Sol-Gel Derived ZnO Thin Films with Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Behavior for Future Memory Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
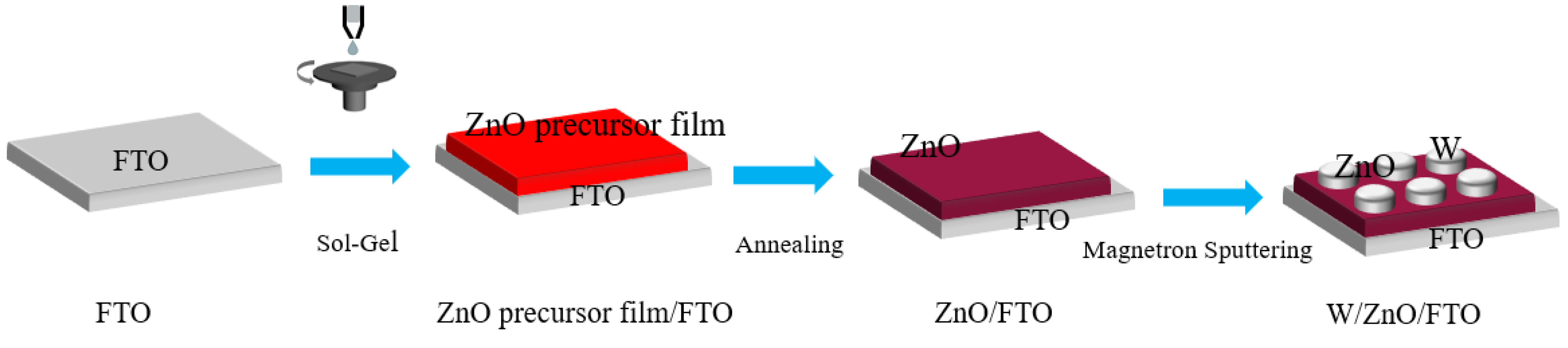
2. Experimental
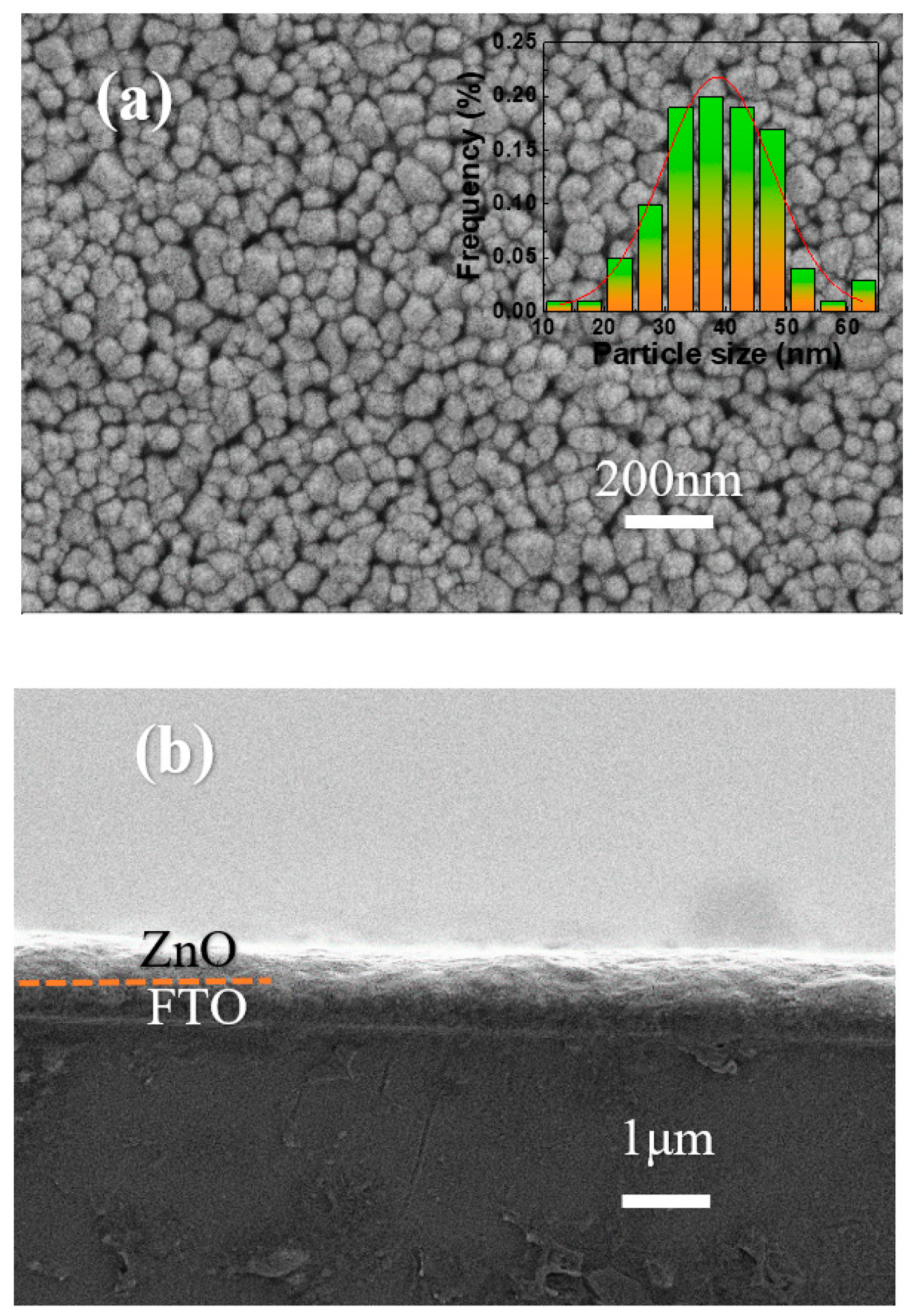
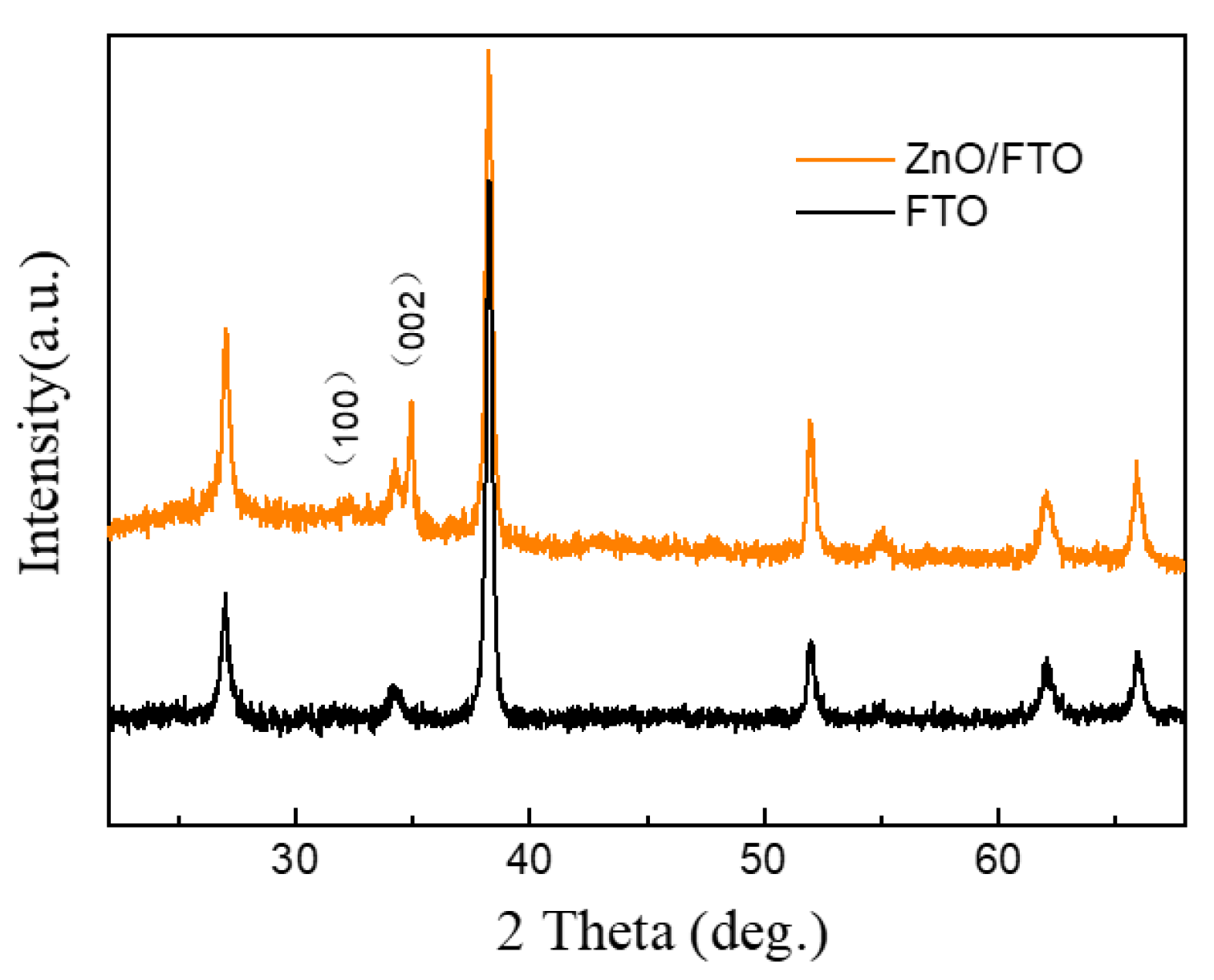
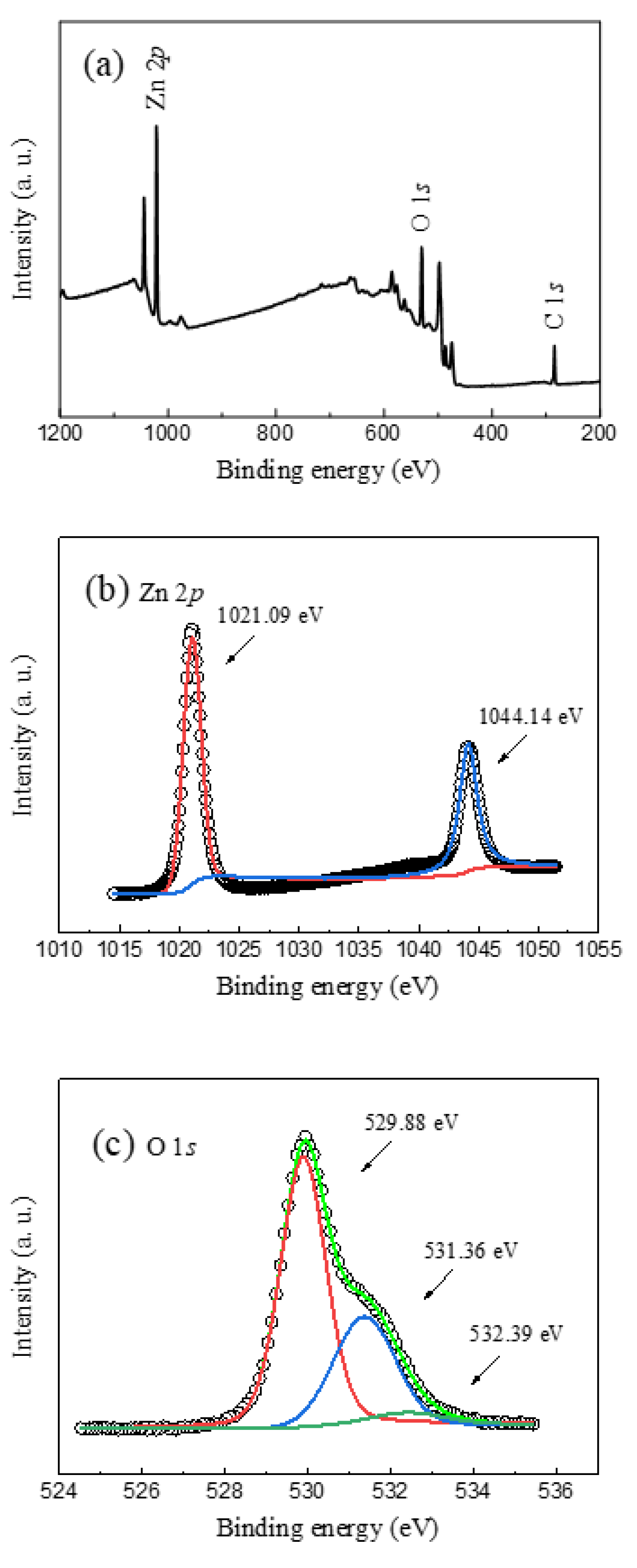
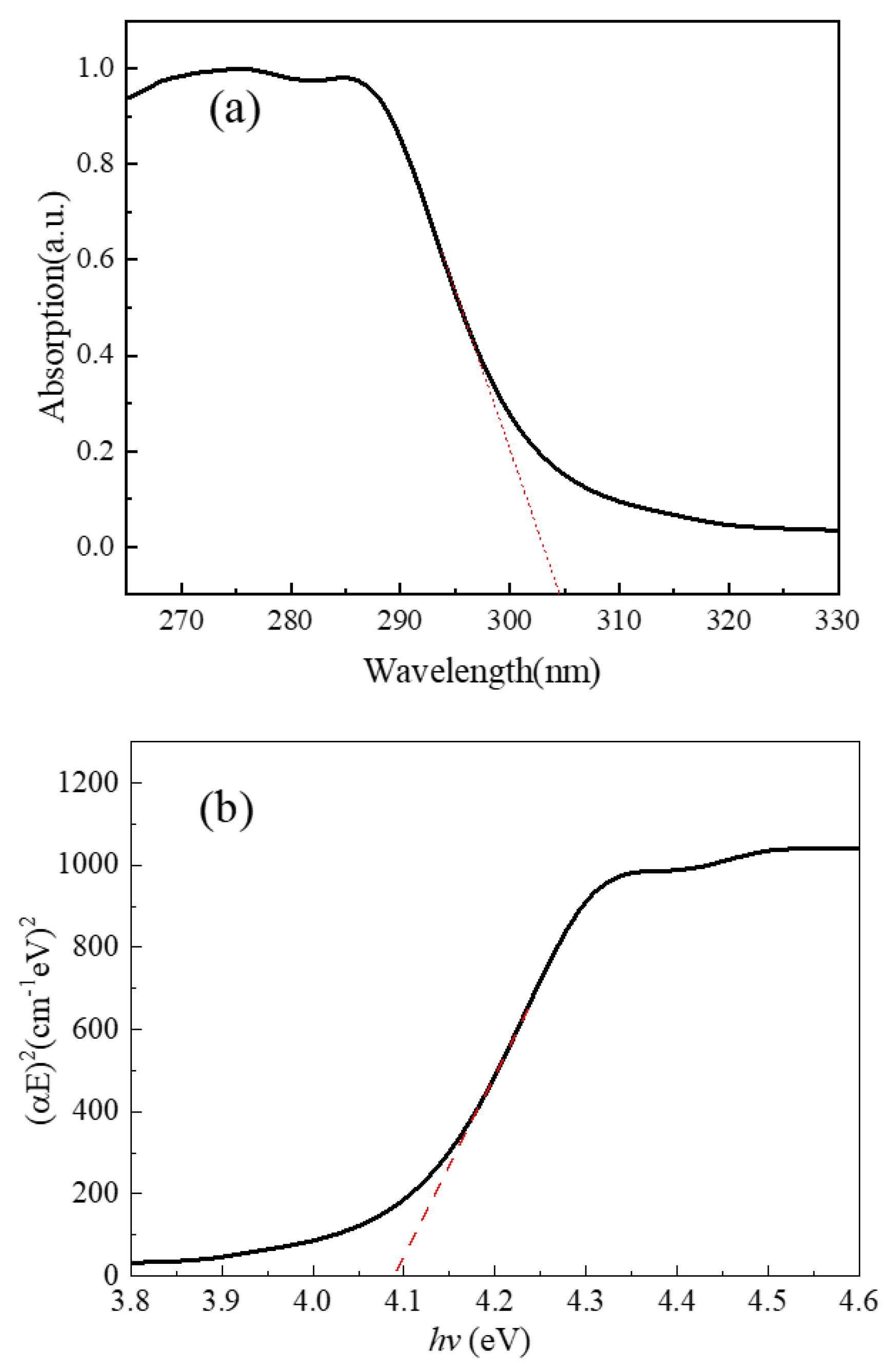
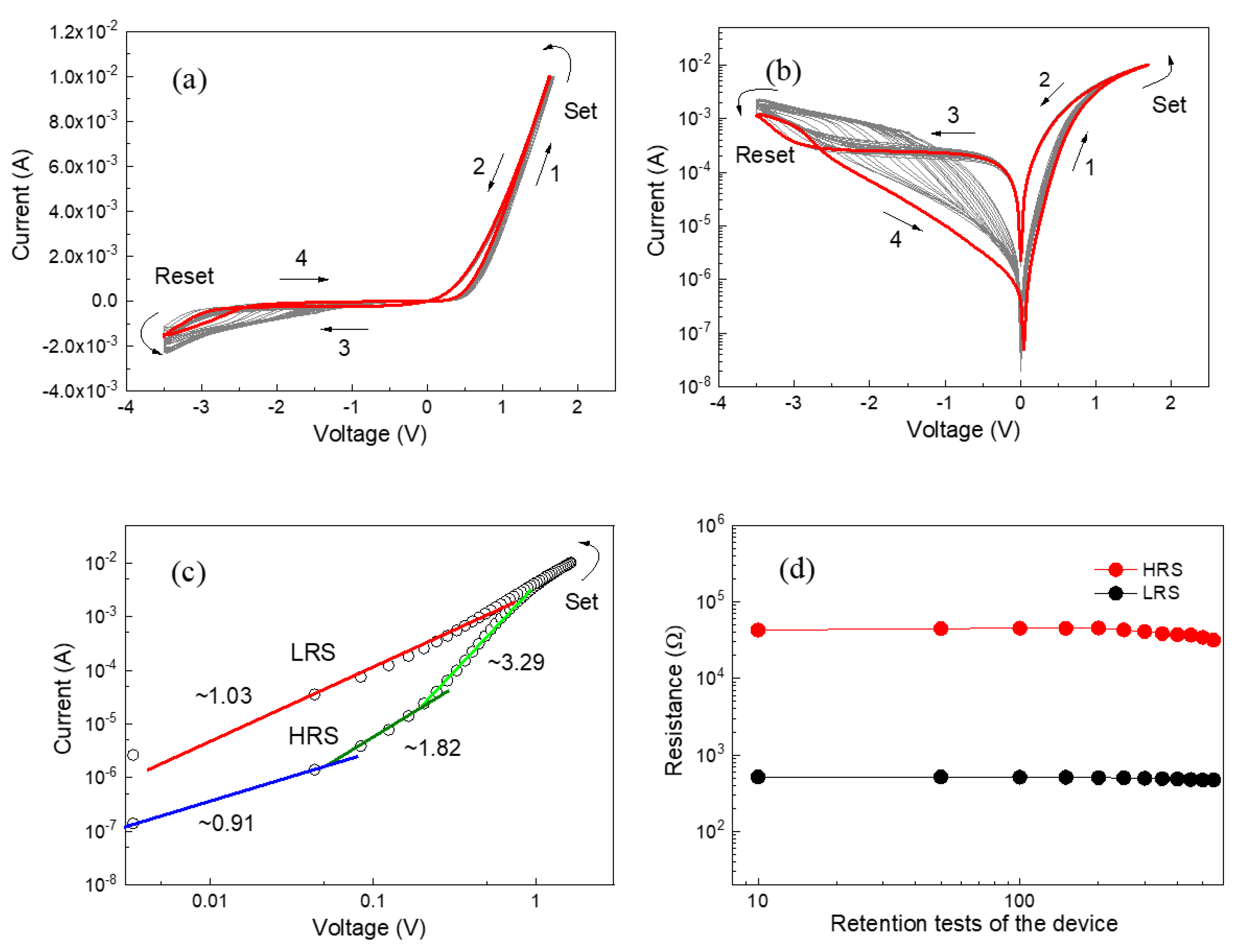
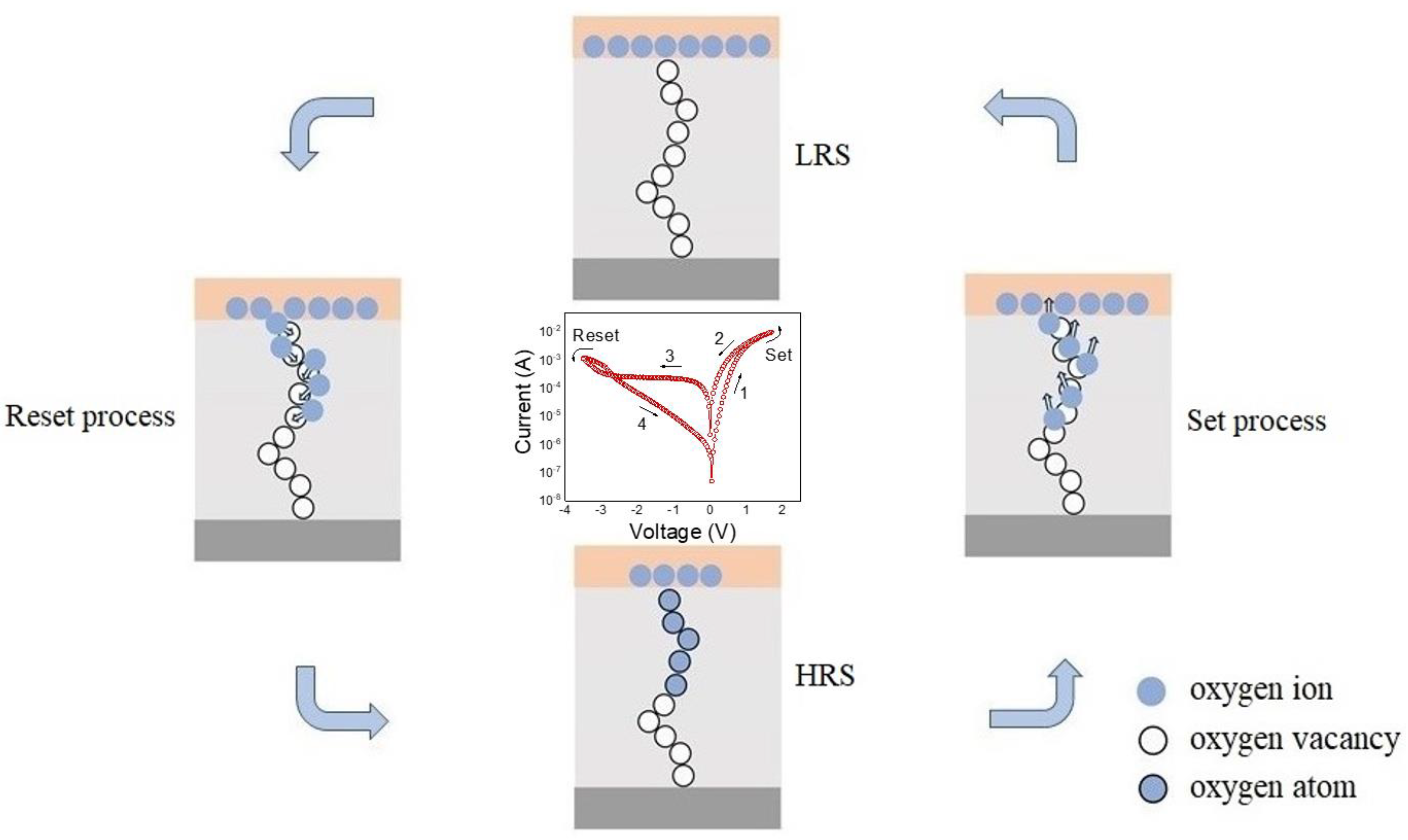
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chua, L.O. Memristor-The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, G.; Luebben, M.; Ma, Z.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.; Boarino, L.; Pirri, C.F.; Waser, R.; Ricciardi, C.; Valov, I. Self-limited single nanowire systems combining allin-one memristive and neuromorphic functionalities. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.X.; Dong, W.C.; Tang, H.; Tang, L.Z.; Li, Z.H.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H.F.; Yang, Z.G.; Zhao, J.J. High-efficiency magnetic modulation in Ti/ZnO/Pt resistive random-access memory devices using amorphous zinc oxide film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Singh, A.K. Mechanism of Nonvolatile Resistive Switching in ZnO/α-Fe2O3 Core-Shell Heterojunction Nanorod Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12953–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Jia, J.H.; Qu, X.R.; Wang, Q.C.; Kang, W.B.; Liu, B.S.; Xiao, Q.Q.; Gao, T.H.; Xie, Q. Tunable resistive switching behaviors and mechanism of the W/ZnO/ITO memory cell. Molecules 2023, 28, 5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, H.Y.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhao, X.N.; Liu, Y.C. Intensity-modulated LED achieved through integrating p-GaN/n-ZnO heterojunction with multilevel RRAM. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 223503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhu, K.L.; Sun, F.; Guo, C.G.; Wu, X.L.; Cheng, G.A.; Zheng, R.T. Core-shell copper nanowire-TiO2 nanotube arrays with excellent bipolar resistive switching properties. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 316, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, M.K.; Byung, J.C.; Yong, C.S.; Seol, C.; Cheol, S.H. Anode-interface localized filamentary mechanism in resistive switching of TiO2 thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 012907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Sun, T.Y.; Liu, B.S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.J.; Fan, X.S.; Sun, Z.J. Self-rectifying and forming-free nonvolatile memory behavior in single-crystal TiO2 nanowire memory device. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.M.; Ram, M.S.; Kilpi, O.P.; Borg, M.; Wernersson, L.E. Cross-Point Arrays with Low-Power ITO-HfO2 Resistive Memory Cells Integrated on Vertical III-V Nanowires. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.A.; Maximilian, S.; Brian, C.O.; Erik, J.L.; Sayed, Y.S.; Marc, T.; Jillian, M.B. Bipolar Resistive Switching in Junctions of Gallium Oxide and p-type Silicon. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Xu, J.M.; Liu, B.S.; Sun, Z.J.; Huang, Q.N.; Ou, M.L.; Wang, Q.C.; Jia, J.H.; Kang, W.B.; Xiao, Q.Q.; et al. A Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis and Resistive Switching Behavior of α-Fe2O3 Nanowire Arrays. Molecules 2023, 28, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.Y.; Li, J.C.; Thatikonda, S.K.; Ke, Y.F.; Qin, N.; Bao, D.H. Introducing a thin MnO2 layer in Co3O4-based memory to enhance resistive switching and magnetization modulation behaviors. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 823, 153731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Nomura, K. Threshold switching of non-stoichiometric CuO nanowire for selector application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 023503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Chen, Y.T. Self-rectifying and interface-controlled resistive switching characteristics of molybdenum oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 779, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.K.; Park, W.I.; Kim, J.M.; Park, K.I.; Seo, H.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, Y.S.; Lee, K.J. Formation in Resistive Memories by Self-Assembled Nanoinsulators Derived from a Block Copolymer. ACS NANO 2014, 9, 9492–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Chang, W.C.; Huang, J.S.; Lin, S.M.; Chueh, Y.L. Resistive Switching of Sn-doped In2O3/HfO2 core-shell nanowire: Geometry Architecture Engineering for Nonvolatile Memory. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6920–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.M.; Song, C.; Yin, J.; Qiao, L.L.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, X.Z.; Yin, S.Q.; Saleem, M.S.; Wu, H.Q.; et al. Modulating metallic conductive filaments via bilayer oxides in resistive switching memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 193502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Chu, D.W.; Li, S.A. Stochastic memristive nature in Co-doped CeO2 nanorod arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 253504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoolfakar, A.S.; Kadir, R.A.; Rani, R.A.; Balendhran, S.; Liu, X.J.; Kats, E.; Bhargava, S.K.; Bhaskaran, M.; Sriram, S.; Zhuiykov, S.; et al. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Biju, K.P.; Jung, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Shin, J.; Hwang, H. Multibit Operation of TiOx-Based ReRAM by Schottky Barrier Height Engineering. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Huang, C.; Lai, C.; Huang, J.; Tsai, H.; Wang, Y.; Shih, Y.; Chang, M.; Lo, S.; Chueh, Y. Single CuOx Nanowire Memristor: Forming-Free Resistive Switching Behavior. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16537–16544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Chen, K.J.; Yi, X.R.; Lin, Y.N.; Zhuang, S.L. A study on sodium alginate based memristor: From typical to self-rectifying. Mater. Lett. 2023, 338, 134037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccoli, I.; Spampinato, R.; Marzo, F.; Prete, P.; Lovergine, N. DC-magnetron sputtering of ZnO:Al films on (00.1)Al2O3 substrates from slip-casting sintered ceramic targets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehraki, N.; Aida, M.S.; Abed, S.; Attaf, N.; Attaf, A.; Poulain, M. ZnO thin films deposition by spray pyrolysis: Influence of precursor solution properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, G.; Porro, S.; Ali, M.Y.; Bejtka, K.; Bianco, S.; Beccaria, F.; Chiolerio, A.; Pirri, C.F.; Ricciardi, C. Unravelling Resistive Switching Mechanism in ZnO NW Arrays: The Role of the Polycrystalline Base Layer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 12, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, E.; Prete, P.; Lovergine, N.; Nikoobakht, B. Observation and Impact of a “Surface Skin Effect” on Lateral Growth of Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 14845–14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Dong, S.R.; Luo, J.K. Bipolar resistive switching characteristics of low temperature grown ZnO thin films by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 012113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Rahmani, M.K.; Khan, W.U.; Kim, J.; Bae, J.; Kang, M.H. Multistate Resistive Switching with Self-Rectifying Behavior and Synaptic Characteristics in a Solution-processed ZnO/PTAA Bilayer Memristor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 063517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.S.; Jeon, Y.R.; Kim, S.; Ku, B.; Choi, C. Bio-realistic synaptic characteristics in the cone-shaped ZnO memristive device. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, A.; Gómez, A.; Baró, M.D.; Suriñach, S.; Pellicer, E.; Sort, J. Self-templating faceted and spongy single-crystal ZnO nanorods: Resistive switching and enhanced piezoresponse. Mater. Des. 2017, 133, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, I.N.; Reddy, C.V.; Sreedhar, M.; Cho, M.; Shim, J.; Reddy, V.R.; Choi, C.-J.; Kim, D. Effect of seed layers (Al, Ti) on optical and morphology of Fe-doped ZnO thin film nanowires grown on Si substrate via electron beam evaporation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 71, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, K.C.; Kamakshi, K.; Bernstorff, S.; Gomes, M.J.M. Effect of annealing temperature on photoluminescence and resistive switching characteristics of ZnO/Al2O3 multilayer nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xiu, F.; Jiang, T.F.; Xu, J.G.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.Q.; Huang, W. Solution-processable zinc oxide nanorods and a reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanostructure for highly flexible and stable memristor. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 10764–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punugupati, S.; Temizer, N.K.; Narayan, J.; Hunte, F. Structural and resistance switching properties of epitaxial Pt/ZnO/TiN/Si(001) heterostructures. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 234501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, A.K.; Dash, P.; Das, D.; Srivastava, S.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Kanjilal, A.; Kanjilal, D.; Varma, S. Resistive switching properties and photoabsorption behavior of Ti ion implanted ZnO thin films. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Yan, X.Q.; Zheng XLiu, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.G.; Shen, Y.W.; Liao, Q.L.; Zhang, Y. High On-Off Ratio Improvement of ZnO-Based Forming-Free Memristor by Surface Hydrogen Annealing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7382–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.D.; Yu, L.N.; Xu, X.G.; Miao, J.; Jiang, Y. Effect of oxide/oxide interface on polarity dependent resistive switching behavior in ZnO/ZrO2 heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 192903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Chin, T.S. Forming-free bipolar memristive switching of ZnO films deposited by cyclic-voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yong, K.J. A Light Incident Angle Switchable ZnO Nanorod Memristor: Reversible Switching Behavior Between Two Non-Volatile Memory Devices. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6423–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Lin, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Long, F.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Han, L. Two-Dimensional Materials for Highly Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.M.; Yang, Z.C.; Zhao, J.S.; Zhang, K.L. High uniformity and forming-free ZnO-based transparent RRAM with HfOx inserting layer. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 087701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Ohno, T.; Samukawa, S.J. Neutral Oxygen Beam Treated ZnO-Based Resistive Switching Memory Device. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kwon, D.; Jung, H.; Lee, K.; Yoon, T.; Kang, C.J.; Lee, H.H. Multistate resistive switching characteristics of ZnO nanoparticles embedded polyvinylphenol device. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 64, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Mustafa, M.; Rahman, K.; Jeong, B.K.; Doh, Y.H. Cost-effective fabrication of memristive devices with ZnO thin film using printed electronics technologies. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 106, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.R.; Chougale, M.Y.; Rane, T.D.; Khot, S.S.; Patil, A.A.; Bagal, O.S.; Jadhav, S.D.; Sheikh, A.D.; Kim, S.; Dongale, T.D. Solution-Processable ZnO Thin Film Memristive Device for Resistive Random Access Memory Application. Electronics 2018, 7, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Y.; Lin, C.; He, J.; Wu, T. Resistive switching behaviors of ZnO nanorod layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 96, 242109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Pan, R.B.; Cao, H.T.; Wang, Y.; Liang, L.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Gao, J.H.; Zhuge, F. Anomalous rectification in a purely electronic memristor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 143505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.R.G.; Prabhakar, R.R.; Hai-, L.; Batabyal, S.K.; Huang, Y.Z.; Mhaisalkar, S.G. A ZnO nanowire resistive switch. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 123114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhao, W.X.; Chen, P. Magnetic-field and white-light controlled resistive switching behaviors in Ag/BiFeO3/γ-Fe2O3/FTO device. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13513–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, J.; Lai, C.; Huang, H.; Lin, S.; Chueh, Y. Manipulated Transformation of Filamentary and Homogeneous Resistive Switching on ZnO Thin Film Memristor with Controllable Multistate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6017–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y. Characteristics of the bipolar resistive switching behavior in memory device with Au/ZnO/ITO structure. Chin. J. Phys. 2018, 56, 3073–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.J.; Kang, S.Y.; Shim, E.L.; Yoon, T.S.; Kang, C.J.; Choi, Y.J. Influence of Incorporated Pt-Fe2O3 Core-Shell Nanoparticles on the Resistive Switching Characteristics of ZnO Thin Film. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 8622–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, J.; Lin, S.; Chang, W.; He, J.; Chueh, Y. ZnO1-x Nanorod Arrays/ZnO Thin Film Bilayer Structure: From Homojunction Diode and High-Performance Memristor to Complementary 1D1R Application. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8407–8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Han, X.; Xu, J.M.; Chen, C.; Qu, X.R.; Liu, B.S.; Sun, Z.J.; Sun, T.Y. The Effect of Nitrogen Annealing on the Resistive Switching Characteristics of the W/TiO2/FTO Memory Device. Sensors 2023, 23, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Y.; Liu, Y.; Tu, J.; Zhou, Z.P.; Cao, L.; Liu, X.P.; Li, H.O.; Li, Q.; Fu, T.; Zhang, F.B.; et al. Wafer-scale high anti-reflective nano/micro hybrid interface structures via aluminum grain dependent self-organization. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Qu, X.P.; Yang, W.P.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.M. A facile hydrothermal synthesis and memristive switching performance of rutile TiO2 nanowire arrays. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Qu, X.P.; Yang, W.P.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.M. Hydrothermal synthesis and memristive switching behaviors of single-crystalline anatase TiO2 nanowire arrays. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Liu, M.L.; Lang, J.X.; Qian, K.; Zhang, C.H. Resistive switching characteristics and resistive switching mechanism of Au/TiO2/FTO memristor. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 157302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan AK, S.; Sharma, D.K.; Datta, A. Rate limited filament formation in Al-ZnO-Al bipolar ReRAM cells and its impact on early current window closure during cycling. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Y.; Yu, F.T.; Tang, X.S.; Li, H.O.; Zhang, F.B.; Xu, Z.M.; Liao, Q.; Yu, Z.Q.; Liu, X.P.; Wangyang, P.H.; et al. Organic-2D composite material-based RRAM with high reliability for mimicking synaptic behavior. J. Mater. 2024, 10, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, V.; Joshi, S.R.; Mishra, I.; Kabiraj, D.; Mishra, N.C.; Avasthi, D.K.; Varma, S. Oxygen vacancy mediated enhanced photo-absorption from ZnO (0001) nanostructures fabricated by atom beam sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 054303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.P.; Yuan, X.C.; Chen, B.L.; Gong, C.H.; Zeng, H.Z.; Wei, X.H. Self-rectifying resistive switching device based on n-ZnO/p-NiO junction. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.S.; Patil, P.A.; Kadam, K.D.; Patil, H.S.; Patil, S.L.; Kamat, R.K.; Kim, S.; Dongale, T.D. Resistive switching and synaptic properties modifications in gallium-doped zinc oxide memristive devices. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Structure | Vset/Vreset (V) | Preparation Process | RHRS/RLRS | Retention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| top-probe/α-Fe2O3/ZnO/bottom-probe | −0.55/− | Spin-coating technique | ~20 | 103 s | [5] |
| Al/Si/Al2O3/ZnO/Al2O3/Al | +7/−7 | Pulsed laser deposition | ~10 | 103 s | [34] |
| Cr/ZnO/Pt–Fe2O3 NPs/ZnO/Cr | −7/+7 | Dip-coating method | ~5 | 104 s | [54] |
| Ag/BaTiO3/γ-Fe2O3/ZnO/Ag | +3.1/−4.7 | Co-precipitation method | ~10 | - | [51] |
| Pt/ZnO/Zn | −4/+5 | Hydrothermal method | ~10 | 10 s | [32] |
| Ag/ZnO/Pt | +1/−1 | Magnetron sputtering | ~10 | 103 s | [21] |
| Ag/ZnO/Ag | ~+1.6/~−2 | Spin-coating technique | <10 | 3.1 × 103 | [46] |
| Au/ZnO nanorods/AZO | −6/+7 | Dip-coating method | ~10 | - | [38] |
| Pt/ZnO nanowire/Pt | +0.5/− | Chemical vapor deposition | ~1.5 | 0.9 × 102 s | [50] |
| Pt/ZnO thin film/Pt | ~−1.75/~+2 | Magnetron sputtering | ~10 | 103 s | [52] |
| Pt/ZnO/Pt | +1.2/−1 | Chemical vapor deposition | ~7 | 104 s | [27] |
| Pt/ZnO/TiN | ~+1.25/~−1 | Pulsed laser deposition | ~2 | - | [36] |
| Ti/ZnO/Pt | ~+2/~−1.5 | Magnetron sputtering | ~10 | 105 s | [49] |
| Pt/ZnO NRL/ITO | +0.72/−0.59 | Hydrothermal method | ~10 | 103 s | [48] |
| Cu/ZnO/ITO | +1/−1.7 | Magnetron sputtering | ~10 | - | [44] |
| ITO/HfOx/ZnO/ITO | ~−3/~+3 | Magnetron sputtering | ~10 | 104 s | [43] |
| Au/ZnO/ITO | ~+2.2/~−3.8 | Magnetron sputtering | >10 | - | [53] |
| Pt/ZnO/ITO | +1/−1 | Cyclic voltammetry deposition | ~50 | 3 × 102 s | [40] |
| Ag/SA+ZnO NPs/ITO | +2.5/−2.5 | Spin-coating technology | ~30 | 103 s | [24] |
| Ag/PTAA/ZnO/ITO | +3/−2 | Magnetron sputtering | ~20 | 2.4 × 103 s | [30] |
| Al/ZnO/NiO/ITO | +4.4/−6.1 | Spin-coating technology | ~104 | - | [64] |
| Al/Ga-doped ZnO/FTO | +2/−2 | Hydrothermal method | ~1.48 | 103 s | [65] |
| W/ZnO/FTO | ~+0.5/~−1 | Spin-coating technique | >102 | >103 s | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Yu, Z. Sol-Gel Derived ZnO Thin Films with Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Behavior for Future Memory Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070824
Shen X, Yu Z. Sol-Gel Derived ZnO Thin Films with Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Behavior for Future Memory Applications. Coatings. 2024; 14(7):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070824
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xiangqian, and Zhiqiang Yu. 2024. "Sol-Gel Derived ZnO Thin Films with Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Behavior for Future Memory Applications" Coatings 14, no. 7: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070824
APA StyleShen, X., & Yu, Z. (2024). Sol-Gel Derived ZnO Thin Films with Nonvolatile Resistive Switching Behavior for Future Memory Applications. Coatings, 14(7), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070824






