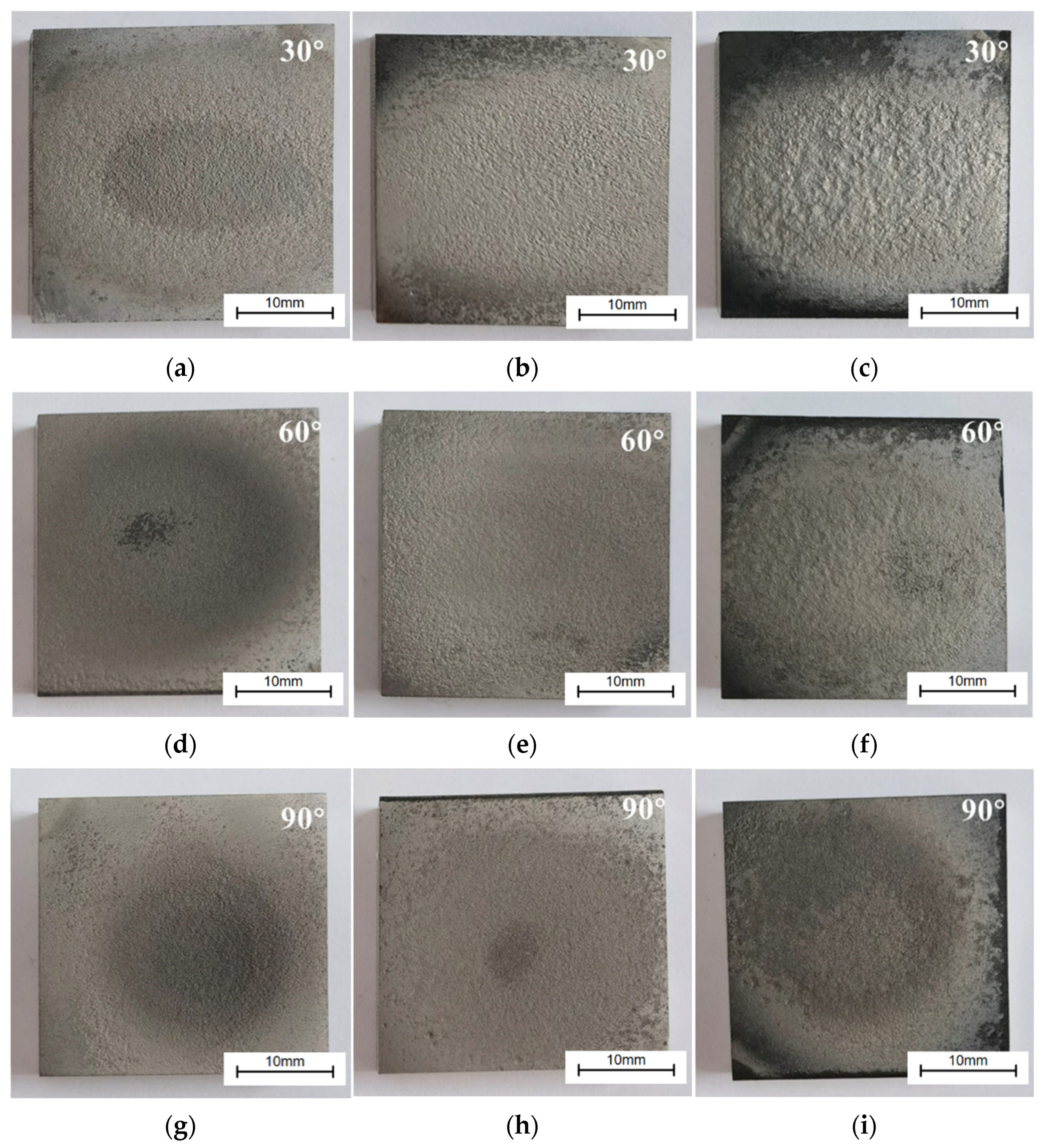
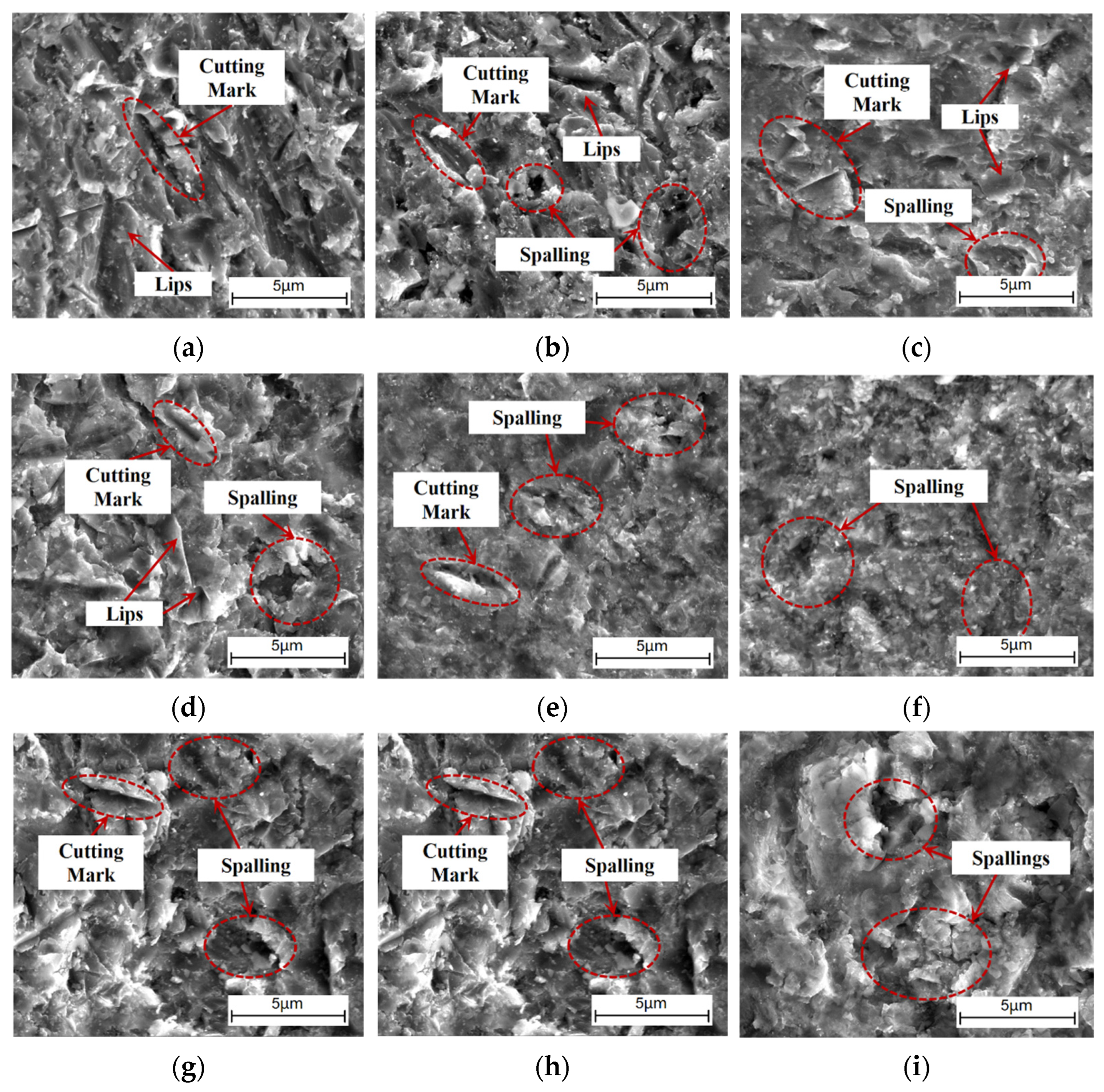
3.4. Coating Surface Erosion Morphology
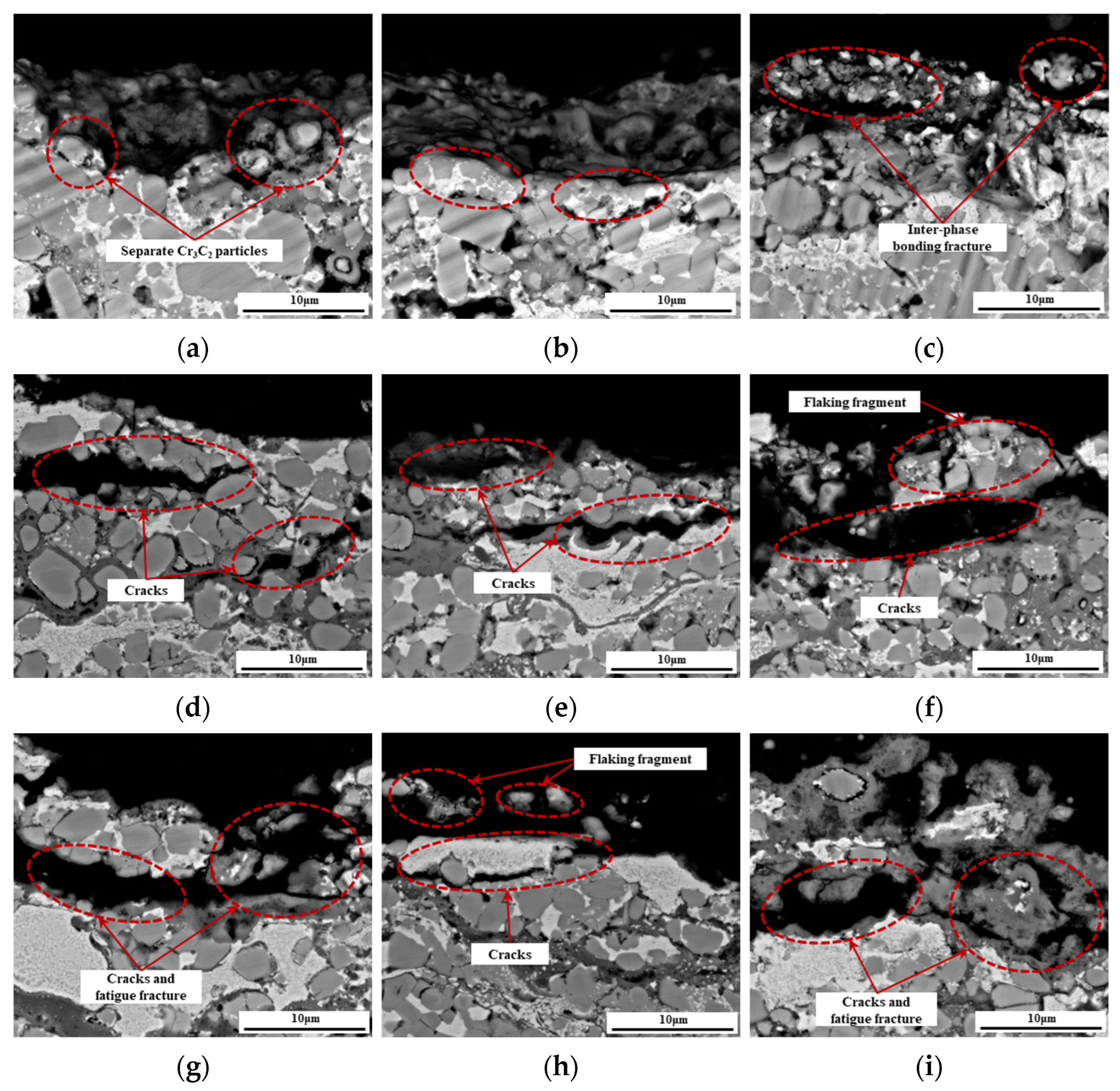
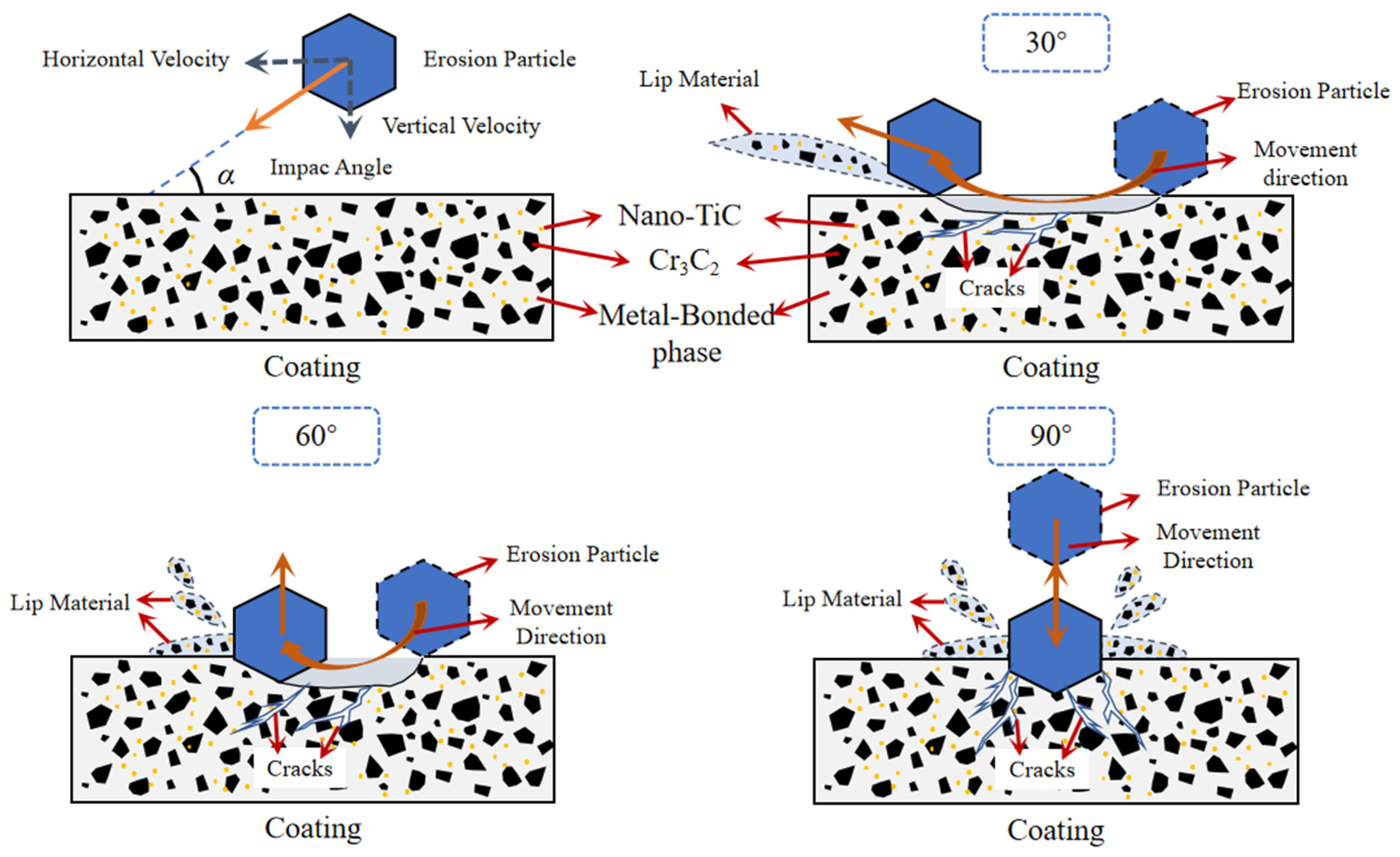
3.5. Erosion Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- (1)
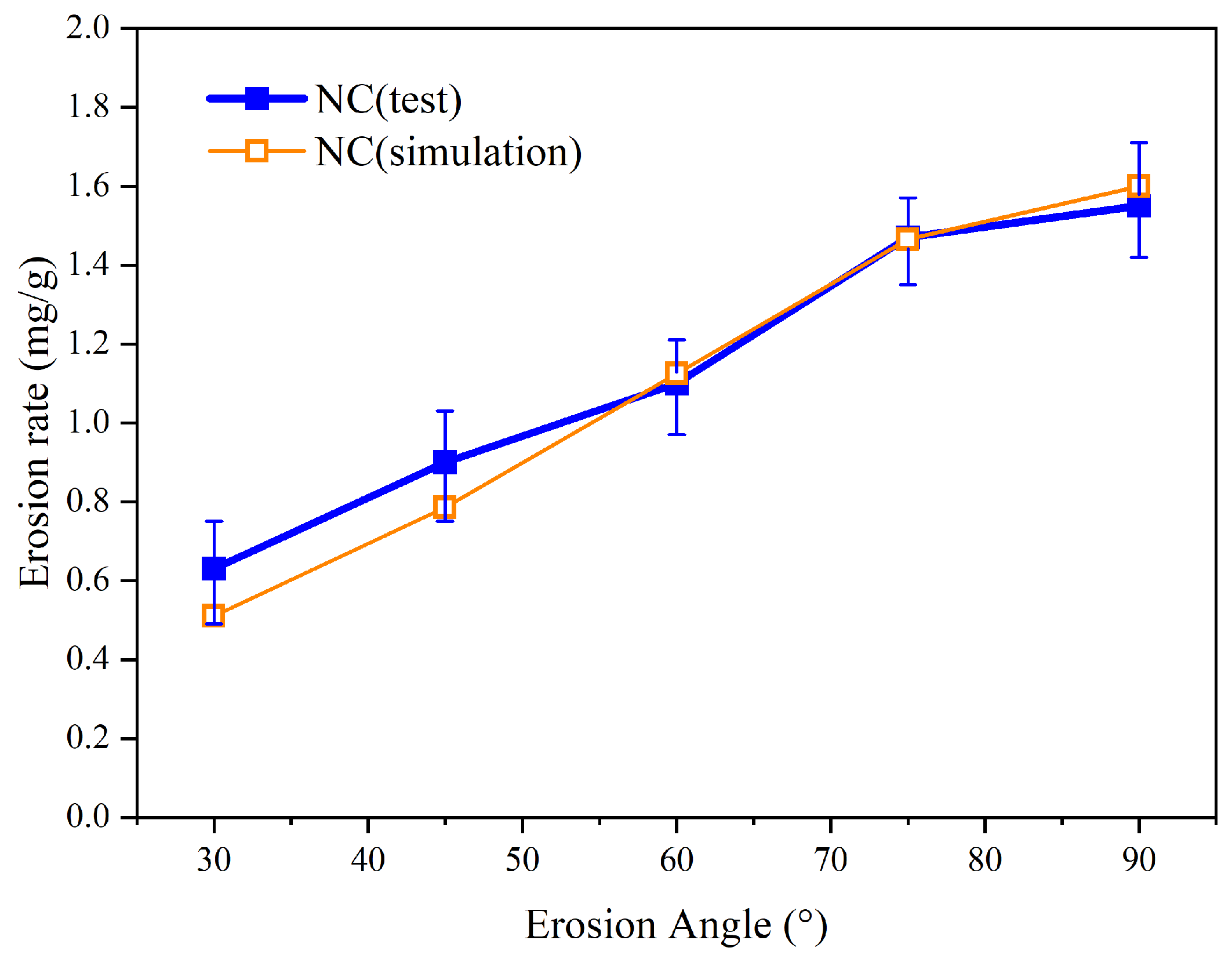
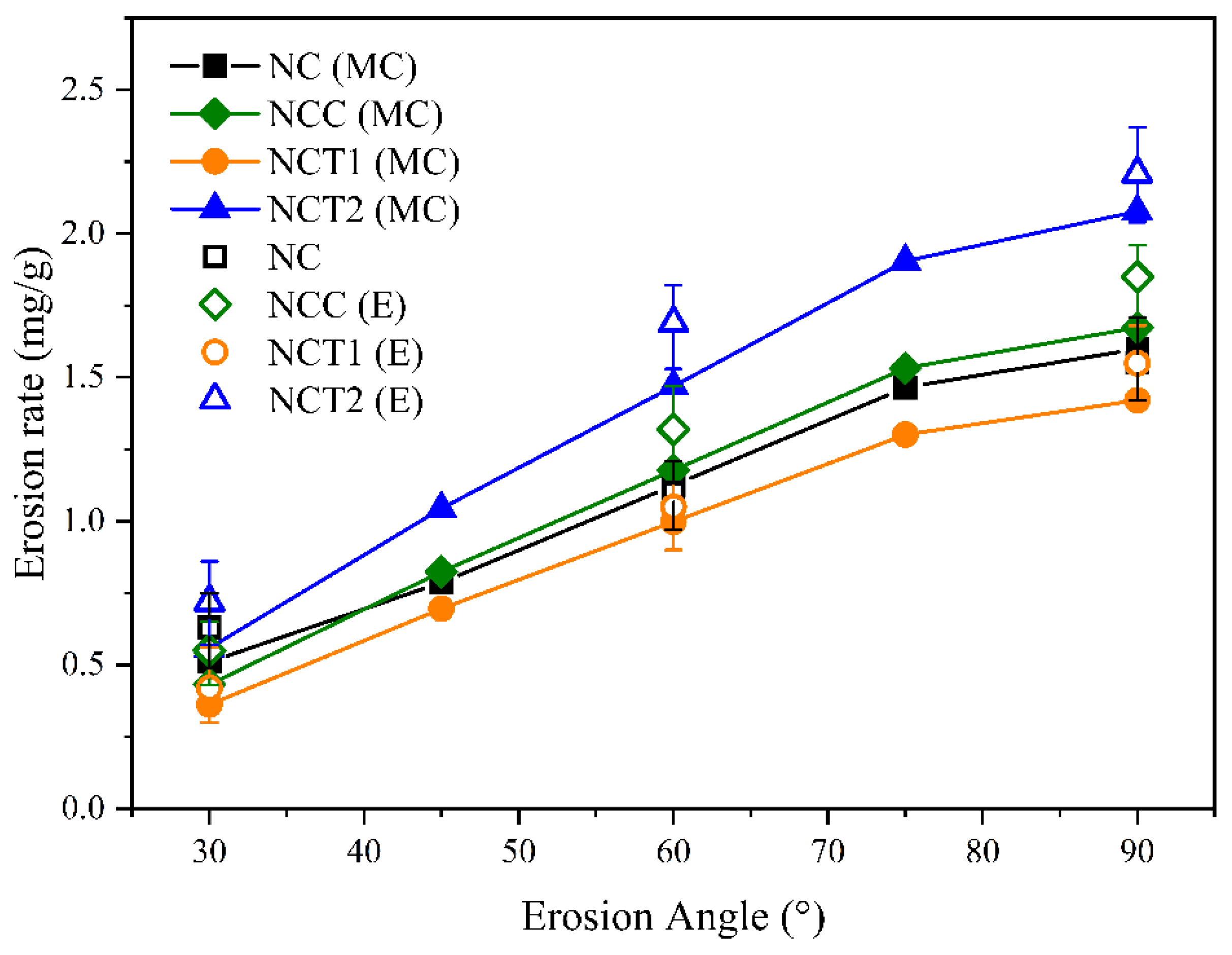
- Based on the collision elasticity–plasticity theory and the energy dissipation equation for the collision process, a detailed analysis was conducted on the elastic compression, plastic deformation, and elastic recovery of individual particles impacting the eroded coating. A comprehensive calculation model for the erosion rate was developed, incorporating factors such as the properties of the eroded particles, the characteristics of the coating, and the conditions of erosion. Predictions of the erosion rate for NCT coatings using this model showed a high degree of concordance with experimental results.
- (2)
- The NCT1 coating exhibited superior erosion resistance compared to the original NC and NCC coatings. At impact angles of 30°, 60°, and 90°, the erosion rates of NCT1 were reduced by 23.64%, 20.45%, and 16.22%, respectively, relative to the NCC coating. These results indicate that a moderate addition of nano-TiC enhances the erosion resistance of chromium carbide coatings. However, excessive nano-TiC content degrades the erosion resistance.
- (3)
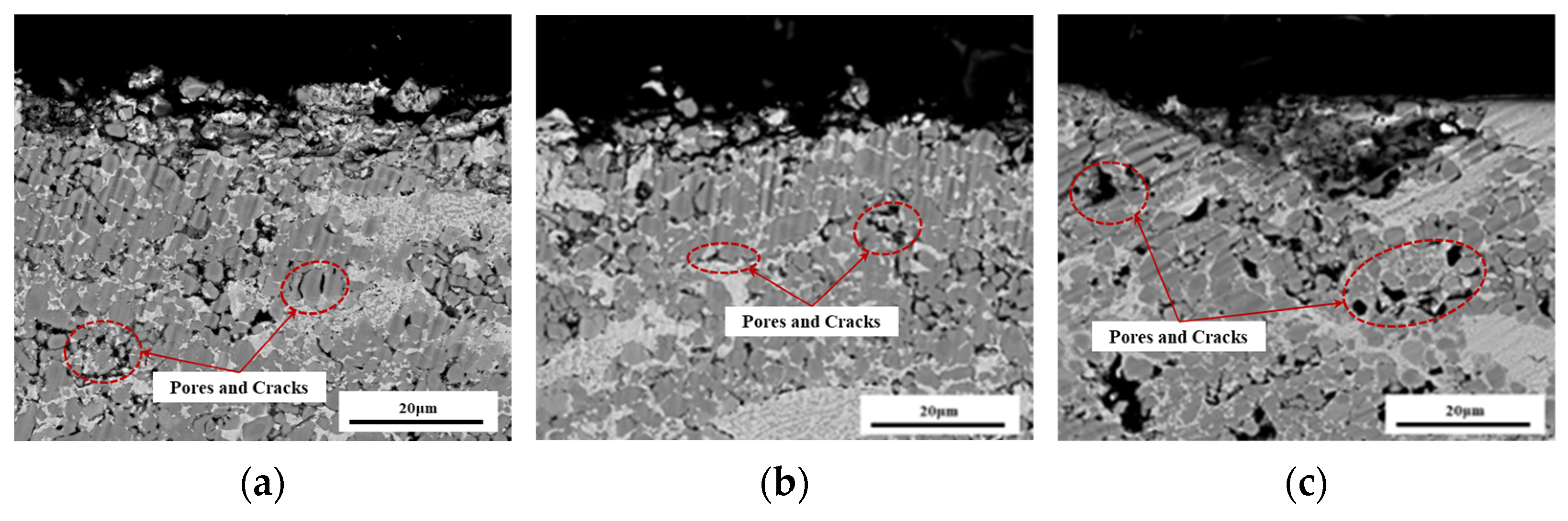
- The erosion mechanisms of the three coatings predominantly involve micro-cutting at low impact angles, while fatigue fracture and spallation dominate at high impact angles. Compared to the NCC coating, the incorporation of nano-TiC in the NCT1 coating enhances the yield strength, impeding the intrusion of erosive particles at low angles and supporting the metal binder phase, eventually reducing fatigue fracture under repeated erosion. However, excessive nano-TiC increases coating porosity and crack formation in the NCT2 coating, leading to the removal of chromium carbide particles and metal binder phase during erosion and consequently deteriorating erosion performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, M.; Pauschitz, A.; Polak, R.; Franek, F. Comparative evaluation of ambient temperature friction behaviour of thermal sprayed Cr3C2-25(Ni20Cr) coatings with conventional and nano-crystalline grains. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Legoux, J.G.; Lima, R.S. Engineering HVOF-sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coatings: The effect of particle morphology and spraying parameters on the microstructure, properties, and high temperature wear performance. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.; Zou, Y.; Wu, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Pulsed laser remelting supersonic plasma sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coatings for regulating microstructure, hardness and corrosion properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Zhao, L.; Öte, M.; Königstein, T.; Steeger, M. Impact wear of an HVOF-sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coating. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 70, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chong, K.; Liu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zou, Y. High-temperature tribological behavior of thermally-treated supersonic plasma sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 95, 105456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Hyland, M.; James, B. Microhardness variation in relation to carbide development in heat treated Cr3C2-NiCr thermal spray coatings. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4267–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lin, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Sun, W. Cavitation erosion characteristics at various flow velocities in NaCl medium of carbide-based cermet coatings prepared by HVOF spraying. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, H.; Prakash, S. Surface engineering analysis of detonation-gun sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coating under high-temperature oxidation and oxidation-erosion environments. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantozzi, D.; Matikainen, V.; Uusitalo, M.; Koivuluoto, H.; Vuoristo, P. Effect of Carbide Dissolution on Chlorine Induced High Temperature Corrosion of HVOF and HVAF Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCrMoNb Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2018, 27, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alroy, R.J.; Kamaraj, M.; Lakshmi, D.V.; Praveen, K.; Babu, P.S.; Sivakumar, G. Tailoring microstructural features of Cr3C2-25NiCr coatings through diverse spray variants and understanding the high-temperature erosion behavior. Tribol. Int. 2023, 188, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, S. Solid particle erosion-wear behaviour of Cr3C2-NiCr coating on Ni-based superalloy. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017694580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alroy, R.J.; Kamaraj, M.; Sivakumar, G. HVAF vs oxygenated HVAF spraying: Fundamental understanding to optimize Cr3C2-NiCr coatings for elevated temperature erosion resistant applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 309, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibe, V.; Chawla, V. Erosion Studies of D-Gun-Sprayed WC-12%Co, Cr3C2-25%NiCr and Al2O3-13%TiO2 Coatings on ASTM A36 Steel. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.C.; Li, C.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, W.Y. Erosion Performance of HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2007, 16, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, P.S.; Tiwari, A.; Seman, S.; Mohamed, S.A.B.; Jayaganthan, R. Erosion-corrosion protection due to Cr3C2-nicr cermet coating on stainless steel. Coatings 2020, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cai, L.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z. Multiparameter Optimization to Improve the Erosion Resistance of Coating by Finite Element Simulation. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2022, 144, 051013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, K.; Thirumalaikumarasamy, D.; Thirumal, P. Experimental investigation on effect of water jet erosion parameters on HVOF sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coatings on stainless steel: A mathematical approach. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 055704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Lu, H.; Du, J.; Ran, X.; Zhang, X. Effect of NiCr content on the solid particle erosion behavior of NiCr-Cr3C2 coatings deposited by atmospheric plasma spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 381, 125144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ban, A.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C. Cavitation Erosion Resistance of TiNi-Based Composite Coating Deposited by APS. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.; Grossman, J.; Šárka Houdková, Š.; Bystrianský, M. Impact wear of the protective Cr3C2-based HVOF-sprayed coatings. Materials 2020, 13, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Deng, C.; Zeng, K. High temperature wear performance of HVOF-sprayed Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo and Cr3C2-NiCr hardmetal coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrhofer, E.; Janka, L.; Mayr, W.P.; Norpoth, J.; Rodriguez Ripoll, M.; Gröschl, M. Cracking resistance of Cr3C2-NiCr and WC-Cr3C2-Ni thermally sprayed coatings under tensile bending stress. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 281, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, K.; Deng, C.; Zeng, K.; Li, Y. Hot corrosion behavior of HVOF-sprayed Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo coating. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9390–9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.S.; Girisha, K.G.; Jamuna, K.; Tejaswini, G.C. Erosion Behaviour of HVOF Sprayed SiC-WC-Cr3C2 Multilayer Coating on 304 Stainless Steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 24685–24690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Qin, J.; Lin, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y. Influences of sand concentration and flow velocity on hydro-abrasive erosion behaviors of HVOF sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr and WC-Cr3C2-Ni coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, L.; Berger, L.M.; Norpoth, J.; Trache, R.; Thiele, S.; Tomastik, C.; Matikainen, V.; Vuoristo, P. Improving the high temperature abrasion resistance of thermally sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coatings by WC addition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, D.G.; Prabhu, T.R.; Rathod, W.S. Sliding and erosion wear behaviour of thermal sprayed WC-Cr3C2-Ni coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 400, 126192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Lin, J. Effect of flow velocity on cavitation erosion behavior of HVOF sprayed WC-10Ni and WC-20Cr3C2–7Ni coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 92, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Ramachandran, C.S. Wear, erosion and corrosion resistance of HVOF-sprayed WC and Cr3C2 based coatings for electrolytic hard chrome replacement. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 81, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, S.; Pan, B. Effects of carbides on abrasion-corrosion performance of carbide reinforced composites in saline silica slurries. Wear 2023, 526–527, 204949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez Barragan, E.E.; González Albarrán, M.A.; Rodríguez de Anda, E.; Vásquez Guillen, G.I.; de Jesús Ibarra Montalvo, J.; Díaz Guillén, J.C.; Chávez Aguilar, J.M. High-Temperature Erosion of SiC-NiCrAlY/Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. Coatings 2023, 13, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, V.; Koivuluoto, H.; Vuoristo, P. A study of Cr3C2-based HVOF- and HVAF-sprayed coatings: Abrasion, dry particle erosion and cavitation erosion resistance. Wear 2020, 446–447, 203188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhurinskiy, D.; Babu, A.; Pathak, P.; Elkin, A.; Dautov, S.; Shornikov, P. Microstructure and wear properties of atmospheric plasma-sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 428, 127904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, K.; Giridhara, G.; Shivalingappa, D. High temperature erosion behaviour of high-velocity oxy-fuel sprayed CNT/NiCr-Cr3C2 composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 448, 128900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Q.; Verstak, A. Elevated temperature erosion of HVOF Cr3C2/TiC-NiCrMo cermet coating. Wear 1999, 233–235, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Li, F.Y.; Ran, X.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Qi, X.X. Research on the high temperature oxidation mechanism of Cr3C2-NiCrCoMo coating for surface remanufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y. Microstructure and properties of in-situ ZrB2-ZrC composite coatings by plasma spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Li, J.F.; Jia, X.J.; Wang, G.C.; Xu, W.H. Establishment and analysis of erosion depth model for impeller material FV520B. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.—Green Technol. 2016, 3, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, S.; Karlsson, H.; Henriksson, B.; Carlson, P.O. Mechanical Testing of Additively Manufactured Superalloy Lugs. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2022, 144, 031018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marri, G.K.; Srikanth, R.; Balaji, C. Multiple Phase Change Material-Based Heat Sink for Cooling of Electronics: A Combined Experimental and Numerical Study. ASME J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 145, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.N.; Al-Hassani, S.T.S.; Chen, J.P.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yin, Z.H. Effective friction coefficient during particle impact on metal. Gongcheng Lixue/Eng. Mech. 2004, 21, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- He, T. Cell-Based Smoothed Finite-Element Framework for Strongly Coupled Non-Newtonian Fluid–Structure Interaction. J. Eng. Mech. 2021, 147, 04021062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, I. Some reflections on the past and future of erosion. Wear 1995, 186–187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
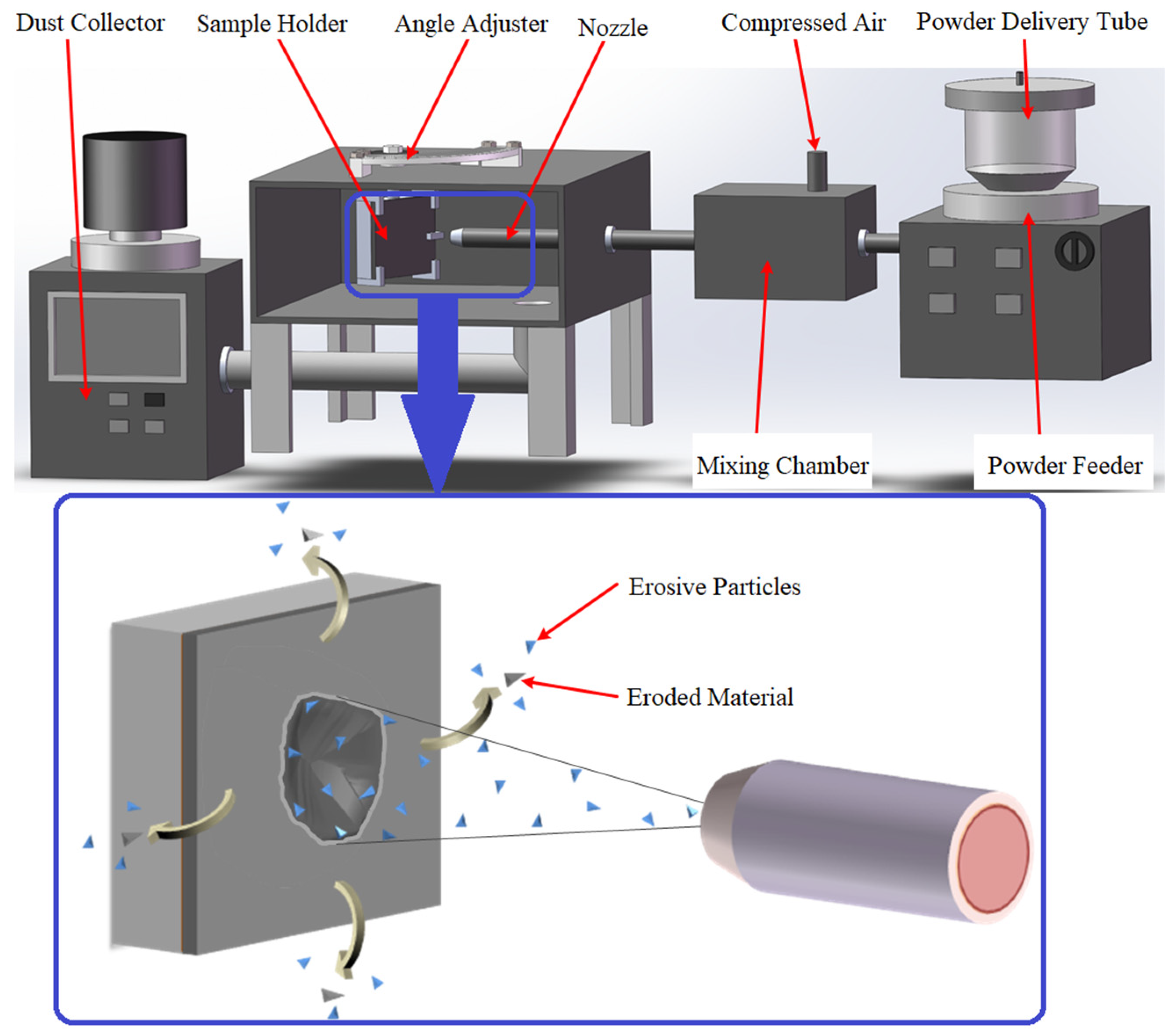
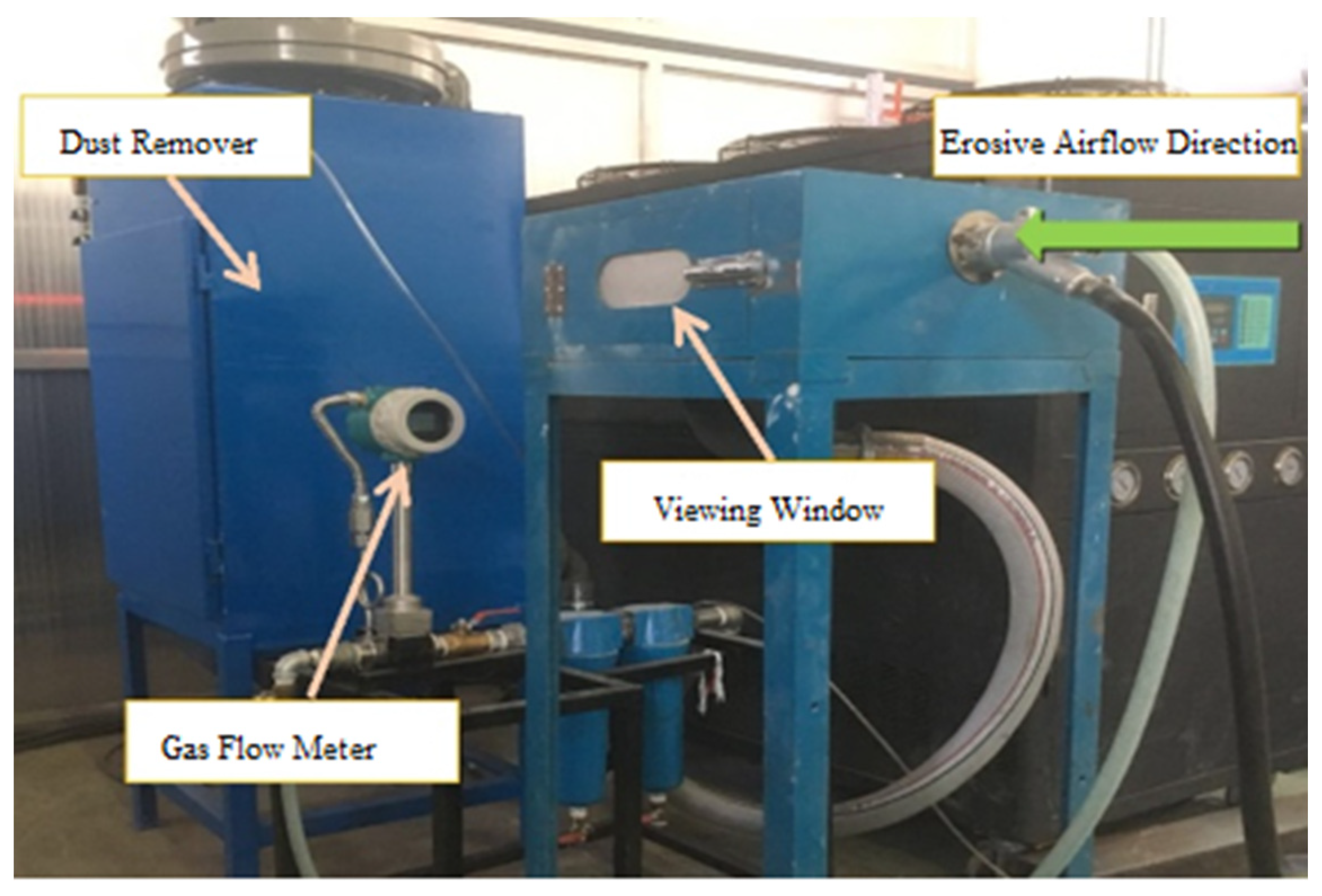



| Powder Formulations | Particle Size | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| NCT1 | 15–45 μm | 87.3 wt.% Cr3C2-NiCr, 9.7 wt.% CoCrMo, 3 wt.% TiC |
| NCT2 | 15–45 μm | 84.6 wt.% Cr3C2-NiCr, 9.4 wt.% CoCrMo, 6 wt.% TiC |
| Coating | Modulus of Elasticity /GPa | Yield Strength /MPa |
|---|---|---|
| NCC | 162.38 | 869.8 |
| NCT1 | 175.09 | 981.6 |
| NCT2 | 148.03 | 632.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Du, J.; Qi, X.; Lu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Meng, W. Enhanced Erosion Resistance of Cr3C2-TiC-NiCrCoMo Coatings: Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Erosion Mechanisms. Coatings 2025, 15, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030294
Wang J, Wang L, Lu H, Du J, Qi X, Lu L, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Meng W. Enhanced Erosion Resistance of Cr3C2-TiC-NiCrCoMo Coatings: Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Erosion Mechanisms. Coatings. 2025; 15(3):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030294
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiawei, Linwen Wang, Haiyang Lu, Jiyu Du, Xiaoxia Qi, Laixiao Lu, Yanhua Zhao, Ziwu Liu, and Weiyun Meng. 2025. "Enhanced Erosion Resistance of Cr3C2-TiC-NiCrCoMo Coatings: Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Erosion Mechanisms" Coatings 15, no. 3: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030294
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, L., Lu, H., Du, J., Qi, X., Lu, L., Zhao, Y., Liu, Z., & Meng, W. (2025). Enhanced Erosion Resistance of Cr3C2-TiC-NiCrCoMo Coatings: Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Erosion Mechanisms. Coatings, 15(3), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030294






