The Effects of Ultrasonic Impact Modification on the Surface Quality of 20CrNiMo Carburized Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principles of Ultrasonic Impact Modification
3. Experimental Design of Ultrasonic Impact Modification
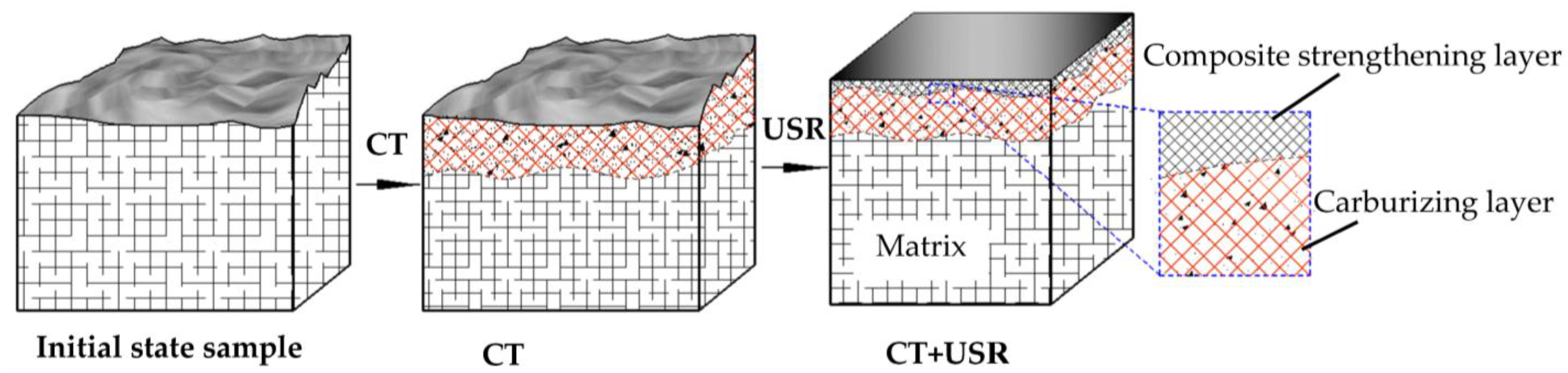
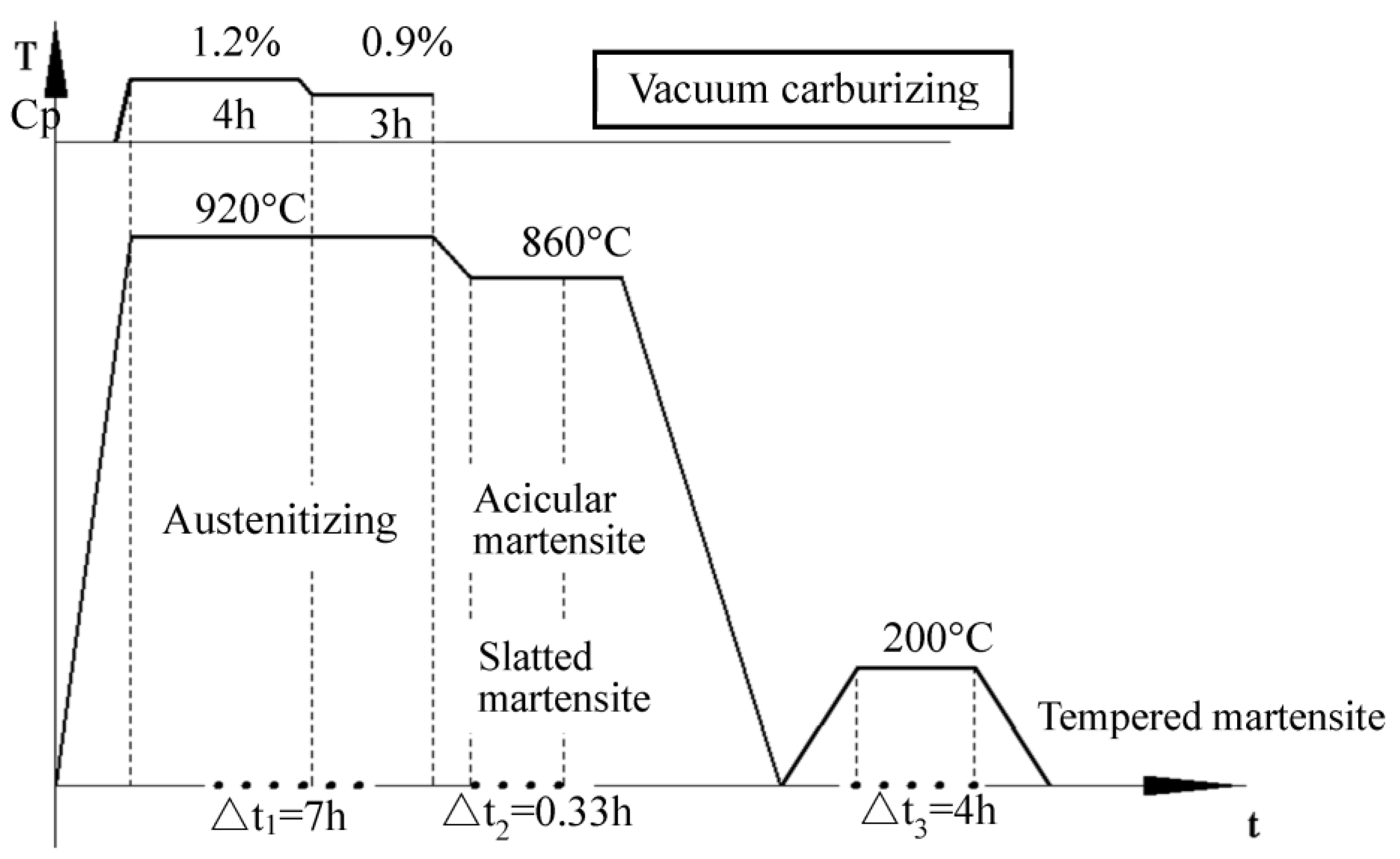
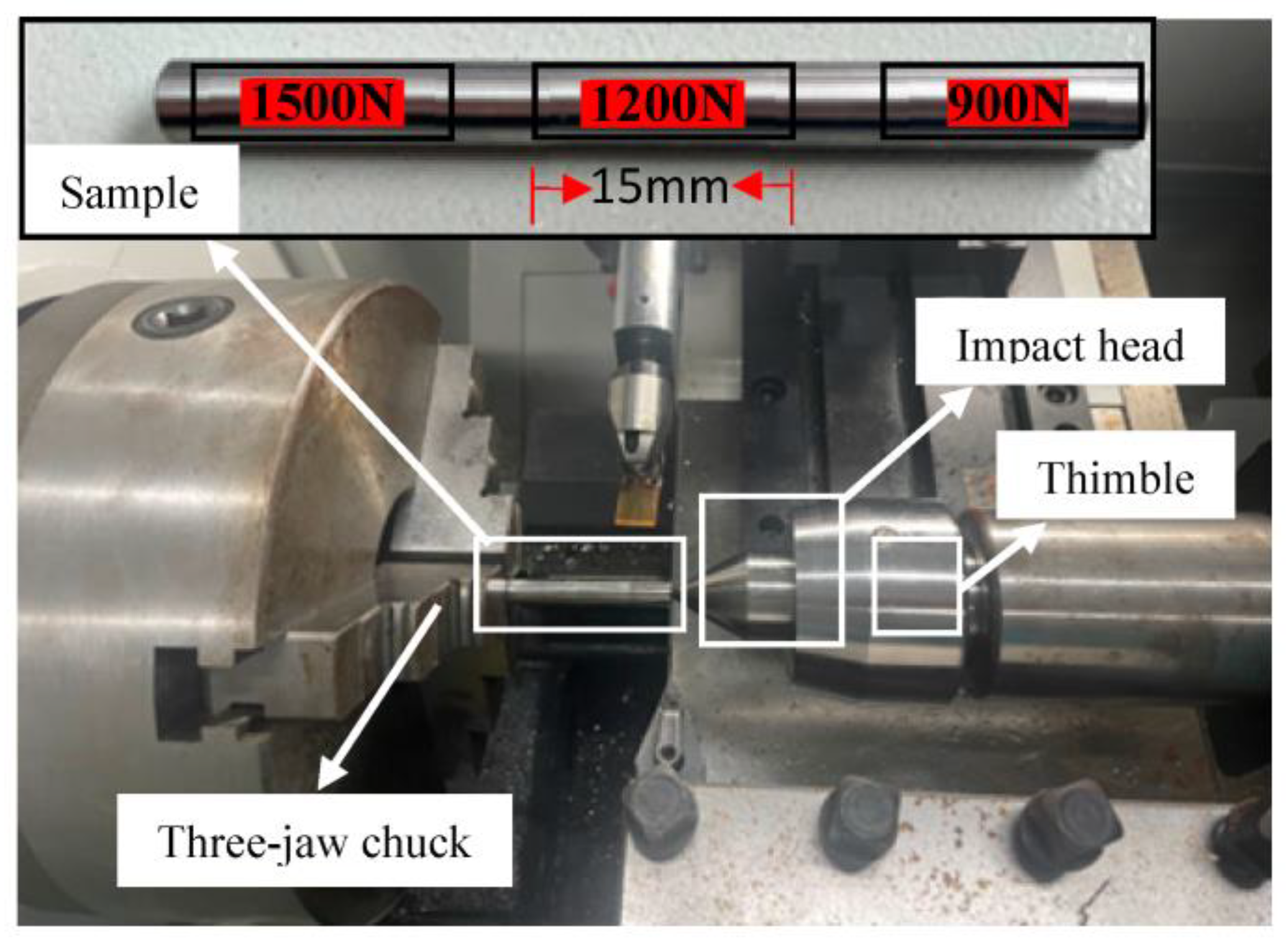
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Ultrasonic Impact Modification Process
4. Performance Analysis
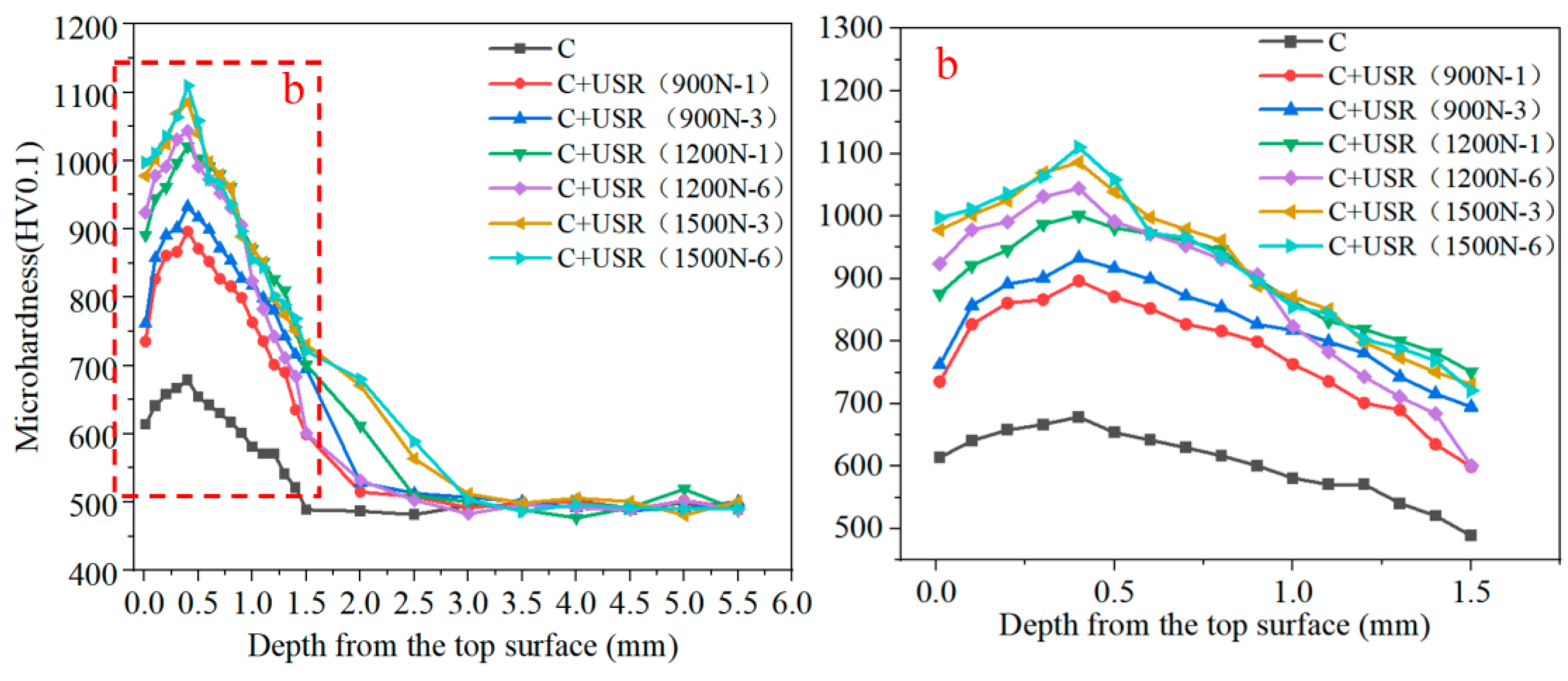
4.1. Surface Hardness Field
4.2. Surface Residual Compressive Stress Field
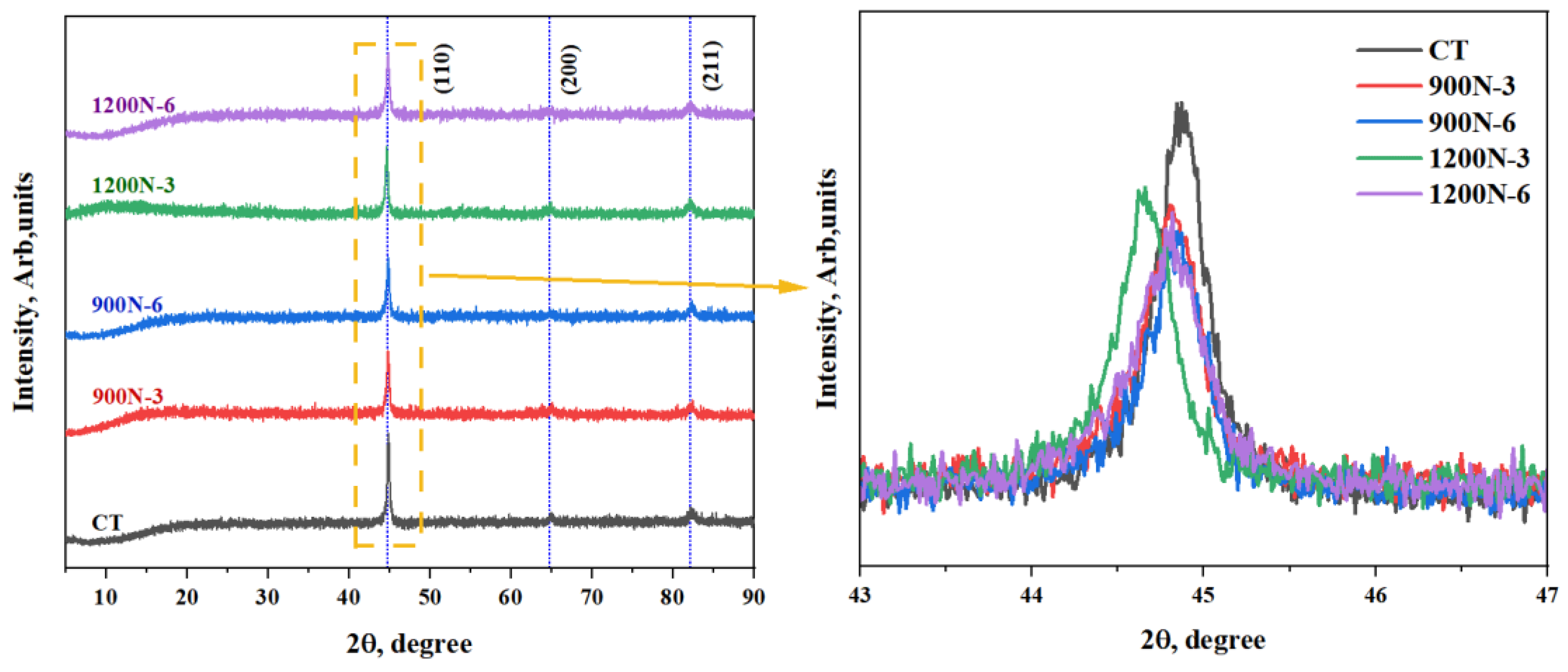
4.3. XRD
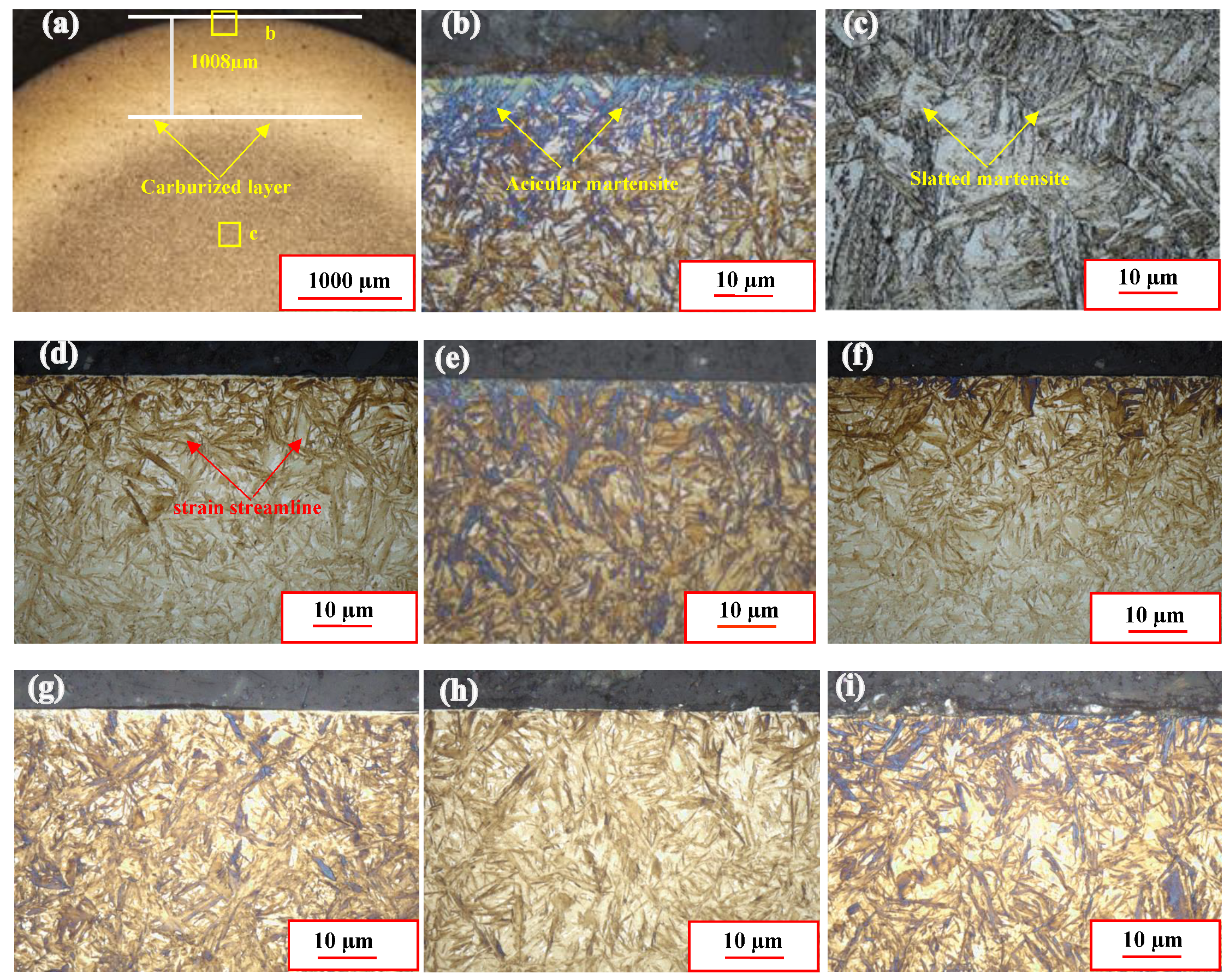
4.4. Microstructure Field on the Surface Layer
5. Conclusions
- Ultrasonic impact can effectively enhance the surface quality of a 20CrNiMo carburized sample within a specific range of static load and impact round without significant deformation. The surface hardness and residual stress are positively correlated with the mean range of static load and impact round, and gradually reach a certain upper limit value as the material’s plasticity losing. The maximum residual stress is up to 1195.36 MPa with the static load of 1500 N and six impact rounds.
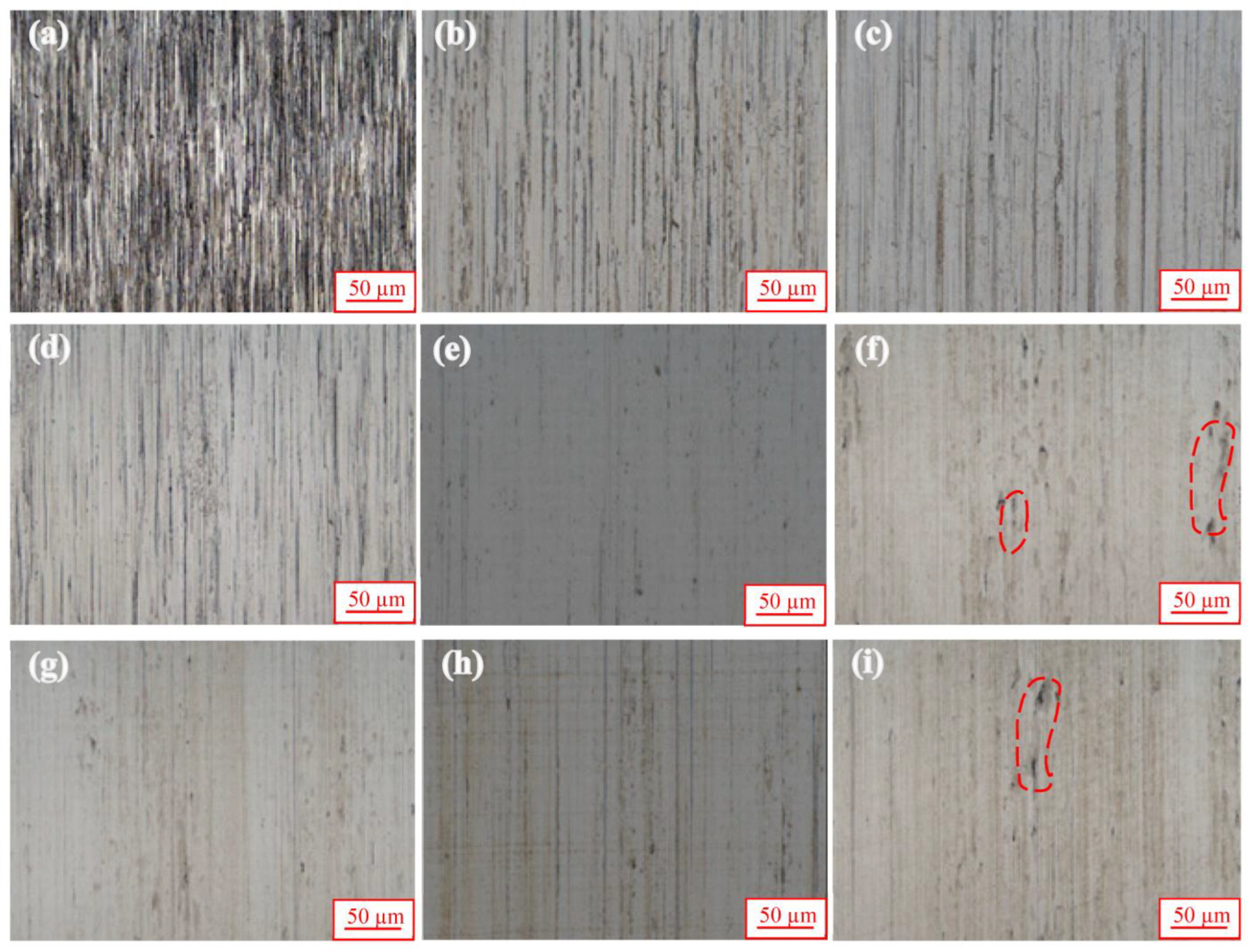
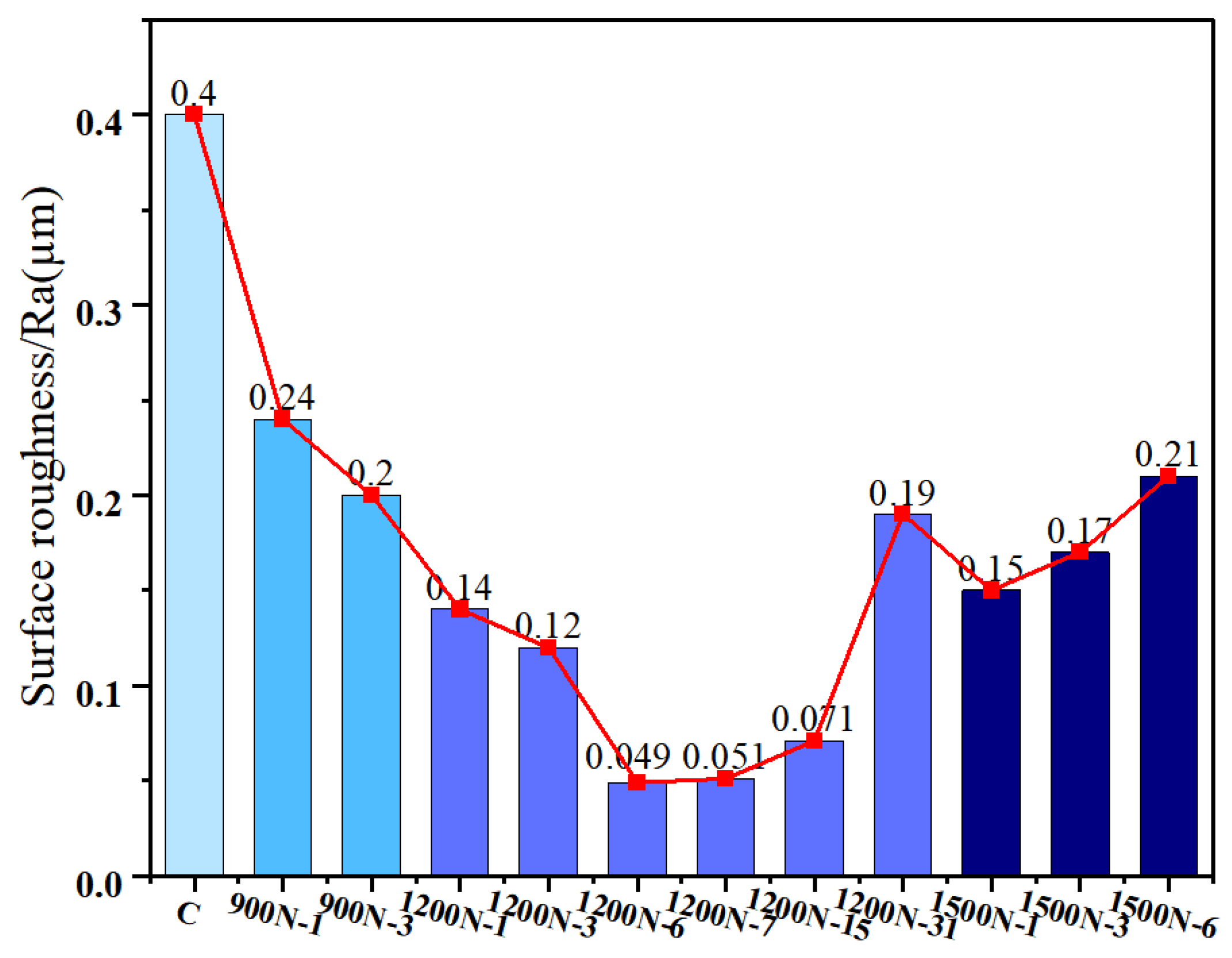
- The surface roughness and effective grain size of the 20CrNiMo carburized sample gradually decrease as the static load of ultrasonic impact increases. However, when the static load reaches 1500 N, defects appeared on the sample’s surface due to local excessive deformation, and the surface roughness increases sharply. As the impact round increases, the overall Ra value exhibits a decreasing trend. After a certain upper impact round reached, the Ra value will increase significantly.
- The best surface quality can be obtained after 6 rounds of impact under a static load of 1200 N. When Ra decreases to 0.04 µm, the machining tool marks on the surface are basically eliminated, the surface hardness increases to 1086 HV0.1, and the maximum residual compressive stress on the surface layer reaches 1137.25 MPa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kayali, Y.; Ucun, I.; Aslantaş, K. Contact Fatigue Failure of a Tapered Roller Bearing Used in a Lorry Wheel. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2009, 9, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Shiozawa, D.; Kikuchi, S.; Obama, T.; Saito, H.; Makino, T.; Neishi, Y. 4D observations of rolling contact fatigue processes by laminography using ultra-bright synchrotron radiation. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 183, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, B.; Gu, D.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X. Strength Test and Reliability Evaluation of 20CrNiMo Materials. Mech. Strength 2023, 45, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Asi, O.; Can, A.C.; Pineault, J.; Belassel, M. The effect of high temperature gas carburizing on bending fatigue strength of SAE 8620 steel. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Zhao, M. Effect of carburizing process on high cycle fatigue behavior of 18CrNiMo7-6 steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fan, G.; Huang, M.; Geng, L.; Cui, X.; Chen, R.; Peng, G. Fracture behavior and strain evolution of laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 163, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.; Unal, O.; Kashyzadeh, K.R. Effects of conventional, severe, over, and re-shot peening processes on the fatigue behavior of mild carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W. Effect of laser shock peening on bending fatigue performance of AISI 9310 steel spur gear. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 94, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, T.; Yang, B. Effects of ultrasonic rolling on surface performance of 7B85-T6 alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.X.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Xiong, Q.C. Study on surface characteristics of 7050-T7451 aluminum alloy by ultrasonic surface rolling process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Study on surface properties of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy by ultrasonic rolling. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2022, 121, 102643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gu, F.; Qin, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. Effect of ultrasonic Impact on Hydrogen Permeability Resistance of 18CrNiMo7-6 alloy steel. Iron Steel 2023, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Lai, F.Q.; Qu, S.G.; Liu, H.P.; Jia, D.S.; Du, S.F. Effect of ultrasonic surface rolling on microstructure and rolling contact fatigue behavior of 17Cr2Ni2MoVNb steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 366, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Influence of ultrasonic rolling parameters on the surface properties of 18CrNiMo7-6 gear steel. Surf. Technol. 2020, 49, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.N.; Xu, H. The effect of nanostructured surface layer on the fatigue behaviors of a carbon steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3811–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lei, L.; Sun, L. Effect of shot peening on the fatigue resistance of laser surface melted 20CrMnTi steel gear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 629, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, K.J.; Liskiewicz, T.W.; Mathia, T.G. Surface morphology in engineering applications: Influence of roughness on sliding and wear in dry fretting. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, T.; Lang, K.H.; Fett, T.; Löhe, D. Influence of residual stresses and mean load on the fatigue strength of case-hardened notched specimens. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 468–470, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, D.; Yao, C.; Ren, J. Effects of Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Parameters on Surface Integrity of TC17 Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 6736–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, Z. Numerical modeling considering initial gradient mechanical properties and experiment verification of residual stress distribution evolution of 12Cr2Ni4A steel generated by ultrasonic surface rolling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 452, 129127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Cai, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X. Experimental study on surface integrity and fatigue life of an ultra-high strength steel by the composite strengthening process of pre-torsion and ultrasonic rolling. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 150, 107333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; He, G.; Xu, X.; Ao, N.; Ma, A.; Liu, D. On the influence of ultrasonic surface rolling process on surface integrity and fatigue performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 370, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, F.; Qiu, Q. Effect of ultrasonic rolling on surface integrity, machining accuracy, and tribological performance of bearing steels under different process schemes. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, G.; Tang, G. Enhanced surface properties of austenitic stainless steel by electropulsing-assisted ultrasonic surface rolling process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 282, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdana, A.T.; Gindy NN, Z. Comparative experimental study on effects of conventional and ultrasonic deep cold rolling processes on Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, D. Mechanical and corrosion fatigue behaviors of gradient structured 7B50-T7751 aluminum alloy processed via ultrasonic surface rolling. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Ren, R. Effect of Surface Ultrasonic Rolling on Evolution of Surface Microstructure of EA4T Axle Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt. % | 0.17–0.23 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.60–0.95 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 | 0.40–0.70 | 0.35–0.75 | 0.20–0.30 | margin |
| Group | Specimen | Frequency /(kHz) | Load/(N) | Axial Feed/ (mm/r) | Spindle Speed/(rpm) | Rounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USR1 | 23 | 900 | 0.1 | 200 | 1 |
| 2 | USR2 | 23 | 900 | 0.1 | 200 | 3 |
| 3 | USR3 | 23 | 900 | 0.1 | 200 | 6 |
| 4 | USR4 | 23 | 1200 | 0.1 | 200 | 1 |
| 5 | USR5 | 23 | 1200 | 0.1 | 200 | 3 |
| 6 | USR6 | 23 | 1200 | 0.1 | 200 | 6 |
| 7 | USR7 | 23 | 1500 | 0.1 | 200 | 1 |
| 8 | USR8 | 23 | 1500 | 0.1 | 200 | 3 |
| 9 | USR9 | 23 | 1500 | 0.1 | 200 | 6 |
| 10 | USR10 | 23 | 1200 | 0.1 | 200 | 7 |
| 11 | USR11 | 23 | 1200 | 0.1 | 200 | 15 |
| 12 | USR12 | 23 | 1200 | 0.1 | 200 | 31 |
| Group | β Obs. [°2Th] | β Std. [°2Th] | Peak Pos. [°2Th] | β Struct. [°2Th] | Crystallite Size [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | 0.291 | 0.054 | 44.911 | 0.237 | 36.3 |
| 900N-3 | 0.331 | 0.054 | 44.620 | 0.277 | 31 |
| 900N-6 | 0.342 | 0.054 | 44.775 | 0.287 | 29.8 |
| 1200-3 | 0.351 | 0.054 | 44.519 | 0.294 | 29 |
| 1200-6 | 0.432 | 0.054 | 44.752 | 0.378 | 22.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Weng, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Z. The Effects of Ultrasonic Impact Modification on the Surface Quality of 20CrNiMo Carburized Steel. Coatings 2023, 13, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091594
Jiang Q, Zhu L, Chen J, Chen X, Weng J, Xu Z, Zhao Z. The Effects of Ultrasonic Impact Modification on the Surface Quality of 20CrNiMo Carburized Steel. Coatings. 2023; 13(9):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091594
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Qingshan, Li Zhu, Junying Chen, Xiuyu Chen, Jianchun Weng, Zhilong Xu, and Zhenye Zhao. 2023. "The Effects of Ultrasonic Impact Modification on the Surface Quality of 20CrNiMo Carburized Steel" Coatings 13, no. 9: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091594
APA StyleJiang, Q., Zhu, L., Chen, J., Chen, X., Weng, J., Xu, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2023). The Effects of Ultrasonic Impact Modification on the Surface Quality of 20CrNiMo Carburized Steel. Coatings, 13(9), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091594






