Three-Dimensional Radiative Bioconvective Flow of a Sisko Nanofluid with Motile Microorganisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling
3. Numerical Solution
4. Solution Verification
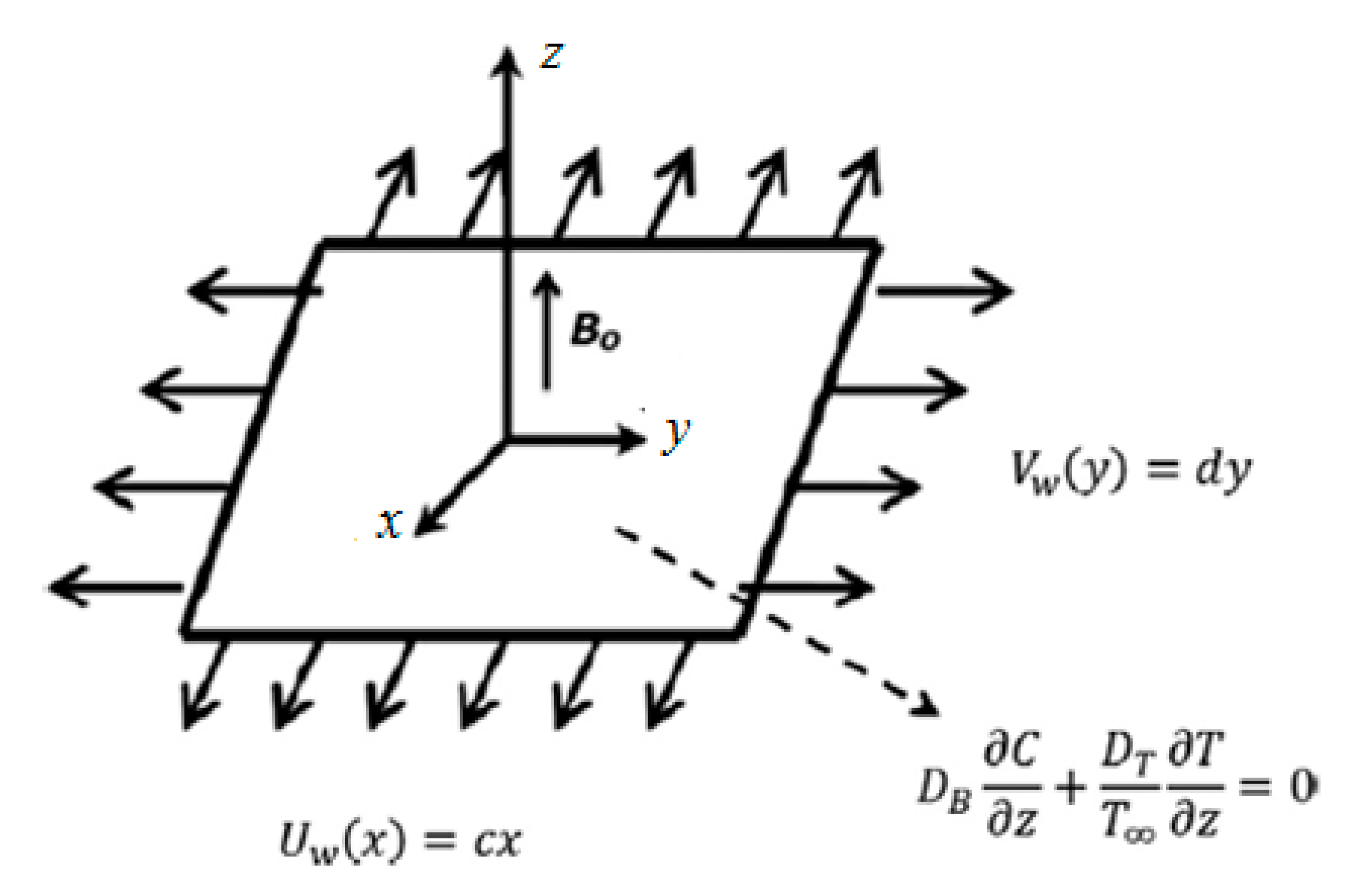
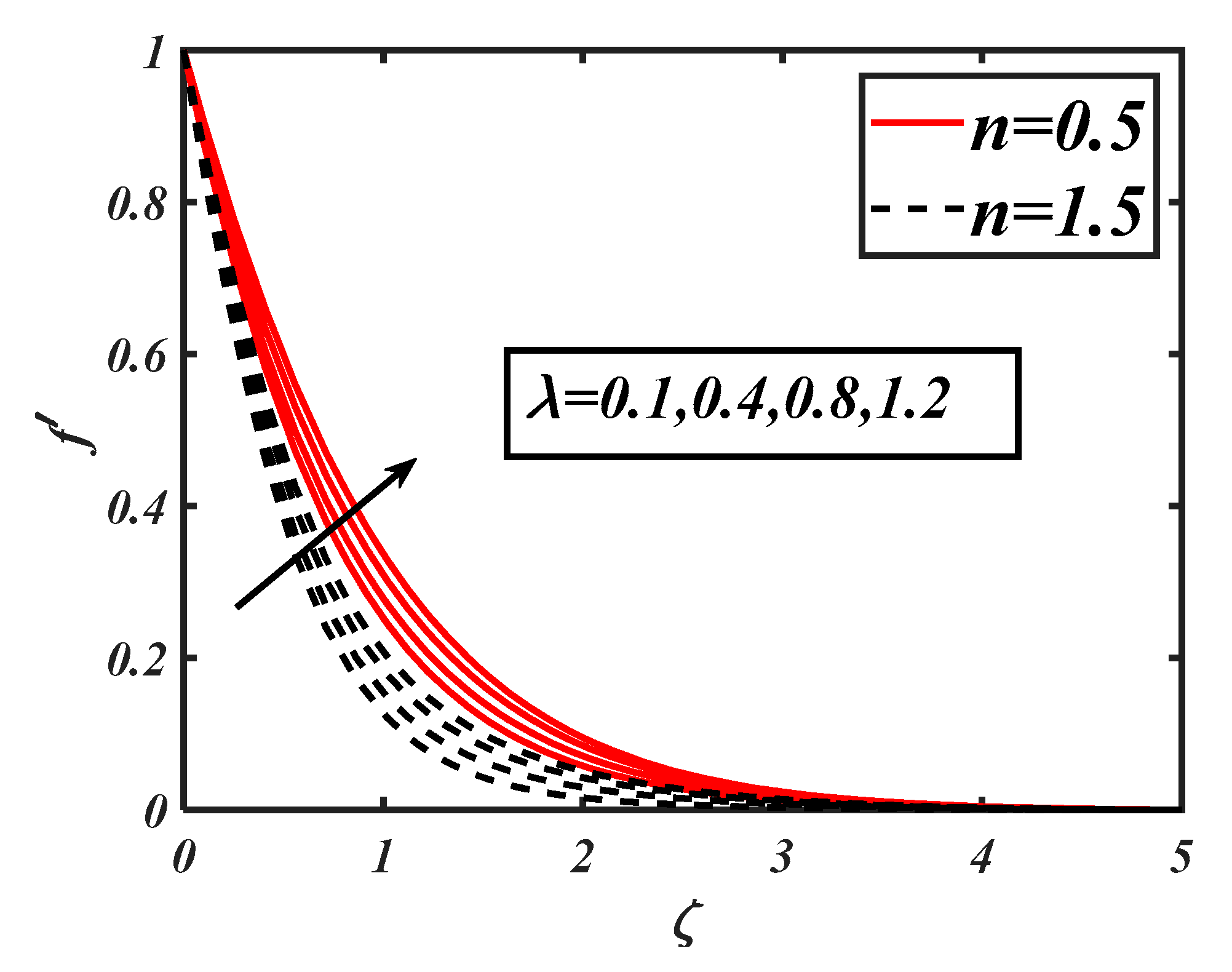
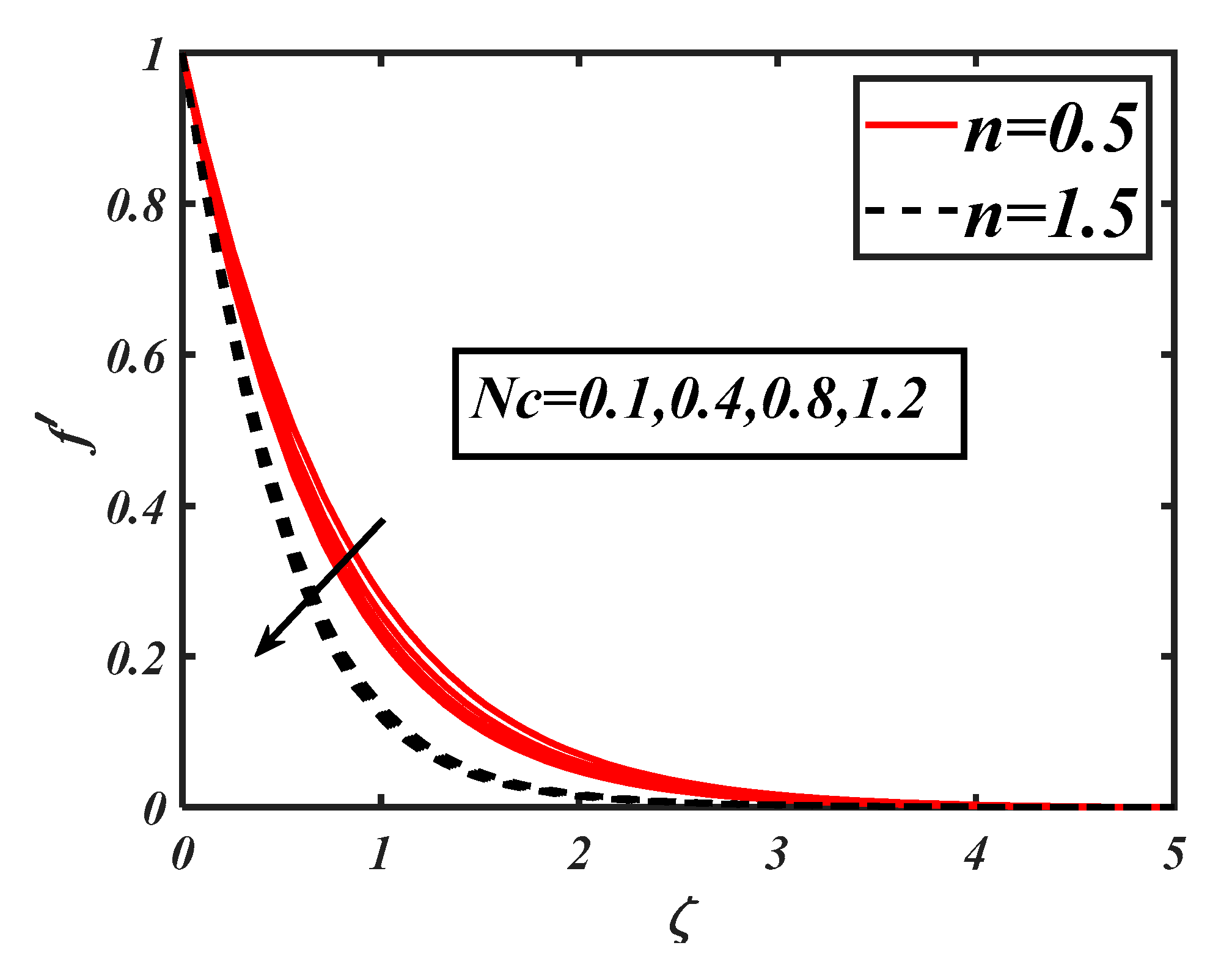
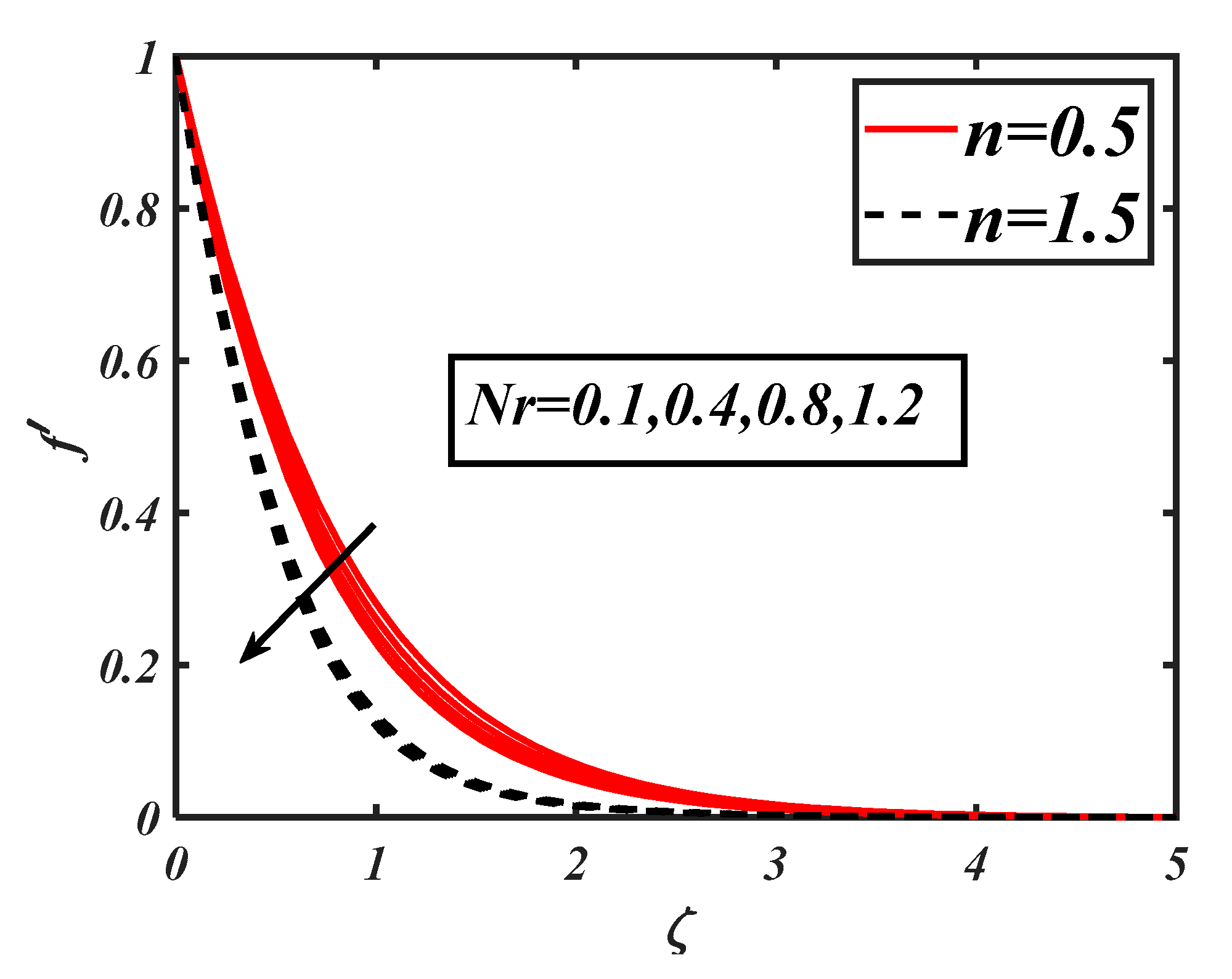
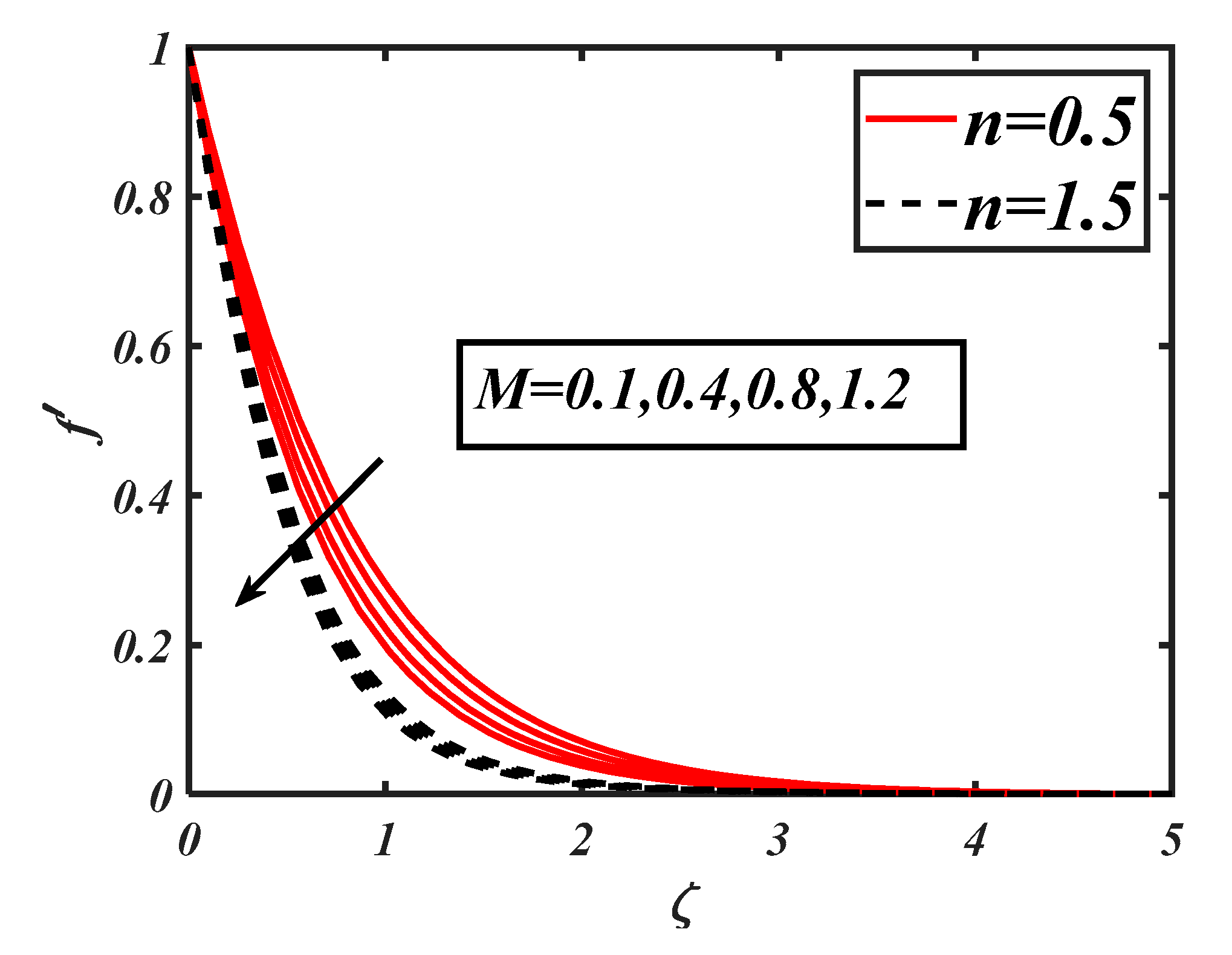
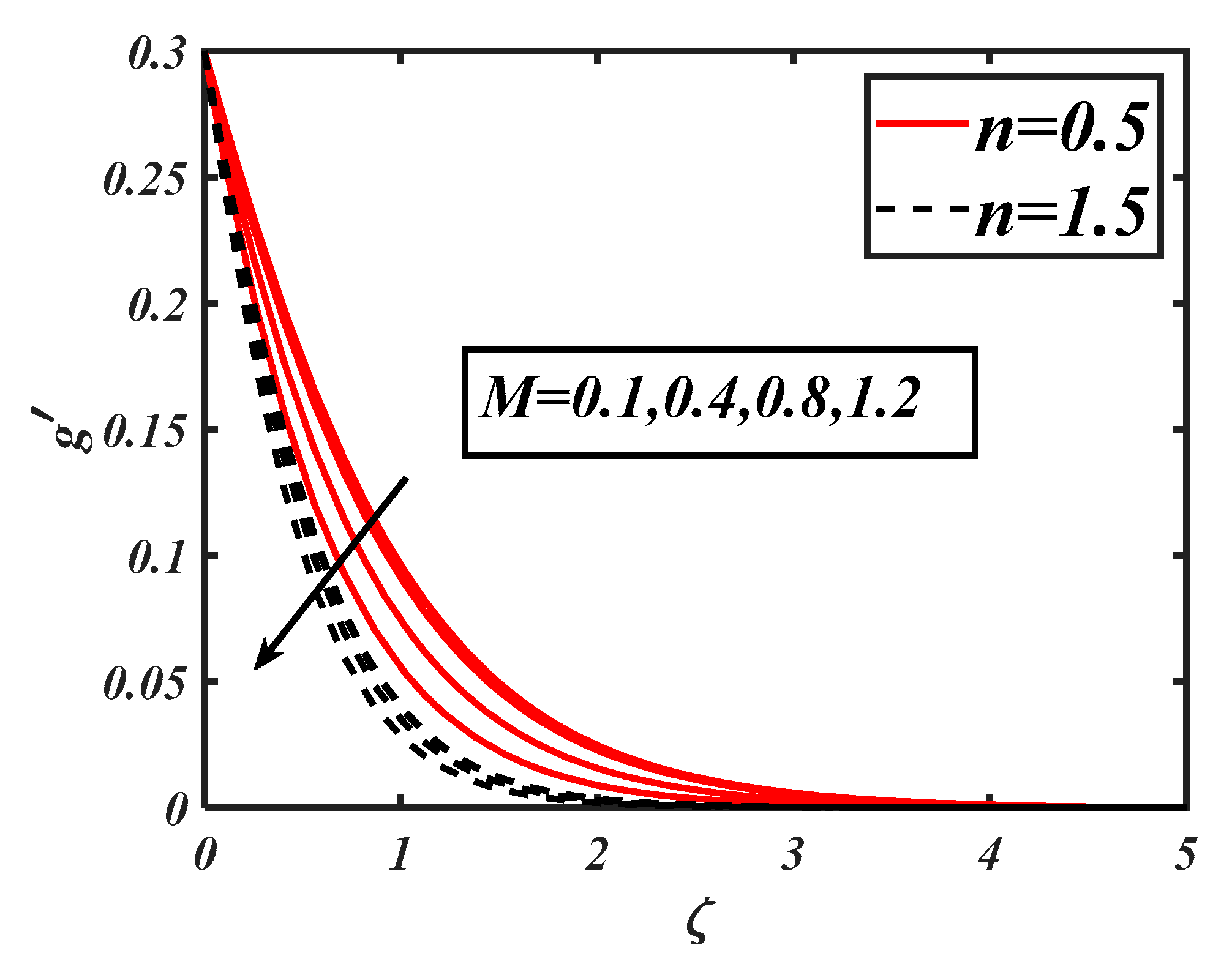
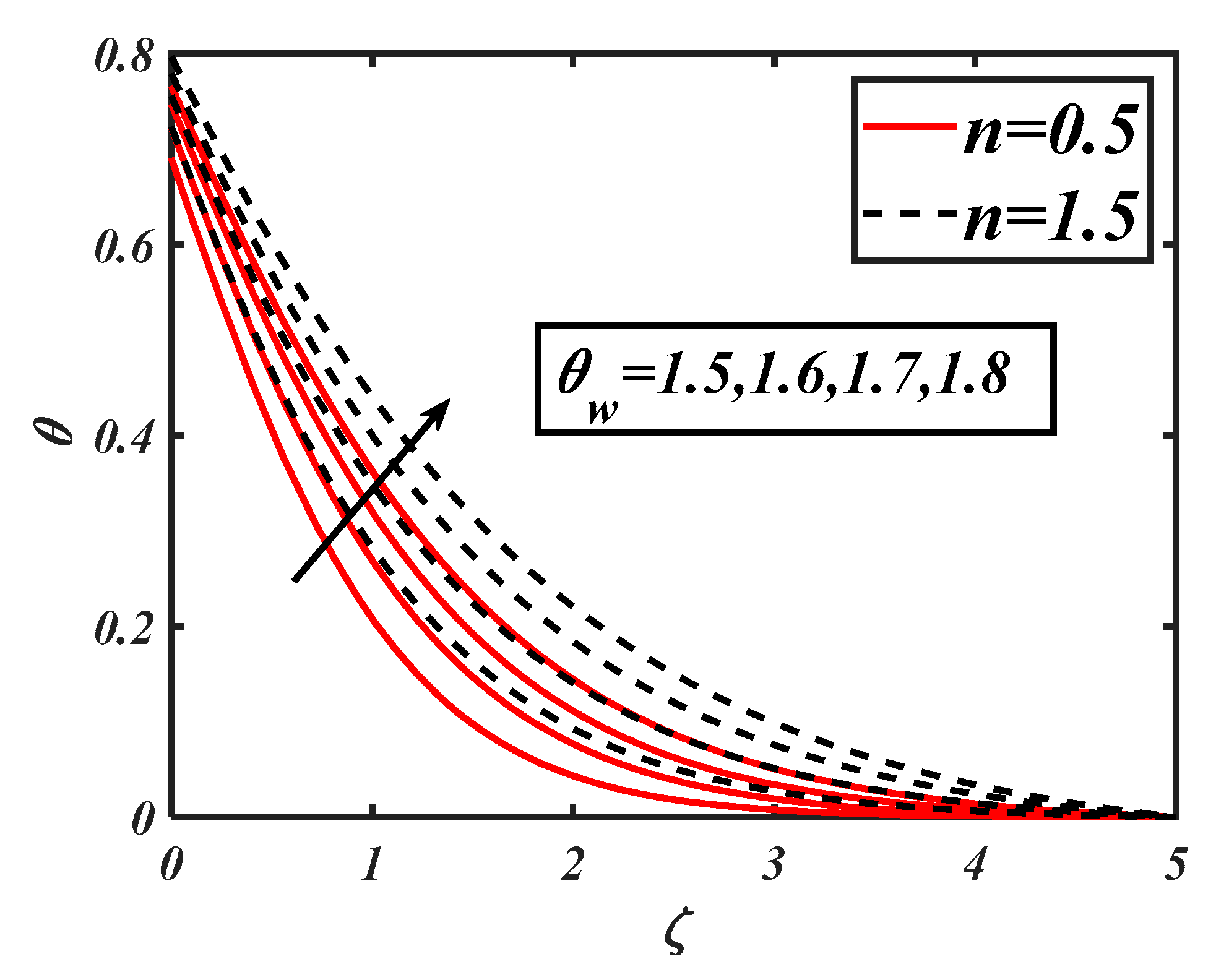
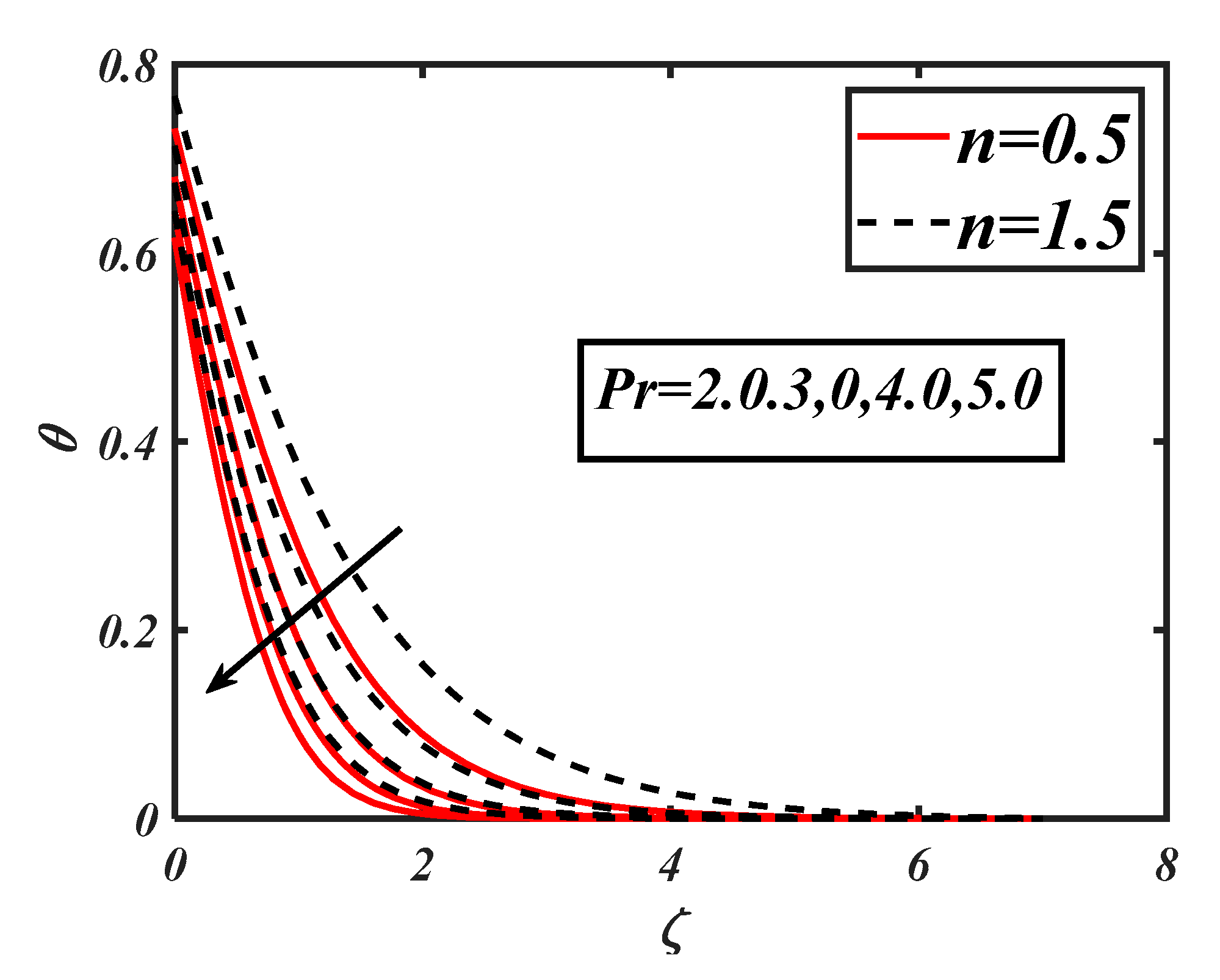
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
- ⮚
- An increase in the velocity due to the mixed convection parameter was observed, which was enhanced in the shear-thinning case.
- ⮚
- The hindering effects on the velocity due to the bioconvection Rayleigh number was relatively slower when shear-thickening effects were dominant.
- ⮚
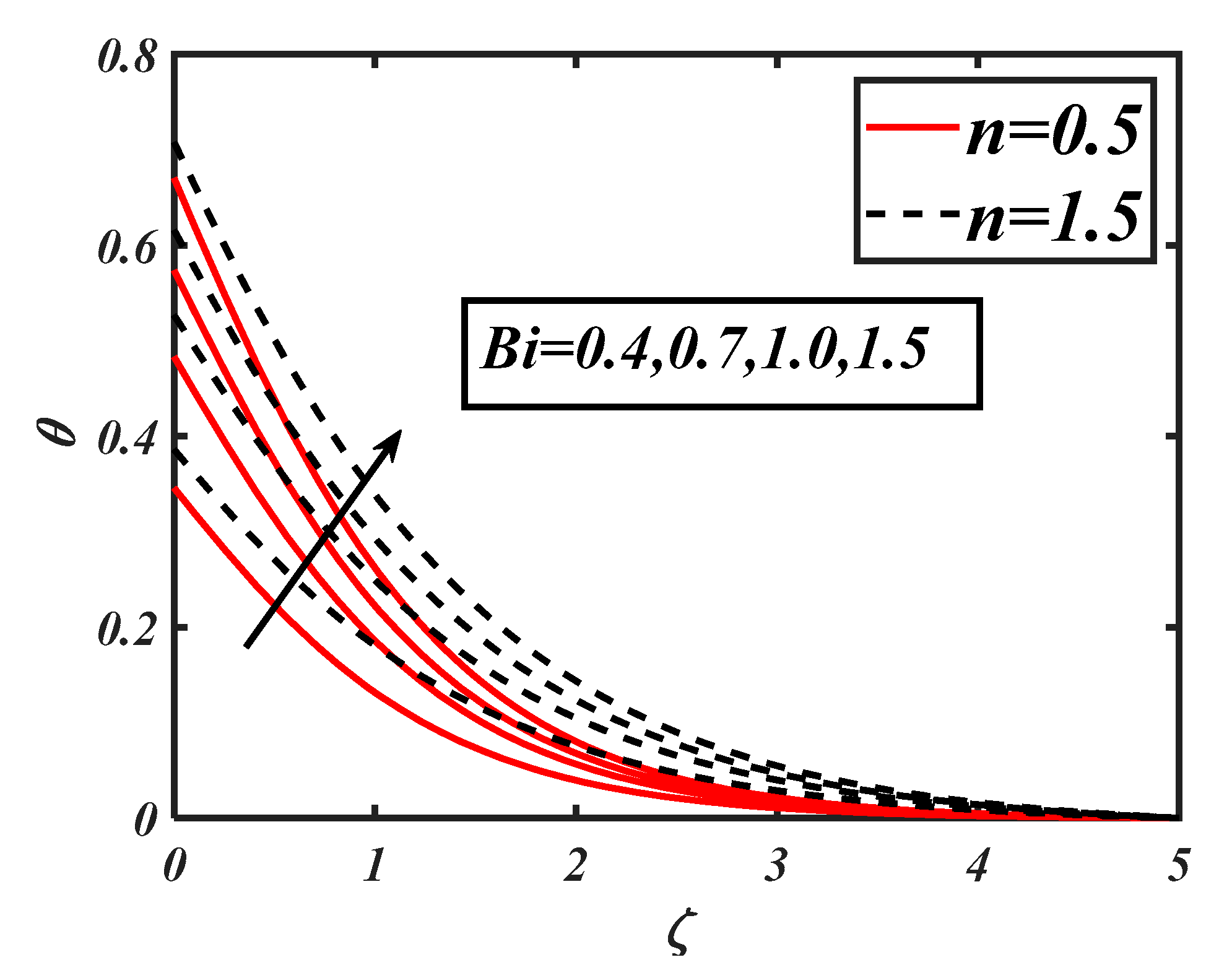
- The nanofluid temperature was enhanced due to the Biot number and surface-heating source parameter. The enhancement in temperature in the case of shear thickening was qualitatively slower as compared to the shear-thinning case.
- ⮚
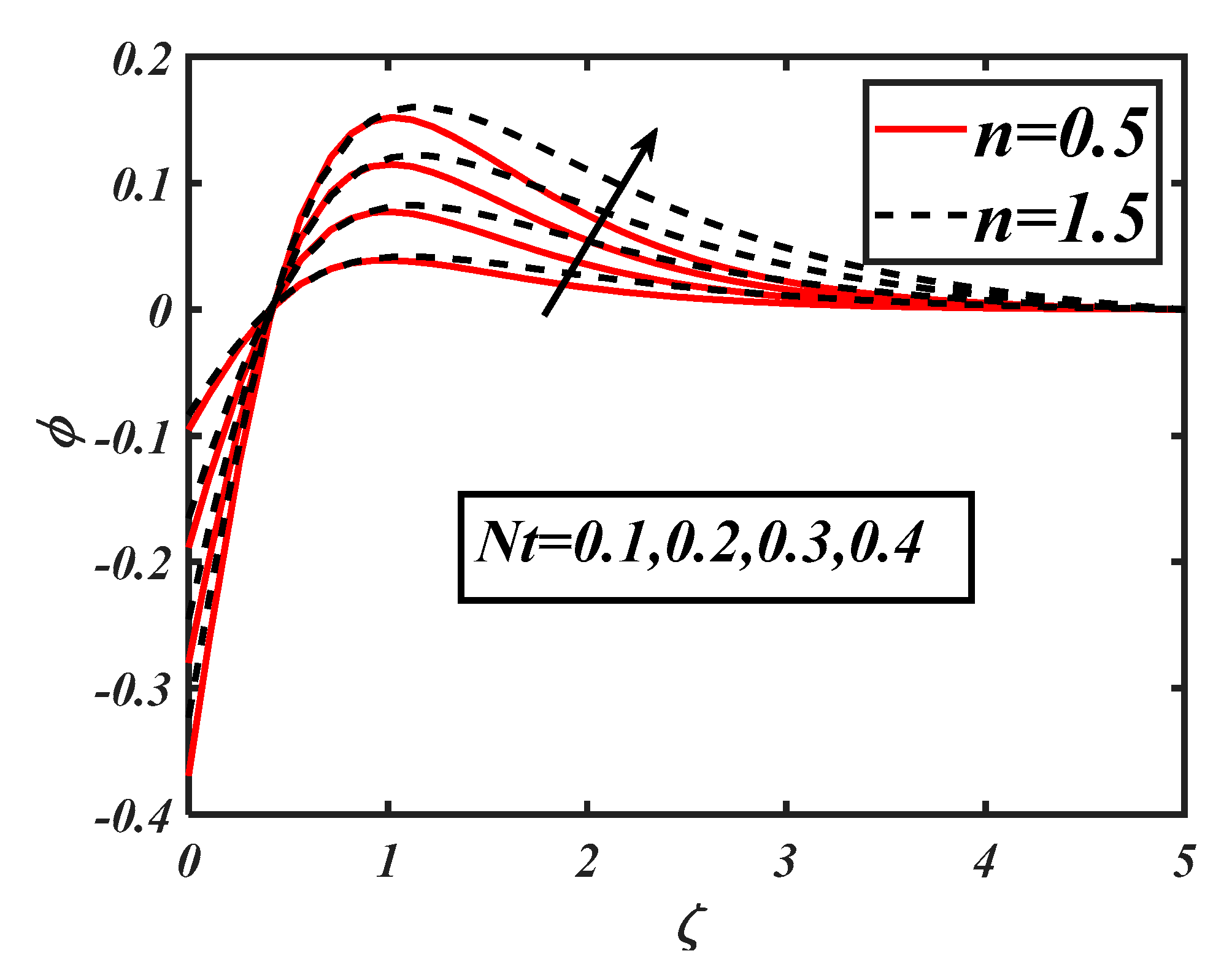
- An increase in the nanofluid concentration due to the thermophoretic parameter was more progressive when shear-thinning features were considered.
- ⮚
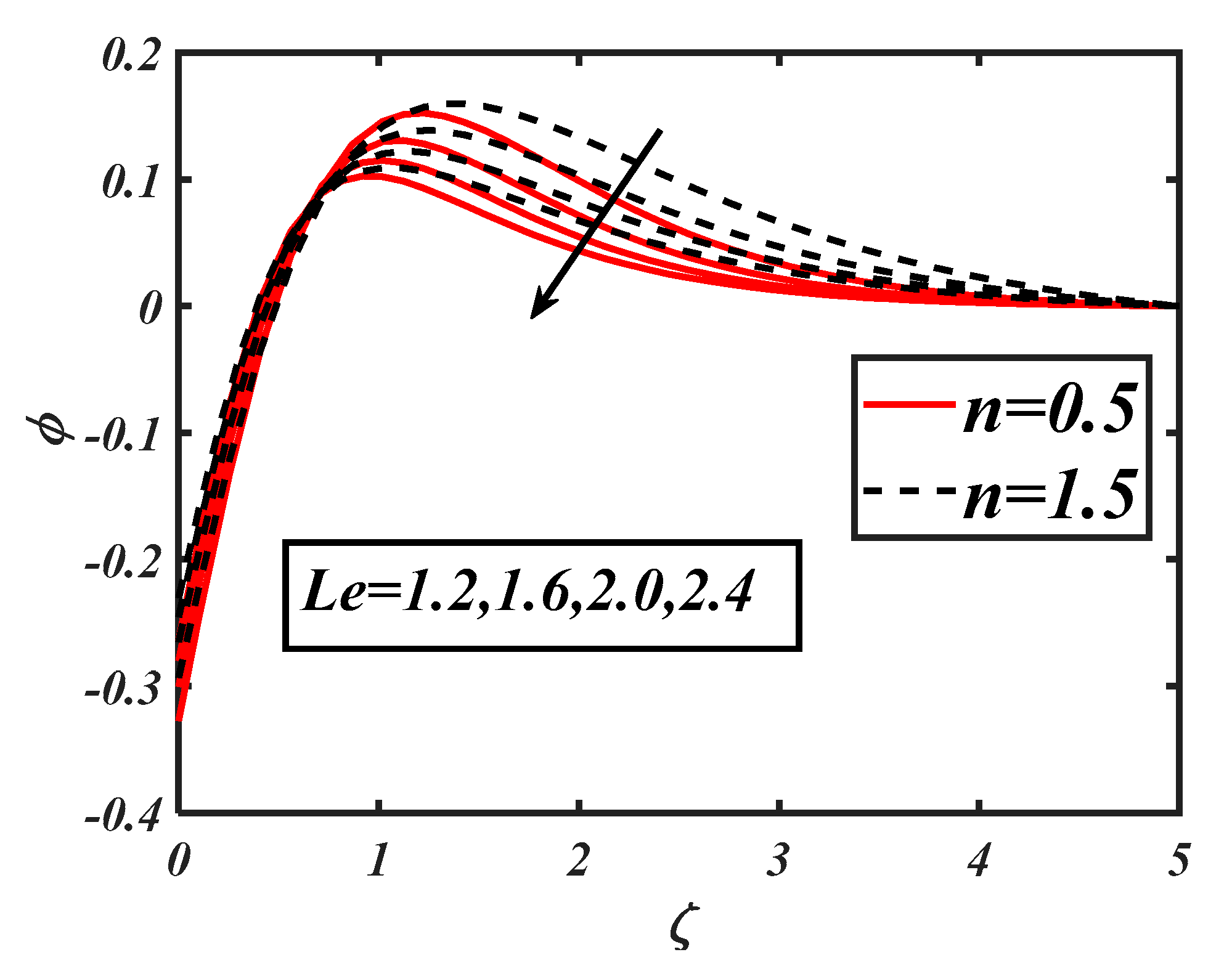
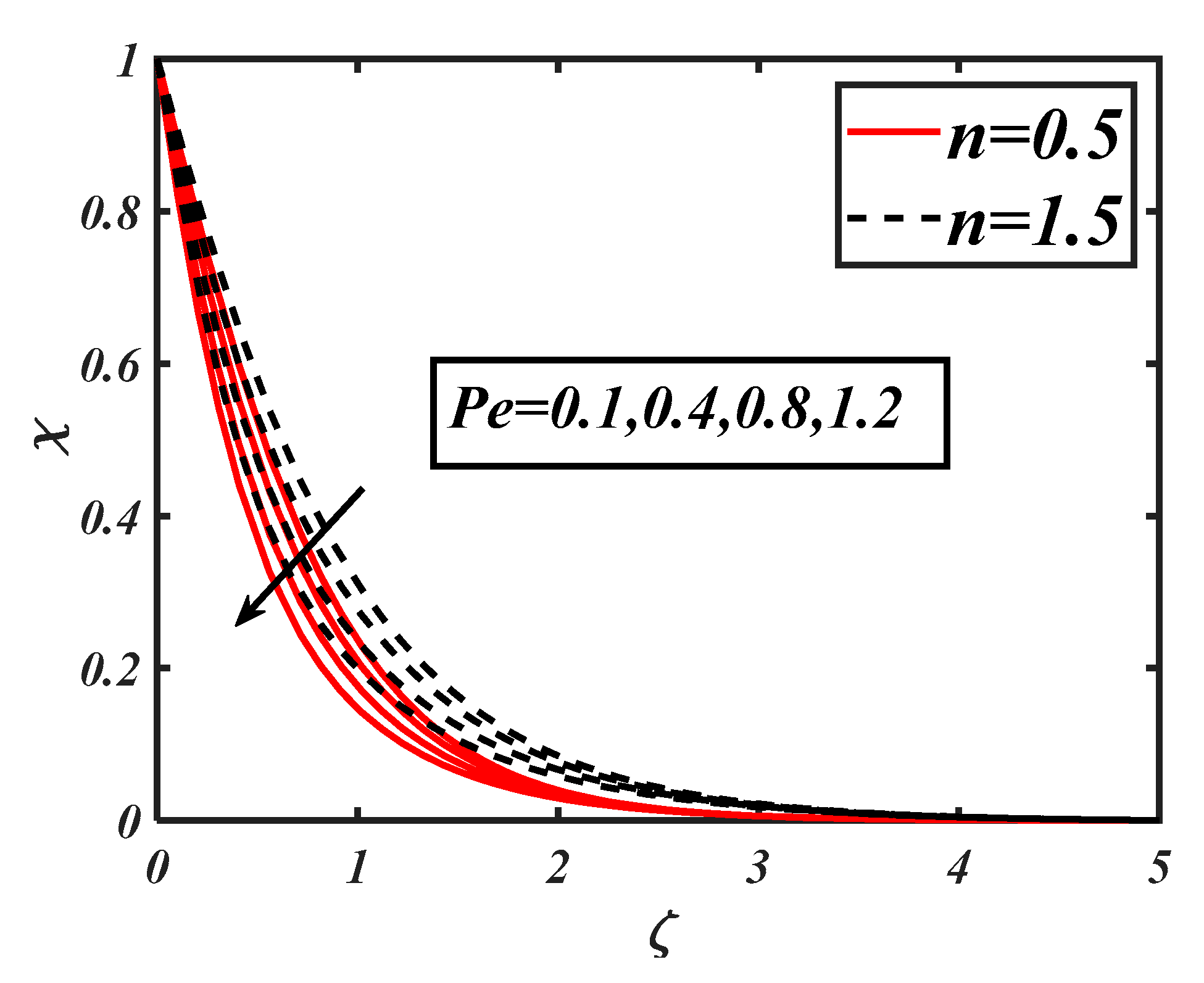
- The microorganism profile decreased with the bioconvection Lewis number and Peclet number.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| velocity components (m·s−1) | coordinate axes (m) | ||
| temperature(K) | nanoparticles concentration (kg·m−3) | ||
| kinematic viscosity (m2·s−1) | wall temperature (K) | ||
| free stream temperature (K) | ambient concentration (kg·m−3) | ||
| density (kg·m−3) | Brownian diffusion coefficient (m2·s−1) | ||
| thermophoresis diffusion coefficient (m2·s−1) | dynamic viscosity (N·s·m−2) | ||
| gravity | heat capacity ratio | ||
| mean absorption coefficient | microorganism diffusion constant | ||
| Stefan–Boltzmann constant | radiative flux | ||
| chemotaxis constant | volume suspension coefficient | ||
| Sisko fluid materials constants | electrical conductivity | ||
| magnetic field strength | volume expansion coefficient | ||
| density of nanoparticles | density of microorganisms | ||
| Sisko fluid material parameter | Prandtl number | ||
| buoyancy ratio parameter | mixed convection parameter | ||
| bioconvection Rayleigh number | magnetic parameter | ||
| radiation parameter | temperature ratio parameter | ||
| thermophoresis parameter | Brownian motion parameter | ||
| Lewis number | Peclet number | ||
| bioconvection Lewis number | Biot number | ||
| local Reynolds number | local Nusselt number | ||
| local Sherwood number | motile density number |
References
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME 2001, 231, 718–720. [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Yasmin, H.; Kometa, B.K.; Attiya, A.A. Effects of convection on Sisko fluid with peristalsis in an asymmetric channel. Math. Comput. Appl. 2020, 25, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Irfan, M.; Khan, W.A.; Sultan, F.; Shahzad, M.; Khan, M. Physical significance of chemical processes and Lorentz’s forces aspects on Sisko fluid flow in curved configuration. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 16213–16223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Rathore, S.K. An analytical investigation of pressure-driven flow and heat transfer of a Sisko fluid flowing through parallel plates with viscous dissipation. Sadhana 2020, 45, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, T.; Mostapha, D.R. Hall current and joule heating effects on peristaltic flow of a Sisko fluid with mild stenosis through a porous medium in a tapered artery with slip and convective boundary conditions. Sains Malays. 2020, 49, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Toghraie, D.; Esfahani, N.N.; Zarringhalam, M.; Shirani, N.; Rostami, S. Blood flow analysis inside different arteries using non-Newtonian Sisko model for application in biomedical engineering. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2020, 190, 105338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agoor, B.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.E.; Alam, H. Peristaltic flow with heat transfer on Sisko fluid in a ciliated arteries. Int. J. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 6, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdows, M.; Reddy, M.G.; Sun, S.; Alzahrani, F. Two-dimensional gyrotactic microorganisms flow of hydromagnetic power-law nanofluid past an elongated sheet. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadhar, K.; Kannan, T.; Sakthivel, G.; Dasaradha Ramaiah, K. Unsteady free convective boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching surface using a spectral relaxation method. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2020, 41, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, M.; Shah, Z.; Khan, A.; Khan, W.; Kumam, P.; Islam, S. Entropy generation and heat transfer analysis in MHD unsteady rotating flow for aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes with nonlinear thermal radiation and viscous dissipation effect. Entropy 2019, 21, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Sultan, F.; Khan, W.A.; Shahzad, M.; Arif, H. Important features of expanding/contracting cylinder for cross magneto-nanofluid flow. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 133, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, Z.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Significance of activation energy in radiative peristaltic transport of Eyring-Powell nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 116, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Waqas, H.; Khan, S.A.; Ellahi, R.; Sait, S.M. Significance of nonlinear thermal radiation in 3D Eyring–Powell nanofluid flow with Arrhenius activation energy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 143, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Melting heat transfer in squeezing flow of base fluid (water), nanofluid (CNTs + water), and hybrid nanofluid (CNTs + CuO + water). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Taseer Muhammad, B.; Ahmad, S.; Shehzad, A. Impact of magnetic field in three-dimensional flow of Sisko nanofluid with convective condition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 413, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Taseer Muhammad, B.; Ahmad, S.; Shehzad, A.; Alsaedi, A. On three-dimensional boundary layer flow of Sisko nanofluid with magnetic field effects. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Mandal, G. Magnetohydrodynamic stagnation-point flow of Sisko nanofluid over a stretching sheet with suction. Propuls. Power Res. 2020, 9, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Transportation of hybrid nanoparticles in forced convective Darcy-Forchheimer flow by a rotating disk. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 122, 105177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.M.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, N.B.; Kadry, S.; Khan, S.U.; Tlili, I.; Nayak, M.K. Significance of activation energy, bio-convection and magnetohydrodynamic in flow of third grade fluid (non-Newtonian) towards stretched surface: A Buongiorno model analysis. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 118, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, H. On the effect of gravity upon the movements and aggregation of Euglena Viridis, Ehrb., and other micro-organisms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1911, 201, 333–390. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, J.R. “Bioconvection pattern” in cultures of the free-swimming organism. Science 1961, 133, 1766–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, A. Bio-thermal convection induced by two different species of microorganisms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohra, F.T.; Uddin, M.J.; Basir, F.; Ismail, A.I.M. Magnetohydrodynamic bio-nano-convective slip flow with Stefan blowing effects over a rotating disc. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2019, 234, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Khan, S.U.; Imran, M.; Tlili, I.; Waqas, H.; Ali, N. Activation energy and thermal radiation aspects in bioconvection flow of rate-type nanoparticles configured by a stretching/shrinking disk. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2020, 142, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, G.; Kolipaula, V.R.; Rao, M.V.S.; Penki, S.; Chamkha, A.J. Internal heat generation on bioconvection of an MHD nanofluid flow due to gyrotactic microorganisms. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiq, M.K.; Ashraf, M. Bioconvection of micropolar nanofluid with modified Cattaneo–Christov theories. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraswamy Naidu, K.; Harish Babu, D.; Harinath Reddy, S.; Satya Narayana, P.V. Radiation and partial slip effects on MHD jeffrey nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms over a stretching surface. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2020, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, Z.; Ullah Khan, S.; Waqas, H.; ANabwey, H.; Tlili, I. Utilization of second-order slip, activation energy, and viscous dissipation consequences in the thermally developed flow of third-grade nanofluid with gyrotactic microorganisms. Symmetry 2020, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, Z.; Khan, S.U.; Waqas, H.; Riaz, A.; Khan, I.A.; Tlili, I. A mathematical model for bioconvection flow of Williamson nanofluid over a stretching cylinder featuring variable thermal conductivity, activation energy, and second-order slip. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, H.; Imran, M.; Muhammad, T.; Sait, S.M.; Ellahi, R. On bio-convection thermal radiation in Dar-cy–Forchheimer flow of nanofluid with gyrotactic motile microorganism under Wu’s slip over-stretching cylinder/plate. In-ternational Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow.tion and Brownian Motion. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 4, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Waqas, H.; Tahir, M.; Imran, M.; Jung, C.Y. Effective prandtl aspects on bio-convective thermally developed magnetized tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid with gyrotactic microorganisms and second-order velocity slip. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 130008–130023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Waqas, H.; Imran, M.; Farooq, U.; Mallawi, F.; Tlili, I. A Numerical exploration of modified second-grade nanofluid with motile microorganisms, thermal radiation, and Wu’s slip. Symmetry 2020, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.; Nabwey, H.A. Microorganisms time-mixed convection nanofluid flow by the stagnation domain of an impulsively rotating sphere due to Newtonian heating. Results Phys. 2020, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Waqas, H.; Muhammad, T.; Imran, M.; Ullah, M.Z. Significance of activation energy and Wu’s slip features in Cross nanofluid with motile microorganisms. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2020, 72, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.S.; Otegbeye, O.; Trivedi, M.; Goqo, S.P. Magnetohydrodynamic bio-convective casson nanofluid flow: A numerical simulation by paired quasilinearisation. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hayat et al. [17] | Present Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1.0394 | 1.0050 | 1.0395 | 1.0048 |
| 0.5 | 1.2730 | 1.2076 | 1.2731 | 1.2075 |
| 1.0 | 1.4700 | 1.4714 | 1.4700 | 1.4714 |
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.0726 1.0709 1.0675 | 1.4402 1.4392 1.4370 |
| 0.1 | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | 1.2735 1.2746 1.2748 | 1.6531 1.6554 1.6573 |
| – | – | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | 1.2999 1.3308 1.3542 | 1.6796 1.7127 1.7380 |
| – | – | – | 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 1.1952 1.2731 1.4160 | 1.5934 1.6512 1.7614 |
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.0911 0.0910 0.0908 | 0.1477 0.1446 0.1444 |
| 0.1 | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | 0.2983 0.2990 0.2997 | 0.4405 0.4499 0.4504 |
| – | – | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | 0.2978 0.2988 0.2996 | 0.4367 0.4435 0.4521 |
| – | – | – | 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 0.2816 0.2986 0.3633 | 0.4307 0.4410 0.4856 |
| Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.3885 0.3891 0.3932 | 0.5128 0.5234 0.5297 | 0.3371 0.3154 0.2904 | 0.4231 0.4346 0.4454 |
| 0.1 | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | – | – | 0.5360 0.5352 0.5346 | 0.4700 0.4686 0.4676 | 0.4267 0.4054 0.3909 | 0.4134 0.3889 0.3667 |
| – | – | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | – | 0.5347 0.5325 0.5307 | 0.4686 0.4655 0.4631 | 0.4378 0.4205 0.4056 | 0.4102 0.4067 0.3956 |
| – | – | – | 0.2 0.4 0.8 | – | – | 0.5443 0.5367 0.5199 | 0.4753 0.4711 0.4617 | 0.4479 0.4334 0.4056 | 0.4156 0.3924 0.3854 |
| – | – | – | – | 2.5 3.0 3.5 | – | 0.5921 0.6383 0.6775 | 0.5259 0.5733 0.6145 | 0.5303 0.5554 0.5934 | 0.4865 0.5276 0.5467 |
| – | – | – | – | – | 0.8 1.4 1.8 | 0.4917 0.4271 0.3963 | 0.4288 0.3713 0.3453 | 0.4165 0.3704 0.32565 | 0.3776 0.3467 0.3156 |
| Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 2.0 | – | 0.8145 0.8256 0.9310 | 0.7954 0.8167 0.8966 |
| 0.1 | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.8040 0.8028 0.8019 | 0.7050 0.7030 0.7014 |
| – | – | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | – | – | – | 0.8021 0.7987 0.7960 | 0.7029 0.6983 0.6947 |
| – | – | – | 0.2 0.4 0.8 | – | – | – | – | 0.8165 0.8050 0.7799 | 0.7129 0.7067 0.6925 |
| – | – | – | – | 2.5 3.0 3.5 | – | – | 0.8882 0.9575 1.0162 | 0.7889 0.8600 0.9218 | |
| – | – | – | – | – | 0.1 0.4 0.8 | – | – | 0.8180 0.8045 0.7956 | 0.7870 0.7756 0.7434 |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | 3.0 4.0 5.0 | 0.7991 0.7952 0.7922 | 0.7012 0.6976 0.6950 | |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.1 0.4 0.8 | 0.8990 1.0234 1.1014 | 0.7854 0.7901 0.9912 |
| Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 0.4 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 1.0853 1.1012 1.1145 | 0.9534 0.9611 0.9917 |
| 0.1 | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | – | – | 1.0751 1.0738 1.0728 | 0.9429 0.9405 0.9386 |
| – | – | 0.8 1.6 2.2 | – | – | – | 1.0724 1.0678 1.0642 | 0.9378 0.9336 0.9287 |
| – | – | – | 0.2 0.4 0.8 | – | – | 1.0916 1.0762 1.0422 | 0.9539 0.9450 0.9243 |
| – | – | – | – | 0.5 1.0 1.5 | – | 1.3580 1.7185 2.0874 | 1.2022 1.5295 1.8625 |
| – | – | – | – | – | 3.0 4.0 5.0 | 0.2375 0.2382 0.2388 | 0.2285 0.2290 0.2293 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge-JiLe, H.; Waqas, H.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.I.; Farooq, S.; Hussain, S. Three-Dimensional Radiative Bioconvective Flow of a Sisko Nanofluid with Motile Microorganisms. Coatings 2021, 11, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030335
Ge-JiLe H, Waqas H, Khan SU, Khan MI, Farooq S, Hussain S. Three-Dimensional Radiative Bioconvective Flow of a Sisko Nanofluid with Motile Microorganisms. Coatings. 2021; 11(3):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030335
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe-JiLe, Hu, Hassan Waqas, Sami Ullah Khan, Muhammad Ijaz Khan, Shahid Farooq, and Sajjad Hussain. 2021. "Three-Dimensional Radiative Bioconvective Flow of a Sisko Nanofluid with Motile Microorganisms" Coatings 11, no. 3: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030335
APA StyleGe-JiLe, H., Waqas, H., Khan, S. U., Khan, M. I., Farooq, S., & Hussain, S. (2021). Three-Dimensional Radiative Bioconvective Flow of a Sisko Nanofluid with Motile Microorganisms. Coatings, 11(3), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030335








