Conductive Coatings of Cotton Fabric Consisting of Carbonized Charcoal for E-Textile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Reagents and Chemicals
2.1.1. Fabric
2.1.2. Wood
2.1.3. Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Procedures
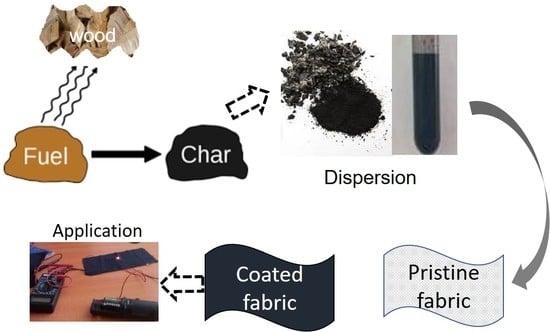
2.2.1. Carbonization of Eucalyptus Wood
2.2.2. Characterization of Eucalyptus Wood Charcoal
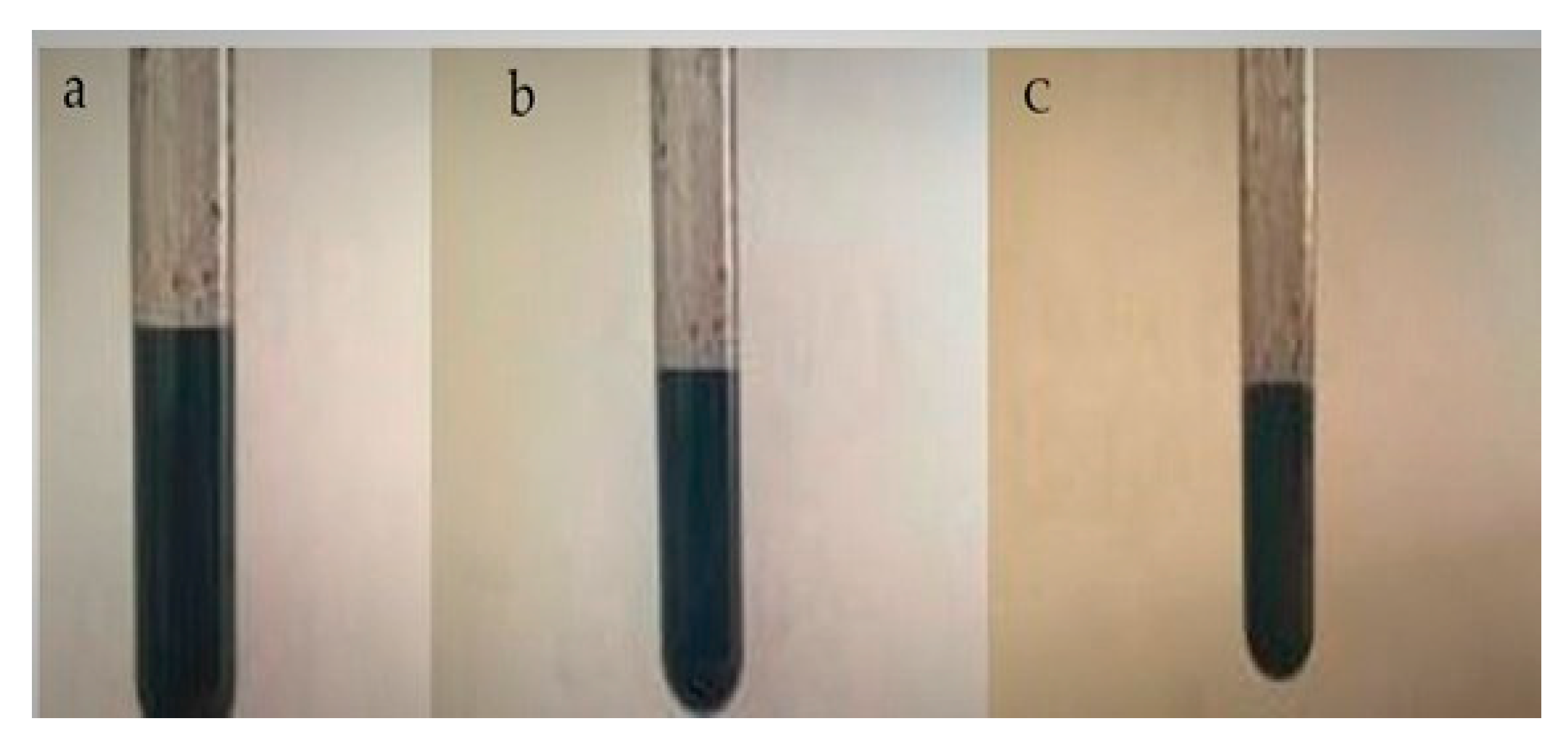
2.2.3. Charcoal Dispersion Preparation
2.2.4. Application of Charcoal Dispersion on to the Cotton Fabric
2.3. Evaluation Parameters
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.3.2. Conductivity Measurement of Carbonized Charcoal
2.3.3. Conductivity Measurement of a Charcoal-Coated Fabric
2.3.4. Assessment of Fastness Properties of Coated Fabric
2.3.5. Durability Test to Washing
2.3.6. Evaluation of Sensorial Comfort Properties
2.3.7. Testing of Fabric Drape
2.3.8. Testing of Tensile Strength
2.3.9. Thermal Comfort
2.3.10. Water Permeability
2.3.11. Air Permeability
3. Results and Discussion
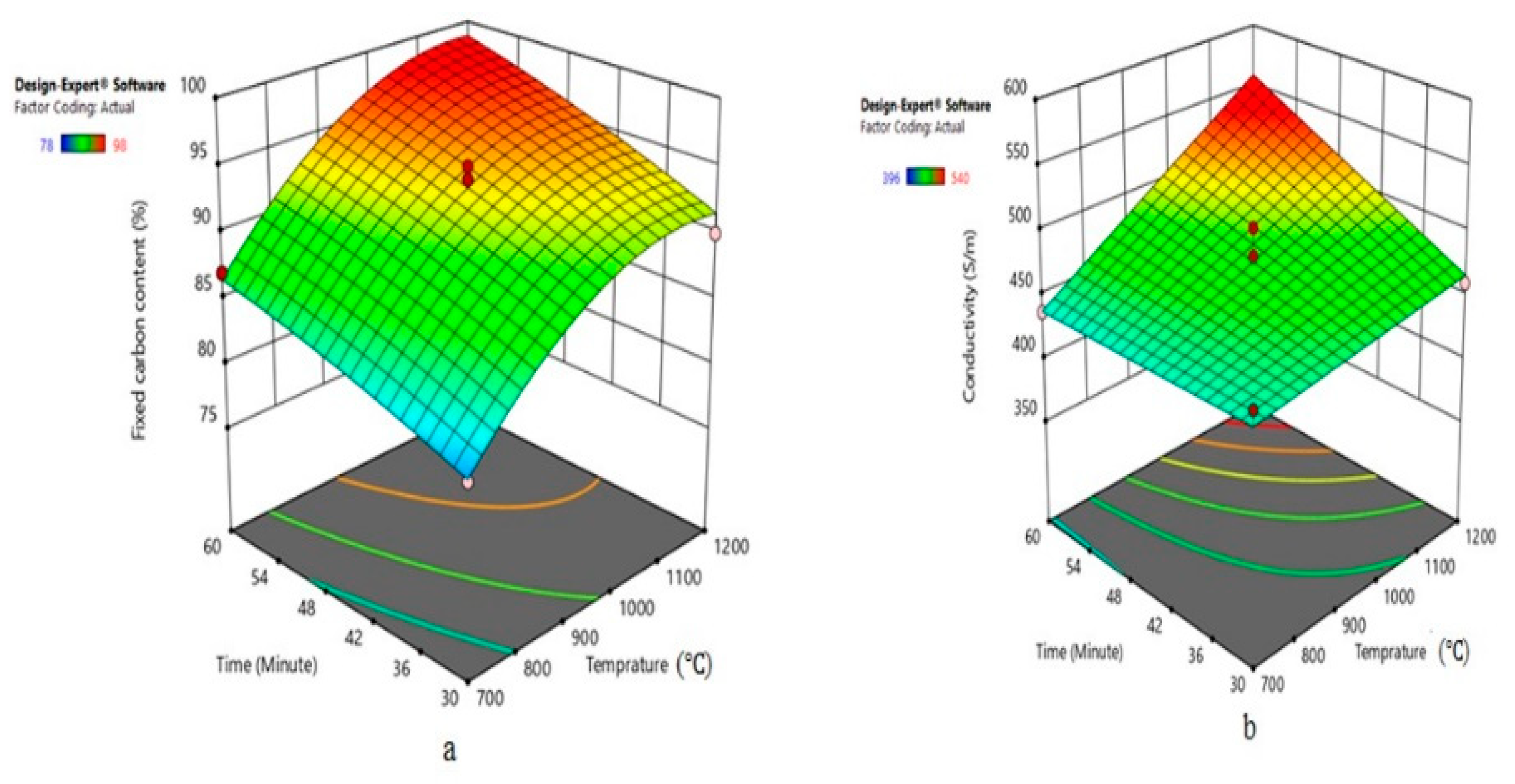
3.1. Optimization of Carbonization Parameters of Eucalyptus Wood and Proximate Analysis of Charcoal
3.2. Coating Formulation and Improved Electrical Conductivity of Charcoal-Coated Fabrics.
3.3. Analysis of Charcoal and Wood Using FTIR
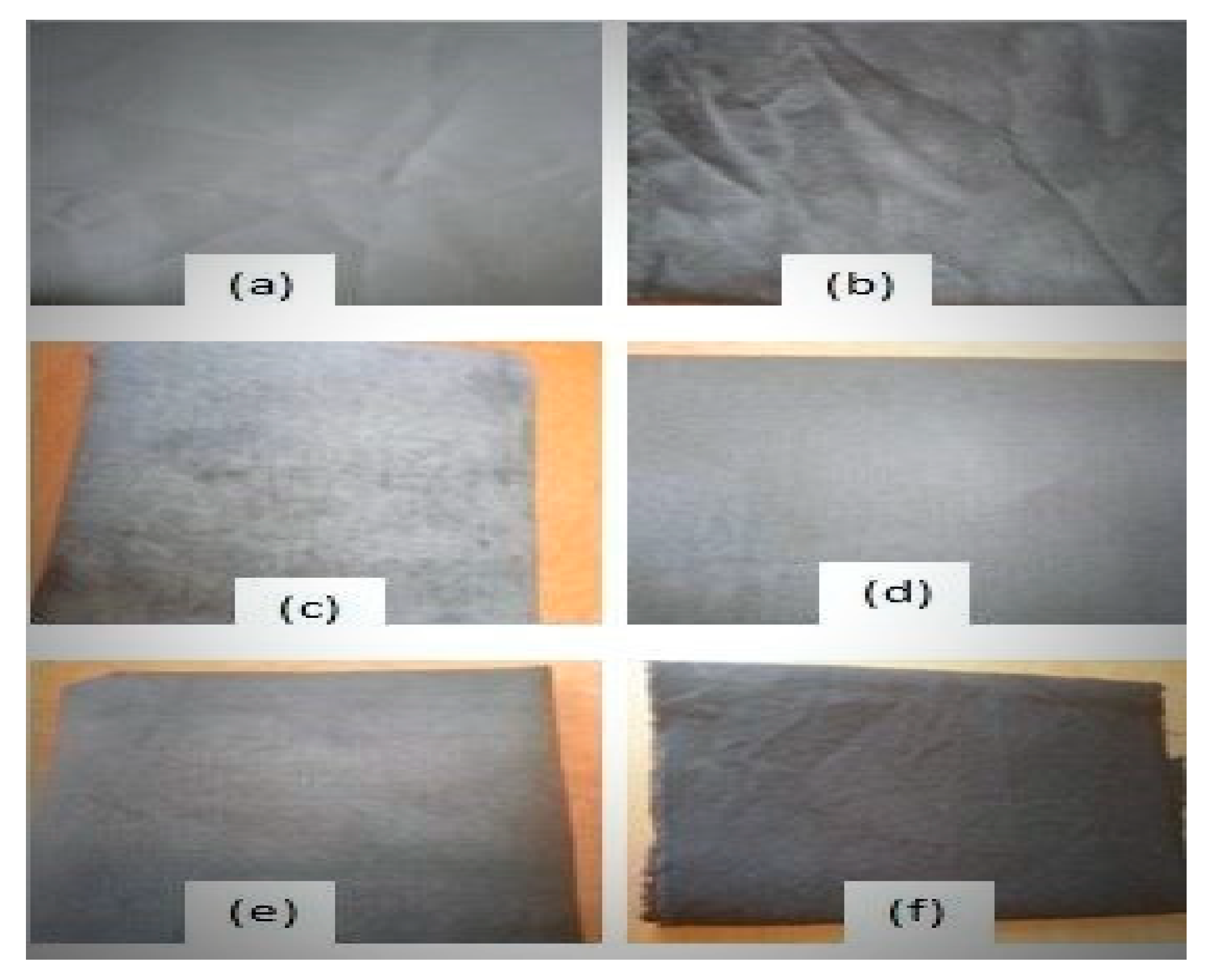
3.4. Coating Fastness Properties and Wash Durability
3.5. Effect of Coating on Tensile Strength and Drapability of Fabric
3.6. Evaluation of Comfort Properties
3.7. Effect of Coating on Thermal Conductivity
3.8. Effect of Coating on Air Permeability
3.9. Water Permeability
4. Proof of Concept
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable electronics and smart textiles: A critical review. Sensors. 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Tian, M.; Qu, L.; Zhu, S.; Han, G. Multifunctional cotton fabrics with graphene/polyurethane coatings with far-infrared emission, electrical conductivity, and ultraviolet-blocking properties. Carbon 2015, 95, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Tomioka, H.; Gunji, T.; Nagao, Y.; Misono, T.; Abe, Y. Preparation of continuous ZrO2-Y2O3 fibers by precursor method using polyzirconoxane. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1993, 101, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meoli, D.; May-Plumlee, T. Interactive electronic textile development: A review of technologies. J. Text. Apparel. Technol. Manag. 2002, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, R.; Khair, N.; Ahmed, D.; Shahariar, H. Fabrication of low cost and scalable carbon-based conductive ink for E-textile applications. Mater. Today. Commun. 2019, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, J.M.; Mieno, T. Conductive cotton textile from safely functionalized carbon nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 16, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Tian, G.; Chen, T.; Qian, Z.; Wei, F. Towards high purity graphene/single-walled carbon nanotube hybrids with improved electrochemical capacitive performance. Carbon 2013, 54, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Coleman, A.; Katsonis, N.; Browne, W.; Wees, B.; Feringa, B. Dispersion of graphene in ethanol using a simple solvent exchange method. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7539–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, F. Models proposed to explain the electrical conductivity of mixtures made of conductive and insulating materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.; Mengistie, A.; Yan, W.; Lichuan, L.; Carmen, M.; Nierstrasz, V. Electrically conductive highly elastic polyamide/lycra fabric treated with PEDOT: PSS and polyurethane. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 9591–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.; Mengistie, A.; Yan, W.; Lichuan, L.; Carmen, M.; Nierstrasz, V. Effect of liquid immersion of PEDOT: PSS-coated polyester fabric on surface resistance and wettability. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 065016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekpittaya, P.; Yanumet, N.; Grady, B.; O’Rear, E. Resistivity of conductive polymer-coated fabric. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, N.; Asaka, K. Performance enhancement of PEDOT:Poly(4-styrenesulfonate) actuators by using ethylene glycol. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17732–17738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.K.; Mabrouk, S.; Qiao, Q. A review on tailoring PEDOT:PSS layer for improved performance of perovskite solar cells. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrifvars, M.; Rehnby, W.; Gustafsson, M. Coating of textile fabrics with conductive polymers for smart textile applications. In Proceedings of the Welcome Ambience’08, Borås, Sweden, 2–3 June 2008; pp. 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Kan, C.; Matinlinna, J.; Tsoi, J. Regenerable antibacterial cotton fabric by plasma treatment with dimethylhydantoin: Antibacterial activity against S. aureus. Coatings 2017, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Kan, C.-W. Visible-light-driven, dye-sensitized TiO2 photo-catalyst for self-cleaning cotton fabrics. Coatings 2017, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleemi, S.; Malik, S.; Syed, U.; Tanwari, A. Surface functionalization of cotton and PC fabrics using SiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles for durable flame retardant properties. Coatings 2020, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Mohapatra, M.R.; Kumar, J. Differential functional finishes for textiles using graphene oxide. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2018, 22, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1762-84. Standard Test Method for Chemical Analysis of Wood Charcoal; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E871-82. Standard Test Method for Moisture Analysis of Particulate Wood Fuels; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E872-82. Standard Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis of Particulate Wood Fuels; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E872-82. Standard Test Method for Ash in Wood; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, J. Graphene-based fabrics and their applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68261–68291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, W.; Jing, X. Preparation of a stable graphene dispersion with high concentration by ultrasound. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2010, 114, 10368–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, F.; Gashti, M.P.; Shamei, A. A novel method for coating of carbon nanotube on cellulose fiber using 1, 2, 3, 4-butanetetracarboxylic acid as a cross-linking agent. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, N.; Mineo, N. Preparation of a concentrated carbon black-PTFE dispersion for micro-porous layer of PEMFC. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2007, 10, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Akerfeldt, M.; Straat, M.; Walkenström, P. Electrically conductive textile coating with a PEDOT-PSS dispersion and a polyurethane binder. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Nigusse, A.B.B.; Van, L. Development and evaluation of resistive pressure sensors from electro-conductive textile fabric. In Proceedings of the Second International Forum on Textiles for Graduate Students, Tianjin, China, 8–10 September 2018; pp. 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Van, L. Development of a flex and stretchy conductive cotton fabric via flat screen printing of PEDOT: PSS/PDMS conductive polymer composite. Sensors 2020, 20, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BS EN ISO 105-C06. Tests for Colour Fastness Part C06: Colour Fastness to Domestic and Commercial Laundering; British Standards Institution (BSI): London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata, S.; Niwa, M. Objective measurement of fabric mechanical property and quality: Its application to textile and clothing manufacturing. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 1991, 3, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrabi, L.; Dolez, P.I.; Vu-Khanh, T.; Lara, J.; Tremblay, G.; Nadeau, S.; Larivière, C. Characterization of protective gloves stiffness: Development of a multidirectional deformation test method. Saf. Sci. 2008, 46, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeroglu, S.; Ulku, S. An investigation about tensile strength, pilling and abrasion properties of woven fabrics made from conventional and compact ring-spun yarns. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2007, 15, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Parfen’eva, L.S.; Orlova, T.S.; Kartenko, N.F.; Smirnov, B.I.; Smirnov, I.A.; Misiorek, H.; Jezowski, A.; Muha, J.; Vera, M.C. Structure, electrical resistivity, and thermal conductivity of beech wood biocarbon produced at carbonization temperatures below 1000 °C. Phys. Solid State 2011, 53, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimiya, K.; Hata, T.; Imamura, Y.; Ishihara, S. Analysis of chemical structure of wood charcoal by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Wood Sci. 1998, 44, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Ofri, I.; Weiner, L.; Boaretto, E.; Mintz, G.; Weiner, S. Modern and fossil charcoal: Aspects of structure and diagenesis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2006, 33, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, J.; Manley-Harris, M.; Fushimi, C.; Dowaki, K.; Nunoura, T.; Antal, M.J. Do all carbonized charcoals have the same chemical structure? 2. A model of the chemical structure of carbonized charcoal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 5954–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.C. Smart Textile Coatings and Laminates; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Atalie, D.; Tesema, A.F.; Rotich, G.K. Effect of weft yarn twist level on thermal comfort of 100 per cent cotton woven fabrics. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2018, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.G.; Nagy, L.; Nierstrasz, V.; Loghin, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Low-stress mechanical property study of various functional fabrics for tactile property evaluation. Materials 2018, 11, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Improving thermal conductivity of cotton fabrics using composite coatings containing graphene, multiwall carbon nanotube or boron nitride fine particles. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.; Periolatto, K. Modification of Surface Energy and Wetting of Textile Fibers, in Wetting and Wettability; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldi, R.; Siores, E.; Shah, T. Electromagnetic shielding characterisation of several conductive fabrics for medical applications. Carbon 2010, 2, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, C.; Cayla, A. Polymer-Based Resistive Sensors for Smart Textiles, in Multidisciplinary Know-How for Smart-Textiles Developers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 129–153. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Jiang, Z. A novel wearable sensor device with conductive fabric and PVDF film for monitoring cardiorespiratory signals. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 128, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, D.; Schollmeyer, E. Electrically high-conductive textiles. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

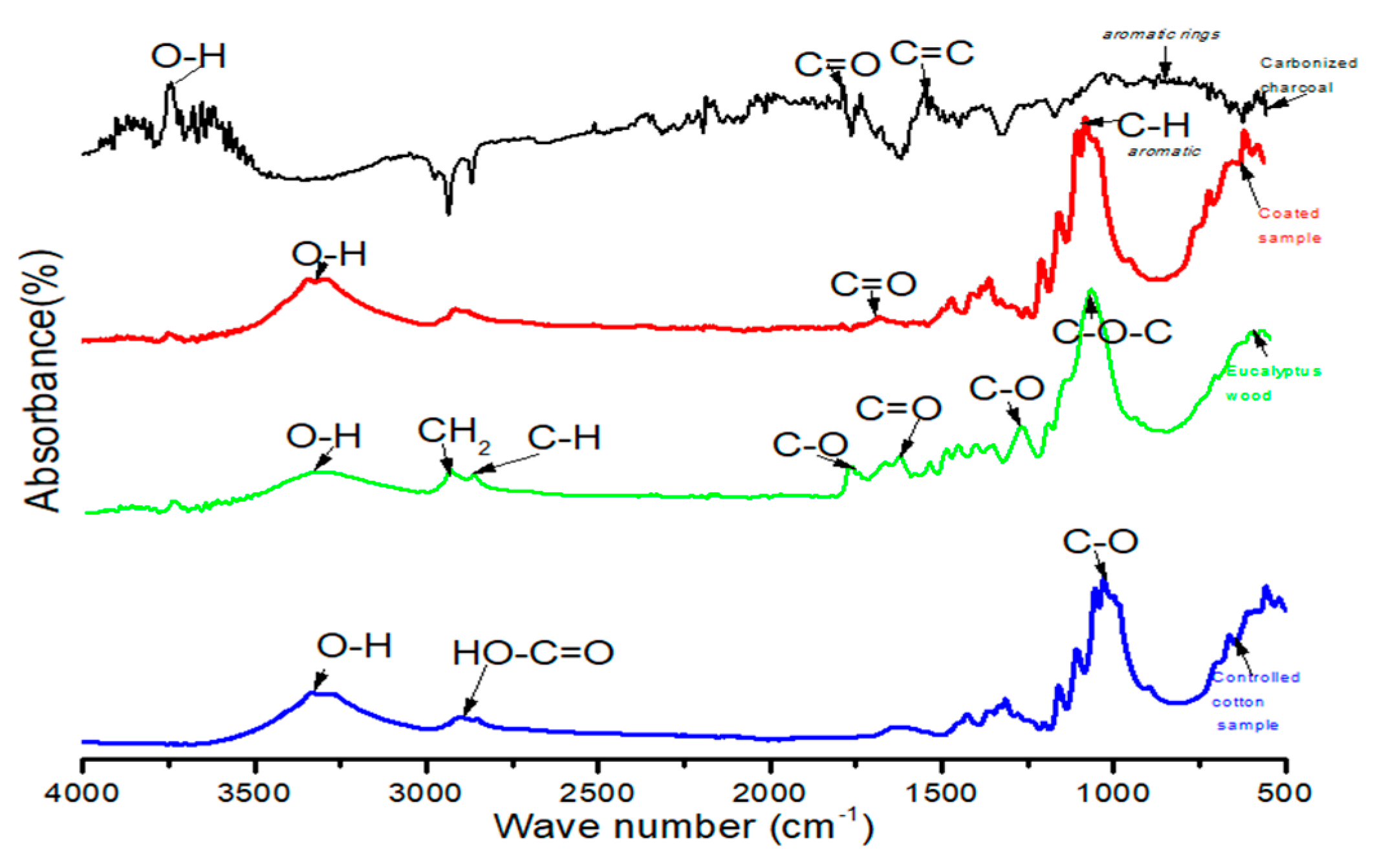
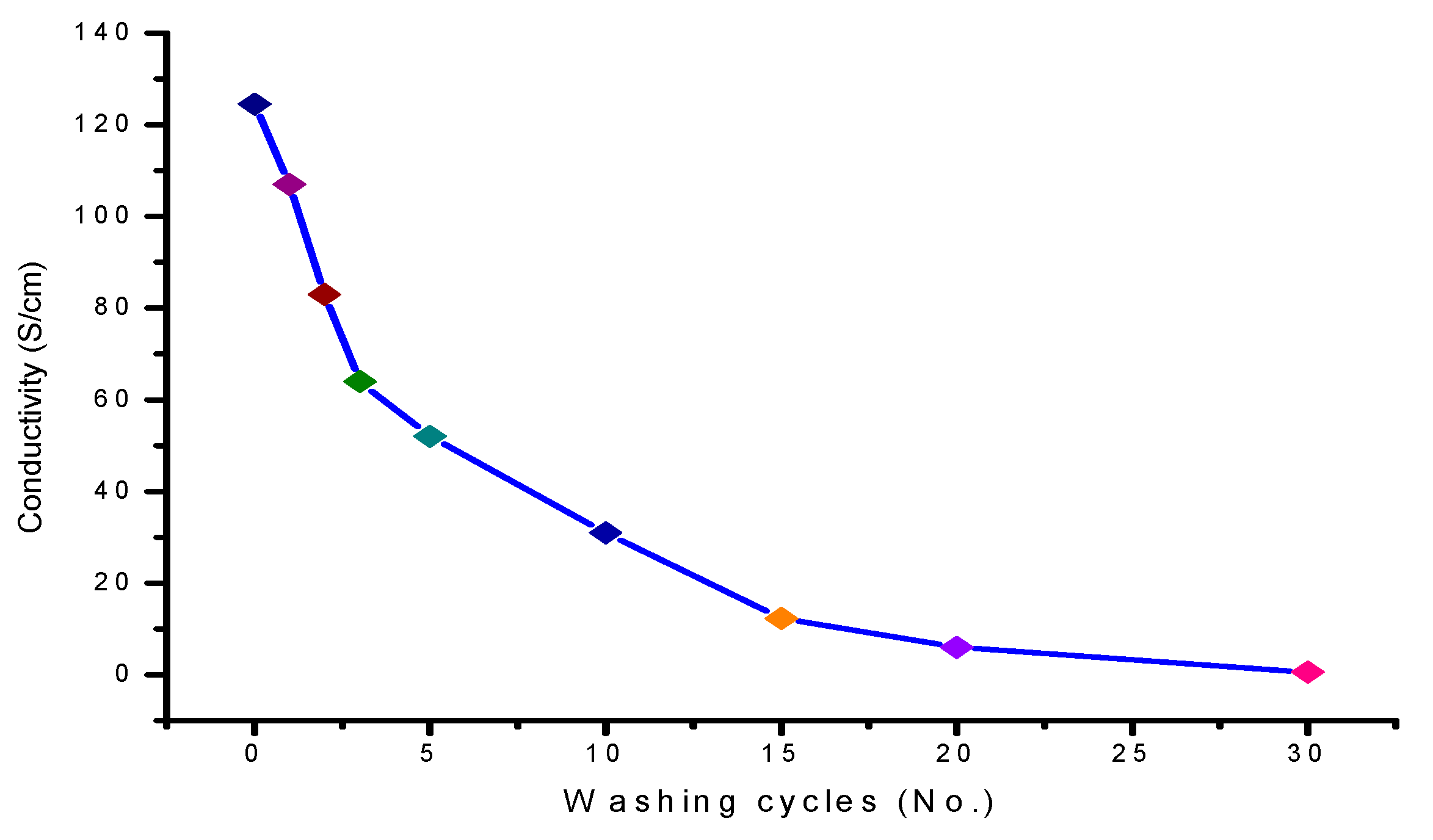
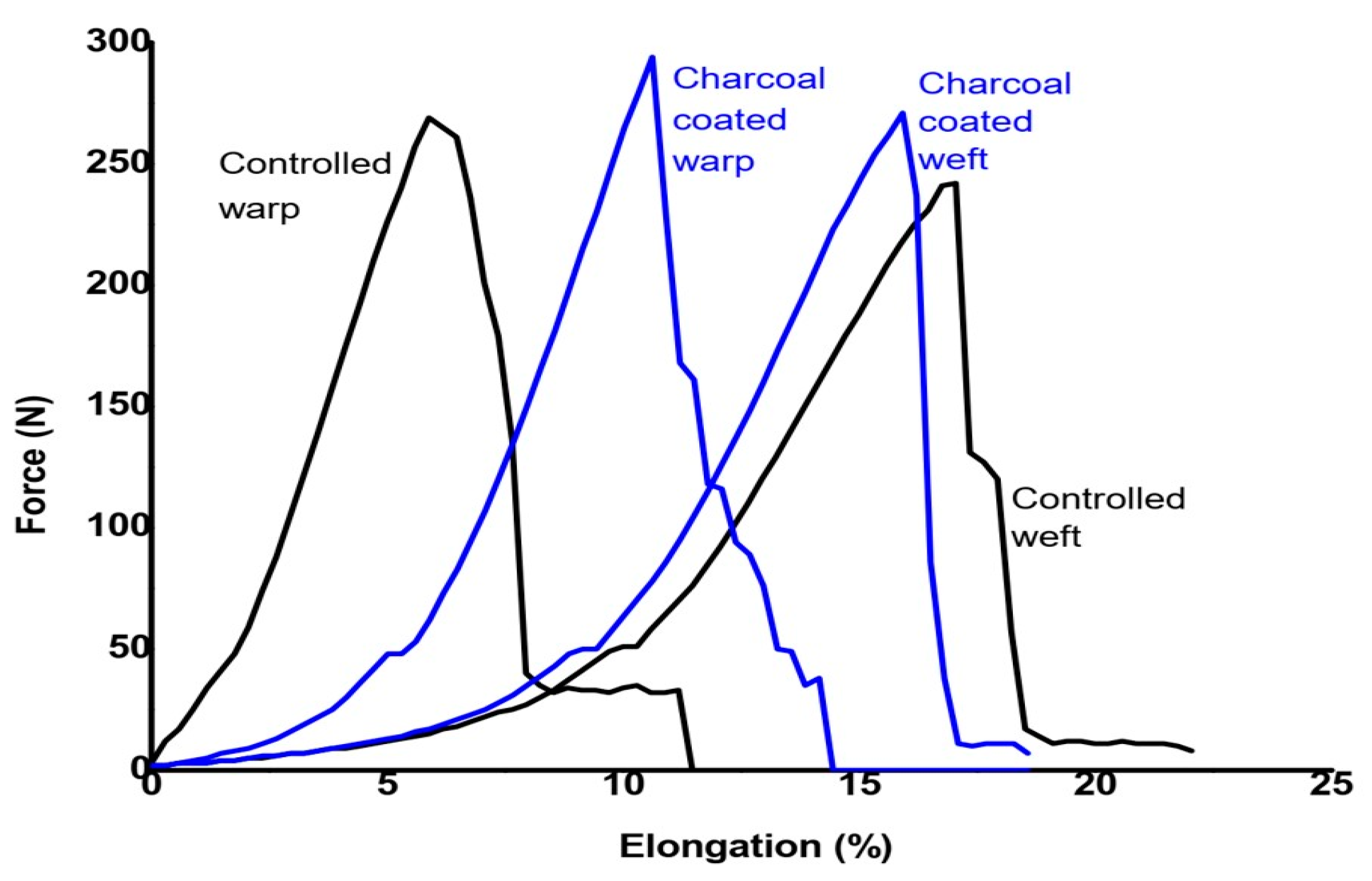
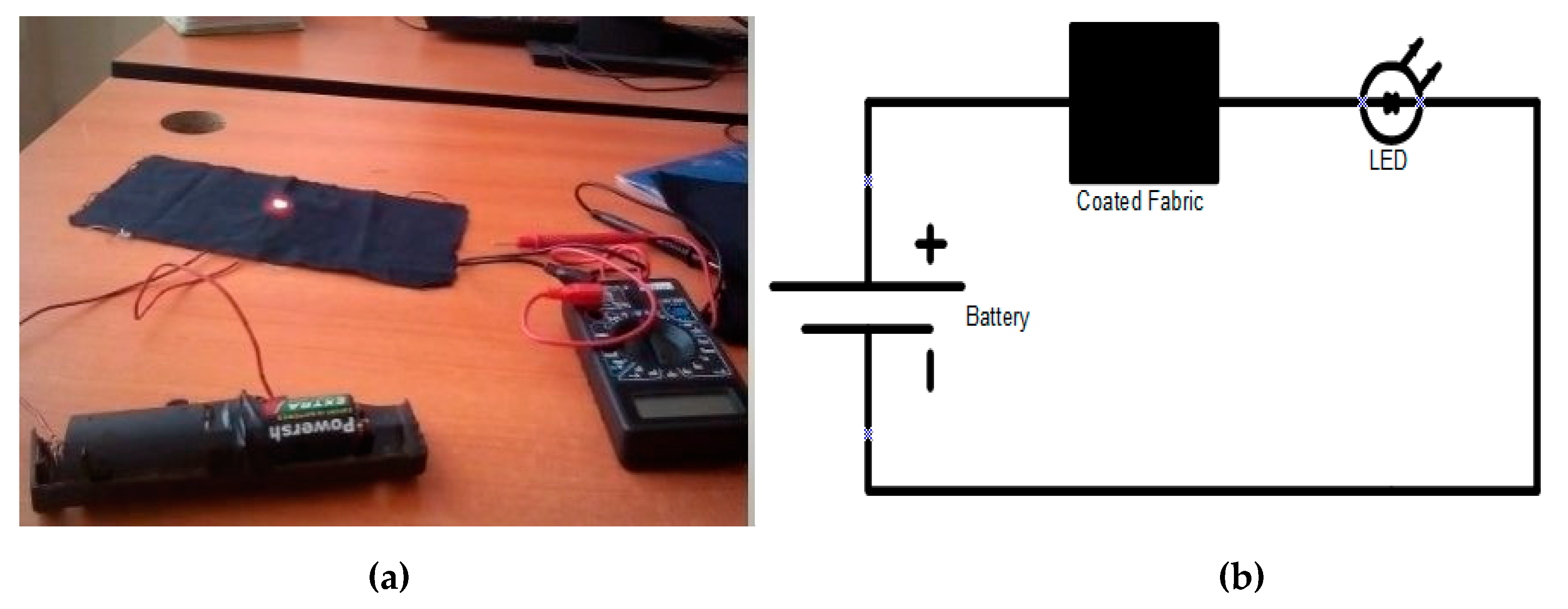
| Run | Temperature (T) (°C) | Time (t) (min) | Fixed Carbon Content (FC) (%) | Conductivity (Sm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 596 | 45 | 78 | 396 |
| 2 | 940 | 35 | 94 | 476 |
| 3 | 700 | 30 | 81 | 455 |
| 4 | 950 | 66 | 97 | 532 |
| 5 | 950 | 40 | 93 | 473 |
| 6 | 950 | 45 | 95 | 503 |
| 7 | 940 | 40 | 94 | 481 |
| 8 | 1200 | 60 | 98 | 540 |
| 9 | 930 | 45 | 91 | 466 |
| 10 | 950 | 23 | 89 | 453 |
| 11 | 1303 | 45 | 96 | 523 |
| 12 | 1200 | 30 | 90 | 460 |
| 13 | 700 | 60 | 87 | 437 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 422.18 | 5 | 84.44 | 37.3500 | <0.0001 | significant |
| T—Temperature | 258.28 | 1 | 258.28 | 114.2600 | <0.0001 | – |
| t—Time | 80.10 | 1 | 80.10 | 35.4400 | 0.0006 | – |
| Tt | 1.00 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.4424 | 0.5273 | – |
| T² | 82.80 | 1 | 82.80 | 36.6300 | 0.0005 | – |
| t² | 1.41 | 1 | 1.41 | 0.6232 | 0.4558 | – |
| Residual | 15.82 | 7 | 2.26 | – | – | – |
| Lack of Fit | 6.62 | 3 | 2.21 | 0.9598 | 0.4930 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 9.20 | 4 | 2.30 | – | – | – |
| Cor Total | 438.00 | 12 | – | – | – | – |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 16513.04 | 3 | 5504.35 | 16.8800 | 0.0005 | significant |
| T–Temperature | 10339.59 | 1 | 10339.59 | 31.7100 | 0.0003 | – |
| t–Time | 3772.45 | 1 | 3772.45 | 11.5700 | 0.0079 | – |
| Tt | 2401.00 | 1 | 2401.00 | 7.3600 | 0.0238 | – |
| Residual | 2934.19 | 9 | 326.02 | – | – | – |
| Lack of Fit | 2143.39 | 5 | 428.68 | 2.1700 | 0.2366 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 790.80 | 4 | 197.70 | – | – | – |
| Cor Total | 19447.23 | 12 | – | – | – | – |
| Parameters | Values (%) |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 3.5 |
| Volatile matter | 5.0 |
| Ash | 0.5 |
| Fixed carbon content | 91.0 |
| Yield | 64.7 |
| FC yield | 59.17 |
| Run | A: Charcoal Particles mg/mL | B: Dispersant mg/mL | C: Ethanol mg/mL | Conductivity Scm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 108 |
| 2 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 4.0 | 109 |
| 3 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 81 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 2.0 | 106 |
| 5 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 2.5 | 89 |
| 6 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 126 |
| 7 | 6.0 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 98 |
| 8 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 119 |
| 9 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 5.0 | 112 |
| 10 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 1.0 | 103 |
| 11 | 4.97 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 79 |
| 12 | 7.5 | 5.9 | 2.5 | 101 |
| 13 | 10.2 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 148 |
| 14 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 1.0 | 96 |
| 15 | 9.0 | 10.0 | 4.0 | 121 |
| 16 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 103 |
| 17 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 0.0 | 73 |
| 18 | 7.5 | 11.0 | 2.5 | 86 |
| 19 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 91 |
| 20 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 1.0 | 87 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3804.06 | 3 | 1268.02 | 8.5400 | 0.0013 | significant |
| Charcoal particles | 2092.41 | 1 | 2092.41 | 14.1000 | 0.0017 | – |
| Dispersant | 10.15 | 1 | 10.15 | 0.0684 | 0.7971 | not significant |
| Ethanol | 1701.50 | 1 | 1701.50 | 11.4600 | 0.0038 | – |
| Residual | 2375.14 | 16 | 148.45 | – | – | – |
| Lack of Fit | 1745.81 | 11 | 158.71 | 1.2600 | 0.4236 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 629.33 | 5 | 125.87 | – | – | – |
| Cor Total | 6179.20 | 19 | – | – | – | – |
| Fastness Properties | Color Change | Staining | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Polyester | |||||
| Wash fastness (ISO 105 C06 2010) | 4/5 | 4/5 | 5 | |||
| Light fastness (AATCC Test Method 16 2007) | 7 | – | – | |||
| Perspiration fastness (AATCC Test Method 15-2009) | Alkaline | Acidic | Alkaline | Acidic | Alkaline | Acidic |
| 4/5 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 5 | |
| Hot pressing (AATCC Test Method 133-2009) | Dry | wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet |
| 5 | 4/5 | 5 | 4/5 | 5 | 4/5 | |
| Rubbing fastness (AATCC Test Method 8-2007) | – | Rubbing cloth | ||||
| Dry | Wet | |||||
| 5 | 4/5 | |||||
| Mechanical Properties | Mean | Standard Error | T Statistics | ± t Critical | Decision p(T<=t) Two-Tail =0.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness and friction properties | |||||||
| MIU | Weft | Controlled | 0.1288 | 0.0028 | −2.9137 | 2.7764 | 0.0435 |
| Coated | 0.1514 | 0.0054 | |||||
| Warp | Controlled | 0.1634 | 0.0034 | −13.4007 | 0.0001 | ||
| Coated | 0.4116 | 0.0178 | |||||
| MMD | Weft | Controlled | 0.0128 | 0.0002 | −1.9367 | 0.1248 | |
| Coated | 0.0143 | 0.0006 | |||||
| Warp | Controlled | 0.0163 | 0.0003 | −13.4008 | 0.0001 | ||
| Coated | 0.0411 | 0.0017 | |||||
| SMD | Weft | Controlled | 1.2832 | 0.0268 | −2.2939 | 0.0834 | |
| Coated | 1.6180 | 0.1437 | |||||
| Warp | Controlled | 1.6320 | 0.0335 | −13.4727 | 0.00017 | ||
| Coated | 4.1660 | 0.1783 | |||||
| Shear Properties | |||||||
| G, go/cm.deg | Weft | Controlled | 1.7220 | 0.0058 | −9.2184 | 2.7764 | 0.0007 |
| Coated | 2.3620 | 0.0688 | |||||
| Warp | Controlled | 1.7780 | 0.0159 | −13.1844 | 0.0001 | ||
| Coated | 2.4880 | 0.0476 | |||||
| 2HG, gf/cm | Weft | Controlled | 3.4680 | 0.0511 | −17.4063 | 0.0000 | |
| Coated | 4.0980 | 0.0662 | |||||
| Warp | Controlled | 3.5380 | 0.0897 | −3.9131 | 0.0173 | ||
| Coated | 4.4080 | 0.1658 | |||||
| 5HG, gf/cm | Weft | Controlled | 5.7940 | 0.1053 | −14.8459 | 0.0001 | |
| Coated | 6.5100 | 0.13453 | |||||
| Warp | Controlled | 6.5400 | 0.1126 | −13.6907 | 0.0001 | ||
| Coated | 7.5520 | 0.1096 | |||||
| Compression Properties | |||||||
| LC(-) | Controlled | 0.4372 | 0.0016 | 4.6761 | 2.7764 | 0.0094 | |
| Coated | 0.4826 | 0.0082 | |||||
| WC (gf.cm/cm2) | Controlled | 0.1894 | 0.0015 | −3.3005 | 0.0299 | ||
| Coated | 0.1798 | 0.0021 | |||||
| RC (%) | Controlled | 36.372 | 0.2813 | 7.6969 | 0.0015 | ||
| Coated | 34.098 | 0.0315 | |||||
| T (mm) | Controlled | 0.5212 | 0.0047 | −20.9027 | 0.0000 | ||
| Coated | 0.6350 | 0.0022 | |||||
| Comfort Properties | Mean | Standard Error | T Statistics | ±t Critical | Decision p(T<=t) Two-Tail | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Properties | ||||||
| Conductivity (w/mk) | Controlled | 0.045 | 0.0012 | −22.4189 | 2.7764 | 0.0000 |
| Coated | 0.079 | 0.0013 | ||||
| Resistance (inch2.k/w) | Controlled | 2.151 | 0.0099 | 34.5621 | 0.0000 | |
| Coated | 1.790 | 0.0007 | ||||
| Insulation (k/w) | Controlled | 2.0718 | 0.0384 | 6.7553 | 0.0025 | |
| Coated | 1.764 | 0.0222 | ||||
| Air Permeability | ||||||
| Air permeability(cm3/cm2/s) | Controlled | 49.380 | 0.5285 | −3.9757 | 2.7764 | 0.0164 |
| Coated | 48.040 | 0.7560 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasaw, E.; Haile, A.; Getnet, M. Conductive Coatings of Cotton Fabric Consisting of Carbonized Charcoal for E-Textile. Coatings 2020, 10, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060579
Kasaw E, Haile A, Getnet M. Conductive Coatings of Cotton Fabric Consisting of Carbonized Charcoal for E-Textile. Coatings. 2020; 10(6):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060579
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasaw, Esubalew, Adane Haile, and Melkie Getnet. 2020. "Conductive Coatings of Cotton Fabric Consisting of Carbonized Charcoal for E-Textile" Coatings 10, no. 6: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060579
APA StyleKasaw, E., Haile, A., & Getnet, M. (2020). Conductive Coatings of Cotton Fabric Consisting of Carbonized Charcoal for E-Textile. Coatings, 10(6), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060579