Preparation of Microcrystalline Cellulose-Derived Carbon Dots as a Sensor for Fe3+ Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization
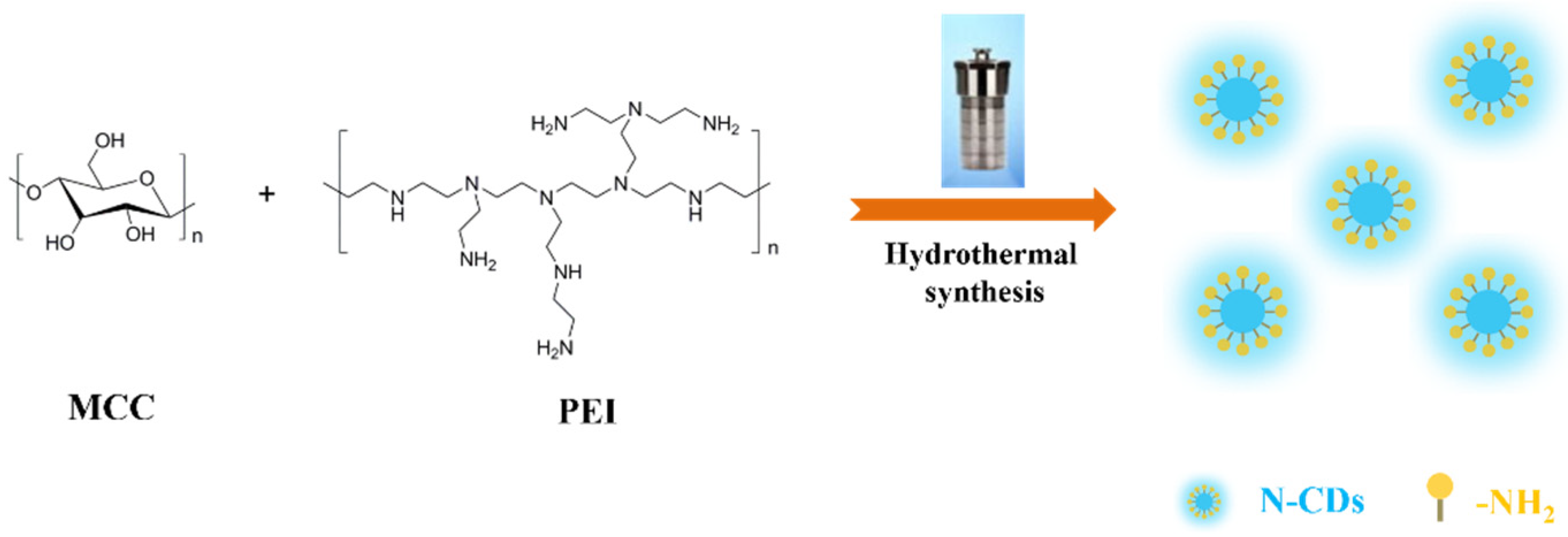
2.3. Preparation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
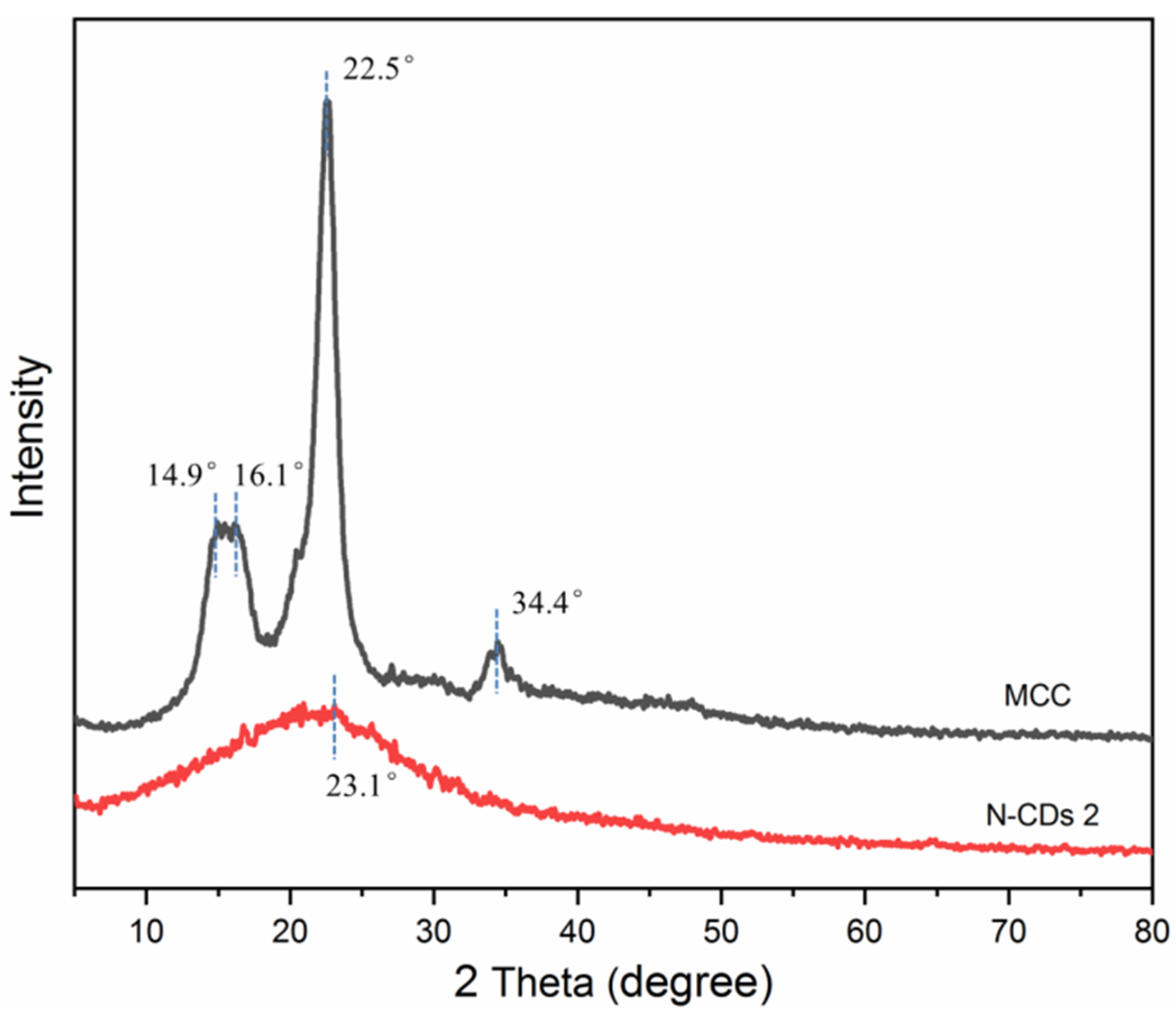
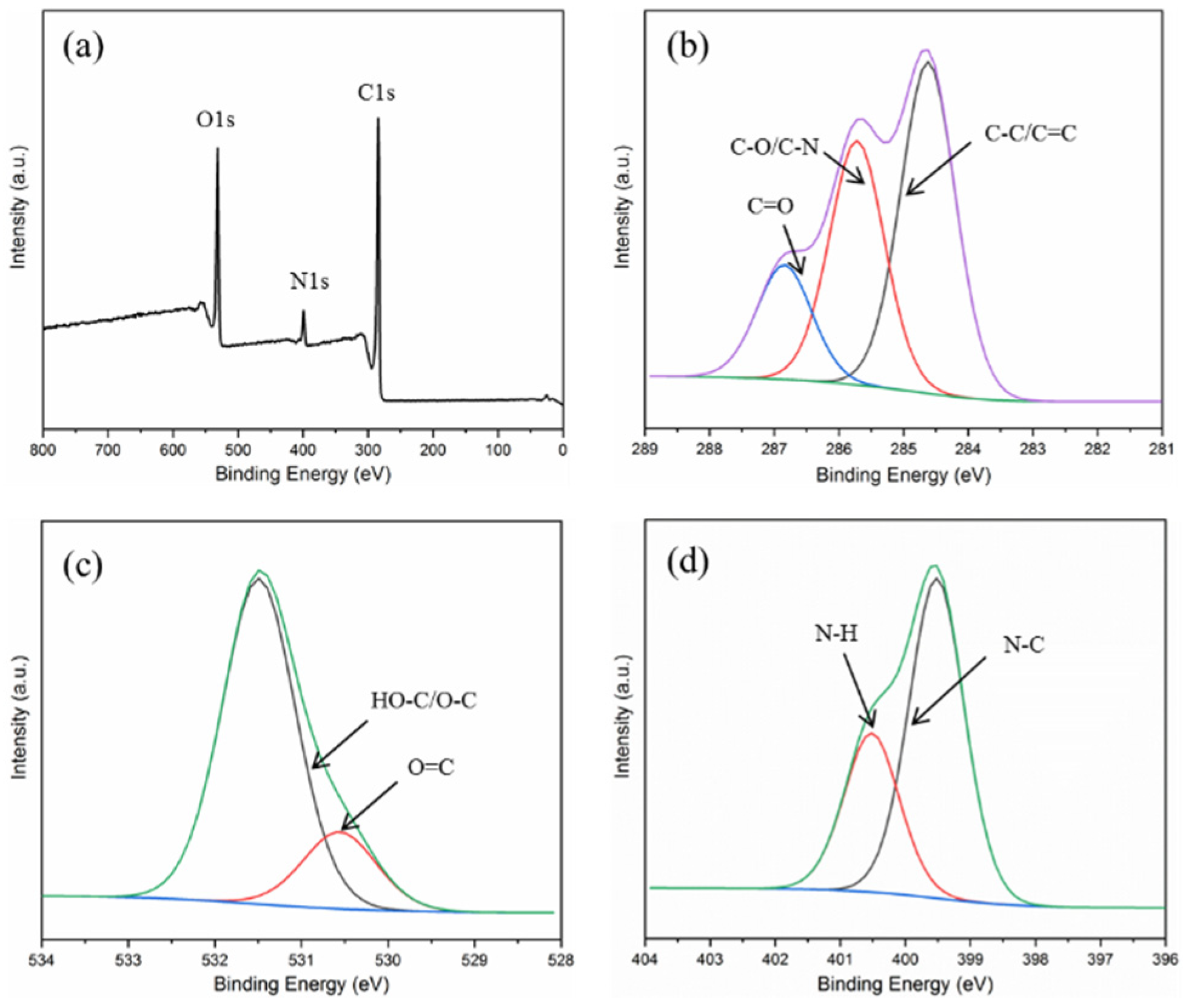
3.1. Characterization of N-CDs
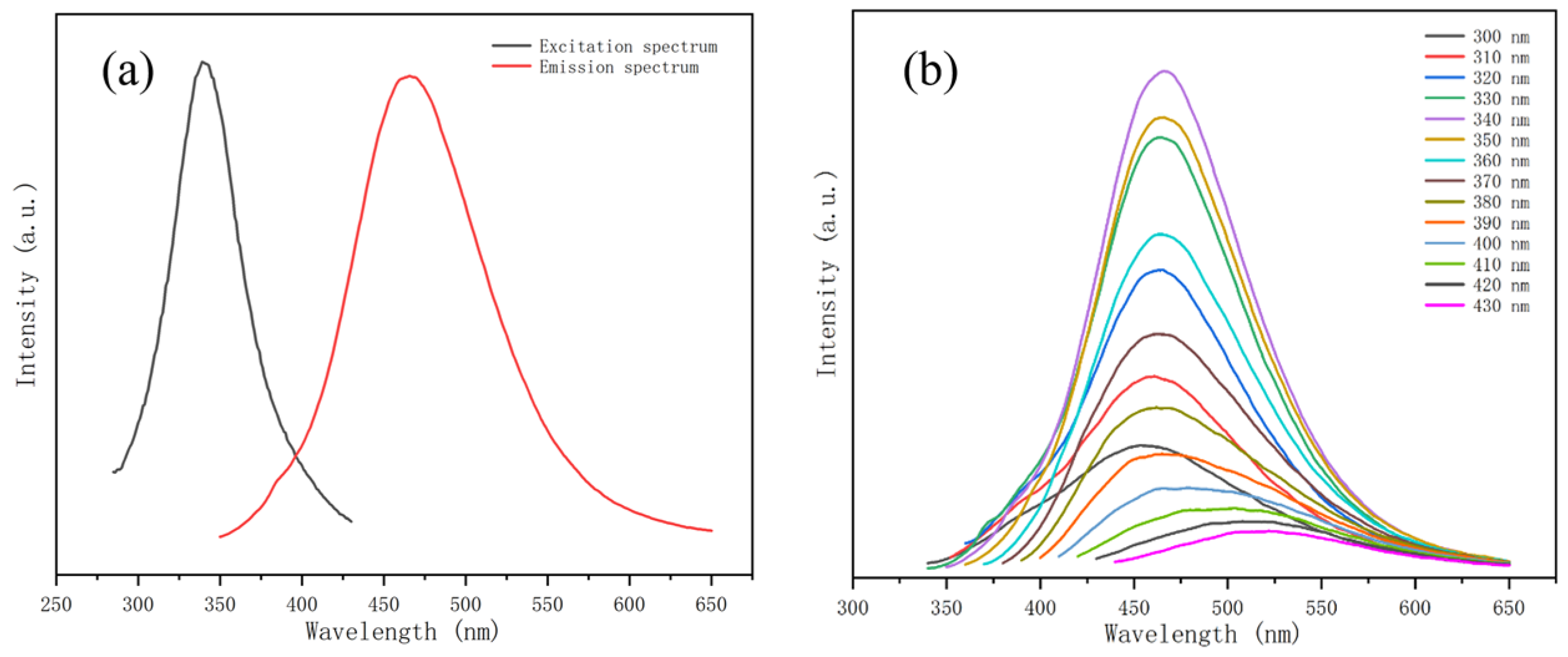
3.2. Optical Properties of N-CDs 2
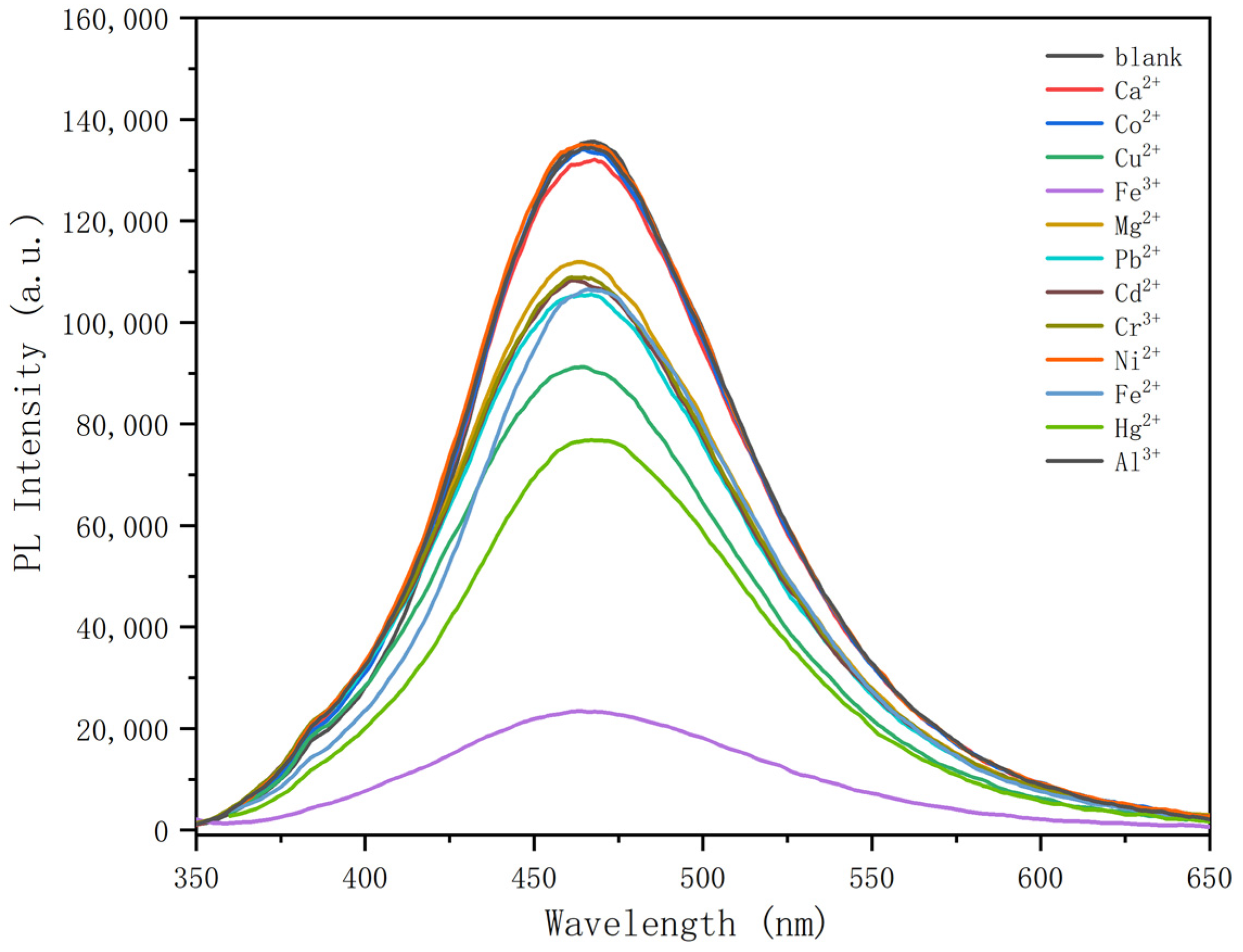
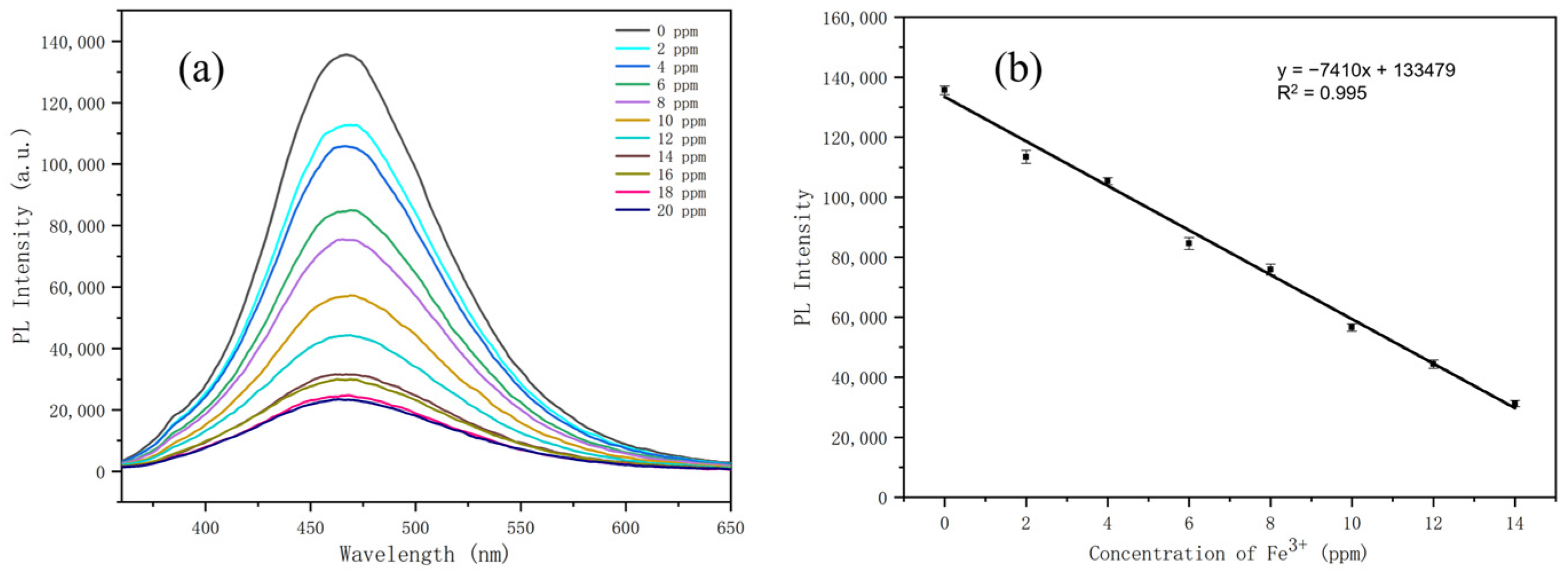
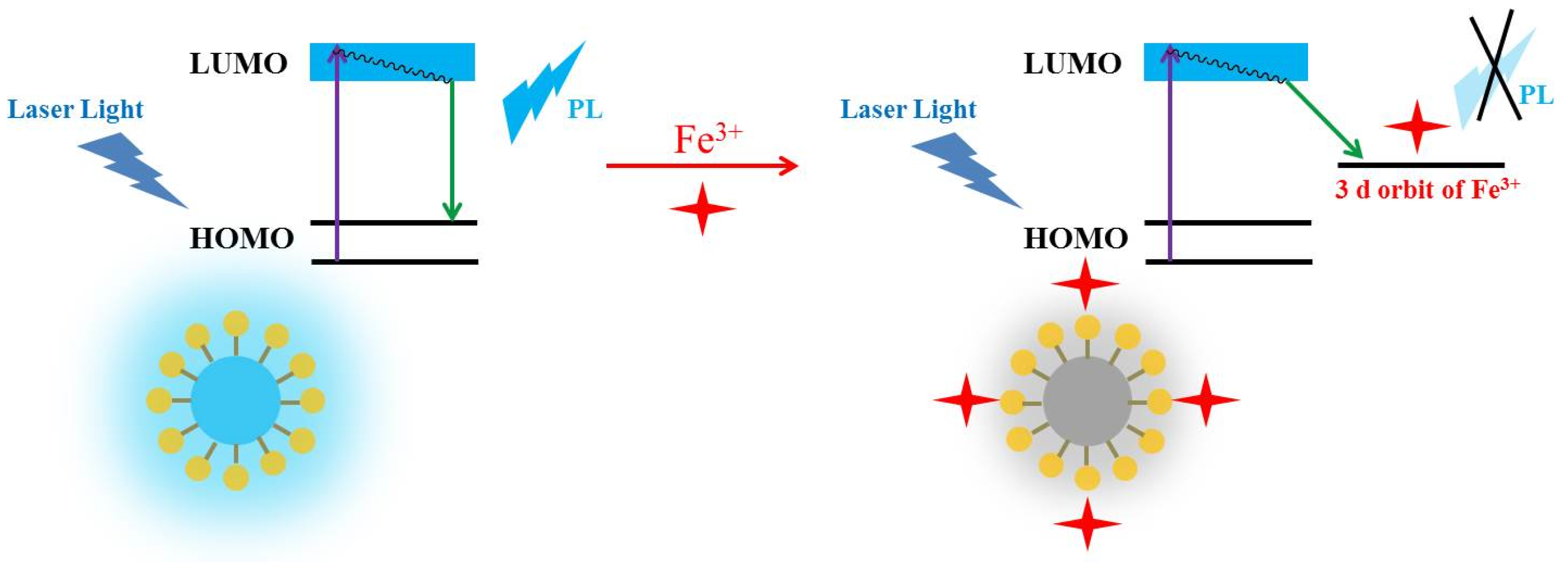
3.3. Detection Properties of N-CDs 2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pang, S.; Liu, S. Dual-emission carbon dots for ratiometric detection of Fe (3+) ions and acid phosphatase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1105, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, V.C.; Cotterchio, M.; Khoo, E. Iron intake, body iron status, and risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, H.C.; Lian, T.H.; Mao, L.; Tang, S.X.; Sun, L.; Huang, X.Y.; Guo, P.; Cao, C.J.; Yu, S.Y.; et al. Iron deposition in substantia nigra: Abnormal iron metabolism, neuroinflammatory mechanism and clinical relevance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e14973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wei, N.; Wan, B.; Qian, L.; Liu, Y. A polyethylenimine/salicylaldehyde modified cellulose Schiff base for selective and sensitive Fe (3+) detection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 228, e115379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.X.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.F.; Wang, C.P.; Chu, F.X. A fluorometric and colorimetric dual-mode sensor based on nitrogen and iron co-doped graphene quantum dots for detection of ferric ions in biological fluids and cellular imaging. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 14751–14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, Y.; Anand, T.; Babu, L.T.; Paira, P.; Kumar Sk, A.; Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Combined use of spectrophotometer and smartphone for the optical detection of Fe (3+) using a vitamin B6 cofactor conjugated pyrene derivative and its application in live cells imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 361, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, J.; Xia, Z. Fabrication of a dual-emitting dye-encapsulated metal-organic framework as a stable fluorescent sensor for metal ion detection. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 6794–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Dong, J.X.; Liu, S.G.; Li, N.; Fan, Y.Z.; Ju, Y.J.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Multifunctional fluorescent sensors for independent detection of multiple metal ions based on Ag nanoclusters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots and Their Applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2019, 2, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Kang, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, S. Modification of Carbon Dots for Metal-Ions Detection. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202300062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Kang, L.; Cheng, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, S. Biomass-Derived Carbon Dots and Their Sensing Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, e4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, K.A.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Lewis, W.K.; Guliants, E.A.; Jafariyan, A.; Wang, P.; Bunker, C.E.; Sun, Y.P. Carbon quantum dots and applications in photocatalytic energy conversion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8363–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Shi, J. Cellulose-based sensors for metal ions detection. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5477–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.F.; Chen, Z.P. A Review of Carbon Dots Produced from Biomass Wastes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, e2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Souza, D.R.; Caminhas, L.D.; de Mesquita, J.P.; Pereira, F.V. Luminescent carbon dots obtained from cellulose. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, P.; Li, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, K. Synthesis of cellulose-derived carbon dots using acidic ionic liquid as a catalyst and its application for detection of Hg (2+). J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cheng, D.; Liu, X.; Han, A. Green Hydrothermal Synthesis of N-doped Carbon Dots from Biomass Highland Barley for the Detection of Hg (2+). Sensors 2019, 19, e3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Gao, J.; Cong, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Yao, J. Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Carbon Dots for Bioimaging. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Leung, K.C.; Wang, Y.X. High Performance Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for In Vitro and In Vivo Bioimaging: Effect of Nitrogen Doping Ratios. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8063–8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Miao, M.; Cao, S.; Fang, J.; Shi, L. Easy synthesis of photoluminescent N-doped carbon dots from winter melon for bio-imaging. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 31250–31254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Pu, P.; Zhao, J.; Dong, C.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H. Preparation of highly photoluminescent sulfur-doped carbon dots for Fe (3+) detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D. Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 2013, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahma, F.; Iwamoto, S.; Hori, N.; Iwata, T.; Takemura, A. Isolation, preparation, and characterization of nanofibers from oil palm empty-fruit-bunch (OPEFB). Cellulose 2010, 17, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Liang, S.; Tan, Y.; Sheng, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.X. Carbon Dots with Continuously Tunable Full-Color Emission and Their Application in Ratiometric pH Sensing. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lu, W.; Paau, M.C.; Hu, Q.; Wu, X.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Choi, M.M. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots for Fe (3+) sensing and cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yan, F.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Formation of N, S-codoped fluorescent carbon dots from biomass and their application for the selective detection of mercury and iron ion. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. Fluorescence Determination of Nitrite in Water Using Prawn-Shell Derived Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanodots as Fluorophores. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ni, G.; Tu, J.; Jin, X.; Peng, J. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive detection of Fe (2+) and hydrogen peroxide. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2017, 19, e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Kang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lian, S.; Tsang, C.H.; Yang, X.; Lee, S.T. Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K.C.; Suresh, R.; Ramamurthy, P. Unravelling the Multiple Emissive States in Citric-Acid-Derived Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: Facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg (2+) ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Bruckner, C.; Lei, Y. One-pot and ultrafast synthesis of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots possessing bright dual wavelength fluorescence emission. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17278–17282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Bai, P.X.; Luo, X.M.; Li, J. Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots Based on Gelatin and Study on It’s Optical Property. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 4, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Macairan, J.R.; Jaunky, D.B.; Piekny, A.; Naccache, R. Intracellular ratiometric temperature sensing using fluorescent carbon dots. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lv, J.J.; Zhou, D.L.; Bao, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, A.J.; Feng, J.J. One-pot green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles as fluorescent probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21691–21696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xing, M.; Wu, Q. A universal facile synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots from cellulose-based biowaste for fluorescent detection of Fe (3+) ions and intracellular bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.F.; Wen, Q.L.; Yang, Y.J.; Cui, X.M.; Ling, J.; Liu, P.; Cao, Q.E. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots synthesized using phenylalanine and citric acid for selective detection of Fe (3+) ions. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, e117944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.F.; Tan, S.C.; Pang, S.C.; Ng, S.M. Nitrogen doped carbon nanodots as fluorescent probes for selective detection and quantification of Ferric (III) ions. Opt. Mater. 2017, 73, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.U.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Z.; Ma, X.; Ding, X.; Du, S.; Wang, Y. High Quantum Yield Green-Emitting Carbon Dots for Fe (III) Detection, Biocompatible Fluorescent Ink and Cellular Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Park, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, T.; Chae, S.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y. One-step synthesis of robust nitrogen-doped carbon dots: Acid-evoked fluorescence enhancement and their application in Fe (3+) detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17747–17754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, C.; Tian, Z.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Z. Facilely synthesized N-doped carbon quantum dots with high fluorescent yield for sensing Fe (3+). New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Panneerselvam, P.; Marieeswaran, M. A green synthetic route for the surface-passivation of carbon dots as an effective multifunctional fluorescent sensor for the recognition and detection of toxic metal ions from aqueous solution. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 490–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. One-Step Hydrothermal Approach to Synthesis Carbon Dots from D-Sorbitol for Detection of Iron (III) and Cell Imaging. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 4457–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Cai, Y. Facile synthesis of fluorescence carbon dots from sweet potato for Fe (3+) sensing and cell imaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.; Aseer, K.R.; Perumal, S.; Karthik, N.; Lee, Y.R. Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from Phyllanthus acidus utilized as a fluorescent probe for label-free selective detection of Fe (3+) ions, live cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Gao, D.; Qiu, Y.; Yi, G.; Li, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xia, Z.; Fu, Q. Carbon source self-heating: Ultrafast, energy-efficient and room temperature synthesis of highly fluorescent N, S-codoped carbon dots for quantitative detection of Fe (iii) ions in biological samples. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Deng, X.; Liang, J.; Li, J.; Tao, Y.; Tan, K. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of down/up-conversion luminescence F-doped carbon quantum dots for label-free detection of Fe (3+). Microchem. J. 2019, 151, e104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.L.; Basu, H.; Saha, S.; Singhal, R.K.; Kailasa, S.K. Investigation of silicon doping into carbon dots for improved fluorescence properties for selective detection of Fe (3+) ion. Opt. Mater. 2019, 96, e109374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammina, S.K.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of N, Zn-doped carbon dots for the detection of Fe (3+) ions and bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 202, e111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, G.; Neogi, S. Devising Mixed-Ligand Based Robust Cd (II)-Framework From Bi-Functional Ligand for Fast Responsive Luminescent Detection of Fe (3+) and Cr (VI) Oxo-Anions in Water With High Selectivity and Recyclability. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, e651866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Senthilkumar, S.; Rajput, S.; Neogi, S. Pore-Functionalized and Hydrolytically Robust Cd (II)-Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Selective, Multicyclic CO2 Adsorption and Fast-Responsive Luminescent Monitoring of Fe (III) and Cr (VI) Ions with Notable Sensitivity and Reusability. Inorganic. Chem. 2020, 5, 3012–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Pan, W.; Yu, G.; Wang, J. Fe (3+)-Sensitive Carbon Dots for Detection of Fe (3+) in Aqueous Solution and Intracellular Imaging of Fe (3+) Inside Fungal Cells. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja Prasannakumaran Nair, S.; Kottam, N.; SG, P.K. Green Synthesized Luminescent Carbon Nanodots for the Sensing Application of Fe (3+) Ions. J. Fluoresc. 2020, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, L.; Li, X. Sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe (3+). Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10201–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, J.; Huang, J.; He, D.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Ye, R.; Yang, X.; Qing, T.; Tang, J. Highly Fe (3+)-Selective Fluorescent Nanoprobe Based on Ultrabright N/P-Codoped Carbon Dots and Its Application in Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, T.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C. Concentration-dependent color tunability of nitrogen-doped carbon dots and their application for iron (III) detection and multicolor bioimaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 521, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Su, H.; Wang, K.; Wong, W.K.; Zhu, X. Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots from porphyrins as efficient probes for bioimaging and biosensing in living cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7375–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, Q.; Jin, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. A fluorescence turn-off chemosensor based on N-doped carbon quantum dots for detection of Fe (3+) in aqueous solution. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sensor | Detection Range/ppm | LOD/ppm | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phe-CDs | 0.28~27.78 | 0.04 | [41] |
| N-CDs | 11.11~277.78 | 4.11 | [42] |
| CDs | 1.39~16.67 | 1.06 | [43] |
| N-CDs | 0.0~2.78 | 0.61 | [44] |
| N-CDs | 0~2.78 | 0.26 | [45] |
| N, O/Iy-CDs | 0~3.33 | 0.34 | [46] |
| CDs | 1.39~19.44 | 0.06 | [47] |
| CDs | 0.056~5.56 | 0.018 | [48] |
| N-CDs | 0.11~1.39 | 0.05 | [49] |
| N, S-CDs | 0.011~33.33 | 0.005 | [50] |
| F-CDs | 0.056~5.56 | 0.0006 | [51] |
| Si-CDs | 0.0006~0.139 | 0.0001 | [52] |
| N, Zn-CDs | 0.014~6.94 | 0.008 | [53] |
| N-CDs 2 | 0~14 | 0.21 | This work |
| Sample | Added/ppm | Found/ppm | Recoveries/% | RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.00 | 4.11 | 102.75 | 1.29 | |
| Tap water | 8.00 | 7.97 | 99.63 | 1.39 |
| 12.00 | 12.09 | 100.75 | 1.03 | |
| 4.00 | 3.93 | 98.25 | 2.33 | |
| Pool water | 8.00 | 7.89 | 98.63 | 1.91 |
| 12.00 | 12.05 | 100.42 | 1.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Kang, L.; Gao, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y. Preparation of Microcrystalline Cellulose-Derived Carbon Dots as a Sensor for Fe3+ Detection. Coatings 2023, 13, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13121979
Fan J, Kang L, Gao J, Cheng X, Zhang Q, Wu Y. Preparation of Microcrystalline Cellulose-Derived Carbon Dots as a Sensor for Fe3+ Detection. Coatings. 2023; 13(12):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13121979
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jiang, Lei Kang, Jinlong Gao, Xu Cheng, Qing Zhang, and Yunlong Wu. 2023. "Preparation of Microcrystalline Cellulose-Derived Carbon Dots as a Sensor for Fe3+ Detection" Coatings 13, no. 12: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13121979
APA StyleFan, J., Kang, L., Gao, J., Cheng, X., Zhang, Q., & Wu, Y. (2023). Preparation of Microcrystalline Cellulose-Derived Carbon Dots as a Sensor for Fe3+ Detection. Coatings, 13(12), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13121979





