XPS and FTIR Studies of DC Reactive Magnetron Sputtered TiO2 Thin Films on Natural Based-Cellulose Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
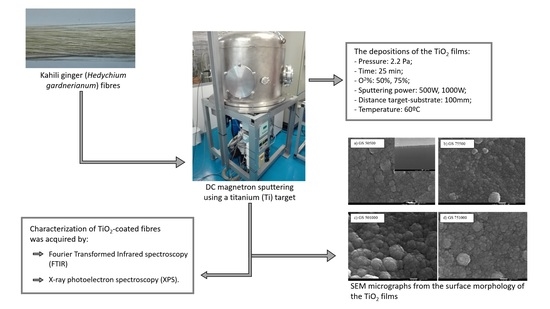
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of TiO2 Films
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
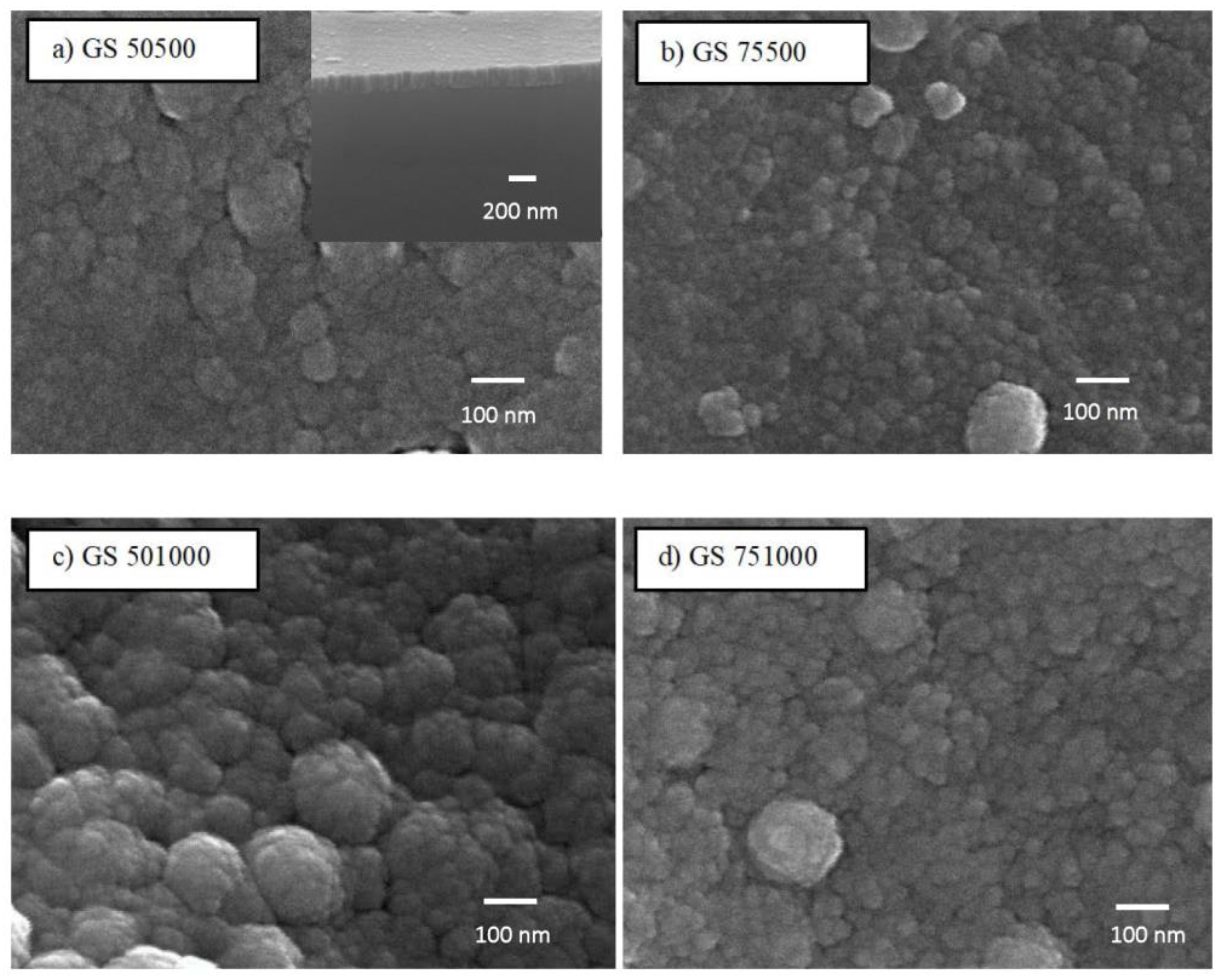
3.1. Surface Morphology
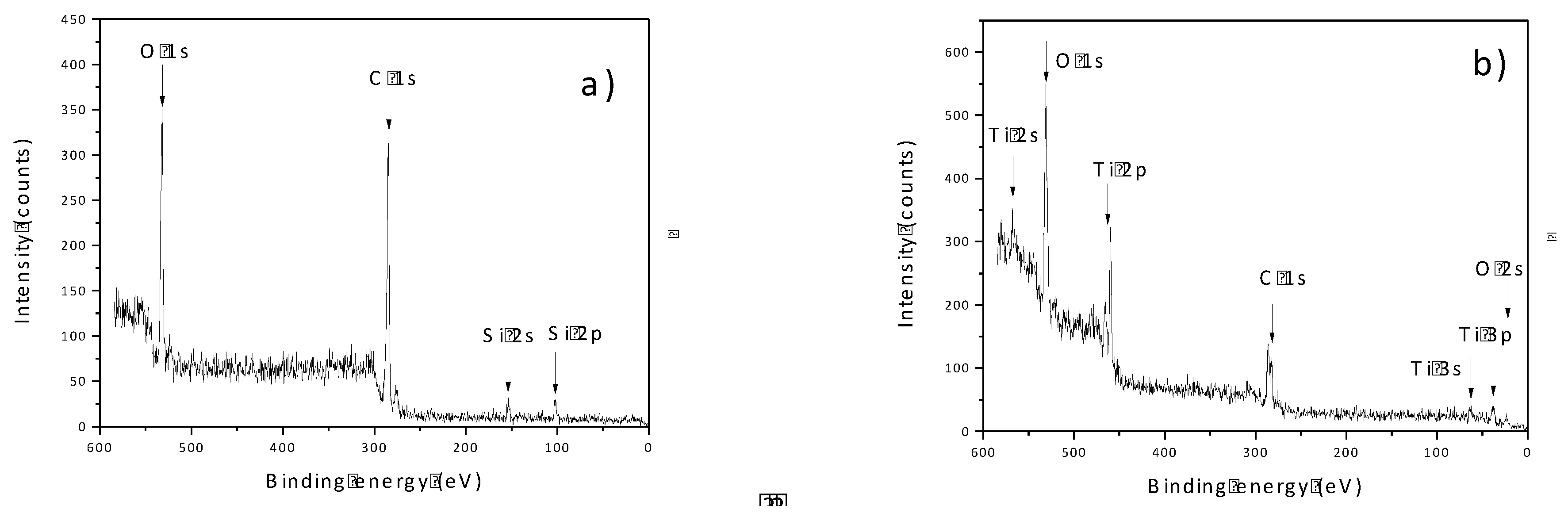
3.2. XPS—Surface Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Analysis
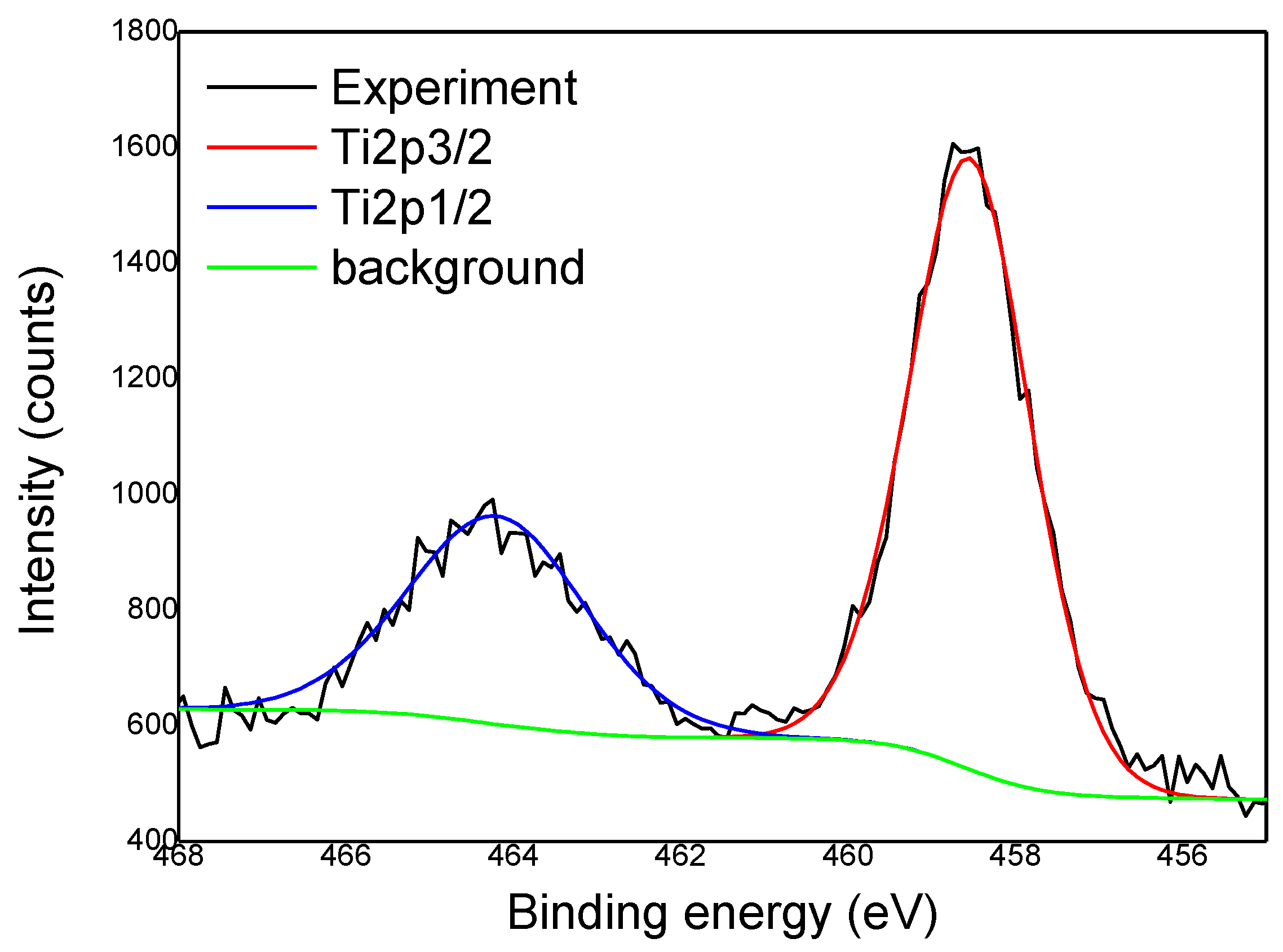
Detailed Analysis of High-Resolution Spectra
- Sample Fiberf
- Samples with Deposited TiO2
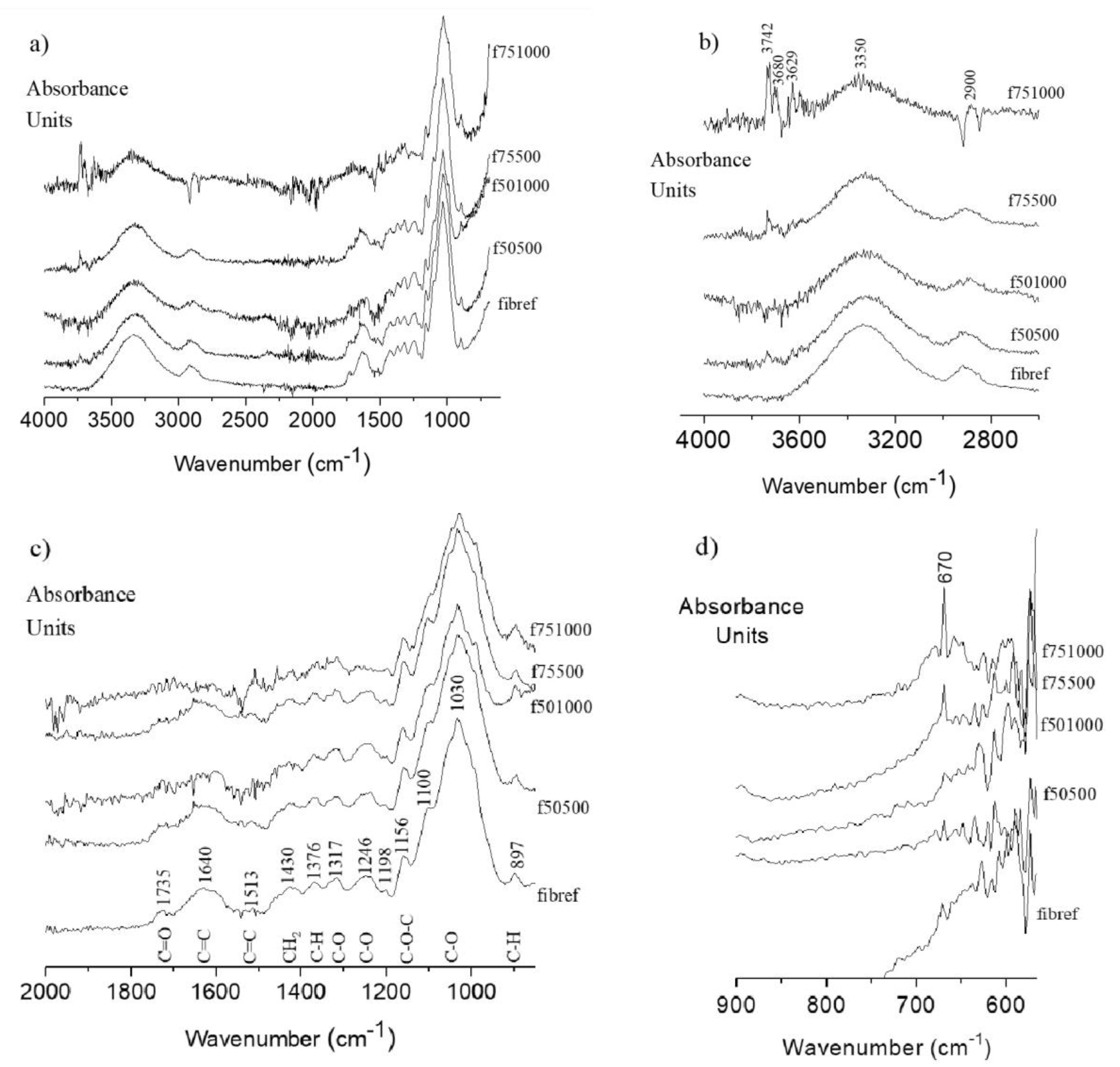
3.3. FTIR-ATR—Surface Functional Group Analysis
4. Conclusions
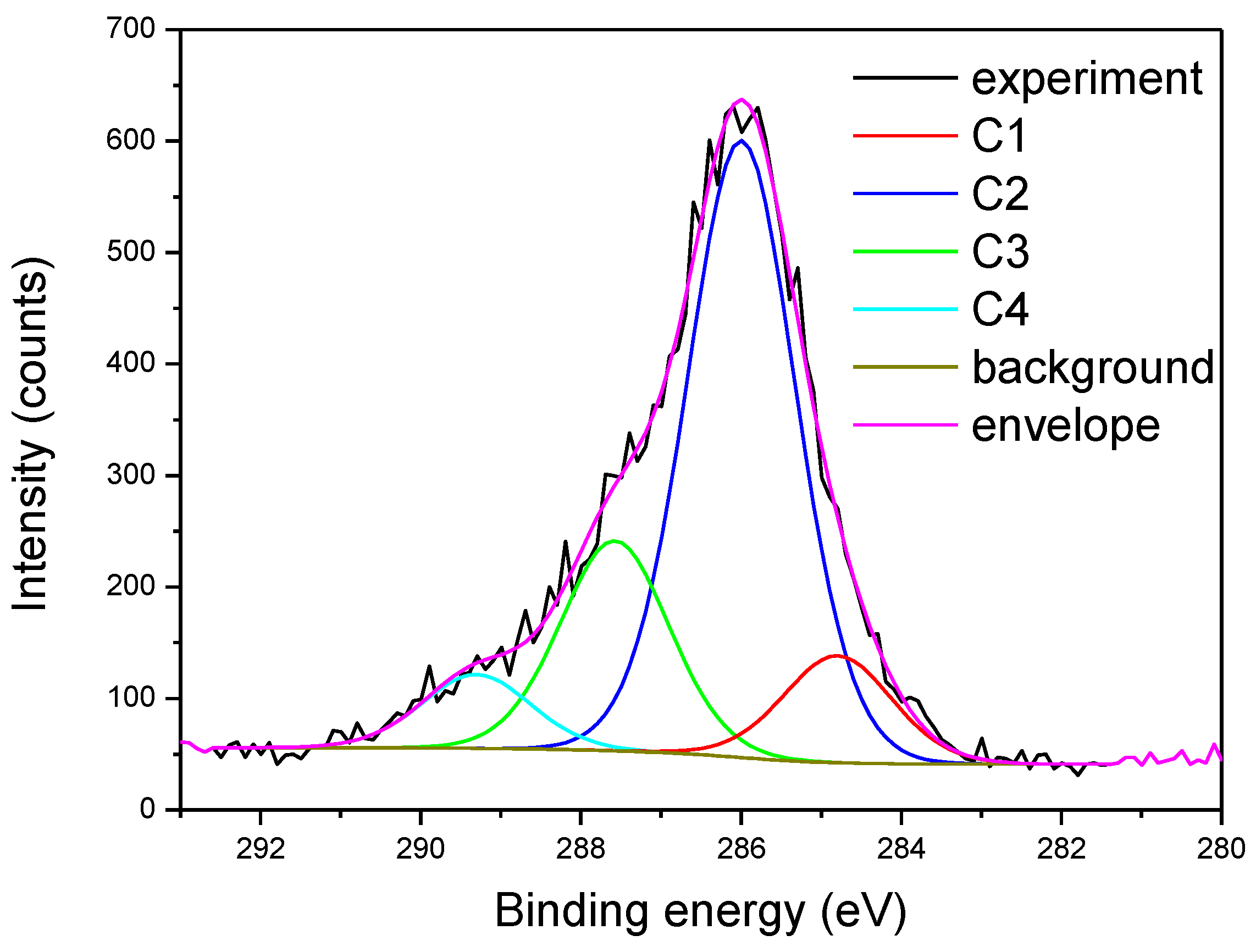
- In the case of the fib75500 sample, it is clearly observed TiO2 signal in both Ti 2p and O 1s lines, while the organic region kept the general structure of the reference sample with the exception that the relative amount of C–OH component (contribution C2) decreased.
- The TiO2 content in fib751000 sample is several times greater than in other samples. The organic region consists mainly of saturated hydrocarbons and O–C–O bonds with a small quantity of adsorbed water. As for the previous sample, TiO2 deposition is accompanied by the drop or even disappearance of C–OH bonds from the surface. This implies that OH groups (including cellulose surface) may serve as nucleation sites for TiO2 growth.
- In the case of fib501000 sample, the amount of TiO2 is comparable to fib75500 (~3 % of Ti), while the amount of Ti in fib50500 is only 1.2 %. C 1s line in both samples can be fitted to the same four contributions, although those related to oxygen bonds are shifted in energy due to the non-uniform charging of organic areas. At the same time, the amount of O in these samples is almost doubled with respect to the reference sample. Apart from the increase the content of oxygen-rich bonds (attributed to contributions C3 and C4) an additional bond seems to appear with the O 1s line at about 532 eV. The later could be attributed to C–O–C or C=O bonds.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Sustainable Bio-composites from renewable resources: Opportunities and challenges in the green materials world. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ching, Y.C.; Chuah, C.H. Applications of Lignoccellulosic Fibers and Lignin in Bioplastics: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.; Ho, M.; Lau, K.; Cardona, F.; Hui, D. Natural fibre-reinforced composites for bioengineering and environmental engineering applications. Comp. Part B 2009, 40, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Arpítha, G.R.; Naik, L.L.; Gopalakrisha, K.; Yogesha, B. Applications of Natural Fibers and its Composites: An Overview. Nat. Resour. 2016, 7, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias Arias, F.E.; Beneduci, A.; Chidichimo, F.; Furia, E.; Straface, S. Study of the adsorption of Mercury (II) on lignocellulosic materials under static and dynamic conditions. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Skrifvars, M.; Persson, A. A Review of Natural Fibers used in biocomposites: Plant, animal, and regenerated cellulose fibers. Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 107–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleutério, T.; Pinto, A.S.; Pereira, M.J.; Vasconcelos, H.C. Preliminary Structural and Thermal Characterization of Conteira’s (Hedychium gardnerianum) fibers for further functionalization with silica colloidal nanoparticles. Procedia Eng. 2017, 200, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csurhes, S.; Hannan-Jones, M. Kahili ginger (Hedychium gardnerianum), white ginger (Hedychium coronarium), yellow ginger (Hedychium flavescens). In Invasive Plant Risk Assessment; Department of Agriculture and Fisheries Biosecurity: Queensland, Australia, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tursi, A. A review on biomass: Importance, chemistry, classification, and conversion. Biofuel Res. J. 2019, 22, 962–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, V.K.; Naithani, S. Chemical Functionalization of Cellulose derived from nonconventional sources. Chap. 2. In Cellulose Fibers: Bio and Nano Polymer Composites, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, A.V.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Olayo, R.; Franco, P.J.H. Effect of fiber surface treatment on the fiber- matrix bond strength of natural fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 1999, 30, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Reihmane, S.; Gassan, J. Properties and modification methods for vegetable fibers for natural fiber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsriraksa, P.; Togashi, K.; Nakai, A.; Hamada, H. Continuous Natural Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites by Fiber surface modification. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, I.A.; Petriceanu, M.; Piticescu, R.R.; Predescu, C. Hydrothermal synthesis of doped ZnO and TiO2 nanomaterials: Opportunities for textile applications. Ser. B Chem. Mater. Sci. 2014, 76, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- De Vietro, N.; Tursi, A.; Beneduci, A.; Chidichimo, F.; Milella, A.; Fracassi, F.; Chatzisymeon, E.; Chidichimo, G. Photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli bacteria in water using low pressure plasma deposited TiO2 cellulose fabric. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, P.A.A.P.; Trindade, T.; Neto, C.P. Titanium dioxide/cellulose nanocomposites prepared by a controlled hydrolysis method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Huang, F. Surface and Interface Analysis of Fibers Sputtered with Titanium Dioxide. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Shu, S. Preparation and Characterization of Composite TiO2/Natural Cotton Nanofiber Material. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 800, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical Treatments of Natural Fiber for Use in Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, O.M.N.D.; Silva, J.M.A.C.; Moutinho, A.M.C. Multitechnique surface analysis system: Apparatus description. Vacuum 1995, 46, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.D.; Davis, L.E.; Zeller, M.W.; Taylor, J.A.; Raymond, R.M.; Gale, L.H. Empirical atomic sensitivity factors for quantitative analysis by electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis. Surf. Interface Anal. 1981, 3, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sério, S.; Jorge, M.E.M.; Maneira, M.J.P.; Nunes, Y. Influence of O2 partial pressure on the growth of nanostructured anatase phase TiO2 thin films prepared by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toku, H.; Pessoa, R.S.; Maciel, H.S.; Massi, M.; Mengui, U.A. The effect of oxygen concentration on the low temperature deposition of TiO2 thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2126–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippler, R.; Cada, M.; Stranak, V.; Hubicka, Z. Ion formation in an argon and argon-oxygen gas mixture of a magnetron sputtering discharge. J. Phys. Commun. 2019, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, P.-A.; Balhamri, A.; Thomann, A.-L.; Dussart, R.; Semmar, N.; Lecas, T.; Snyders, R.; Konstantinidis, S. Titanium oxide thin film growth by magnetron sputtering: Total energy flux and its relationship with the phase constitution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 254, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Chen, J.Y.; Qi, S.K.; Zhao, J.Z.; Zhang, X.D. Characterization of surface oxide films on titanium and bioactivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Jie, Q.; Chen, C. Preparation and Performance of Nickel Oxide Films by Ion Beam Sputtering Deposition and Oxidation Annealing. Sens. Mater. 2010, 22, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Jaya, H.; AbdulKadir, H.K.; Noriman, N.Z.; Dahham, O.S.; Mazelan, A.H.; Latip, N.A.; Aini, A.K. The influences of chicken feathers loading on tensile and physical properties of R-Hdpe/Eva/CffComposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 454, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bredzona, T.; Puchkovska, G.; Shymanovska, V.; Baran, J.; Ratajczak, H. IR-Analysis of H-Bonded H2O on the Pure TiO2 Surface. J. Mol. Struct. 2004, 700, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Beamson, G.; Briggs, D. Appendices 3.1 and 3.2. In High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers; The Scienta ESCA300 Database; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, B.P.; Biesinger, M.C.; McIntyre, N.S. The study of polycrystalline nickel metal oxidation by water vapour. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2009, 175, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surfaxe chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxide and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švagelj, Z.; Mandić, V.; Ćurković, L.; Biošić, M.; Žmak, I.; Gaborardi, M. Titania-Coated Alumina Foam Photocatalyst for Memantine Degradation Derived by Replica Method and Sol-Gel Reaction. Materials 2020, 13, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddick, S.Z.; Lai, C.W.; Juan, J.C. An investigation of the dye-sensitized solar cell performance using graphene-titania (TrGO) photoanode with conventional dye and natural green chlorophyll dye. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 74, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, C.; Fois, E.; Coluccia, S.; Martra, G. Surface Structure of TiO2 P25 Nanoparticles: Infrared Study of Hydroxy Groups on Coordinative Defect Sites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21531–21538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuk, A.Š.; Ješe, R.; Orel, B.; Dražc, G. The effect of surface hydroxyl groups on the adsorption properties of nanocrystalline TiO2 films. Int. J. Photoenergy 2005, 7, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, K.S.; Cassidy, D.J.; Bartlett, J.R.; Woolfrey, J.L. IR Spectroscopy of Surface Water and Hydroxyl Species on Nanocrystalline TiO2 Films. Langmuir 2001, 17, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B.; Takriff, M.S.; Sopian, K. Synthesis and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for photochemical oxidation of concentrated chlorophenols under direct solar radiation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 4871–4888. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | O2 Concentration (%) | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Sputtering Power (W) | Deposition Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fib50500 | 50 | 478 | 1.14 | 500 | 50 |
| fib75500 | 75 | 474 | 1.14 | 500 | 50 |
| fib501000 | 50 | 505 | 2.02 | 1000 | 75 |
| fib751000 | 75 | 498 | 2.07 | 1000 | 75 |
| Sample | O2 Concentration (%) | Sputtering Power (W) | Thickness (nm) | Deposition Rate (Rd) (nm/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fib50500 | 50 | 500 | 160 ± 6 | 3.2 |
| fib75500 | 75 | 500 | 133 ± 4 | 2.7 |
| fib501000 | 50 | 1000 | 333 ± 6 | 4.4 |
| fib751000 | 75 | 1000 | 319 ± 8 | 4.3 |
| Sample | C (%) | O (%) | Ti (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| fiberf | 74.3 | 25.7 | - |
| fib75500 | 53.4 | 42.5 | 4.1 |
| fib751000 | 52.5 | 38.9 | 8.6 |
| fib50500 | 60.4 | 38.4 | 1.2 |
| fib501000 | 47.7 | 48.2 | 4.1 |
| Sample | C 1s Line (eV/%) | O 1s Line (eV/%) | Ti 2p3/2 (eV) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | O1 | O2 | O3 | ||
| fiberf | 284.8/ 10.6 | 286.0/ 61.2 | 287.6/ 20.9 | 289.3/ 7.3 | 532.7/ 39.5 | 533.8/ 60.5 | - | - |
| fib75500 | 284.8/ 17.2 | 286.1/ 43.0 | 287.7/ 26.1 | 289.6/ 13.7 | 532.7/ 33.5 | 534.1/ 53.0 | 529.8 */ 14.5 | 458.5 * |
| fib751000 | 284.8/ 57.4 | - | 287.9/ 42.6 | - | 532.7/ 94.0 | 535.2/ 6.0 | - | 458.5 * |
| fib50500 | 284.8/ 15.4 | 287.0/ 47.2 | 288.7/ 24.4 | 290.6/ 13.0 | 533.7/ 64.4 | - | 532.0/ 35.6 | 458.5 * |
| fib501000 | 284.8/ 22.7 | 287.0/ 32.3 | 288.7/ 31.5 | 290.7/ 13.4 | 533.8/ 35.1 | 535.3/ 29.4 | 529.6 */ 35.4 | 458.5 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eleutério, T.; Sério, S.; Teodoro, O.M.N.D.; Bundaleski, N.; Vasconcelos, H.C. XPS and FTIR Studies of DC Reactive Magnetron Sputtered TiO2 Thin Films on Natural Based-Cellulose Fibers. Coatings 2020, 10, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030287
Eleutério T, Sério S, Teodoro OMND, Bundaleski N, Vasconcelos HC. XPS and FTIR Studies of DC Reactive Magnetron Sputtered TiO2 Thin Films on Natural Based-Cellulose Fibers. Coatings. 2020; 10(3):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030287
Chicago/Turabian StyleEleutério, Telmo, Susana Sério, Orlando M. N. D. Teodoro, Nenad Bundaleski, and Helena C. Vasconcelos. 2020. "XPS and FTIR Studies of DC Reactive Magnetron Sputtered TiO2 Thin Films on Natural Based-Cellulose Fibers" Coatings 10, no. 3: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030287
APA StyleEleutério, T., Sério, S., Teodoro, O. M. N. D., Bundaleski, N., & Vasconcelos, H. C. (2020). XPS and FTIR Studies of DC Reactive Magnetron Sputtered TiO2 Thin Films on Natural Based-Cellulose Fibers. Coatings, 10(3), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10030287