Research and Development on Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Influencing Factors of Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
2.1. Powder Characteristics
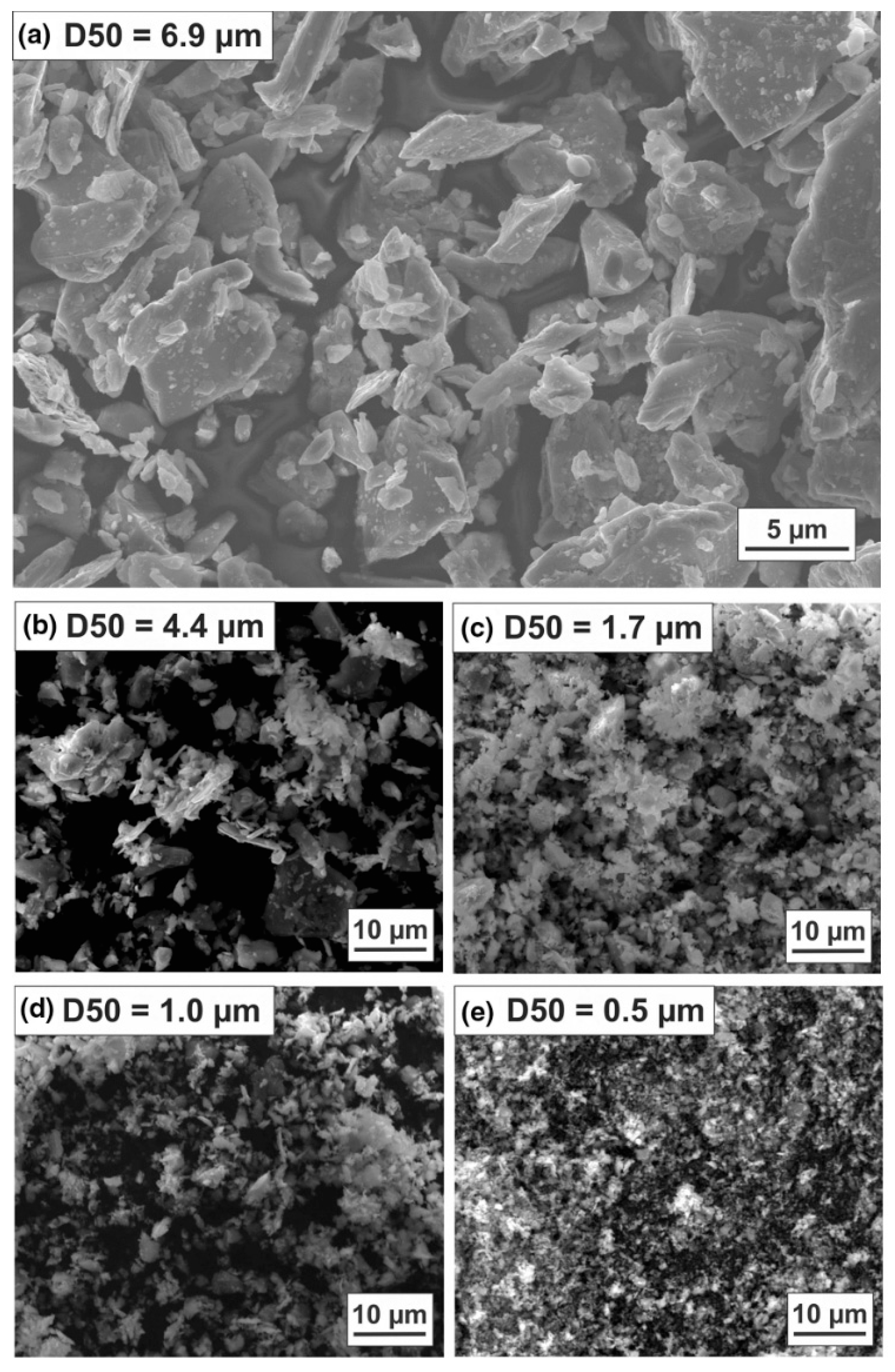
2.1.1. Particle Size
2.1.2. Particle Size Distribution
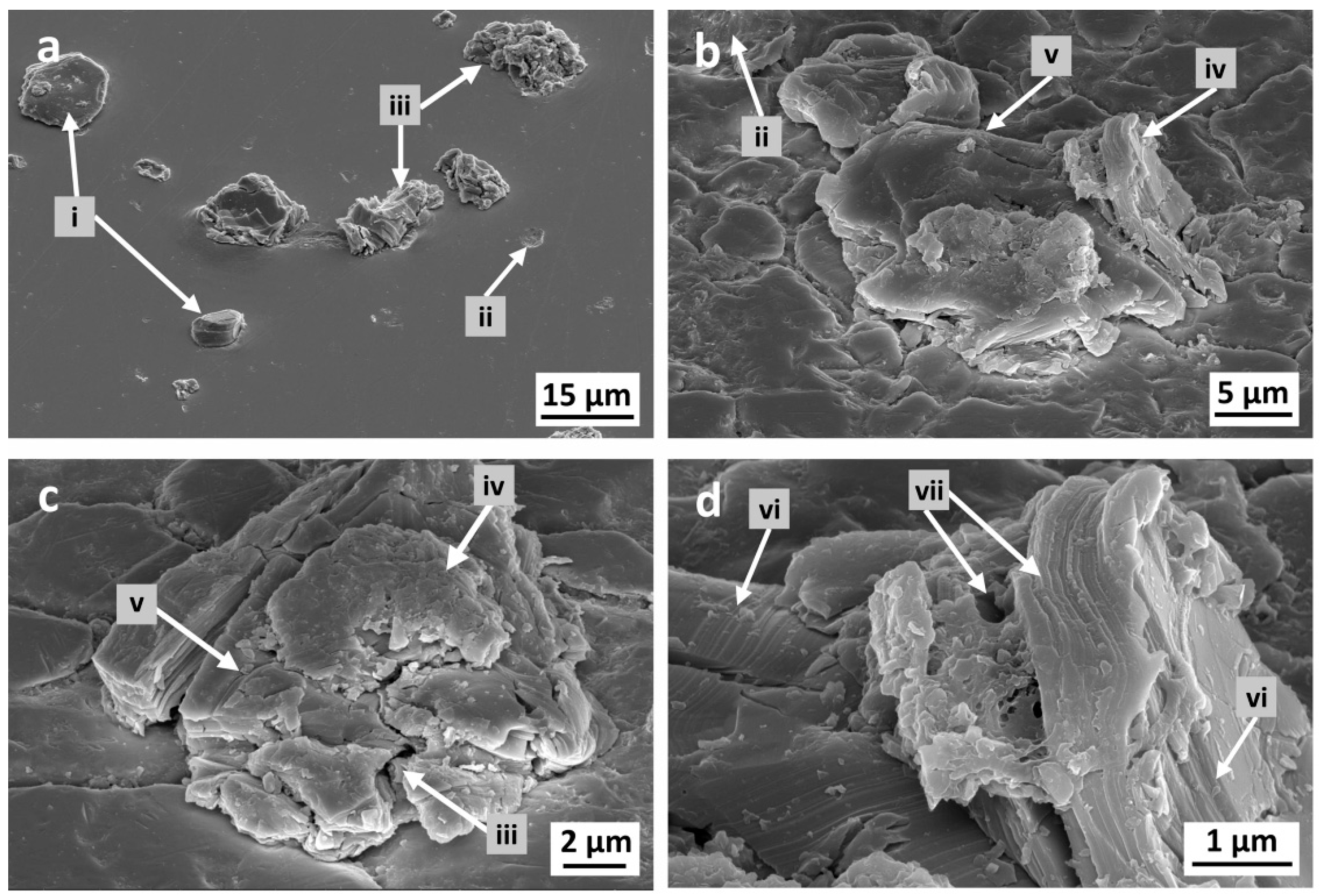
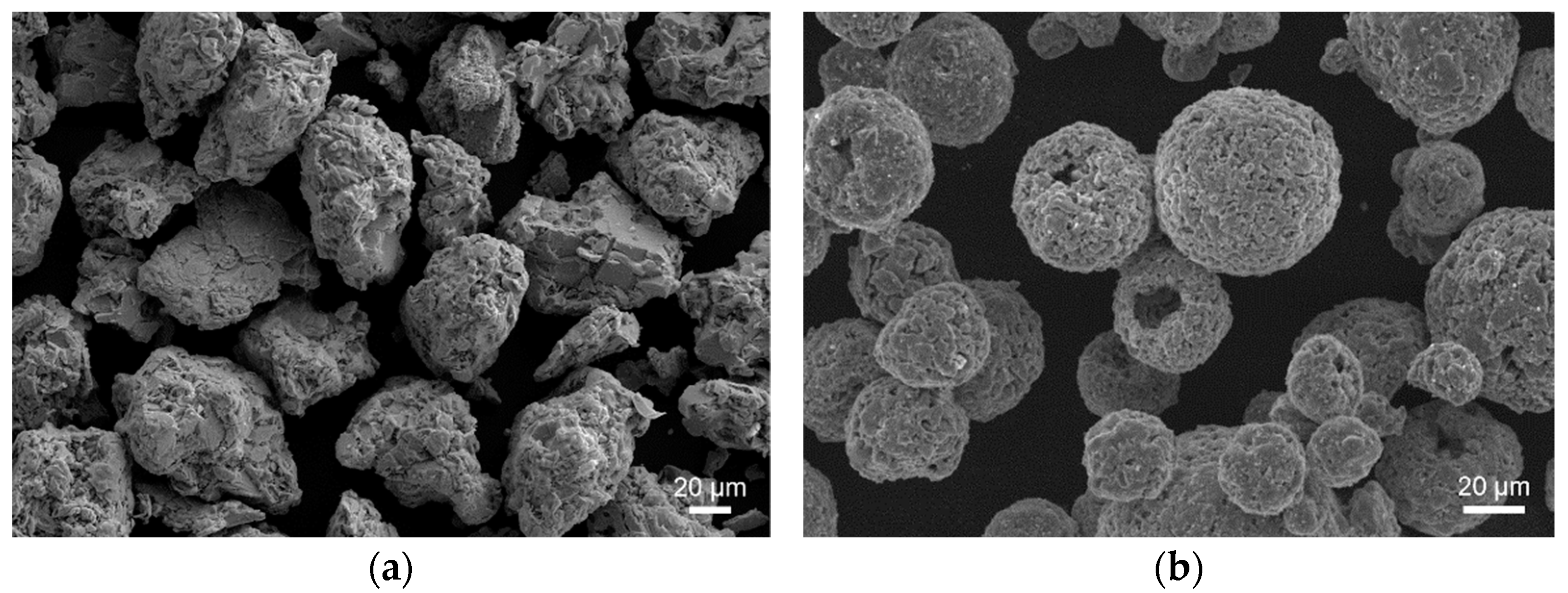
2.1.3. Particle Morphology
2.2. Driving Gases
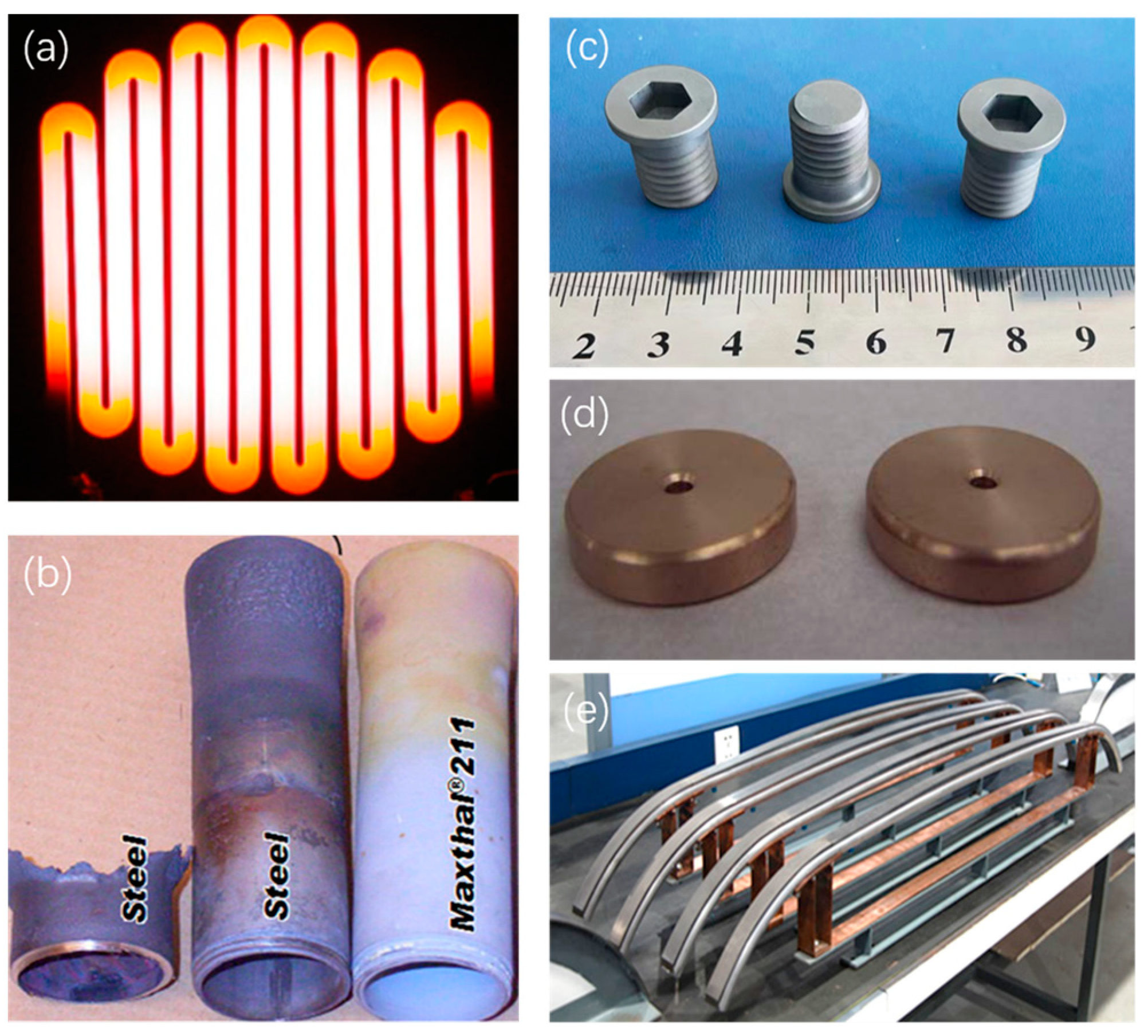
2.3. Substrates
3. Bonding Mechanisms in Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
3.1. Microstructural Evolution
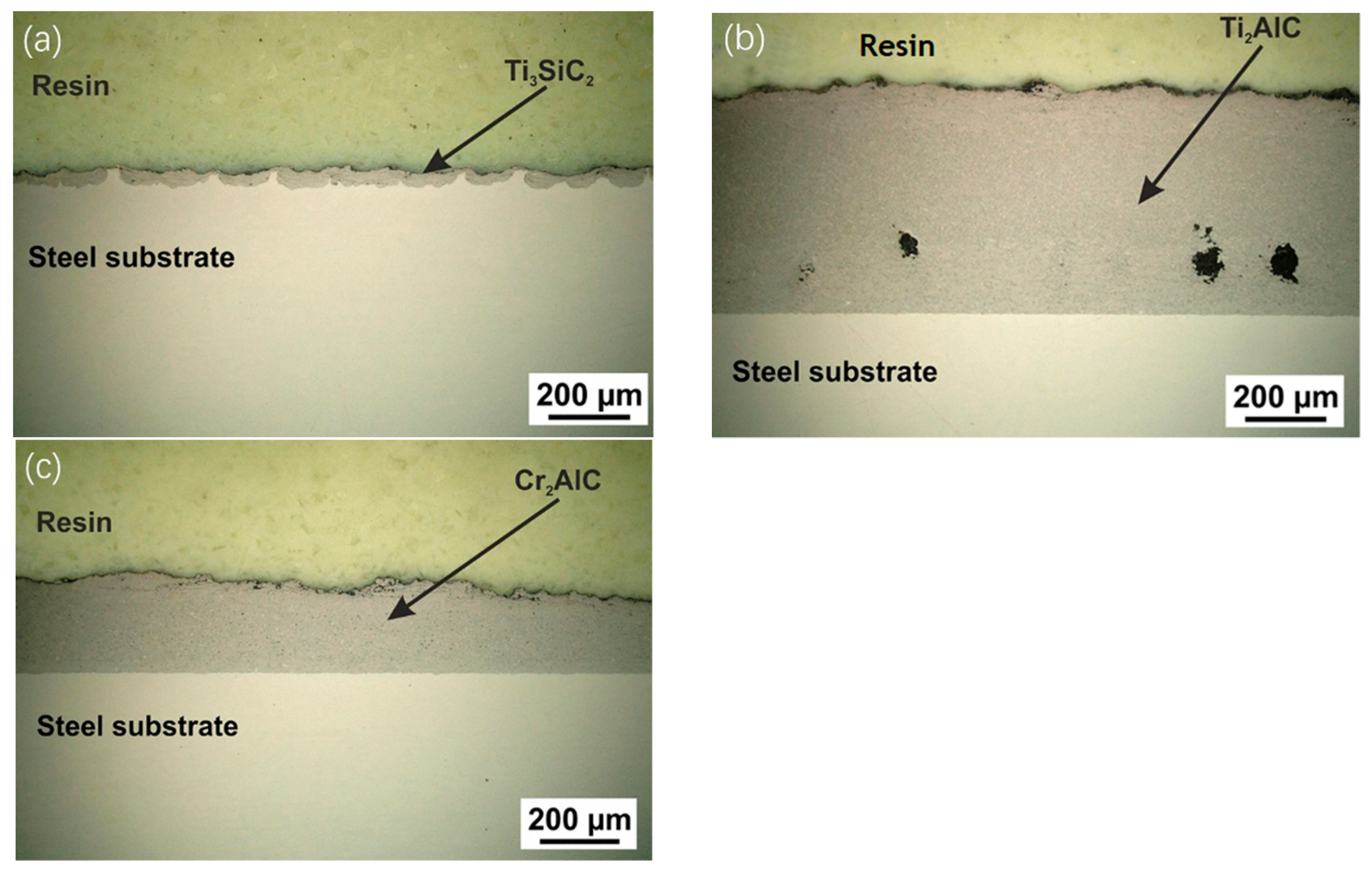
3.2. Bonding Strength of Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
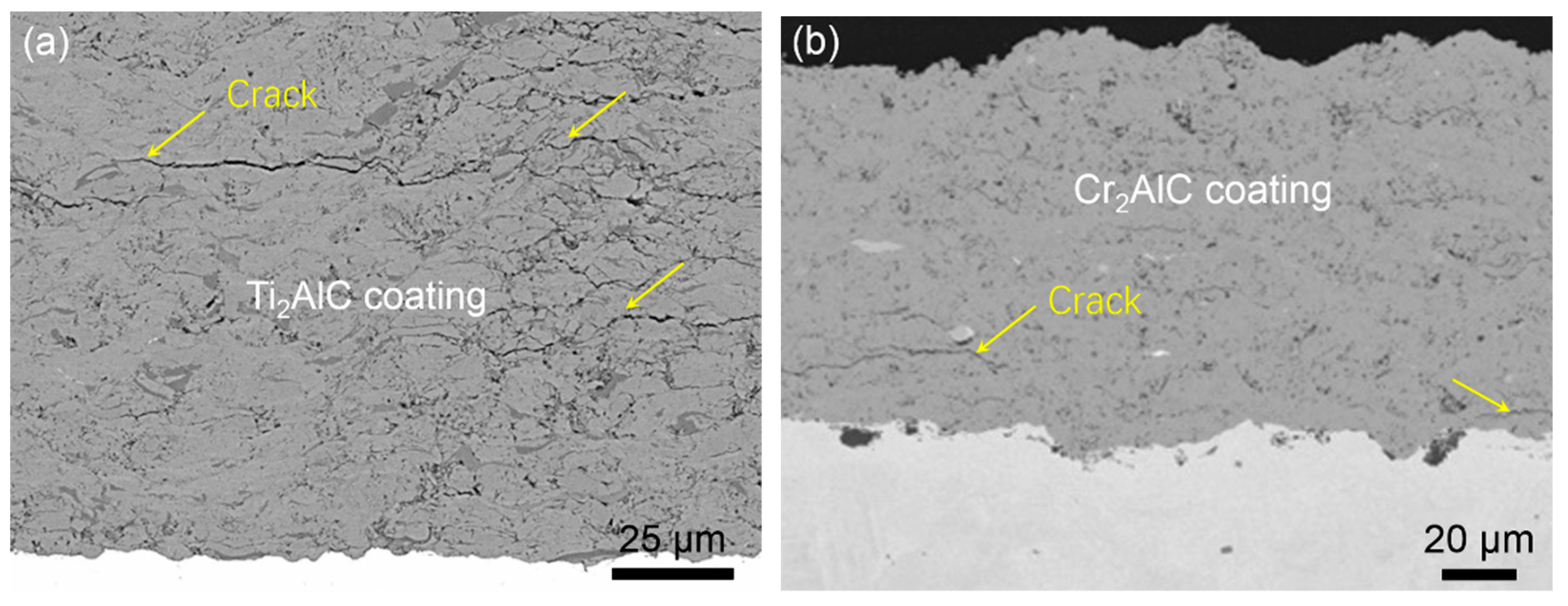
3.3. Residual Stresses in Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
4. Mechanical Properties and Tribological Behaviors of Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
4.1. Hardness of Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
4.2. Tribological Behaviors of Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings
5. Summary and Outlook
- (1)
- Powder size and morphology
- (2)
- Interface characterization
- (3)
- Bonding mechanisms
- (4)
- Expand the types of MAX phase coatings and substrates.
- (5)
- Computational simulation of cold-sprayed MAX phase coatings.
- (6)
- Performance of cold-sprayed MAX phase coatings
- (7)
- The post-heat-treatment is essential for coating consolidation and microstructure modification.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Ying, G.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, P. From Structural Ceramics to 2D Materials with Multi-Applications: A Review on the Development from MAX Phases to MXenes. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 1194–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W. The Mn+1AXn phases: A new class of solids. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2000, 28, 201–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M. Progress in research and development on MAX phases: A family of layered ternary compounds. Int. Mater. Rev. 2011, 56, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, L.; Feng, Q.; Grasso, S.; Hu, C. Synthesis and Characterization of Ternary Layered Nb2SB Ceramics Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 878, 160344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhai, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L. Layered ternary MAX phases and their MX particulate derivative reinforced metal matrix composite: A review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 856, 157313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodelius, J.; Sonestedt, M.; Bjorklund, S.; Palmquist, J.P.; Stiller, K.; Hogberg, H.; Hultman, L. Ti2AlC coatings deposited by high velocity oxy-fuel spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 5976–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chu, M.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B. Microstructure and performance of Cr2AlC coatings deposited by HVOF spraying. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2012, 36, 568–573. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Fasth, A.; Nylen, P.; Choi, W.B. Microindentation and inverse analysis to characterize elastic-plastic properties for thermal sprayed Ti2AlC and NiCoCrAlY. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonestedt, M.; Frodelius, J.; Palmquist, J.P.; Hogberg, H.; Hultman, L.; Stiller, K. Microstructure of high velocity oxy-fuel sprayed Ti2AlC coatings. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markocsan, N.; Manitsas, D.; Jiang, J.; Bjorklund, S. MAX-phase coatings produced by thermal spraying. J. Superhard Mater. 2017, 39, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lim, S.H.; Chai, J.; Lai, D.M.Y.; Lim, P.C.; Cheong, A.K.H.; Wang, S.; Jin, H.; Pan, J. Kerosene-fuelled high velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) spray of Ti2AlC MAX phase powders. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 735, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, J. Modem Cold Spray-Materials, Process and Application, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Poza, P.; Garrido-Maneiro, M.A. Cold-sprayed coatings: Microstructure, mechanical properties, and wear behaviour. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 123, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupoi, R.; O’Neill, W. Deposition of metallic coatings on polymer surfaces using cold spray. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalkhali, Z.; Xie, W.; Champagne, V.K.; Lee, J.H.; Rothstein, J.P. A comparison of cold spray technique to single particle micro-ballistic impacts for the deposition of polymer particles on polymer substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 351, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, T.B.; Khalkhali, Z.; Champagne, V.; Schmidt, D.P.; Rothstein, J.P. Optimization of cold spray deposition of high-density polyethylene powders. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2017, 26, 1548–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliemann, J.O.; Gutzmann, H.; Gärtner, F.; Hübner, H.; Borchers, C.; Klassen, T. Formation of cold-sprayed titanium dioxide layers on metal surface. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Hong, Y.P.; Ko, K.H. Thin film coatings of WO3 by cold gas dynamic spray: A technical note. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2005, 14, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Sayar, D.; Ogawa, K. SiO2 and MoSi2 formation on Inconel 625 surface via SiC coating deposited by cold spray. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, A.; Sallot, P.; Badea, V.; Duport, P.; Popescu, C.; Denoirjean, A. The dual character of MAX phase nano-layered structure highlighted by supersonic particles deposition. Coatings 2021, 11, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsenberg, A.; Busato, M.; Gärtner, F.; List, A.; Bruera, A.; Bolelli, G.; Lusvarghi, L.; Klassen, T. Influence of MAX-phase deformability on coating formation by cold spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 617–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, B.R.; Garcia-Diaz, B.L.; Hauch, B.; Olson, L.C.; Sindelar, R.L.; Sridharan, K. Cold spray deposition of Ti2AlC coatings for improved nuclear fuel cladding. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 466, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Strock, C.W.; Sharon, J.A.; Klecka, M.A.; Nardi, A.T. Cold Spray Manufacturing of MAXMET Composites. U.S. Patent 10000851, 19 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Hua, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, C.; Wu, L. Composite Material for Piston Ring Coating, Piston Ring Coating and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent 102517577A, 12 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Y.; Li, C.J. Optimization of spray conditions in cold spraying based on the numerical analysis of particle velocity. T. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2004, 14, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Elsenberg, A.; Gärtner, F.; Klassen, T. Aerosol deposition of Ti3SiC2-MAX-phase coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C. Computational research on factors affecting particle velocity in a vacuum kinetic spray process. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Xie, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, T.; Xiong, T.; Yang, R. Method for Preparing Ti2AlC Phase Ceramic Coating through Cold Spraying In-Situ Formation. CN Patent 201610210730.3, 26 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rech, S.; Surpi, A.; Vezzù, S.; Patelli, A.; Trentin, A.; Glor, J.; Frodelius, J.; Hultman, L.; Eklund, P. Cold-spray deposition of Ti2A1C coatings. Vacuum 2013, 94, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzmann, H.; Gartner, F.; Hoche, D.; Blawert, C.; Klassen, T. Cold spraying of Ti2A1C max-phase coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Xie, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, C.; Xiong. T. Influences of agglomeration powder preparation on deposition of cold-sprayed Ti2AlC coating. Chn. Surf. Eng. 2018, 31, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, W.; Vo, P.; Irissou, E.; Ryabinin, A.N.; Legoux, J.G.; Yue, S. Effect of particle morphology and size distribution on cold-sprayed pure titanium coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, V.N.V.; Chakrabarty, R.; Song, J.; Chromik, R.R. Effect of metal powder properties on the deposition characteristics of cold-sprayed Ti6Al4V-TiC coatings: An experimental and finite element study. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 25, 101208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Isago, H.; Nakano, H.; Fukumoto, M. Cold spraying of TiO2 photocatalyst coating with nitrogen process gas. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2010, 19, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockley, J.M.; Descartes, S.; Voc, P.; Irissou, E.; Chromik, R.R. The influence of Al2O3 particle morphology on the coating formation and dry sliding wear behavior of cold sprayed Al-Al2O3 composites. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 270, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Assadi, H.; Gärtner, F.; Richter, H.; Stoltenhoff, T.; Kreye, H.; Klassen, T. From particle acceleration to impact and bonding in cold spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, A.; Sahu, A.; Rudolf, C.; Zhang, C.; Rengifo, S.; Laha, T.; Boesl, B.; Agarwal, A. Multi-scale tribological and nanomechanical behavior of cold sprayed Ti2AlC MAX phase coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, B.; Olson, L.; Verst, C.; Sindelar, R.; Hoffman, E.; Hauch, B.; Sridharan, K. MAX phase coatings for accident tolerant nuclear fuel. Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc. 2014, 110, 994–996. [Google Scholar]
- Go, T.; Sohn, Y.J.; Mauer, G.; Vaßen, R.; Gonzalez-Julian, J. Cold spray deposition of Cr2AlC MAX phase for coatings and bondcoat layers. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigax, J.G.; Kennas, M.; Kim, H.; Wang, T.; Maier, B.R.; Yeom, H.; Johnson, G.O.; Sridharan, K.; Shao, L. Radiation response of Ti2AlC MAX phase coated Zircaloy-4 for accident tolerant fuel cladding. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 523, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Hong, Y.P.; Ko, K.H. Interfacial studies between cold-sprayed WO3, Y2O3 films and Si substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 227, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toibah, A.R.; Sato, M.; Yamada, M.; Fukumoto, M. Cold-Sprayed TiO2 coatings from nanostructured ceramic agglomerated powders. Mater Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.Q.; Yang, G.J.; Li, C.J.; Liu, G.J.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, L.Z. Characterization of microstructure of nano-TiO2 coating deposited by vacuum cold spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2006, 15, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C633-13; Standard Test Method for Adhesion or Cohesion Strength of Thermal Spray Coatings. R&B, Inc.: Colmar, PA, USA, 2021.
- Irissou, E.; Legoux, J.G.; Arsenault, B.; Moreau, C. Investigation of Al-Al2O3 cold spray coating formation and properties. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2007, 16, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, F.; Stoltenhoff, T.; Schmidt, T.; Kreye, H. The cold spray process and its potential for industrial applications. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2006, 15, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinca, N.; Barbosa, M.; Dosta, S.; Guilemany, J.M. Study of Ti deposition onto Al alloy by cold gas spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Xie, J.X.; Zhang, L.T.; Cheng, L.F. Synthesis and some properties of Ti3SiC2 by hot pressing of Ti, Si and C powders. part II: Mechanical and other properties of Ti3SiC2. Mater. Sci. Techol. 2005, 21, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, I.M. Vickers contact damage of micro-layered Ti3SiC2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 18, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, B.J.; Poppen, R.J.; Carvalho, N.J.M.; De Hosson, J.T.M.; Barsoum, M.W. Ti3SiC2: A damage tolerant ceramic studied with nanoindentations and transmission electron microscopy. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2859–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzenov, N.V.; Barsoum, M.W. Synthesis and characterization of Ti3AlC2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Hu, S.J.; Hee, A.C.; Zhao, Y. Surface modification of a Ti2AlC soft ceramic by plasma nitriding treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 281, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W.; Ali, M.; El-Raghy, T. Processing and characterization of Ti2AlC, Ti2AlN, and Ti2AlC0.5N0.5. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Wani, M.F.; Banday, S.; Shekhar, C.; Singh, G. Nano scratch and nanoindentation: An approach to understand the tribological behavior of MAX phase material Ti2AlC. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 561, 012111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Yu, W.B.; Zhai, H.X.; Song, G.M.; Sloof, W.G.; van der Zwaag, S. Mechanical properties of low temperature synthesized dense and fine grained Cr2AlC ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Kan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, D. Synthesis and thermal and electrical properties of bulk Cr2AlC. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Kan, Y.; Li, Y. Mechanical properties of Cr2AlC ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, S.J.; Page, T.F.; Yoffe, E.H. An explanation of the indentation size effect in ceramics. Phil. Mag. Lett. 1989, 59, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, N.M.; Kiran, B.; Jyothirmayi, A.; Sudharshan, P.P.; Sundararajan, G. The corrosion behavior of cold sprayed zinc coatings on mild steel substrate. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.T.; Li, C.X.; Shang, F.L.; Yang, G.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, C.J. High velocity impact induced microstructure evolution during deposition of cold spray coatings: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 254, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.C.; Bae, G.; Zahiri, S.; Jahedi, M.; Lee, C. An experimental and finite element study of cold spray copper impact onto two aluminum substrates. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2010, 19, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Li, C.J.; Liao, H.; Coddet, C. Study on impact fusion at particle interfaces and its effect on coating microstructure in cold spraying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 254, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Shipway, P.H.; McCartney, D.G. Cold gas dynamic spraying of aluminium: The role of substrate characteristics in deposit formation. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2005, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Coating Material | Particle Size (µm) | Substrate Material | Driving Gas | Gas Pressure (MPa) | Gas Temperature (°C) | Particle Speed (m/s) | Stand of Distance (mm) | Thickness (µm) | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3AlC2 | 20–40 | Ti4Al6V | N2 | 3.5–5 | 600–1000 | 723–780 | 30 | 50 | No oxidation at 1000 °C; internal cracks in coatings. | [20] |
| Ti3SiC2 | 42 (D50) | 304 SS Cu | N2 | 4–5 | 800–1100 | 699–801 | 60 | - | No oxidation; non-uniform Ti3SiC2 coating. | [21] |
| Ti2AlC | <62 | Stainless steel | N2 | 3.7 | - | - | 20 | 55 | Continuous transversal cracks in Ti2AlC coating. | [10] |
| 11 (D50) | 304 SS Cu | N2 | 5 | 1000 | 717–802 | 60 | 300–530 | No oxidation; low porosity; lateral cracks in coatings. | [21] | |
| <20 | Zr alloy | N2 | 3.5 | 600 | - | - | 90 | No oxidation or phase transformation; low porosity; no delamination in coating. | [22] | |
| 5–150 | TiAl alloy | Air | 1–5 | 100–1000 | - | - | 5–300 | No oxidation; low porosity. | [23] | |
| 5.9 (D50) | Zr alloy | Air | 2–2.5 | 400 | - | 20 | 100 | No oxidation; low porosity. | [31] | |
| 34 (D50) | Cu Stainless steel | N2 | 4 | 600 1000 | - | 60 | 110 155 | No oxidation or phase transformation; low porosity; cracks and internal delamination in coatings. | [30] | |
| 25–40 | Al alloy Stainless steel | N2 | 3.4 3.9 | 500–800 | - | 20 | 50 80 | No oxidation; a continuous transversal crack in coating. | [29] | |
| <20 | Inconel 625 | - | - | - | - | - | 70 | No processing details; voids and microcracks in coating. | [37] | |
| 5–50 | Zr alloy | N2 He | - | 500 800 | - | 26 | 25–30 | Non-uniform coating; microcracks in coating. | [38] | |
| Cr2AlC | 9 (D50) | 304 SS Cu | N2 | 5 | 1000 | 733–849 | 60 | 200–320 | No oxidation; low porosity; lateral cracks in coatings. | [21] |
| 7.6 (D50) | Stainless Steel | N2 | 4 | 650–950 | - | 60 | 40–97 | No oxidation; low porosity; cracks in coating. | [39] |
| MAX Phase | GRAIN Size (μm) | Microhardness (GPa) | Nanohardness (GPa) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3SiC2 | Bulk Coating | 3–200 | 2–6 | 7.3 | [48,49,50] |
| 42 (D50) | 3.75 | 7.9 | [21] | ||
| Ti3AlC2 | Bulk Coating | 25 | 3.5 | - | [51] |
| 20-40 | - | - | [20] | ||
| Ti2AlC | Bulk Coating | 25–50 | 3.3-4.5 | 8.2 | [52,53,54] |
| 11 (D50) | 3.68 | 7.89 | [21] | ||
| 25–40 | - | 10.1 | [29] | ||
| <20 | - | 7–8 | [37] | ||
| <20 | - | 11.8 | [40] | ||
| Cr2AlC | Bulk Coating | 2–35 | 3.5–6.4 | - | [55,56,57] |
| 9 (D50) | 5.73 | 11.3 | [21] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Research and Development on Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050869
Zhang W, Li S, Zhang X, Chen X. Research and Development on Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings. Coatings. 2023; 13(5):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050869
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weiwei, Shibo Li, Xuejin Zhang, and Xu Chen. 2023. "Research and Development on Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings" Coatings 13, no. 5: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050869
APA StyleZhang, W., Li, S., Zhang, X., & Chen, X. (2023). Research and Development on Cold-Sprayed MAX Phase Coatings. Coatings, 13(5), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050869







