Abstract
1H-Perimidine (PMD) and 1H-perimidine-2-thiol (SPMD) were developed as inhibitors for reinforcing steel in a simulated concrete pore (SCP) solution. Electrochemical measurements, contact angle experiments, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and quantum chemical calculations were used to investigate the corrosion performance and adsorption mechanisms. The experimental results showed that owing to the structure of SPMD containing a 2-position sulfhydryl group, SPMD is superior to PMD as a corrosion inhibitor for HRB400 reinforced steel in the SCP solution, and its corrosion efficiency can reach more than 80%. Moreover, the introduction of nitrogen and sulfur atoms into the inhibitor not only can coordinate with Fe atoms to form strong bonds but also is useful for preventing charge transfer in the metal corrosion process. More importantly, the perimidine derivatives can spontaneously adsorb on iron, and the adsorption process obeys the Langmuir isotherm. The research results show that the perimidine derivatives can improve the durability of concrete structures.
1. Introduction
In a chloride salt and marine environment, the reinforcement in concrete is more vulnerable to corrosion by chlorine ions, which quickens the corrosion of steel and then shortens the service life of the concrete structure [1,2]. This not only has hidden social security dangers but likewise causes huge economic losses for the country [3,4]. Accordingly, it is of great significance to solve the corrosion problem of steels in concrete. There are numerous approaches to averting the corrosion of steels in concrete, such as concrete surface coating, epoxy reinforcement, stainless steel reinforcement, cathodic protection, electrochemical chloride removal and corrosion inhibitors for reinforcement, etc. [5]. Due to the simple application, low cost and remarkable rust resistance effect of corrosion inhibitors, which are widely used in the concrete industry, people are paying more and more attention to the research of inhibitors for reinforced steel in concrete [6]. Currently, there are three types of corrosion inhibitors: inorganic, organic and mixed corrosion inhibitors [7]. The inorganic inhibitors are mainly nitrite. On the one hand, nitrite has a poor resistance effect. On the other hand, it has carcinogenic effects. Hence, many countries have banned the use of nitrite in the concrete field [8,9].
In recent years, numerous people have begun to study the synthesis of organic corrosion inhibitors with simple methods and good rust resistance effects. The efficiency of a corrosion inhibitor is linked to its structure [10]. The corrosion inhibition mechanism mainly includes physical adsorption, chemical adsorption and π bond adsorption. Generally, heteroatoms such as sulfur, phosphorus, oxygen, nitrogen and π electrons interact with the empty d orbital of iron to form a coordination bond [11]. Therefore, the inhibitors are adsorbed on the iron surface, showing good inhibition efficiency [12]. For example, naphthalene and pyrimidine derivatives, which are electron-rich aromatic and heteroaromatic compounds, have been proven to be superior corrosion inhibitors in corrosive media [13]. It is predicted that perimidine derivatives can play an effective inhibitory role in aggressive media because their naphthalene rings are fused with pyrimidine rings. In this study, 1H-perimidine (PMD) and 1H-perimidine-2-thiol (SPMD) were prepared, and their corrosion properties on metal in a simulated concrete pore (SCP) solution were investigated. The mechanism of perimidine derivatives adsorbing on the iron surface was equally further studied through theoretical chemical calculations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Inhibitors
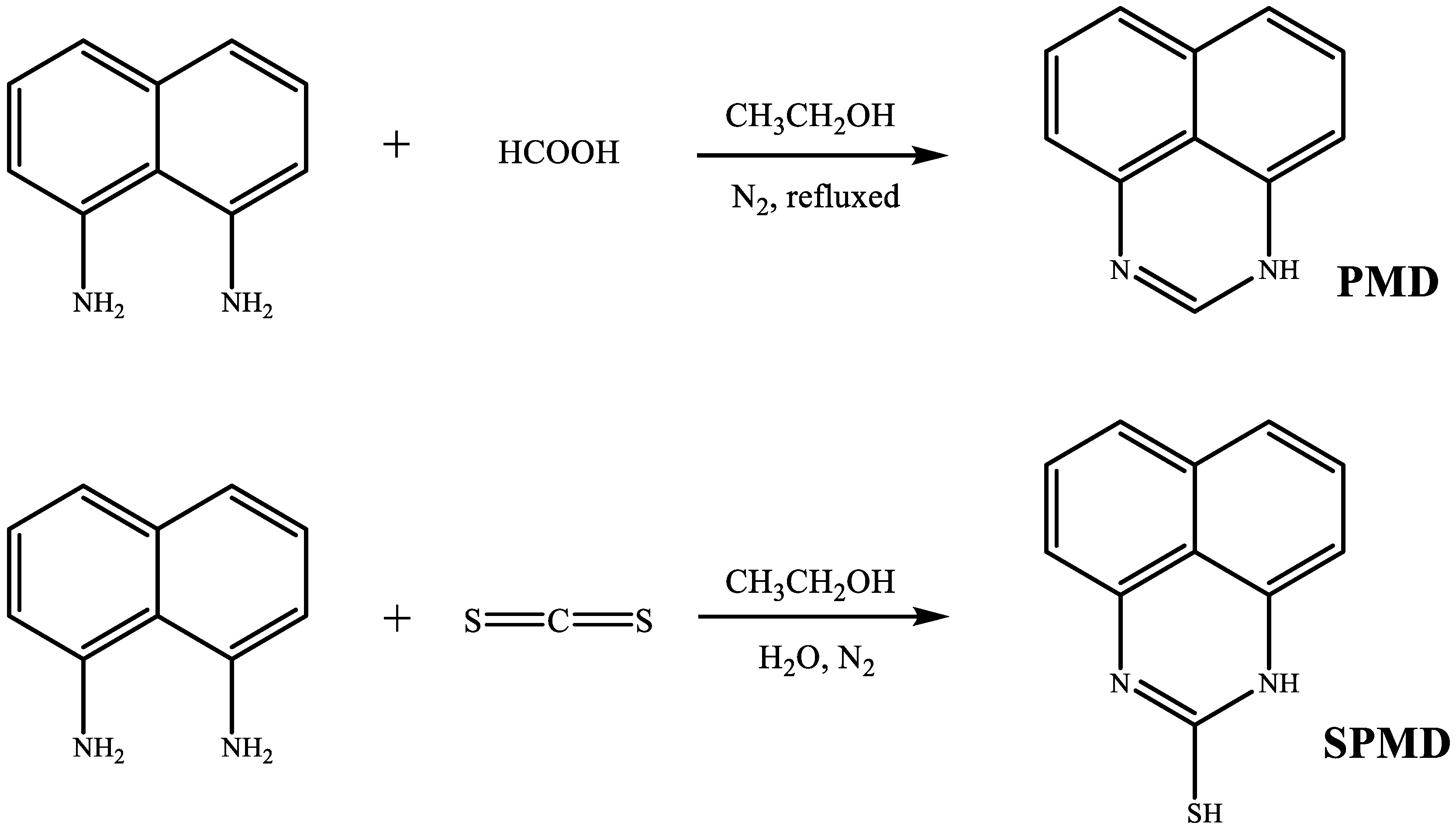
PMD and SPMD were synthesized through a modified procedure reported previously [14,15], as shown in Figure 1.
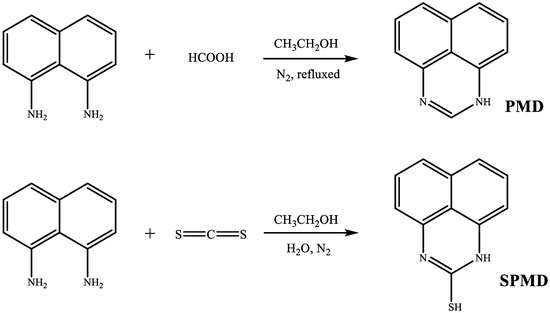
Figure 1.
Synthesis routes of PMD and SPMD.
2.1.1. 1H-perimidine (PMD)
To naphthalene-l,8-diamine (7.49 g, 47.40 mmol) in ethanol (25 mL), formic acid (10.53 mL, 0..27 mol) was added. The resulting mixture was refluxed under N2 for 2 h, and then the reaction mixture was diluted with water and alkalized with NH4OH (17.3%). The sediment was dried under vacuum. The product was recrystallized from ethanol to obtain yellow crystals. Yield 6.53 g (87 %). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, D2O) δ ppm: 8.43 (s, 1H), 7.37 (br s, NH), 7.05 (d, 2H), 6.92 (t, 2H), 6.05 (d, 2H). IR (KBr) v: 3430, 2914, 1628, 1503, 1379, 1039.
2.1.2. 1H-Perimidine-2-thiol (SPMD)
To naphthalene-l,8-diamine (5.93 g, 37.50 mmol) in 95% aqueous ethanol (30 mL) solution, KOH (15.00 mg, 0.27 mmol) and CS2 (2.70 mL, 45.00 mmol) were added under a nitrogen atmosphere. Precipitation of the product began almost immediately, and after 30 min, the mixture was filtered to give 1H-perimidine-2-thiol as a gray solid. Yield 6.76 g (90%). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 10.35 (s, 1H, NH), 7.82 (t, 2H), 7.59 (t, 2H), 7.43 (d, 2H), 2.88 (s, 1H, SH). IR (KBr) v: 3425, 2944, 2543, 1605, 1510, 1385, 1042.
2.2. Materials
The chemicals were analytical grade (>98.5% pure). The specimens were HRB400 reinforced steel containing 0.24 wt.% C, 1.6 wt.% Mn, 0.75 wt.% Si, 0.05 wt.% S, 0.045% P and balance iron. The test solution used in all experiments was a simulated concrete pore (SCP) solution, which was 3.5% NaCl saturated with a Ca(OH)2 solution (pH 12.5). Ultrapure water was used to prepare the experimental solution for electrochemical measurements. Different concentrations (0.02 to 0.12 mM) of corrosion inhibitors were prepared in the simulated concrete pore solution.
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were performed using a PARSTAT 4000 electrochemical workstation. A typical three-electrode cell was used, equipped with a platinum electrode as the auxiliary electrode and a Ag/AgCl, KClsat electrode as the reference electrode. An epoxy-encapsulated HRB400 reinforced electrode with an exposed area of 1.0 cm2 was employed as the working electrode. Before the test, the HRB400 reinforced electrode was ground with different sandpapers (grades 500, 800, 1000, 1500 and 2000), cleaned with distilled water and ethanol for 3 minutes, and finally dried under N2 for standby use. The HRB400 reinforced electrode was submersed in the SCP solution with perimidine derivatives. After three days, potentiodynamic polarization curves were measured in a range of −0.5 V to 1.0 V with a scan rate of 0.5 mV/s. EIS tests were conducted at 25 °C in the three-electrode cell. The measurement was conducted at open-circuit potential (OCP) over the frequency range of 100 kHz–10−2 Hz with an amplitude of 10 mV. The test data were analyzed by the software of the PARSTAT 4000 electrochemical workstation.
2.4. Surface Morphological Test and Contact Angle Analysis
HRB400 reinforced steel was submersed in the SCP solution with perimidine derivatives. The steel specimens were immediately taken out for three days, the corrosion products on the steels were removed with distilled water and anhydrous ethanol successively, and then scanning electron microscope measurements were conducted using a Quanta 250 instrument(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Contact angles of specimens exposed to the SCP solution without and with 0.12 mM PMD and SPMD were measured using a DSA255 Contact Angle Tester (KRUSS, Hamburg, Germany). with a 2 mL liquid drop.
2.5. Quantum Chemical Calculations
GAMESS-US software was used to the study of the perimidine derivative molecules using density functional theory (DFT), with the B3LYP functional under the 6-31G (d) basis sets [16,17]. The removal of imaginary frequencies was carried out to confirm that the optimized geometries are true minima. The Debye (μ), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy (ELUMO) and highest occupied molecular orbital energy (EHOMO) were calculated using the software. Other electronic properties were obtained by the following equations:
where ΔE is the gap energy between the HOMO and LUMO, A is electronic affinity, I is ionization potential, χ is electronegativity and η is chemical hardness. In addition, the transferred electrons (ΔN) can be computed from Equation (6) [18]:
where is 7 eV, is the electronegativity of the inhibitor, is the absolute electronegativity of the inhibitor, and is the absolute electronegativity of iron, which is 0 eV [19].
ΔE = ELUMO – EHOMO
A = −ELUMO
I = −EHOMO
χ = (I + A)/2
η = (I − A)/2
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Experiments
3.1.1. Potentiodynamic Polarization (PDP)
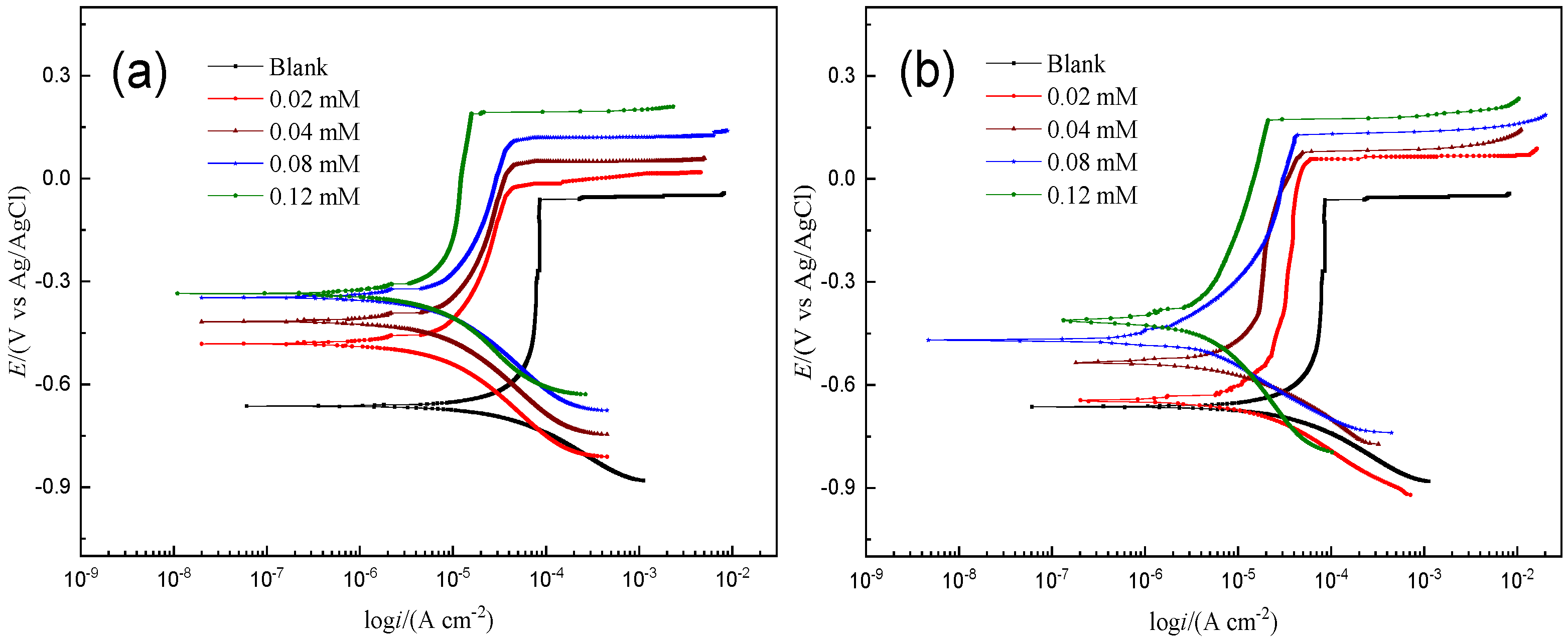
Figure 2 shows the potentiodynamic polarization curves of reinforced HRB400 steel in the SCP solution at 25 °C. From the polarization curve, the corrosion potential (Ecorr), the pitting potential (Epit), the corrosion current density (Icorr), cathodic and anodic Tafel slopes (βc and βa) and inhibition efficiency (IE) can be obtained [20]. All parameters are listed in Table 1. The inhibition efficiency is expressed as [21]:
where and are the current densities of the working electrode without and with a corrosion inhibitor.
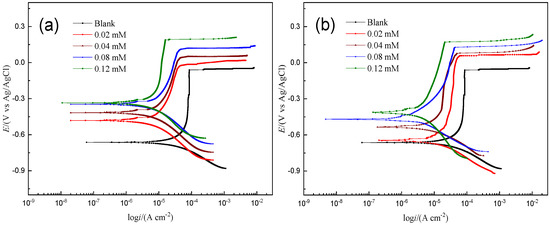
Figure 2.
Potentiodynamic polarization for the corrosion of HRB400 reinforced steel in SCP solution with different concentrations of PMD (a) and SPMD (b) at 25 °C.

Table 1.
PDP parameters for HRB400 reinforced steel in SCP solution.
In general, as the concentration of PMD or SPMD increases, the corrosion current density gradually decreases in the SCP solution. In other words, as the concentrations of inhibitors increase, the inhibitors gradually adsorb on iron. Therefore, iron can effectively prevent corrosion from chloride ions. For the anodic curve, the addition of inhibitors significantly inhibited the dissolution of HRB400 reinforcement in the SCP, and with the increase in the perimidine derivative concentration, the inhibition of iron anode dissolution was greater, and the shape of the Tafel curve remained unchanged. The results show that the process of the anode inhibiting the iron reaction has not changed [22,23]. The cathodic curve also effectively inhibited corrosion and prevented the oxygen reduction reaction. In addition, the inhibitory effect was more pronounced in the anode part, indicating that the perimidine derivatives are inhibitor molecules with a better anodic inhibition performance.
The electrochemical parameters for HRB400 reinforced steel in the SCP solution with different concentrations of PMD (a) and SPMD (b) at 25 °C are presented in Table 1. The surface coverage (θ) is equal to the inhibition efficiency (IE). It can be seen from Table 1 that with the increase in the perimidine derivative concentration, the corrosion potential gradually shifts positively, and the potential shifts by more than 85 mV after adding the inhibitor; the results indicate that the two perimidine derivatives PMD and SPMD are anodic corrosion inhibitors [24,25,26]. The pitting potential is the potential at which the anode current rapidly increases to a higher value when the surface passivation film breaks. The results show that the pitting potential increases gradually with the increase in the perimidine derivative concentration, suggesting that the inhibitors can inhibit the corrosion of chloride ions on the surface of the reinforced steel. This can be attributed to perimidine derivative molecules and chloride ions competing for the surface of the specimen, and the inhibitor is adsorbed on the metal to prevent the adsorption of chloride ions onto steel surfaces [27,28]. Moreover, after adding the inhibitor, the positive corrosion potential shift will reduce the interaction between chlorine ions and active sites on the iron surface, indicating that greater activation energy is needed if pitting corrosion occurs between chlorine ions and the steel, thus improving the pitting resistance of the sample [29,30].
Furthermore, as the concentration of the perimidine derivative increases, the Icorr value gradually decreases and the surface coverage gradually increases, indicating that the corrosion inhibitory effect is getting better. This effect can be ascribed to the perimidine derivative gradually occupying the active centers of the iron surface and gradually covering the iron surface. Furthermore, the Icorr value of SPMD was smaller than that of PMD, suggesting that SPMD had a better inhibitory effect than PMD.
3.1.2. EIS
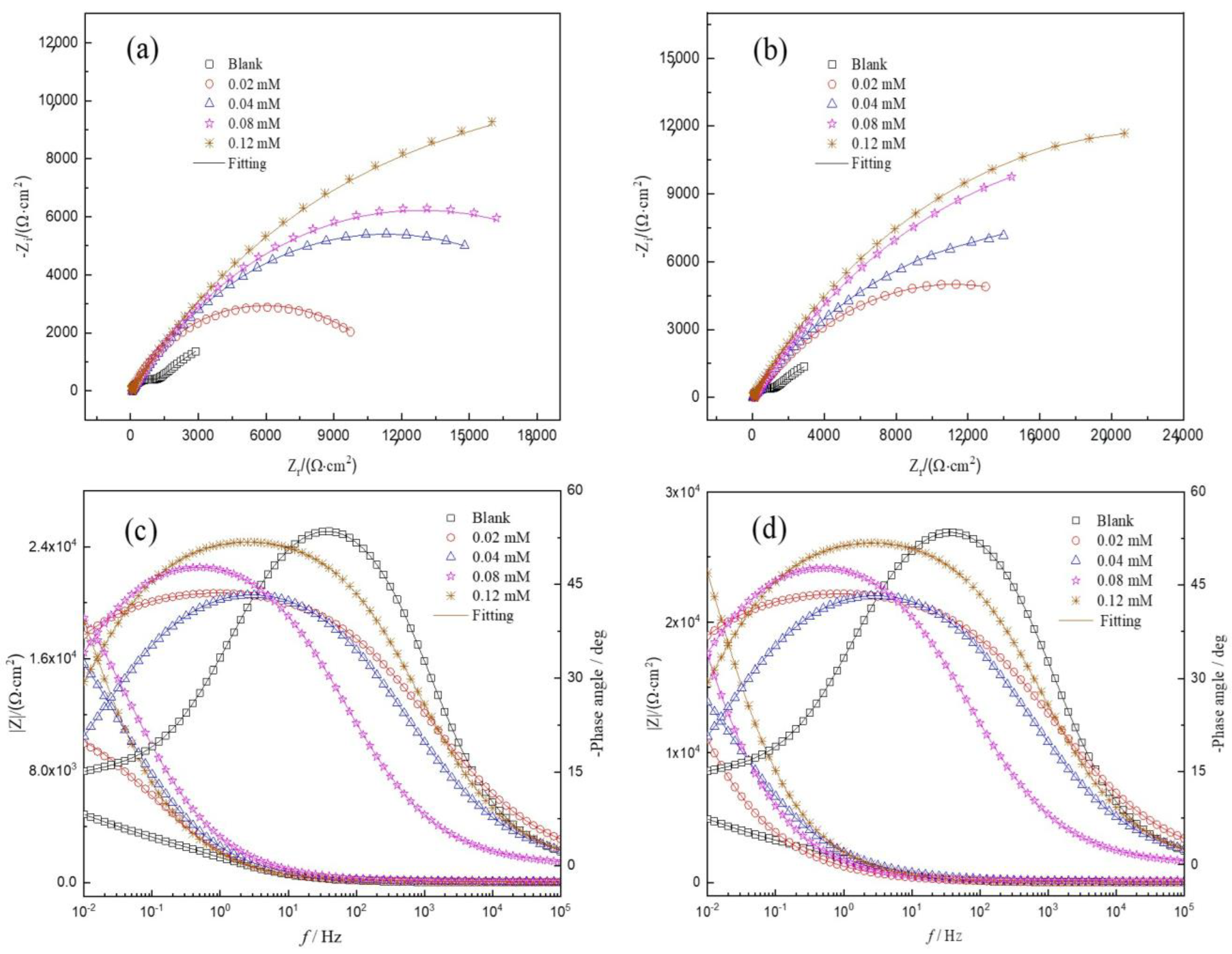
Figure 3 presents the Nyquist plots and Bode plots for HRB400 reinforced steel in the SCP solution with the perimidine derivatives at 25 °C. In the blank SCP solution, pitting corrosion occurred on iron due to corrosion by Cl-. As the immersion time increases, the surface of the steel is more seriously corroded. Therefore, the Nyquist plots show lower capacitive resistance. After adding the perimidine derivative, it can be adsorbed on iron to form an adsorption film to resist erosion by chlorine ions and protect the steel. As the concentration of the perimidine derivative increases, the protective film becomes more complete and dense. Hence, chlorine ions have more difficulty coming into contact with the steel. These results suggest that with the increase in the concentration of the perimidine derivative, the Nyquist capacitive reactance becomes larger and the inhibitory effect becomes stronger, which can also be obtained by analyzing the Bode diagram. It can be observed from the EIS in Figure 3 that the capacitive reactance of SPMD is larger than that of PMD at the same concentration, which suggests that the IE of SPMD is better than that of PMD in the SCP solution.
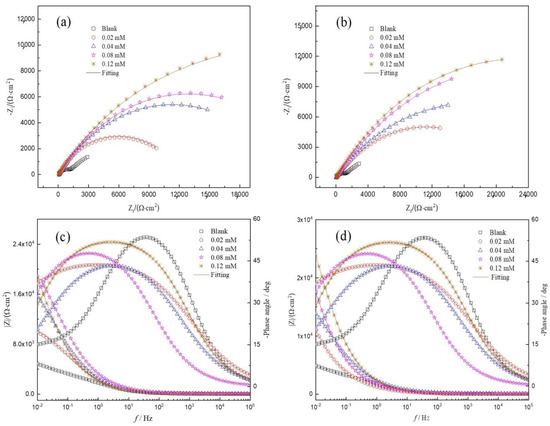
Figure 3.
EIS plots for reinforced steel in SCP with perimidine derivatives at 25 °C. Top: Nyquist diagrams; bottom: Bode diagrams. PMD (a) and (c); SPMD (b) and (d).
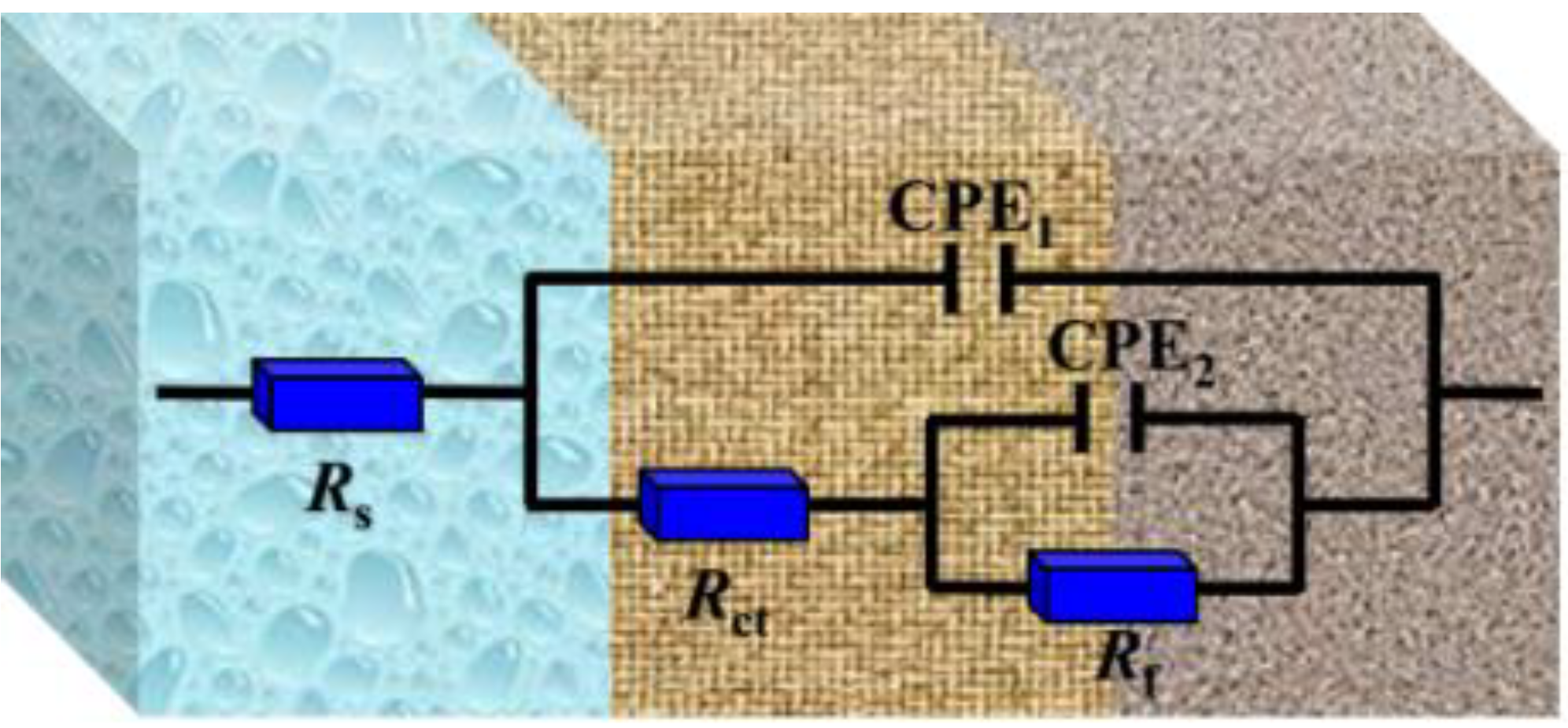
In addition, the capacitive reactance of Nyquist plots is slightly depressed as a semicircular shape in the absence and presence of perimidine derivatives, where the deformation of the capacitance semicircle is attributed to surface roughness or unevenness [31]. Figure 3 shows that the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy has two characteristics of time constants in the SCP solution without and with inhibitors. These results reveal that the first time constant is related to the properties of the charged double electric layer; that is, charge transfer or material transfer occurs in the corrosion process [32]. A high frequency is related to the protective film on the iron, which is the film formed by inhibitor molecules, iron oxide and hydroxide [33]. The electrochemical parameters were obtained by the equivalent circuit in Figure 4. In the equivalent circuit diagram, RS is the solution resistance, Rf is the passivation/adsorption film resistance and Rct is the charge transfer resistance. CPE1 and CPE2 are the double electric layer and the adsorption film constant phase element, respectively. In order to obtain a fitting curve that is more consistent with the experimental data, the constant phase component CPE is used in the equivalent circuit to replace the pure capacitor, thereby obtaining more reliable fitting data. The constant phase element (ZCPE) is shown in the following equation [34]:
where Y0 is a proportional coefficient, ω is the angular frequency, n is the phase shift, j is the imaginary number and j2 = −1. For n = −1, CPE is a pure inductance element. For n = 0, CPE is a pure resistance element. For n = 0.5, CPE is a Warburg element, and for n = 1, CPE is a pure capacitor element. The value of n depends on the non-uniformity and roughness of the metal surface. The inhibition efficiency (IE) is given as:
where and are the charge transfer resistance of the steel electrode without and with the perimidine derivatives.
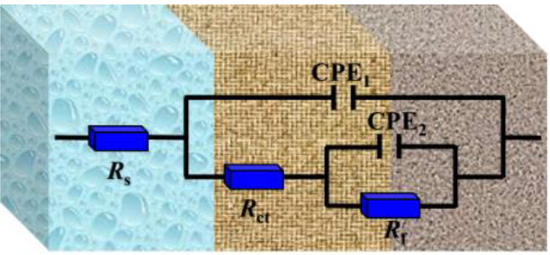
Figure 4.
Equivalent circuit used to fit the impedance spectra.
The EIS parameters are displayed in Table 2, which could be obtained by the equivalent circuit. It was observed that with the increase in the perimidine derivative concentration, the Y0 value in CPE1 and CPE2 gradually decreased, where the decrease in Y0 in CPE1 indicates that inhibitor molecules gradually replace water and other substances on the surface of reinforcement, leading to a decrease in the dielectric constant or an increase in the thickness of the double electric layer, which reduces the double-layer capacitance in turn. In addition, corrosion inhibitor molecules gradually adsorb onto iron, resulting in a decrease in film capacitance (CPE2) and an increase in film resistance (Rf) and charge transfer resistance (Rct) [35], thereby inhibiting the erosion effect of chloride ions on the reinforcement. On the one hand, inhibitors are adsorbed on iron, reducing chloride ion adsorption on active sites [36] and reducing pitting corrosion and local rust. On the other hand, inhibitor molecules adsorb to form a film on the reinforcement, and with the increase in the perimidine derivative concentration, the protective film becomes more complete and dense so as to prevent erosion by chloride ions. Furthermore, both PMD and SPMD at a concentration of 0.12 mM can obviously inhibit corrosion by chlorine ions in the SCP solution. It is worth noticing that SPMD has better IE than PED at the same concentration. In other words, SPMD has better corrosion resistance than PED, which is also consistent with the results of the potentiodynamic polarization test.

Table 2.
EIS parameters of reinforced steel in SCP solution with perimidine derivatives.
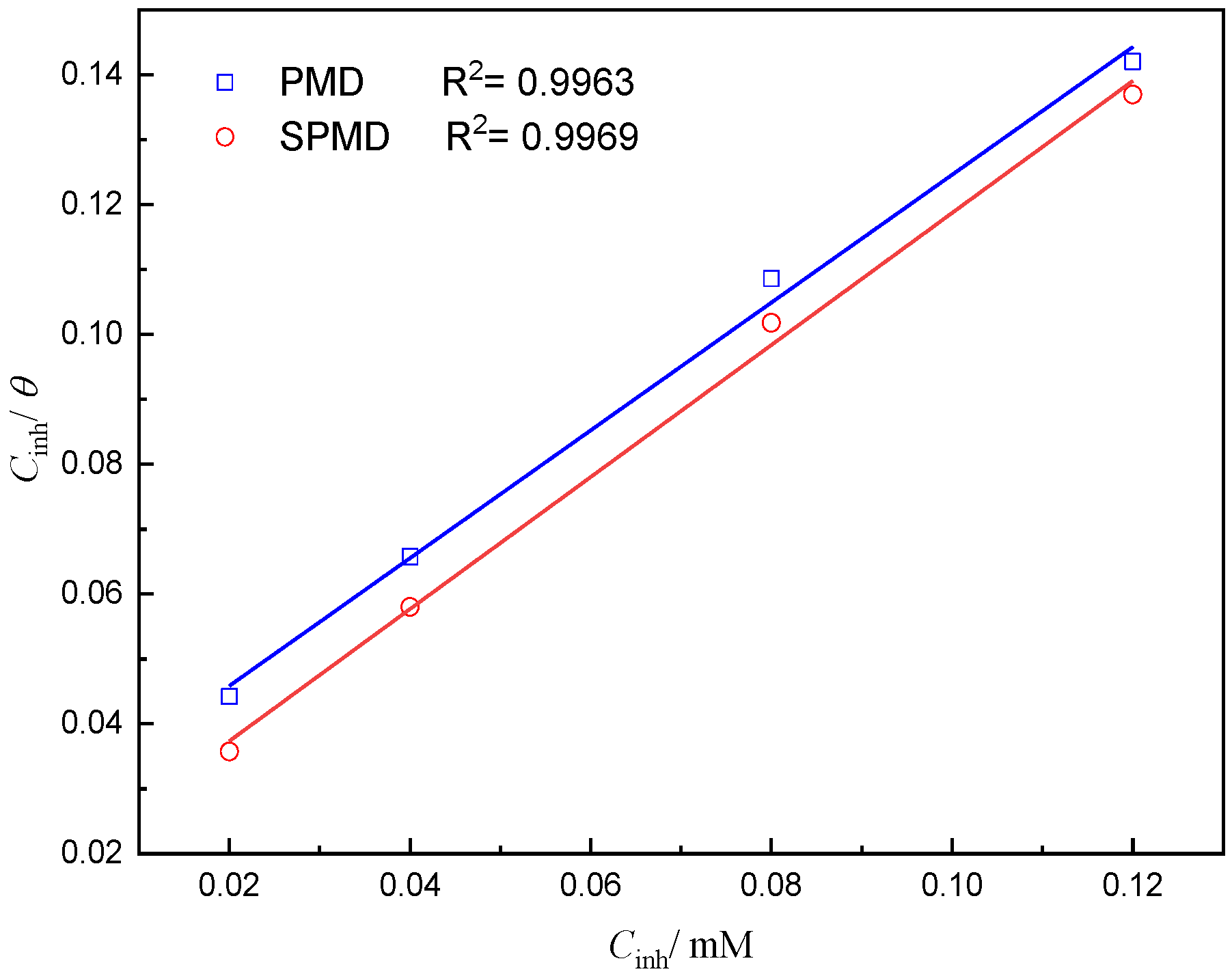
3.2. Adsorption Isotherm and Thermodynamic Calculation
Information on the interaction between the perimidine derivative and the metal surface can be obtained from the adsorption isotherm. The surface coverage (θ) can be obtained from PDP measurements. The PDP results of PMD and SPMD were plotted as C/θ versus C to obtain two adsorption curves that almost showed a straight line and a linear correlation coefficient (R2) > 0.99 (Figure 5). It can be seen that the adsorption of perimidine derivatives on the iron obeys the Langmuir isotherm, and the formula is as follows [37]:
where C is the concentration of the perimidine derivative, Kads is the equilibrium constant of adsorption, and θ is the surface coverage rate of steel [38]. In addition, the standard adsorption free energy () can be defined as follows (11):
where R is the molar gas constant, which is 8.314 J/(mol·k), and T is the thermodynamic temperature [39].
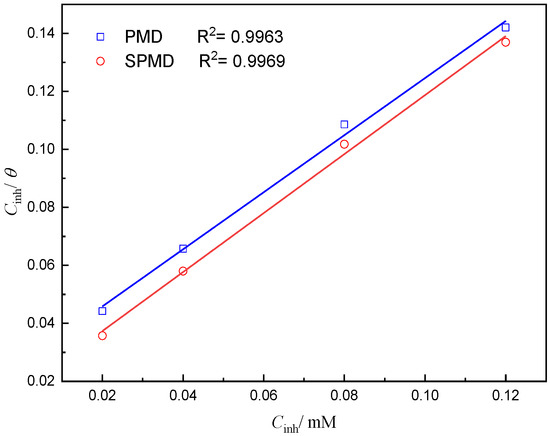
Figure 5.
Curve fitting of corrosion data for reinforced steel in SCP solution with different concentrations of perimidine derivatives to Langmuir adsorption isotherm at 25 °C.
Table 3 presents the thermodynamic parameters from the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The values for PMD and SPMD are −36.11 and −37.18 kJ/mol, respectively, suggesting that the perimidine derivative molecules can be spontaneously adsorbed on iron. Generally, the absolute value is between 20 and 40 kJ·mol−1, indicating that the perimidine derivatives undergo both physical and chemical adsorption through electrostatic action on the surface of the metal [40,41]. Furthermore, the larger the adsorption equilibrium constant of SPMD means that there is a stronger force between SPMD and the metal surface than PMD.

Table 3.
Thermodynamic and equilibrium adsorption parameters for inhibitor adsorption behavior on iron in SCP solution.
3.3. Surface Morphology
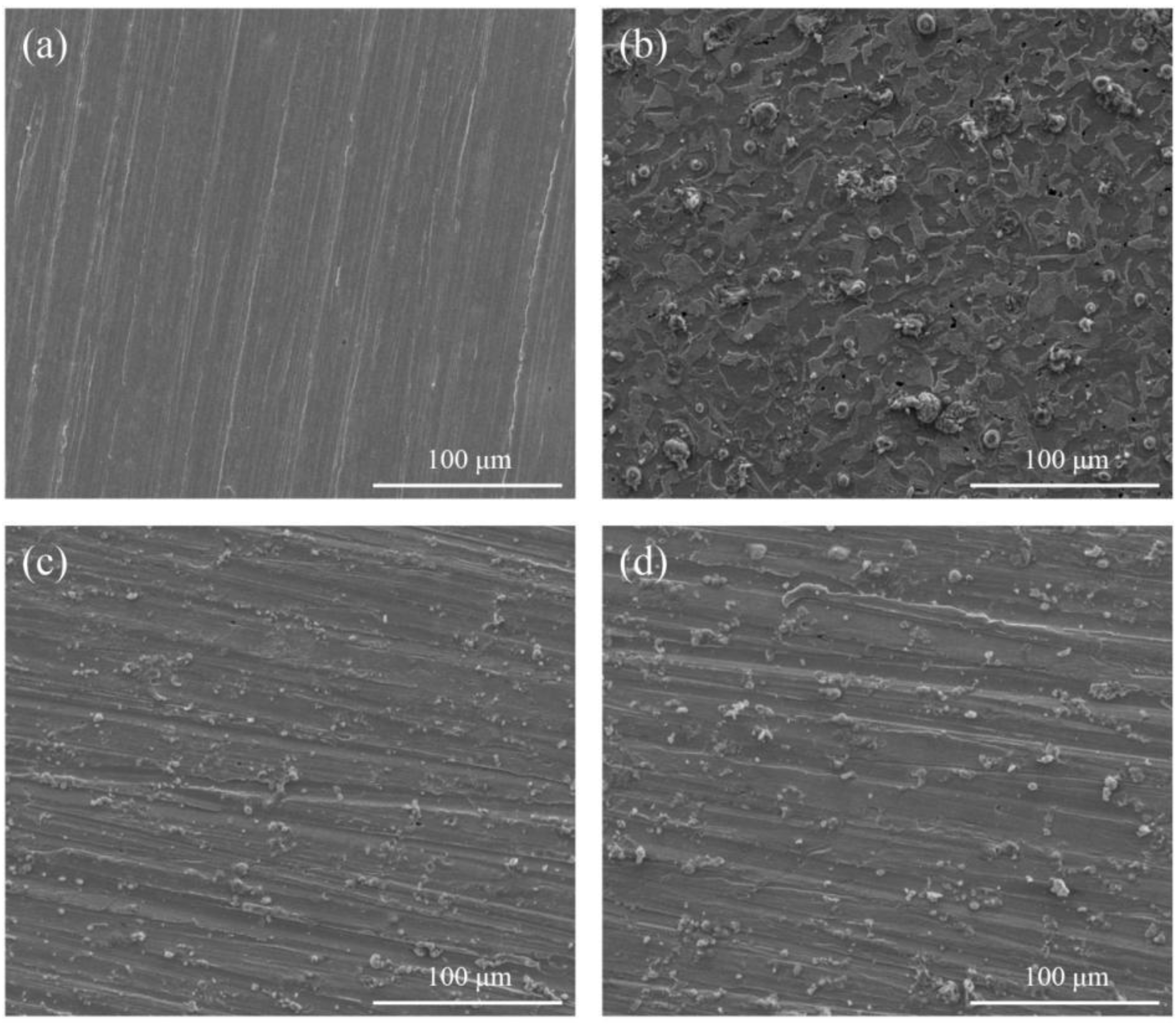
In order to further verify the corrosion inhibition effect of PMD and SPMD on reinforced steel, SEM was used to analyze the morphology of the steel before and after immersion. Figure 6 displays the SEM pictures of specimens immersed in SCP in the absence and presence of 0.12 mM perimidine derivatives after 3 days: (a) before submersion, (b) after submersion in the SCP solution without an inhibitor, (c) after submersion in SCP with 0.12 mM PMD, (d) after submersion in SCP with 0.12 mM SPMD. The reinforced steel surface is smooth without holes, and there are distinct abrading stripes (Figure 6a). Due to the corrosion effect of chlorine ions on reinforced steel, the surface has obvious pitting holes and has a seriously damaged morphology in the uninhibited SCP solution (Figure 6b). After immersion in SCP with an inhibitor, the corrosion of the iron surface is significantly improved (Figure 6c,d), and the abrading stripes can still be observed. Because the perimidine derivatives adsorb on iron to form a film to protect the steel, erosion by chloride ions is prevented. Furthermore, the clearer the polishing stripe of steel submersed in SCP with SPMD, the fewer the pitting holes in the steel. The results indicate that SPMD is more effective than PMD in the concentration range of this study.
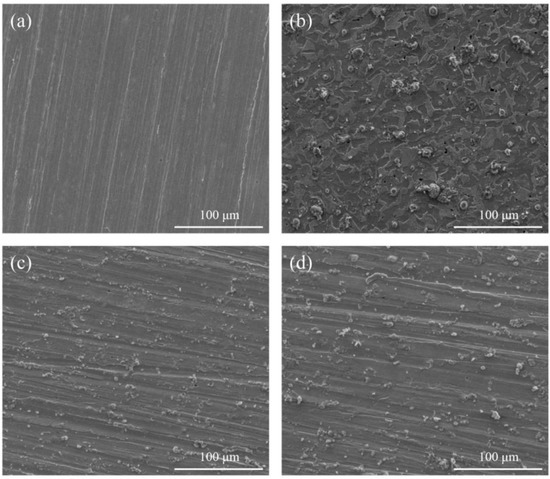
Figure 6.
SEM of the specimen after submersion in SCP solution with inhibitors. (a) Clean specimen; (b) reinforced steel in SCP; (c) reinforced steel in SCP with 0.12 mM PMD; (d) reinforced steel in SCP with 0.12 mM SPMD.
3.4. Contact Angle and Surface Free Energy
The adsorption of perimidine derivatives can be tested by performing a contact angle experiment. The surface free energy value calculation formula is as follows [42,43]:
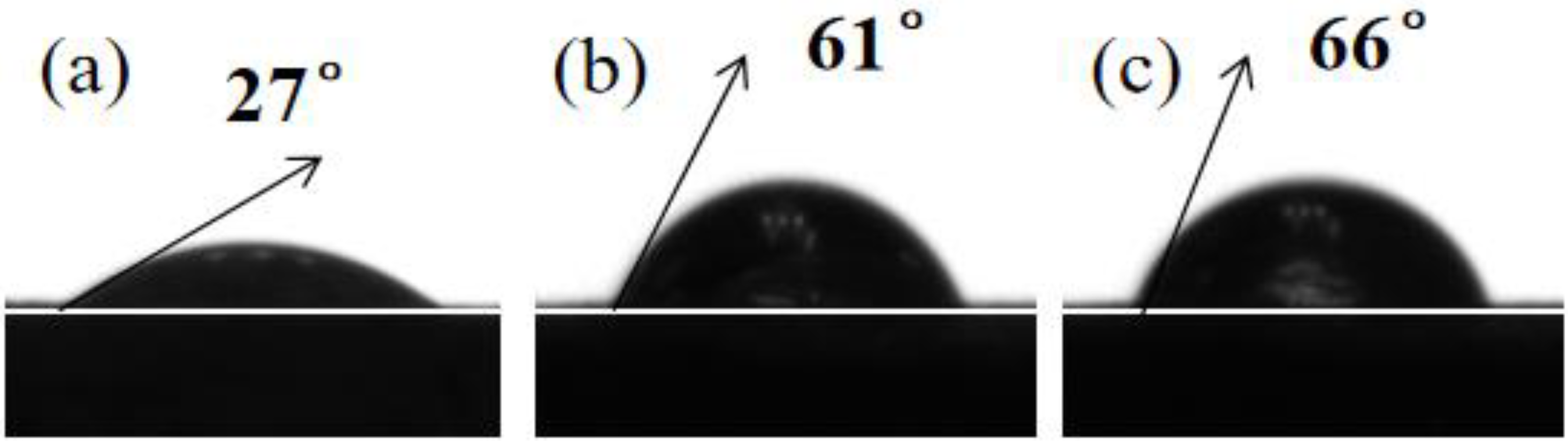
where γlv is the surface tension of water, γsv is the surface free energy of the iron specimen, α is the contact angle, WA is the work of adhesion, and β is a constant value, which is 0.0001247 (mJ/m2)−2 [44]. The contact angle images for reinforced steel in the SCP solution in the absence and presence of 0.12 mM PED and HPED are shown in Figure 7.
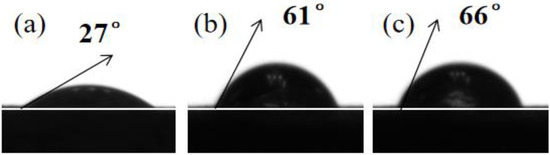
Figure 7.
Contact angle pictures for the specimen exposed to SCP with and without 0.12 mM PMD and SPMD: (a) SCP; (b) SCP + 0.12 mM PMD; (c) SCP + 0.12 mM SPMD.
From Table 4, it is evident that the order of the contact angles of HRB400 reinforced steel in different solutions is αSCP (27°) < αPED (61°) < αHPED (66°). The low α value is due to the presence of oxides and corrosives on iron that caused water droplets to spread on the sample surface [45]. The α value of SPMD is higher than that of PMD, indicating that SPMD has fewer corrosion products on iron. In addition, with the addition of perimidine derivatives, the γsv value of SPMD decreases, and the γsv value of SPMD is lower than that of PMD. In other words, the higher the γsv value, the more active the metal surface, and the more likely chloride ions are to corrode the metal. Therefore, these results suggest that SPMD has higher inhibition efficiency according to α and γsv.

Table 4.
Obtained α and γsv values for samples exposed to SCP without and with 0.12 mM PMD and SPMD.
3.5. Quantum Chemical Calculations
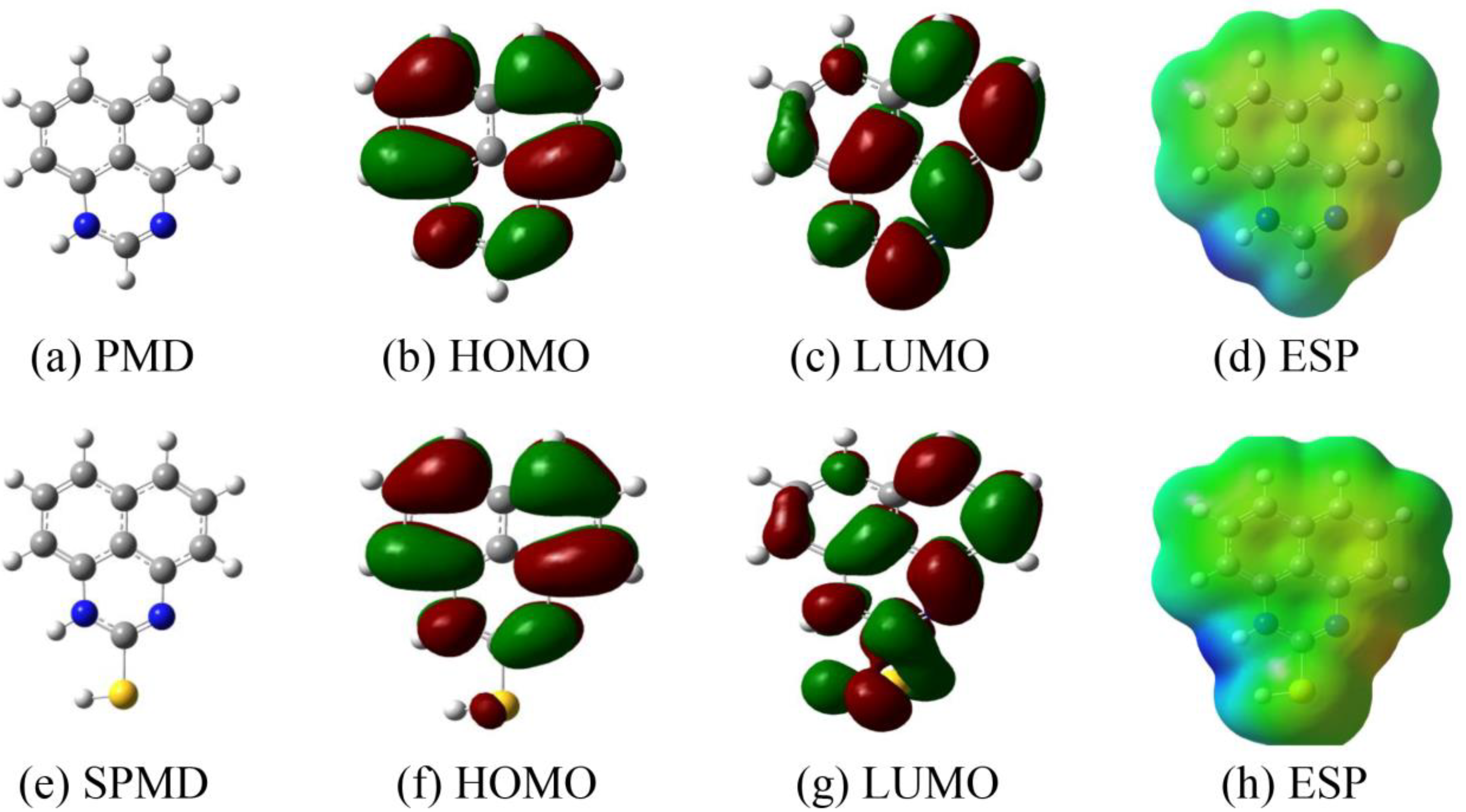
Figure 8 shows the PMD and SPMD molecular structure optimization, ESP and the frontier molecular orbitals (HOMO and LUMO). When the molecular structure is optimized, the frequency calculation is positive, and the molecules have reached the ground state, indicating that the potential surface was at the minimum value. The study of the lowest unoccupied orbital (LUMO) and the highest occupied orbital (HOMO) is an indispensable method in analyzing the adsorption effect of perimidine derivatives [46,47]. For molecular structure optimization, the fusion of large bonds with the N-heterocyclic ring makes PMD and SPMD appear as planar structures. The HOMO distribution of PMD and SPMD is relatively uniform in the whole molecular structure, which indicates that both the large bond and the N-heterocyclic ring can provide electrons to metal atoms. However, the LUMO of PMD is obviously concentrated in N-heterocyclic fragments and one of the benzene rings, and the distribution is not uniform, which also indicates that these fragments play a more important role in receiving electrons. While the LUMO distribution of SPMD is relatively uniform, each fragment has the same ability to receive electrons from metal.
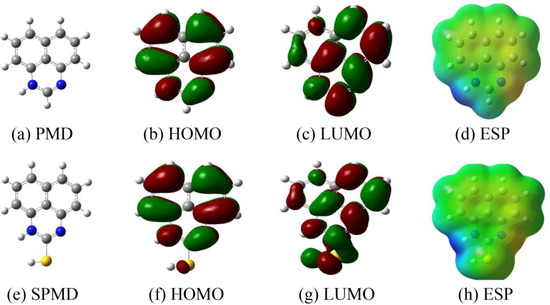
Figure 8.
Structures of HOMO, LUMO and ESP of perimidine derivatives.
In order to quantitatively measure the reactivity of PMD and SPMD and the ability to donate/receive electrons, the global quantization parameters are presented in Table 5. The highest occupied orbital energy (EHOMO) reflects the ability to donate electrons. The greater the EHOMO value, the stronger the electron-donating ability of the molecule. The lowest unoccupied orbital energy (ELUMO) reflects its ability to accept electrons. Furthermore, the difference between the two is the energy gap (ΔE); the smaller its value, the stronger the adsorption of the molecules on iron, and the better effect [48]. From Table 5, the energy gap (ΔE) of SPMD is smaller than that of PMD, indicating that SPMD has a stronger electron-donating ability [49].

Table 5.
Quantum chemical parameters of perimidine derivatives.
The 2-position sulfhydryl group of SPMD tends to bond with the empty d orbital of the iron atom [13], and its strong electron-accepting ability means that SPMD has a better inhibitory effect [50]. In addition, electronegativity is related to chemical potential. A higher electronegativity means a greater effect. Table 5 shows that χSPMD > χPMD, indicating that the inhibition efficiency of SPMD is better than that of PMD, which is also consistent with the experimental results. The transferred electrons (ΔN) can be calculated by Equation (6), and ΔN > 0 indicates electron transfer to the metal atoms [18,51]. The results reveal that the perimidine derivatives provide electrons to iron to form coordination bonds and are more strongly adsorbed on the metal.
3.6. Mechanism of Adsorption
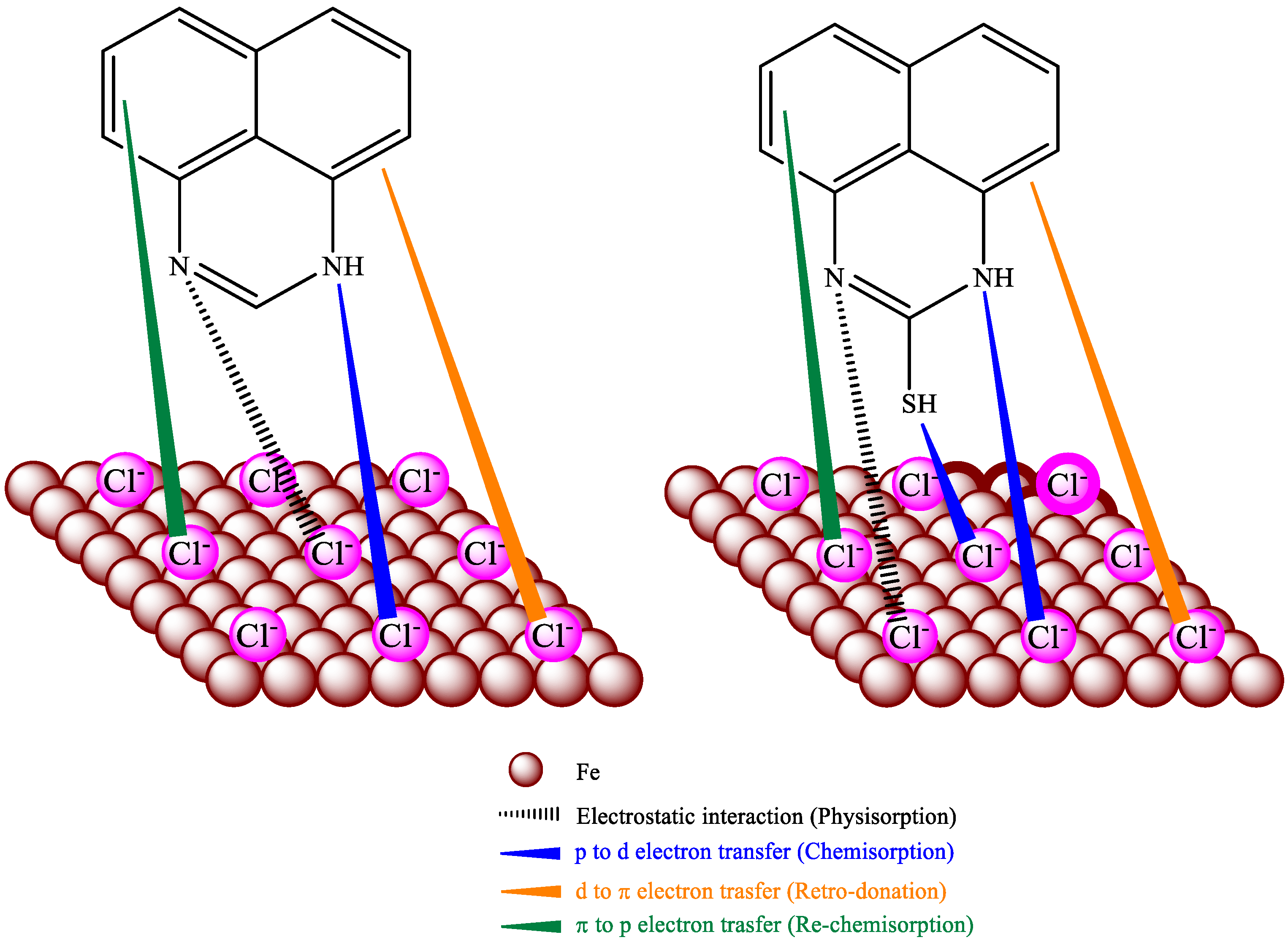
Figure 9 clearly describes the adsorption mechanism of perimidine derivatives on HRB400 steel. The perimidine derivatives are effectively adsorbed on iron. Through physical, chemical and re-chemisorption on iron, it can inhibit corrosion by Cl− on steel in an alkaline medium [52]. Nitrogen atoms in perimidine derivatives are physically adsorbed by protonation with negatively charged chloride ions on the steel. In addition, the lone pair of electrons in the heteroatoms are combined with the empty d orbital of iron atoms and adsorbed on the iron through chemical action [53]. For example, the lone pair of electrons of nitrogen and sulfur atoms in the SPMD molecule can coordinate with iron atoms to form bonds and adsorb strongly on the metal surface, preventing charge transfer in the corrosion process and enhancing the stability of the protective film. Furthermore, retro-donation occurs, in which the filled iron orbitals share d-electron pairs with the vacant anti-bonding π orbitals in the phenyl rings. The delocalized π-electron pairs transfer to the vacant 3d orbitals of iron to promote the chemical action, which is re-chemisorption. It can be concluded that perimidine derivatives isolated iron from the free Cl− by forming a protective layer.
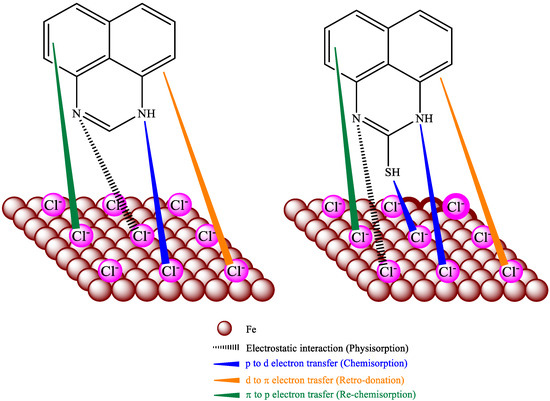
Figure 9.
Inhibition and adsorption mechanisms of PMD and SPMD.
4. Conclusions
(1) PMD and SPMD are perimidine derivatives, which can inhibit the corrosion of reinforced steels in a simulated concrete pore solution. With the increase in the concentration of the inhibitor, the inhibition efficiency is gradually improved. The perimidine derivatives can effectively inhibit the corrosion of chloride ions. Moreover, SPMD has a better inhibition efficiency in the concentration range of this study.
(2) The adsorption types of perimidine derivatives on reinforced steel obey Langmuir adsorption isotherms. The standard adsorption free energy values for PMD and SPMD are −36.11 and −37.18 kJ/mol, respectively. The inhibitor molecules can spontaneously adsorb on iron to form a protective film, and the interaction is stronger between SPMD and the iron surface than PMD.
(3) The various chemical parameters of PMD and SPMD can be calculated through quantum chemical calculations. The energy gap of SPMD is smaller than that of PED, and SPMD has a stronger ability to accept and donate electrons. In addition, the electronegativity of SPMD is greater than that of PMD. Therefore, SPMD exhibits a higher inhibition efficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and Q.M.; methodology, J.C.; software, H.Z.; formal analysis, Q.M.; resources, J.L.; data curation, K.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.M.; project administration, J.H.; funding acquisition, S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (No. 2021YFF0500803), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51908254 and 52078240) and the National Science Foundation for Outstanding Youth project of China (Grant No. 51825203).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhi, F.; Jiang, L.; Jin, M.; Xu, P.; Xiao, B.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, L.; Gu, Y. Inhibition effect and mechanism of polyacrylamide for steel corrosion in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 120425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Shu, H.; Wang, J. Study on the influence of compound rust inhibitor on corro-sion of steel bars in chloride concrete by electrical parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120763–120777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.; Ebenso, E.E. Quinoline and its derivatives as corrosion inhibitors: A review. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.G.; Yunovich, M.; Dunmire, D. Cost of corrosion and corrosion maintenance strategies. Corros. Rev. 2007, 25, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, G.; Escadeillas, G.; Arliguie, G. Electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) from steel-reinforced concrete specimens contaminated by “artificial” sea-water. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, D.; Criado, M.; La Iglesia, V.; Fajardo, S.; La Iglesia, A. Comparative study of three sodium phosphates as corrosion inhibitors for steel reinforcements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 43, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Chen, N.; He, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, K.; Wang, P.; Xu, P. Effects of corrosion inhibitor and functional components on the elec-trochemical and mechanical properties of concrete subject to chloride environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119724–119737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Alonso, M. Electrochemical chloride removal in reinforced concrete structures: Improvement of effectiveness by simultaneous migration of calcium nitrite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarce, M.B.; Vazquez, M. Carbon steel passivity examined in alkaline solutions: The effect of chloride and nitrite ions. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5007–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Quraishi, M.; Prakash, R. A self-doped conducting polymer “polyanthranilic acid”: An efficient corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic solution. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzadeh, M.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Sanaei, Z. Adsorption mechanism and synergistic corrosion-inhibiting effect between the green Nettle leaves extract and Zn2+ cations on carbon steel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 77, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. Experimental and theoretical studies for corrosion inhibition of carbon steel by imidazoline deriv-ative in 5% NaCl saturated Ca(OH)2 solution. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 58, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Mao, J.; Ma, Q.; Tang, Y. Corrosion inhibition of perimidine derivatives for mild steel in acidic media: Electrochemical and computational studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, J.; Woodgate, P.; Denny, W. Potential antitumor agents. 53. Synthesis, DNA binding properties, and biological activity of perimidines designed as minimal DNA-intercalating agents. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 2081–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Sturla, S.J. A Synthetic Nucleoside Probe that Discerns a DNA Adduct from Unmodified DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4882–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Zhang, B.; Chi, H. Corrosion inhibition efficiency of compound nitrite with D-sodium gluconate on carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 288, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, R.G.; Vengatesh, G.; Sundaravadivelu, M. Surface morphological and quantum chemical studies of some expired drug molecules as potential corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in chloride medium. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 22, 100841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Banerjee, P. A theoretical approach to understand the inhibition mechanism of steel corrosion with two aminoben-zonitrile inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71120–71130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Safi, Z.; Shi, W.; Tüzün, B.; Altunay, N.; Kaya, C. Anticorrosive effects of some thiophene derivatives against the corrosion of iron: A computational study. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Ansari, K.; Quraishi, M.; Obot, I. Pyranpyrazole derivatives as novel corrosion inhibitors for mild steel useful for industrial pickling process: Experimental and Quantum Chemical study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 52, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, J.; Ansari, K.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M.; Obot, I. Pyrimidine derivatives as novel acidizing corrosion inhibitors for N80 steel useful for petroleum industry: A combined experimental and theoretical approach. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 49, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Jin, M.; Bai, S.; Song, S.; Yan, X. Deoxyribonucleic acid as an inhibitor for chloride-induced corro-sion of reinforcing steel in simulated concrete pore solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Tang, Y. Inhibition effect and mechanism of sodium oleate on passivation and pitting corrosion of steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. Investigation on the inhibition behavior of a pentaerythritol glycoside for carbon steel in 3.5% NaCl saturated Ca(OH)2 solution. Corros. Sci. 2012, 54, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, Z.; Ramezanzadeh, M.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Use of Rosa canina fruit extract as a green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution: A complementary experimental, molecular dynamics and quantum mechanics investigation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 69, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, F.A.; Al-Rashed, O.A.; Nazeer, A.A. Controlling of mild-steel corrosion in acidic solution using environmentally friendly ionic liquid inhibitors: Effect of alkyl chain. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, T.; Yu, X.; Chen, D. Corrosion inhibition efficiency of triethanolammonium dodecylbenzene sulfonate on Q235 carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2019, 158, 108097–108109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Nishihara, H.; Aramaki, K. The inhibition of passive film breakdown on iron in a borate buffer solution con-taining chloride ions by organic anion inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valek, L.; Martinez, S.; Mikulić, D.; Brnardić, I. The inhibition activity of ascorbic acid towards corrosion of steel in alkaline media containing chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2705–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Nishihara, H.; Aramaki, K. The inhibition of pit growth on an iron surface in a borate buffer solution containing chloride ion by inhibitors classified as soft bases in the HSAB principle. Corros. Sci. 1995, 37, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, J.; Castaneda, H. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel by an imidazolium ionic liquid compound: The effect of pH and surface pre-corrosion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95160–95170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Koleva, D.; Petrov, P.; Breugel, K. Polymeric vesicles for corrosion control in reinforced mortar: Electrochemical behav-ior, steel surface analysis and bulk matrix properties. Corros. Sci. 2012, 65, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.G.; Searson, P.C.; Dawson, J.L. Use of AC impedance technique in studies on steel in concrete in immersed conditions. Br. Corros. J. 1981, 16, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K.; Quraishi, M. Bis-Schiff bases of isatin as new and environmentally benign corrosion inhibitor for mild steel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2819–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mehthel, M.; Al-Dulaijan, S.; Al-Idi, S.H.; Shameem, M.; Ali, M.; Maslehuddin, M. Performance of generic and proprietary corrosion inhibitors in chloride-contaminated silica fume cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, H.B.; Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; Carpenter, G.J.; Wu, X. Characterization of atomic structure of oxide films on carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solutions using EELS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrini, M.; Suedile, F.; Salvin, P.; Roos, C.; Zarrouk, A.; Jama, C.; Bentiss, F. Bagassa guianensis ethanol extract used as sustain-able eco-friendly inhibitor for zinc corrosion in 3% NaCl: Electrochemical and XPS studie. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100588–100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemapriya, V.; Prabakaran, M.; Parameswari, K.; Chitra, S.; Kim, S.; Chung, I. Dry and wet lab analysis on benzofused hetero-cyclic compounds as effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Qi, S.; He, X.; Tang, Y.; Lu, G. 1,2,3-Triazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium: Experimental and computational chemistry studies. Corros. Sci. 2017, 129, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrag, L.; Hammouti, B.; Elkadiri, S.; Aouniti, A.; Jama, C.; Vezin, H.; Bentiss, F. Adsorption properties and inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric solution by some newly synthesized diamine derivatives: Experimental and theoretical investigations. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3042–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ba, H.; Wu, Z. Sustainable corrosion inhibitor for steel in simulated concrete pore solution by maize gluten meal extract: Electrochemical and adsorption behavior studies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 117080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinejad, S.; Naderi, R.; Mahdavian, M. Effect of inhibition synergism of zinc chloride and 2-mercaptobenzoxzole on protec-tive performance of an ecofriendly silane coating on mild steel. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 48, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Neumann, A.W. A reformulation of the equation of state for interfacial tensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 137, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Le, J.; Chen, Z. Corrosion inhibition properties of two imidazolium ionic liq-uids with hydrophilic tetrafluoroborate and hydrophobic hexafluorophosphate anions in acid medium. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandarinathan, V.; Lepková, K.; Bailey, S.I.; Becker, T.; Gubner, R. Adsorption of corrosion inhibitor 1-Dodecylpyridinium chloride on carbon steel studied by in Situ AFM and electrochemical methods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 5858–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, S.; Mohajernia, S.; Moayed, M.; Davoodi, A.; Rahimizadeh, M.; Momeni, M.; Eslami, A.; Shiri, A.; Kosari, A. Electrochem-ical and quantum chemical study of Thiazolo-pyrimidine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors on mild steel in 1 M H2SO4. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 25, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrefaee, S.H.; Rhee, K.Y.; Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.; Ebenso, E.E. Challenges and advantages of using plant extract as inhibitors in modern corrosion inhibition systems: Recent advancements. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 321, 114666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi-Egbedi, N.; Obot, I. Inhibitive properties, thermodynamic and quantum chemical studies of alloxazine on mild steel corro-sion in H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, N.; Awe, F.; Gimba, C.; Ibisi, N.; Ebenso, E. Experimental and Computational Chemistry Simulation Studies on the inhi-bition potentials of some amino acids for the corrosion of mild steel in 0.1 M. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 931–957. [Google Scholar]
- Machnikova, E.; Whitmire, K.H.; Hackerman, N. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid by furan derivatives. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6024–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.; Awad, M.; Shaker, M.; El-Tahawy, M. The role of structural chemistry in the inhibitive performance of some aminopyrimidines on the corrosion of steel. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdimurodov, E.; Kholikovb, A.; Akbarov, K.; Guo, L. Inhibition properties of 4,5-dihydroxy-4,5-di-p-tolylimidazolidine-2-thione for use on carbon steel in an aggressive alkaline medium with chloride ions: Thermodynamic, electrochemical, surface and theoretical analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114813–114830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.; Quraishi, M.; Rhee, K. Phthalocyanine, naphthalocyanine and their derivatives as Corrosion Inhibi-tors: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116441–116449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).