Reinforcement and Antibacterial Properties of Hand Embroidery Threads Based on Green Nanocoatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnONPs)
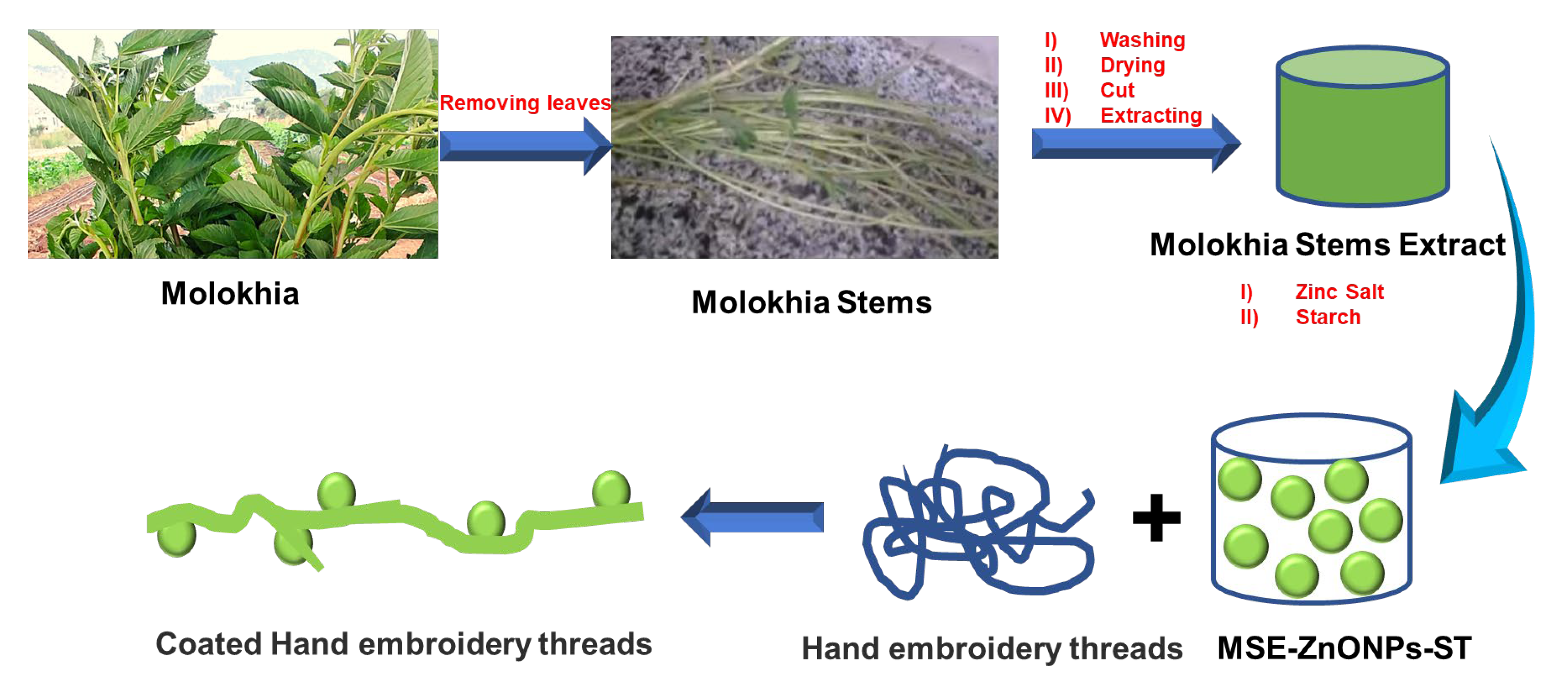
2.3. Preparation of Hand Embroidery Thread Coatings
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
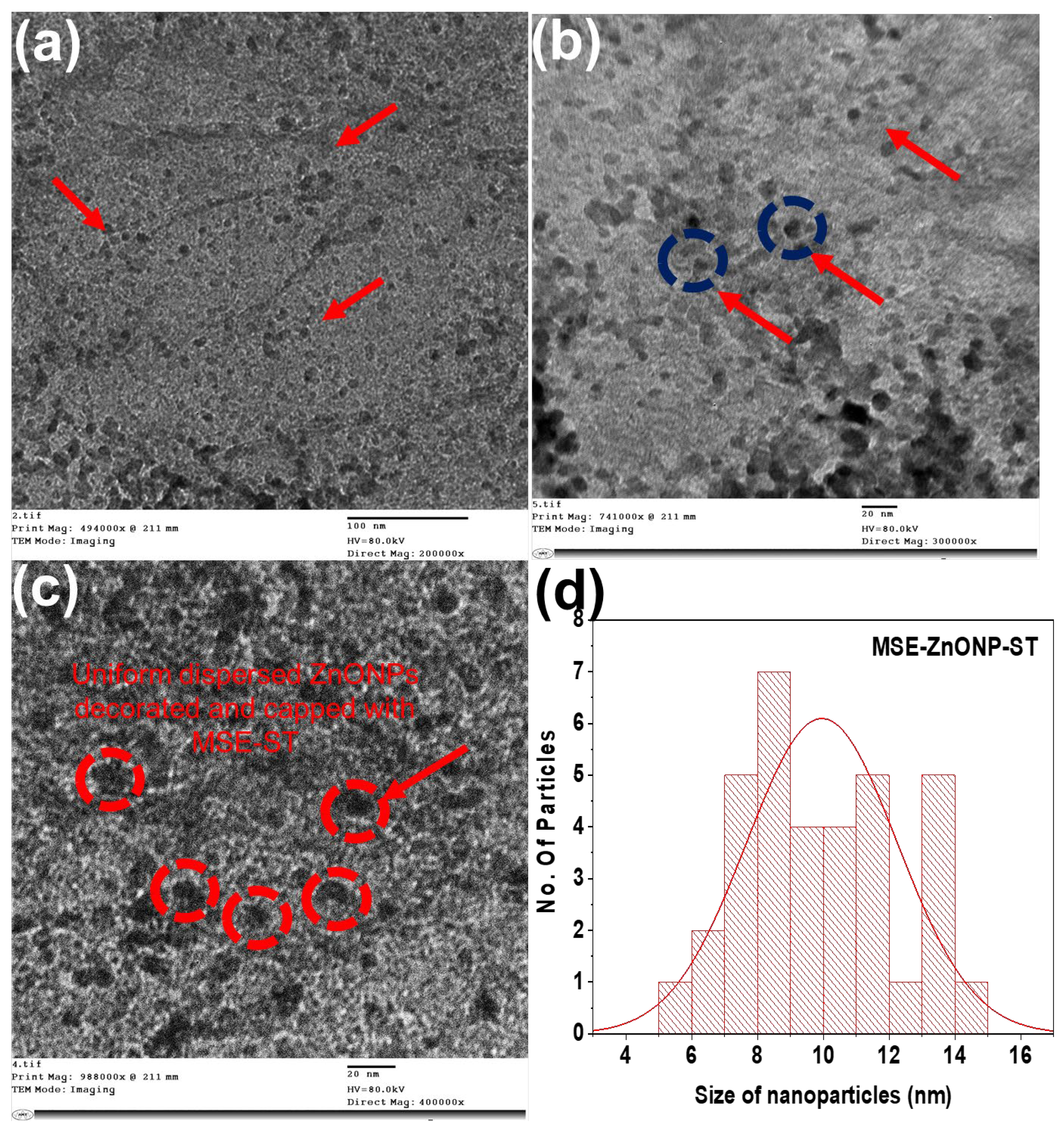
3.1. Fabrication, Composition, and Surface Characterization of Nanocoatings
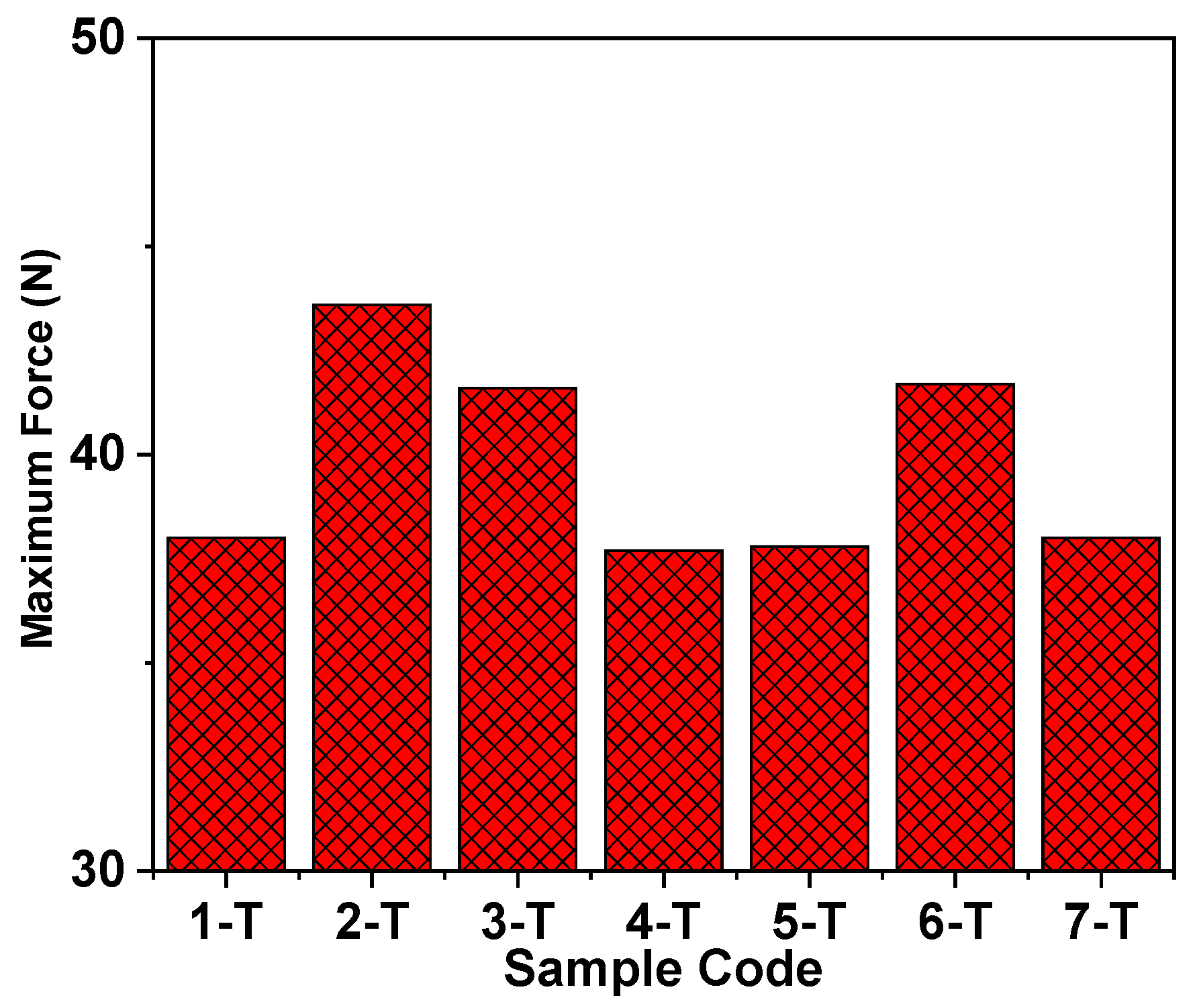
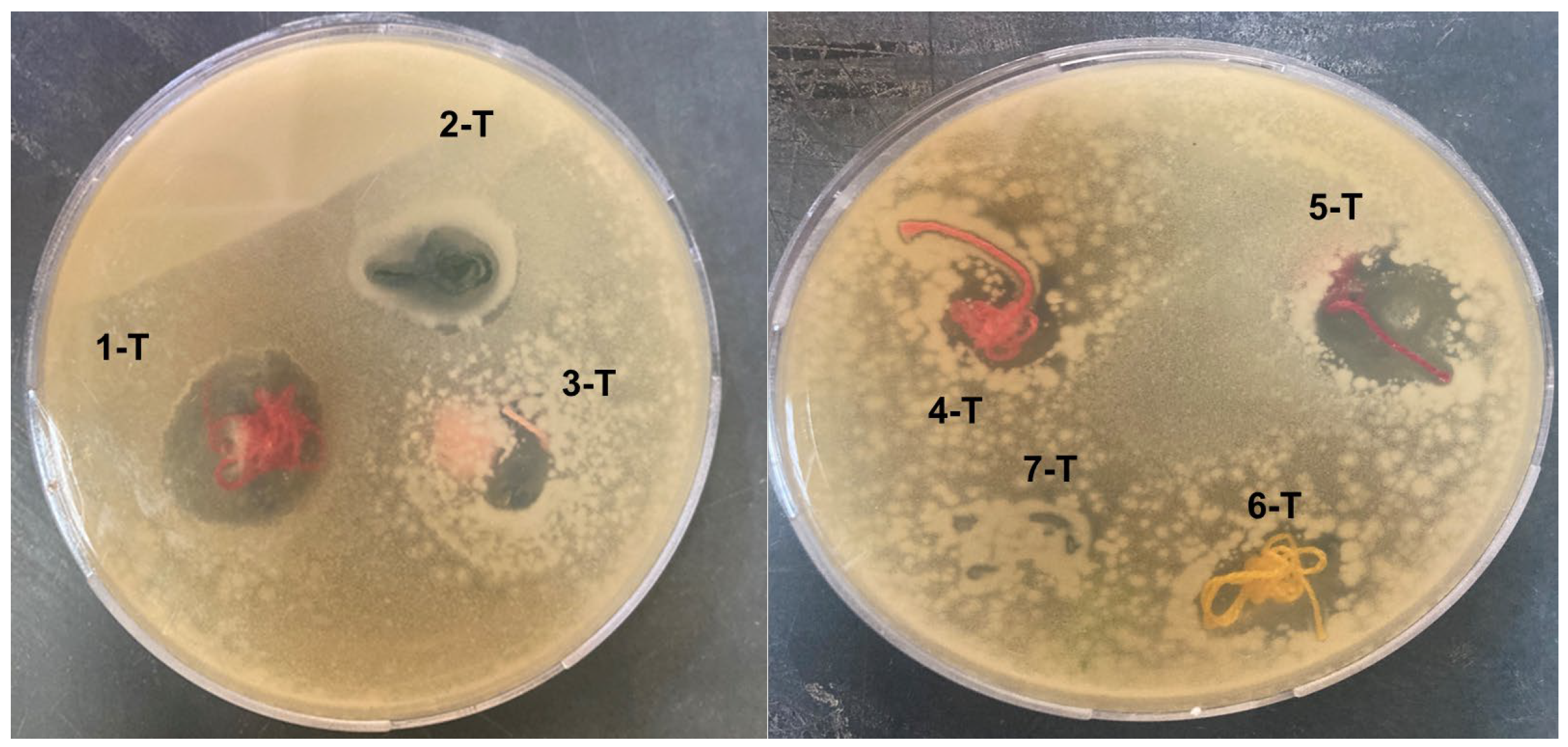
3.2. Tensile and Antibacterial Properties of Cotton Hand Embroidery Threads
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attia, N.F.; Ebissy, A.A.E.; Morsy, M.S.; Sadak, R.A.; Gamal, H. Influence of textile fabrics structures on thermal, UV shielding, and mechanical properties of textile fabrics coated with sustainable coating. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y. A novel efficient nonflammable coating containing gC3N4 and 8 intumescent flame retardant fabricated via layer-by-layer assembly on cotton fiber. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 9678–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafei, A.; El Shemy, M.; Abou-Okeil, A. Eco-friendly finishing agent for cotton fabrics to improve flame retardant and antibacterial properties. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 118, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, E.; McNeill, M. Blackwork Embroidery; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Goswami, R.; Roy, D.N. A critical assessment on biochemical and molecular mechanisms of toxicity developed by emerging nanomaterials on important microbes. Environ. Nanotech. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, M.; Khan, S.A.; Nandi, N.B.; Roy, S.; Panja, A.S.; Roy, D.N.; Misra, T.K. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles for investigation of biofilm inhibition property. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 13575–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.F.; Osama, R.; Elashery, S.E.A.; Abul, K.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Algarni, H. Recent advances of sustainable textile fabric coatings for UV protection properties. Coatings 2022, 12, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, L. Blackwork Made Easy: Techniques, Patterns and Samplers; Search Press: Wellwood, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Dong, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Fully biobased coating from chitosan and phytate for fire-safety and antibacterial cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, W.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Construction of durable flame-retardant and robust superhydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics for water-oil separation application. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Qin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shan, X. constructing polyaniline nanowire arrays as efficient traps on graphene sheets to promote compound synergetic effect in the assembled coating for multifunctional protective cotton fabrics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, E.M.; Attia, N.F.; Alshehri, L.A. Innovative flame retardant and antibacterial fabrics coating based on inorganic nanotubes. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 2961–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, D.; Fu, S. Layer-by-layer self-assembled nanocoatings of mxene and P, N-co-doped cellulose nanocrystals onto cotton fabrics for significantly reducing fire hazards and shielding electromagnetic interference. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 153, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Song, L.; Jie, G.; Hu, Y. Durable electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding ramie fabric with excellent flame retardancy and self-healing performance. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2021, 602, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.F.; Ahmed, H.E.; El Ebissy, A.A.; El Ashery, S.E.A. Green and novel approach for enhancing flame retardancy, UV protection and mechanical properties of fabrics utilized in historical textile fabrics conservation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 166, 106822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghichi, S.; Kallithraka, S.; Simopoulos, A.P. Nutritional composition of molokhia (Corchorus olitorius) and stamnagathi (Cichorium spinosum). World Rev. Nutrit Diet. 2003, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Simopoulos, A.P.; Norman, H.A.; Gillaspy, J.E. Purslane in human nutrition and its potential for world agriculture. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1995, 77, 47–74. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma, K.; Nakayama, M.; Koshioka, M.; Ippoushi, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kohata, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Ito, H.; Higashio, H. Phenolic Antioxidants from the Leaves of Corchorus olitorius L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3963–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.H.; Saqer, A.M.A.; Assirey, E.; Arshi Naqvi, A.; Okasha, R.M. Successful green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a corchorus olitorius extract and their antiproliferative effect in cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.J.; Bellah, M.M.; Hassan, M.R.; Rahman, S. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by two different methods comparison of their structural, antibacterial, photocatalytic and optical properties. Nano Express 2020, 1, 010007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath Roy, D. Terpenoids Against Human Diseases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- BS 1932; Part 2 Knot Strength of Yarn and Thread. British Standards Institution (BSI): London, UK, 1989.
- AATCC Test Method 147; Antibacterial Activity Assessment of Textile Materials Parallel Streak Methods: Parallel Streak Method. American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC): Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2004.
- Amin, G.; Asif, M.H.; Zainelabdin, A.; Zaman, S.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Influence of pH, precursor concentration, growth time, and temperature on the morphology of ZnO nanostructures grown by the hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 269692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Zhao, Q.X.; Willander, M. Size-controlled growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorod arrays with two-step chemical bath deposition method. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 469, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, U.; Kudret, A.; Kerli, S. Influence of pH on structural, optical and morphological properties of ZnO rod arrays fabricated by hydrothermal method. Opt. Adv. Mater.-Rapid Commun. 2012, 6, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, N.F.; Moussa, M.; Sheta, A.M.F.; Taha, R.; Gamal, H. Effect of different nanoparticles based coating on the performance of textile properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 104, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.K.; Kan, C.K. Effects of TiO2 and curing temperatures on flame retardant finishing of cotton. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 121, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zennie, T.; Ogzewalla, D. Ascorbic acid and vitamin A content of edible wild plants of Ohio and Kentucky. Econ Bot. 1977, 31, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiumi, S.; Yabushita, Y.; Fukuda, I.; Mukai, R.; Yoshida, K.; Ashida, H. Molokhia (Corchorus olitorius L.) extract suppresses transformation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor induced by dioxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-W.; Chen, S.-L.; Zhuang, S.-R.; Wang, C.-K. Anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic crude extracts from five fractions of Corchorus olitorius L. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.F.; Saleh, B.K. Novel synthesis of renewable and green flame-retardant, antibacterial and reinforcement material for styrene–butadiene rubber nanocomposites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.F.; Moussa, M.; Sheta, A.M.F.; Taha, R.; Gamal, H. Synthesis of effective multifunctional textile based on silica nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 106, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Code | C (At.%) | O (At.%) | Zn (At.%) | P (At.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43.96 | 56.04 | 0 | 0 |
| 1-T | 44.29 | 53.76 | 1.46 | 0.49 |
| Sample Code | Tensile Strength (N) | Sample Code | Tensile Strength (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37.6 ± 3 | 1-T | 38 ± 3.1 |
| 2 | 41.6 ± 0.5 | 2-T | 43.6 ± 1.9 |
| 3 | 41.6 ± 1.6 | 3-T | 41.6 ± 0.5 |
| 4 | 35.4 ± 3.3 | 4-T | 37.7 ± 2 |
| 5 | 35.6 ± 1.1 | 5-T | 37.8 ± 0.9 |
| 6 | 39.1 ± 1.4 | 6-T | 41.7 ± 1.8 |
| 7 | 36.7 ± 1.5 | 7-T | 38 ± 1.2 |
| Sample Code | Antibacterial Inhibition Zone (mm) |
|---|---|
| 1-T | 8.4 |
| 2-T | 7.5 |
| 3-T | 5 |
| 4-T | 5 |
| 5-T | 8 |
| 6-T | 5 |
| 7-T | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshehri, L.A.; Attia, N.F. Reinforcement and Antibacterial Properties of Hand Embroidery Threads Based on Green Nanocoatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040747
Alshehri LA, Attia NF. Reinforcement and Antibacterial Properties of Hand Embroidery Threads Based on Green Nanocoatings. Coatings. 2023; 13(4):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshehri, Layla Abdulrahman, and Nour F. Attia. 2023. "Reinforcement and Antibacterial Properties of Hand Embroidery Threads Based on Green Nanocoatings" Coatings 13, no. 4: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040747
APA StyleAlshehri, L. A., & Attia, N. F. (2023). Reinforcement and Antibacterial Properties of Hand Embroidery Threads Based on Green Nanocoatings. Coatings, 13(4), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040747





