Influence of Processing Time in Hydrogen Plasma to Prepare Gallium and Aluminum Codoped Zinc Oxide Films for Low-Emissivity Glass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abundiz-Cisneros, N.; Sanginés, R.; Rodríguez-López, R.; Peralta-Arriola, M.; Cruz, J.; Machorro, R. Novel Low-E filter for architectural glass pane. Energy Build 2020, 206, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.; Chong, A.; Wei, Z.; Thangavelu, S.R. Energy Saving Potential of Low-e Coating Based Retrofit Double Glazing for Tropical Climate. Energy Build 2020, 206, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, A.; Le Baron, E. Longtime solar performance estimations of low-E glass depending on local atmospheric conditions. Sol. Energy Mater Sol. Cells 2022, 240, 111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelle, B.P.; Kalnæs, S.E.; Gao, T. Low-emissivity materials for building applications: A state-of-the-art review and future research perspectives. Energ. Build. 2015, 96, 329–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumrukcu, A.E.; Kaplan, H.; Akin Sonmez, N.; Ozcelik, S. Electrical, optical and structural properties of silver-based multilayer films deposited by magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 18519–18523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Clavero, C. Silver-based low-emissivity coating technology for energy-saving window applications. In Modern Technologies for Creating the Thin-film Systems and Coatings, 1st ed.; Nikitenkov, N., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Chapter 20; pp. 418–422. [Google Scholar]
- Finley, J.J. Heat treatment and bending of low-e glass. Thin Solid Film. 1999, 351, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; Ghosh, S.; Basak, D. Highly conducting and transparent low-E window films with high figure of merit values based on RF sputtered Al and in co-doped ZnO. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 119, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwona-Agyeman, B.; Nakao, M.; Kohno, T.; Liyanage, D.; Murakami, K.; Kitaoka, T. Preparation and characterization of sputtered aluminum and gallium co-doped ZnO films as conductive substrates in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Park, J.B.; Song, P.K. Characteristics of Al-doped, Ga-doped and In-doped zinc-oxide films as transparent conducting electrodes in organic light-emitting diodes. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, S488–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, R. Optimization of Al-doped ZnO films by RF magnetron sputtering at room temperature for Cu (In, Ga) Se2 solar cells. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1549, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; Basak, D. Revisiting the electrical and optical transmission properties of co-doped ZnO thin films as n-type TCOs. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 96, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H. ZnO-based transparent conductive thin films: Doping, performance, and processing. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 196521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.U.; Shin, S.W.; Moholkar, A.V.; Yun, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Effects of dopant (Al, Ga, and In) on the characteristics of ZnO thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering system. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, S463–S467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimifard, R.; Golobostanfard, M.R.; Abdizadeh, H. Sol–gel derived Al and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films: An optoelectronic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKahlout, A. A Comparative Study of Spin Coated Transparent Conducting Thin Films of Gallium and Aluminum Doped ZnO Nanoparticles. Phys. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 238123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muchuweni, E.; Sathiaraj, T.S.; Nyakotyo, H. Low temperature synthesis of radio frequency magnetron sputtered gallium and aluminium co-doped zinc oxide thin films for transparent electrode fabrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Gupta, C.A.; Singh, U.P. Impact of Al and Ga co-doping with different proportion in ZnO thin film by DC magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7161–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, D.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, R. Investigation of aluminum–gallium Co-doped zinc oxide targets for sputtering thin film and photovoltaic application. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 575, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, E.; Rubens, H. Über Beziehungen des Reflexions- und Emissionsvermögens der Metalle zu ihrem elektrischen Leitvermögen. Annin. Phys. 1903, 11, 873–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yang, Y.; Song, W.J. Effects of substrate temperature on the structural, morphological, electrical and optical properties of Al and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films grown by DC magnetron sputtering. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.C.; Park, S.U.; Koh, J.H. Comparative studies of Al-doped ZnO and Ga-doped ZnO transparent conducting oxide thin films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.H.; Chang, H.P.; Tseng, C.C.; Huang, C.C. Effects of H2 plasma treatment on properties of ZnO:Al thin films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 5269–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Hu, E.T.; Guo, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yu, K.H.; Wei, W.; Zheng, Y.X.; Wang, S.Y.; et al. Ellipsometric study on optical properties of hydrogen plasma-treated aluminum-doped ZnO thin film. Vacuum 2019, 163, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.V.; Cerqueira, M.F.; Rebouta, L.; Alpuim, P.; Garcia, C.B.; Júnior, G.L.; Tavares, C.J. Influence of hydrogen plasma thermal treatment on the properties of ZnO:Al thin films prepared by dc magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2014, 107, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, D.W.; Lim, Y.S.; Seo, W.S.; Choi, H.J. The annealing effect on damp heat stability of AGZO thin films prepared by DC moving magnetron sputtering. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, S333–S336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Shin, S.; Jung, D.R.; Kim, J.; Nahm, C.; Moon, T.; Park, B. Investigation of electronic and optical properties in Al-Ga codoped ZnO thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C. In-line sputtered gallium and aluminum codoped zinc oxide films for organic solar cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 916189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Chan, H.T. Post-annealed Aluminum-Doped Zinc Oxide/Tin-Doped Indium Oxide Bilayer Films for Low Emissivity Glass. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C. Post-annealed gallium and aluminum co-doped zinc oxide films applied in organic photovoltaic devices. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, S.-C.; Chen, H.-J. Thin film & device process Properties of hydrogen plasma treated Gallium and Aluminum co-doped Zinc Oxide films. In Innovation in Design, Communication and Engineering, 1st ed.; Meen, T.-H., Prior, S., Lam, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Guiyang, China, 2015; pp. 907–910. [Google Scholar]
- Yanfeng, S.; Liu, W.; Zhidan, H.; Shaolin, L.; Yi, Z.Z.; Du, G. Novel properties of AZO film sputtered in Ar + H2 ambient at high temperature. Vacuum 2006, 80, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Du, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Chang, Y.; Qiu, F. Al-doped ZnO thin films deposited by reactive frequency magnetron sputtering: H2-induced property changes. Thin Solid Film 2007, 515, 3057–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Walle, C.G. Hydrogen as a Cause of Doping in Zinc Oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daza, L.G.; Perez-Quintana, I.V.; Cruz-Muñoz, B.; Herrera-Salvador, M.; Castro-Rodríguez, R. Twisted-motion substrate with sustained azimuthal rotation effect on the growth of AZO thin films by rf-sputtering. Optik 2021, 234, 166561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
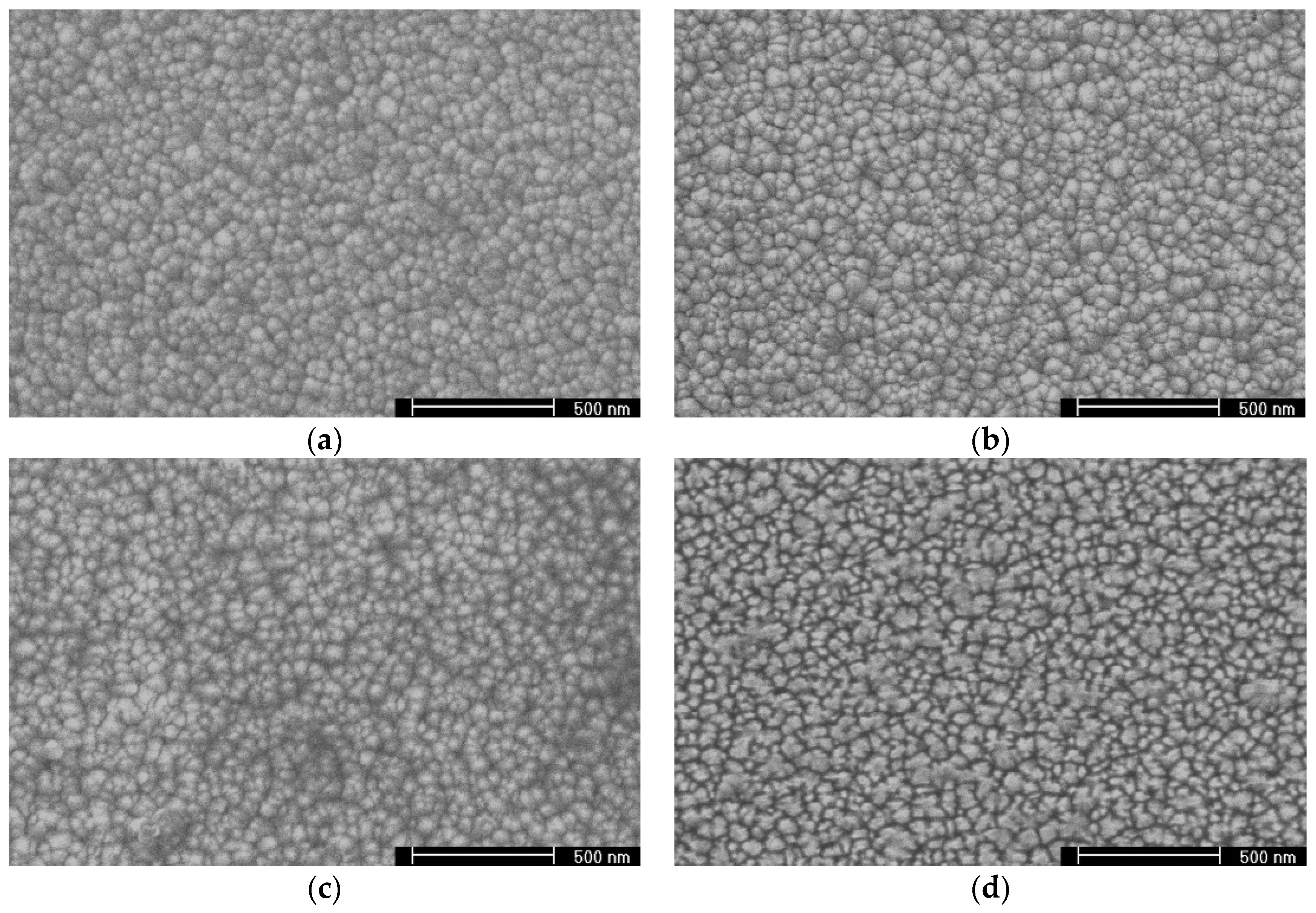

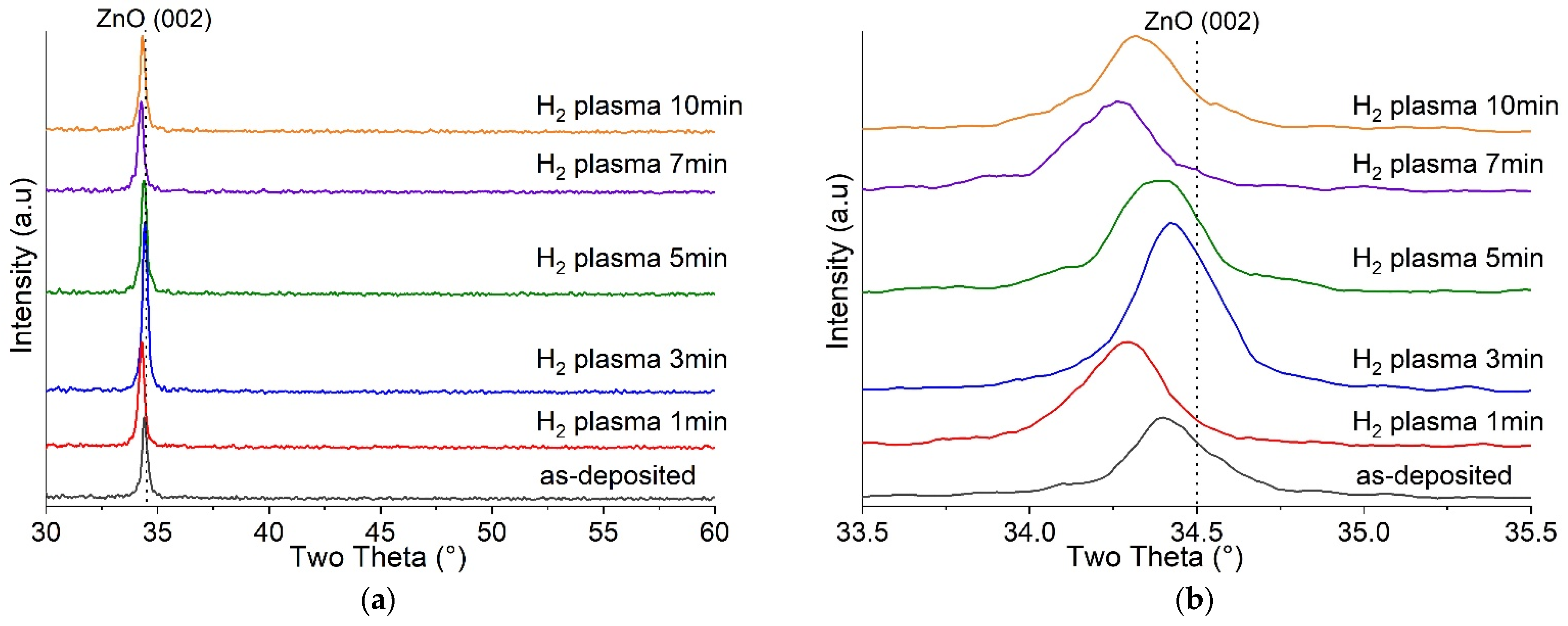
| Plasma Time | None | 1 min | 3 min | 5 min | 7 min | 10 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO Plane (002) 2θ (°) | 34.40° | 34.30° | 34.42° | 34.38° | 34.26° | 34.32° |
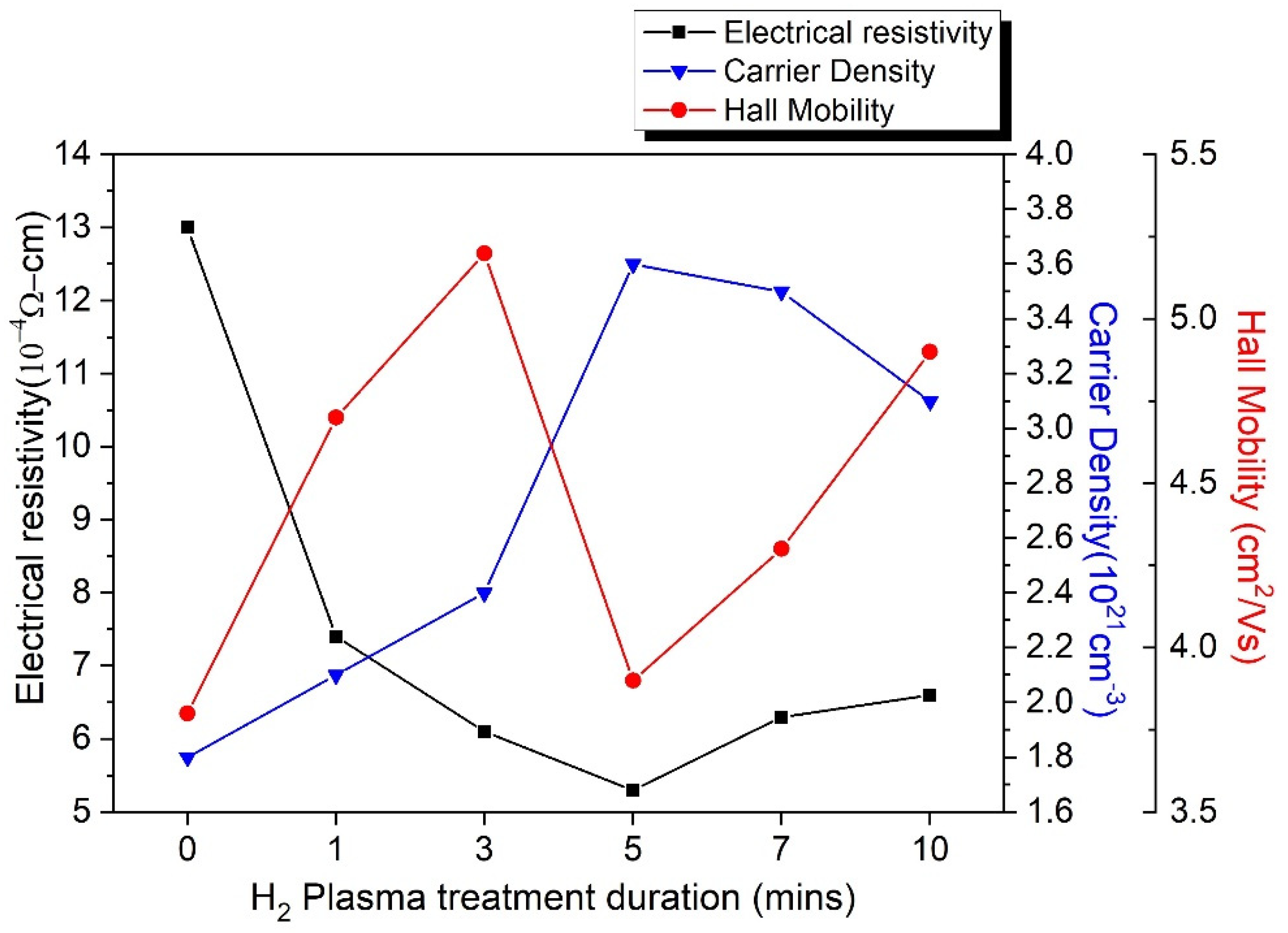
| Electrical Resistivity (10−4 Ω-cm) | 13.0 ± 0.23% | 7.4 ± 0.25% | 6.1 ± 0.22% | 5.3 ± 0.23% | 6.3 ± 0.23% | 6.6 ± 0.22% |
| Carrier Concentration (1021 cm−3) | 1.8 ± 0.22% | 2.1 ± 0.23% | 2.4 ± 0.22% | 3.6 ± 0.22% | 3.5 ± 0.24% | 3.1 ± 0.23% |
| Hall Mobility (cm2/vs) | 3.8 ± 0.25% | 4.7 ± 0.22% | 5.2 ± 0.24% | 3.9 ± 0.22% | 4.3 ± 0.22% | 4.9 ± 0.23% |
| Emissivity | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
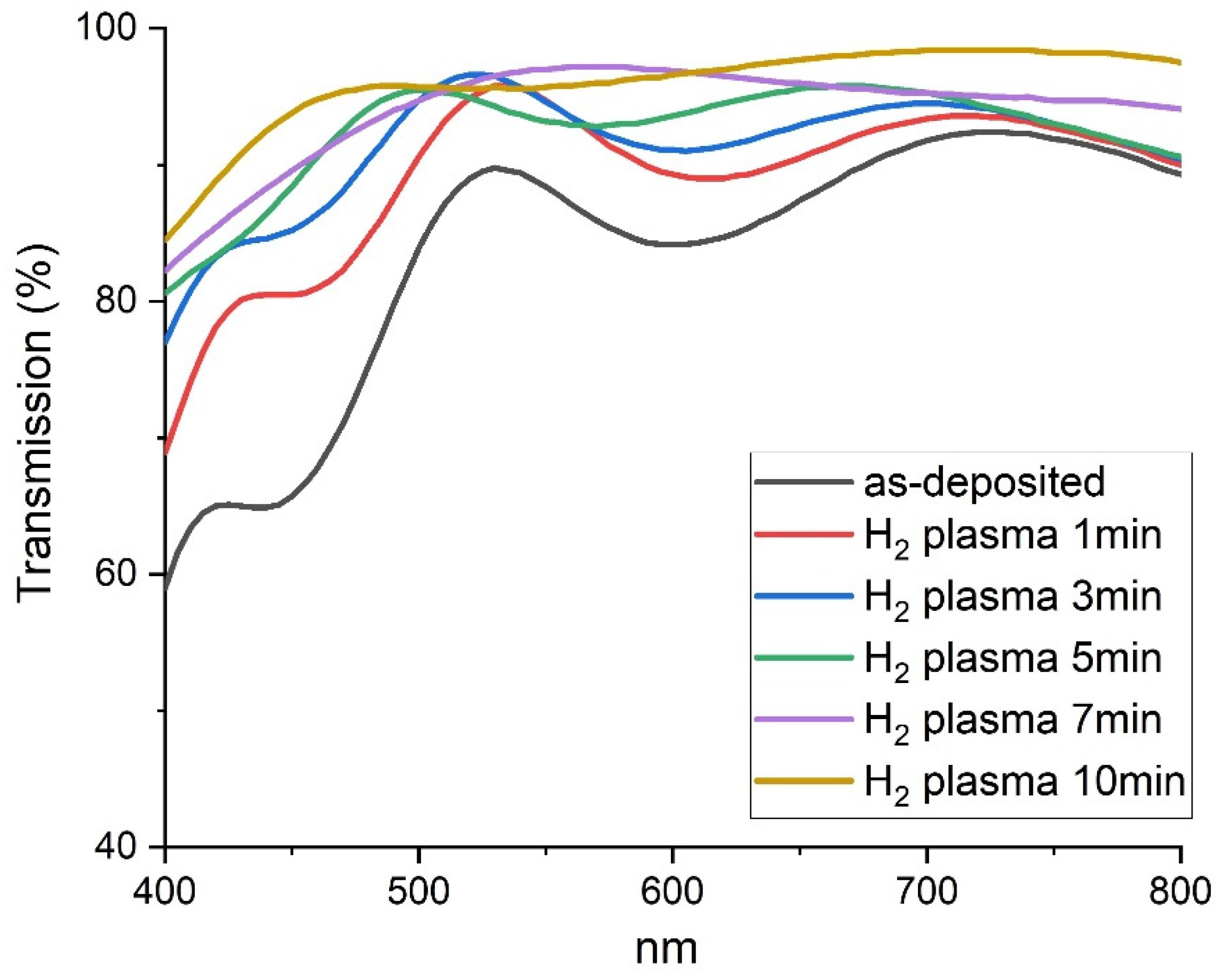
| Average Transmittance in Visible (400–800 nm) Region (%) | 85 | 90 | 92 | 94 | 95 | 96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, S.-C.; Hu, J.-C.; Chan, H.-T.; Hsiao, C.-A. Influence of Processing Time in Hydrogen Plasma to Prepare Gallium and Aluminum Codoped Zinc Oxide Films for Low-Emissivity Glass. Coatings 2022, 12, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12070945
Chang S-C, Hu J-C, Chan H-T, Hsiao C-A. Influence of Processing Time in Hydrogen Plasma to Prepare Gallium and Aluminum Codoped Zinc Oxide Films for Low-Emissivity Glass. Coatings. 2022; 12(7):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12070945
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Shang-Chou, Jhih-Ciang Hu, Huang-Tian Chan, and Chuan-An Hsiao. 2022. "Influence of Processing Time in Hydrogen Plasma to Prepare Gallium and Aluminum Codoped Zinc Oxide Films for Low-Emissivity Glass" Coatings 12, no. 7: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12070945
APA StyleChang, S.-C., Hu, J.-C., Chan, H.-T., & Hsiao, C.-A. (2022). Influence of Processing Time in Hydrogen Plasma to Prepare Gallium and Aluminum Codoped Zinc Oxide Films for Low-Emissivity Glass. Coatings, 12(7), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12070945






