Symbiosis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Total General Bacteria Affects Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Pretreatment
2.2. Cultivation and Inoculation
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
2.4. Surface Characterizations and Corrosion Product Analyses
2.5. Weight Loss Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Weight Loss
3.2. Morphological Study of Corroded Samples
3.3. EDS and XPS Study of Corrosion Products
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaines, R.H. Bacterial Activity as a Corrosive Influence in the Soil. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1910, 2, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.; Kora, A.J.; Chandramohan, P.; Panigrahi, B.; Narasimhan, S. Biofouling and microbial corrosion problem in the thermo-fluid heat exchanger and cooling water system of a nuclear test reactor. Biofouling 2009, 25, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starosvetsky, J.; Starosvetsky, D.; Armon, R. Identification of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) in industrial equipment failures. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videla, H.A.; Herrera, L.K. Microbiologically influenced corrosion: Looking to the future. Int. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zhu, W. Localized corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel in the presence of sulfate-reducing and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 443, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.H.; Xu, L.-C.; Chan, K.-Y. Effects of toxic metals and chemicals on biofilm and biocorrosion. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4709–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.; Korber, D.; Lappin-Scott, H. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar]
- Gerchakov, S.; Little, B.; Wagner, P. Probing microbiologically induced corrosion. Corrosion 1986, 42, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooters, M.; Harneit, K.; Wöllbrink, M.; Sand, W.; Stadler, R.; Fürbeth, W. Novel Steel Corrosion Protection by Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS)—Biofilm-Induced Corrosion Inhibition. Adv. Mater. Res. 2007, 20–21, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastra, M.; Salvin, P.; Roos, C. MIC of carbon steel in Amazonian environment: Electrochemical, biological and surface analyses. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 112, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, E.; Bethencourt, M.; Botana, F.J.; Cano, M.J.; Sánchez-Amaya, J.M.; Corzo, A.; de Lomas, J.G.; Fardeau, M.L.; Ollivier, B. Biocorrosion of carbon steel alloys by an hydrogenotrophic sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio capillatus isolated from a Mexican oil field separator. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2417–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walch, M. Corrosion, Microbial, Encyclopaedia of Microbiology; Lederberg, J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Javaherdashti, R. A review of some characteristics of MIC caused by sulfate-reducing bacteria: Past, present and future. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1999, 46, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord-Ruwisch, R.; Kleinitz, W.; Widdel, F. Sulfate-reducing Bacteria and Their Activities in Oil Production. J. Pet. Technol. 1987, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipaničev, M.; Turcu, F.; Esnault, L.; Schweitzer, E.W.; Kilian, R.; Basseguy, R. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria in seawater environment. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen-Saarivirta, E.; Rajala, P.; Carpén, L. Corrosion behaviour of copper under biotic and abiotic conditions in anoxic ground water: Electrochemical study. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 203, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Zhai, X.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Hou, B. Influence of sulfate-reducing bacteria on the corrosion behavior of 5052 aluminum alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 316, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.A. Microbially Influenced Corrosion as a Model System for the Study of Metal Microbe Interactions: A Unifying Electron Transfer Hypothesis. Biofouling 2003, 19, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Tan, J.L.; Jin, P.; Blackwood, D.J.; Xu, D.; Gu, T. Effects of biogenic H2S on the microbiologically influenced corrosion of C1018 carbon steel by sulfate reducing Desulfovibrio vulgaris biofilm. Corros. Sci. 2018, 130, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhao, K.; Nesic, S. A new mechanistic model for MIC based on a biocatalytic cathodic sulfate reduction theory. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2009, Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–26 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Enning, D.; Garrelfs, J. Corrosion of iron by sulfate-reducing bacteria: New views of an old problem. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Song, F.; Gu, T. Laboratory investigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion of C1018 carbon steel by nitrate reducing bacterium Bacillus licheniformis. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, T. Mechanistic modeling of biocorrosion caused by biofilms of sulfate reducing bacteria and acid producing bacteria. Bioelectrochemistry 2016, 110, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usher, K.; Kaksonen, A.; Cole, I.; Marney, D. Critical review: Microbially influenced corrosion of buried carbon steel pipes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 93, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulenta, F.; Catervi, A.; Majone, M.; Panero, S.; Reale, P.; Rossetti, S. Electron transfer from a solid-state electrode assisted by methyl viologen sustains efficient microbial reductive dechlorination of TCE. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2554–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Yang, D.; Xu, D.; Gu, T. Anaerobic Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel Caused by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zhu, W. Pitting corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel in the media of sulphate-reducing and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.J.; Pehkonen, S.O. AFM study of microbial colonization and its deleterious effect on 304 stainless steel by Pseudomonas NCIMB 2021 and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans in simulated seawater. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassia, G.S.; McLean, K.M.; Glénat, P.; Bauld, J.; Sheehy, A.J. A systematic survey for thermophilic fermentative bacteria and archaea in high temperature petroleum reservoirs. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1996, 21, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Haridon, S.; Reysenbacht, A.L.; Glénat, P.; Prieur, D.; Jeanthon, C. Hot subterranean biosphere in a continental oil reservoir. Nature 1995, 377, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuroff, T.R.; Curtis, W.R. Developing symbiotic consortia for lignocellulosic biofuel production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Du, M.; Li, X.; Yue, Y.; Chen, X. Mechanism of microbiologically influenced corrosion of X65 steel in seawater containing sulfate-reducing bacteria and iron-oxidizing bacteria. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4066–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, C.; Gu, T.; Zhang, G.; Lv, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in the presence of sulfate reducing bacteria and iron oxidizing bacteria cultured in oilfield produced water. Corros. Sci. 2015, 100, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, T.; Jia, R.; Kumseranee, S.; Punpruk, S.; Gu, T. Laboratory investigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion of carbon steel in hydrotest using enriched artificial seawater inoculated with an oilfield biofilm consortium. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 100, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batmanghelich, F.; Li, L.; Seo, Y. Influence of multispecies biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Desulfovibrio vulgaris on the corrosion of cast iron. Corros. Sci. 2017, 121, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standards G1-03; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- ASTM Standards G31; Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1994.
- Neville, A.; Wang, C. Erosion–corrosion mitigation by corrosion inhibitors—An assessment of mechanisms. Wear 2009, 267, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Du, M.; Hou, B. Corrosion of carbon steel influenced by anaerobic biofilm in natural seawater. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Gu, T. Carbon source starvation triggered more aggressive corrosion against carbon steel by the Desulfovibrio vulgaris biofilm. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 91, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, E.; Jiang, C.; Jia, R.; Liu, S.; Xu, D.; Gu, T.; Wang, F. Endogenous phenazine-1-carboxamide encoding gene PhzH regulated the extracellular electron transfer in biocorrosion of stainless steel by marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 94, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Jia, R.; Unsal, T.; Xu, D. Toward a better understanding of microbiologically influenced corrosion caused by sulfate reducing bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.W. The biofilm matrix–an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Corrosion of low alloy steel and stainless steel in supercritical CO2/H2O/H2S systems. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.D.; Duque, Z.; Rodríguez, L.; Rincón, O.D.; Pérez, O.; Araujo, I. A Study of Microbiologically Induced Corrosion by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on Carbon Steel Using Hydrogen Permeation. Corrosion 2005, 61, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.A.; Miller, J.D.A. Corrosion by the sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature 1971, 233, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Smith, C.K.; LaPara, T.M.; Hozalski, R.M. Sulfate Reducing Bacteria and Mycobacteria Dominate the Biofilm Communities in a Chloraminated Drinking Water Distribution System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8432–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emde, K.M.E.; Smith, D.W.; Facey, R. Initial investigation of microbially influenced corrosion (MIC) in a low temperature water distribution system. Water Res. 1992, 26, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
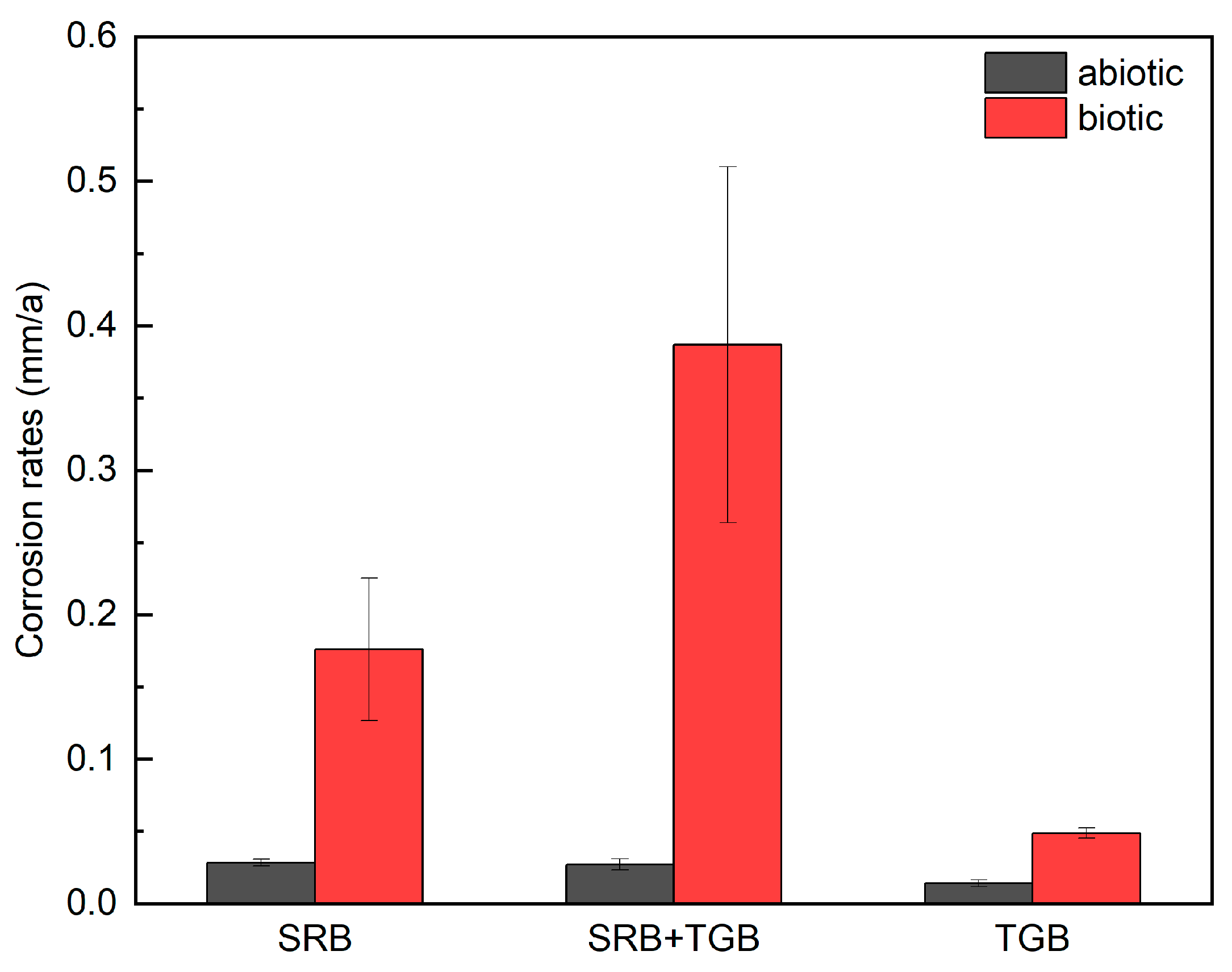
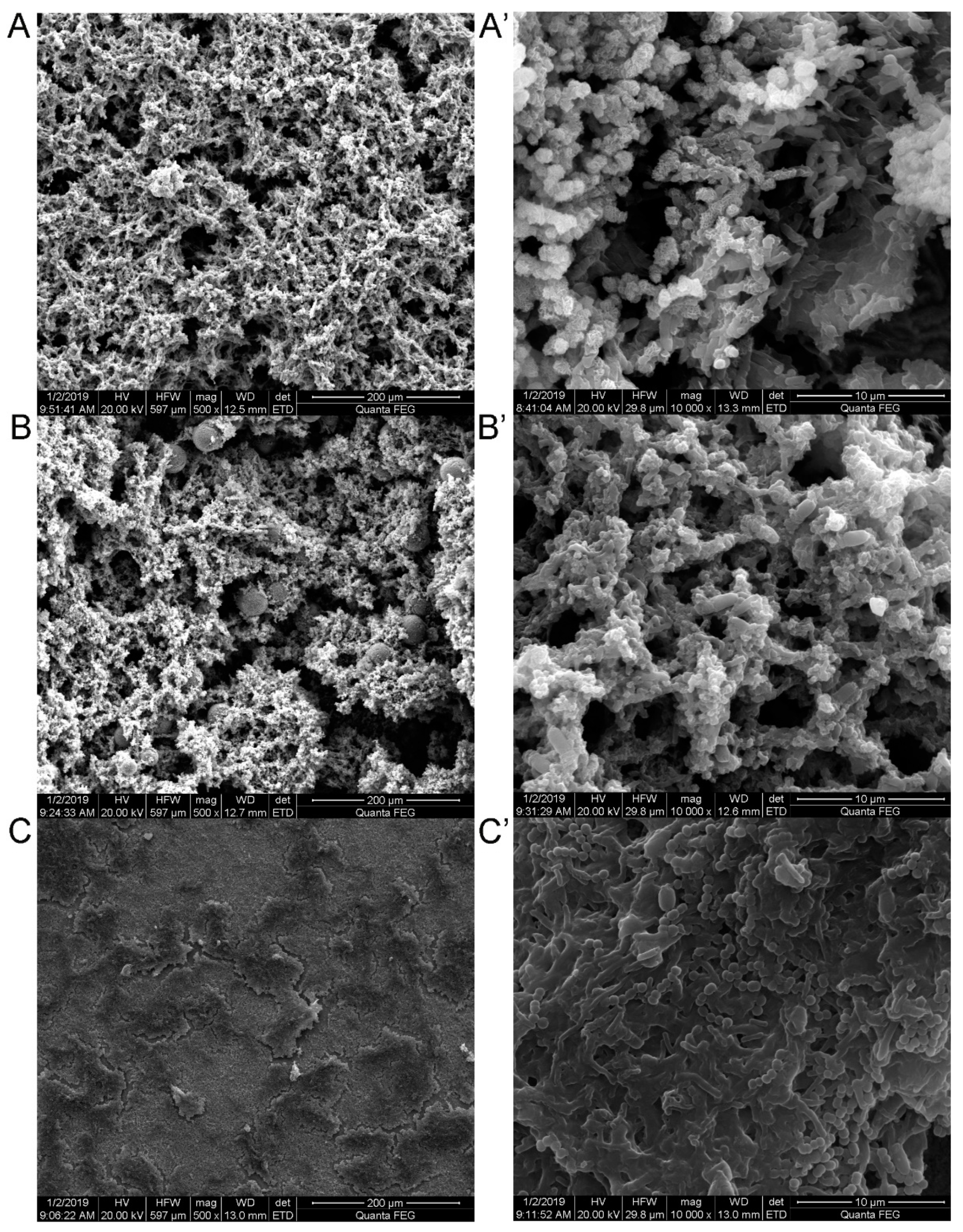


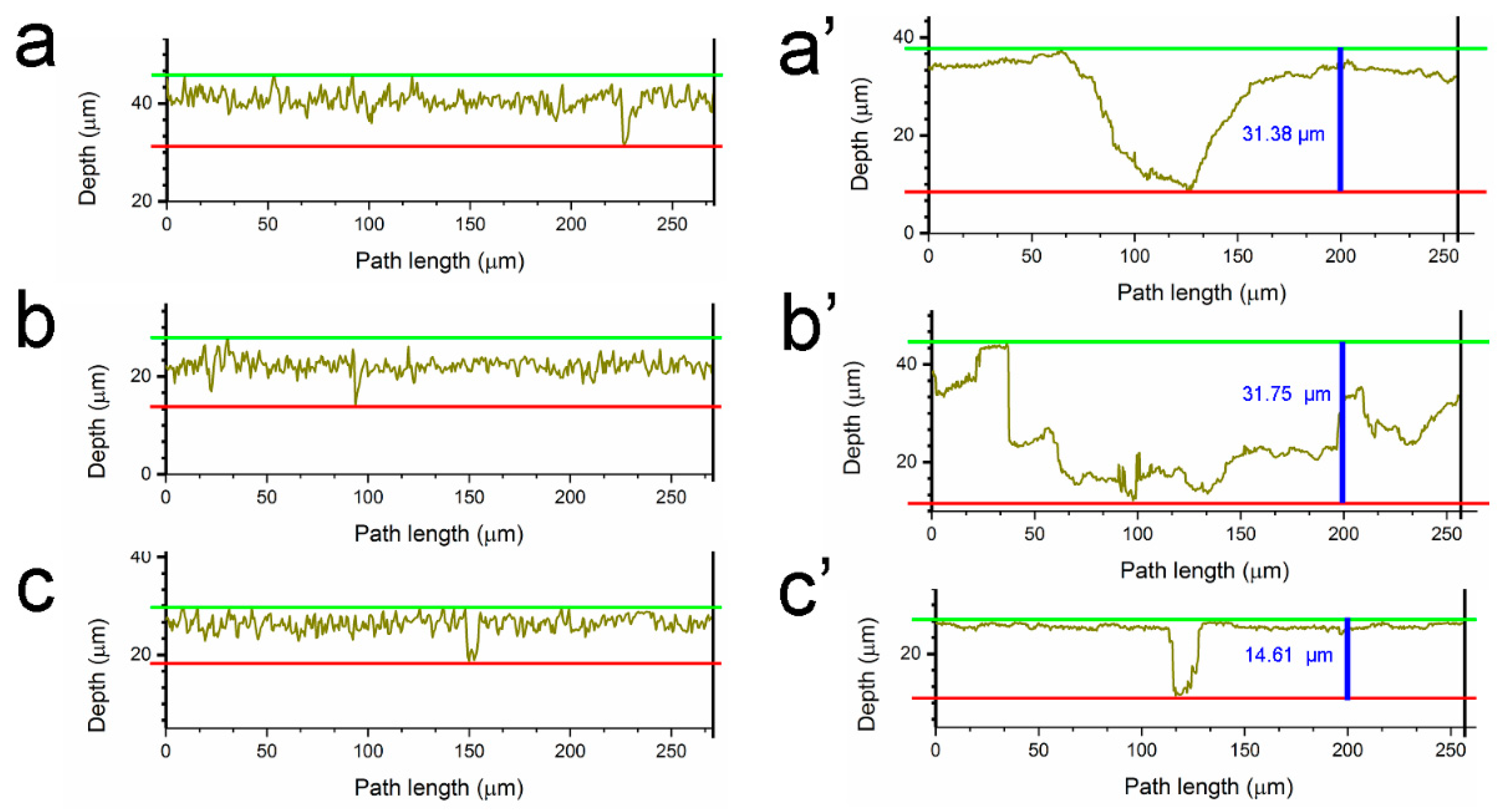
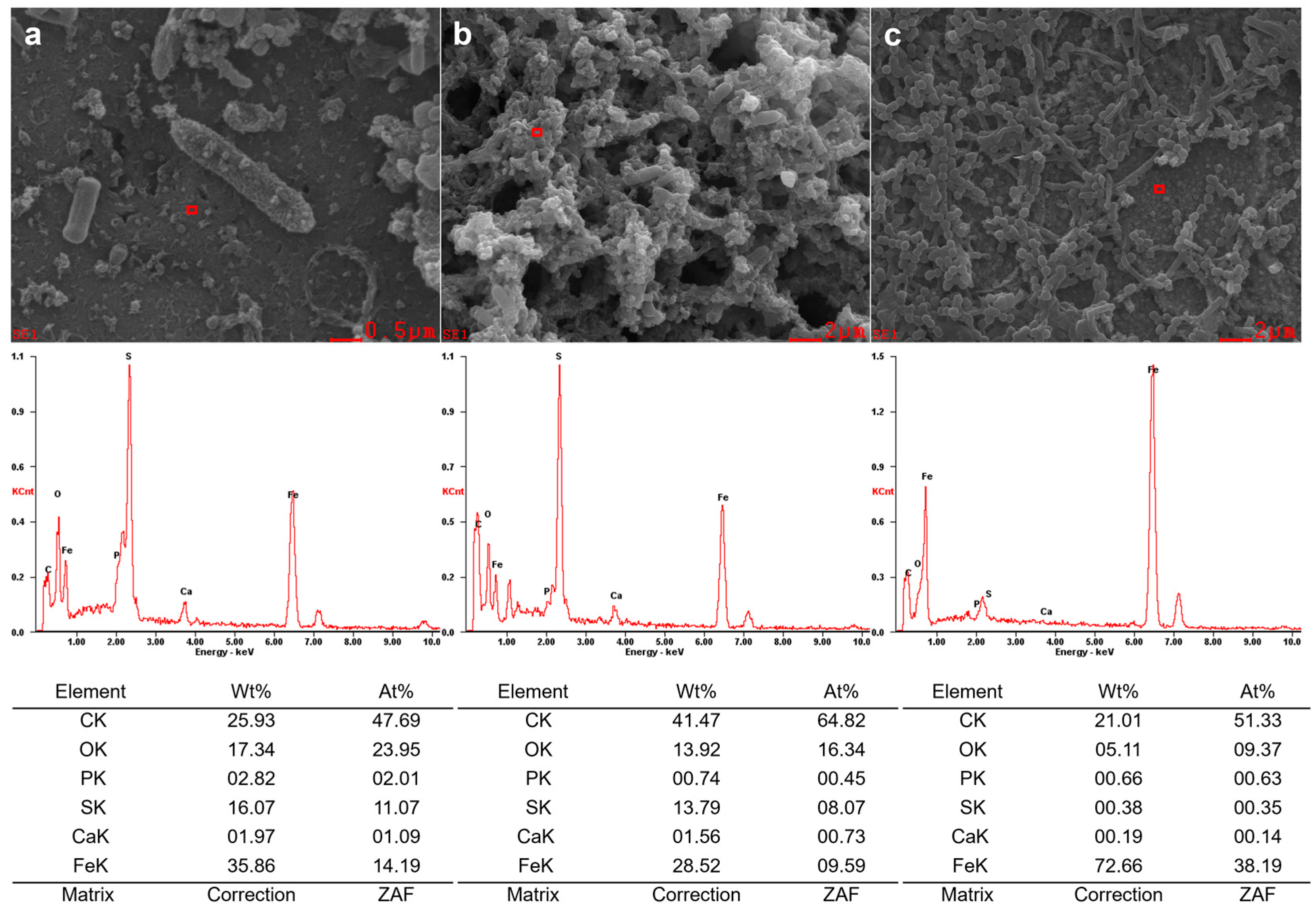

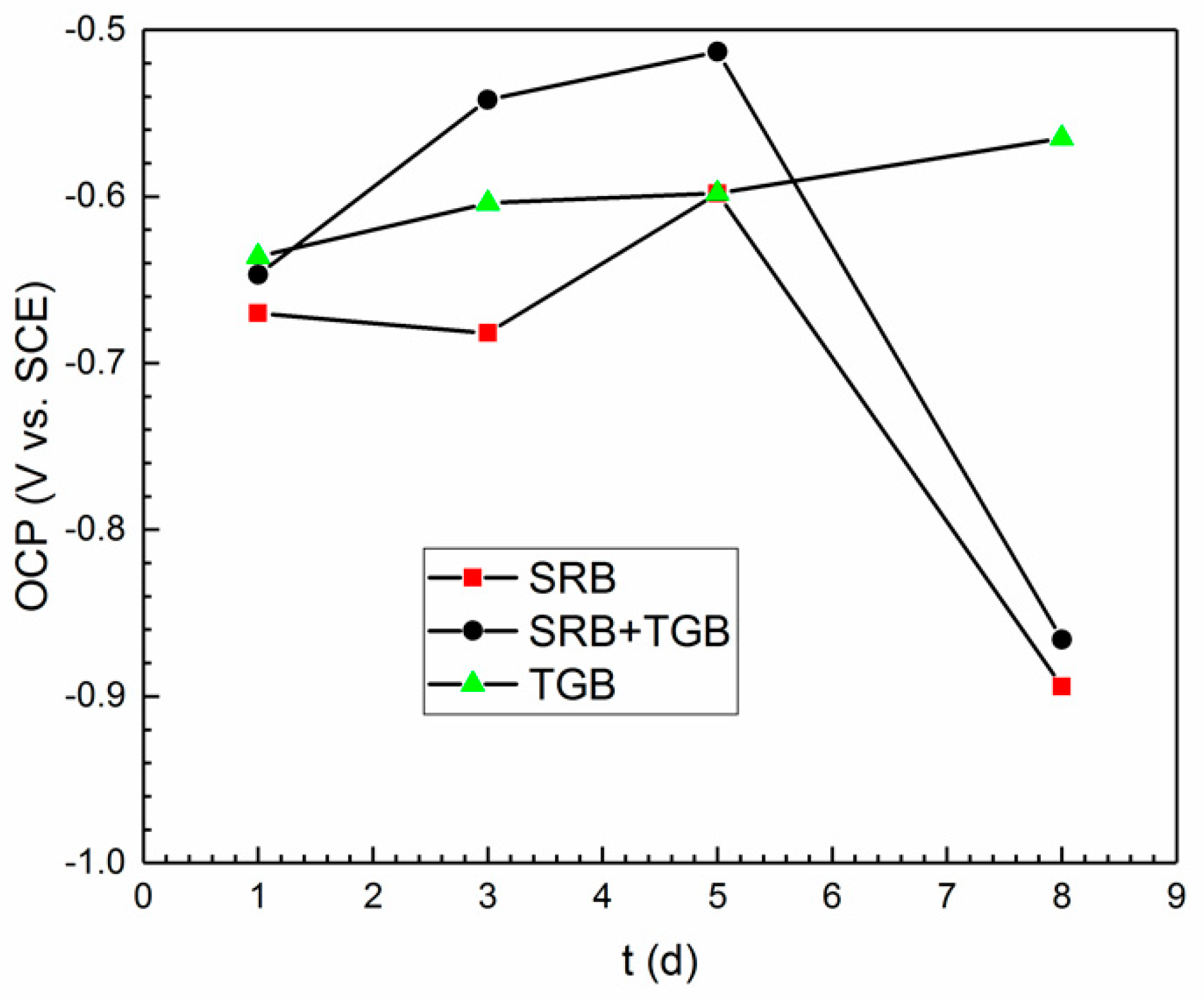
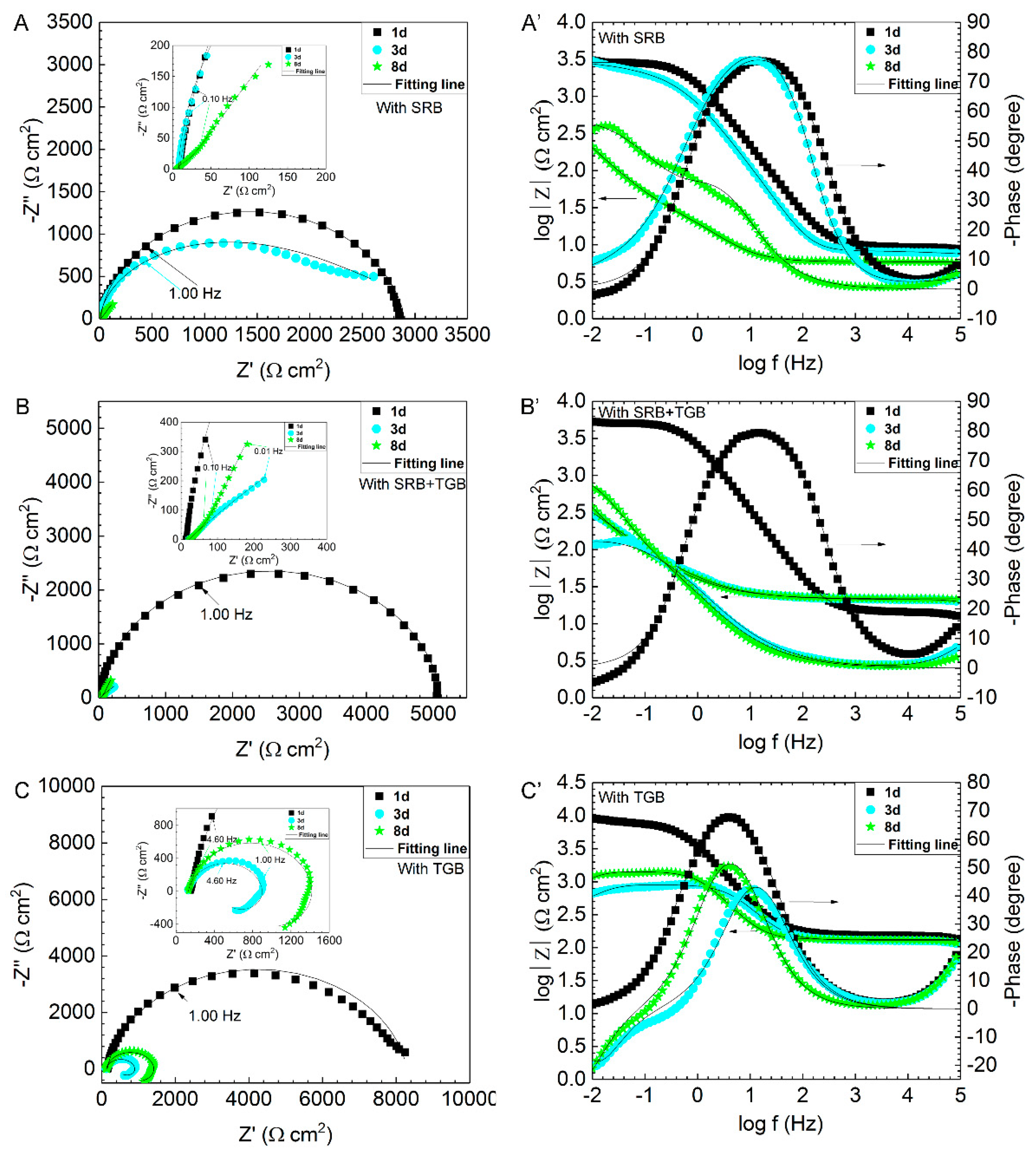
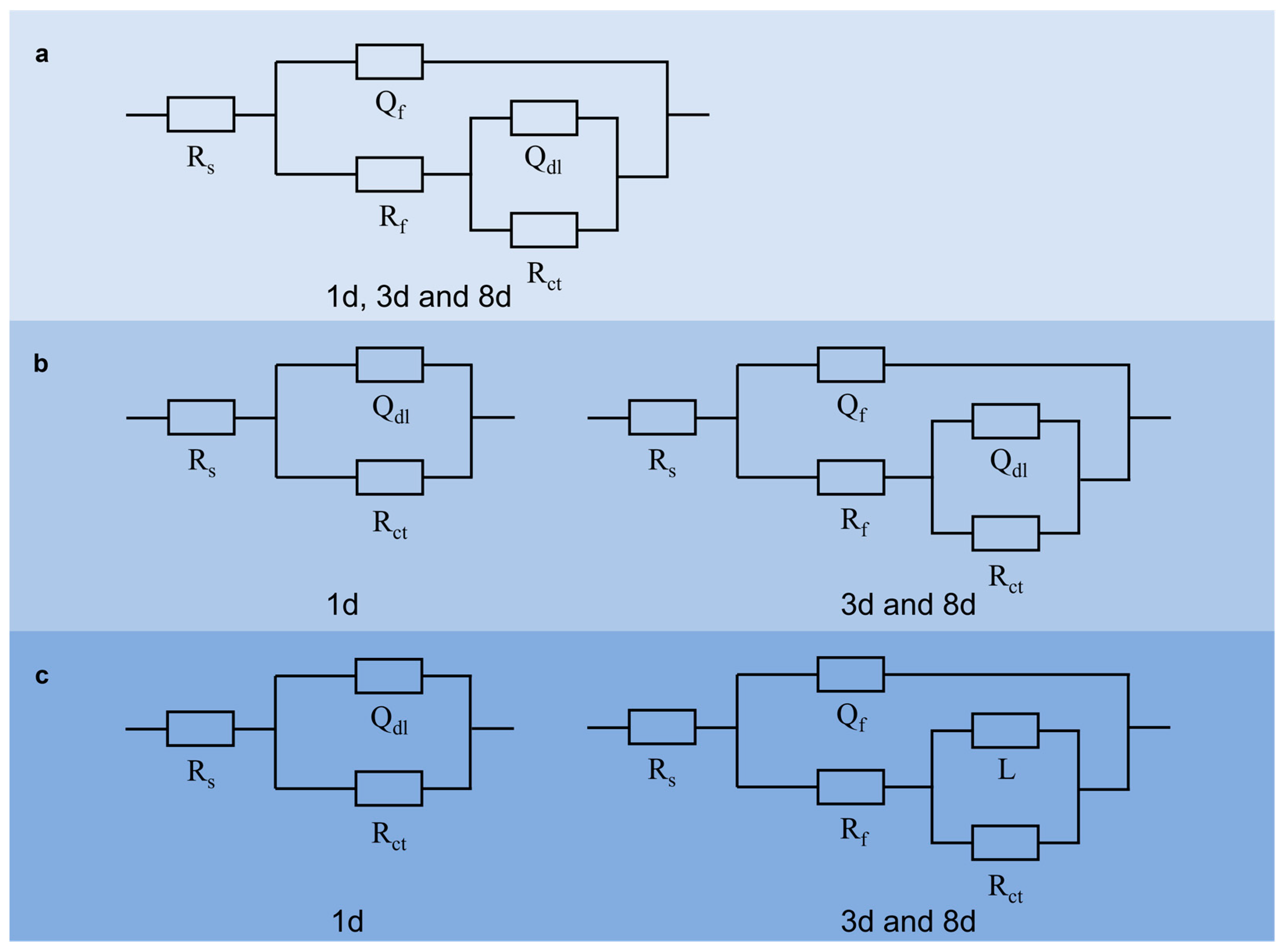
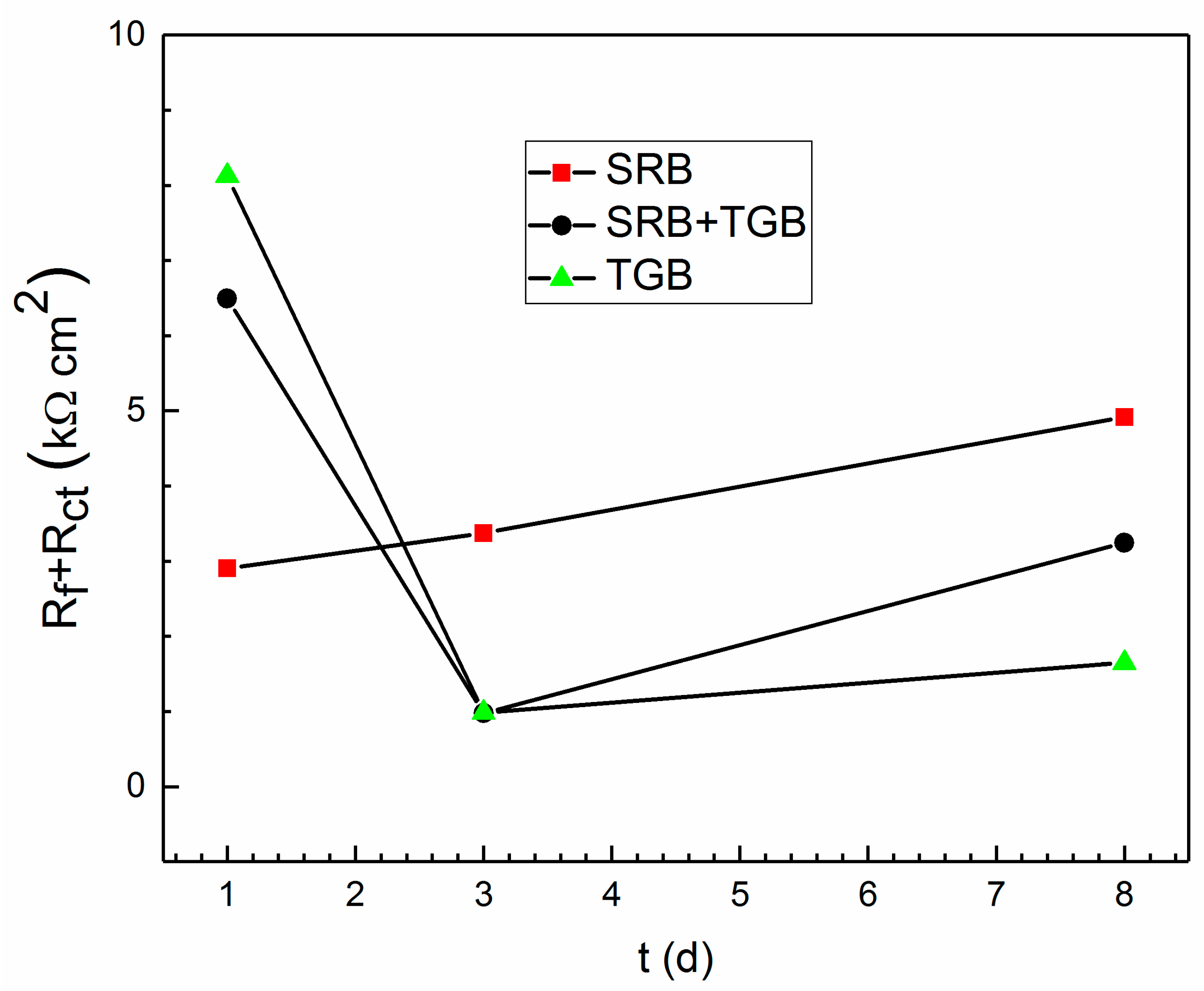

| Condition | Control SRB | Control SRB + TGB | Control TGB | SRB | SRB + TGB | TGB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (μm) | 10.44 | 10.02 | 8.70 | 31.38 | 31.75 | 14.61 |
| Condition | Day | Rs (Ω cm2) | Rf (Ω cm2) | Rct (Ω cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRB | 1 | 5.5 | 4.0 | 2898 |
| 3 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 3369 | |
| 8 | 5.9 | 27.7 | 4889 | |
| SRB + TGB | 1 | 18.3 | - | 6495 |
| 3 | 11.1 | 161.8 | 814 | |
| 8 | 12.6 | 41.8 | 3203 | |
| TGB | 1 | 154.1 | - | 8127 |
| 3 | 166.9 | 422.6 | 563 | |
| 8 | 170.3 | 540.7 | 1109 |
| Condition | Ecorr (mV) vs. SCE | icorr (μA cm−2) | βa (mV dec−1) | βc (mV dec−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRB | −763 | 14.5 | 114 | −59 |
| SRB + TGB | −779 | 21.1 | 126 | −140 |
| TGB | −562 | 3.1 | 57 | −162 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Xiang, Y.; Yan, W. Symbiosis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Total General Bacteria Affects Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel. Coatings 2024, 14, 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070788
Jin J, Li Y, Huang H, Xiang Y, Yan W. Symbiosis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Total General Bacteria Affects Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel. Coatings. 2024; 14(7):788. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070788
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Juxing, Yingchao Li, Huaiwei Huang, Yong Xiang, and Wei Yan. 2024. "Symbiosis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Total General Bacteria Affects Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel" Coatings 14, no. 7: 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070788
APA StyleJin, J., Li, Y., Huang, H., Xiang, Y., & Yan, W. (2024). Symbiosis of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Total General Bacteria Affects Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Carbon Steel. Coatings, 14(7), 788. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14070788








