Review of the Application of Graphene-Based Coatings as Anticorrosion Layers
Abstract
1. Characterization of Graphene
2. Graphene as an Anticorrosion Coating
2.1. Graphene-Based Coatings Deposited by CVD
2.2. Electrophoretically Deposited Graphene Coatings
2.3. Graphene Coatings Deposited by Other Methods
2.4. Other Methods Used to Deposit GO Films
2.5. Mechanically Properties of Graphene Layers
3. Inorganic Functionalization of Graphene Coatings
4. Graphene as a Component of Organic Coatings
4.1. Influence of Graphene Dispersion in the Polymer Resin, Coating Hydrophobicity, and Coating Adhesion Strength on the Anticorrosion Properties of Organic Coatings
4.2. Positive and Negative Effects of Conductivity on Barrier Properties
5. Modification of Graphene-Based Polymer Coatings
5.1. Effects of the Dispersibility of Organic-Functionalized Graphene, Coating Hydrophobicity, and Coating Adhesion Strength on the Protective Properties
5.2. Effects of the Dispersibility of Inorganic Functionalized Graphene, Coating Hydrophobicity, and Coating Adhesion Strength on the Protective Properties
5.3. Positive and Negative Aspects of Enhanced Conductivity
6. Protective Mechanism of Graphene Coatings, Problems Resulting from Coating Preparation, and the Effects of These Problems on Corrosion Resistance
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cataldi, P.; Steiner, P.; Raine, T.; Lin, K.; Kocabas, C.; Young, R.J.; Bissett, M.; Kinloch, I.A.; Papageorgiou, D.G. Multifunctional biocomposites based on polyhydroxyalkanoate and graphene/carbon nanofiber hybrids for electrical and thermal applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3525–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.H.; Williams, C.J.; Derby, B.; Szekely, G. Oil-in-water separation with graphene-based nanocomposite membranes for produced water treatment. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 603, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, H.; Lin, C.-W.; Faruque Hasan, M.M.; Kaner, R.; Sant, G.N. Highly permeable polyaniline–graphene oxide nanocomposite membranes for CO2 separations. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, A.; Jahanshahi, R.; Sobhani, S.; Skibsted, J.; Sansano, J.M. Immobilized piperazine on the surface of graphene oxide as a heterogeneous bifunctional acid-base catalyst for the multicomponent synthesis of 2-amino-3-cyano-4: H -chromenes. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4604–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cseri, L.; Baugh, J.; Alabi, A.; AlHajaj, A.; Zou, L.; Dryfe, R.A.W.; Budd, P.M.; Szekely, G. Graphene oxide-polybenzimidazolium nanocomposite anion exchange membranes for electrodialysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 24728–24739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, M.; He, C.; Li, S.; Fan, X.; Nie, C.; Luo, H.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, C. Graphene-based advanced nanoplatforms and biocomposites from environmentally friendly and biomimetic approaches. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4887–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Cseri, L.; Szekely, G.; Blanford, C.F. Robust covalently cross-linked polybenzimidazole/graphene oxide membranes for high-flux organic solvent nanofiltration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16140–16147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y. Supercapacitor devices based on graphene materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 13103–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Subrahmanyam, K.S.; Krishna, K.S.; Datta, S.; Govindaraj, A.; Pati, S.K.; Rao, C.N.R. Uptake of H2 and CO2 by graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15704–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, P.K.; Chen, W.; Loh, K.P. Wee ATS solution-gated epitaxial graphene as pH sensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 14392–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ghauri, F.A.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, R.; Raffi, M. Corrosion study of electrophoretically deposited graphene oxide coatings on copper metal. Thin Solid Films 2016, 620, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan Lim, C.H.Y.; Sorkin, A.; Bao, Q.; Li, A.; Zhang, K.; Nesladek, M.; Loh, K.P. A hydrothermal anvil made of graphene nanobubbles on diamond. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1556–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyhl, L.; Nielsen, S.F.; Čabo, A.G.; Cassidy, A.; Miwa, J.A.; Hornekær, L. Graphene as an anti-corrosion coating layer. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 180, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field in atomically thin carbon films. Science (80) 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, M.S.A.; Uddin, M.N.; Islam, M.M.; Bipasha, F.A.; Hossain, S.S. Synthesis of graphene. Int. Nano Lett. 2016, 6, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cao, H.; Xue, Y.; Li, B.; Cai, W. Liquid-phase exfoliation of graphene: An overview on exfoliation media, techniques, and challenges. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C. Review of chemical vapor deposition of graphene and related applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, Q.; Tang, L.A.L.; Zhong, Y.; Loh, K.P. Hydrothermal dehydration for the “green” reduction of exfoliated graphene oxide to graphene and demonstration of tunable optical limiting properties. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2950–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; An, J.; Potts, J.R.; Velamakanni, A.; Murali, S.; Ruoff, R.S. Hydrazine-reduction of graphite- and graphene oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2011, 49, 3019–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, K.K.; Benayad, A.; Yoon, S.M.; Park, H.K.; Jung, I.S.; Jin, M.H.; Jeong, H.K.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Efficient reduction of graphite oxide by sodium borohydride and its effect on electrical conductance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Merino, M.J.; Guardia, L.; Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Solís-Fernández, P.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Vitamin C is an ideal substitute for hydrazine in the reduction of graphene oxide suspensions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6426–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, I.M.; Soto, E.; Vaquero, F.; Mota, N.; Garcia, B.; Liuzzi, D.; Guil-López, R.; Navarro, R.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Influence of the reduction of graphene oxide with hydroiodic acid on the structure and photoactivity of CdS–rGO hybrids. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Peng, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F. Deoxygenation of exfoliated graphite oxide under alkaline conditions: A green route to graphene preparation. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4490–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhao, X.S. The electrocapacitive properties of graphene oxide reduced by urea. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6391–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, M. Reduction of graphene oxide by thiourea. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 10082–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Reducing graphene oxide via hydroxylamine: A simple and efficient route to graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 11957–11961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Gui, T.; Li, B.; Han, P.; Tian, H.; Liu, A.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. A brief review of corrosion protective films and coatings based on graphene and graphene oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.K.; Sudin, I.; Basheer, U.M.; Yusop, M.Z.M. A review on graphene-based polymer composite coatings for the corrosion protection of metals. Corros. Rev. 2019, 37, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, A.; Heidari, A.A.; Sajedi, M. Graphene and graphene/polymer composites as the most efficient protective coatings for steel, aluminum and copper in corrosive media: A review of recent studies. Chem. Rec. 2019, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Z. A comprehensive review on graphene-based anti-corrosive coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nine, M.J.; Cole, M.A.; Tran, D.N.H.; Losic, D. Graphene: A multipurpose material for protective coatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12580–12602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hui, F.; Duan, H.L. A review on the use of graphene as a protective coating against corrosion. Ann. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Singh Raman, R.K.; Chakraborty Banerjee, P.; Lobo, D.E.; Gullapalli, H.; Sumandasa, M.; Kumar, A.; Choudhary, L.; Tkacz, R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Majumder, M. Protecting copper from electrochemical degradation by graphene coating. Carbon N. Y. 2012, 50, 4040–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, N.T.; Schiller, T.; Medhekar, N.; Birbilis, N. Exploring graphene as a corrosion protection barrier. Corros. Sci. 2012, 56, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasai, D.; Tuberquia, J.C.; Harl, R.R.; Jennings, G.K.; Bolotin, K.I. Graphene: Corrosion-inhibiting coating. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Chu, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, S.Y. Enhancement of seawater corrosion resistance in copper using acetone-derived graphene coating. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Rentería, J.A.; Cházaro-Ruiz, L.F.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) films onto carbon steel by cathodic electrophoretic deposition: Anticorrosive coating. Carbon N. Y. 2017, 122, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Jaleh, B.; Ehsani, A. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide on aluminum: Characterization, low thermal annealing, surface and anticorrosive properties. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 88, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hares, E.; El-Shazly, A.H.; El-Kady, M.F.; Hammad, A.S. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide nanosheets on copper pipe for corrosion protection. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 5559–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sammarraie, A.M.A.; Raheema, M.H. Reduced graphene oxide coating for corrosion protection enhancement of carbon steel in sea water. Iraqi J. Sci. Part B (Special Issue) 2016, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Lih, E.T.Y.; Zaid, R.b.M.; Tan, L.L.; Chong, K.F. Facile corrosion protection coating from graphene. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2012, 3, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, M.; Ghahfarokhi, Z.S.; Yazdi, E.G. Electrochemical and surface evaluation of the anti-corrosion properties of reduced graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22007–22015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H.; Nan, H.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide as a corrosion inhibitor for sintered NdFeB. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, J.M. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide on mild carbon steel for anti-corrosion application. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 254, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha Kiran, N.; Dey, S.; Singh, B.P.; Besra, L. Graphene coating on copper by electrophoretic deposition for corrosion prevention. Coatings 2017, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Raza, M.A.; Ghauri, F.A.; Kanwal, R.; Ahmad, A.; Inam, A. Graphene oxide coatings deposited on steel substrate using electrophoretic deposition and electrochemical evaluation of coatings in saline media. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 778, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Ali, A.; Ghauri, F.A.; Aslam, A.; Yaqoob, K.; Wasay, A.; Raffi, M. Electrochemical behavior of graphene coatings deposited on copper metal by electrophoretic deposition and chemical vapor deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 332, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, K.; Hamid, Z.A.; Eldin, T.A.S.; Khalil, M.W.; Hassan, H.B. Anti-corrosion nickel/reduced graphene oxide-titanium dioxide coating for mild steel in organic acids. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2019, 10, 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, C.; Liu, D.; Jin, K.; Fang, L.; Sha, T. Corrosion resistance and micro-tribological properties of nickel hydroxide-graphene oxide composite coating. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 76, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotheender, K.S.; Srivastava, C. Ni-graphene oxide composite coatings: Optimum graphene oxide for enhanced corrosion resistance. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshgi Asl, S.; Afshar, A.; Yaghoubinezhad, Y. An Electrochemical Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Zinc Nanocomposite Coating through Pulse-Potential Electrodeposition Technique and the Consequent Corrosion Resistance. Int. J. Corros. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wei, D.; Huang, X.; Mai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jie, X. Electrodeposition of Co–Ni–P/graphene oxide composite coating with enhanced wear and corrosion resistance. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Veerapandian, M.; Ramasundaram, S.; Hong, S.W.; Sudhagar, P.; Nagarajan, S.; Raman, V.; Ito, E.; Kim, S.; Yun, K.; et al. Sodium functionalized graphene oxide coated titanium plates for improved corrosion resistance and cell viability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amudha, A.; Shashikala, H.D.; Asiq Rahman, O.S.; Keshri, A.K.; Nagaraja, H.S. Effect of graphene oxide loading on plasma sprayed alumina-graphene oxide composites for improved anticorrosive and hydrophobic surface. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hua, L.; Li, S.; Yu, M. Graphene dip coatings: An effective anticorrosion barrier on aluminum. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 327, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Pavan, A.S.; Ramanan, S.R. A study on corrosion resistant graphene films on low alloy steel. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, M.Y.; Srivastava, C. High corrosion resistance of metal-graphene oxide-metal multilayer coatings. Philos. Mag. 2020, 100, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lim, Y.S.; Han, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Shin, K. A graphene oxide oxygen barrier film deposited via a self-assembly coating method. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Brown, L.; Levendorf, M.; Cai, W.; Ju, S.-Y.; Edgeworth, J.; Li, X.; Magnuson, C.W.; Velamakanni, A.; Piner, R.D.; et al. Oxidation resistance of graphene-coated Cu and Cu Ni alloy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1321–7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.J.; Zhu, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Stoller, M.D.; Emilsson, T.; Park, S.; Velamakanni, A.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Thin film fabrication and simultaneous anodic reduction of deposited graphene oxide platelets by electrophoretic deposition. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Lim, A.T.O.; Huang, J. A cautionary note on graphene anti-corrosion coatings. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 834–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Narayan, J. Reduced Graphene Oxide/Amorphous Carbon P-N Junctions: Nanosecond Laser Patterning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24318–24330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Joshi, P.; Narayan, J. Electron mobility modulation in graphene oxide by controlling carbon melt lifetime. Carbon N. Y. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusovas, R.; Ratautas, K.; Račiukaitis, G.; Barkauskas, J.; Stankevičiene, I.; Niaura, G.; Mažeikiene, R. Reduction of graphite oxide to graphene with laser irradiation. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 52, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Crespo, R.A.; Mao, L.; Wen, J.; Nguyen, H.T.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Huang, J.; Nguyen, S.B.T.; Espinosa, H.D. Atomically thin polymer layer enhances toughness of graphene oxide monolayers. Matter 2019, 1, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Crespo, R.A.; Gao, W.; Mao, L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Roenbeck, M.R.; Paci, J.T.; Huang, J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Espinosa, H.D. The role of water in mediating interfacial adhesion and shear strength in graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6089–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhan Kumar, A.; Suresh Babu, R.; Obot, I.B.; Gasem, Z.M. Fabrication of nitrogen doped graphene oxide coatings: Experimental and theoretical approach for surface protection. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 19264–19272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollik, K.; Rybarczyk, M.; Karczewski, J.; Lieder, M. Fabrication of anti-corrosion nitrogen doped graphene oxide coatings by electrophoretic deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 499, 143914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Cui, M.; Li, W.; Pu, J.; Xue, Q.; Wang, L. N-doping of graphene: Toward long-term corrosion protection of Cu. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.N.; El-Tagoury, M.M.; Radi, A.A.; Hassan, S.M. Carboxylic acids as corrosion inhibitors for aluminium in acidic and alkaline solutions. Anti-Corrosion Methods Mater. 1990, 37, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar, H.; Deen, K.M.; Rahman, Z.U.; Shah, U.H.; Raza, M.A.; Haider, W. Functionalized graphene oxide coating on Ti6Al4V alloy for improved biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Liang, J.; Li, W. Electrochemical deposition of Mg(OH)2/GO composite films for corrosion protection of magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2015, 3, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lai, X.; Jia, R.; Yuan, X. Graphene oxide modified by zirconium dioxide to enhance the corrosion resistance of Zinc/Aluminum coatings. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Shahid, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Ammar, A.U.; Saboor, A.; Khalid, A.; Hayat, A.; Saeed, A.; Koohgilani, M. Electrochemical comparison of SAN/PANI/FLG and ZnO/GO coated cast iron subject to corrosive environments. Materials 2018, 11, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, M.A.; Aneja, K.S.; Shaikh, A.; Bohm, S.; Sarkar, K.; Bohm, H.L.M.; Raja, V.S. Graphene-based anticorrosive coatings for copper. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Rashed, G.R.; Zaarei, D. Assessment of graphene oxide/epoxy nanocomposite as corrosion resistance coating on carbon steel. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Vaezi, M.R.; Rashidi, A.; Bagherzadeh, M.R. Exploring corrosion protection properties of solvent based epoxy-graphene oxide nanocomposite coatings on mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2017, 115, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Ji, W.F.; Li, C.W.; Chang, C.H.; Peng, Y.Y.; Yeh, J.M.; Liu, W.R. The effect of varying carboxylic-group content in reduced graphene oxides on the anticorrosive properties of PMMA/reduced graphene oxide composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, R.; Du, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cao, X. Investigation of the anticorrosion properties of graphene oxide doped thin organic anticorrosion films for hot-dip galvanized steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 480, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Lu, H.I.; Lai, M.C.; Liu, P.J.; Hsu, C.H.; Ji, W.F.; Chuang, T.L.; Wei, Y.; Yeh, J.M.; et al. Room-temperature cured hydrophobic epoxy/graphene composites as corrosion inhibitor for cold-rolled steel. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 66, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gu, L.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Yu, H. Corrosion resistance of graphene-reinforced waterborne epoxy coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Self-aligned graphene as anticorrosive barrier in waterborne polyurethane composite coatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14139–14145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, L.; Song, Y. The multiscale effects of graphene oxide on the corrosion resistance properties of waterborne alkyd resin coatings. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, J.; Jiang, F.; Ma, L. Comparative corrosion resistance of graphene sheets with different structures in waterborne epoxy coatings. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 556, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. A mechanistic study of corrosion of graphene and low zinc- rich epoxy coatings on carbon steel in salt environment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 9671–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z.; Guo, N.; Lei, Y.; Chang, X.; Yin, Y. Promoting barrier performance and cathodic protection of zinc-rich epoxy primer via single-layer graphene. Polymers 2018, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huang, F.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.F. Preparation of graphene nanoplate added zinc-rich epoxy coatings for enhanced sacrificial anode-based corrosion protection. Corros. Sci. 2019, 159, 108120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Roohi, H. Influence of functionalized multi-layer graphene on adhesion improvement and corrosion resistance performance of zinc-rich epoxy primer. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, J.; Jiang, F.; Wu, Y.; Ma, L. Designing reduced graphene oxide/zinc rich epoxy composite coatings for improving the anticorrosion performance of carbon steel substrate. Mater. Des. 2019, 169, 107694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghauri, F.A.; Raza, M.A.; Baig, M.S.; Ibrahim, S. Corrosion study of the graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide-based epoxy coatings. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Vaezi, M.R.; Rashidi, A. Investigating the effect of SiO2-graphene oxide hybrid as inorganic nanofiller on corrosion protection properties of epoxy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 311, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Di, H.; Yu, Z.; Liang, L.; Lv, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, D. Fabrication of silica-decorated graphene oxide nanohybrids and the properties of composite epoxy coatings research. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Haeri, Z.; Ramezanzadeh, M. A facile route of making silica nanoparticles-covered graphene oxide nanohybrids (SiO2–GO); fabrication of SiO2–GO/epoxy composite coating with superior barrier and corrosion protection performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Rashidi, A.; Vaezi, M.R.; Bagherzadeh, M.R. Excellent corrosion protection performance of epoxy composite coatings filled with amino-silane functionalized graphene oxide. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 317, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Vaezi, M.R.; Rashidi, A.; Bagherzadeh, M.R. Distinctive roles of silane coupling agents on the corrosion inhibition performance of graphene oxide in epoxy coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadeh, P.; Ghaffari, M.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Bahlakeh, G.; Saeb, M.R. The role of functionalized graphene oxide on the mechanical and anti-corrosion properties of polyurethane coating. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 86, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calovi, M.; Rossi, S.; Deflorian, F.; Dirè, S.; Ceccato, R. Effect of functionalized graphene oxide concentration on the corrosion resistance properties provided by cataphoretic acrylic coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, G.; Liu, B. Reinforcing the corrosion protection property of epoxy coating by using graphene oxide–poly(urea–formaldehyde) composites. Corros. Sci. 2017, 123, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli-Shokouhi, S.; Nasirpouri, F.; Khatamian, M. Polyaniline-modified graphene oxide nanocomposites in epoxy coatings for enhancing the anticorrosion and antifouling properties. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Bahlakeh, G.; Mohamadzadeh Moghadam, M.H.; Miraftab, R. Impact of size-controlled p-phenylenediamine (PPDA)-functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets on the GO-PPDA/Epoxy anti-corrosion, interfacial interactions and mechanical properties enhancement: Experimental and quantum mechanics investigations. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Chan, C.C.; Huang, Y.C. High-performance polystyrene/graphene-based nanocomposites with excellent anti-corrosion properties. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajitha, K.; Mohana, K.N. Application of modified graphene oxide–Polycaprolactone nanocomposite coating for corrosion control of mild steel in saline medium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 241, 122050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Zhu, R.; Sheng, X.; Xie, D.; Mei, Y. Facile modification of graphene oxide with Lysine for improving anti-corrosion performances of water-borne epoxy coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, L.; Feng, L.; Lu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, B.; Zou, X. Polydopamine functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposites reinforced the corrosion protection and adhesion properties of waterborne polyurethane coatings. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Ren, S.; Zhao, H.; Xue, Q.; Wang, L. Polydopamine coated graphene oxide for anticorrosive reinforcement of water-borne epoxy coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shan, W.; Cui, J.; Qiu, H.; Yang, G.; Zheng, S.; Yang, J. Enhanced corrosion resistance and weathering resistance of waterborne epoxy coatings with polyetheramine-functionalized graphene oxide. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.G.; Geng, W.; Geng, H.Z.; Zhao, H.; Jing, L.C.; Yuan, X.T.; Tian, Y.; Wang, T.; Ning, Y.J.; Wu, L. Improvement of corrosion resistance of waterborne polyurethane coatings by covalent and noncovalent grafted graphene oxide nanosheets. ACS Omega 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, H.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, D. Phytic acid intercalated graphene oxide for anticorrosive reinforcement of waterborne epoxy resin coating. Polymers 2019, 11, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Di, H.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.; Liang, L.; Lv, L.; Ran, X.; Pan, Y.; Luo, Z. Preparation of graphene oxide modified by titanium dioxide to enhance the anti-corrosion performance of epoxy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, N.; Cole, I.S.; Caballero-Briones, F.; Manickam, S.; Lal, C.; Sathiskumar, J. Neodymium-decorated graphene oxide as a corrosion barrier layer on Ti6Al4V alloy in acidic medium. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8537–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Zhu, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, G. Superhydrophobic epoxy coating modified by fluorographene used for anti-corrosion and self-cleaning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 401, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.; Yu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Lv, L.; Pan, Y.; Shi, H.; He, Y. Corrosion-resistant hybrid coatings based on graphene oxide–zirconia dioxide/epoxy system. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X.; Long, Z.; He, S.; He, Y. Epoxy composites coating with Fe3O4 decorated graphene oxide: Modified bio-inspired surface chemistry, synergistic effect and improved anti-corrosion performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Di, H.; Ma, Y.; Lv, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. Fabrication of graphene oxide-alumina hybrids to reinforce the anti-corrosion performance of composite epoxy coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.H.; Huang, T.C.; Tseng, I.H.; Huang, B.S.; Yang, T.I.; Tsai, M.H. Transparency anticorrosion coatings prepared from alumina-covered graphene oxide/polyimide nanocomposites. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, M. Polyaniline-cerium oxide (PAni-CeO2) coated graphene oxide for enhancement of epoxy coating corrosion protection performance on mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2018, 137, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, N.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Shahrabi, T. The epoxy coating interfacial adhesion and corrosion protection properties enhancement through deposition of cerium oxide nanofilm modified by graphene oxide. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 64, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhong, F.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, T. Non-covalently functionalized boron nitride by graphene oxide for anticorrosive reinforcement of water-borne epoxy coating. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 124337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wen, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Sun, K. Graphene oxide-loaded zinc phosphate as an anticorrosive reinforcement in waterborne polyurethane resin. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 14, 5271–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Wang, T.; Cheng, S. Si3N4 @RGO hybrids for epoxy coatings with enhanced anticorrosion performance. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lei, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, T.; Zhang, F.; Sun, S.; Chang, X.; Fan, R.; Yin, Y. Insight into the impact of conducting polyaniline/graphene nanosheets on corrosion mechanism of zinc-rich epoxy primers on low alloy DH32 steel in artificial sea water. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, C878–C889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Mohamadzadeh Moghadam, M.H.; Shohani, N.; Mahdavian, M. Effects of highly crystalline and conductive polyaniline/graphene oxide composites on the corrosion protection performance of a zinc-rich epoxy coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, H.; Ji, D.; Xu, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, H. Achieving long-term anticorrosion: Via the inhibition of graphene’s electrical activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Wen, S.; Yu, D.; Wu, Y.; Sun, K. Improved corrosion resistance based on APTES-grafted reduced sulfonated graphene/waterborne polyurethane coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lv, L.; Ma, Y.; Di, H.; He, Y. Covalent modification of graphene oxide by metronidazole for reinforced anti-corrosion properties of epoxy coatings. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18217–18226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, K.S.; Böhm, H.L.M.; Khanna, A.S.; Böhm, S. Functionalised graphene as a barrier against corrosion. FlatChem 2017, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlasny, I.; Dabrowski, P.; Rogala, M.; Kowalczyk, P.J.; Pasternak, I.; Strupinski, W.; Baranowski, J.M.; Klusek, Z. Role of graphene defects in corrosion of graphene-coated Cu(111) surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Li, Z.; Shenoy, G.J.; Li, L.; Liu, H. Enhanced room-temperature corrosion of copper in the presence of graphene. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6939–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisur, M.R.; Chakraborty Banerjee, P.; Easton, C.D.; Singh Raman, R.K. Controlling hydrogen environment and cooling during CVD graphene growth on nickel for improved corrosion resistance. Carbon N. Y. 2018, 127, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diba, M.; Fam, D.W.H.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Shaffer, M.S.P. Electrophoretic deposition of graphene-related materials: A review of the fundamentals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 82, 83–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
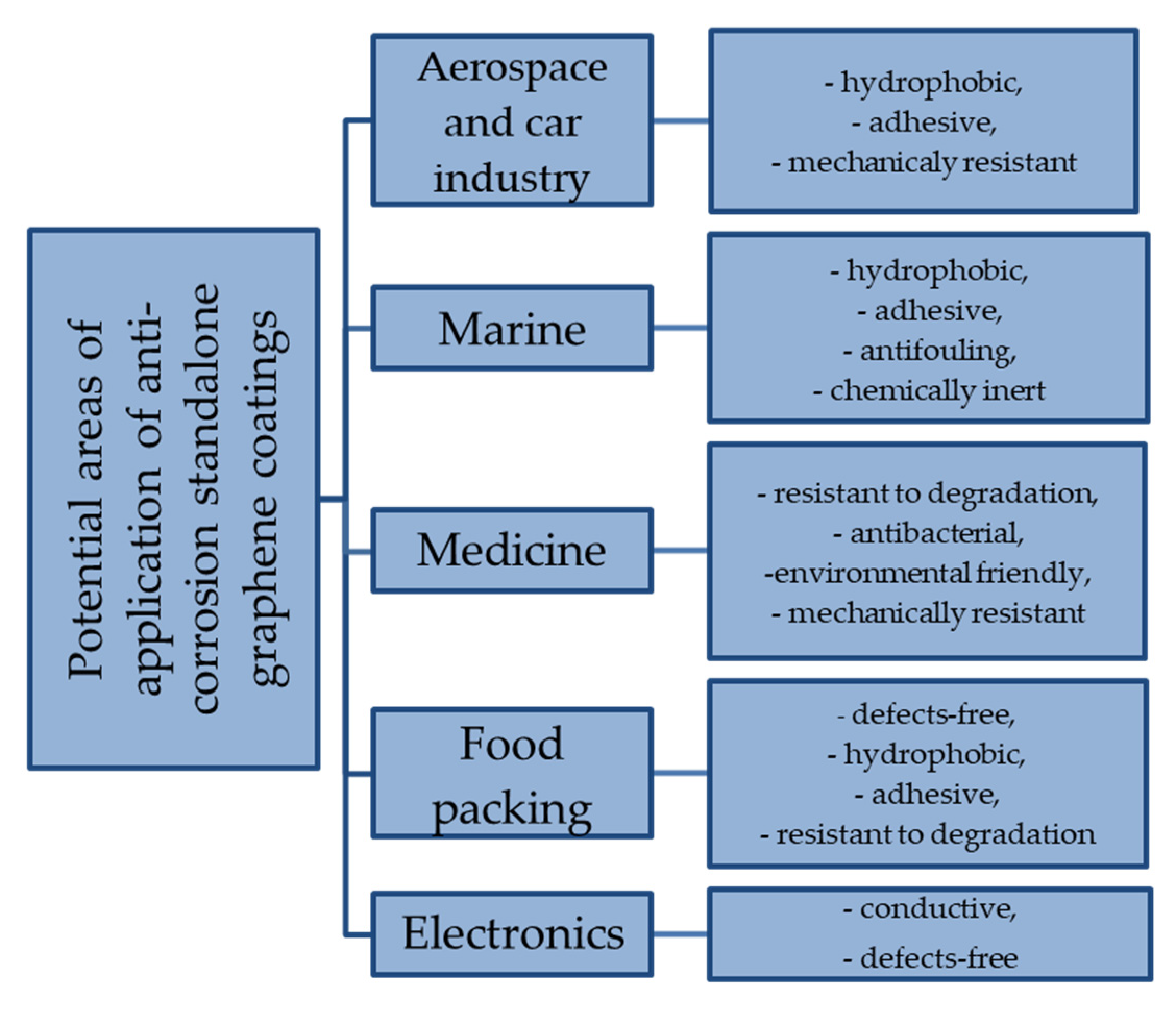
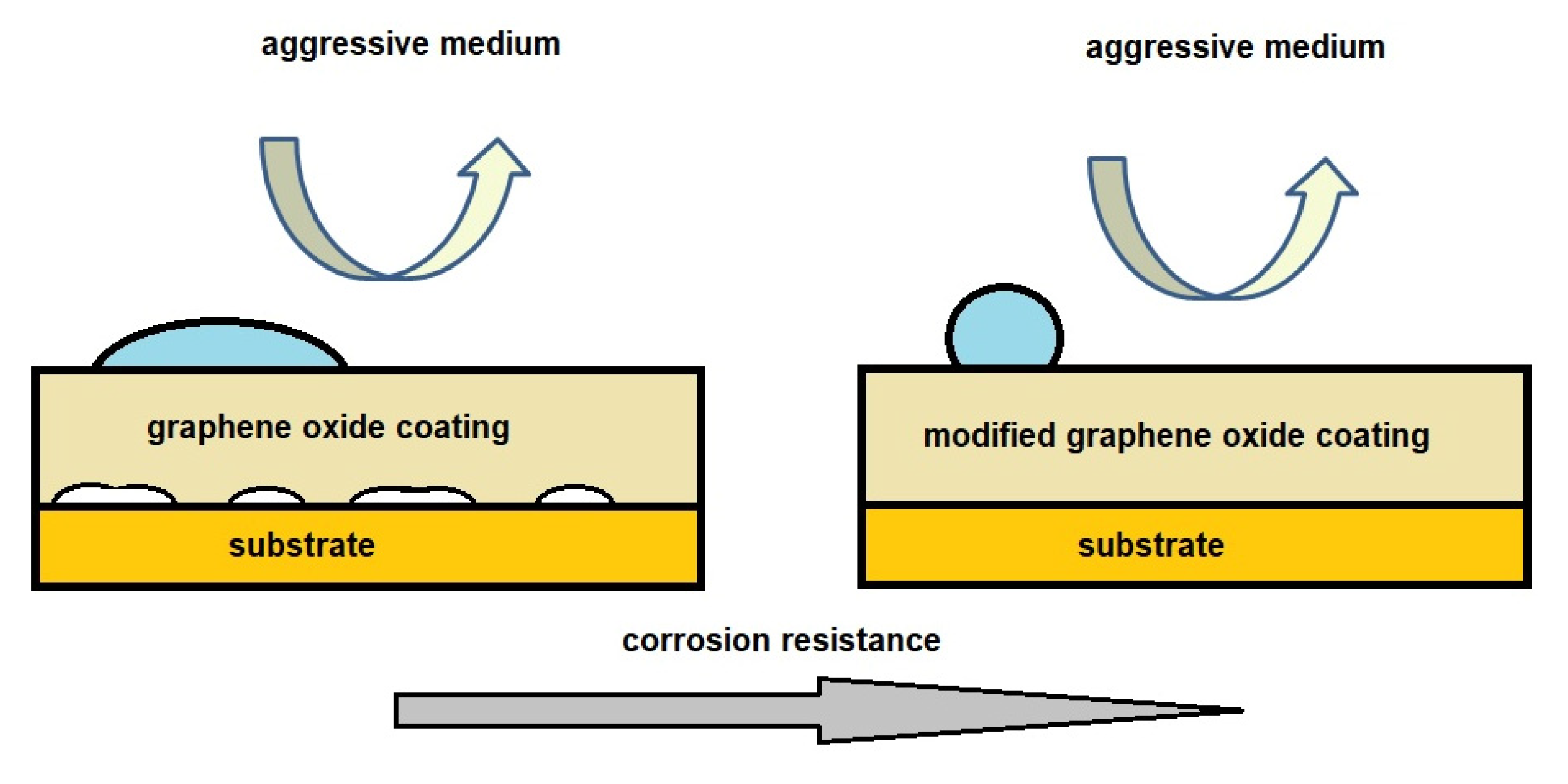
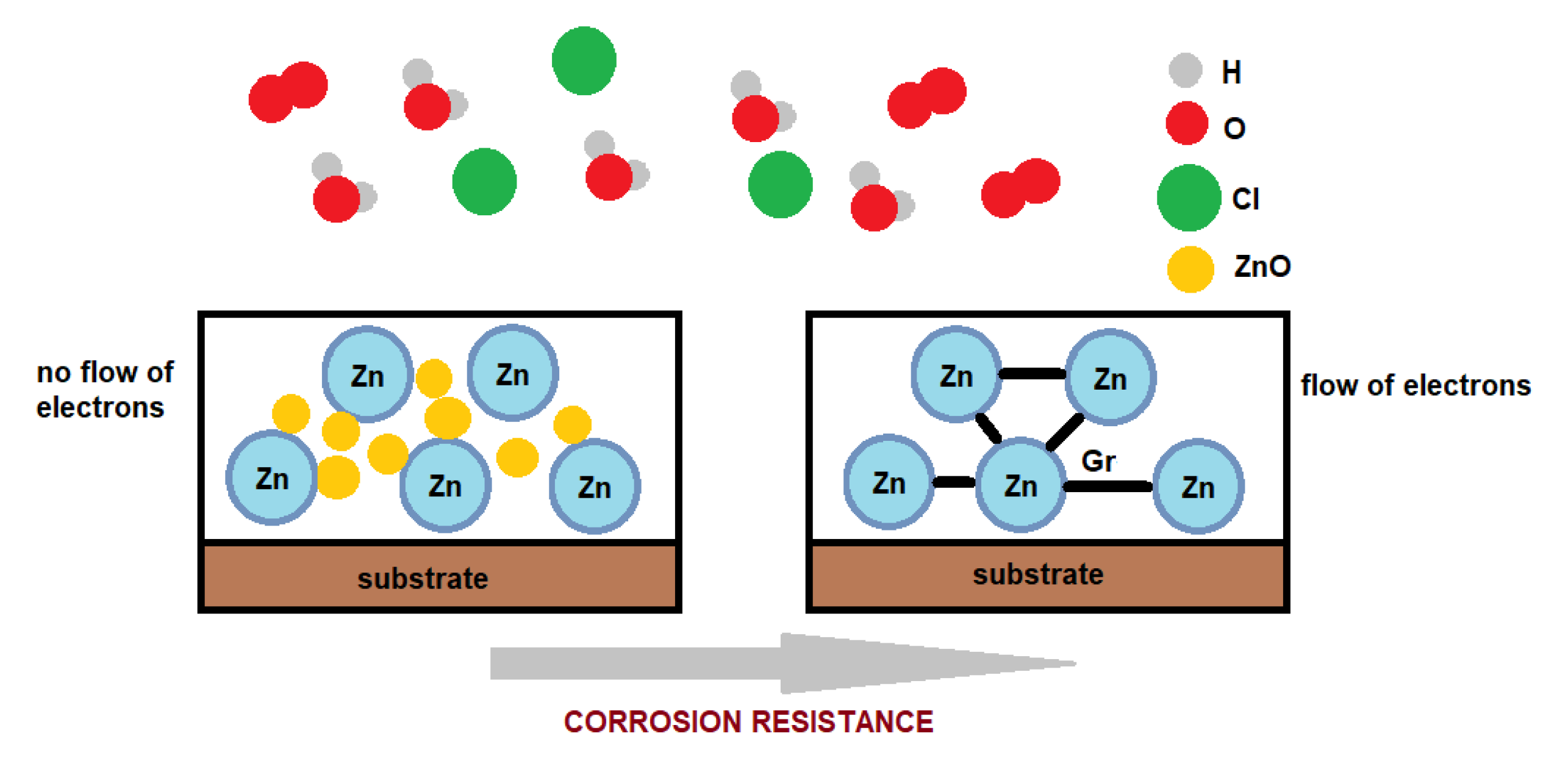
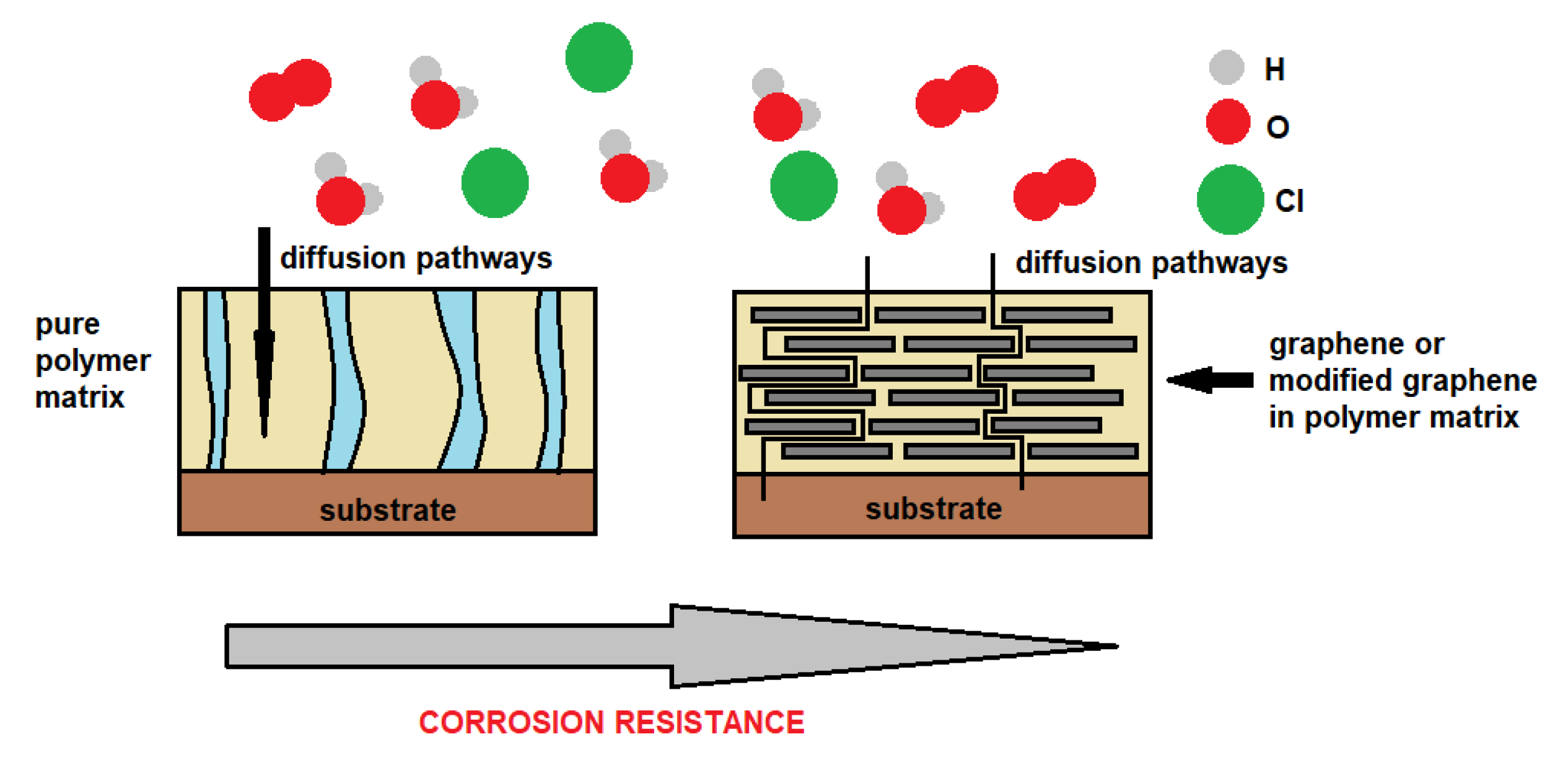
| Method | Description of Method | Pros and Cons | Literature References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micromechanical Cleavage | Using adhesive tape, a single layer of graphene is peeled from highly ordered pyrolytic graphene | Pros: uncomplicated process; Cons: nonuniform thickness of layer, very small-scale production | [14,15] |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation | Graphene layers are obtained by the exfoliation of graphite in solvent. Because graphene is hydrophobic, different additives (surfactants or polymer) or appropriate solvents are used to obtain a stable and uniform suspension of graphene | Pros: simple technique; Cons: environmental pollution, poor quality | [16] |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | The graphene layer is formed by the decomposition of hydrocarbons under high temperature. The carbon sources are various hydrocarbons such as ethylene, benzene, acetylene, and methane | Pros: large size, good quality, and purity, small production scale; Cons: high temperature, expensive process, sophisticated equipment, toxic by-products | [15,17] |
| Reduction Methods | The deoxygenation of graphene oxide (GO) occurs as a result of thermal treatment or treatment with chemical reagents such as hydrazine, sodium borohydride, vitamin C, hydroiodic acid, sodium or potassium hydroxide solution, urea, thiourea, or hydroxylamine | Pros: simple technique, economical, large scale production; Cons: poor quality, harmful and toxic reagents | [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26] |
| Methods | Substrate | Coating Thickness | Corrosion Measurements | Literature References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | Copper, nickel | 1–2 layers, Single or few layers | Potentiodynamic polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry | [33,34,35] |
| Rapid Thermal Annealing | Copper | 1 layer | Potentiodynamic polarization, EIS | [36] |
| Electrophoretic Deposition | Copper, carbon steel, aluminum, NdFeB (Neodymium–Iron-Boron alloy) | <10 nm, 12.4 µm (20 V), 25.4 µm (30 V), 40 nm (2 V), 400 nm (5 V), 1.5 µm (15 V), 3 µm, 1 µm (1 min), 2.5 µm (2 min) single layer or few layers | Potentiodynamic polarization, EIS, cyclic corrosion test, weight loss measurements | [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Electrodeposition | Mild steel, stainless steel, low-carbon steel | 40 nm, 2.3 µm, | Potentiodynamic polarization, EIS | [48,49,50,51,52] |
| Spin Coating | Titanium substrates | Few layers | Potentiodynamic polarization | [53] |
| Spray Coating | Carbon steel | 300 µm | Linear polarization resistance, EIS | [54] |
| Dip Coating | Aluminum, low alloy steel | Single-layer and multilayer | Potentiodynamic polarization, EIS | [55,56] |
| Drop Casting | Mild steel | Not available | EIS, Tafel polarization | [57] |
| Layer-by-Layer Deposition | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 30–40 nm | Oxygen transmittance rate | [58] |
| Methods | ID/IG | Oxygen Content (%) | SEM Analysis | Corrosion Resistance | Literature References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | Not available | Not available | Fold, wrinkles, edges | Lower corrosion rate than nickel and copper surface | [34] |
| Rapid Thermal Annealing | Less than ~0.1 | Not available | No significant changes (or defects) | Significantly reduced corrosion current density (Icorr) | [36] |
| Electrophoretic Deposition | −1.09 (GO powder), 1.71 (GO/steel) | C/O: 0.76 (GO), 1.4 (rGO coating) | Nonuniform | Icorr (µA·cm−2): | [37,45] |
| 1.183 × 104 (steel), 4140 (rGO/steel) | |||||
| −1.03 (GO powder), 1.009 (GO/Cu) | Not available | Uniform, thin, transparent coating | 15.375 (Cu), 12.44 GO/Cu | ||
| Electrodeposition | Not available | Partial reduction of GO during electrodeposition | Rough surface with no distinguishable delamination | Icorr (µA·cm−2): | [49,50,51,52] |
| 0.0912(SS), 0.0108 (GO), 0.00268 (GO–Ni(OH)2) | |||||
| Not available | Not available | Compact and free crack morphology | 6.138 (Ni), 0.956 ÷ 4.845 (Ni–GO, depend on GO amounts) | ||
| 1.33 (GO powder) 0.58 (rGO–Zn) | Reduction of GO during electrodeposition | Thin and few layers | 1.5 (bare steel), 1.6 (rGO), 0.007 (rGO–Zn) | ||
| 0.95 (GO), 1.27 (Co–Ni–P/GO) | Not available | Rough morphology | 14.33 (Co–Ni–P), 3.05 (Co–Ni–P/GO) | ||
| Spin Coating | 1.028 (GO), 1.027 (NaGO) | Not available | Lesser wrinkles and wavy features than GO coating | Corrosion potential (Ecorr) (V): −0.509 (titanium substrates), −0.290 (GO), −0.200 (NaGO) | [53] |
| Spray Coating | 1.33 ÷ 1.42 (alumina–GO composites, depend on GO content) | Not available | Smaller amounts of pores for alumina–GO coatings than alone alumina coating | Icorr (µA·cm−2): 47.306 (alumina coating) 8.463 ÷ 1.0 × 10−5 (alumina–GO coatings, depend on GO amounts) | [54] |
| Dip Coating | 0.95 (GO powder), 1.15 (GO/Al) | Most functional oxygen groups were removed during dip procedure | Not available | Icorr (µA·cm−2): 10.316 (bare Al), 8.324 × 10−3 (G-coating) | [55] |
| Drop Casting | Not available | Not available | Uniform morphology metal coating, uniform and nonuniform morphology metal-GO coating (depending on time deposition on top metal coating) | Icorr (µA·cm−2): 29.8 (SnZn), 23.7 ÷ 6.66 (SnZn–GO–SnZn, depending on time deposition of top SnZn layer); 8.03 (ZnNi), 6.66 ÷ 3.26 (ZnNi–GO–ZnNi, depending on time deposition of top ZnNi layer) | [57] |
| Layer-by-Layer Deposition | Not available | Not available | Not available | OTR (cc·m−2·d−1) 8.119 (bare PET), 8.229–0.05 (depending on GO-PEI layers) | [58] |
| Coatings | Adhesion Strength | Wettability | Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy | Potentiodynamic Polarization | Literature References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-doped GO (N–GO/SS) | Not available | 42.5° (GO), 121.5° (NGO) | Charge transfer resistance (RCT) (Ω·cm−2) 5930 (SS), 2.138 × 104 (GO/SS), 2.1834 × 105 (N–GO/SS) | Icorr (µA·cm−2): 5.660 (SS), 0.951 (GO/SS), 0.007 (N–GO/SS) | [69] |
| Silane coupling (EP/SiO2–GO) | 8.5 ± 0.5 MPa (EP), 11.1 ± 1 MPa (EP/GO), 17.7 ± 1.5 MPa (EP/GO–SiO2) | 73.1 ± 2° (EP), 70.7 ± 2° (EP/GO), 84.3 ± 1° (EP/GO–SiO2) | RCT for EP/GO–SiO2 higher than other coatings, | Icorr (µA·cm−2) 14.6 (EP), 0.22 (EP/GO), 0.09 (EP/GO–SiO2) | [91] |
| Aminosilane coupling (EP/A-GO) | 8.5 ± 0.5 MPa (EP), 11 ± 1 MPa (EP/0.1GO), 17.7 ± 0.5 MPa (EP/0.1A-GO) | Not available | RCT for EP/0.1A-GO higher than other coatings, | Not available | [94] |
| Nitrogen coupling (GUF)/EP) | Not available | Not available | RCT (Ω·cm−2): 1.85 × 1010 (EP), 6.22 × 1010 (EP/GO), 7.2 × 1011 (EP/GO-GUF) | Not available | [98] |
| Nitrogen coupling (EP/FGO) | Enhancement of adhesion strength by incorporation functionalized graphene oxide | 91.7° (PCL), 101.7° (PCL/GO), 106.0° (PCL/FGO) | RCT (Ω·cm−2) 1.942 × 103 (PCL), 3.946 × 107 (PCL/GO), 1.784 × 108 (PCL/FGO) | Icorr (µA·cm−2): 5.138 (PCL), 0.2132 (PCL/GO), 0.01033 (PCL/FGO) | [102] |
| With zirconia dioxide (EP/GO–ZrO2) | 10.73 MPa (EP), 11.13 MPa MPa (EP/GO), 12.52 MPa(EP/GO–ZrO2) | Not available | RC (coating resistance) higher for composite coatings than pure EP | Icorr (µA·cm−2) 3.54 (EP), 0.49 (EP/GO), 0.37 (EP/GO–ZrO2) | [112] |
| With fluorographene (EP/FG) | Enhancement of adhesion strength by incorporation of FG | 82° (EP), 116° (EP/GO), 154° (EP/FG) | RCT (Ω·cm−2) 1.38 × 105 (EP) 2.5 × 106 (EP/GO) 5.24 × 108 (EP/FG) | Icorr (µA·cm−2) 1.05 (EP) 0.144 (EP/GO) 0.000501 (FG/GO) | [111] |
| With hexagonal boron nitride (EP/GO–hBN) | Not available | 86.9° (waterborne epoxy coating; WBE), 92.8° (WBE/GO), 94.9 ÷ 98.0° (WBE/GO–hBN, depend on added amounts of GO) | RC (Ω·cm−2): 4.95 × 105 (WBE), 2.89 × 106 (WBE/GO), 4.05 × 106–2.17 × 106 (WBE/GO–hBN, depend on added amounts of GO) | Not available | [118] |
| With zinc phosphate (waterborne polyurethane (WPU)/GO-ZP) | Not available | Not available | RCT (Ω·cm−2): 826 (WPU), 3762 (WPU/ZP), 4726-11040 (WPU/GO-ZP, depend on added amounts of GO) | Icorr (µA·cm−2) 49.4 (steel), 24.2 (WPU), 5.54 (WPU/ZP), 2.73 ÷ 0.441 (WPU/GO-ZP, depend on added amounts of GO) | [119] |
| Coatings | Description | Literature References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-doped graphene coating (NG) | Graphene (PG) and three samples NG (NG1, NG2, NG3, the different doping concentration of nitrogen, the flow rate of NH3 1, 2, 4 sccm, respectively) deposited by CVD. Exposure time in the air: 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months | After two weeks, no obvious difference in the surface morphology for PG, whereas for NG1 and NG3—inhomogeneous corrosion on the form of patches, for NG2 no signs of corrosion. After 1 month: corroded area for PG, 50%; NG1, 10%; NG2, 30%; NG2, no color change of surface. After 3 months: PG—severely corroded, NG coatings less corroded than PG. | [69] |
| APTES/Gr | Samples: APTES and APTES/Gr coatings (with different content of graphene: 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5 wt.% content). Exposure time in 3.5% NaCl up 480 h | Water permeation and breakpoint frequencies are used to evaluate the electrochemical activity of the surface. The uptake of water decreases with the increase of graphene content at a given time. Breakpoint frequencies occur immediately after immersion for APTES coatings, whereas for graphene-based coating gets delayed as the content of graphene increases. For APTES/Gr (5%), breakpoint frequencies occur after 48 h exposure, making this coating the most resistant to corrosion. | [126] |
| ZrO2–GO/ZnAl coatings | After 480 h salt spray test: - For ZnAl coatings, visible traces of red rust; - For ZrO2/ZnAl—small amount of red rust; - For GO–ZrO2/ZnAl—no obvious red rust. | [73] | |
| GO/EP | Cotaings of three samples with different amounts of GO: 0.125, 0.25, 0.5 %. Exposure time in 3.5% NaCl: 1, 34, 64 days. | Rc (Ω·cm−2) for coatings after 1 days’ immersion in chloride solution: EP—5.387 × 107, EP/0.125GO—4.613 × 107, EP/0.25GO–1.771 × 108, EP/0.5GO—8.639 × 107. Rc (Ω·cm−2) After 34 days: EP—6.72 × 106, EP/0.125GO—2.797 × 106, EP/0.25—6.722 × 109, EP/0.5GO—1.127 × 107 Rc (Ω·cm−2) After 64 days: EP—2.757 × 105, EP/0.125GO—2.094 × 106, EP/0.25—2.257 × 107, EP/0.5GO—2.037 × 107 | [76] |
| GO and rGO in EP coating | Time of exposure in 3.5% NaCl: 1 h, 24 h | RCT (Ω·cm−2): rGO/EP 1 h: 1.455 × 104 rGO/EP 24 h: 1450 GO/EP 1 h: 2470 GO/EP 24 h: 2010 | [90] |
| Graphene (Gr) in zinc-rich epoxy (ZRC) coating | Two kinds of coatings with different time of exposure (1, 10, 25 days) with the same amount of graphene (wt. 0.6%) | Rc (Ω·cm−2): ZRC1: 6630 ZRC10: 3350 ZRC25: 3030 Gr0.6/ZRC1: 6630 Gr0.6/ZRC10: 6100 Gr0.6/ZRC25: 11,200 | [86] |
| Multilayer graphene (FMLG) in ZRC | Five kinds of coatings: pure ZRC and four coatings with different amounts (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0 wt.%) of graphene in ZRP | Salt spray test after 500 h: Pure ZRC: red rusts appeared at scratched regions, some blisters on the surface, FMLG0.25/ZRC: red rust at the scratched region, no blisters on the surface FMLG0.5/ZRC: small amount of red rust on the surface FMLG0.75/ZRC: no red rust on the surface. FMLG1.0/ZRC: some blisters on the surface | [88] |
| PANI/EP | Six kinds of coatings: pure EP, PANI/EP, and four coatings with different amounts of added GO (3, 6, 12, 24 wt.%). Time of exposure in 3.5% NaCl: 2, 24, 144, 194 h | Rc (Ω·cm−2) EP 2 h 1.01 × 104 EP 24 h 2.13 × 103 EP 144 9.90 × 103 EP 192 h 1.00 × 104 EP/PANI 2 h 9.29 × 103 EP/PANI 24 h 1.67 × 104 EP/PANI 144 3.49 × 104 EPPANI 192 h 6.82 × 103 EP/PANI-GO (3 wt.%) 2 h 1.45 × 105 EP/PANI-GO (3 wt.%) 24 h 8.01 × 103 EP/PANI-GO (3 wt.%) 144 2.73 × 105 EPPANI-GO (3 wt.%) 192 h 3.41 × 105 EP/PANI-GO (6 wt.%) 2 h 2.67 × 107 EP/PANI-GO (6 wt.%) 24 h 2.93 × 106 EP/PANI-GO (6 wt.%) 144 6.86 × 105 EPPANI-GO (6 wt.%) 192 h 4.37 × 105 EP/PANI-GO (12 wt.%) 2 h 2.40 × 107 EP/PANI-GO (12 wt.%) 24 h 2.70 × 107 EP/PANI-GO (12 wt.%) 144 4.91 × 106 EPPANI-GO (12 wt.%) 192 h 2.70 × 106 EP/PANI-GO (24 wt.%) 2 h 2.78 × 105 EP/PANI-GO (24 wt.%) 24 h 5.73 × 104 EP/PANI-GO (24 wt.%) 144 6.36 × 104 EPPANI-GO (24 wt.%) 192 h 3.21 × 105 | [99] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ollik, K.; Lieder, M. Review of the Application of Graphene-Based Coatings as Anticorrosion Layers. Coatings 2020, 10, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090883
Ollik K, Lieder M. Review of the Application of Graphene-Based Coatings as Anticorrosion Layers. Coatings. 2020; 10(9):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090883
Chicago/Turabian StyleOllik, Karolina, and Marek Lieder. 2020. "Review of the Application of Graphene-Based Coatings as Anticorrosion Layers" Coatings 10, no. 9: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090883
APA StyleOllik, K., & Lieder, M. (2020). Review of the Application of Graphene-Based Coatings as Anticorrosion Layers. Coatings, 10(9), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090883





