Abstract
Metal coins discovered during archaeology have artistic and cultural value. Careful cleaning is required for artifact conservation. Metal artifacts must be cleaned to remove corrosion, which can range from tarnishing to a thick crust, in addition to dust, previous coatings, and burial deposits. Cleaning corrosion is still a challenging conservation process, but the advantages of using traditional cleaning methods outweigh the disadvantages. The current study aimed to evaluate the use of a nanosecond infrared Q-switched Nd: YAG pulsed laser for biodeteriogen elimination by laser cleaning and elemental analysis via LIBS analysis on old, corroded coins. The corroded coins used in this study were found in Egyptian burial dirt. Four different varieties of unknown corroded coins were exposed to laser cleaning testing. Throughout the cleaning process, LIBS diagnostics was used to monitor the laser ablation process as it removed various types of corrosion products. The coins were analyzed with a scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray analyzer before and after the laser cleaning to assess the efficacy of the suggested laser setup technique used in this experiment (SEM-EDX). The results show a reduction in the spectral lines of corroded metals (Cu, Ca, and Mg) in the investigated coins after cleaning when compared to the original analyses. However, the surface morphology of each coin changes somewhat due to the presence of CuOx, which was recognized by increasing the strength of O lines, ensuring the viability of utilizing LIBS to identify the unknown coins tested.
1. Introduction
Artifact conservation is gratifying work for historians and archaeologists alike. They are a valuable resource for learning about the past and a wealth of other information [1]. Kom el-Khanzir’s hill (Pachnemounis) [2,3], located in the Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate (Figure 1) [4], is one of Egypt’s most prominent archaeological cities. It has a 13-m elevation above sea level. A cemetery and an abandoned military base separate the vast property, which measures 500 m by 500 m and rises to a height of 12 m. Redbrick and earthenware were used to cover the floor. Hogarth referred to the location as ancient Pachnemounis [5]. In this area, the pottery dates to the medieval era, which began long after the Arab conquest of Egypt in the 10th century AD. In this place, three engraved slabs, a well-preserved life-size portrait head in Parian marble, and several coins were discovered during excavation. This makes it a crucial location for gaining insight into Ancient Egypt’s commercial network, sociological evolution, and political past [5,6].
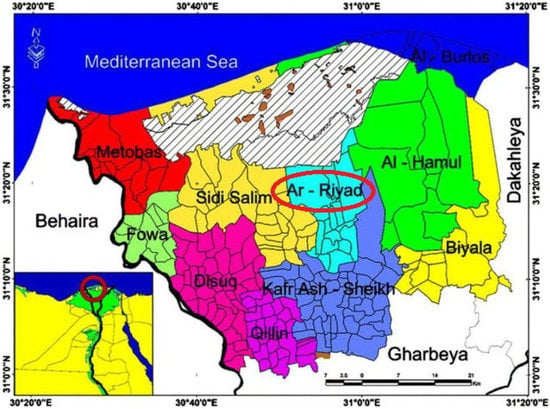
Figure 1.
Map of sample collection site, Kom el-Khanzir’s hill.
Ancient coins are rare and valuable archaeological finds because they document, reveal, and understand human progress across time. Coins, in addition to statues, little inscriptions, and valuable indications, are valuable sources of historical information [7]. The undesirable subject is the composition of unwanted materials on their faces, such as corrosion products, pollutants, and dirt. Various corrosion processes modify the appearance, form, nature, and resistance of archaeological coins [8,9].
Cleaning an artifact for conservation is a critical operation that normally necessitates tremendous care. Metal artifacts must be cleaned of corrosion, which can range from a thin layer of tarnishing to a thick corrosion crust, in addition to pollutants such as dust, prior coatings, or burial deposits [10]. Copper, iron, lead, silver, and gold are the most common metals discovered in museum and gallery collections [11]. They are, however, frequently alloyed. The issue with metal archaeological artifacts that have been buried in the ground or submerged underwater for long periods of time, particularly copper and iron alloys, is to uncover the “original surface” on which tool traces and embellishments frequently exist [12,13]. According to the literature [14,15,16], the original surface of metal artifacts discovered during archaeological excavation is usually found within the corrosion crust. This means that the corrosion cover will almost definitely persist even after conservators thoroughly clean an antique copper or iron artifact. In the last two decades, the use of laser ablation in cultural asset protection has progressed dramatically. Recent advances in the removal of black crusts and undesirable coatings from stone, metal, coinage, and wall paintings have aided conservation approaches. By improving irradiation conditions for a series of conservation issues, the effectiveness and selectivity of ablation procedures were demonstrated. S. Siano et al. proved in 2012 the capability of removing bio-deteriogens and graffiti from stone antiquities using the Nd: YAG laser’s 2nd harmonic (532 nm) or 1st harmonic (1064 nm), with the 1st harmonic allowing greater control over a photomechanical and photo-thermal generation during cleaning [17]. Furthermore, in 2015, M. Sanz et al. revealed the effect of a laser on the removal of biodeteriogen layers from heritage sites in central Spain by 1064 (IR) or 355 nm (UV), which resulted in the partial removal of the samples’ outer surface, whereas the IR-UV laser resulted in significant sample damage [18]. G. S. Senesi et al. also investigated the changes in the physicochemical parameters of an old artifact from Italy using Q-switched Nd: YAG (1064 and 532 nm) and the LIBS technology in 2016 [19]. Furthermore, H. Zhao et al. employed 1064 nm in 2020 to remove paint from the skin of an aircraft with a high repetition rate, which may be improved by choosing the proper laser scanning speed and repetition rate [20]. There are several ways to get rid of corrosion products, which are multi-component substances. However, some of these methods might make it hard to see current drawings on the original metal surfaces or, in the worst case, damage the object [21]. Laser cleaning is a high-efficiency and ecologically friendly cleaning technique [22,23]. It is a promising method for eliminating contaminants such as oil [24,25,26], paint [27,28], and oxide coatings [29,30,31]. Mateo et al. [26] employed laser cleaning to clear up oil spills on rocks and tools, and the non-contact cleaning method significantly minimized surface damage. Han et al. [28] studied the fundamental mechanism of paint removal. The thermal effect is the most effective for laser pain eradication, according to the findings, and the vaporization and laser-plasma effects should be avoided to improve the quality of the cleaned surface. Before thermal spraying of a Ti alloy, Li et al. [29] employed in situ laser cleaning instead of degreasing and sandblasting. To eliminate surface contaminants and the oxide layer, the interfacial physical contact was improved. This method is a very selective, non-contact way to remove harmful reactive corrosion products from a wide range of archaeological materials, which helps preserve the surface [32,33,34]. It works by vaporizing the corrosion products on the surface, which is safer than using traditional cleaning methods that could cause damage.
Archaeologists have recently shown a strong interest in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) as a method of acquiring insight into the samples they are studying to determine the composition variations [35,36]. It is superior for determining the elemental composition of a wide variety of objects. It has several advantages over conventional techniques. The minimal amount of sample (ng to µg) used in LIBS measurements makes it a fast, accurate, quasi-non-destructive, multi-element analytical method [37,38]. LIBS has been successfully used for elemental analysis of a wide range of artifact types, including metal artifacts, ancient coins, pottery, glass, geological samples, ink and pigments, cultural heritage material, paintings, sculptures, and zoo-archaeological relics [1]. This technique can be utilized for the in-situ studies of valuable artifacts, reducing the danger of damage while maintaining the sensitivity and value of archaeological objects. LIBS technique has recently been investigated to extract relevant information about archaeological and cultural heritage artifacts [10]. LIBS spectra typically contain a large number of variables (spectral emission lines corresponding to various wavelengths).
Herein, corrosion has obscured the identity of four previously unknown artifact coins. The coins were characterized by the combined use of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray (SEM-EDX) techniques, which allow exploration of the historical period to which the coins belong [39]. After that, the use of LIBS as effective physical instrumentation to reduce the rust-and-corrosion layer improves the efficiency of the analysis. As a result, this research is an important contribution to archaeology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Studied Corroded Ancient Coins
In this work, four archaeological metal coins (collected from Kom el-Khanzir’s hill in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, North Nile delta, Egypt), which had a diameter dimension from 1” to 1.1” and weight from 0.9 to 2.4 g, were examined for further identification. These coins have developed heavy coatings of corrosion products on their surfaces after being buried for an extended period of time. Because their appearances were so damaged, it was impossible to discern any trace of the original surface on them. Mineralized and metallic, insoluble phases were also present in the corrosion layer and products were generated by the interaction of soil components with metal corrosion compounds and soil particles.
2.2. Experimental Set-Up for the Cleaning and Investigation of Corroded Coins
Figure 2 shows the experimental setup. The equipment has cleaning and analyzing lasers. The specification of the used laser source is a Q-switched Nd: YAG Laser (PL9000, Continuum Electro-Optics, Inc. Laser, Boston, MA, USA), which emits a laser beam with a diameter of 0.5 mm, the energy of 100 mJ/pulse, repetition rate of 10 Hz, and fundamental wavelength of 1064 nm, which was splatted to two paths by a 50/50 beam splitter. The first path was directed for cleaning while another path was directed to the LIBS measurement. It was performed on a sample mounted on a holder, coupled to the X-Y-Z motorized stage, at atmospheric pressure.
In the case of LIBS measurement, the instrumental set-up was produced by the same laser source to generate a plasma plume, which was generated from the interaction of the focusing laser beam with the studied samples, which were placed on a sample mounted on a holder, coupled to the X-Y-Z motorized stage, at atmospheric pressure controlled by stepper motors, with the velocity set to 0.8 cm/s, while the focusing laser beam was produced from passing the laser beam through a 70 mm plano-convex quartz lens. The motorized stage allows to the movement of the sample horizontally in two directions. Before any cleaning step, a third translational motorized stage positioned the focus lens at specific distances to control the spot size on the sample, which is the irradiated area and laser fluence. The sample was far from the lens’ focal point. In-house software controls the system and laser. Before each analysis, the pulse’s energy was measured. This plasma plume was captured and transported using Czerny-Turner spectrometer fiber optics (0.6 mm diameter, 50 cm length) (Acton SP2500, made in the USA). The dispersion grating utilized has 2400 lines/mm and scans wavelengths from 200 to 900 nm with a resolution of 0.05 nm. The monochromator is linked to an ICCD camera (1KRB-FG-43, gating time 2 ns). WinSpec/32, LIBS++, and the necessary database were used to acquire and analyze spectroscopic data (open tools for analyzing the LIBS).
A scanning electron microscope with an energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (Model Quanta 250 FEG (Field Emission Gun), the accelerating voltage is 30 kV, the magnification is 14×, and the resolution is Gun.1n) was used to evaluate the analytical LIBS technique and the preservation status of the aforementioned coinage. Consequently, each coin’s surface morphology can be thoroughly investigated. The corrosion layer of the four coins was chemically analyzed using SEM with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) at the designated uncontaminated areas.
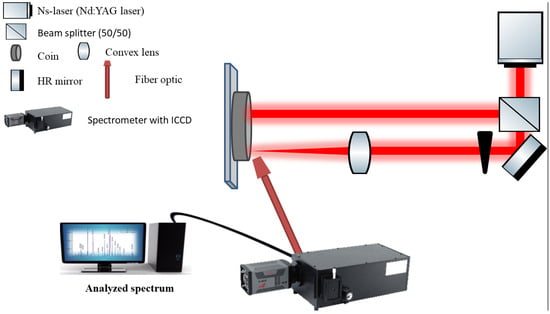
Figure 2.
Experimental set-up for the use of a pulsed laser beam for laser cleaning and LIBS investigation.
2.3. Pulsed Laser for Cleaning
Material removal by nanosecond laser pulses can be generated through pressure confinement or spallation and above the vaporization threshold by the quick thermal explosion. Plasma-mediated ablation produces substantial recoil stress in the millisecond range (Figure 3).
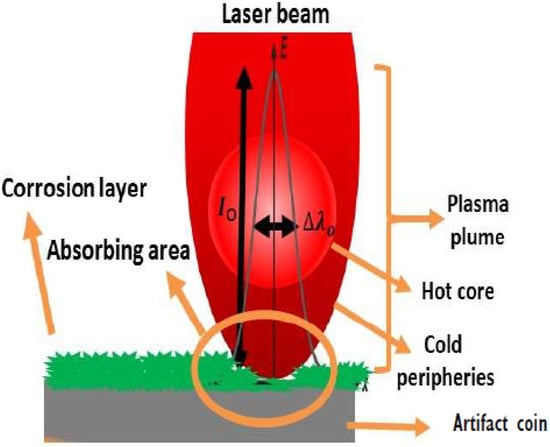
Figure 3.
Laser-cleaning model for coin sample-based metal artifacts.
2.4. Pulsed Laser Ablation for LIBS Analysis
Using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation, a plasma plume is generated, which can be utilized to assess the surface’s elemental composition. To produce a spectrum, the plasma plume’s generated emission was sent through a fiber optic to an apparatus that analyzes wavelengths. Each piece of material provides an itemized fingerprint [21]. For in situ applications, the LIBS technique is critical because of its ability to perform multi-element characterizations quickly and without the need for sample preparation and its reasonable depth of resolution [38].
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Visual Examination of Coin Samples
Figure 4 depicts the samples of four coins (A–D) before and after the ablation procedure directed to a tiny section using LIBS. It shows the cleaned portions of the coins. During cleaning, optical microscope pictures were taken to examine the coin’s microstructure and texture. Visual and microscopic studies revealed that the coins were significantly damaged and had a broad corrosion layer, but laser cleaning demonstrated effective results in reducing the amount of accumulated corrosion on the surface of unknown-identity coins. This detection improves the coin’s surface morphology, making it appear more unique. The tested laser radiation was utilized to cure the superficial corrosion layer on coins (A–D) until the principal surface of the coin was revealed. Visual inspection of Figure 3 exposed the degraded coins prior to laser cleaning, with a thick rust layer impeding the examined coin surface. There was visible corrosion in a variety of colors, including black, light blue, and blue-green surfaces coated with burial leftovers. Before laser cleaning, coins have a raw hard crust and green-bluish corrosion layer. This coating of corrosion products mixed with soil relics covered its features, making it unattractive, while the results of the tested coin after laser cleaning revealed that the major surfaces of the studied coins (cleaned surface of the coin) were provided after 10 s of continuous shooting with the laser beam. The matter interactions within the laser plasma can eliminate undesired corrosion products (green in the image), which absorb the laser irradiation beam and leave a protective covering of corrosion products behind (brown in the picture). The metal surface that reflects the laser beam is unaffected.
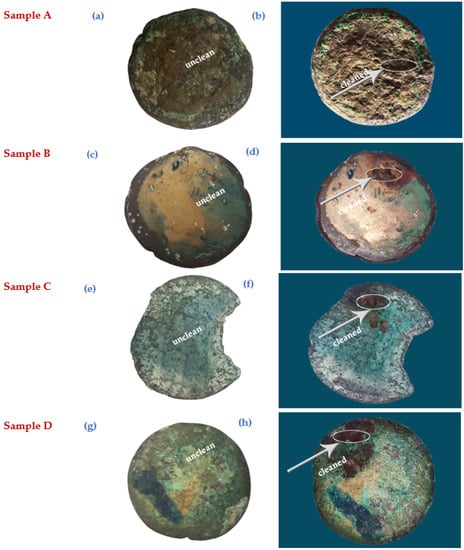
Figure 4.
Process of laser cleaning of the studied corroded coins before and after cleaning via continuous shooting for 10 s (a,b) coin A; (c,d) coin B; (e,f) coin C; (g,h) coin D.
3.2. LIBS Analysis
The application of LIBS produces effective results in reducing the amount of corrosion products accumulated on the surface of unknown-identity coins. This detection improves the surface morphology of the coin and makes it appear more unique. The data shows the total number of elements identified from all LIBS spectra acquired by averaging three shots used to acquire the LIBS spectra prior to cleaning. After 10 s of continuous firing with the plasma plume, comprehensive data was provided on the effect of the cleaning procedure with LIBS. Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 clearly illustrate the spectral signatures of lead (Pb), copper (Cu), calcium (Ca), tin (Sn), iron (Fe), and magnesium (Mg) in the LIBS spectra of coins (A-D) in four different spectral ranges (275–291, 307–330, 391–409, and 508–525 nm) before and after cleaning. The ablation process reduces the main contaminating components Cu, Ca, and Mg, with the appearance of the lead element alternating between rising and decline. Although the diminishment behavior is achieved for all analyzed coins, this tendency occurs at distinct line intensities, indicating that the coins are completely different. The amount of contaminated components left after cleaning demonstrates that the layer is rather thick, which may be addressed with a long-time shooting to make the coins somewhat smooth and original. In our example, with a medium layer of corrosion, a shooting period of 10 s is an appropriate condition for cleaning with LIBS. Furthermore, it was observed that the primary contaminant elements Cu, Ca, and Mg were reduced. However, the surface morphology of each coin changes mildly probably due to the existence of CuOx, which was detected by increasing the intensity of Cu lines.
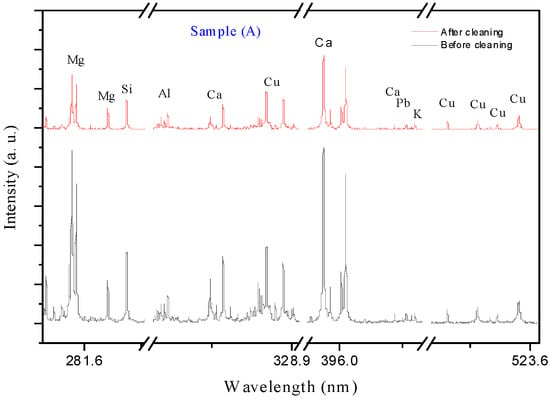
Figure 5.
The LIBS spectra of the corroded coin sample (A) before and after cleaning.
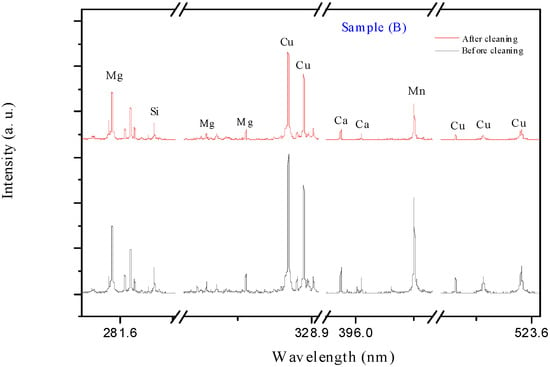
Figure 6.
The LIBS spectra of the corroded coin sample (B) before and after cleaning.
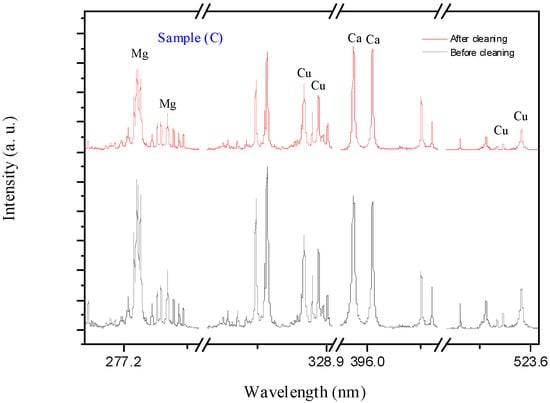
Figure 7.
The LIBS spectra of the corroded coin sample (C) before and after cleaning.
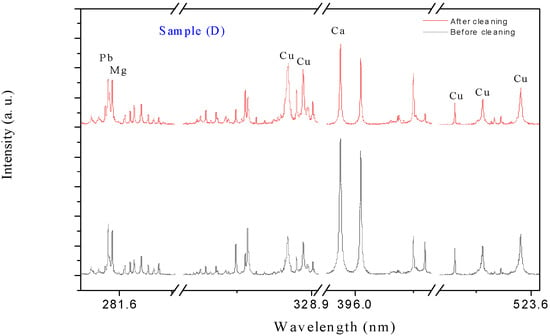
Figure 8.
The LIBS spectra of the corroded coin sample (D) before and after cleaning.
3.3. SEM Analysis
Authenticating ancient coins by analyzing their main, minor, and trace components is a time-honored method that comprehends the manufacturing and corrosion processes that affect the exterior surface. Ancient coin analysis relies heavily on elemental composition analyses. Some coins are covered in corrosion products or metal oxide, so a cross-section is necessary to disclose the metallic core [40,41]. It is possible for corrosion processes to enrich the outer layer of the surface with noble components [42,43,44]. For coins (A-D), Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 show the results of the SEM morphological examinations before and after laser cleaning. A 500-times magnification was used to capture these photos for analysis. Before the laser cleaning, the coins could clearly be seen to have a layer of corrosion products on them. It was possible to precisely select the micro-areas of interest in the sample using the SEM approach. The analysis was performed at an average working distance of about 20 mm. Using SEM imaging, we were able to evaluate the surface quality and uniformity, identify characteristic areas and describe corroded layers. The morphological and compositional differences in the coins investigated are shown in these photos of the representative regions. One can clearly see massive and elongated phase grains on the coins (A-D) beneath an irregular corrosion layer that has local fissures and crevices on the surface. Figure 9b, Figure 10b, Figure 11b and Figure 12b indicate that following laser cleaning, the corrosion layer on the coins’ surfaces was largely removed by continuous laser ablation for 10 s, resulting in a clearer and more homogeneous surface [45,46].
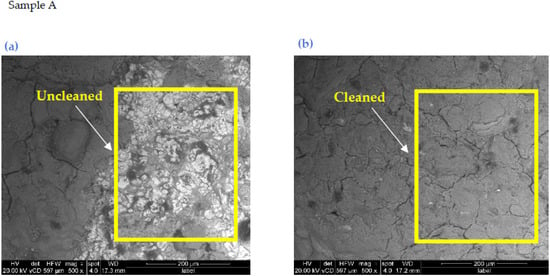
Figure 9.
SEM image of sample (A) (a) before and (b) after cleaning at 500× magnification.

Figure 10.
SEM image of sample B (a) before and (b) after cleaning at 500× magnification.

Figure 11.
SEM image of sample C (a) before and (b) after cleaning at 500× magnification.

Figure 12.
SEM image of sample D (a) before and (b) after cleaning at 500× magnification.
3.4. EDX Analysis
The EDX spectra of the studied coins before and after cleaning were produced in the same experimental conditions to obtain further insight into the compositional features, which show a very good agreement with LIBS (Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16). Table 1 presents the weight percentage values of the elements of the coins’ corroded layer. Following laser cleaning, the elemental examination of the metallic unknown coins found that the coins include a 61.4–45.3 weight percent for Cu, 12.8–2.29 weight percent for Pb, and 7.5–1.5 weight percent for Sn. As impurities, calcium, magnesium, and other trace elements are present. According to the elemental analysis, the four unknown coins are a binary alloy of copper and lead, with tin and other trace elements as impurities. The presence of lead can be attributed to industrial processes such as a need for fluidity and casting [42,47,48,49,50], which reduces the copper proportion and makes the coin lighter. Lead can also occur if the coin is buried near or in contact with other objects composed of lead or its alloys, or if the coin is coated with lead [51]. This result gives information on the economic situation at the time of minting. Furthermore, the EDX spectra show the presence of other minor elements such as Cl, S, and O, which are connected with Cu corrosion, while Si and O are associated with the soil in which the coins were buried. Remarkably, the percentage of O is higher after cleaning as Cu objects under the influence of oxygen may form a layer of CuO on their surface, which acts as a protective (passive) layer. A significant discrepancy was discovered for the unknown corroded coins, most likely due to the technique’s known differing depths of penetration and a higher degree of corrosion observed by EDX [52,53,54].
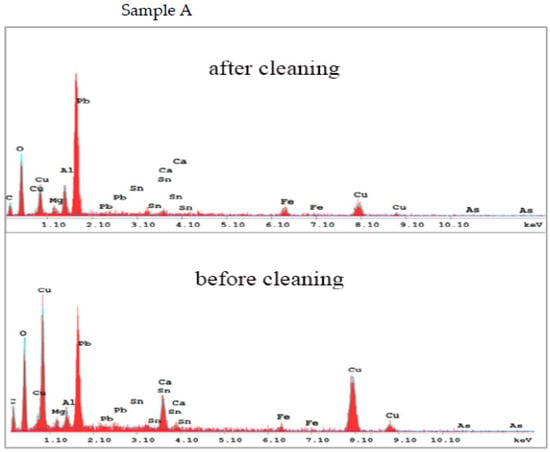
Figure 13.
The EDX analysis of the coin (A) before and after laser cleaning.
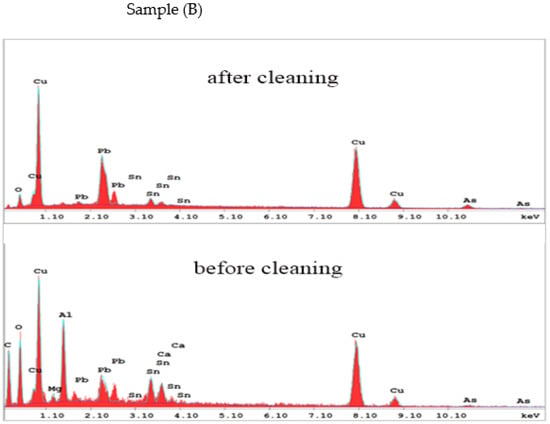
Figure 14.
The EDX analysis of the coin (B) before and after laser cleaning.
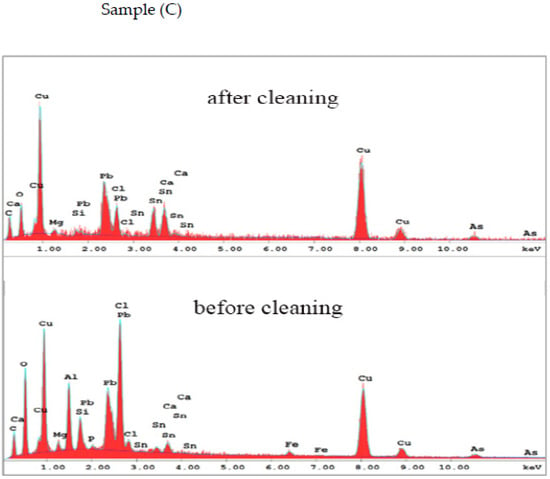
Figure 15.
The EDX analysis of the coin (C) before and after laser cleaning.
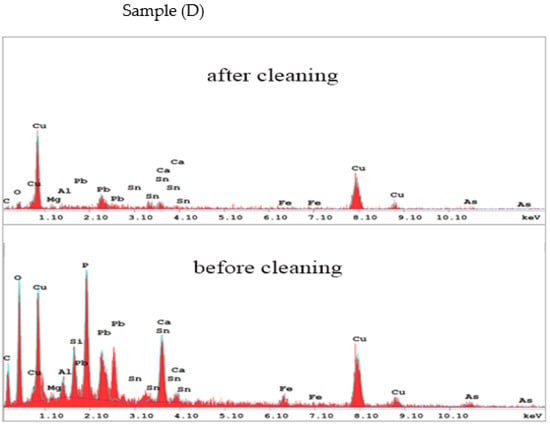
Figure 16.
The EDX analysis of the coin (D) before and after laser cleaning.

Table 1.
Mass percentage values of the elements of the coins’ corroded layer before and after cleaning determined by EDX.
4. Conclusions
Cleaning with lasers is becoming an increasingly well-known and important conservation technique due to the irradiation of laser-matter interaction. To ablate and remove the rust covering of ancient, damaged coins, laser cleaning is a low-cost method that is both effective and safer than other earlier technologies. Before and after laser cleaning, four unidentified coins were tested with SEM/EDX morphologies to verify the results of the treatment with LIBS. The LIBS technique has several benefits over conventional analysis methods, such as an easier parameter setting and better interpretability. Diminishment behavior was shown for all coins analyzed, albeit at varying line intensities, indicating that each coin is unique. A long period of firing could thin out the coating and return the coins to their original smoothness and authenticity, as seen by the high number of contaminated components that persisted after cleaning. Additionally, the concentrations of the three most common contaminating elements (Cu, Ca, and Mg) were observed to decrease. However, the presence of CuOx was recognized by an increase in the intensity of O lines, resulting in little change in the surface morphology of each coin. Using SEM/EDX, we were able to observe the morphology from microchemical studies in some areas of the coins. Upon close inspection, the coins’ granular surface texture became apparent. Using the SEM images, we can analyze the surface quality and homogeneity, and locate and characterize corroded layers. These pictures of the sample areas really bring out the variety in the coin shape and composition that we found. Below an uneven corrosion layer with local fractures and crevices on the surface, the coins’ (A:D) massive and elongated phase grains were plain to see. After 10 s of continuous laser ablation, the coins’ surfaces were cleaner and more uniform because the rust layer had been largely removed. The EDX spectra of the analyzed coins demonstrated the weight % values of the coins’ corroded layer before and after cleaning under the same experimental conditions to evaluate the compositional features. The unknown coins had 61.4%–45.3% Cu, 12.8%–2.29% Pb, and 7.5%–1.5% Sn. Trace elements include calcium, magnesium, and others. Elemental research shows the four unknown coins are a copper-lead alloy with tin and other trace components. Most copper alloys contain silver or tin. Some studies found lead mistaken for tin or for copper. Lead likely formed a binary alloy with copper. Lead was less expensive than silver or tin throughout the minting period. Moreover, the EDX spectra also revealed the existence of trace elements such as Si and O, which are linked to the soil the coins were buried in, and Cl, S, and O, which are related to Cu corrosion. CuO, a coating that can form on the surface of Cu objects, explains the unexpected increase in the O content after cleaning. The corroded areas’ SEM/EDX results were consistent with the LIBS findings. This motivates archaeologists to investigate the coin’s time period in order to better identify it.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.R., N.A.A.G. and A.M.M.; methodology, R.A.R. and A.M.M.; software, R.A.R. and A.M.M.; validation, R.A.R., N.A.A.G. and A.M.M.; formal analysis, R.A.R. and A.M.M.; investigation, R.A.R., N.A.A.G. and A.M.M.; resources, N.A.A.G.; data curation, R.A.R. and N.A.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.R. and A.M.M.; writing—review and editing, R.A.R., N.A.A.G. and A.M.M.; visualization, A.M.M.; supervision, N.A.A.G.; funding acquisition, R.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This paper draws on work supported by the facilities of the Laser Technology Unit, National Research Centre, Egypt.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Awasthi, S.; Kumar, R.; Rai, G.K.; Rai, A.K. Study of archaeological coins of different dynasties using libs coupled with multivariate analysis. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 79, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P. Landscape s of the Bashmur: Settlements and Monasteries in the Northern Egyptian Delta from 7th–9th Century. Mainz Hist. Cult. Sci. 2017, 36, 345. [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth, D.G. Three North Delta Nomes. J. Hell. Stud. 1904, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elmorshedy, H.; Bergquist, R.; Abou El-Ela, N.E.; Eassa, S.M.; Elsakka, E.E.; Barakat, R. Can human schistosomiasis mansoni control be sustained in high-risk transmission foci in Egypt? Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.R. The Excavations at Kausambi (1957-59): The Defences and Syenaciti of the Purusamedha; Department of Ancient History, Culture and Archaeology, University of Allahabad: Allahabad, India, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.R. Excavations at Kausambi 1949–1950; MASI No. 74; Archaeological Survey of India: Delhi, India, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Reale, R.; Plattner, S.H.; Guida, G.; Sammartino, M.P.; Visco, G. Ancient coins: Cluster analysis applied to find a correlation between corrosion process and burial soil characteristics. Chem. Central J. 2012, 6, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Zahrani, M.; Ghoniem, M. A Characterization of coins from the Nagran Hoard, Saui Arabia, prior to conservation. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2012, 3, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ruan, F.; Li, R.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, T.; Tang, H.; Li, H. In situ simultaneous quantitative analysis multi-elements of archaeological ceramics via laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning strategy. Microchem. J. 2022, 182, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertasa, M.; Korenberg, C. Successes and challenges in laser cleaning metal artefacts: A review. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 53, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, D.T.M.; Watkinson, D.; Ganiaris, H. Guidelines for the Storage and Display of Archaeological Metalwork; English Heritage: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ICOM-Symposium. Conservation of Metal Statuary and Architectural Decoration in Open-Air Exposure, in, Paris; Symposium: Paris, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Weil, P.D. Conservation of metal statuary and architectural decoration in open-air exposure: An overview of current status with suggestions regarding needs and future trends. In Conservation of Metal Statuary and Architectural Decoration in Open-Air Exposure= Conservation des Oeuvres d’art et Decorations, en Métal Exposées en Plein Air; Symposium: Paris, France, 1986; Volume 6–8. X. pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bertholon, R. The location of the original surface: A review of the conservation literature. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Metals Conservation, Metal 2001, Santiago, Chile, 2–6 April 2001; pp. 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Garbassi, F.; Mello, E. Surface spectroscopic studies on patinas of ancient metalobjects. Stud. Conserv. 1984, 29, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.A. An examination of the patina and corrosion morphology of some Roman bronzes. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 1994, 33, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, S.; Agresti, J.; Cacciari, I.; Ciofini, D.; Mascalchi, M.; Osticioli, I.; Mencaglia, A. Laser cleaning in conservation of stone, metal, and painted artifacts: State of the art and new insights on the use of the Nd: YAG lasers. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 106, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Oujja, M.; Ascaso, C.; de los Ríos, A.; Pérez-Ortega, S.; Souza-Egipsy, V.; Wierzchos, J.; Speranza, M.; Cañamares, M.V.; Castillejo, M. Infrared and ultraviolet laser removal of crustose lichens on dolomite heritage stone. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, G.S.; Carrara, I.; Nicolodelli, G.; Milori, D.M.B.P.; De Pascale, O. Laser Cleaning and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy applied in removing and characterizing black crusts from limestones of Castello Svevo; Bari, Italy: A case study. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiao, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zang, Y.; Liu, X. Laser cleaning performance and mechanism in stripping of Polyacrylate resin paint. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ayhan, B.; Kwan, C.; Qi, H.; Vance, S. A Novel and Effective Multivariate Method for Compositional Analysis using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 17, 12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guan, Y. Real-Time Monitoring of Laser Cleaning for Hot-Rolled Stainless Steel by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Metals 2021, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, S.; Sezer, H.K.; Kamara, A.M. Applications of laser cleaning process in high value manufacturing industries. In Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning: Application of Cleaning Techniques; Kohli, R., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 11, pp. 251–288. [Google Scholar]
- Veiko, V.; Samohvalov, A.; Ageev, E. Laser cleaning of engraved rolls coupled with spectroscopic control. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 54, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.Q.; Song, Y.; Guan, Y.C. Tailoring metallic surface properties induced by laser surface processing for industrial applications. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2019, 2, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.P.; Nicolas, G.; Piñon, V.; Ramil, A.; Yañez, A. Laser cleaning, an alternative method for removing oil-spill fuel residues. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 247, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, S.S.; Lin, X.C.; Li, X.Y. Removal of paint layer by layer using a 20 kHz 140 ns quasi-continuous wave laser. Optics 2018, 174, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Cui, X.D.; Wang, S.; Feng, G.Y.; Deng, G.L.; Hu, R.F. Laser effects based optimal laser parameter identifications for paint removal from metal substrate at 1064nm: A multi-pulse model. J. Mod. Opt. 2017, 64, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Costil, S.; Liao, H.L.; Coddet, C. Surface preparation by using laser cleaning in thermal spray. J. Laser Appl. 2008, 20, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, H.G.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, G.; Shan, Z.Z. Effect of single pulsed picosecond and 100 nanosecond laser cleaning on surface morphology and welding quality of aluminium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 1061197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Hua, X.M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Cheng, J. Investigation on mechanism of oxide removal and plasma behavior during laser cleaning on aluminum alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Yu, J.E.; Koh, Y.S. Experimental study on the effect of wavelength in the laser cleaning of silver threads. J. Cult. Herit. 2003, 4, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M. In-Process and Intelligent Monitoring Systems for Laser Cleaning Process. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Siano, S.; Salimbeni, R.; Pini, R.; Giusti, A.; Matteini, M. Laser cleaning methodology for the preservation of the Porta del Paradiso by Lorenzo Ghiberti. J. Cult. Herit. 2003, 4, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Hamed, S.A.M.; Afifi, H.; Mohamady, S. A comparative study on the color change of pigments due to the consolidation of conventional spectroscopic techniques and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElFaham, M.M.; Okil, M.; Mostafa, A.M. Effects of post-laser irradiation on the optical and structure properties of Al2O3 nanoparticles produced by laser ablation. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 153104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElFaham, M.M.; Okil, M.; Mostafa, A.M. Limit of detection and hardness evaluation of some steel alloys utilizing optical emission spectroscopic techniques. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 108, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.G.; Aradhana, J.; Rohit, K.; Kumar, A.; Rai, A.K. Analysis of deposited impurity material on the surface of the optical window of the Tokamak using LIBS. Phys. Scr. 2014, 89, 075601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakis, C.; Anglos, D.; Zafiropulos, V.; Georgiou, S.; Tornari, V. Lasers in the Preservation of Cultural Heritage Principles and Applications; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, V.K.; Agrawal, R.; Rai, S.; Rai, A.K. Assessment of LIBS for spectrochemical analysis: A review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2013, 47, 14–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, F.J.; Cabalín, L.M.; Laserna, J.J. The potential of laser-induced breakdown spectrometry for real time monitoring the laser cleaning of archaeometallurgical objects. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2008, 63, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, R.; Rai, A. New Insights on Modern Age Coins by Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Method and Chemometric Approaches. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2022, 89, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, Y.; Mohamed, E. The role of archaeometallurgical characterization of ancient coins in forgery detection. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2019, 461, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, F.J.; Cuñat, J.; Cabalín, L.M.; Laserna, J.J. In situ analytical assessment and chemical imaging of historical buildings using a man-portable laser system. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridi, F.; Torrisi, L.; Cutroneo, M.; Barreca, F.; Gentile, C.; Serafino, T.; Castrizio, D. XPS and XRF depth patina profiles of ancient silver coins. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 272, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.J.; Asuero, A.G.; Jiménez, A.M. A review of energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) as an analytical tool in numismatic studies. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager, F.J.; Moreno-Suarez, A.I.; Scrivano, S.; Ortega-Feliu, I.; Gomez-Tubio, B.; Respaldiza, M.A. Silver surface enrichment in ancient coins studied by micro-PIXE. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2013, 306, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieta, E.; Lekki, J.; Meléndez, J.M.; Paluszkiewicz, C.; Nowakowski, M.; Matosz, M.; Kwiatek, W. Surface characterization of medieval silver coins minted by the early Piasts: FTIR mapping and SEM/EDX studies. Surf. Interface Anal. 2018, 50, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, R.; Uhlir, K.; Griesser, M. Micro-invasive depth profile analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): The case of mercury layers on Sasanian coins. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudbashi, O.; Hasanpour, A.; Jahanpoor, A.; Rahjoo, Z. Microscopic and microanalytical study on Sasanian metal objects from Western Iran: A case study. STAR Sci. Technol. Archaeol. Res. 2017, 3, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-López, M.L.; Pérez-Bueno, J.J.; Rodríguez-García, M.E. Characterizations of silver alloys used in modern Mexican coins. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inberg, A.; Ashkenazi, D.; Cohen, M.; Iddan, N.; Cvikel, D. Corrosion products and microstructure of copper alloy coins from the Byzantine-period Ma’agan Mikhael B shipwreck, Israel. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Cutroneo, M.; Torrisi, A. Mass Quadrupole Spectrometry Coupled to Laser Ablation for Cultural Heritage Applications. In Handbook of Cultural Heritage Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 445–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ioanid, E.G.; Ioanid, A.; Rusu, D.E.; Doroftei, F. Surface investigation of some medieval silver coins cleaned in high-frequency cold plasma. J. Cult. Herit. 2011, 12, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).