Cutting Energy Consumption Modelling of End Milling Cutter Coated with AlTiCrN
Abstract
1. Introduction
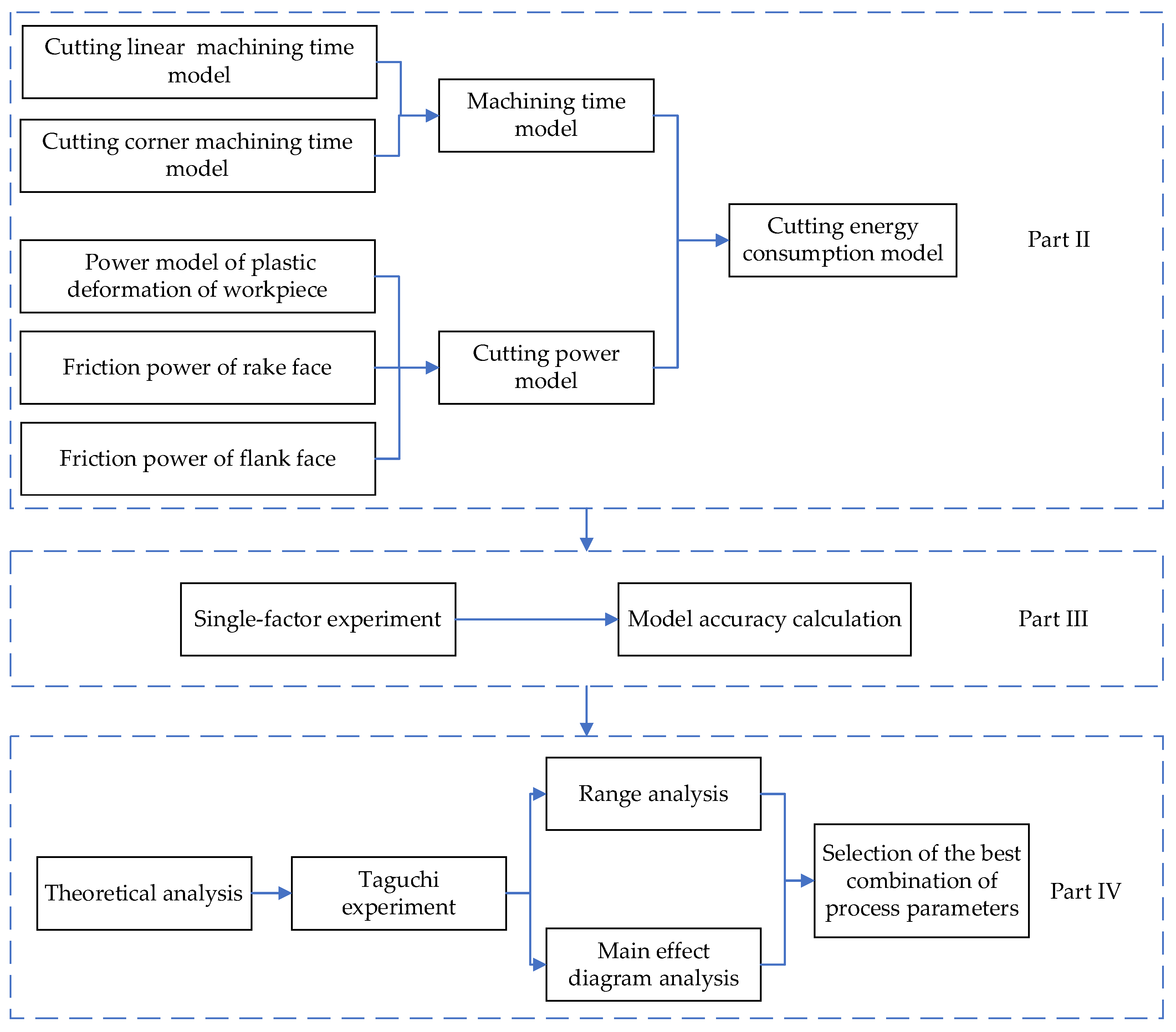
2. Modelling of Cutting Energy Consumption
2.1. Cutting Power Model of Machine Tool
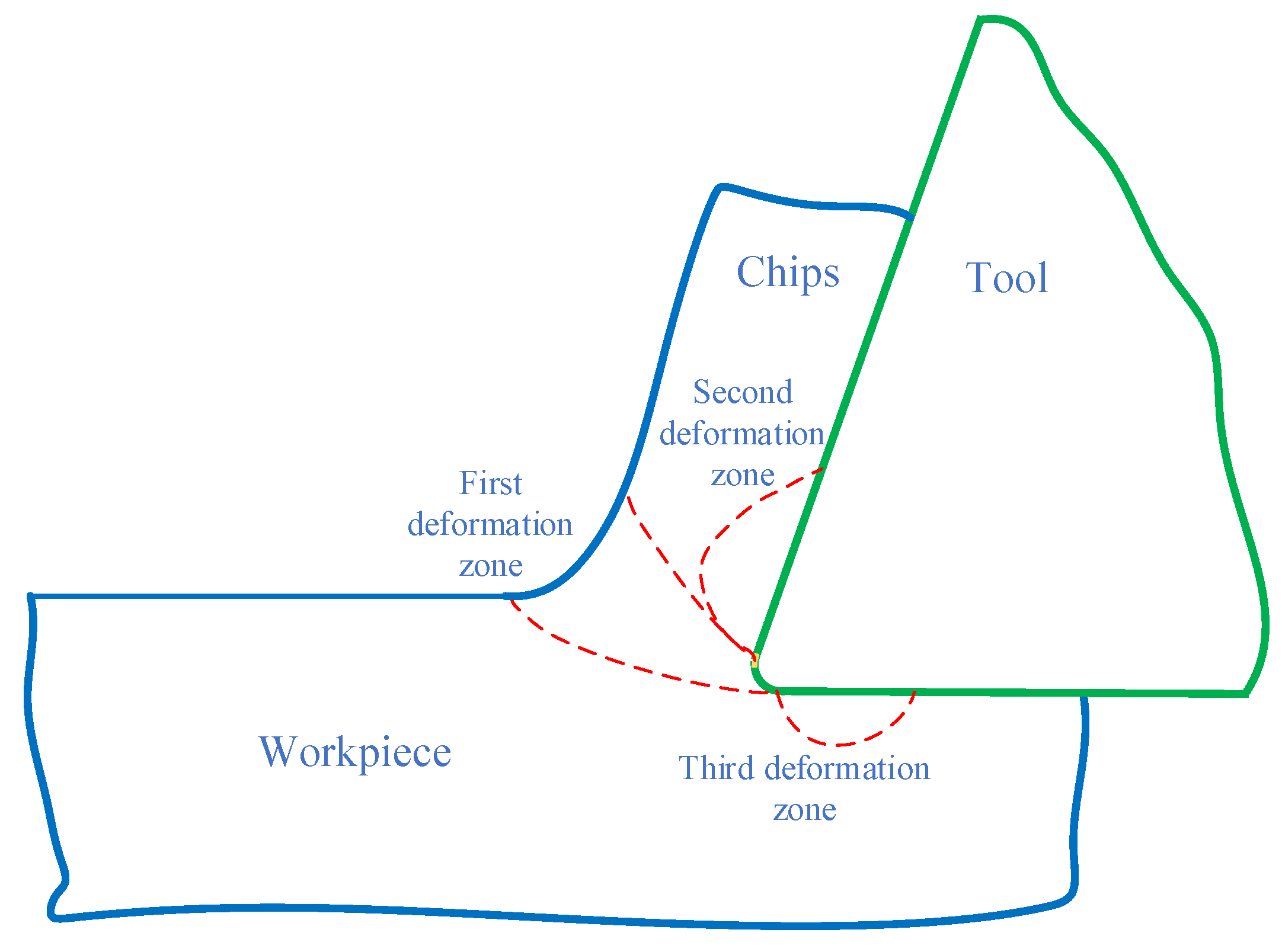
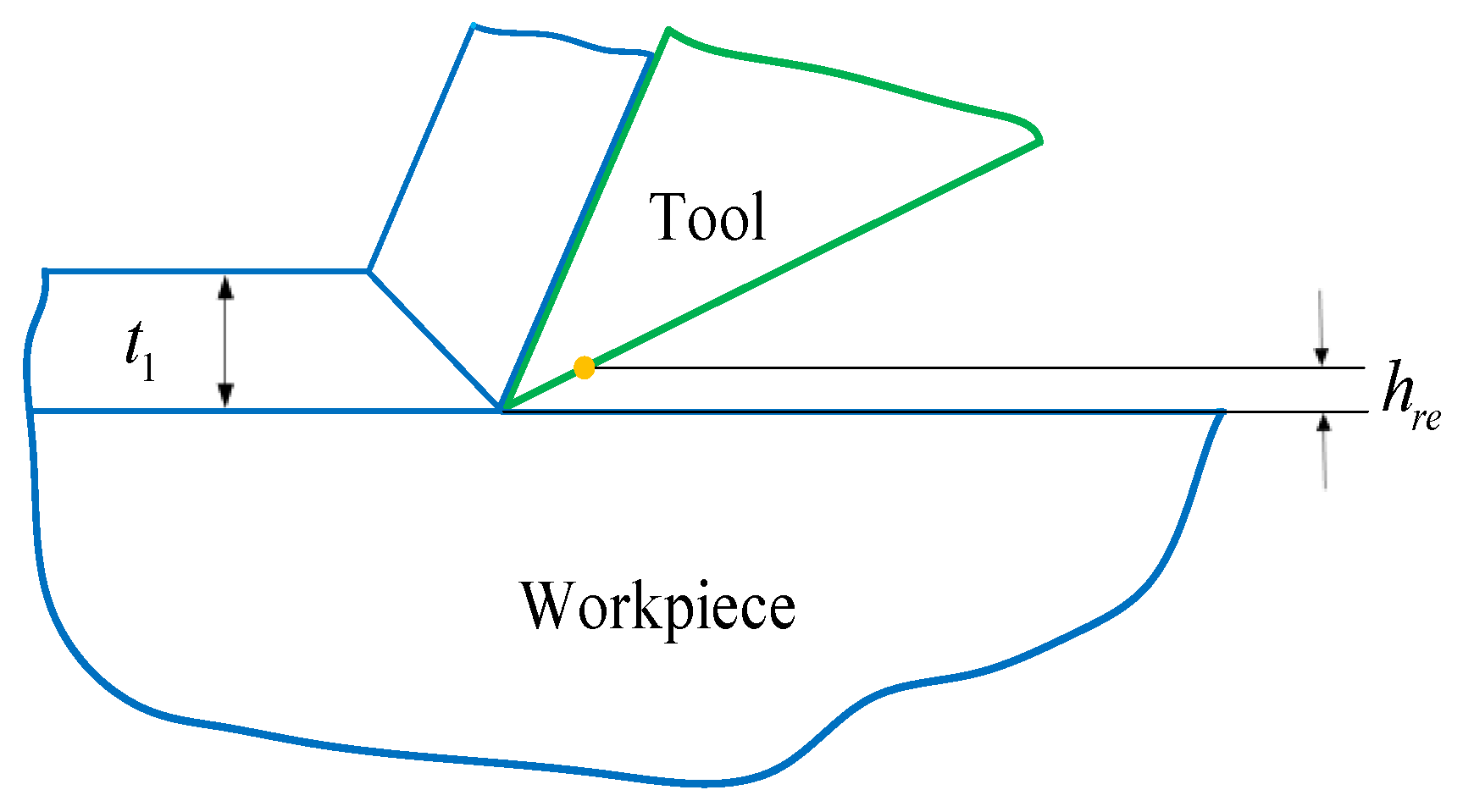
2.2. Power Model of Plastic Deformation of Workpiece
2.3. Friction Power Model of Rake Face
2.4. Friction Power Model of Flank Face
2.5. Machining Time Model
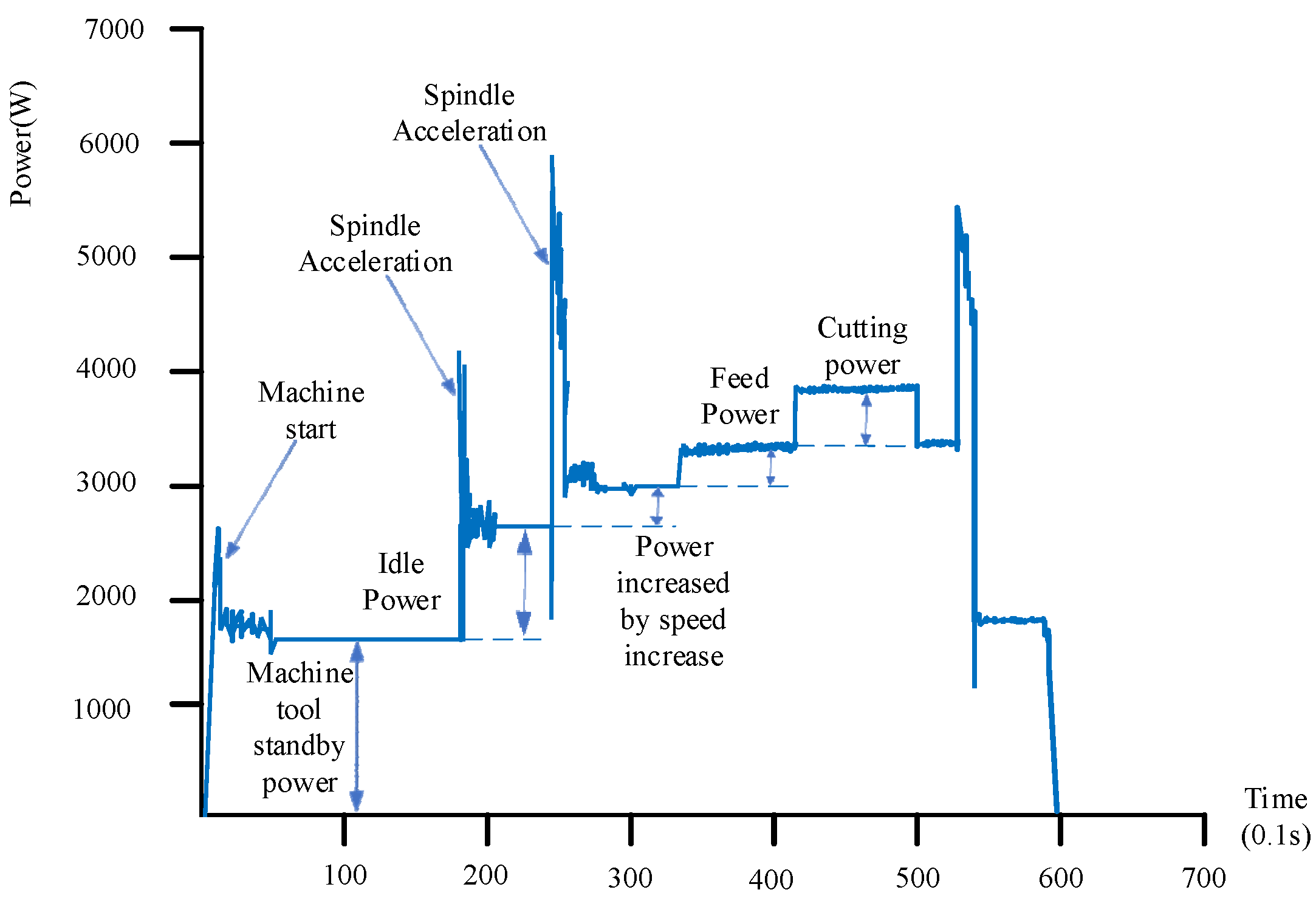
3. Experimental Setup
4. Analysis of the Influence of Cutting Parameters on Cutting Energy Consumption
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, S.T.; Nassehi, A.; Imani-Asrai, R.; Dhokia, V. Energy efficient process planning for CNC machining. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z. Revisiting system paradigms from the viewpoint of manufacturing sustainability. Sustainability 2011, 3, 1323–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, T.; Dahmus, J.; Thiriez, A. Electrical energy requirements for manufacturing processes. In Proceedings of the 13th CIRP International Conference on Life Cycle Engineering, Leuven, Belgium, 31 May–2 June 2006; Volume 31, pp. 623–638. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Sutherland, J.W. Characterizing the effect of process variables on energy consumption in end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 101, 2837–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, V.A.; Gu, H.; Mativenga, P.T. Improving the integrity of specific cutting energy coefficients for energy demand modelling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 229, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alabanda, O.; Bonilla, M.T.; Guerrero-Vaca, G.; Romero, P.E. Selection of parameters and strategies to reduce energy consumption and improve surface quality in EN-AW 7075 molds machining. Metals 2018, 8, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.R.; Coelho, R.T. Influence of the tool edge geometry on specific cutting energy at high-speed cutting. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2007, 29, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.B.; Sealy, M.P.; Liu, Z.Q. Energy consumption and process sustainability of hard milling with tool wear progression. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 229, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Sealy, M.P.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Fang, X.Y.; Guo, Y.B.; Liu, Z.Q. Energy consumption characteristics in finish hard milling. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, L.; Zhu, G. Investigation on specific milling energy and energy efficiency in high-speed milling based on energy flow theory. Energy 2019, 192, 116596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, R.; Yusof, N.M.; Sudin, I.; Nor, F.M.; Kurniawan, D. Determination of Energy Consumption during Turning of Hardened Stainless Steel Using Resultant Cutting Force. Metals 2021, 11, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wang, H.L.; Zhao, X.M. A cutting power model for tool wear monitoring in milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tian, X.; Zhang, M. Modeling and multi-objective optimization method of machine tool energy consumption considering tool wear. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2022, 71, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.N.; Zhang, D.H.; Liu, N.; Wang, S.B.; Ren, J.X.; Wang, S.L. A novel energy consumption model for milling process considering tool wear progression. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Li, H.; Fan, L.; Zhao, P. A Model for Energy Consumption of Main Cutting Force of High Energy Efficiency Milling Cutter under Vibration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.R.; Rojas, H.A.G.; Hameed, S.; Riaz, F.; Hamid, S.; Hussain, A. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Specific Energy Consumption for Cut-Off Grinding. Sensors 2022, 22, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillinger, M.; Wuwer, M.; Hadi, M.A.; Haas, F. Energy prediction for CNC machining with machine learning. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawanr, S.; Garg, G.K.; Routroy, S. Modelling of Variable Energy Consumption for CNC Machine Tools. Procedia CIRP 2021, 98, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhao, G.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Zheng, Z. Prediction models for energy consumption and surface quality in stainless steel milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 3777–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawanr, S.; Garg, G.K.; Routroy, S. Development of a Transient Energy Prediction Model for Machine Tools. Procedia CIRP 2021, 98, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Su, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C. Tool tip cutting specific energy prediction model and the influence of machining parameters and tool wear in milling. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 234, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ge, X.; Chang, S.I.; Lei, S. Assessment of cutting energy consumption and energy efficiency in machining of 4140 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, E.; Braun, S.; Schraml, P. Holistic Simulation Environment for Energy Consumption Prediction of Machine Tools. Procedia CIRP 2015, 29, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.S.; Bera, T.C.; Sangwan, K.S. Energy consumption modelling in milling of variable curved geometry. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1967–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. A new energy consumption model suitable for processing multiple materials in end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 2521–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammarullah, M.I.; Santoso, G.; Sugiharto, S.; Supriyono, T.; Wibowo, D.B.; Kurdi, O.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Jamari, J. Minimizing Risk of Failure from Ceramic-on-Ceramic Total Hip Prosthesis by Selecting Ceramic Materials Based on Tresca Stress. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammarullah, M.I.; Santoso, G.; Sugiharto, S.; Supriyono, T.; Kurdi, O.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Wonarni, T.I.; Jamari, J. Tresca stress study of CoCrMo-on-CoCrMo bearings based on body mass index using 2D computational model. J. Tribol. 2022, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Seçgin, Ö.; Sogut, M.Z. Surface roughness optimization in milling operation for aluminum alloy (Al 6061-T6) in aviation manufacturing elements. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2021, 93, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
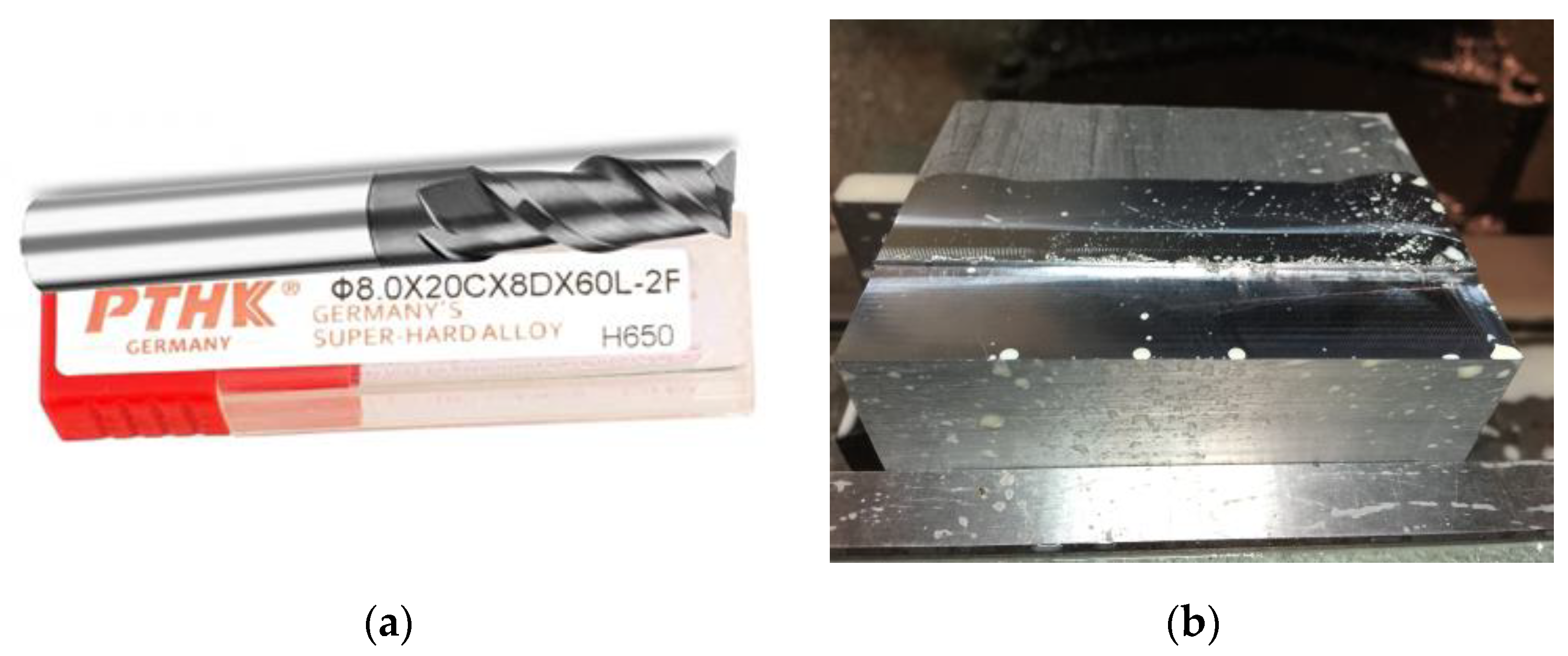
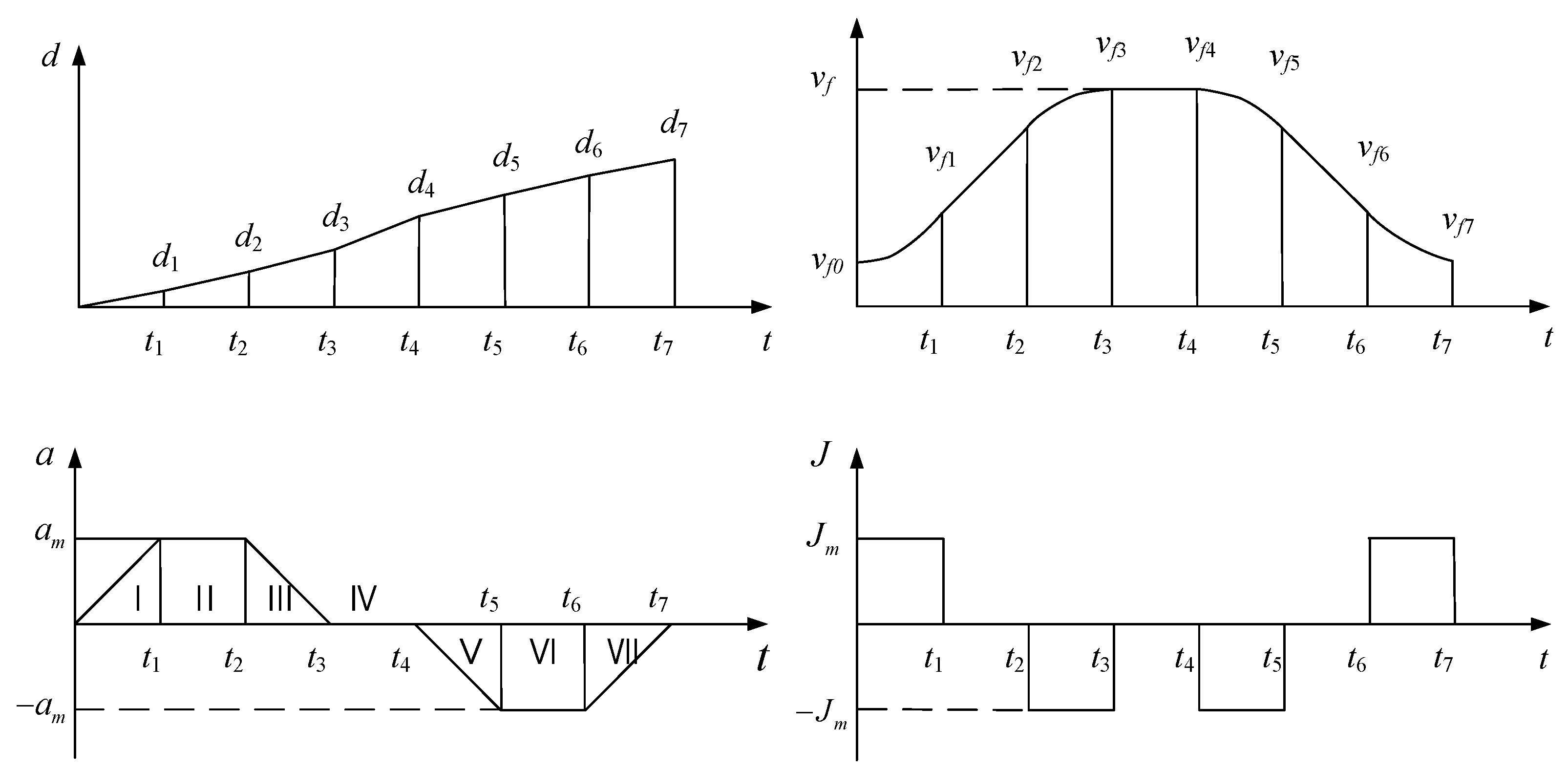




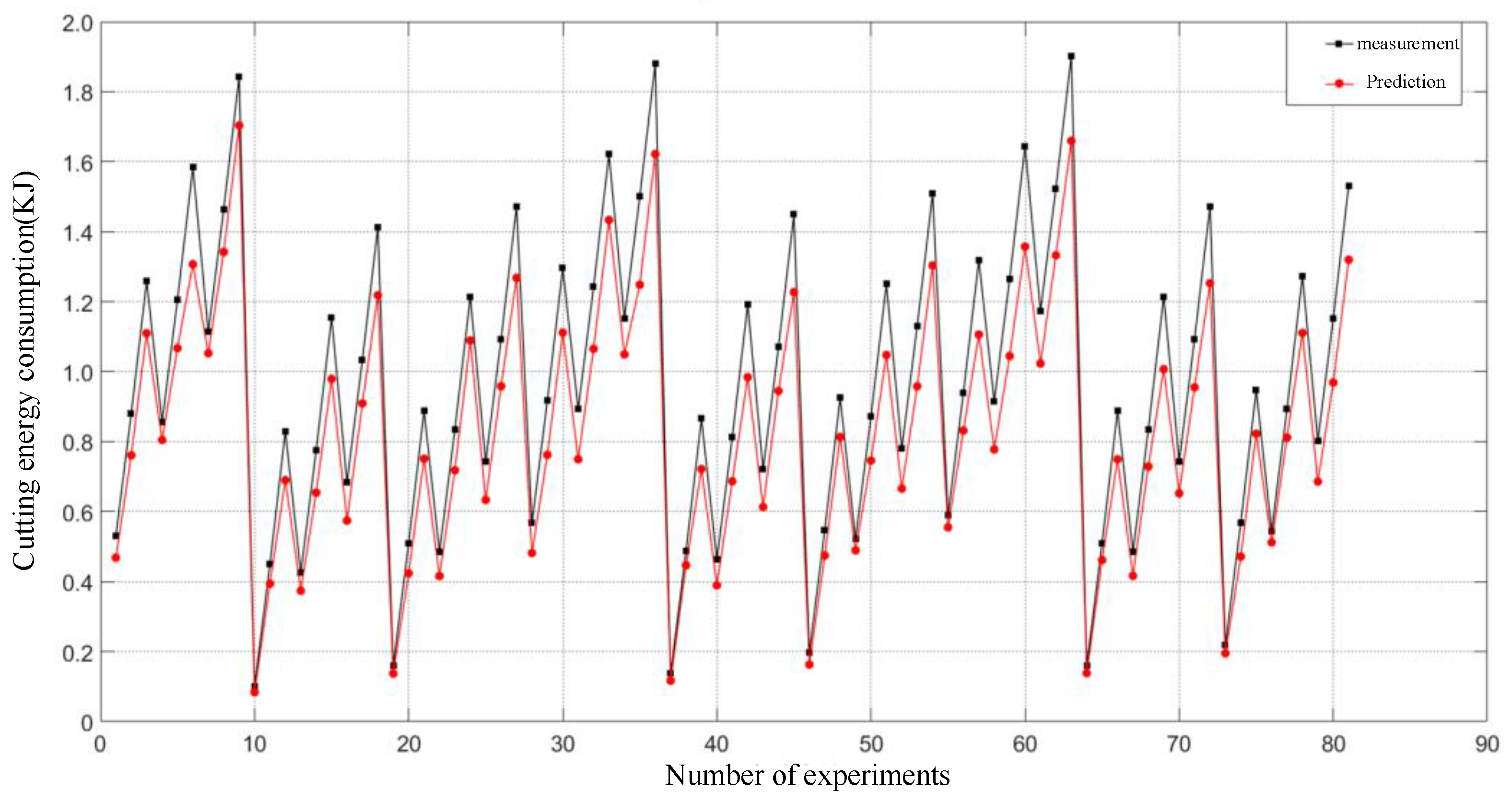
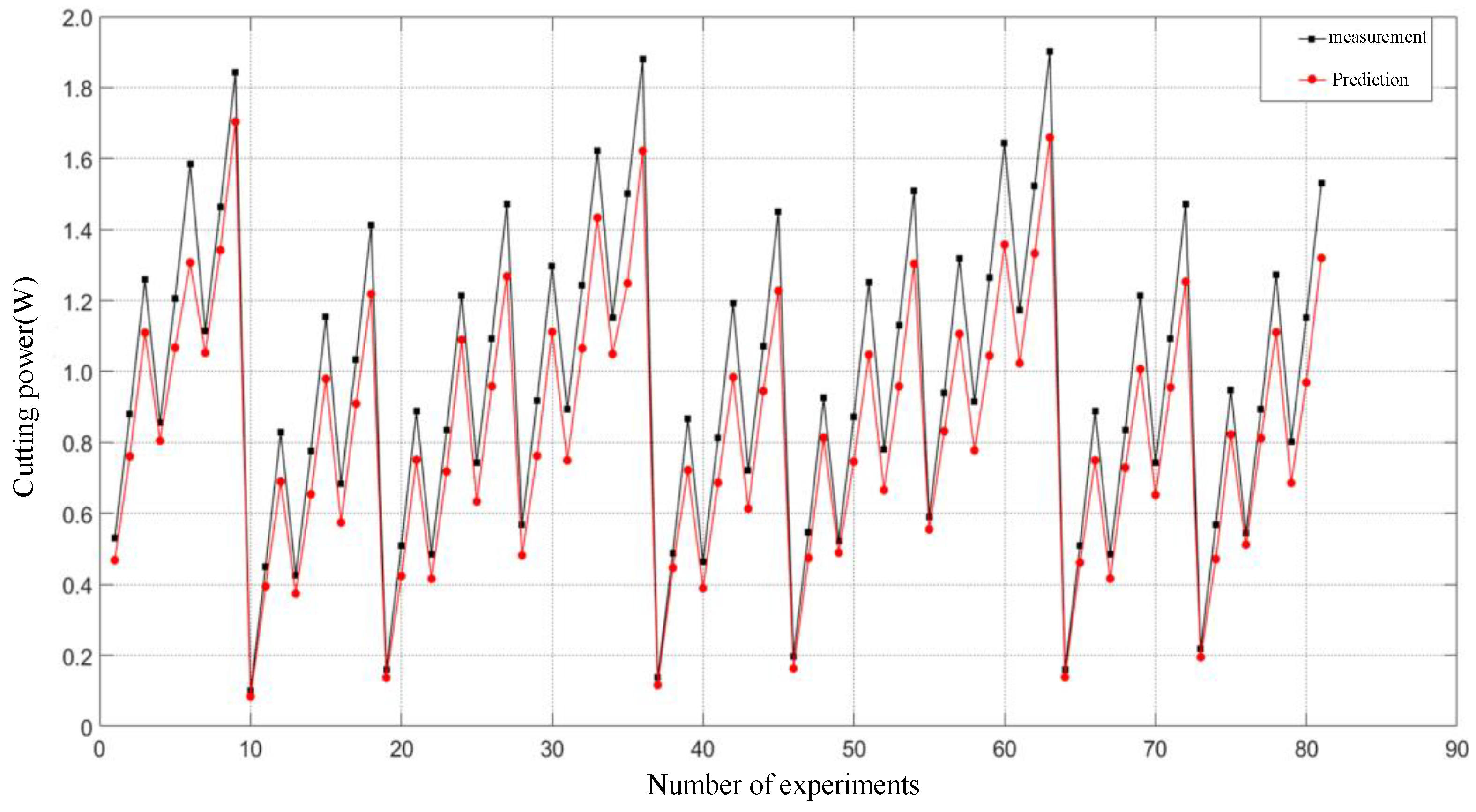
| Type of Cutter | Particle Size | Hardness | Coating | Helix Angle | Number of Edges | Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| End milling cutter | 0.6μm | ≤65° | AlTiCrN | 35° | 2 | Tungsten steel |
| Material | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Vickers Hardness (HV) | Density (gr/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al 6061 | 286 | 318 | 5.44 | 106 | 2.7 |
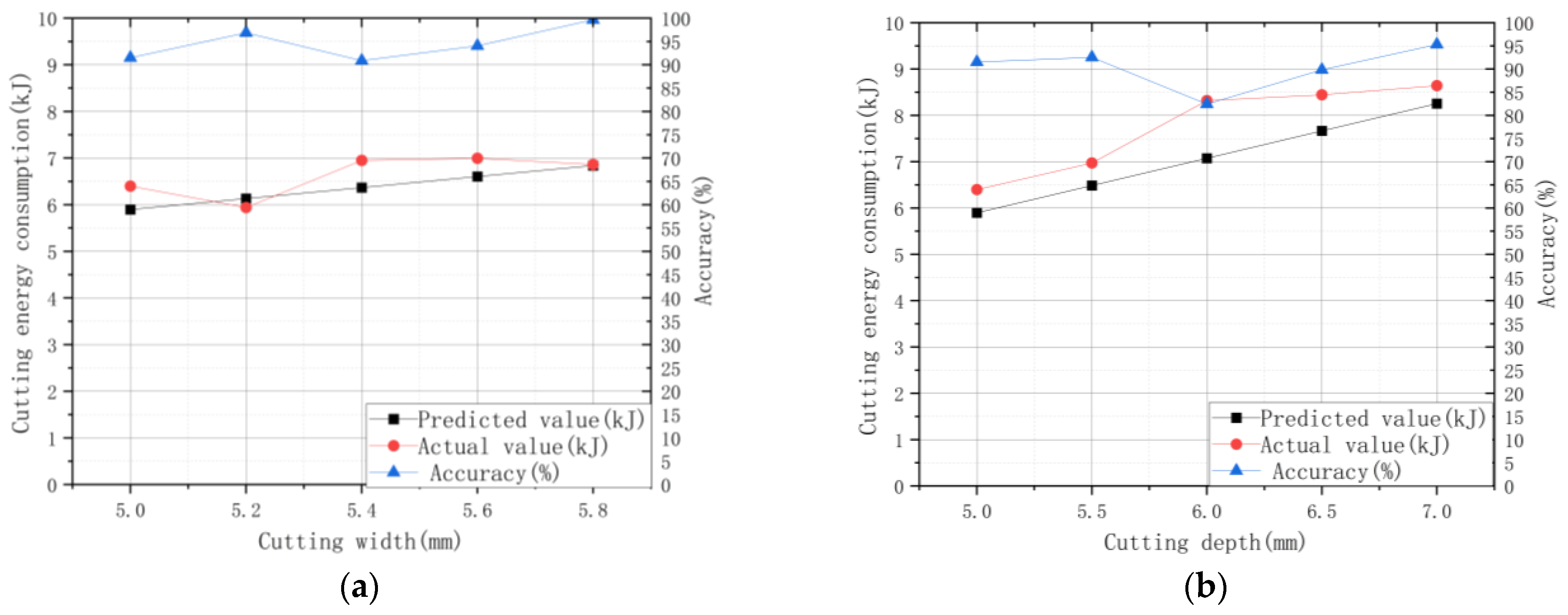
| Experiment Number | ae (mm) | ap (mm) | Ecal (J) | Emea (J) | Prediction Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 5896 | 6397 | 8.50 |
| 2 | 5.2 | 5 | 6132 | 5940 | 3.13 |
| 3 | 5.4 | 5 | 6368 | 6949 | 9.12 |
| 4 | 5.6 | 5 | 6603 | 6995 | 5.94 |
| 5 | 5.8 | 5 | 6840 | 6863 | 0.34 |
| 6 | 5 | 5 | 5896 | 6397 | 8.50 |
| 7 | 5 | 5.5 | 6486 | 6971 | 7.48 |
| 8 | 5 | 6 | 7075 | 8319 | 17.58 |
| 9 | 5 | 6.5 | 7665 | 8443 | 10.15 |
| 10 | 5 | 7 | 8254 | 8641 | 4.69 |
| Experiment Number | n (rpm) | vf (mm/min) | ap (mm) | ae (mm) | Pc (W) | E (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2500 | 200 | 2 | 0.3 | 7.05 | 530.16 |
| 2 | 2500 | 300 | 4 | 0.6 | 15.51 | 775.50 |
| 3 | 2500 | 400 | 6 | 0.9 | 39.36 | 1472.06 |
| 4 | 3000 | 200 | 4 | 0.9 | 21.56 | 1621.31 |
| 5 | 3000 | 300 | 6 | 0.3 | 14.41 | 720.50 |
| 6 | 3000 | 400 | 2 | 0.6 | 14.62 | 546.79 |
| 7 | 3500 | 200 | 6 | 0.6 | 20.26 | 1523.55 |
| 8 | 3500 | 300 | 2 | 0.9 | 17.77 | 888.5 |
| 9 | 3500 | 400 | 4 | 0.3 | 14.55 | 544.17 |
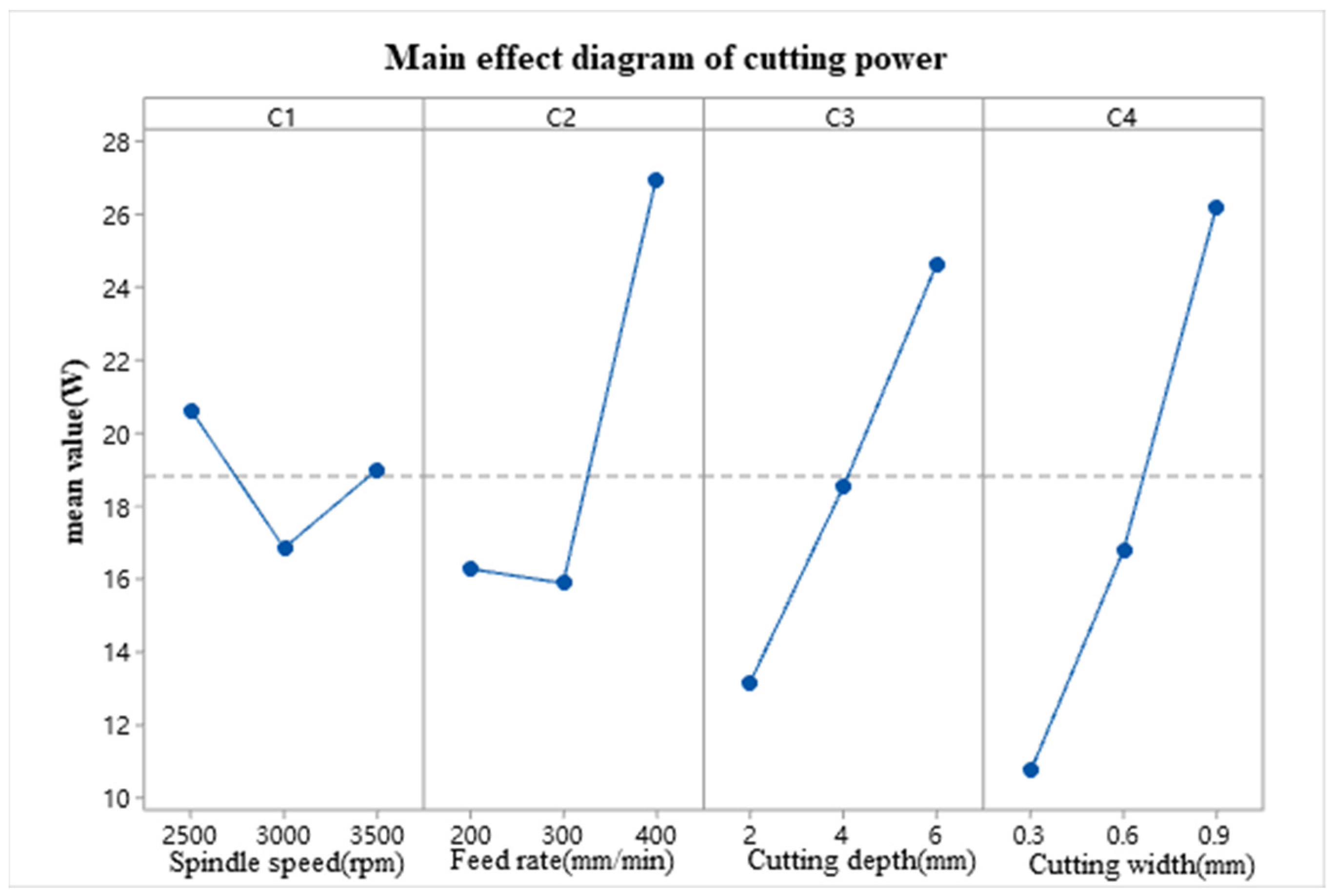
| Experiment Number | n (rpm) | vf (mm/min) | ap (mm) | ae (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.65 | 16.29 | 13.15 | 12.01 |
| 2 | 16.87 | 15.90 | 17.21 | 16.80 |
| 3 | 17.53 | 22.85 | 24.68 | 26.24 |
| Calculation rank | 3.78 | 6.95 | 11.54 | 14.23 |
| Rank | ||||
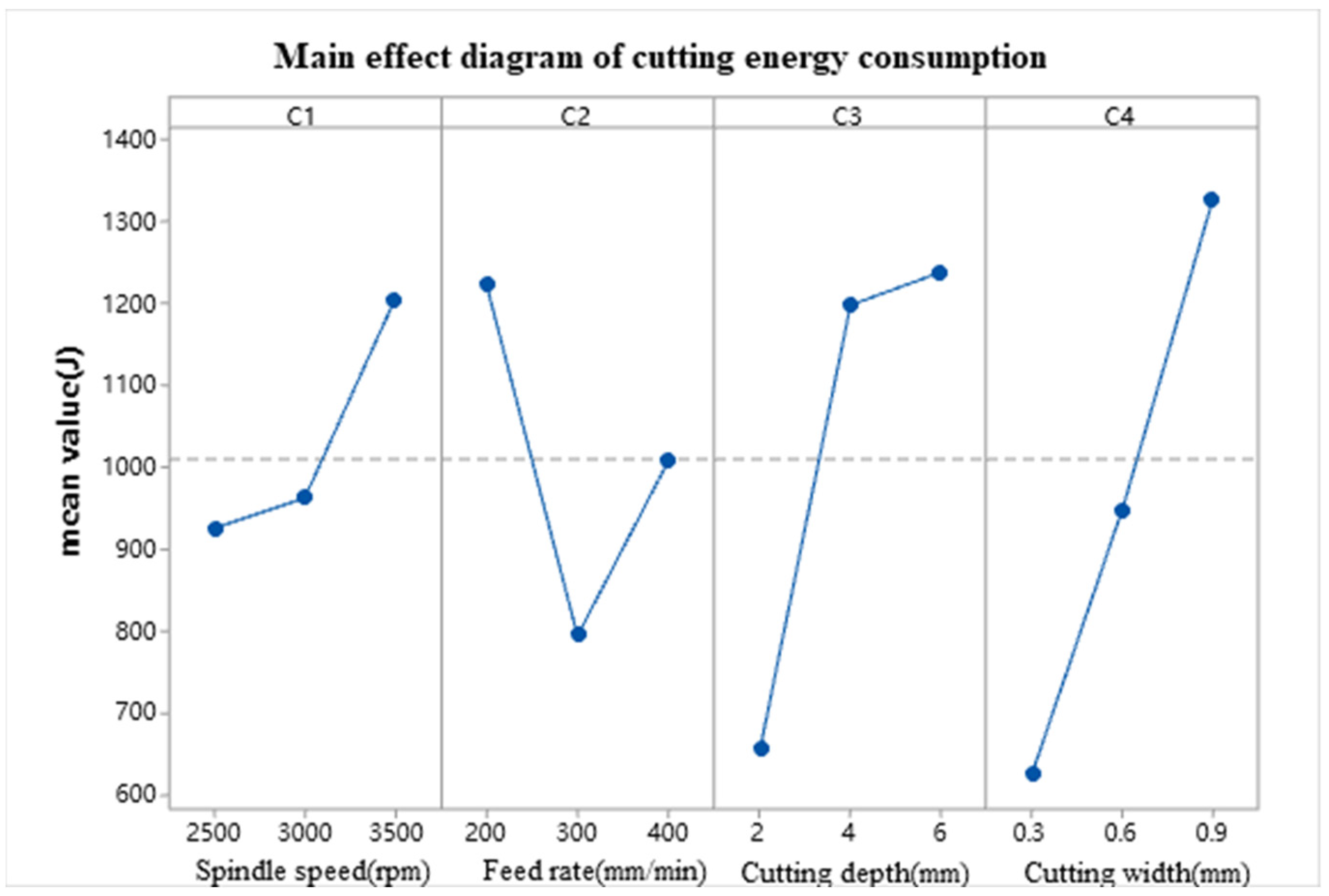
| Experiment Number | n (rpm) | vf (mm/min) | ap (mm) | ae (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 925.9 | 1225.0 | 655.1 | 598.3 |
| 2 | 962.9 | 794.8 | 980.3 | 948.6 |
| 3 | 985.4 | 854.3 | 1238.7 | 1327.3 |
| Calculation rank | 59.5 | 430.2 | 583.6 | 729.0 |
| Rank | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Cutting Energy Consumption Modelling of End Milling Cutter Coated with AlTiCrN. Coatings 2023, 13, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040679
Meng Y, Sun X, Dong S, Wang Y, Liu X. Cutting Energy Consumption Modelling of End Milling Cutter Coated with AlTiCrN. Coatings. 2023; 13(4):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040679
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yue, Xinsheng Sun, Shengming Dong, Yue Wang, and Xianli Liu. 2023. "Cutting Energy Consumption Modelling of End Milling Cutter Coated with AlTiCrN" Coatings 13, no. 4: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040679
APA StyleMeng, Y., Sun, X., Dong, S., Wang, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). Cutting Energy Consumption Modelling of End Milling Cutter Coated with AlTiCrN. Coatings, 13(4), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13040679







