Internal Factors Affecting the Surface Rumpling of a β-NiAlHf Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
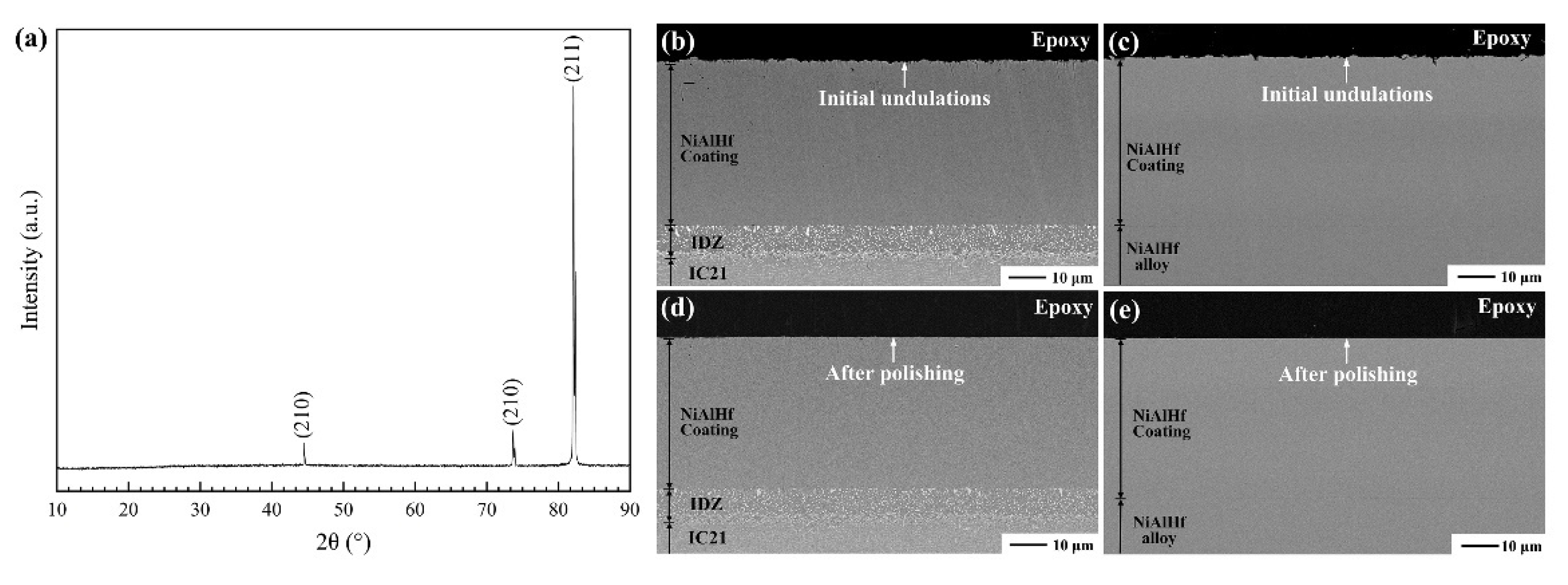
3.1. Coating Characterization
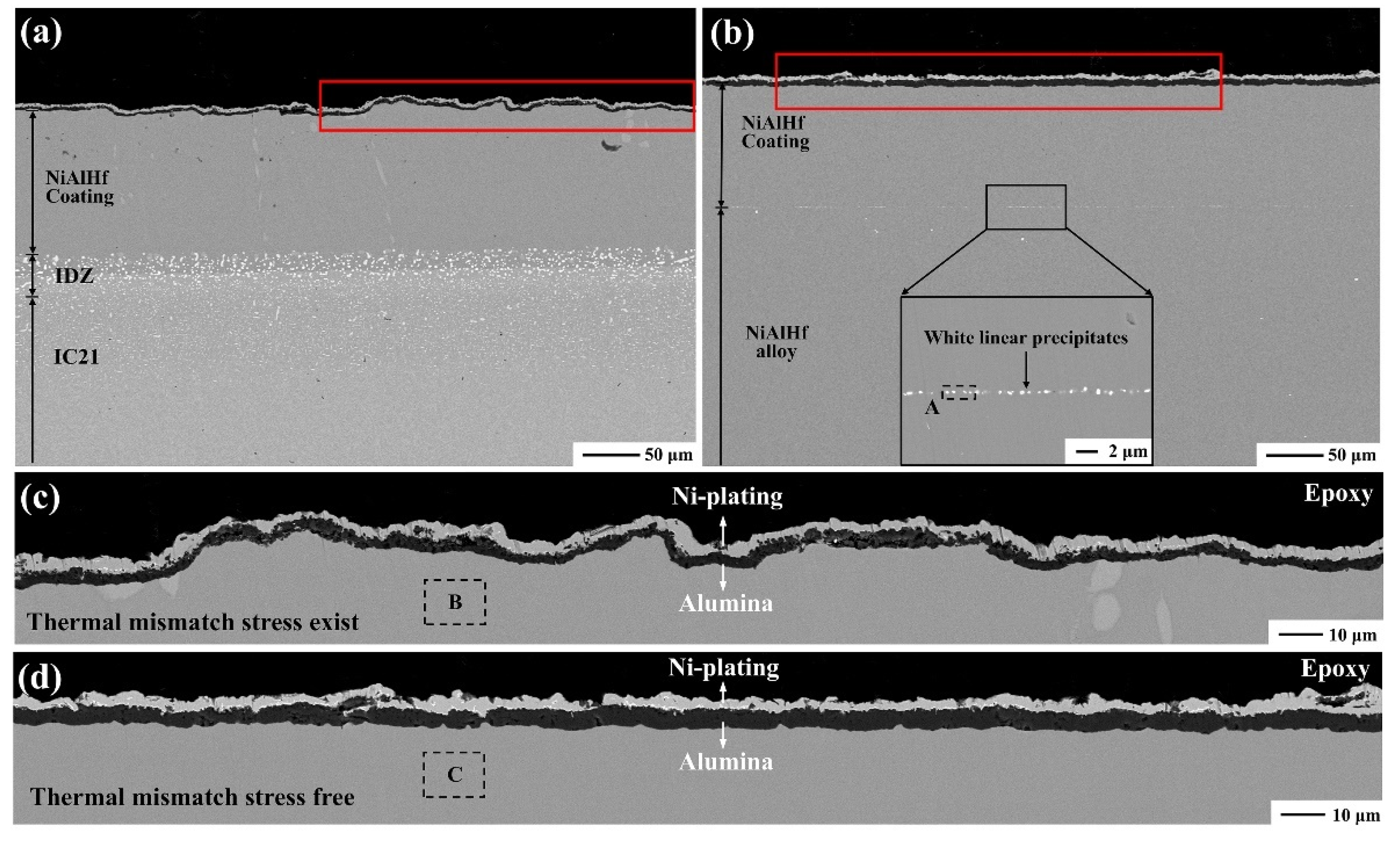
3.2. Effect of the Substrate during Cyclic Oxidation
3.3. Effect of the Stress in the Oxide Scale
3.3.1. Effect of Oxide Scale Growth Stress
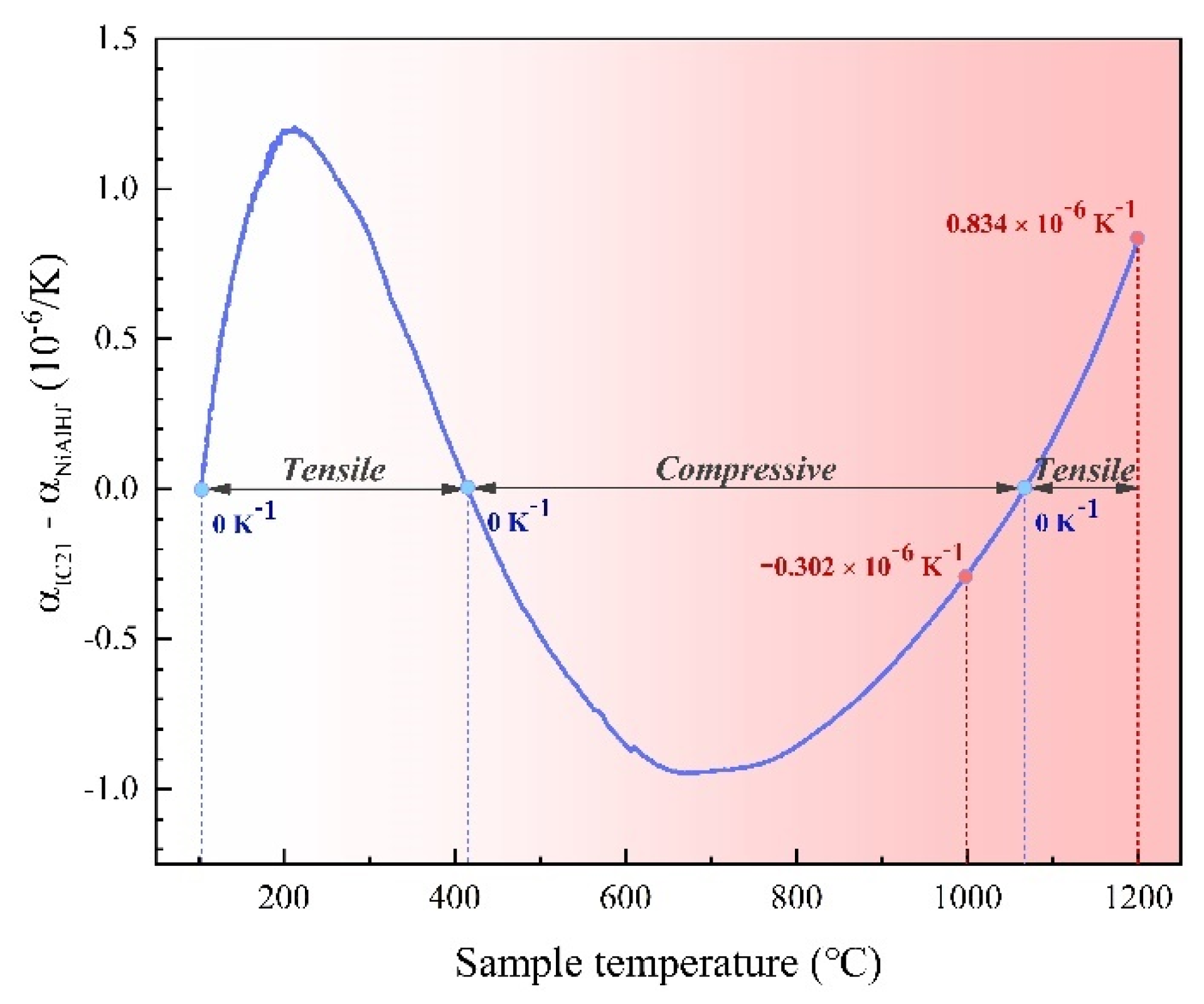
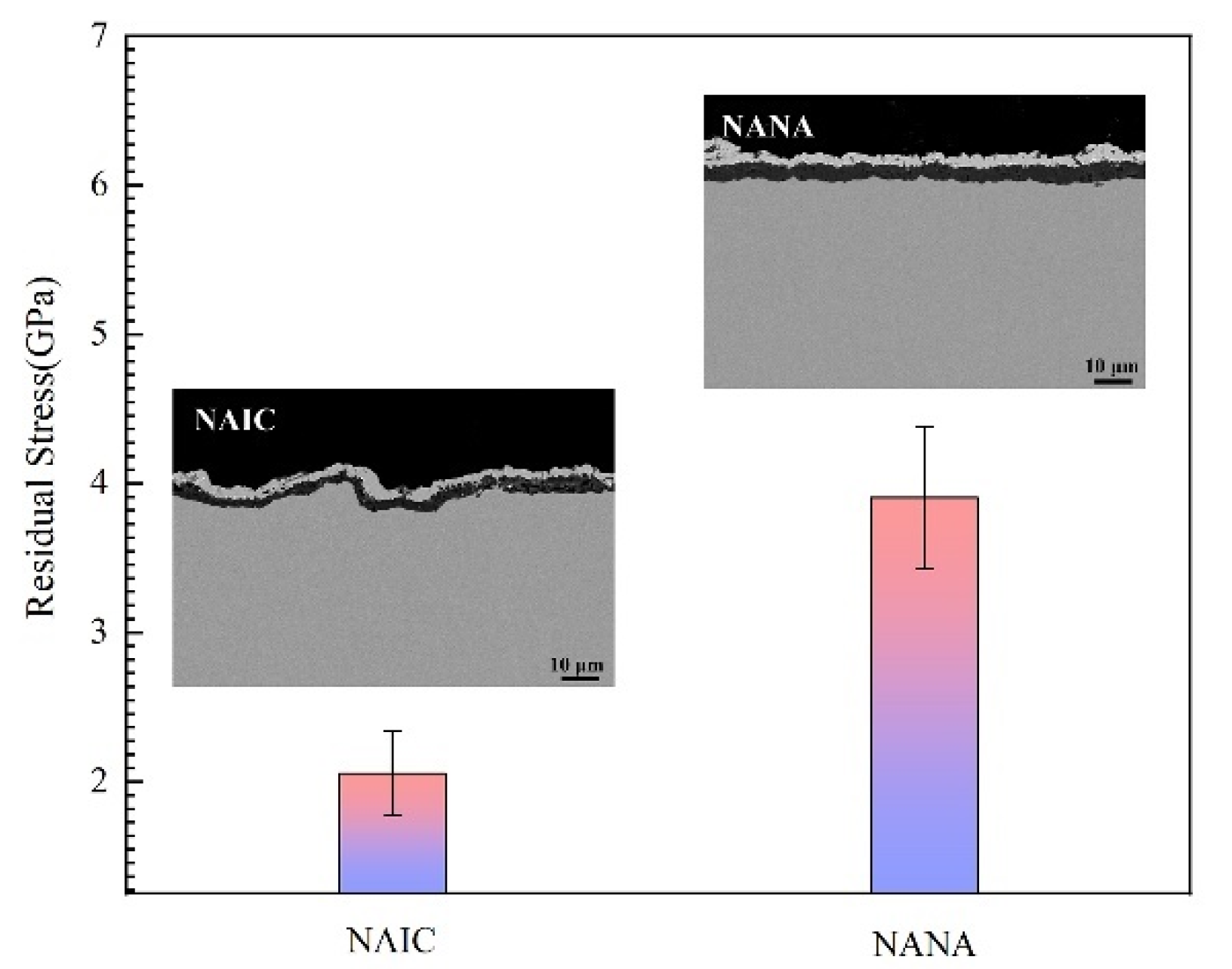
3.3.2. Effect of Mismatch Stress between Scale and Coating
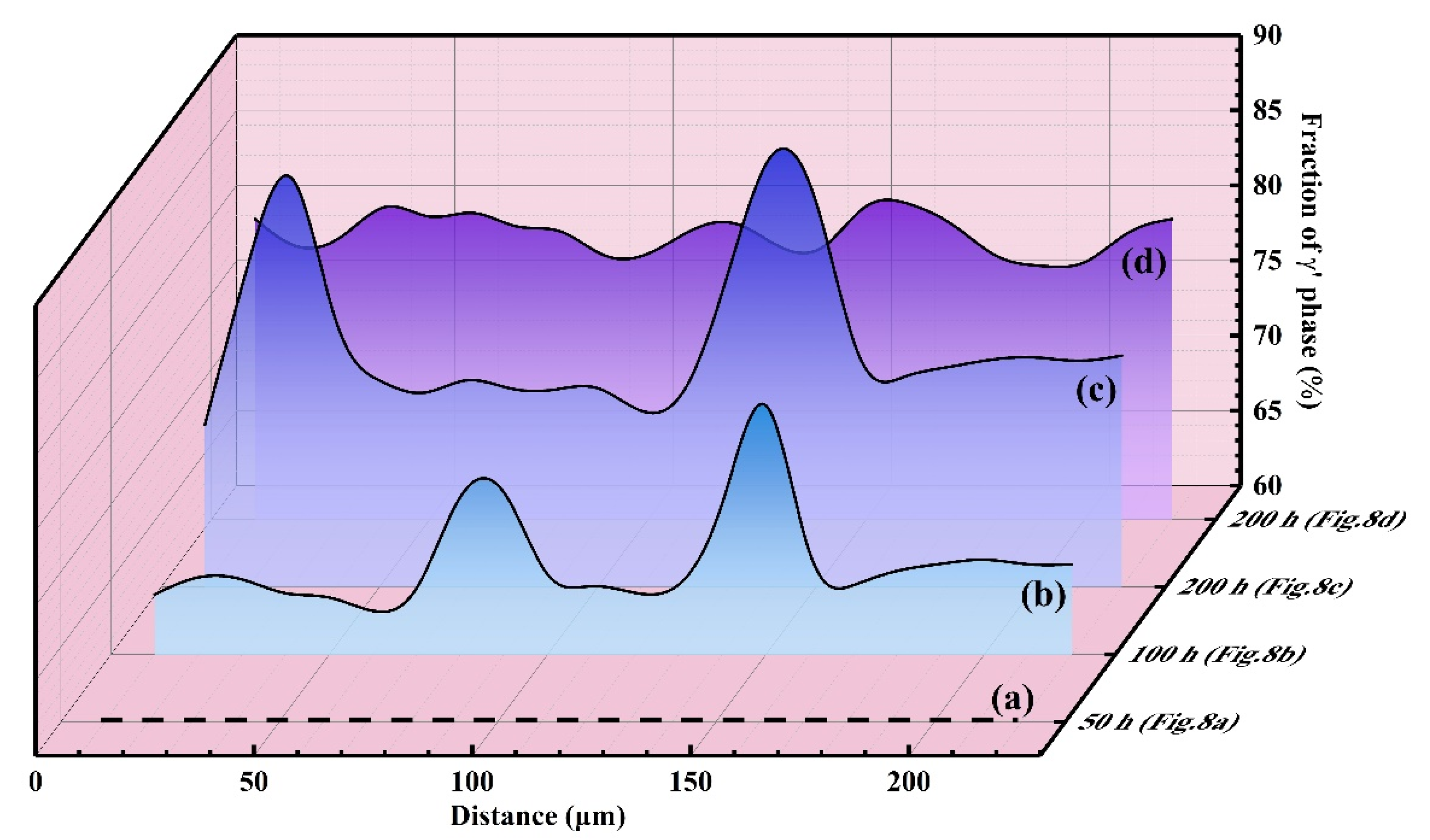
3.4. Effect of Phase Transformation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- During the thermal cycling test, the reduced yield strength of the β-NiAl coating due to high temperature and the thermal mismatch stresses between the β-NiAl coating and IC21 superalloy substrate are the major internal factor to induce surface rumpling.
- The growth stress of oxide scale and thermal mismatch stress between the oxide scale and the β-NiAl coating is insufficient to deform the coating, while the Kirkendall voids formed in the oxidation stage are noteworthy, bringing a group of sinusoidal periodic undulations onto the surface and degrading the oxide scale adherence.
- Concentrated phase transformation is the major internal factor inducing rumpling during isothermal oxidation. Continuous and concentrated β→γ’ transformation brings distinct volume reduction, thereafter contributing to the rumpling of the coating.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miracle, D.B. The physical and mechanical properties of NiAl. Acta Mater. 1993, 41, 649–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, I. A review of the mechanical properties of B2 compounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, J.A.; Pint, B.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wright, I.G. Comparison of the cyclic oxidation behavior of β-NiAl, β-NiPtAl and γ/γ’-NiPtAl coatings on various super alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennefather, R.C.; Boone, D.H. Mechanical degradation of coating systems in high-temperature cyclic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 76, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.E. Oxidation failure of tbc systems: An assessment of mechanisms. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, P. Effect of Al content on the lifetime of thermally grown oxide formed on Ni-Al alloys after isothermal oxidation. Corros. Sci. 2014, 89, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R. Temperature and cycle-time dependence of rumpling in platinum-modified diffusion aluminide coatings. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryepondt, S.; Porter, J.R.; Clarke, D.R. On the initiation of cyclic oxidation-induced rumpling of platinum-modified nickel aluminide coatings. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R. Rumpling of CVD (Ni,Pt)Al diffusion coatings under intermediate temperature cycling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Jiang, C.Y.; Yao, H.R.; Bao, Z.B.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, F.H. Cyclic oxidation and rumpling behaviour of single phase β-(Ni,Pt)Al coatings with different thickness of initial Pt plating. Corros. Sci. 2016, 111, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R. Rumpling induced by thermal cycling of an overlay coating: The effect of coating thickness. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R. Surface rumpling of a (Ni, Pt)Al bond coat induced by cyclic oxidation. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3283–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panat, R.; Zhang, S.; Hsia, K.J. Bond coat surface rumpling in thermal barrier coatings. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R. On the rumpling mechanism in nickel-aluminide coatings Part I. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5115–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.B.; Sun, L.D.; Li, H.F.; Gong, S.K. High temperature oxidation behavior of hafnium modified NiAl bond coat in EB-PVD thermal barrier coating system. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 5732–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Guo, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Gong, S.; Xu, H. Cyclic oxidation of β-NiAl with various reactive element dopants at 1200 °C. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K. Microstructure and high temperature oxidation behavior of Pt-modified aluminide coatings on Ni-base superalloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 151–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, V.; Esin, V.A.; Sallot, P.; Gaslain, F.; Gailliegue, S.; Rémy, L. Rumpling of nickel aluminide coatings: A reassessment of respective influence of thermal grown oxide and phase transformations. Mater. High Temp. 2016, 33, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Peng, H.; Gong, S.; Guo, H. Synergistic effect of reactive element co-doping in two-phase (γ’ + β) Ni-Al alloys. Corros. Sci. 2017, 120, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Jin, D.; Hao, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, P. Influence of substrate composition on the oxidation performance of nickel aluminide coating prepared by pack cementation. Corros. Sci. 2016, 110, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.J.; Lipkin, D.M.; Clarke, D.R. Nondestructive evaluation of the oxidation stresses through thermal barrier coatings using Cr3+ piezospectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 69, 3754–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, G. Artificial neural network to predict the effects of coating parameters on layer thickness of chromium carbonitride coating on pre-nitrided steels. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 23, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, G.; Nazari, A.; Khoie, S.M.M.; Khalaj, M.J.; Pouraliakbar, H. Chromium carbonitride coating produced on DIN 1.2210 steel by thermo-reactive deposition technique: Thermodynamics, kinetics and modeling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 225, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Boone, D.H.; Manley, T.F. Surface instability of platinum modified aluminide coatings during 1100 °C cyclic testing. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1987, 5, 3366–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panat, R.P. On the Rumpling Instability in Thermal Barrier Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign-Urbana, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, H.; Ghosh, S.; Walter, M.E. Parametric studies of failure mechanisms in elastic EB-PVD thermal barrier coatings using FEM. Int. J. Sol. Struct. 2006, 43, 4384–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, C.; Song, Y. Evaluation of cyclic oxidation of thermal barrier coatings exposed to NaCl vapor by finite element method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 490, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Chen, M.W.; Wright, P.K.; Hemker, K.J. Evolution of a diffusion aluminide coating for thermal barrier coatings during thermal cycling. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xin, L.; Qian, Y.; Li, T. A Review on studies of internal stress in oxide scales. Corros. Sci. Technol. Prot. 1999, 11, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Guo, H.; Peng, H.; Peng, L.; Gong, S. Cyclic oxidation and interdiffusion behavior of a NiAlDy/RuNiAl coating on a Ni-based single crystal superalloy. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2721–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumm, M.W.; Grabke, H.J. Oxidation behaviour of NiAl—II. Cavity formation beneath the oxide scale on NiAl of different stoichiometries. Corros. Sci. 1993, 34, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Mechanism of Martensite Aging Effects and New Aspects. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 312, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

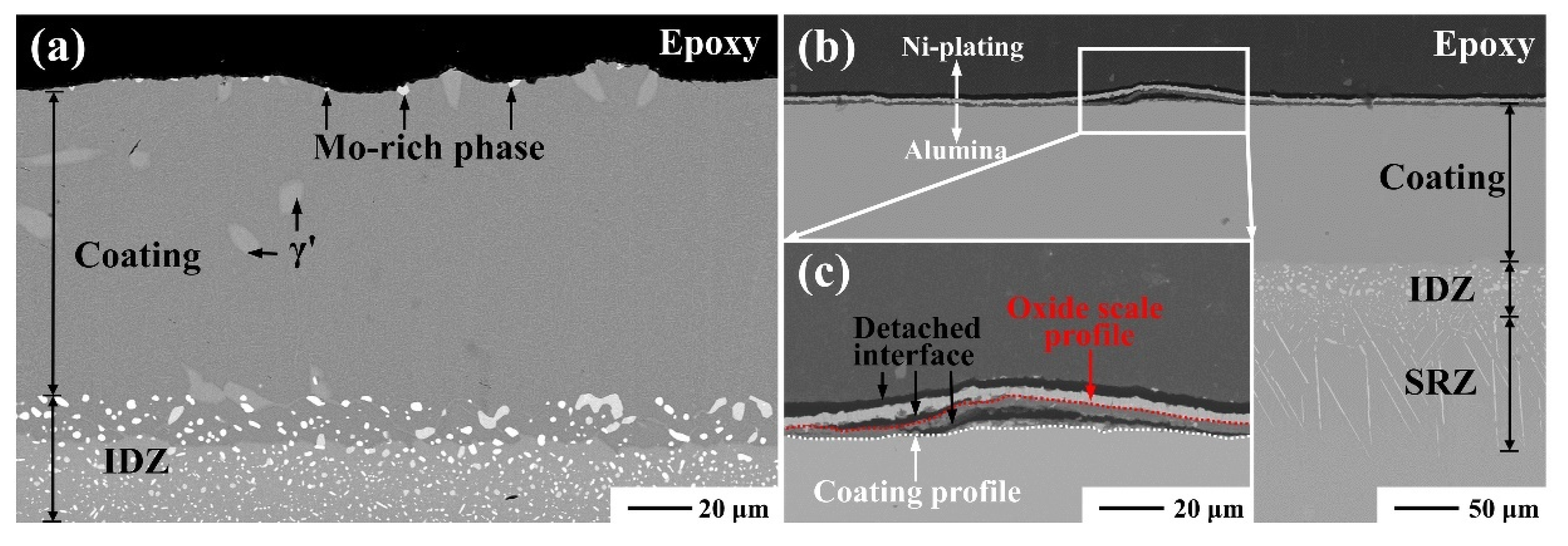
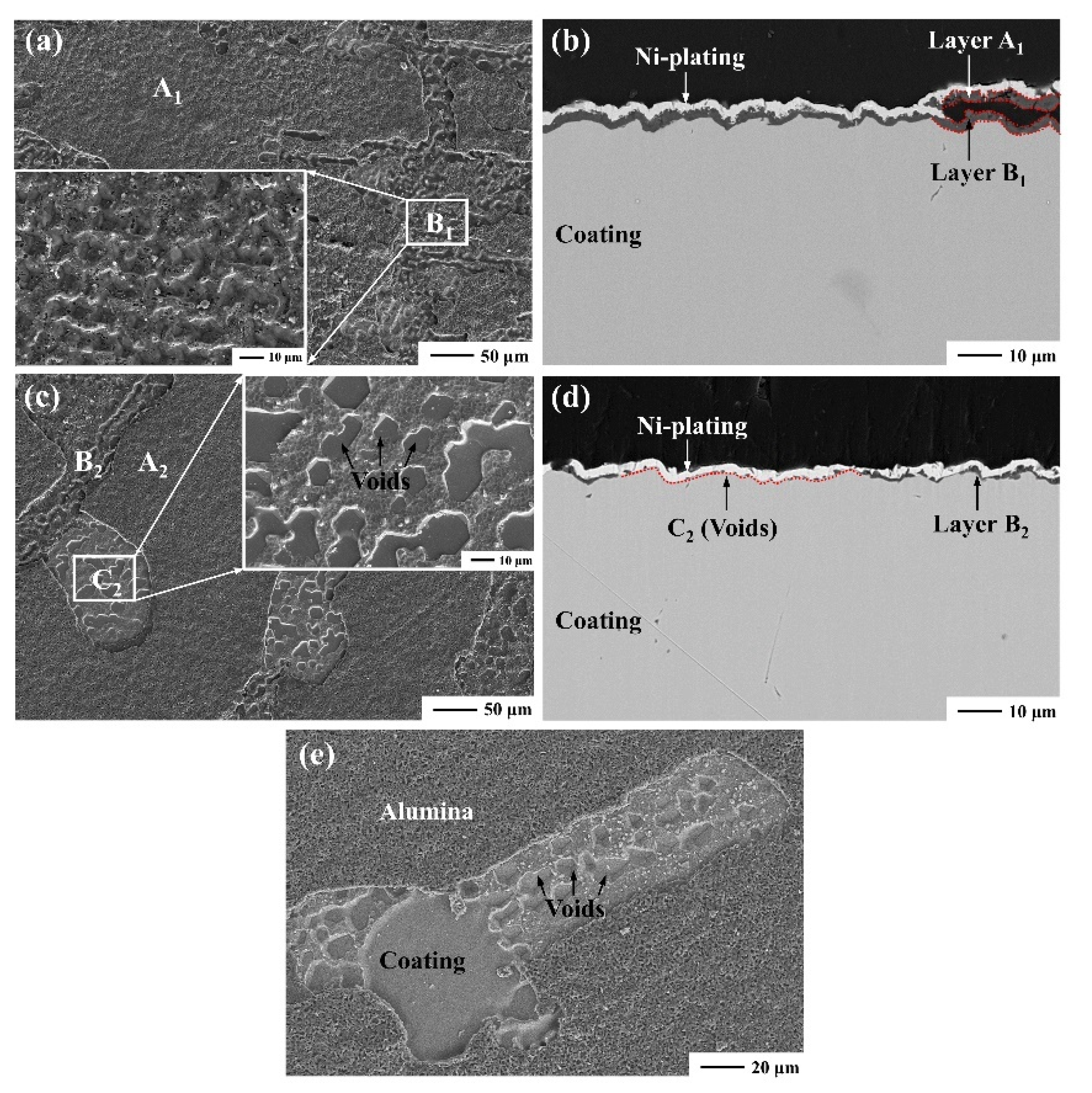
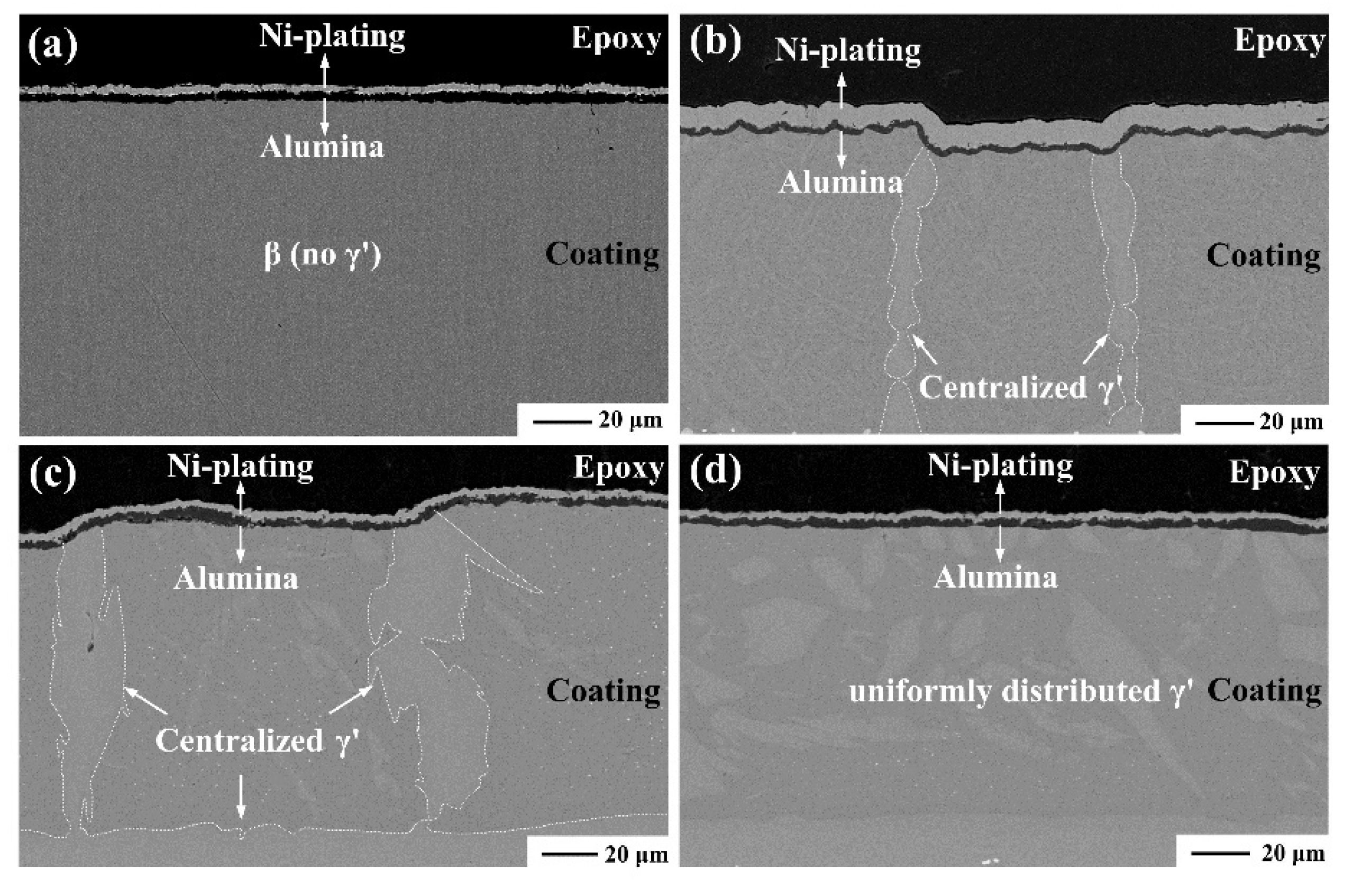
| Element | Ni | Al | Hf |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal composition | 50.00 | 49.90 | 0.10 |
| Actual composition | 59.93 | 40.07 | - |
| Element | Ni | Al | Hf |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 38.88 | 37.25 | 23.87 |
| B | 66.63 | 33.37 | - |
| C | 61.82 | 38.18 | - |
| Element | Ni | Al | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | - | 42.55 | 57.45 |
| B1 | - | 43.31 | 56.69 |
| A2 | - | 43.13 | 56.87 |
| B2 | - | 42.96 | 57.04 |
| C2 | 51.10 | 41.95 | 6.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; He, J.; Dong, Y.; Guo, H. Internal Factors Affecting the Surface Rumpling of a β-NiAlHf Coating. Coatings 2021, 11, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040436
Liu L, He J, Dong Y, Guo H. Internal Factors Affecting the Surface Rumpling of a β-NiAlHf Coating. Coatings. 2021; 11(4):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Liang, Jian He, Yaoge Dong, and Hongbo Guo. 2021. "Internal Factors Affecting the Surface Rumpling of a β-NiAlHf Coating" Coatings 11, no. 4: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040436
APA StyleLiu, L., He, J., Dong, Y., & Guo, H. (2021). Internal Factors Affecting the Surface Rumpling of a β-NiAlHf Coating. Coatings, 11(4), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040436






