Synthesis and Electron-Beam Evaporation of Gadolinium-Doped Ceria Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of the Target Material and the Formation of Thin Films
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Powders
3.2. Characterization of the Pellets
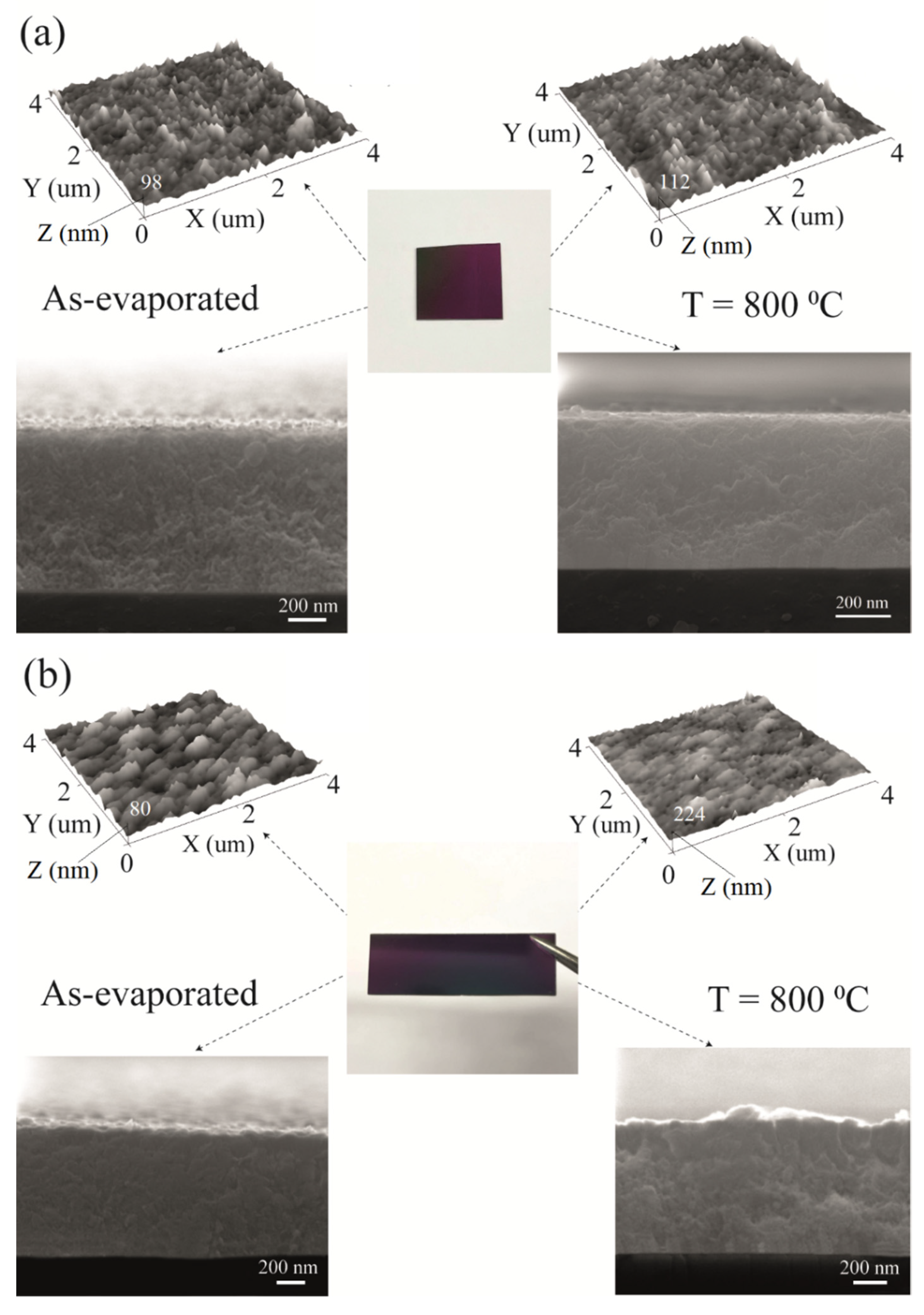
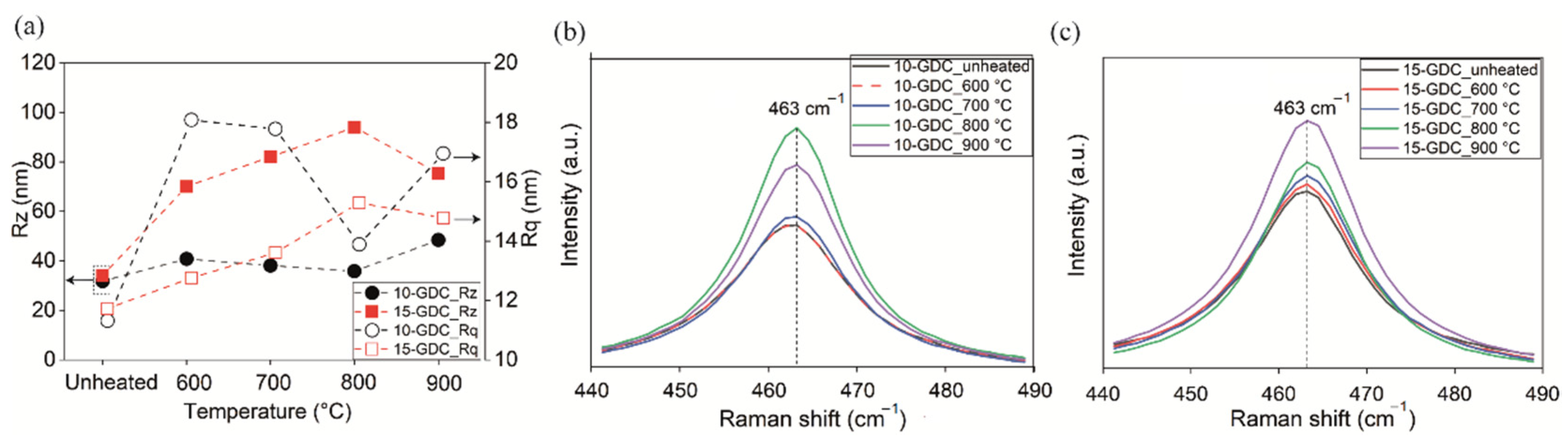
3.3. Characterization of Thin Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, A.; Bieberle-Hütter, A.; Rupp, J.L.M.; Gauckler, L.J. Review on microfabricated micro-solid oxide fuel cell membranes. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Park, B.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, Y.; Bae, H.; Choi, G.M. Micro solid oxide fuel cell fabricated on porous stainless steel: A new strategy for enhanced thermal cycling ability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, J.L.M.; Gauckler, L.J. Microstructures and electrical conductivity of nanocrystalline ceria-based thin films. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckel, D.; Bieberle-Hütter, A.; Harvey, A.; Infortuna, A.; Muecke, U.P.; Prestat, M.; Rupp, J.L.M.; Gauckler, L.J. Thin films for micro solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieberle-Hütter, A.; Beckel, D.; Infortuna, A.; Muecke, U.P.; Rupp, J.L.M.; Gauckler, L.J.; Rey-Mermet, S.; Muralt, P.; Bieri, N.R.; Hotz, N.; et al. A micro-solid oxide fuel cell system as battery replacement. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, O. Solid oxide fuel cells: Fundamental aspects and prospects. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2423–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsman, E.D.; Singhal, S.C. Solid oxide fuel cell commercialization, research, and challenges. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2009, 18, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gestel, T.; Sebold, D.; Buchkremer, P.H. Processing of 8YSZ and CGO thin film electrolyte layers for intermediate- and low-temperature SOFCs. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Lee, D.; Hong, S.; Yang, H.; Kim, Y.B. Three-dimensional hexagonal GDC interlayer for area enhancement of low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 279, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; An, J.; Jang, D.Y.; Jee, Y.; Shim, J.H.; Cha, S.W. On the reduced electrical conductivity of radio-frequency sputtered doped ceria thin film by elevating the substrate temperature. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.P. Thermally and Electrochemically Induced Electrode/Electrolyte Interfaces in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: An AFM and EIS Study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1119–F1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öksüzömer, M.A.F.; Dönmez, G.; Sariboǧa, V.; Altinçekiç, T.G. Microstructure and ionic conductivity properties of gadolinia doped ceria (GdxCe1-xO2-x/2) electrolytes for intermediate temperature SOFCs prepared by the polyol method. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 7305–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mori, T.; Li, J.G.; Yajima, Y. Low-temperature fabrication and electrical property of 10 mol% Sm 2O3-doped CeO2 ceramics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2003, 4, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chourashiya, M.G.; Jadhav, L.D. Synthesis and characterization of 10%Gd doped ceria (GDC) deposited on NiO-GDC anode-grade-ceramic substrate as half cell for IT-SOFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 14984–14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, R.O.; Baker, R.T. Synthesis and properties of Gadolinium-doped ceria solid solutions for IT-SOFC electrolytes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 3480–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkov, A.; Stanulis, A.; Salkus, T.; Kezionis, A.; Jasulaitiene, V.; Ramanauskas, R.; Tautkus, S.; Kareiva, A. Synthesis of nanocrystalline gadolinium doped ceria via sol-gel combustion and sol-gel synthesis routes. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 3972–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Agli, G.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Marocco, A.; Accardo, G.; Ferone, C.; Cioffi, R. Effect of the mineralizer solution in the hydrothermal synthesis of gadolinium-doped (10% mol Gd) ceria nanopowders. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14, e189–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dönmez, G.; Sariboʇa, V.; Altinçekiç, T.G.; Öksüzömer, M.A.F. Polyol synthesis and investigation of Ce1-535 xRExO2-x/2 (RE = Sm, Gd, Nd, La, 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25) electrolytes for IT-SOFCs. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 98, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Z.; Wang, J.X.; He, C.R.; Miao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.W. Synthesis and characterization of Gd0.1Ce0.9O 1.95 nanopowder via an acetic-acrylicmethod. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 6229–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Dell’Agli, G.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Ferone, C.; Sglavo, V.M. Conventional and field-assisted sintering of nanosized Gd-doped ceria synthesized by co-precipitation. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 11766–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Ray, D.T.; Fu, Y.P. Co-precipitation synthesis and AC conductivity behavior of gadolinium-doped ceria. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 7967–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.H.; Kim, H.R.; Park, J.S.; Son, J.W.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.H. Superior sinterability of nano-crystalline gadolinium doped ceria powders synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 495, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuma, Y.; Takao, K.; Kamiya, M.; Shimada, E. X-ray study of cerium oxide doped with gadolinium oxide fired at low temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2003, 99, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Xia, C.; Meng, G. Effect of Gd (Sm) doping on properties of ceria electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2003, 115, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianshu, Z.; Hing, P.; Huang, H.; Kilner, J. Ionic conductivity in the CeO2-Gd2O3 system (0.05 ≤ Gd/Ce ≤ 0.4) prepared by oxlate coprecipitation. Solid State Ion. 2002, 148, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, A.; Solak, N. High Temperature—FTIR Characterization of Gadolinia Doped Ceria. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 72, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabac, A.; Öksüzömer, M.F. Preparation and characterization of 10 mol% Gd doped CeO 2 (GDC) electrolyte for SOFC applications. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 6509–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z. Advanced synthesis of materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 804–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, J.Y.; Chang, I.; Park, J.H.; Ji, S.; Cha, S.W. A study on properties of yttrium-stabilized zirconia thin films fabricated by different deposition techniques. Renew. Energy 2014, 65, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.H.; Diao, C.C.; Yang, C.F.; Huang, C.J. Effects of substrate temperatures on the crystallizations and microstructures of electron beam evaporation YSZ thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 500, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukaitis, G.; Dudonis, J. Microstructure of gadolinium doped ceria oxide thin films formed by electron beam deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 459, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdikas, A.; Čerapaite-Trušinskiene, R.; Laukaitis, G.; Dudonis, J. Real-time kinetic modeling of YSZ thin film roughness deposited by e-beam evaporation technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 62, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaliuniene, J.; Čyviene, J.; Abakevičiene, B.; Dudonis, J. Investigation of structural and optical properties of GDC thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 120, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.J.; Yoon, H.H. Fabrication and characterization GDC electrolyte thin films by e-beam technique for IT-SOFC. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, S163–S168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmanová, M.; Jergel, M.; Thurzo, I.; Kundracik, F.; Gmucová, K.; Chromik, S.; Ortega, L. Thin Film Electrolytes: Yttria Stabilized Zirconia and Ceria. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2003, 39, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukaitis, G.; Virbukas, D. The structural and electrical properties of GDC10 thin films formed by e-beam technique. Solid State Ion. 2013, 247–248, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, P.R.; Arjunan, T.V. A review of materials used for solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 7, 488. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Chang, I.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, J.; Paek, J.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Cha, S.W. Fabrication of low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells with a nanothin protective layer by atomic layer deposition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saporiti, F.; Juarez, R.E.; Audebert, F.; Boudard, M. Yttria and ceria doped zirconia thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlenbruck, S.; Jordan, N.; Sebold, D.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Haanappel, V.A.C.; Stöver, D. Thin film coating technologies of (Ce,Gd)O2-δ interlayers for application in ceramic high-temperature fuel cells. Thin Solid Film. 2007, 515, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, R.A.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, E.S.; Munir, B.; Kim, K.H. Single step preparation of quaternary Cu2 ZnSnSe4 thin films by RF magnetron sputtering from binary chalcogenide targets. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2007, 68, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Mori, T.; Ishigaki, T. Reactive 10 mol% RE2O3 (RE = Gd and Sm) doped CeO2 nanopowders: Synthesis, characterization, and low-temperature sintering into dense ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2005, 121, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Moore, A.; Abernathy, H.; Liu, M. GDC-Based Low-Temperature SOFCs Powered by Hydrocarbon Fuels. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A1128–A1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygün, B.; Özdemir, H.; Öksüzömer, M.A.F. Structural, morphological and conductivity properties of samaria doped ceria (SmxCe1-xO2-x/2) electrolytes synthesized by electrospinning method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 232, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Wen, T.-L.; Tu, H.; Lu, Z.-Y. AC Impedance Investigation of Samarium-Doped Ceria. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A427–A432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, S.Y.; Croiset, E. Reducing sintering temperature while maintaining high conductivity for SOFC electrolyte: Copper as sintering aid for Samarium Doped Ceria. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.A.; Liu, M.; Liu, M. Impedance Spectroscopy Study of an SDC-based SOFC with High Open Circuit Voltage. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 177, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koettgen, J.; Martin, M. The ionic conductivity of Sm-doped ceria. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 3776–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalyk, F.; Stankevičiūtė, A.; Budrytė, G.; Gaidamavičienė, G.; Žalga, A.; Kriūkienė, R.; Kavaliauskas, Ž.; Leszczyńska, M.; Abakevičienė, B. Comparative study of samarium-doped ceria nanopowders synthesized by various chemical synthesis routes. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 24385–24394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathana, W.; Veranitisagul, C.; Wannapaiboon, S.; Klysubun, W.; Koonsaeng, N.; Laobuthee, A. Samarium doped ceria (SDC) synthesized by a metal triethanolamine complex decomposition method: Characterization and an ionic conductivity study. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9823–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, S.B.; Bauri, R. Effect of sintering atmosphere on densification, redox chemistry and conduction behavior of nanocrystalline Gd-doped CeO2 electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9421–9428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokkelbost, T.; Kaus, I.; Grande, T.; Einarsrud, M.A. Combustion synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline CeO2-based powders. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5489–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, R.O.; Baker, R.T. Structural, morphological and electrical properties of Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 prepared by a citrate complexation method. J. Power Sources 2009, 186, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murutoglu, M.; Ucun, T.; Ulasan, O.; Buyukaksoy, A.; Tur, Y.K.; Yilmaz, H. Cold sintering-assisted densification of GDC electrolytes for SOFC applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 19772–19779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lenser, C.; Menzler, N.H.; Guillon, O. Comparison of solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) electrolyte materials for operation at 500 °C. Solid State Ion. 2020, 344, 115138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, N.; Tanwar, K.; Suman, R.; Kumar, D.; Upadhyay, S.; Parkash, O. A brief review on ceria based solid electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 984–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.; van Wesenbeeck, I. Correlation of chemical evaporation rate with vapor pressure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10259–10263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajakbari, F.; Ensandoust, M. Study of thermal annealing effect on the properties of silver thin films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 129, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, F.; Airo, M.; Erasmus, R.M.; Quandt, A.; Billing, D.G.; Wamwangi, D. Annealing effect on the structural and optical behavior of ZnO:Eu3+ thin film grown using RF magnetron sputtering technique and application to dye sensitized solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medisetti, S.; Ahn, J.; Patil, S.; Goel, A.; Bangaru, Y.; Sabhahit, G.V.; Babu, G.U.B.; Lee, J.H.; Dasari, H.P. Synthesis of GDC electrolyte material for IT-SOFCs using glucose & fructose and its characterization. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2017, 11, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalipova, O.S.; Lair, V.; Ringuedé, A. Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of Gadolinia-Doped Ceria thin films. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 116, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, J.; Courcot, D.; Abi-Aad, E.; Aboukaïs, A. Identification of vanadium oxide species and trapped single electrons in interaction with the CeVO4 phase in vanadium-cerium oxide systems. 51V MAS NMR, EPR, Raman, and thermal analysis studies. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4118–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, L.D.; Patil, S.P.; Jamale, A.P.; Chavan, A.U. Solution combustion synthesis: Role of oxidant to fuel ratio on powder properties. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 757, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkov, A.; Stanulis, A.; Mikoliunaite, L.; Katelnikovas, A.; Jasulaitiene, V.; Ramanauskas, R.; Tautkus, S.; Kareiva, A. Chemical solution deposition of pure and Gd-doped ceria thin films: Structural, morphological and optical properties. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 4280–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitzek, S.; Blach, J.F.; Villain, S.; Gavarri, J.R. Nanostructured ceria: A comparative study from X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and BET specific surface measurements. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2008, 205, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Sugiyama, N.; Subramani, A.K.; Wagata, H.; Matsushita, N.; Yoshimura, M. Identifying defects in ceria-based nanocrystals by UV resonance Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19789–19793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.S.; Chao, L.S. The effect of thermal annealing processes on structural and photoluminescence of zinc oxide thin film. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 424953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habib, A.; Addou, M.; Aouni, A.; Diani, M.; Zimou, J.; Bouachri, M.; Brioual, B.; Allah, R.F.; Rossi, Z.; Jbilou, M. Oxygen vacancies and defects tailored microstructural, optical and electrochemical properties of Gd doped CeO2 nanocrystalline thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 145, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Expected Molar Ratio of Gd to Ce in GDC | Gd Content in GDC from ICP-OES (r.u.) | Gd Content in GDC from EDS (r.u.) | SBET (m2/g) | D (nm) | dth (g/cm3) | DBET (nm) | ϕ (r.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-GDC | 0.18: 0.82 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 11.7 | 32.6 | 7.235 | 70.3 | 2.156 |
| 15-GDC | 0.26: 0.74 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 10.19 | 32.7 | 7.244 | 81.4 | 2.489 |
| 20-GDC | 0.33: 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 7.7 | 31.1 | 7.251 | 108.0 | 3.472 |
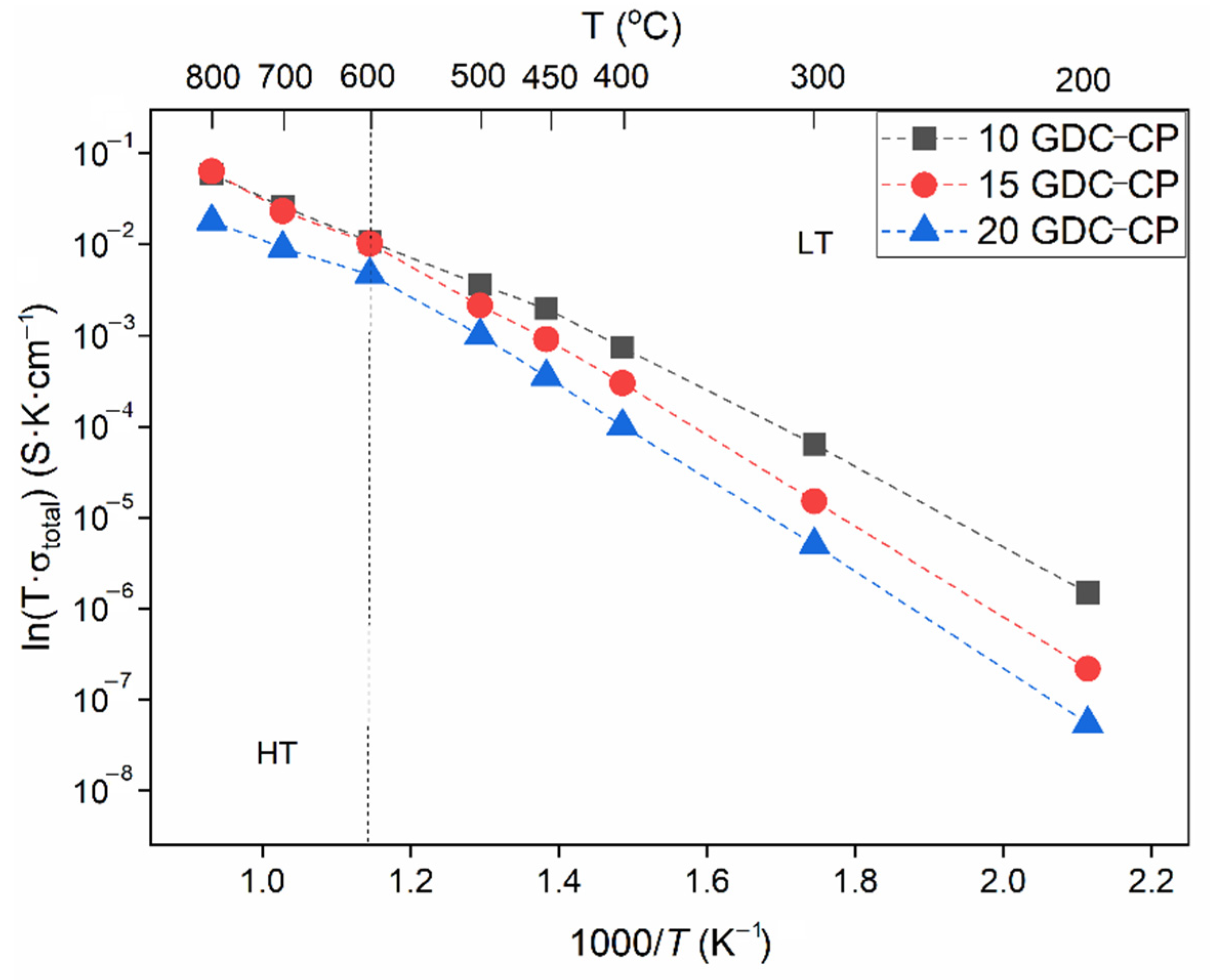
| Sample | ΔEa (eV) | Total Conductivity (S∙cm−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT | HT | 400 °C | 600 °C | 800 °C | |
| 10-GDC | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.7 × 10−3 | 11 × 10−3 | 5.9 × 10−2 |
| 15-GDC | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.3 × 10−3 | 10 × 10−3 | 6.3 × 10−2 |
| 20-GDC | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.1 × 10−3 | 4.7 × 10−3 | 1.8 × 10−2 |
| Notation | Gd Content in GDC from ICP-OES (r.u.) | Gd Content in Thin Film from XPS (r.u.) | Molar Content of Gd2O3 in Thin Film (mol%) | Decrease in the Molar Content of Gd2O3 in Thin Film (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-GDC | 0.13 | 0.13 | 6.90 | 31.0 |
| 15-GDC | 0.21 | 0.20 | 11.3 | 24.7 |
| 20-GDC | 0.27 | 0.26 | 14.4 | 28.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalyk, F.; Žalga, A.; Vasiliauskas, A.; Tamulevičius, T.; Tamulevičius, S.; Abakevičienė, B. Synthesis and Electron-Beam Evaporation of Gadolinium-Doped Ceria Thin Films. Coatings 2022, 12, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060747
Kalyk F, Žalga A, Vasiliauskas A, Tamulevičius T, Tamulevičius S, Abakevičienė B. Synthesis and Electron-Beam Evaporation of Gadolinium-Doped Ceria Thin Films. Coatings. 2022; 12(6):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060747
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalyk, Fariza, Artūras Žalga, Andrius Vasiliauskas, Tomas Tamulevičius, Sigitas Tamulevičius, and Brigita Abakevičienė. 2022. "Synthesis and Electron-Beam Evaporation of Gadolinium-Doped Ceria Thin Films" Coatings 12, no. 6: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060747
APA StyleKalyk, F., Žalga, A., Vasiliauskas, A., Tamulevičius, T., Tamulevičius, S., & Abakevičienė, B. (2022). Synthesis and Electron-Beam Evaporation of Gadolinium-Doped Ceria Thin Films. Coatings, 12(6), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060747









