The Effect of Nb on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties of Co-Ti-V Superalloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
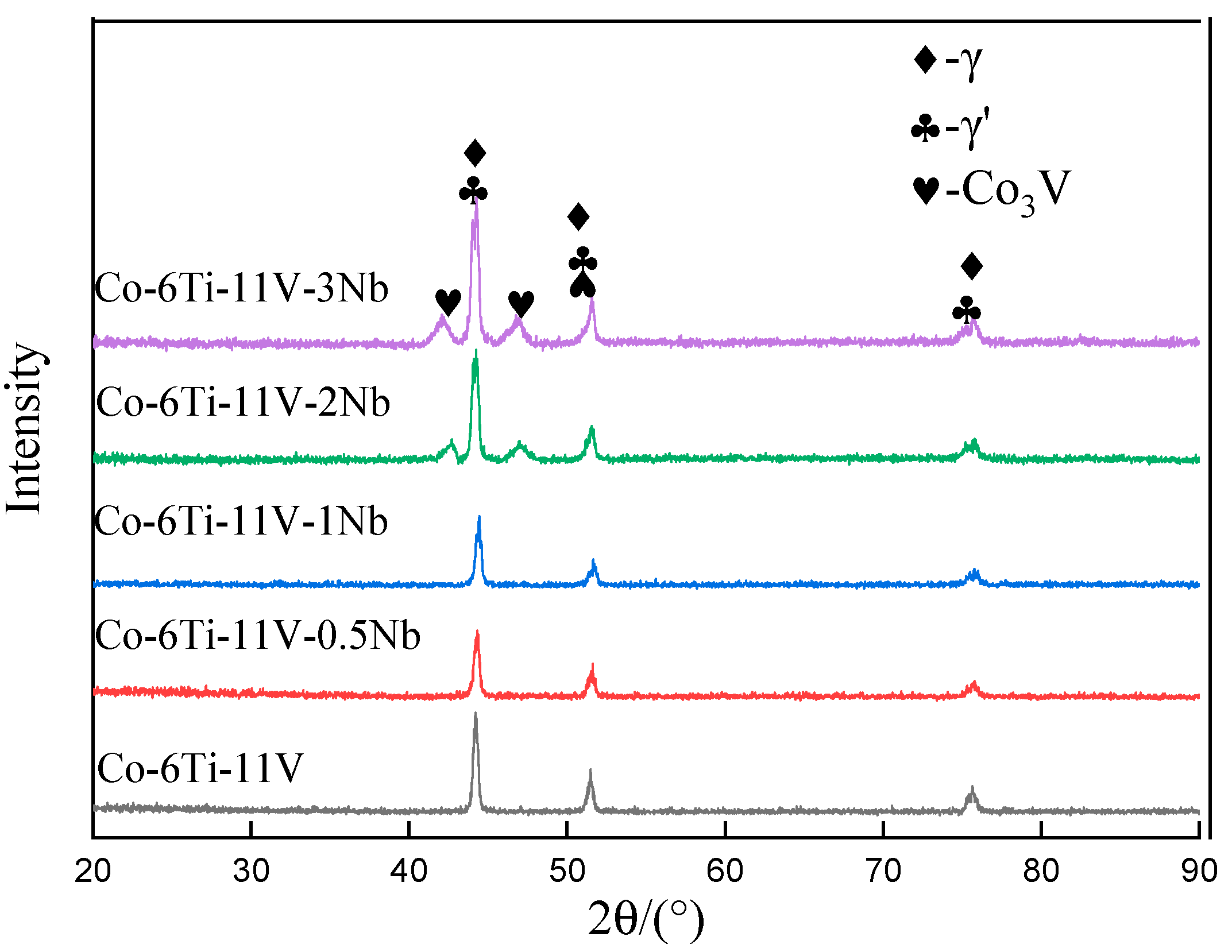
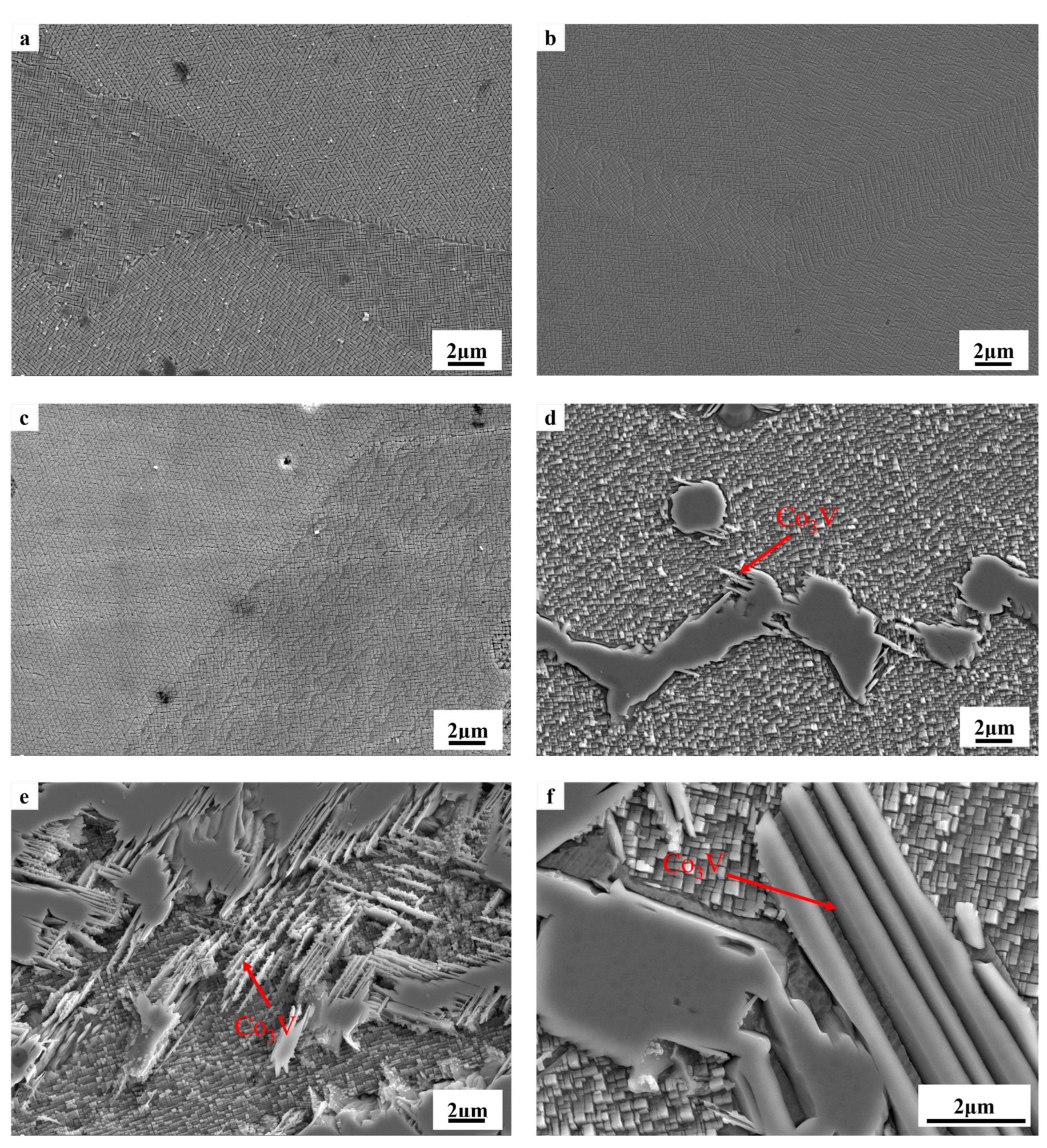
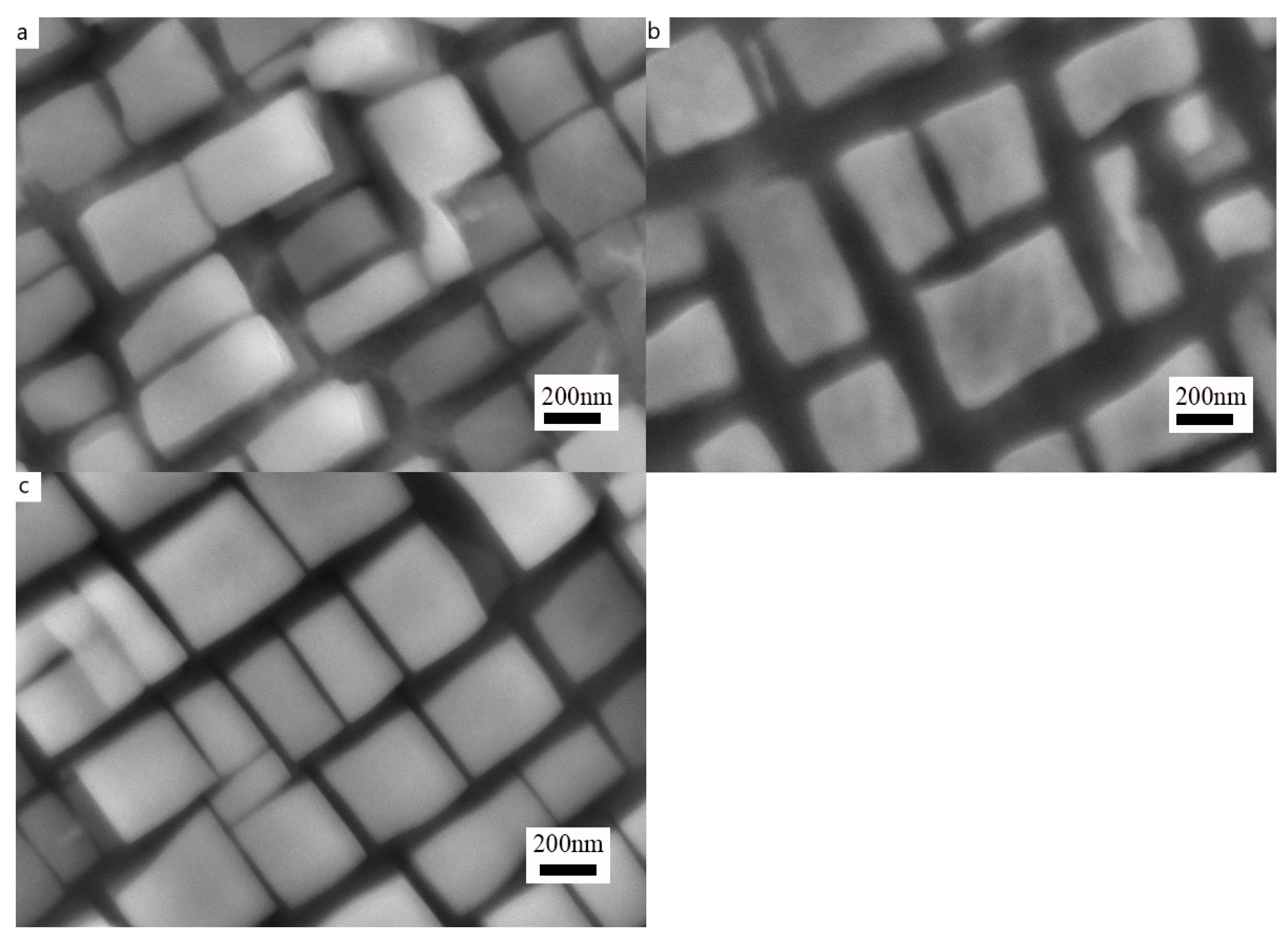
3.1. Microstructure of Alloys with Varied Nb Content
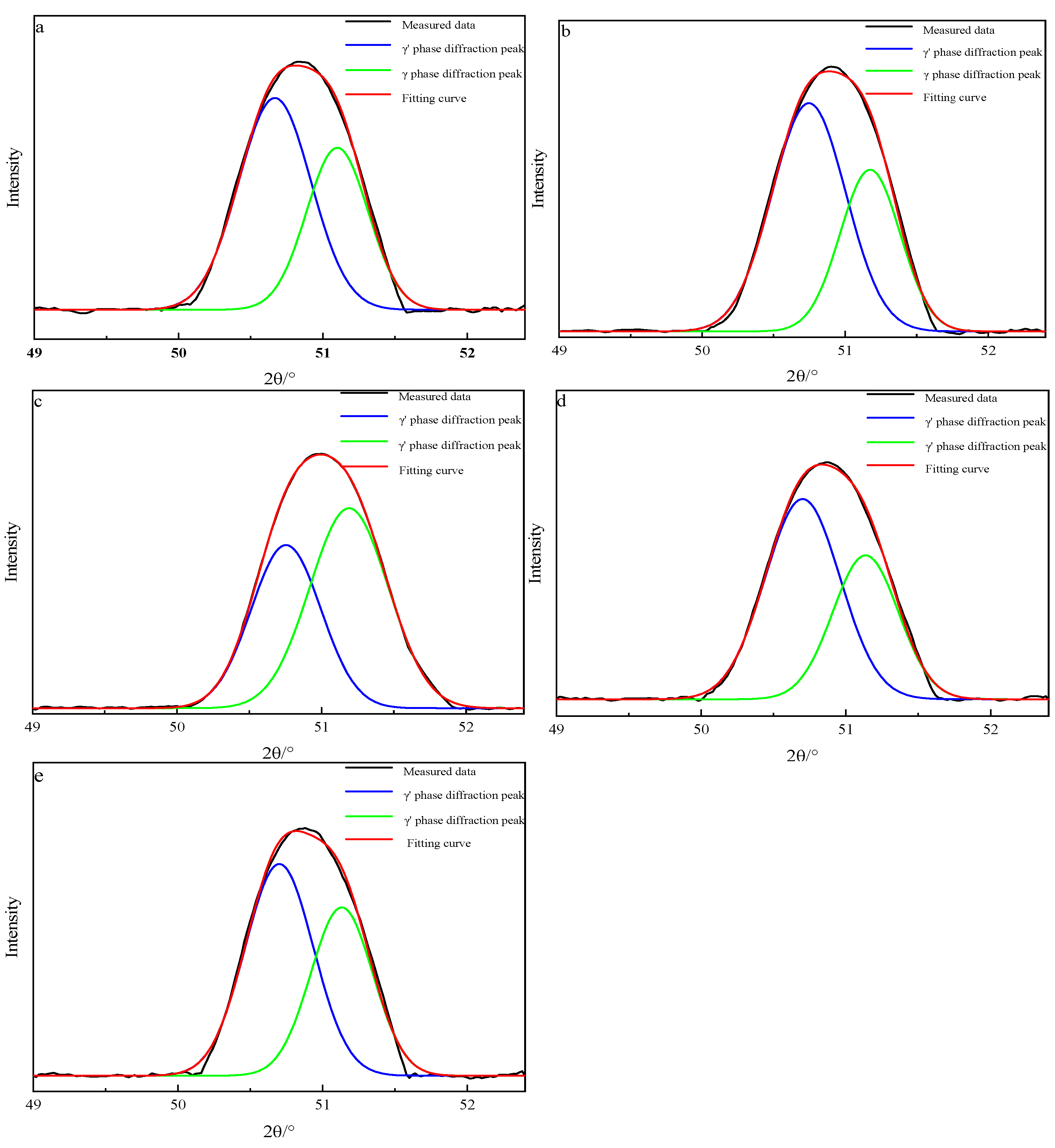
3.2. Lattice Mismatch Between γ/γ′ Phases
3.3. γ′-Phase Morphologies of Alloys with Varied Nb Content
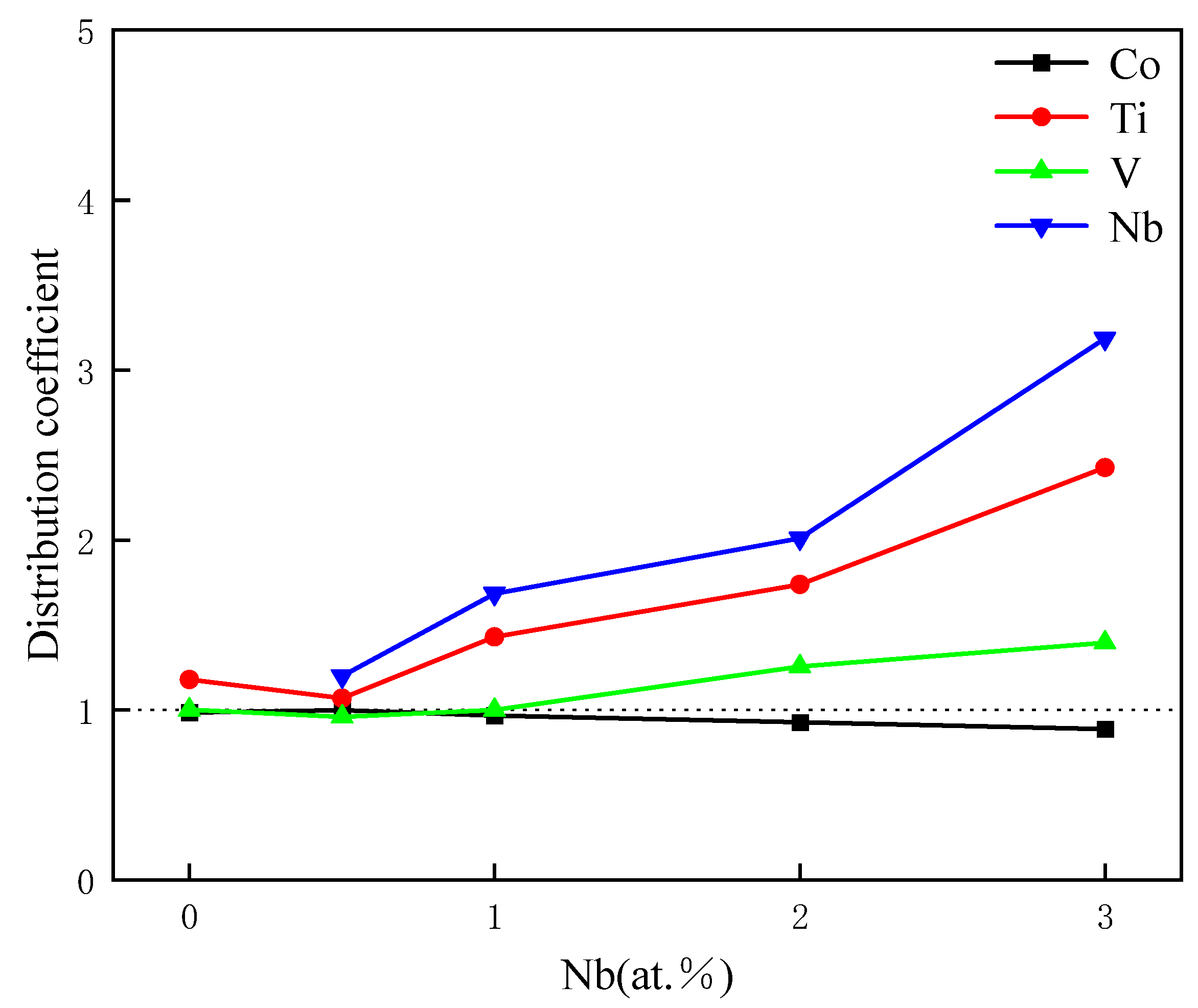
3.4. Distribution of Alloying Elements in γ Phase and γ′ Phase
3.5. Strength at Elevated Temperature
3.6. The γ′-Phase Morphologies of Alloys After Compression at 900 °C
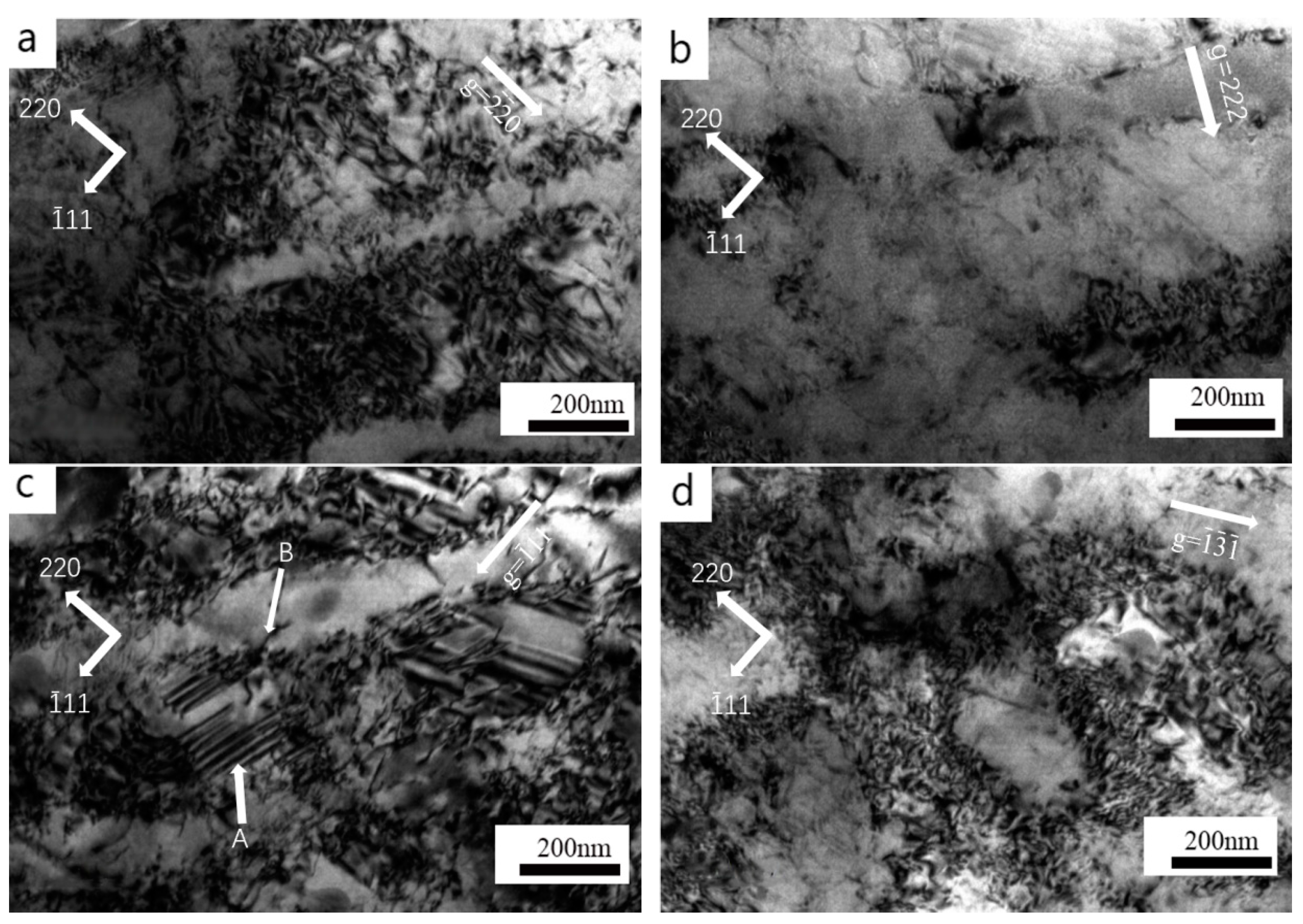
3.7. Deformation Behavior of Alloys
4. Conclusions
- After solution treatment at 1100 °C/48 h and aging treatment at 870 °C/72 h, for the alloys containing less than 1Nb, they show a γ and γ′ dual-phase microstructure and are free of deleterious phases. The Co3V phase with a platelet shape is present in the 2Nb and 3Nb alloys.
- With the increase in Nb content, the lattice mismatch of the γ/γ′ two-phase microstructure increases gradually. After compression at 900 °C, the size of the γ′ phase in the 0Nb alloy increases from 222.2 nm to 271.7 nm; the volume ratio of the γ′ phase in the three investigated alloys decrease gradually. The 1Nb alloy shows the minimum size increase and the smallest volume drop of the γ′ precipitate. These results show that Nb improves the phase stability of the γ′ phase.
- The yield strength of the Co-Ti-V alloy increases with the increase in Nb content, and the yield strength of the 3Nb alloy is the highest when compressed at 900 °C, at 496 Pa.
- When compressed at 900 °C, the <101>-type dislocation causing shearing of the γ′ phase in the {111} plane in the Nb-free alloy was observed. For the 1Nb alloy, some <0> dislocations reacted at the γ/γ′ interface to generate 1/3 [11], and then the γ′ precipitate was cut by this dislocation, leaving R = <21> stacking faults.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donachie, M.; Donachie, S. Superalloys: A Technical Guide, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2002; p. 439. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, J.; Omori, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ohnuma, I.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Cobalt-base high-temperature alloys. Science 2006, 312, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, C.T. A contemporary view of cobalt-base alloys. J. Met. 1969, 21, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, T.M. Alloy design for aircraft engines. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.; Inui, H.; Pollock, T.M. L12-Strengthened Cobalt-Base Superalloys. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2015, 45, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, P.J.; Sudbrack, C.K.; Noebe, R.D.; Dunand, D.C.; Seidman, D.N.; Northwestern Univ, E.I.L. Effects of titanium substitutions for aluminum and tungsten in Co-10Ni-9Al-9W (at%) superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 705, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, P.J.; Sudbrack, C.K.; Sauza, D.J.; Noebe, R.D.; Seidman, D.N.; Dunand, D.C.; Northwestern Univ, E.I.L. Effect of tungsten concentration on microstructures of Co-10Ni-6Al-(0,2,4,6)W-6Ti (at%) cobalt-based superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 700, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooshima, M.; Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, N.L.; Kishida, K.; Inui, H. Effects of quaternary alloying elements on the γ′ solvus temperature of Co-Al-W based alloys with fcc/L12 two-phase microstructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 508, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyczak, F.; Bauer, A.; GöKen, M.; Lorenz, U.; Neumeier, S.; Oehring, M.; Paul, J.; Schell, N.; Schreyer, A.; Stark, A.; et al. The effect of tungsten content on the properties of L12-hardened Co–Al–W alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, A.V.; Kattner, U.R.; Josell, D.; Waterstrat, R.M.; Boettinger, W.J.; Blendell, J.E.; Shapiro, A.J. Determination of the CoTi congruent melting point and thermodynamic reassessment of the Co-Ti system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Takasugi, T.; Izumi, O. Alloying behavior of Co3Ti. Metall. Trans. A 1986, 17, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.J.; Wang, C.P.; Zhao, C.C.; Yang, S.Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.J. Experimental investigation of phase equilibria and microstructure in the Co–Ti–V ternary system. Intermetallics 2014, 49, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.J.; Wang, C.P.; Yang, S.Y.; Omori, T.; Yang, T.; Kimura, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Experimental investigations of microstructures and phase equilibria in the Co–V–Ta ternary system. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.J.; Tang, J.G.; Zhou, Y.; An, W.K.; Cai, A.H. Phase equilibria in the Co-Ti-V system at 873 K. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 602, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, C. Assessment of atomic mobilities for fcc Co-Ti-V alloys. Calphad 2018, 61, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Pramanik, A.; Jyothsna, K.; Vamsi, K.V.; Karthikeyan, S. Phase transformation temperatures, γ–γ′ lattice parameter misfit, and γ′ precipitate morphology in Co–Ti–V alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2022, 53, 4011–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.J.; Liu, X.J.; Yang, S.Y.; Xu, W.W.; Omori, T.; Yang, T.; Deng, B.; Jiang, H.X.; Wang, C.P.; Kainuma, R.; et al. Novel Co-Ti-V-base superalloys reinforced by L12-ordered γ′ phase. Intermetallics 2018, 92, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Gao, X.; Song, D.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J. Effect of Ni on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of a Co-Ti-V-Based Superalloy. Scanning 2021, 2021, 678085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Gao, X.; Song, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J. Role of Ru on the microstructure and property of novel Co-Ti-V Superalloy. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, J.; Yang, S.; Ruan, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Effects of Nb and W Additions on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Novel gamma/gamma′ Co-V-Ti-Based Superalloys. Metals 2018, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, T.; Yan, J. Effect of alloying elements to hot corrosion behavior of novel Co-Al-W superalloy. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2010, 30, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Migas, D.; Moskal, G.; Niemiec, D. Surface Condition of New γ–γ′ Co-Al-Mo-Nb and Co-Al-W Cobalt-Based Superalloys After Oxidation at 800 °C. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.; Bauer, A.; Neumeier, S.; Göken, M.; Virtanen, S. High temperature oxidation of γ/γ′-strengthened Co-base superalloys. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makineni, S.K.; Nithin, B.; Chattopadhyay, K. Synthesis of a new tungsten-free γ–γ′ cobalt-based superalloy by tuning alloying additions. Acta Mater. 2015, 85, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasugi, T.; Honjo, H.; Kaneno, Y.; Inoue, H. Plastic flow instabilities of L12Co3Ti alloys at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; DeNolf, G.C.; Pollock, T.M. Flow stress anomalies in γ/γ′ two-phase Co–Al–W-base alloys. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.J.; Feng, Q.; Pollock, T.M. Interfacial Dislocation Networks and Creep in Directional Coarsened Ru-Containing Nickel-Base Single-Crystal Superalloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 1290–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Murakumo, T.; Harada, H.; Koizumi, Y. Dependence of creep strength on the interfacial dislocations in a fourth generation SC superalloy TMS-138. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Koizumi, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Murakumo, T.; Harada, H. Strengthening by γ/γ′ interfacial dislocation networks in TMS-162—Toward a fifth-generation single-crystal superalloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilensten, L.; Antonov, S.; Gault, B.; Tin, S.; Kontis, P. Enhanced creep performance in a polycrystalline superalloy driven by atomic-scale phase transformation along planar faults. Acta Mater. 2021, 202, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Alloy | Nominal Composition (at.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Ti | V | Nb | |
| Base | Bal | 6 | 11 | - |
| 0.5 Nb | Bal | 6 | 11 | 0.5 |
| 1 Nb | Bal | 6 | 11 | 1 |
| 2 Nb | Bal | 6 | 11 | 2 |
| 3 Nb | Bal | 6 | 11 | 3 |
| Alloy (at. %) | γ′-Phase Lattice Constant αγ/Å | γ-Phase Lattice Constant αγ/Å | Lattice Mismatch δ/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0Nb | 0.3594 | 0.3567 | 0.76 |
| 0.5Nb | 0.360 | 0.357 | 0.81 |
| 1Nb | 0.359 | 0.356 | 0.82 |
| 2Nb | 0.3597 | 0.357 | 0.85 |
| 3Nb | 0.3595 | 0.3564 | 0.86 |
| Alloy | Average Size (nm) | Volume Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0Nb | 222.2 | 84.3 |
| 0.5Nb | 303.9 | 84.4 |
| 1Nb | 252.4 | 84.7 |
| 2Nb | 191.0 | - |
| 3Nb | 189.0 | - |
| Alloy | Composition (at. %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Ti | V | Nb | ||
| Co6Ti11V | γ | 81 | 6 | 13 | - |
| γ′ | 79.9 | 7.1 | 13 | - | |
| Co6Ti11V0.5Nb | γ | 78.4 | 6.9 | 14.1 | 0.6 |
| γ′ | 78.4 | 7.4 | 13.5 | 0.7 | |
| Co6Ti11V1Nb | γ | 81.2 | 4.7 | 13.4 | 0.8 |
| γ′ | 78.6 | 6.7 | 13.4 | 1.4 | |
| Co6Ti11V2Nb | γ | 85.5 | 3.3 | 10.2 | 1.1 |
| γ′ | 79.3 | 5.8 | 12.8 | 2.1 | |
| Co6Ti11V3Nb | γ | 86.4 | 2.5 | 10.1 | 1.1 |
| γ′ | 76.6 | 6.1 | 14.1 | 3.4 | |
| Alloy | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|
| Co-6Ti-11V | 323 |
| Co-6Ti-11V-0.5Nb | 351 |
| Co-6Ti-11V-1Nb | 391 |
| Co-6Ti-11V-2Nb | 404 |
| Co-6Ti-11V-3Nb | 496 |
| Hayness | 280 [6] |
| Mar-M247 | 392 [6] |
| In939 | 520 [18] |
| Mar-M302 | 361 [18] |
| Co9Al9W | 263 [27] |
| Alloy | Average Size (nm) | Volume Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Co-6Ti-11V | 271.7 | 58.5 |
| Co-6Ti-11V-0.5Nb | 302.1 | 48.4 |
| Co-6Ti-11V-1Nb | 264.4 | 65.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Ni, S.; Luo, K.; Zhao, W.; Liu, E.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, S. The Effect of Nb on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties of Co-Ti-V Superalloys. Coatings 2025, 15, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010053
Zhou P, Ni S, Luo K, Zhao W, Liu E, Qiao Y, Chen S. The Effect of Nb on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties of Co-Ti-V Superalloys. Coatings. 2025; 15(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Pengjie, Shenfa Ni, Kunjie Luo, Wanxiang Zhao, Enze Liu, Yanxin Qiao, and Shujin Chen. 2025. "The Effect of Nb on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties of Co-Ti-V Superalloys" Coatings 15, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010053
APA StyleZhou, P., Ni, S., Luo, K., Zhao, W., Liu, E., Qiao, Y., & Chen, S. (2025). The Effect of Nb on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties of Co-Ti-V Superalloys. Coatings, 15(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010053







