Structure and Void Connectivity in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles
Abstract
1. Introduction
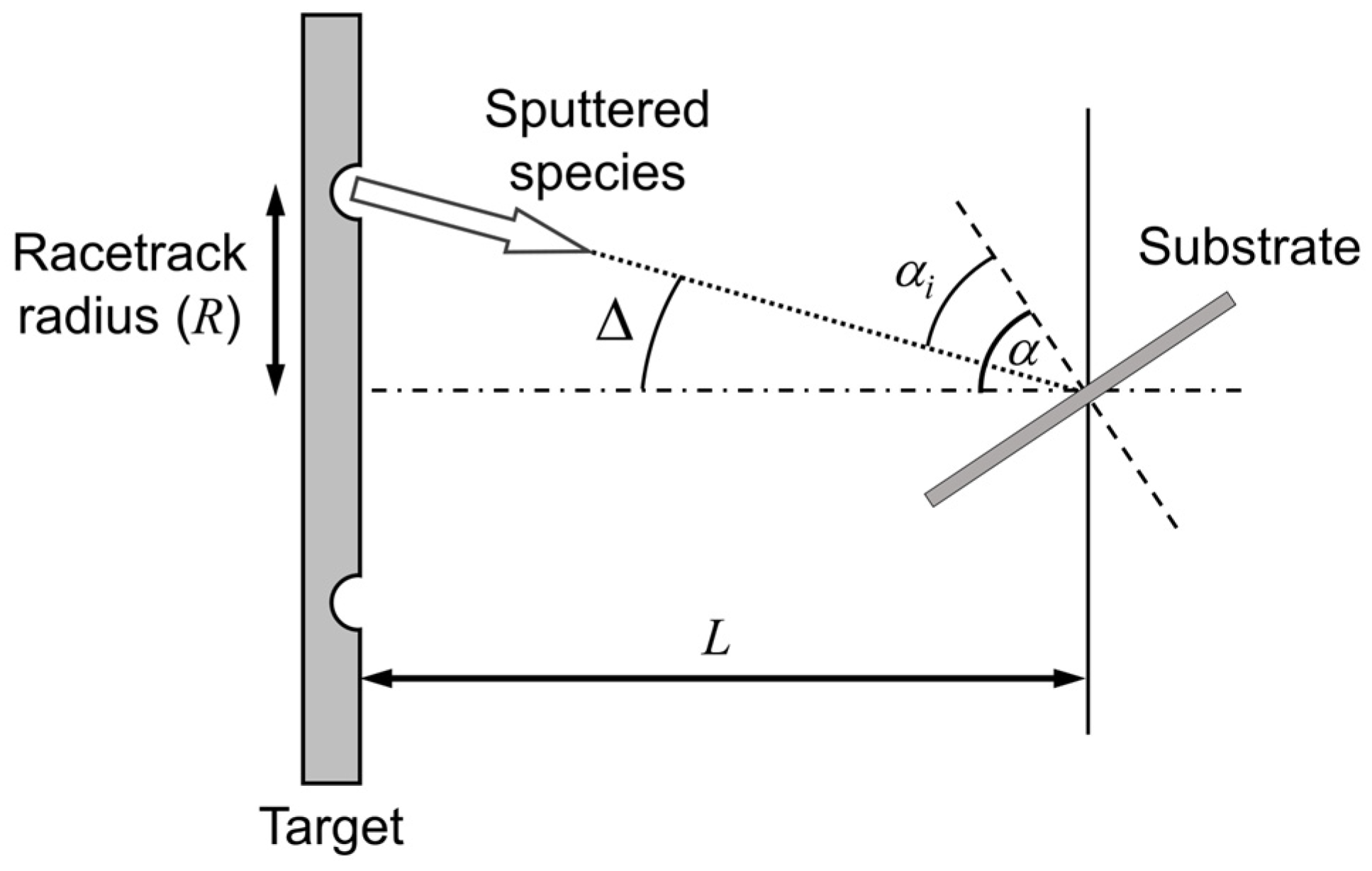
2. Growth Model and Pore Analysis
2.1. Growth Simulation
2.2. Simulation Conditions
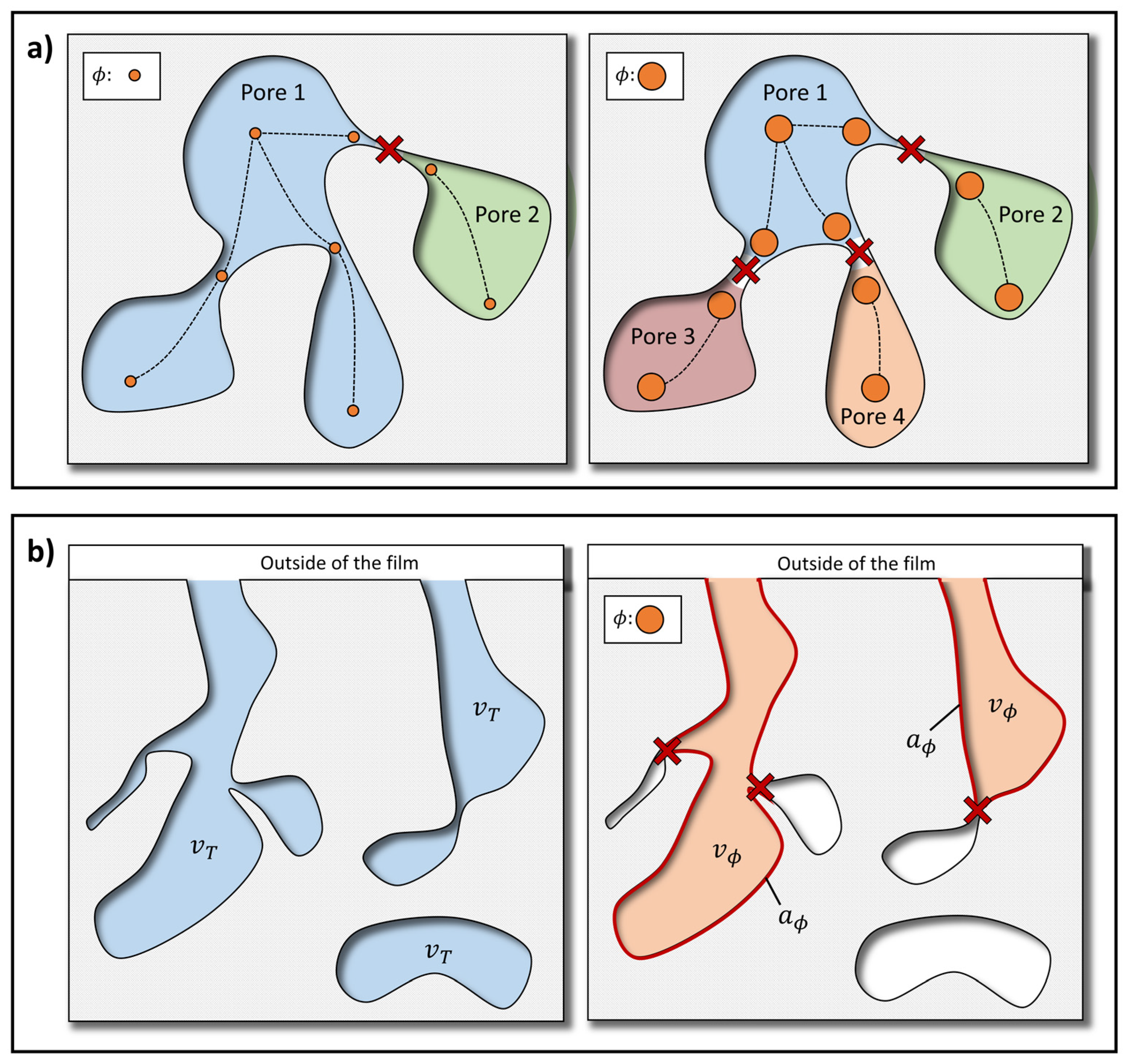
2.3. Pore Network Characterization
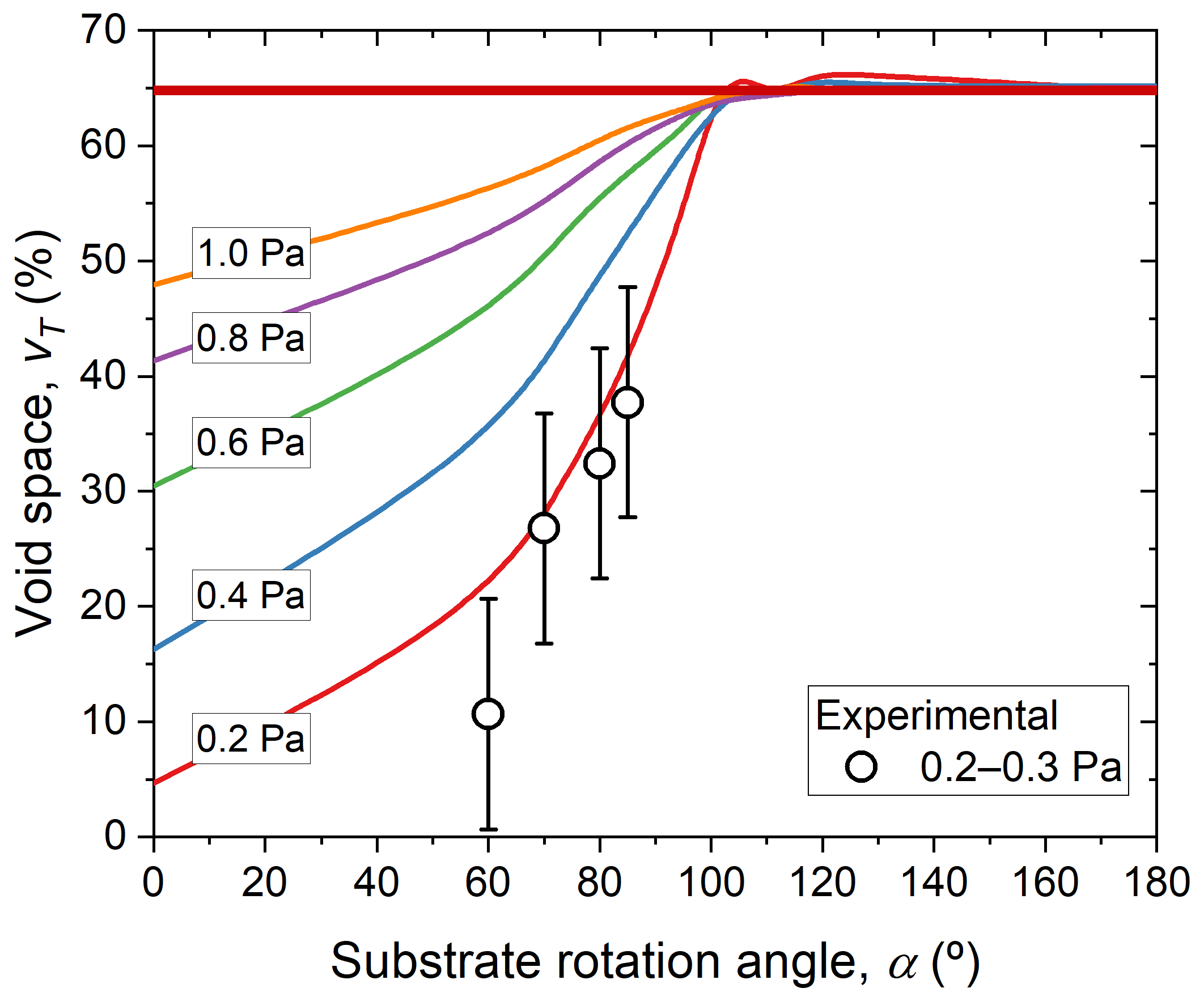
- The void space, , defined as the total volume inside the film not occupied by material (see Figure 2b for a scheme). This quantity, therefore, does not consider any type of connectivity, and can be calculated by means of the film density, , through the formula , where is the density of a fully compact film.
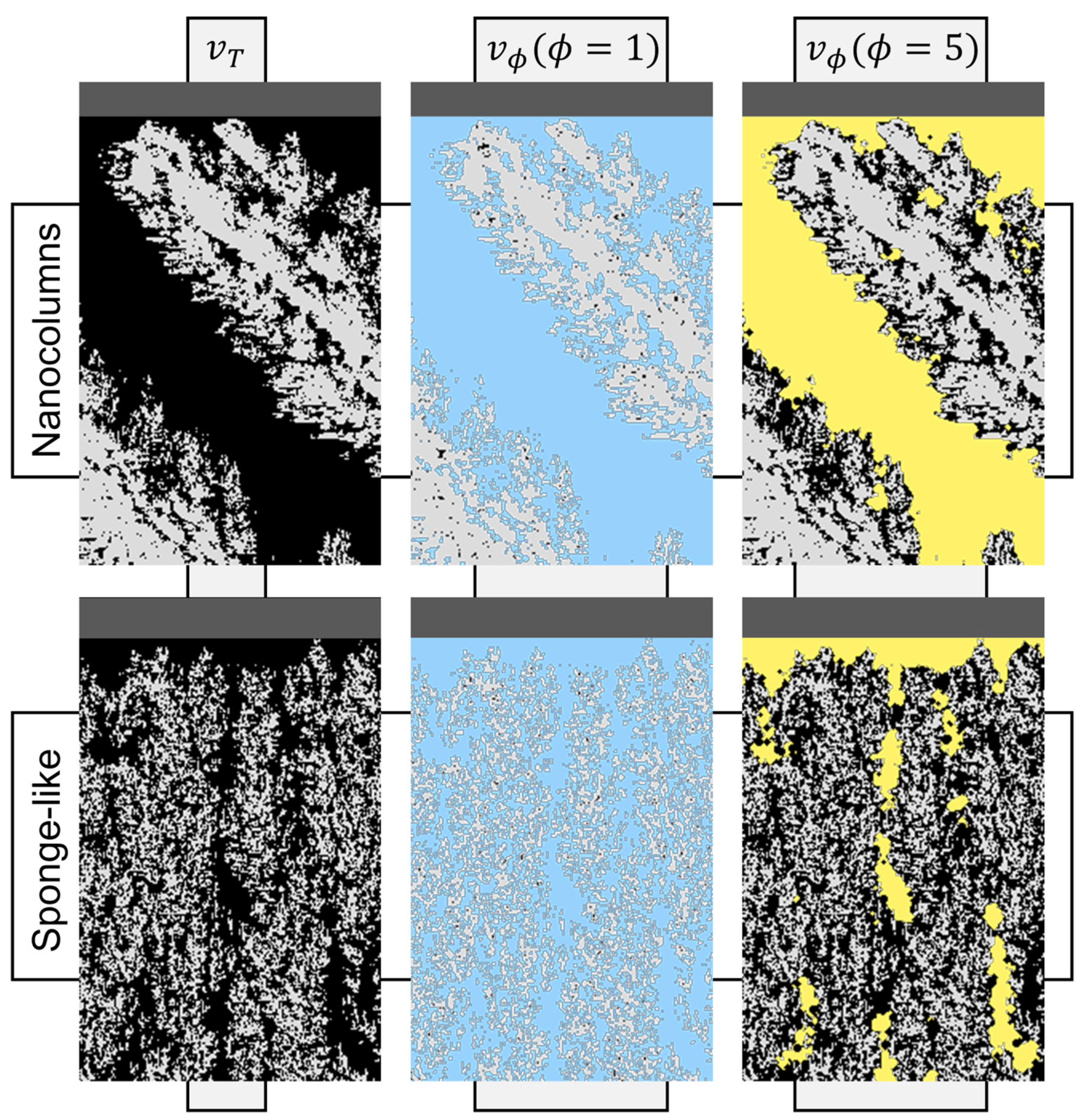
- The void volume connected with the outside, , (see Figure 2b for a scheme) defined as the volume of the voids within the film that are connected with the outside by means of a pore throat . Therefore, according to the definition of connectivity made above, a sphere with a diameter may follow a continuous path from any point within this volume to the exterior of the film, not touching any material.
- The contact area of the void volume connected with the outside, (see Figure 2b for a scheme), as the area corresponding to .
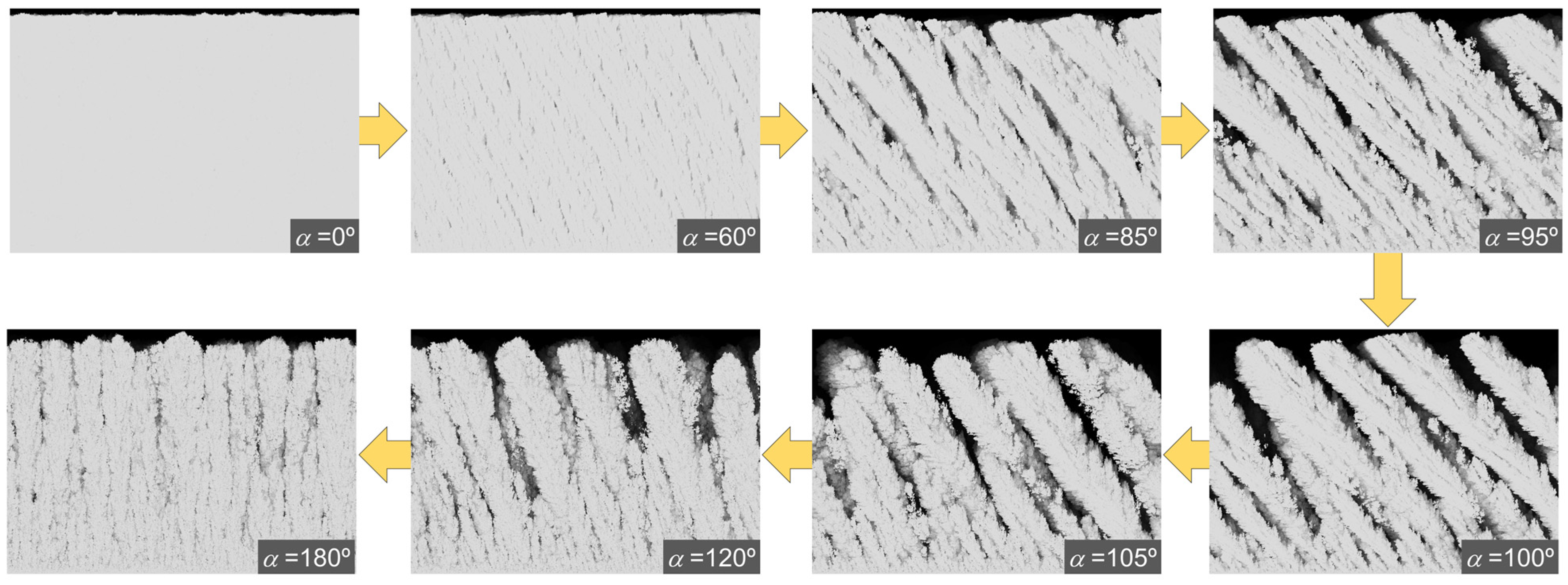
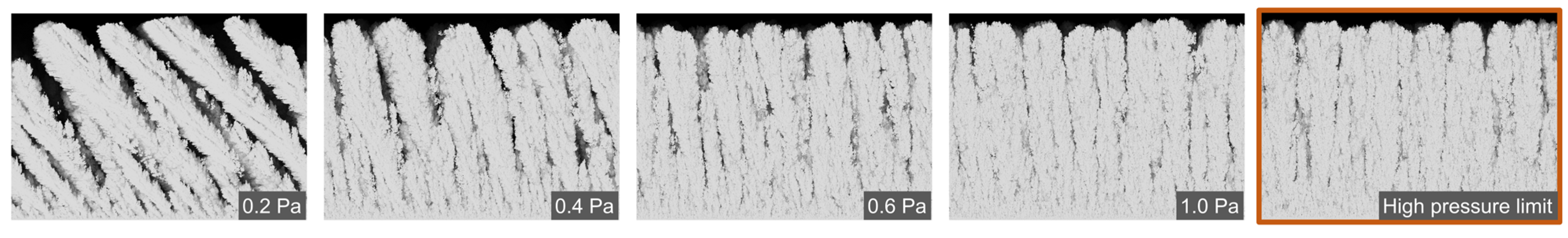
3. Results and Discussion
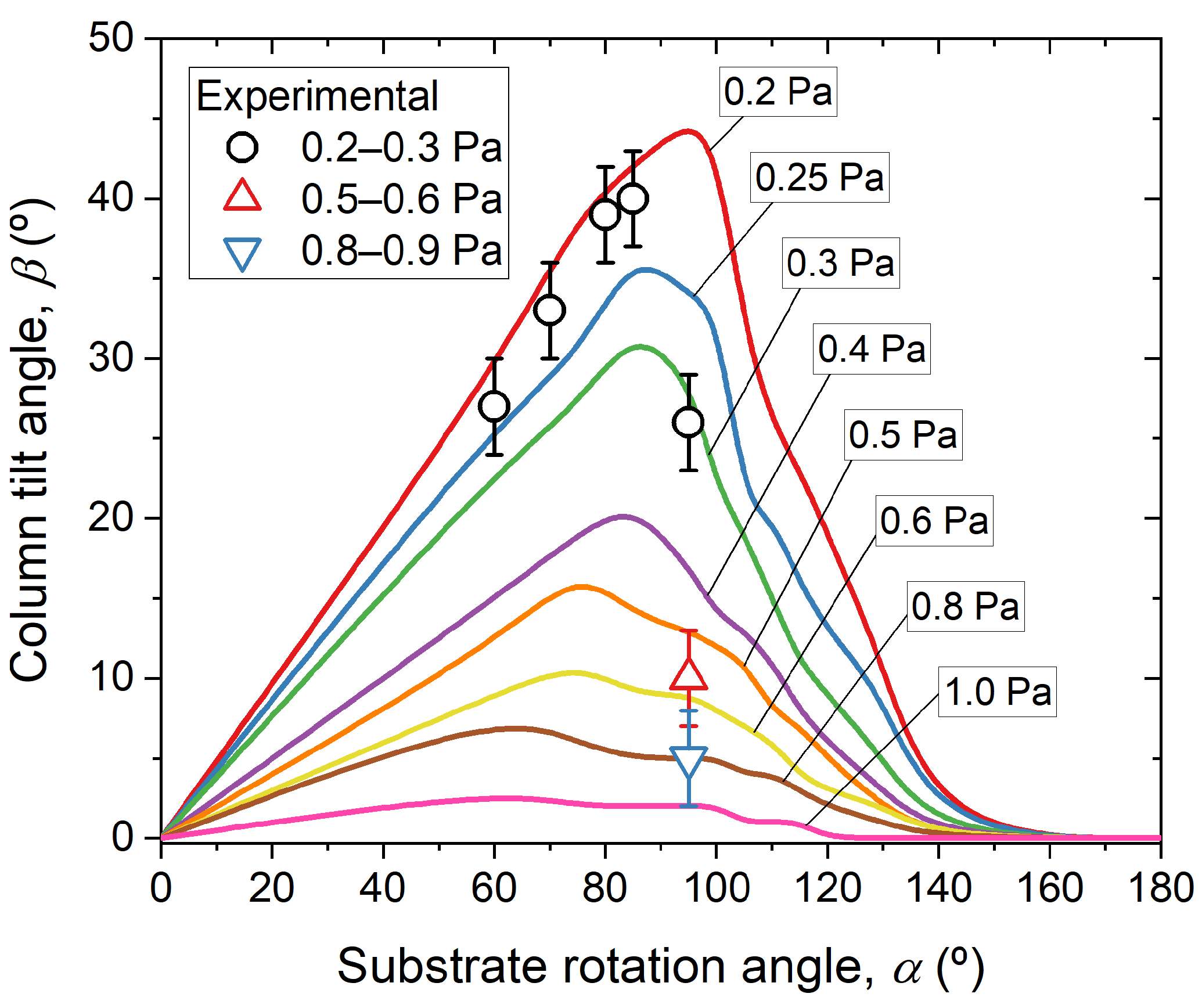
3.1. Morphology of the Films
3.2. Topology of the Porous Structure in Contact with the Outside
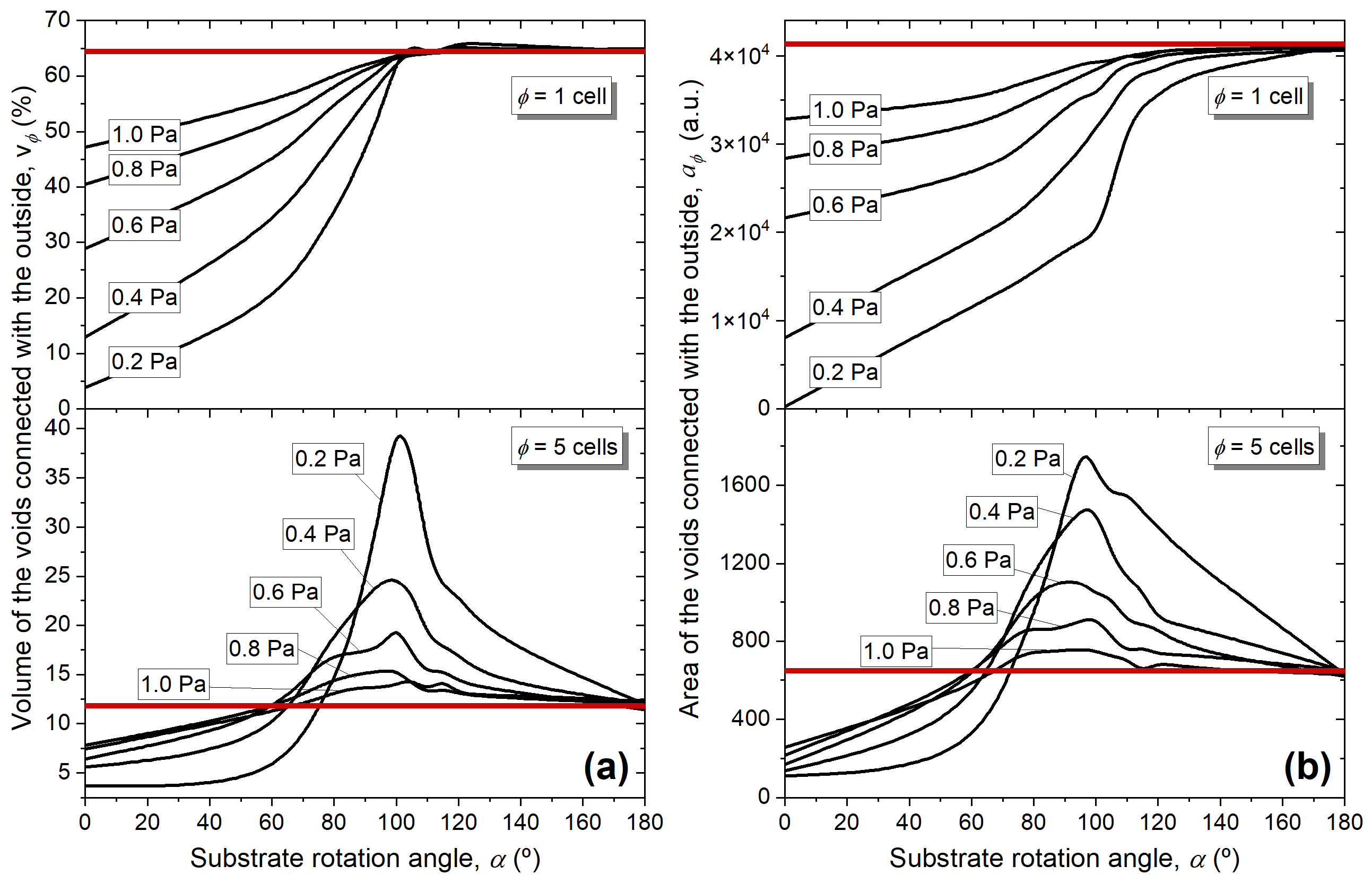
- When the connectivity through micropores ( is analyzed, the maximum volume of the voids in contact with the outside is obtained when , i.e., during the whole structural transition from nanocolumnar to sponge-like morphologies. However, its area is only maximum for this second morphology. Consequently, the maximum values of and are achieved when the morphology is formed by vertically aligned sponge-like nanostructures, i.e., when the growth is dominated by Brownian-like species (at high pressures irrespective of the angle or at low pressures when ).
- When the connectivity through mesopores ( is analyzed, the maximum volume and area of the voids connected with the outside is obtained when the film morphology is nanocolumnar, when .
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barranco, A.; Borras, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: From fundamentals to devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 59–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhao, Y. Oblique angle deposition and its applications in plasmonics. Front. Phys. 2014, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louloudakis, D.; Mouratis, K.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Koudoumas, E.; Alvarez, R.; Palmero, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. Electrochromic response and porous structure of WO3 cathode layers. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 376, 138049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundak, M.; Khalakhan, I.; Kúš, P.; Duchoň, T.; Potin, V.; Cacucci, A.; Tsud, N.; Matolín, V.; Veltruská, K. Tailoring of highly porous SnO2 and SnO2-Pd thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 232, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintymer, J.; Martin, N.; Chappé, J.-M.; Delobelle, P.; Takadoum, J. Nanoindentation of chromium zigzag thin films sputter deposited. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhalfa, H.; Potin, V.; Martin, N. Structural and electrical properties of nanocolumnar W-Mo thin films with a Janus-like structure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 448, 128928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, F.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Terriza, A.; González, J.; Cotrino, J.; Frutos, F.; Ferrer, F.; González-Elipe, A.; Yubero, F. Low refractive index SiOF thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2013, 542, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maudet, F.; Lacroix, B.; Santos, A.J.; Paumier, F.; Paraillous, M.; Hurand, S.; Corvisier, A.; Marsal, C.; Giroire, B.; Dupeyrat, C.; et al. Optical and nanostructural insights of oblique angle deposited layers applied for photonic coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 520, 146312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, A.; Probst, A.-C.; Emmerich, F.; Damm, C.; Rellinghaus, B.; Döhring, T.; Stollenwerk, M. Influence of sputtering pressure on microstructure and layer properties of iridium thin films. Thin Solid Films 2018, 662, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrey, A.; Alvarez, R.; Palmero, A.; González, M.U.; García-Martín, J.M. Fabrication of black-gold coatings by glancing angle deposition with sputtering. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, M.; Dizaji, H.R.; Ehsani, M.; Ghazi, M. Effect of GLAD technique on optical and electrical properties of SnO2/Ag/SnO2 structure. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 106, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; González, M.U.; Béron, F.; Tejo, F.; Escrig, J.; García-Martín, J.M. Large-Area Nanopillar Arrays by Glancing Angle Deposition with Tailored Magnetic Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Borges, J.; Proença, M.; Pedrosa, P.; Martin, N.; Romanyuk, K.; Kholkin, A.L.; Vaz, F. Nanoplasmonic response of porous Au-TiO2 thin films prepared by oblique angle deposition. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 225701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.; Salazar, P.; Álvarez, R.; Palmero, A.; López-Santos, C.; González-Mora, J.; González-Elipe, A.R. Cholesterol biosensing with a polydopamine-modified nanostructured platinum electrode prepared by oblique angle physical vacuum deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollitrault, J.; Martin, N.; Rauch, J.-Y.; Sanchez, J.-B.; Berger, F. Improvement of ozone detection with GLAD WO3 films. Mater. Lett. 2015, 155, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengstock, C.; Lopian, M.; Motemani, Y.; Borgmann, A.; Khare, C.; Buenconsejo, P.J.; Schildhauer, T.; Ludwig, A.; Köller, M. Structure-related antibacterial activity of a titanium nanostructured surface fabricated by glancing angle sputter deposition. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 195101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.J.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, G.J.; Jang, K.-I.; Song, Y.M. Ultra-thin films with highly absorbent porous media fine-tunable for coloration and enhanced color purity. Nanoscale 2016, 9, 2986–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shen, J.; Liang, X.; Huang, J.; Min, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, W. The influence of incident angle on physical properties of a novel back contact prepared by oblique angle deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 363, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, B.; Keles, O. The effect of copper coating on nanocolumnar silicon anodes for lithium ion batteries. Thin Solid Films 2015, 589, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Yang, Z.-P.; Lo, F.-Y.; Siao, J.-J.; Xie, Z.-H.; Chuang, Y.-L.; Lin, T.-Y.; Sheu, J.-K. Slanted n-ZnO/p-GaN nanorod arrays light-emitting diodes grown by oblique-angle deposition. APL Mater. 2014, 2, 056101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. Growth of highly porous ZnO nanostructures for carbon monoxide gas sensing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 343, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Rostra, J.; García-García, F.; Yubero, F.; González-Elipe, A.R. Tuning the transmittance and the electrochromic behavior of CoxSiyOz thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at glancing angle. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 123, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani-Haghighi, S.; Khare, C.; Trócoli, R.; Dushina, A.; Kieschnick, M.; LaMantia, F.; Ludwig, A. Synthesis of nanostructured LiMn2O4thin films by glancing angle deposition for Li-ion battery applications. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 455402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limwichean, S.; Kasayapanand, N.; Ponchio, C.; Nakajima, H.; Patthanasettakul, V.; Eiamchai, P.; Meng, G.; Horprathum, M. Morphology-controlled fabrication of nanostructured WO3 thin films by magnetron sputtering with glancing angle deposition for enhanced efficiency photo-electrochemical water splitting. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 34455–34462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mohajir, A.; Pour Yazdi, M.A.; Krystianiak, A.; Heintz, O.; Martin, N.; Berger, F.; Sanchez, J.-B. Nanostructuring of SnO2 Thin Films by Associating Glancing Angle Deposition and Sputtering Pressure for Gas Sensing Applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbillon, G.; Humbert, C.; González, M.U.; García-Martín, J.M. Gold Nanocolumnar Templates for Effective Chemical Sensing by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Muñoz-Piña, S.; González, M.U.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Fernández-Martínez, I.; Rico, V.; Arcos, D.; García-Valenzuela, A.; Palmero, A.; Vallet-Regi, M.; et al. Antibacterial Nanostructured Ti Coatings by Magnetron Sputtering: From Laboratory Scales to Industrial Reactors. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobini, S.; González, M.U.; Caballero-Calero, O.; Patrick, E.E.; Martín-González, M.; García-Martín, J.M. Effects of nanostructuration on the electrochemical performance of metallic bioelectrodes. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 3179–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, V.; Moskovkin, P.; Álvarez, R.; Caballero-Hernández, J.; Schierholz, R.; Bera, B.; Demarche, J.; Palmero, A.; Fernández, A.; Lucas, S. On the formation of the porous structure in nanostructured a-Si coatings deposited by dc magnetron sputtering at oblique angles. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 355705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Valenzuela, A.; Butterling, M.; Liedke, M.O.; Hirschmann, E.; Trinh, T.T.; Attallah, A.G.; Wagner, A.; Alvarez, R.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Rico, V.J.; et al. Positron annihilation analysis of nanopores and growth mechanism of oblique angle evaporated TiO2 and SiO2 thin films and multilayers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 295, 109968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, L.; Parra-Barranco, J.; Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Barranco, A.; Borrás, A.; González-Elipe, A.R.; García-Gutiérrez, M.-C.; Hernández, J.J.; Rueda, D.R.; Ezquerra, T.A. Correlation lengths, porosity and water adsorption in TiO2thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 205701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.M.; Thommes, M.; Brett, M.J. Pore analysis of obliquely deposited nanostructures by krypton gas adsorption at 87K. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 143, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Piña, S.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Oyarzabal, E.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Rico, V.; Alcalá, G.; Alvarez, R.; Tabares, F.; Palmero, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A. Wetting and spreading of liquid lithium onto nanocolumnar tungsten coatings tailored through the topography of stainless steel substrates. Nucl. Fusion 2020, 60, 126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkeye, M.M.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Glancing Angle Deposition of Thin Films: Engineering the Nanoscale; Wiley Series in Materials for Electronic & Optoelectronic Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-118-84756. [Google Scholar]
- Pelliccione, M.; Lu, T.-M. Evolution of Thin Film Morphology: Modeling and Simulations; Springer Series Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 108, ISBN 978-0-387-75108-5. [Google Scholar]
- Vári, G.; Óvári, L.; Kiss, J.; Kónya, Z. LEIS and XPS investigation into the growth of cerium and cerium dioxide on Cu(111). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 5124–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Óvári, L.; Bugyi, L.; Majzik, Z.; Berkó, A.; Kiss, J. Surface Structure and Composition of Au−Rh Bimetallic Nanoclusters on TiO2(110): A LEIS and STM Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 18011–18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Santos, C.; Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Rico, V.; Loeffler, M.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Nanocolumnar association and domain formation in porous thin films grown by evaporation at oblique angles. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 395702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depla, D.; Mahieu, S. (Eds.) Reactive Sputter Deposition; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 109, ISBN 978-3-540-76662-9. [Google Scholar]
- Depla, D. (Ed.) Magnetrons, Reactive Gases and Sputtering; Diederik Depla: Ghent, Belgium, 2020; ISBN 978-1-304-34781-7. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Alvarez, R.; Rico, V.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.; Palmero, A. Growth of nanocolumnar porous TiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering using particle collimators. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 343, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; García-Martín, J.M.; Macías-Montero, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, L.; González, J.C.; Rico, V.; Perlich, J.; Cotrino, J.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Growth regimes of porous gold thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique incidence: From compact to columnar microstructures. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 045604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.P.; Romero-Gomez, J.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Cotrino, F.; Yubero, A.; Palmero, A.R.; Gonzalez-Elipe, J. Influence of plasma-generated negative oxygen ion impingement on magnetron sputtered amorphous SiO2 thin films during growth at low temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 064316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Martin, J.M.; Lopez-Santos, M.C.; Rico, V.; Ferrer, F.J.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. On the Deposition Rates of Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films at Oblique Angles. Plasma Process. Polym. 2014, 11, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A. Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 212–232. ISBN 978-1-4020-2303-3. [Google Scholar]
- García-Valenzuela, A.; Alvarez, R.; Espinós, J.P.; Rico, V.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Palmero, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. SiOx by magnetron sputtered revisited: Tailoring the photonic properties of multilayers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Ramirez, M.; Barranco, A.; Löffler, M.; Yubero, F.; González-Elipe, A.R. Optofluidic Modulation of Self-Associated Nanostructural Units Forming Planar Bragg Microcavities. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Regodon, G.; Ferrer, F.J.; Rico, V.; Garcia-Martin, J.M.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Hyperthermal Relaxation Schemes in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023; in progress. [Google Scholar]
- SRIM 2013. Available online: www.srim.org/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Van Aeken, K. SIMTRA. Available online: www.draft.ugent.be/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Van Aeken, K.; Mahieu, S.; Depla, D. The metal flux from a rotating cylindrical magnetron: A Monte Carlo simulation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 20530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Martin, J.M.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Macias-Montero, M.; Ferrer, F.J.; Santiso, J.; Rico, V.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Nanostructured Ti thin films by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 045303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A. Influence of apparatus geometry and deposition conditions on the structure and topography of thick sputtered coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1974, 11, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A. Influence of substrate temperature and deposition rate on structure of thick sputtered Cu coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1975, 12, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Lopez-Santos, C.; Ferrer, F.J.; Rico, V.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Modulating Low Energy Ion Plasma Fluxes for the Growth of Nanoporous Thin Films. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Lopez-Santos, C.; Ferrer, F.J.; Rico, V.; Guillen, E.; Alcon-Camas, M.; Escobar-Galindo, R.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. High-Rate Deposition of Stoichiometric Compounds by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Romero-Gomez, P.; Gil-Rostra, J.; Cotrino, J.; Yubero, F.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Growth of SiO2 and TiO2 thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering and PECVD by the incorporation of non-directional deposition fluxes. Phys. Status Solidi A 2013, 210, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, (The “Gold Book”), 2nd ed.; McNaught, A.D., Wilkinson, A., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 0-9678550-9-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, V.J.; Turk, H.; Yubero, F.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. Titania Enhanced Photocatalysis and Dye Giant Absorption in Nanoporous 1D Bragg Microcavities. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Barranco, J.; Sanchez-Valencia, J.R.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Silver and gold nanoparticles in nanometric confined templates: Synthesis and alloying within the anisotropic pores of oblique angle deposited films. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 485602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez, R.; Regodon, G.; Acosta-Rivera, H.; Rico, V.; Alcala, G.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Structure and Void Connectivity in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles. Coatings 2023, 13, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13060991
Alvarez R, Regodon G, Acosta-Rivera H, Rico V, Alcala G, González-Elipe AR, Palmero A. Structure and Void Connectivity in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles. Coatings. 2023; 13(6):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13060991
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez, Rafael, Guillermo Regodon, Hiedra Acosta-Rivera, Victor Rico, German Alcala, Agustín R. González-Elipe, and Alberto Palmero. 2023. "Structure and Void Connectivity in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles" Coatings 13, no. 6: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13060991
APA StyleAlvarez, R., Regodon, G., Acosta-Rivera, H., Rico, V., Alcala, G., González-Elipe, A. R., & Palmero, A. (2023). Structure and Void Connectivity in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles. Coatings, 13(6), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13060991







