Phosphonium Modified Nanocellulose Membranes with High Permeate Flux and Antibacterial Property for Oily Wastewater Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Tunicate Cellulose Nanofibers (TCNFs)
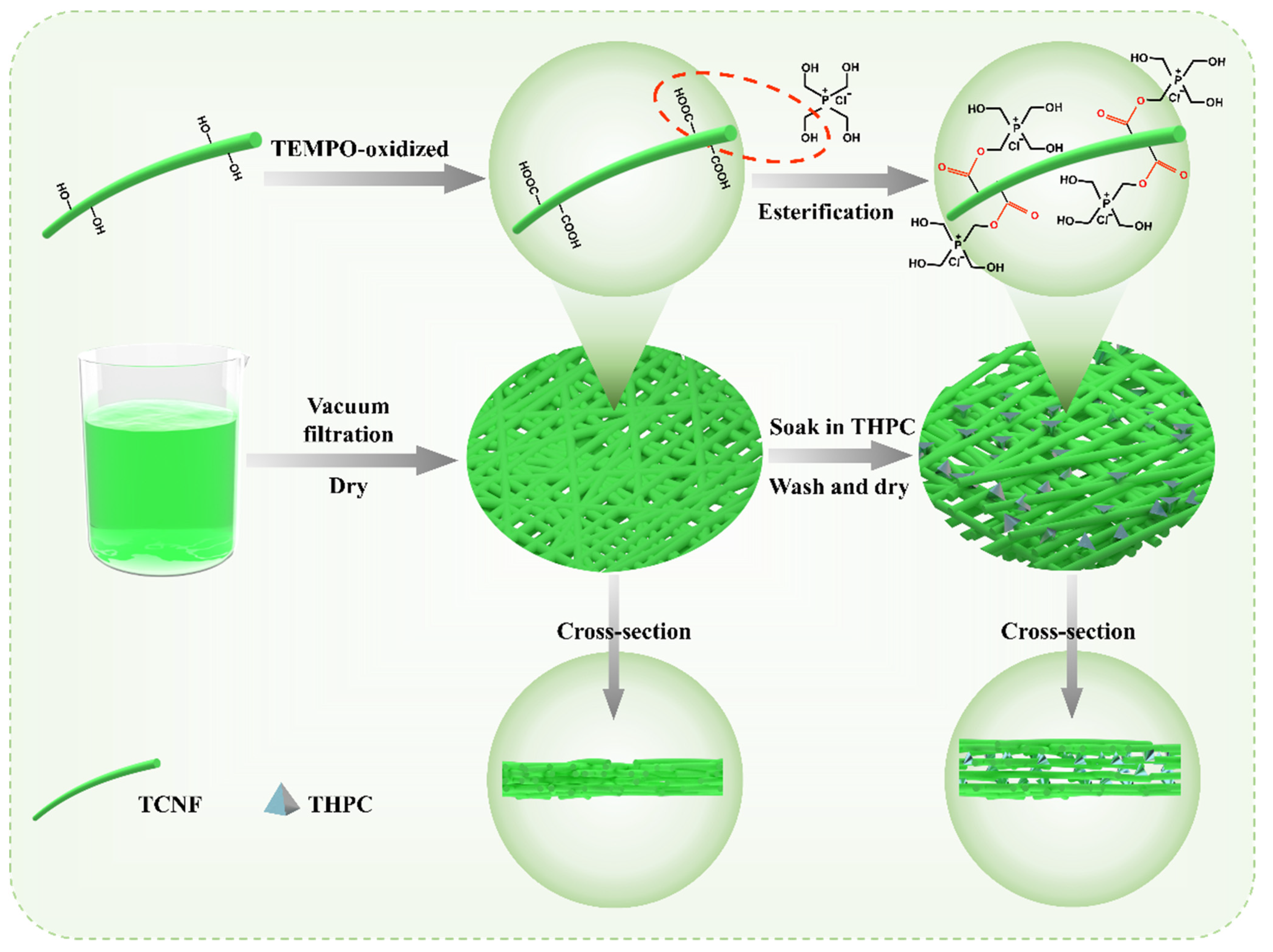
2.3. Fabrication of THPC@TCNF Membranes
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Oil/Water Nano-Emulsion Separation
2.6. Antibacterial Property
3. Results and Discussion
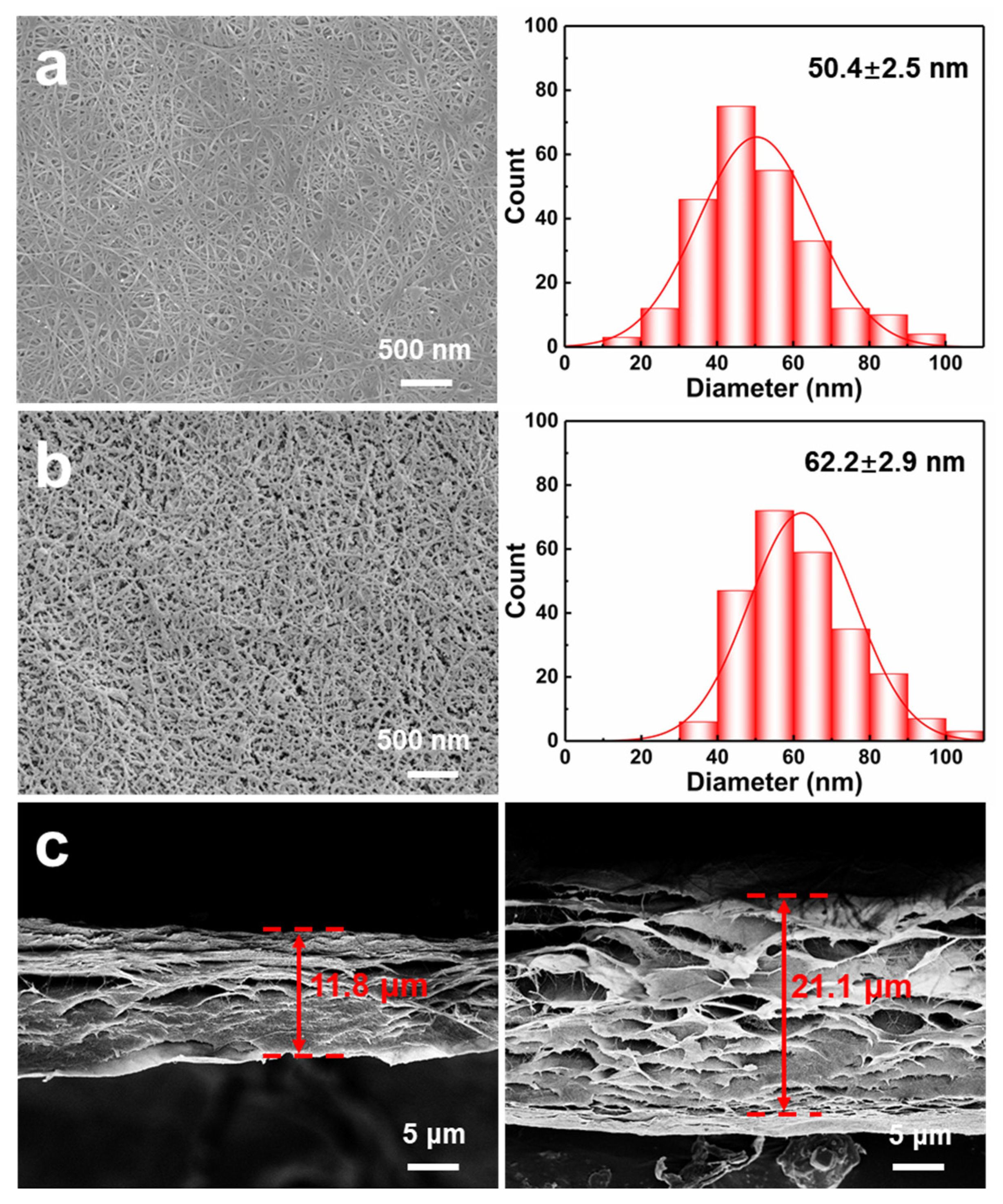
3.1. Fabrication and Morphology of THPC@TCNF Membranes
3.2. Structure of THPC@TCNF Membranes
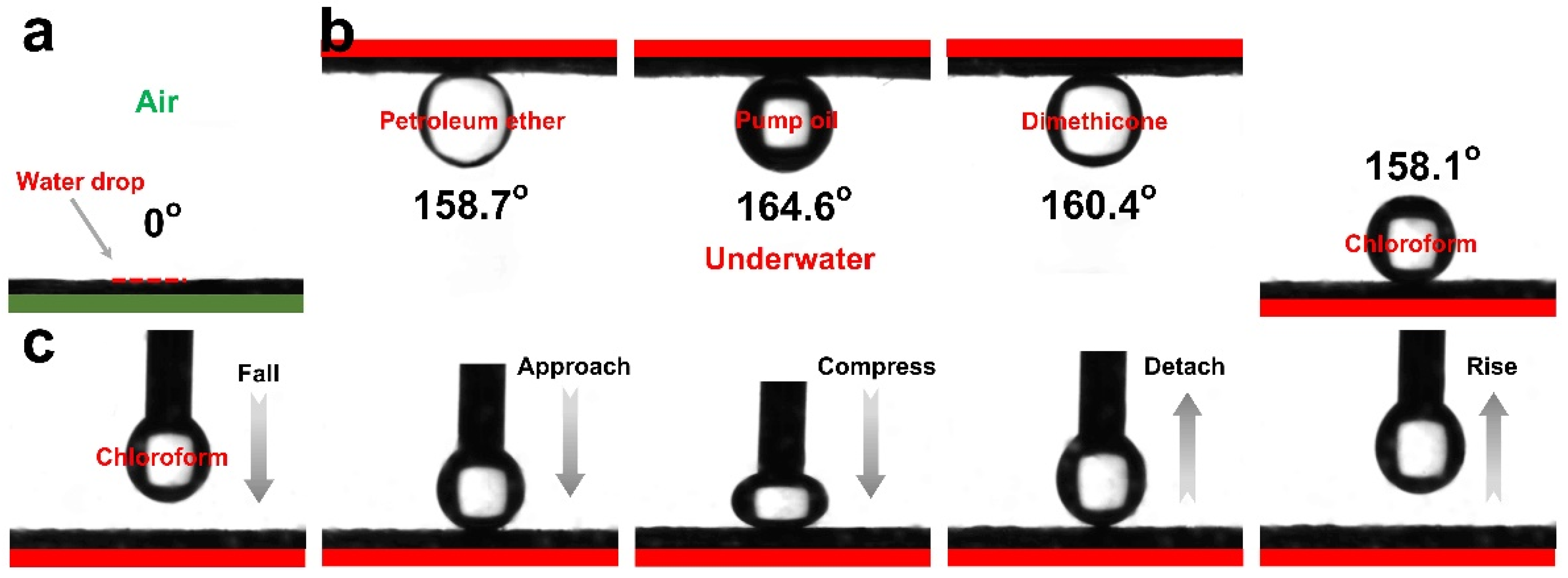
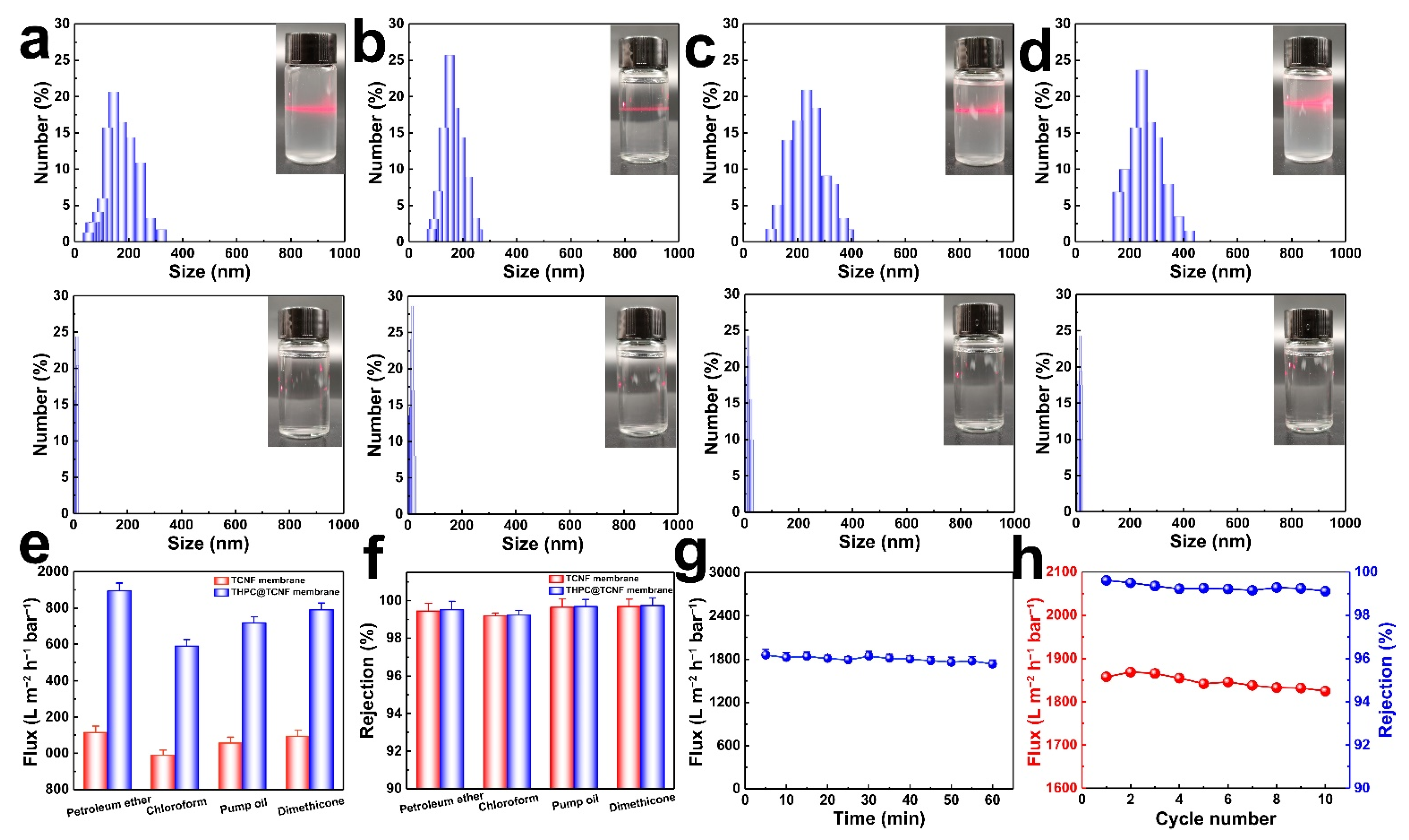
3.3. Wettability and Separation Performance of THPC@TCNF Membranes
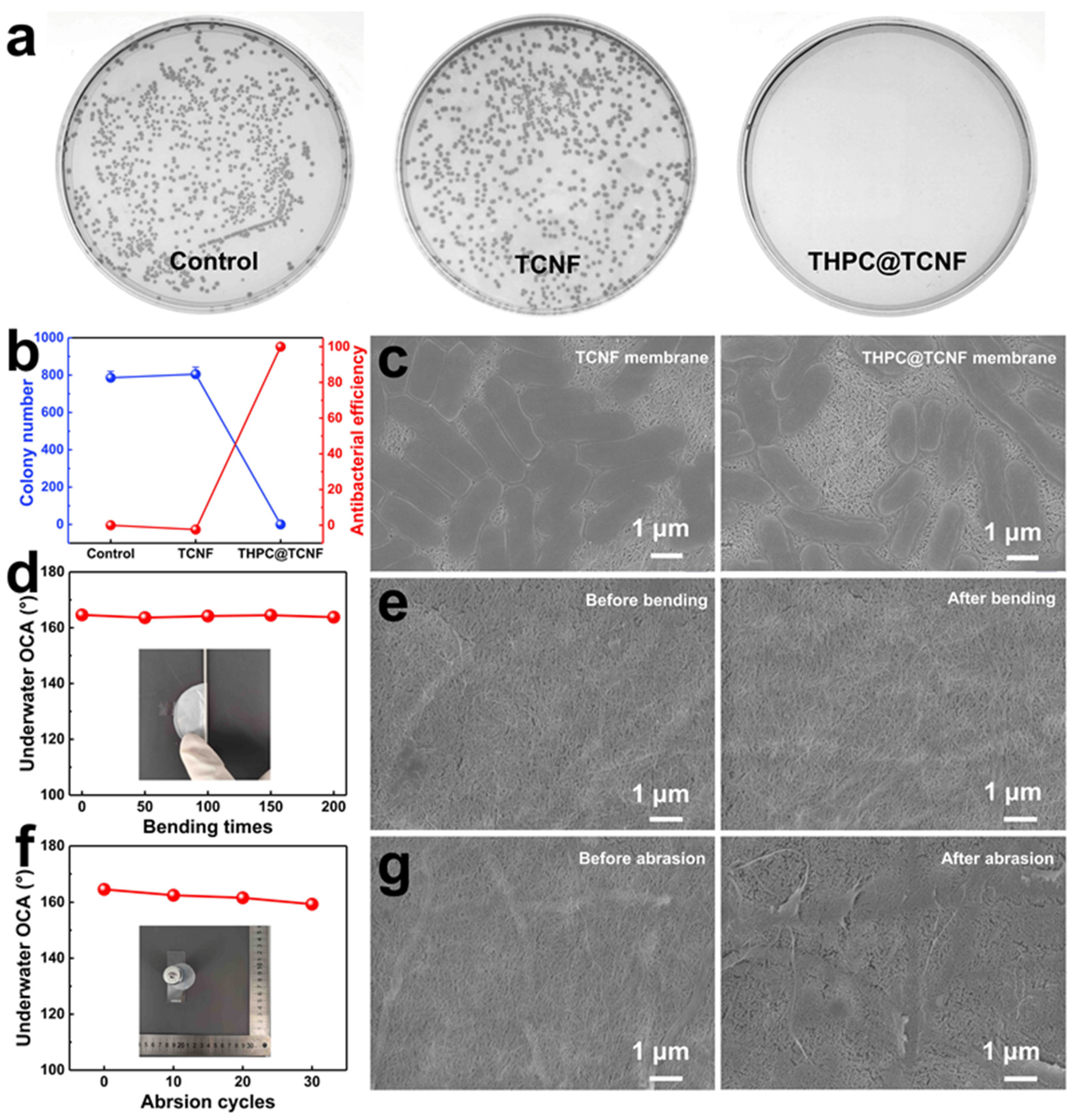
3.4. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanical Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, S. Nonflammable and Magnetic Sponge Decorated with Polydimethylsiloxane Brush for Multitasking and Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Guo, Z. Recent advances in biomimetic thin membranes applied in emulsified oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15749–15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J.; Taylor, M.K.; Shin, D.M.; Jarenwattananon, N.N.; Colwell, K.A.; Long, J.R. Functionalized Porous Aromatic Frameworks as High-Performance Adsorbents for the Rapid Removal of Boric Acid from Water. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1808027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Hsiao, B.S. Novel thin-film nanofibrous composite membranes containing directional toxin transport nanochannels for efficient and safe hemodialysis application. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Ge, M.; Teng, L.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Advanced Materials with Special Wettability toward Intelligent Oily Wastewater Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.Y.; Peng, C.S.; Dai, M.; Lin, D.C.; Ali, I.; Alhewairini, S.S.; Zheng, X.L.; Chen, G.Q.; Li, J.Y.; Naz, I. Recent development of super-wettable materials and their applications in oil-water separation. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 266, 121624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zuo, T.; Tao, R.J.; Chang, C.Y. Robust Tunicate Cellulose Nanocrystal/Palygorskite Nanorod Membranes for Multifunctional Oil/Water Emulsion Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10833–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Huang, Y.; Peng, N.; Chang, C.Y. Antibacterial nanocellulose membranes coated with silver nanoparticles for oil/water emulsions separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. A Self-Cleaning Heterostructured Membrane for Efficient Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation with Stable Flux. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2001265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodar, R.A.; You, S.J.; Chou, H.H. Study the self cleaning, antibacterial and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 entrapped PVDF membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xu, L.; Jia, C.; Dai, J.; Song, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Anisotropic, Transparent Films with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, J.M.; Sánchez, M.J.; Pena, P.; Rodríguez, M.A. Development of a new high porosity ceramic membrane for the treatment of bilge water. Desalination 2007, 214, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Ultrafast Separation of Emulsified Oil/Water Mixtures by Ultrathin Free-Standing Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Network Films. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Hu, L. Nanocellulose toward Advanced Energy Storage Devices: Structure and Electrochemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3154–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heise, K.; Kontturi, E.; Allahverdiyeva, Y.; Tammelin, T.; Linder, M.B.; Nonappa; Ikkala, O. Nanocellulose: Recent Fundamental Advances and Emerging Biological and Biomimicking Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2004349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, A. Emerging Nanocellulose Technologies: Recent Developments. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2000630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De France, K.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, T.; Nystrom, G. Functional Materials from Nanocellulose: Utilizing Structure-Property Relationships in Bottom-Up Fabrication. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2000657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.Y.; Ye, D.D.; Chang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.N. Facile fabrication of superhydrophilic membranes consisted of fibrous tunicate cellulose nanocrystals for highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norfarhana, A.S.; Ilyas, R.A.; Ngadi, N. A review of nanocellulose adsorptive membrane as multifunctional wastewater treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.D.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhu, L.P.; Yang, M.C.; Chen, Y. Nanocellulose-based membranes for highly efficient molecular separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Lindstrom, T.; Sharma, P.R.; Chi, K.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose for sustainable water purification. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 8936–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, S.M.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q.Q. Sustainable cellulose nanomaterials for environmental remediation—Achieving clean air, water, and energy: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 285, 119251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bai, T.; Yue, Y.Y.; Cheng, W.L.; Bai, L.; Wang, D.; Lu, J.Q.; Cao, M.L.; Shi, S.Q.; Huan, S.Q.; et al. Nanostructured superior oil-adsorbent nanofiber composites using one-step electrospinning of polyvinylidene fluoride/nanocellulose. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 224, 109490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Xia, D.W.; Wang, B.T.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhu, L.P. Highly permeable polyamide nanofiltration membrane incorporated with phosphorylated nanocellulose for enhanced desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 647, 120339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.X.; Wang, D.; Cheng, W.L.; Huang, J.Q.; Cao, M.L.; Niu, Z.X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yue, Y.Y.; Han, G.P. Spider-web-inspired membrane reinforced with sulfhydryl-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals for oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.W.; Zhang, M.X.; Tong, C.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhu, L.P. In-situ incorporating zwitterionic nanocellulose into polyamide nanofiltration membrane towards excellent perm-selectivity and antifouling performances. Desalination 2022, 521, 115397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, J.; Chen, X.; Beaumont, M.; Hassinen, J.; Orelma, H.; Dumee, L.F.; Tardy, B.L.; Rojas, O.J. Impact of incubation conditions and post-treatment on the properties of bacterial cellulose membranes for pressure-driven filtration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, S.; Ahn, J.; Kim, H. High performance and sustainable CNF membrane via facile in-situ envelopment of hydrochar for water treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yue, M.; Yuan, F.S.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, C.T.; Sun, D.P. Bio-inspired fabrication of highly permeable and anti-fouling ultrafiltration membranes based on bacterial cellulose for efficient removal of soluble dyes and insoluble oils. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 621, 118982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Lee, M.; Hong, S.K.; Park, C.; Cho, S.J.; Lim, G. Comprehensive Electrokinetic-Assisted Separation of Oil Emulsion with Ultrahigh Flux. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15815–15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Gao, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Photothermal-Responsive Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Ultrathin Membranes for On/Off Switchable Separation of Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4835–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, M.E.; Li, K.; Qian, J.; Wang, L.; Lavoine, N.; Newman, R.; Gardner, D.J.; Li, T.; Hu, L.; Ragauskas, A.J.; et al. Recent Advances in Functional Materials through Cellulose Nanofiber Templating. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, C.; Brozena, A.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Xu, L.; Driemeier, C.; Dai, J.; Rojas, O.J.; Isogai, A.; Wagberg, L.; et al. Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 2021, 590, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.T.; Chiu, H.L.; Liao, Y.C. Multifunctionalized Cellulose Nanofiber for Water-Repellent and Wash-Sustainable Coatings on Fabrics. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8144–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, F.; Zhao, X.J.; Duan, Y.X.; Zhao, X.Q.; Jia, S.R.; Zhong, C. Designing of bacterial cellulose-based superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic membrane for oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, P.; Marchesi D’Alvise, T.; Boi, C.; Geiger, T.; Caseri, W.R.; Zimmermann, T. Nanofibrillated Cellulose Templated Membranes with High Permeance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33943–33954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, Y.; Ge, J.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Yin, X.; Ding, B. Ultrathin Cellulose Voronoi-Nanonet Membranes Enable High-Flux and Energy-Saving Water Purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 31852–31862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olkiewicz, M.; Caporgno, M.P.; Font, J.; Legrand, J.; Lepine, O.; Plechkova, N.V.; Pruvost, J.; Seddon, K.R.; Bengoa, C. A novel recovery process for lipids from microalgæ for biodiesel production using a hydrated phosphonium ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2813–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, W.H.; Hung, W.S.; Wang, N.; Sun, J.; Lee, K.R.; An, Q.F.; Liu, C.M.; Zhao, Q. Phosphonium Modification Leads to Ultrapermeable Antibacterial Polyamide Composite Membranes with Unreduced Thickness. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2001383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, E.F.; Lienkamp, K.; Gillies, E.R.; Ragogna, P.J. Antibacterial Activity of Polymers: Discussions on the Nature of Amphiphilic Balance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3690–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.N.; Zhan, H.; Li, D.; Tian, H.F.; Chang, C.Y. Tunicate cellulose nanocrystals modified commercial filter paper for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.Y.; Ye, D.D.; Yang, W.T.; Zhang, S.H.; Chen, H.Z.; Chang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.N. Construction of Transparent Cellulose-Based Nanocomposite Papers and Potential Application in Flexible Solar Cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8040–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.N. Phase transition identification of cellulose nanocrystal suspensions derived from various raw materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A.; Saito, T.; Fukuzumi, H. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Sun, P.; Kuga, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, Y. Thin Cellulose Nanofiber from Corncob Cellulose and Its Performance in Transparent Nanopaper. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yuan, J.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Wei, P.; Cheng, G.J.; Chang, C.Y. Additive printing of recyclable anti-counterfeiting patterns with sol-gel cellulose nanocrystal inks. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 11808–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.F.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.Z.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.N.; Feng, L. Superwetting Porous Materials for Wastewater Treatment: From Immiscible Oil/Water Mixture to Emulsion Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, K.; Palantoken, S.; Andrei, V.; Ross, M.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Kettemann, F.; Greis, K.; Ingber, T.T.K.; Stuckrath, J.B.; Valiyaveettil, S.; et al. Functionalized Cellulose for Water Purification, Antimicrobial Applications, and Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, K.; Wang, C.; Chang, C.; Peng, N. Phosphonium Modified Nanocellulose Membranes with High Permeate Flux and Antibacterial Property for Oily Wastewater Separation. Coatings 2022, 12, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101598
Peng K, Wang C, Chang C, Peng N. Phosphonium Modified Nanocellulose Membranes with High Permeate Flux and Antibacterial Property for Oily Wastewater Separation. Coatings. 2022; 12(10):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101598
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Kun, Chenglong Wang, Chunyu Chang, and Na Peng. 2022. "Phosphonium Modified Nanocellulose Membranes with High Permeate Flux and Antibacterial Property for Oily Wastewater Separation" Coatings 12, no. 10: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101598
APA StylePeng, K., Wang, C., Chang, C., & Peng, N. (2022). Phosphonium Modified Nanocellulose Membranes with High Permeate Flux and Antibacterial Property for Oily Wastewater Separation. Coatings, 12(10), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101598





