Damping Behavior of Layered Aluminium and Aluminide Coatings on AISI 316 Austenitic Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
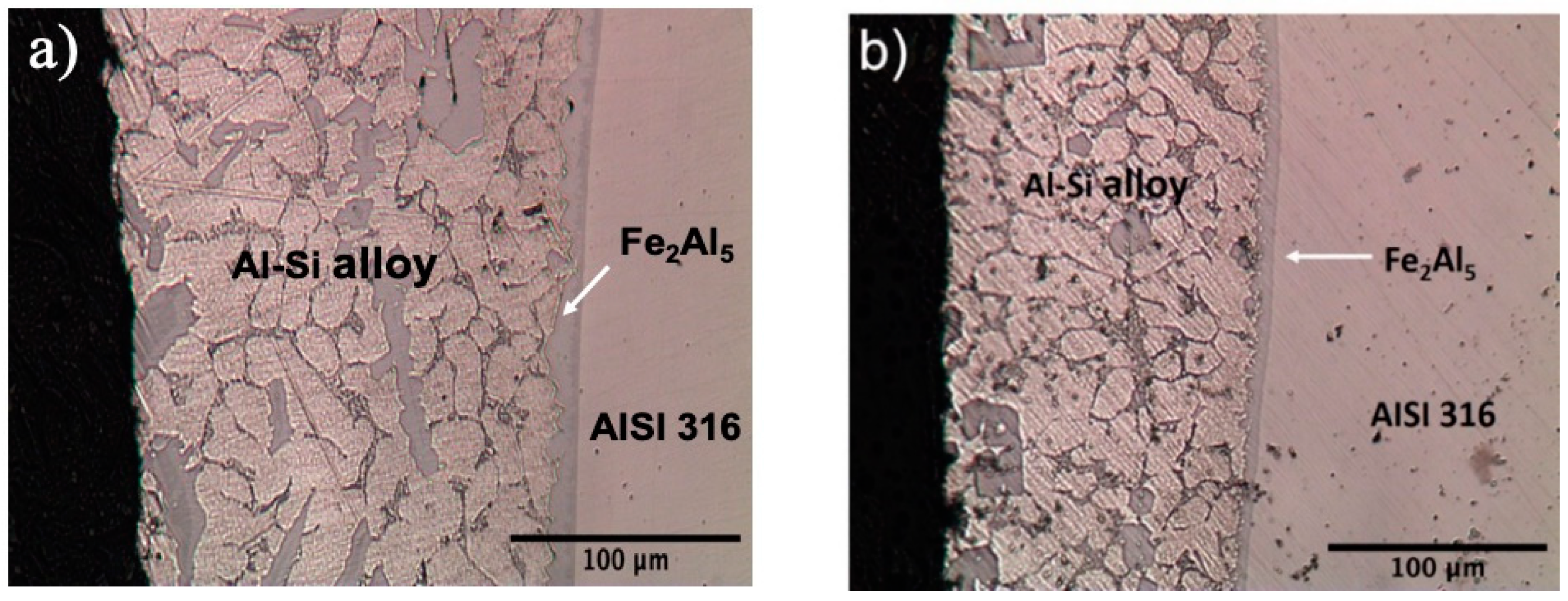
- As aluminized by a 5 min hot-dipping (Figure 1a), having an inner intermetallic layer and an outer Al-Si alloy layer, 200 μm thick.
- (2)
- As aluminized by a 3 min hot-dipping (Figure 1b), having an inner intermetallic layer and an outer Al-Si alloy layer, 130 μm thick.
- (3)
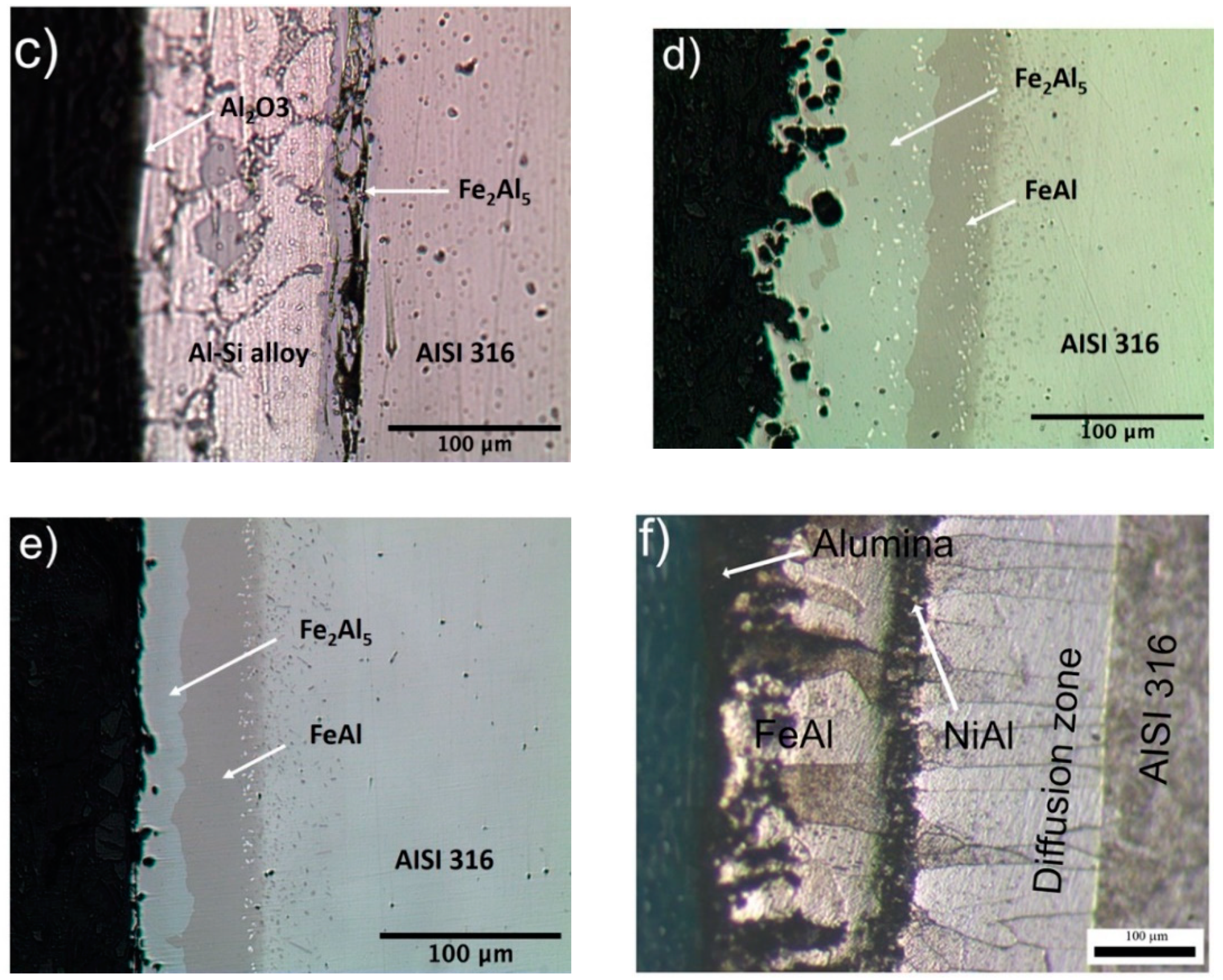
- As aluminized by hot-dipping and successively oxidized in furnace at 900 °C for 1 h (Figure 1c). The resulting multilayered coating consists of an inner intermetallic Fe-Al layer, an intermediate Al-Si alloy layer and an outer Aluminium oxide layer, having about 10 µm thickness.
- (4)
- As aluminized and then layered by a short isothermal interdiffusion process (Figure 1d). The hot-dipped sheets where diffusion annealed at 900 °C for 3 h in a box furnace containing a metallic Titanium sheet getter in order to reduce the Oxygen content in the treating atmosphere and to promote the formation of a diffusion coating consisting of an inner FeAl and an outer Fe2Al5 layer. These sheets were subsequently oxidized in O2-rich atmosphere at 900 °C for 30 min.
- (5)
- Same thermal treatment as in 4, except that the diffusion annealing at 900 °C lasted for 4 h (Figure 1e).
- (6)
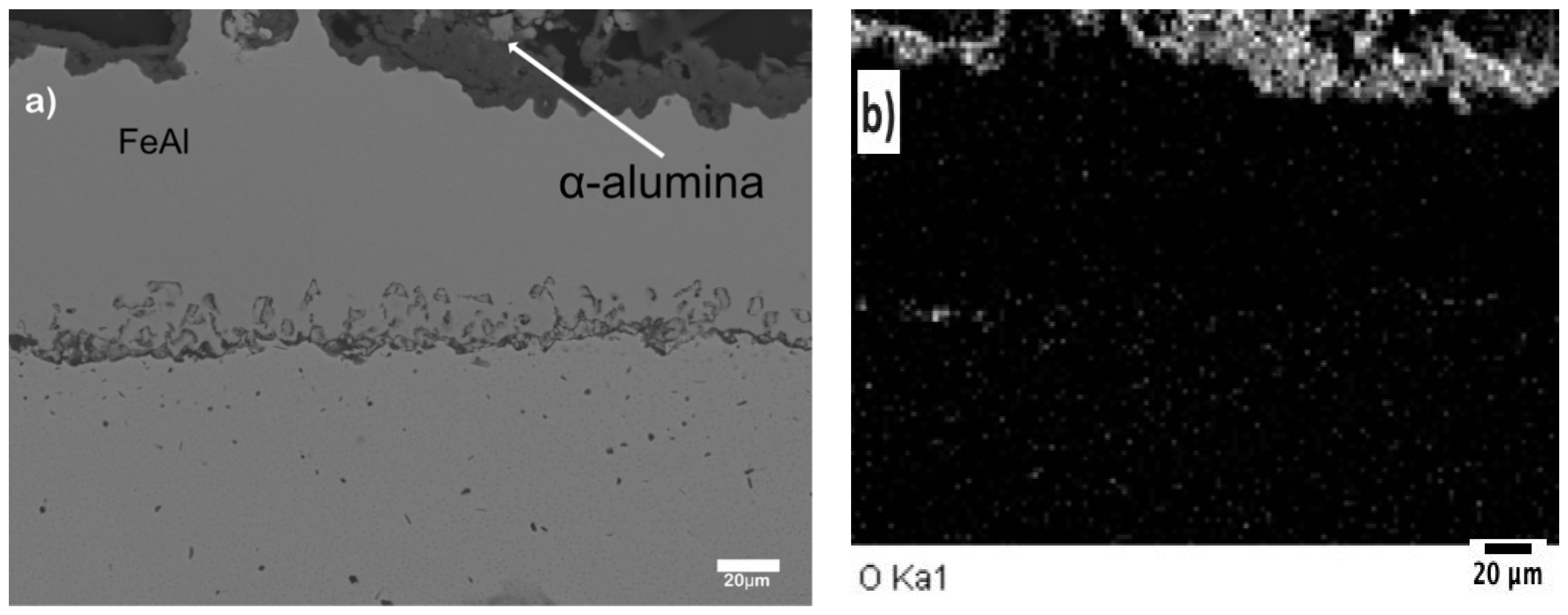
- As aluminized and layered by extended isothermal interdiffusion process (Figure 1f). The hot-dipped sheets were diffusion annealed at 850 °C for 50 h to complete the Fe2Al5 transformation in FeAl and to simultaneously form a Ni-aluminide at the substrate/FeAl interface by inward Al diffusion from the coating and outward Ni diffusion from the substrate. These specimens were subsequently oxidized at 900 °C for 5 h in a box furnace. The resulting coating therefore consists of a NiAl layer at the substrate interface, a FeAl layer on top of it and an outer Al2O3 layer.
3. Results and Discussion
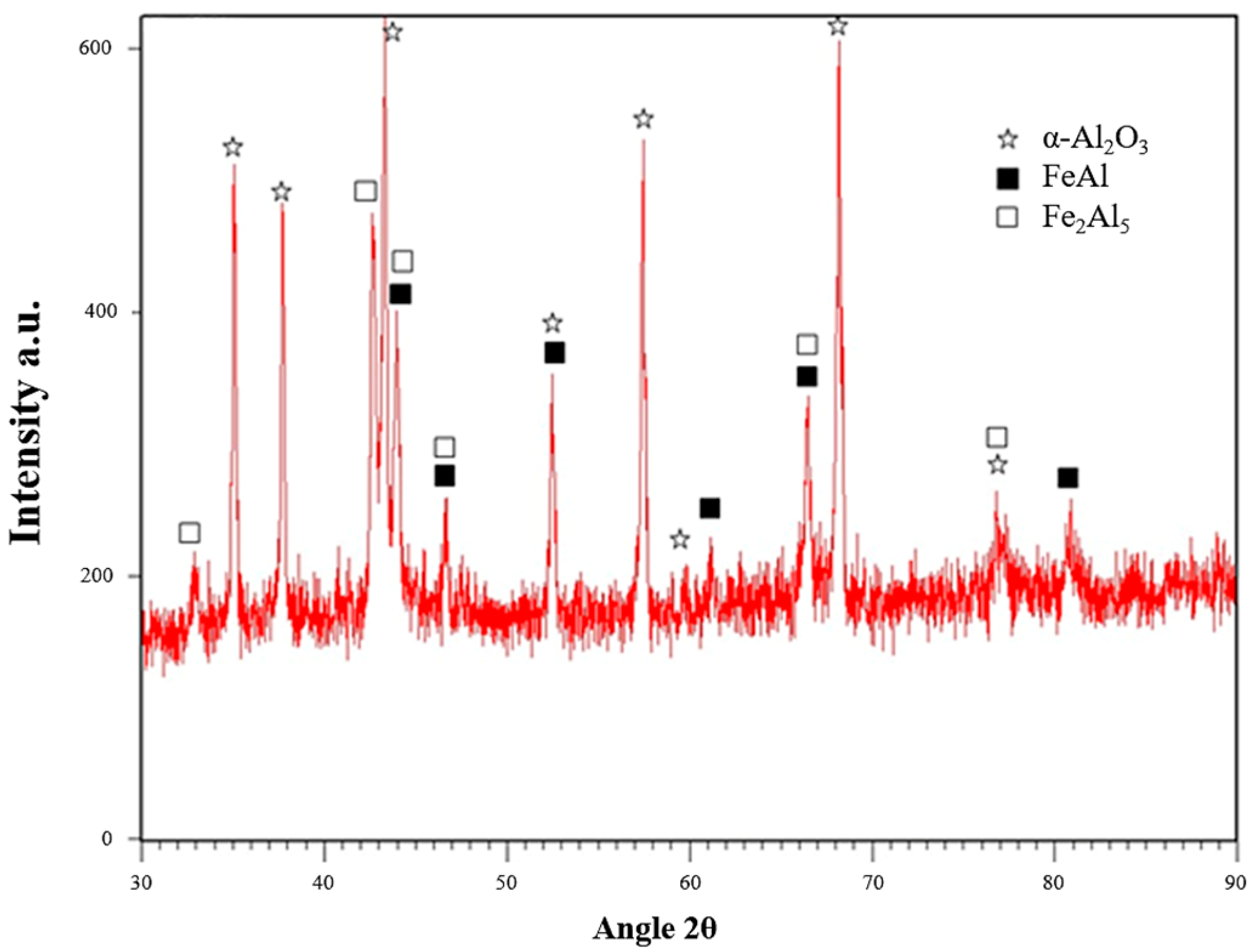
3.1. Microstructural Characterization and Composition Identification
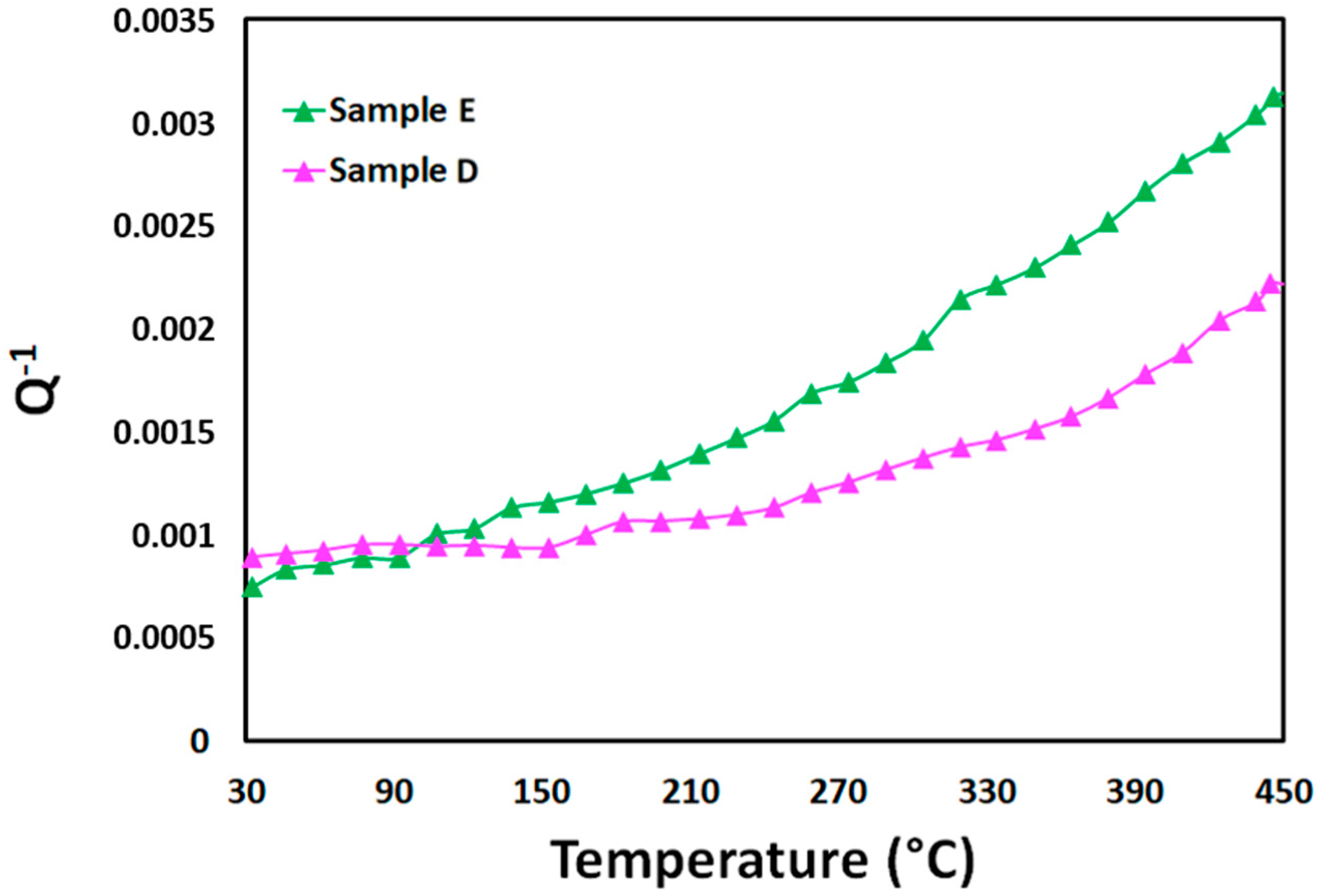
3.2. Damping Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchaud, B.; Balmain, J.; Pedraza, F. Cyclic and Isothermal Oxidation at 1100 °C of a CVD Aluminised Directionally Solidified Ni Superalloy. Oxid. Met. 2008, 69, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Su, Y. Hot Corrosion Behavior of Stainless Steel with Al-Si/Al-Si-Cr Coating. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2017, 36, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissonnet, G.; Chalk, C.; Nicholls, J.; Bonnet, G.; Pedraza, F. Phase stability and thermal insulation of YSZ and erbia-yttria co-doped zirconia EB-PVD thermal barrier coating systems. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 389, 125566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meetham, G.W.; Van De Voorde, M.H. Materials for High Temperature Engineering Applications; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Young, D.J. High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion of Metals; Elsevier Corrosion Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2008; Volume 1, ISBN 978-0-08-044587-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, D.D.L. Review: Materials for vibration damping. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 5733–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, I.G.; Pan, Z.-L. High-damping metals and alloys. Trans. A Met. Mater. Sci. 1991, 22, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, F.; Bertoldi, K.; Clarke, D.R. Vibration Damping of Thermal Barrier Coatings Containing Ductile Metallic Layers. J. Appl. Mech. 2014, 81, 101001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, E.M., Jr.; Ungar, E.E. Proceedings of the ACS Division of Polymeric Materials: Science and Engineering, Dallas, Spring 1989; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 60, p. 816. [Google Scholar]
- De Batist, R. High Damping Materials: Mechanisms and Applications. J. Phys. Colloq. 1983, 44, C9-39–C9-50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.H. A Review of Friction Damping of Turbine Blade Vibration. Int. J. Turbo Jet-Engines 1990, 7, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Casagrande, A.; Sambogna, G. Effect of Ni, Si and Cr in the structural formation of diffusion aluminide coatings on commercial-purity titanium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xu, H. Damping efficiency of the coating structure. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysik, P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Czujko, T. Characterization of Low-Symmetry Structures from Phase Equilibrium of Fe-Al System—Microstructures and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2015, 8, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Tang, S. Damping behavior in Al18B4O33w/Al composite containing an interfacial layer with low melting point metal particles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 513, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pint, B.A.; Garner, G.; Cooley, K.; Haynes, J. Effect of cycle length on the oxidation performance of iron aluminide coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, E.; Campari, E.G.; Pasquini, L.; Savini, L. Automated resonant mechanical analyzer. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2001, 72, 2148–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadori, S.; Campari, E.; Fiorini, A.; Montanari, R.; Pasquini, L.; Savini, L.; Bonetti, E. Automated resonant vibrating-reed analyzer apparatus for a non-destructive characterization of materials for industrial applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 442, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanter, M.S.; Golovin, I.S.; Neuhäuser, H.; Sinning, H.-R. Internal Friction in Metallic Materials; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.W.; Jones, R.D.; Clements, P.D.; Clarke, H. Metallurgy of continuous hot dip aluminizing. Int. Mater. Rev. 1994, 39, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yako, T. Control of intermetallic compound layers at interface between steel and aluminum by diffusion-treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 338, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepa, T.; Pedraza, F.; Rouillard, F. Intermetallic formation of Al-Fe and Al-Ni phases by ultrafast slurry aluminization (flash aluminizing). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 397, 126011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuezue, H.C.; Whittle, D.P. Interdiffusion in Fe–Al system: Aluminizing. Met. Sci. 1983, 17, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorici, P.C.; Dayananda, M.A. Phase formation and interdiffusion in Al-clad 430 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 244, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švec, M.; Hanus, P.; Vodičková, V. Coefficient Thermal Expansion of Fe3Al and FeAl-type iron aluminides. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 13, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, N.; Balasubramaniam, R.; Ghosh, A. High-temperature oxidation of Fe3Al-based iron aluminides in oxygen. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 2239–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM. ASM Handbook, Alloys Phase Diagrams; ASM International Materials Park: Novelty, OH, USA, 1992; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, B.S. Anelastic Relaxation and Diffusion in Thin-Layer Materials. In Diffusion Phenomena in Thin Films and Microelectronic Materials; Gupta, D., Ho, P.S., Eds.; Noyes Press: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 73–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zamanzade, M.; Barnoush, A.; Motz, C. A Review on the Properties of Iron Aluminide Intermetallics. Crystals 2016, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanzade, M.; Barnoush, A. An Overview of the Hydrogen Embrittlement of Iron Aluminides. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 3, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, K.A.; Chia, C.T.; Gu, Y.W.; Boey, F.Y.C. High Temperature Damping Behavior of Plasma Sprayed NiCoCrAlY Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2002, 11, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

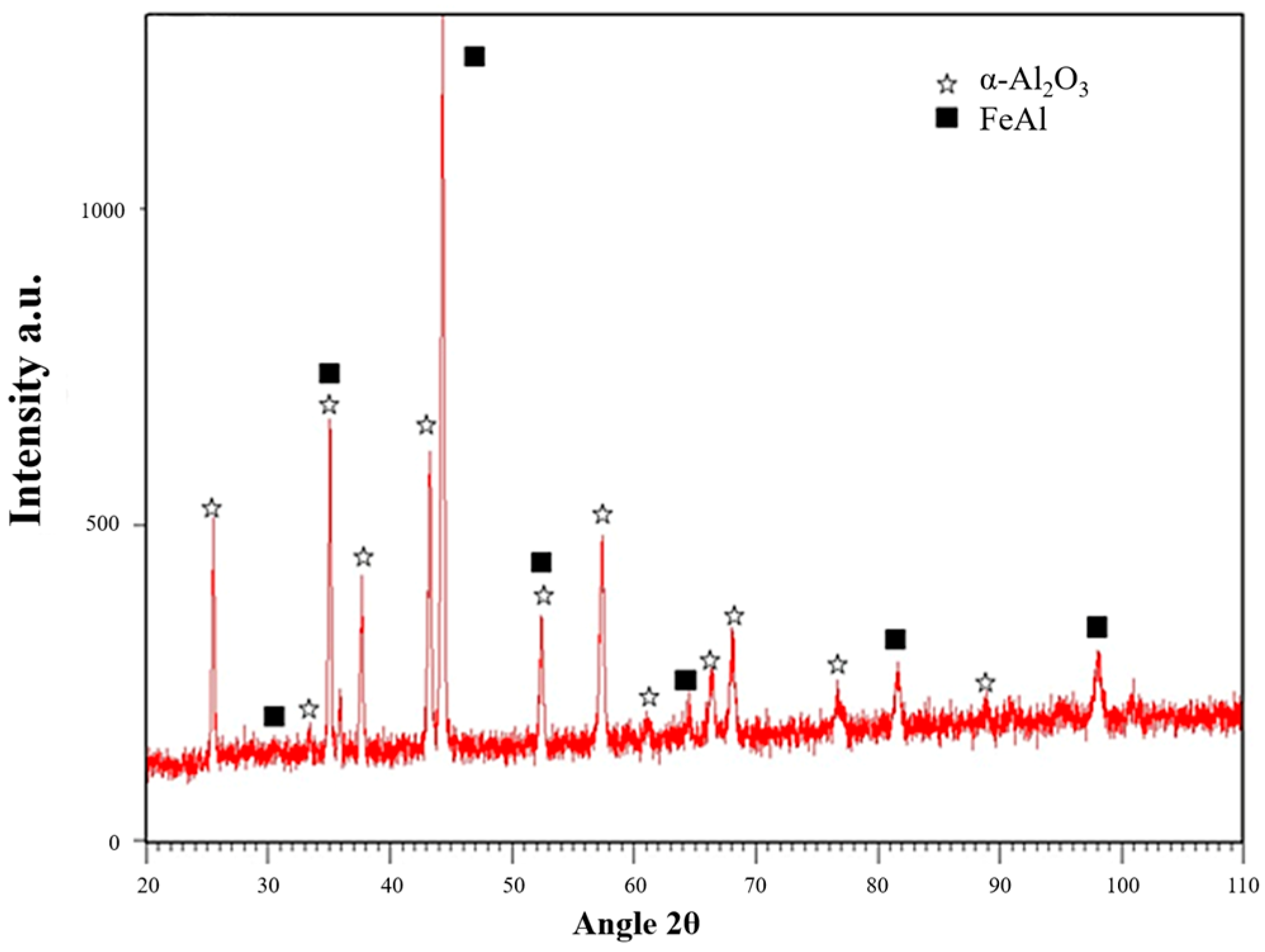

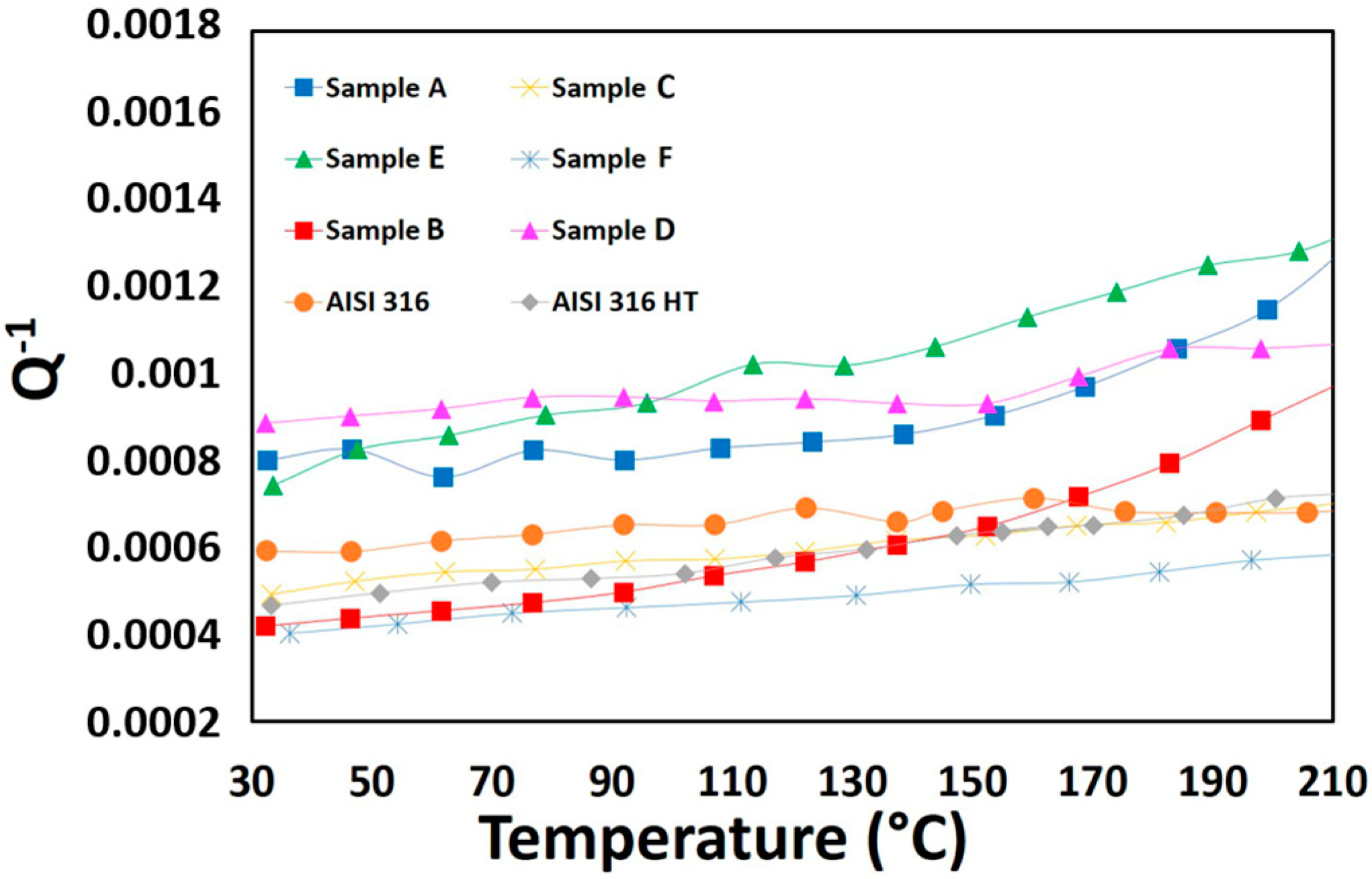

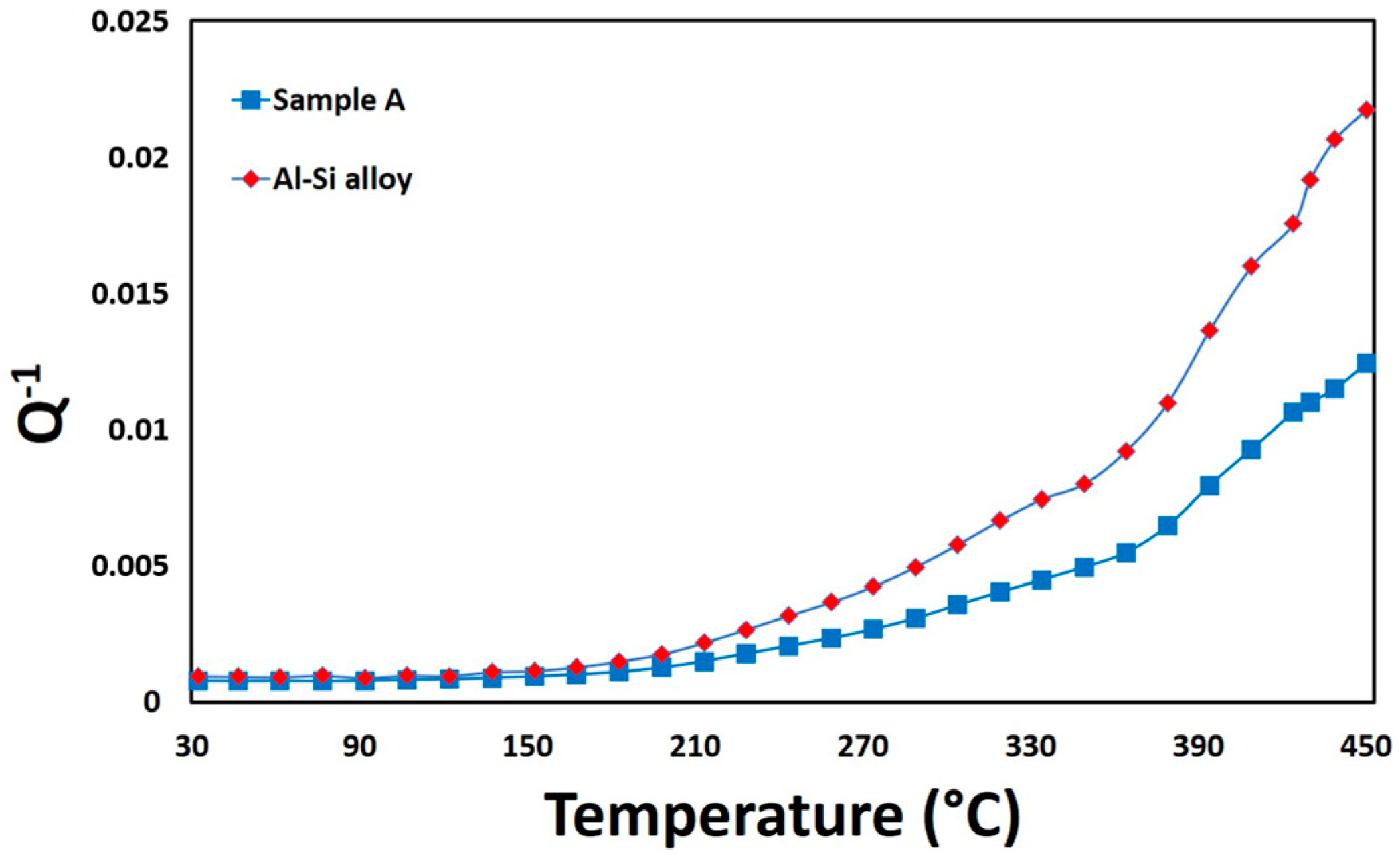
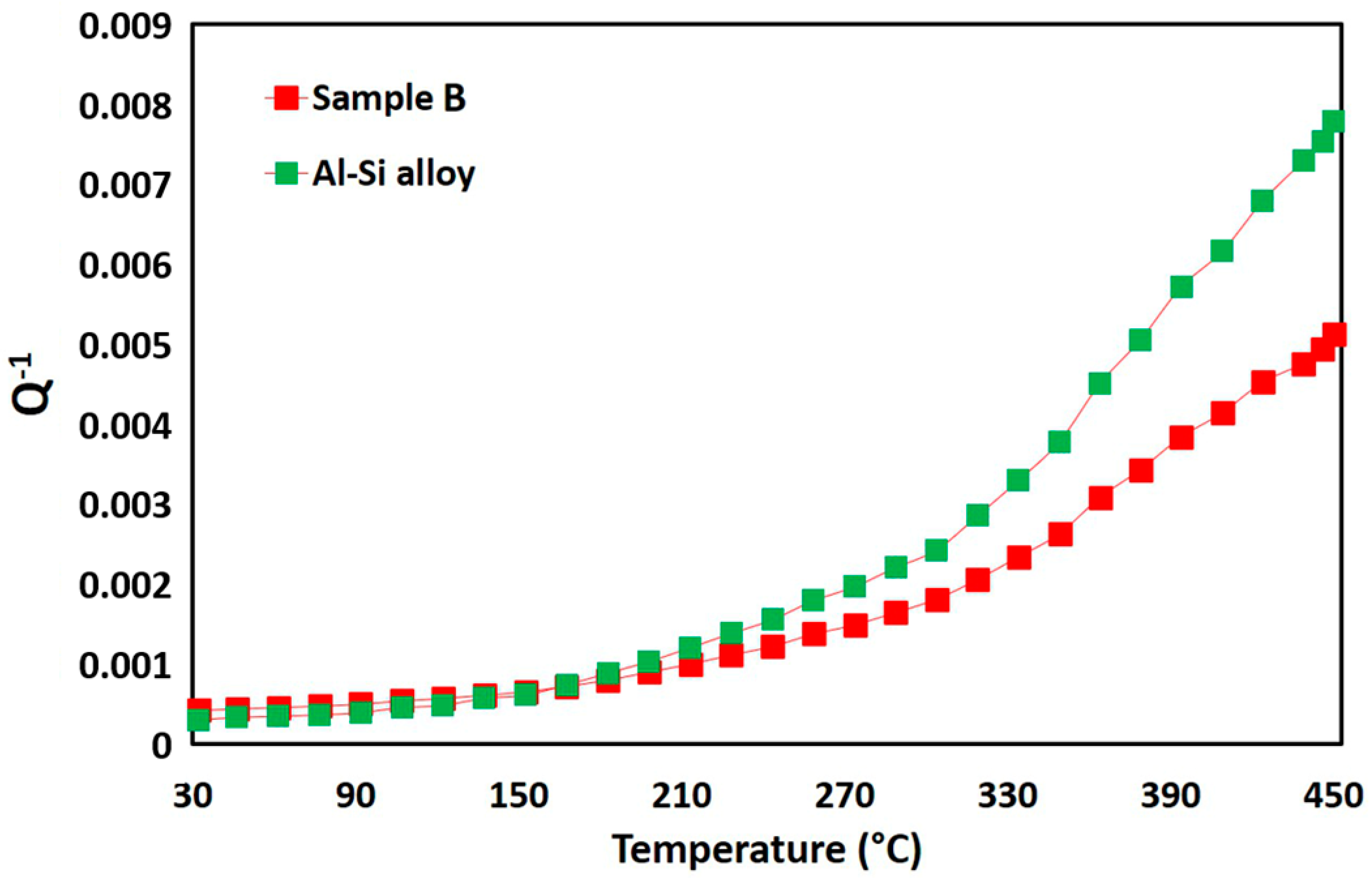
| wt.% | Fe | Cr | V | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | P | Nb | Al | C | N | S | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 316 | Bal | 18.29 | 0.10 | 8.75 | 1.94 | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.021 | 0.08 | ≤0.01 | 0.35 | 0.079 | 0.0033 | 0.0049 |
| AISI 316 * | O at.% | Al at.% | Fe at.% | Cr at.% | Ni at.% | Si at.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer oxyde layer # | 64.5 | 30.6 | 1.3 | 2.9 | - | 0.7 |
| Diffusion layer (FeAl) * and # | - | 47.2 | 40.3 | 4.3 | 6.5 | 1.2 |
| Intermediate Layer (Fe2Al5) * | - | 56.2 | 30.3 | 6.2 | - | 7.3 |
| Inner layer (NiAl) # | - | 36.1 | 22.8 | 4.1 | 34.4 | 2.6 |
| Solid solution by Al diffusion into substrate # | - | 8.4–12.1 | 63.6 | 19.1 | 6.6 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonetti, E.; Campari, E.G.; Casagrande, A.; Catania, G.; Garzoni, A. Damping Behavior of Layered Aluminium and Aluminide Coatings on AISI 316 Austenitic Steel. Coatings 2020, 10, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090888
Bonetti E, Campari EG, Casagrande A, Catania G, Garzoni A. Damping Behavior of Layered Aluminium and Aluminide Coatings on AISI 316 Austenitic Steel. Coatings. 2020; 10(9):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090888
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonetti, Ennio, Enrico Gianfranco Campari, Angelo Casagrande, Giuseppe Catania, and Andrea Garzoni. 2020. "Damping Behavior of Layered Aluminium and Aluminide Coatings on AISI 316 Austenitic Steel" Coatings 10, no. 9: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090888
APA StyleBonetti, E., Campari, E. G., Casagrande, A., Catania, G., & Garzoni, A. (2020). Damping Behavior of Layered Aluminium and Aluminide Coatings on AISI 316 Austenitic Steel. Coatings, 10(9), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090888





